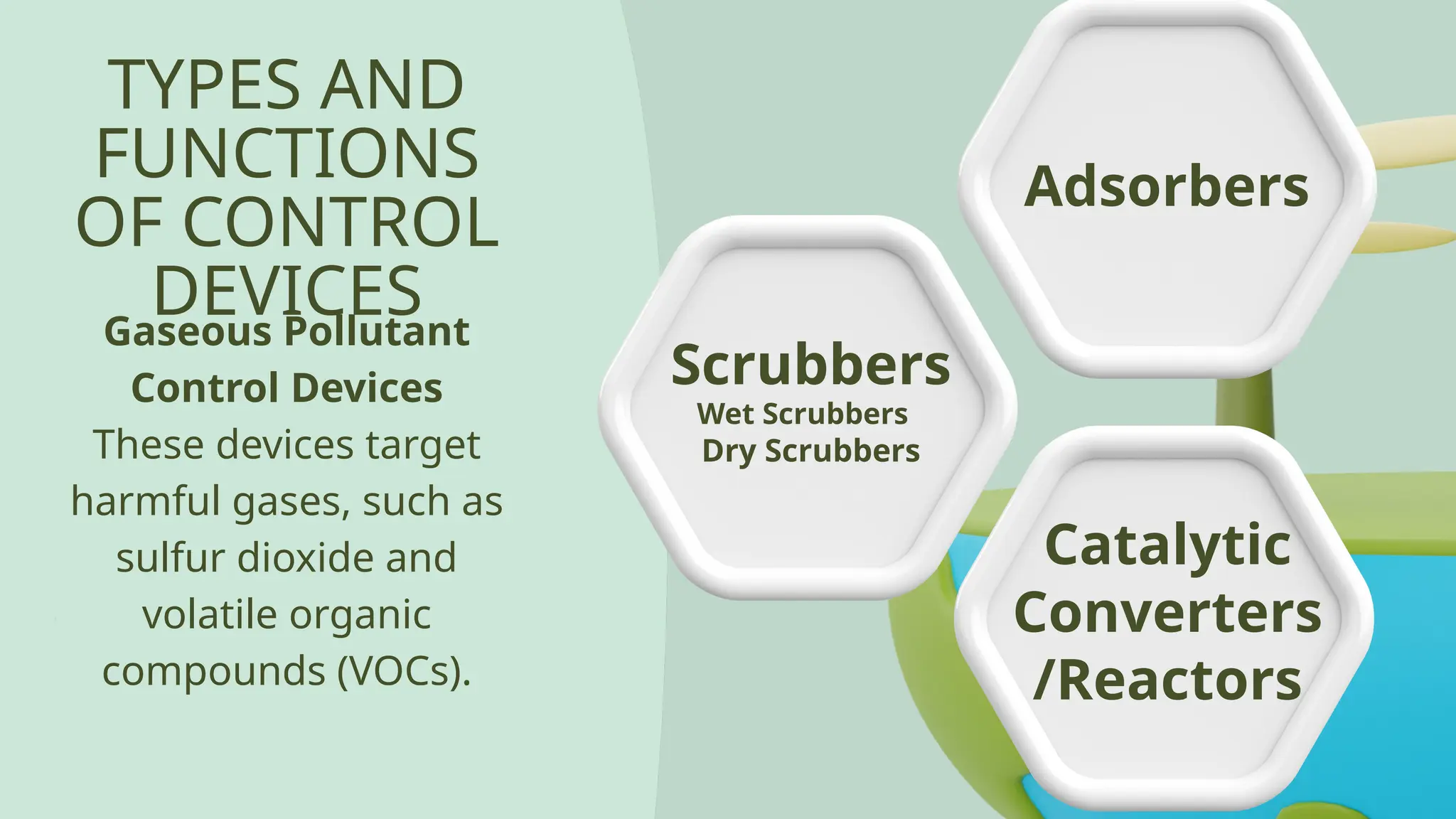
