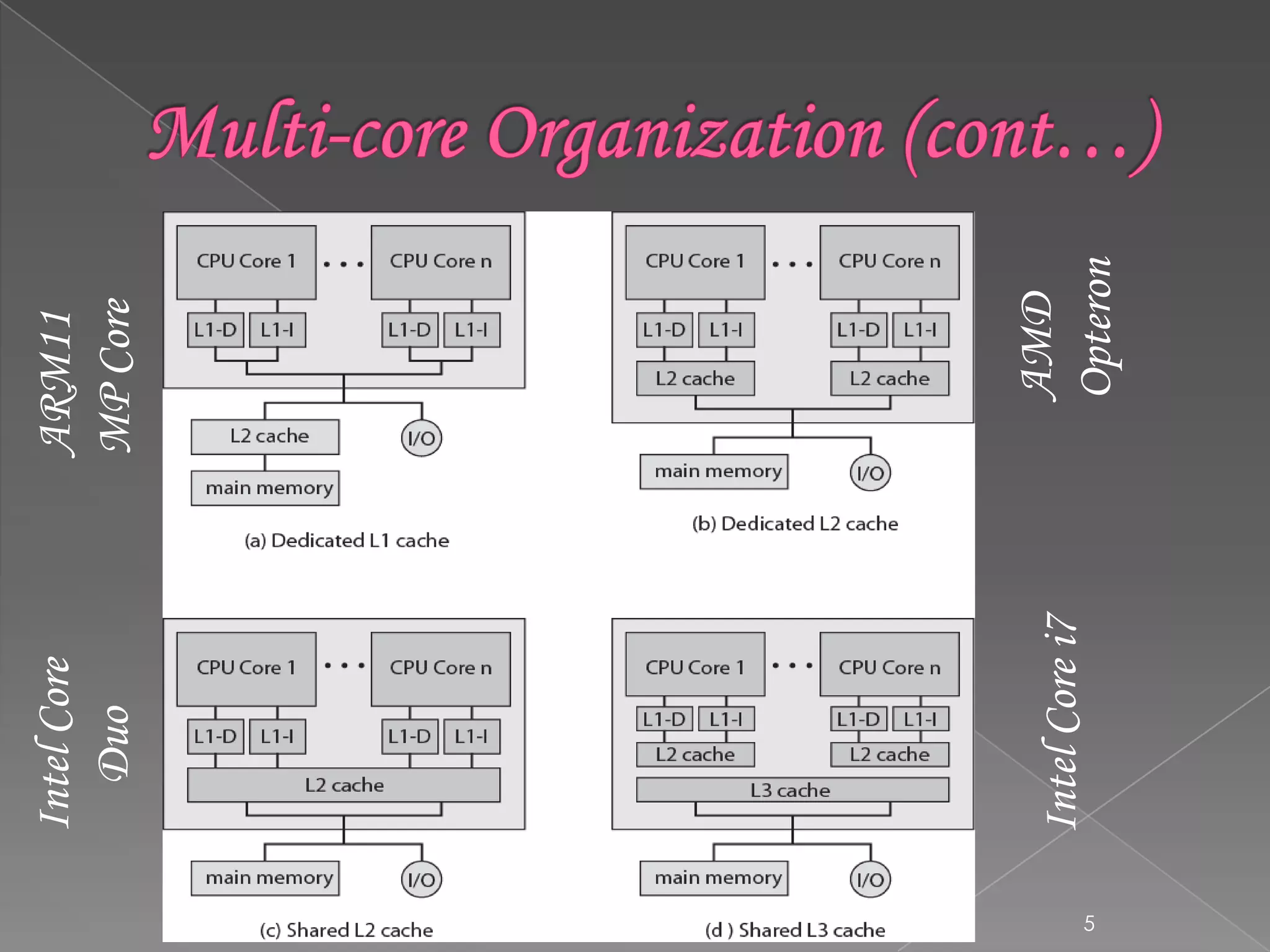
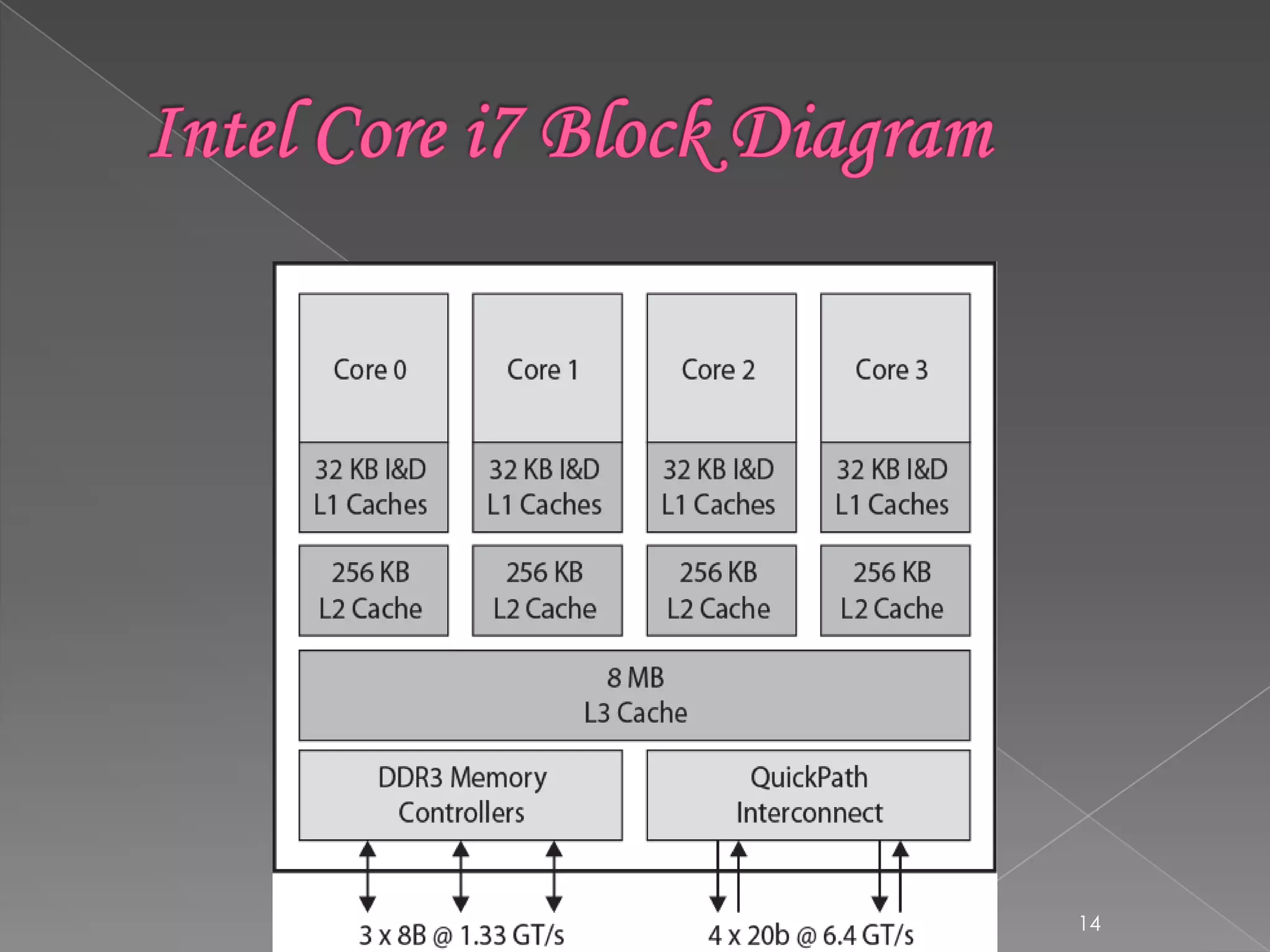
This document discusses Intel's multi-core processor organization. It describes how a multi-core processor combines two or more processor cores onto a single silicon chip. It identifies key variables in multi-core organization as the number of cores, levels of cache memory, and amount of shared cache. It provides examples of Intel's Core i7, Core Duo, AMD Opteron, and ARM11 MP Core multi-core processors and highlights their core configurations and cache architectures.