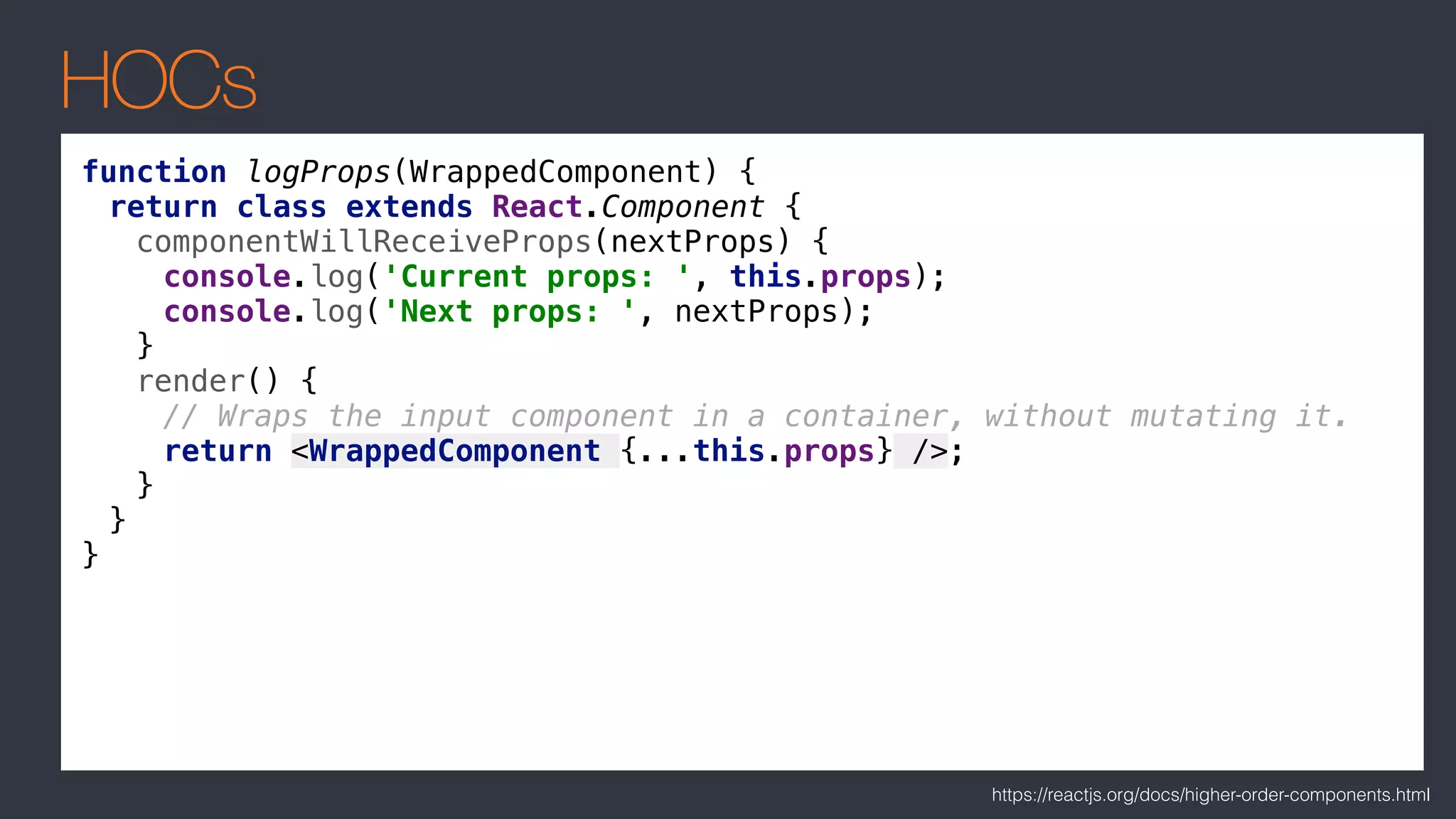
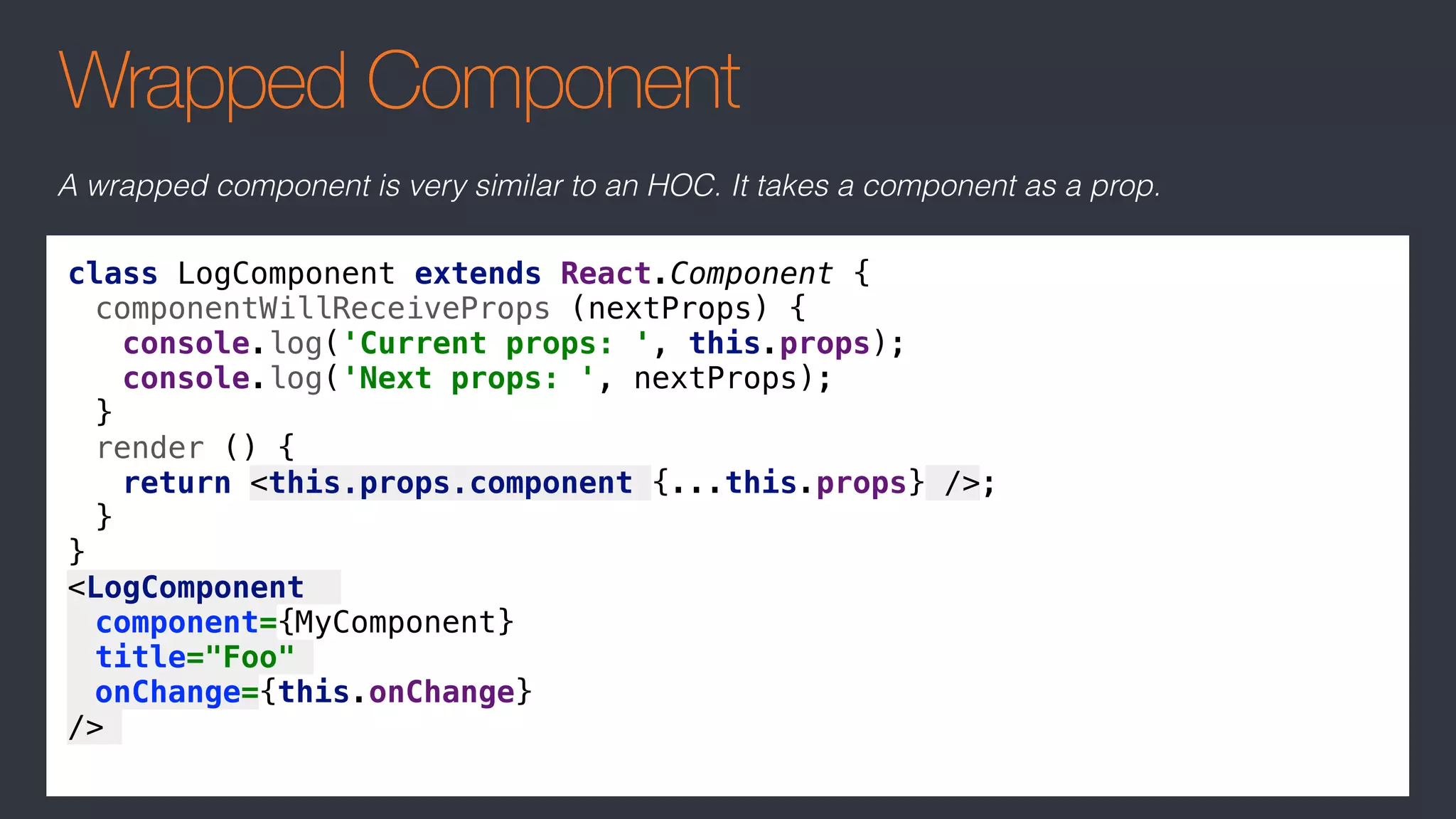
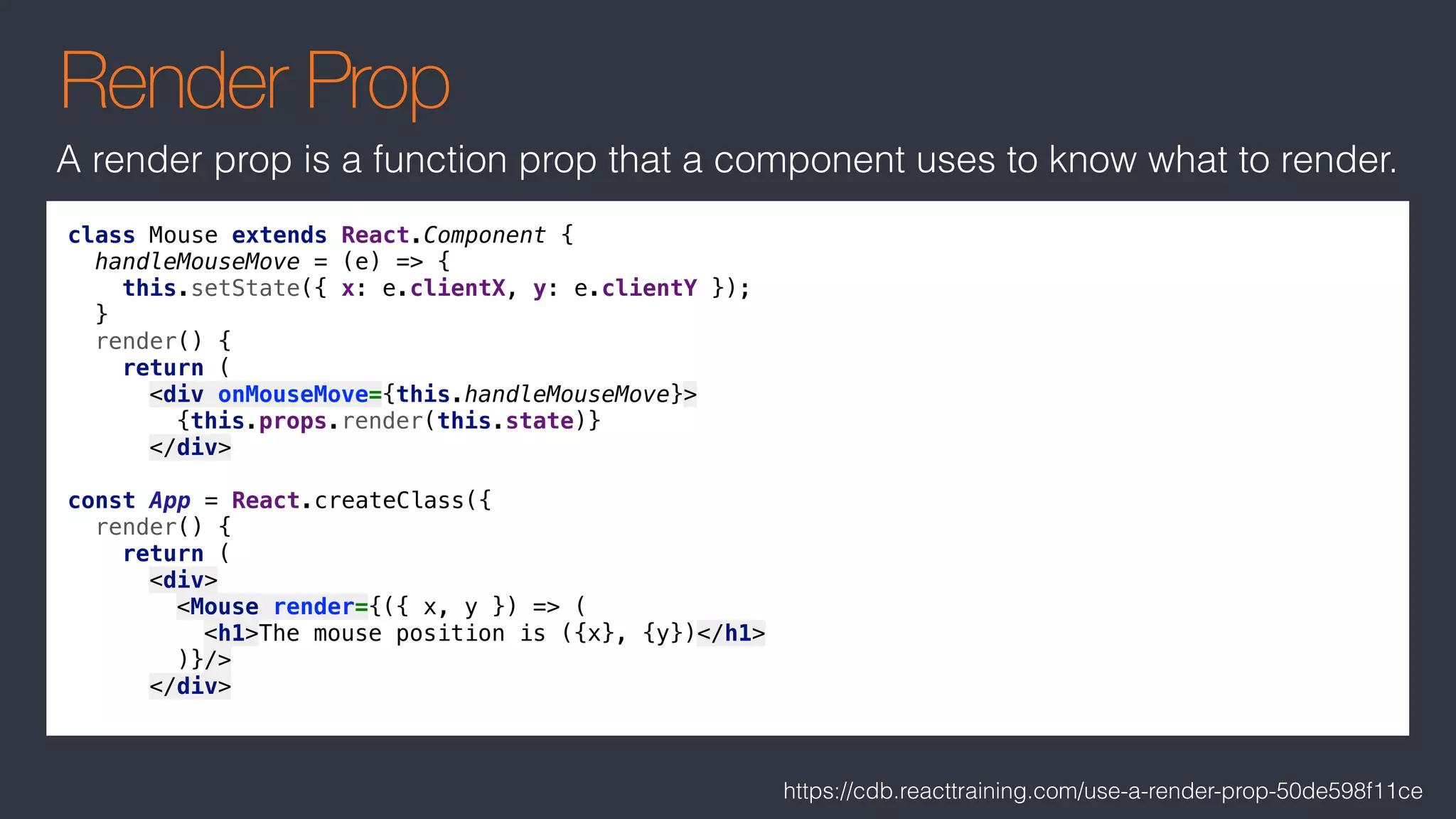
The document covers advanced React topics including the use of Redux, React Router, presentational and container components, and higher-order components. It emphasizes that Redux may be unnecessary for many applications and provides specific guidance on structuring components and data management. Additionally, it discusses the utility and patterns of higher-order functions and render props in React development.







![React Router
You don’t have to use React Router
const routes = [
{ path: '/', action: () => <HomePage /> },
{ path: '/tasks', action: () => <TaskList /> },
{ path: '/tasks/:id', action: () => <TaskDetails /> }
];
function renderComponent(component) {
ReactDOM.render(component, container);
}
function render(location) {
router.resolve(routes, location)
.then(renderComponent)
.catch(error => router.resolve(routes, { ...location, error })
.then(renderComponent));
}
For complete code, see reference: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/you-might-not-need-react-router-38673620f3d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancedreact-171108134413/75/Advanced-React-9-2048.jpg)




![HOFs
const upperCase = (arr) => arr.map(str => str.toUpperCase());
const trim = (arr) => arr.map(str => str.trim());
const dashify = (arr) => arr.map(str => str.replace(/s/g, '-'));
const compose = (...fns) => {
return (...args) => {
return fns.reduce((a, b) => {
return b(a);
}, ...args);
}
};
hof = compose(trim, upperCase, dashify);
hof([' my house ', ' in the middle ', ' of our street ‘]);
// ['MY-HOUSE', 'IN-THE-MIDDLE', 'OF-OUR-STREET']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancedreact-171108134413/75/Advanced-React-15-2048.jpg)