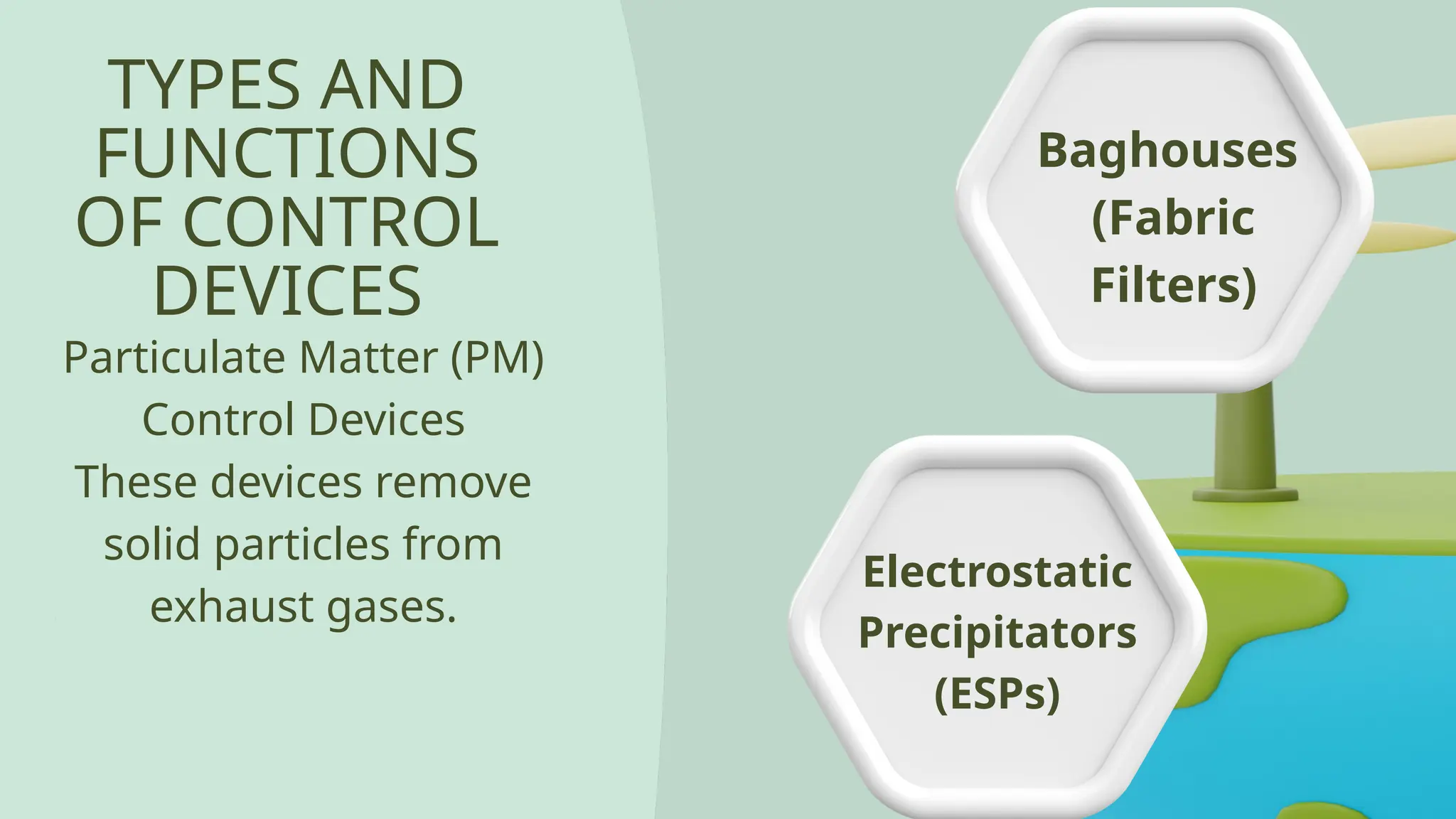
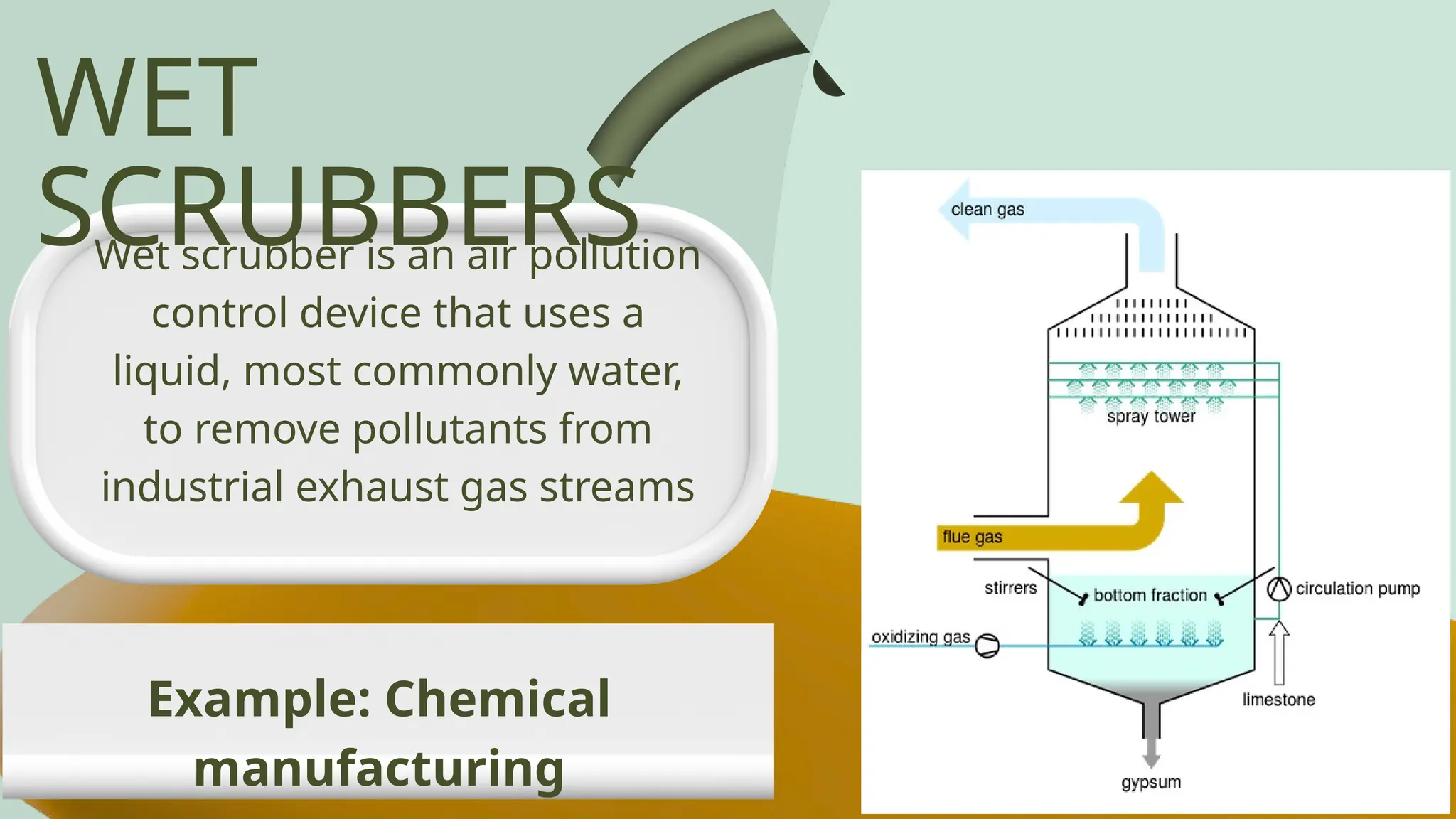
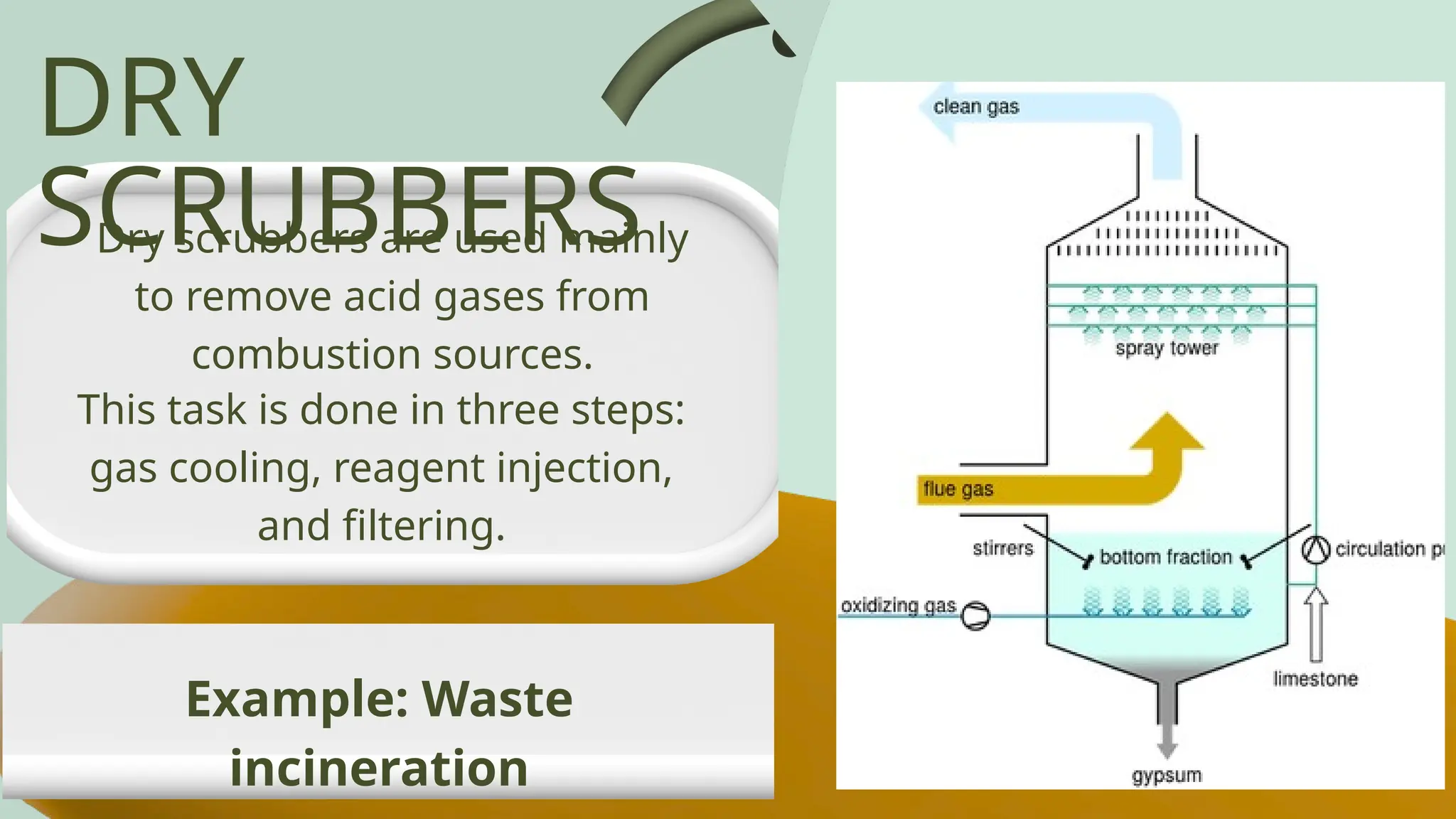
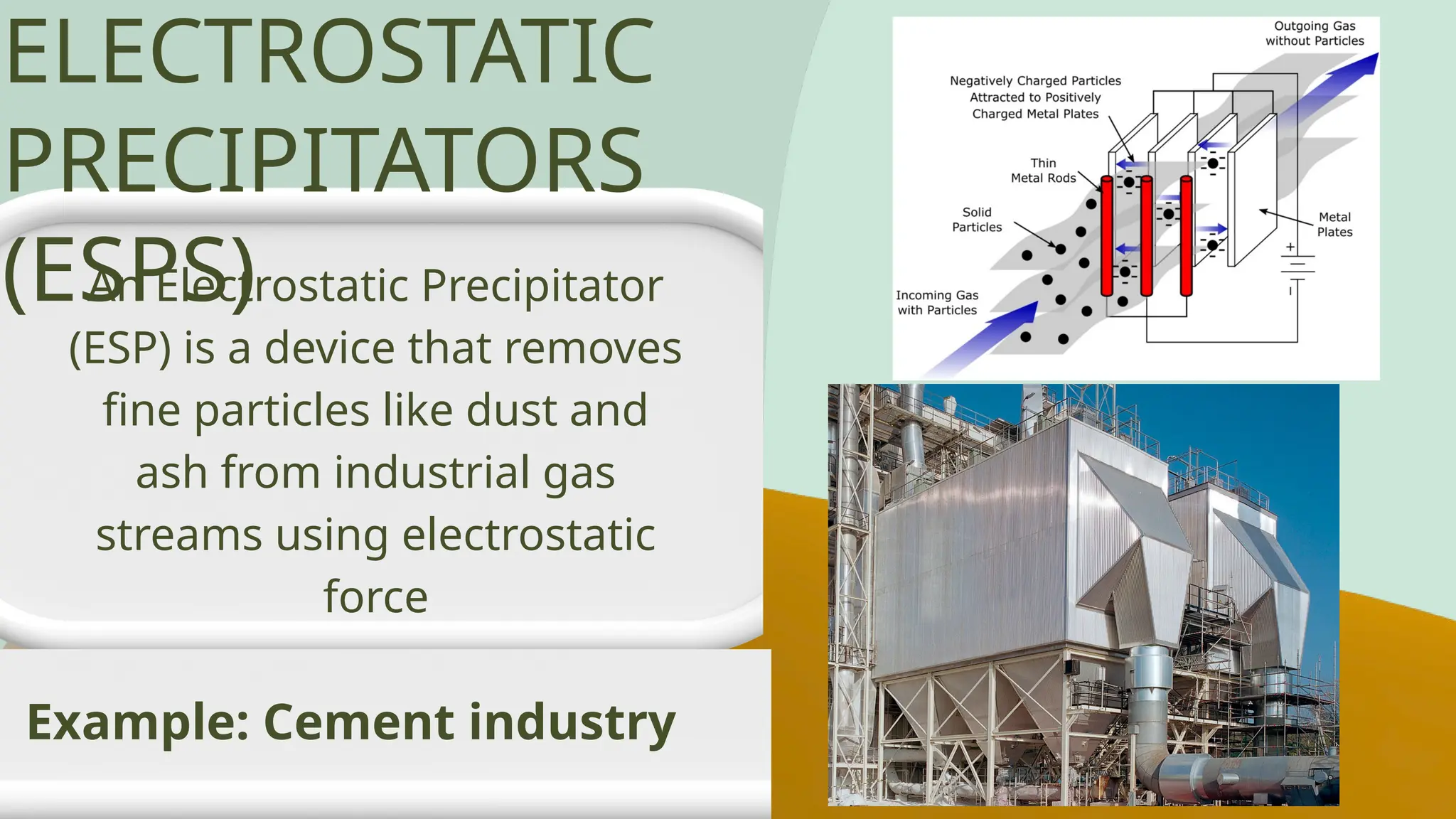
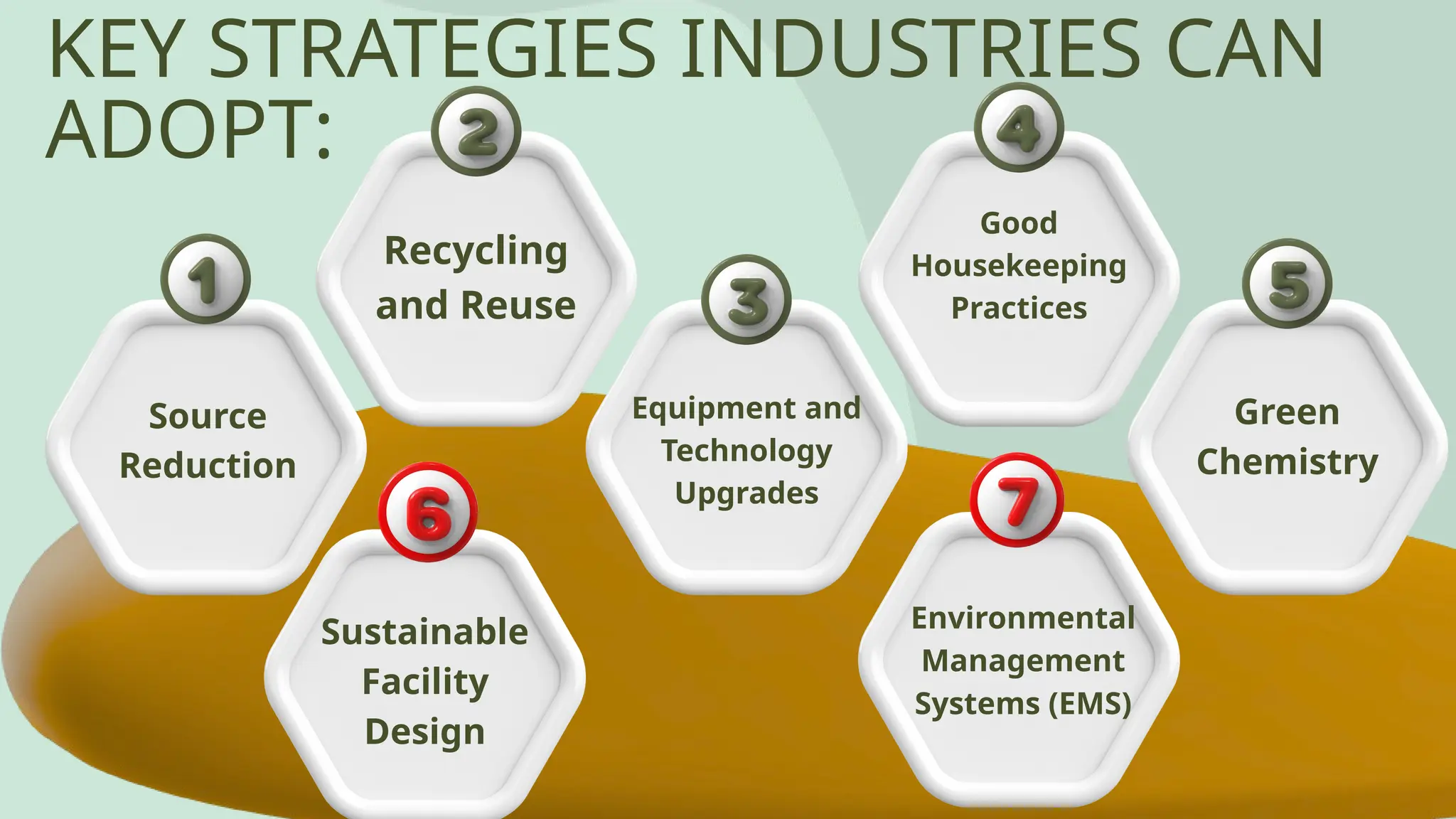
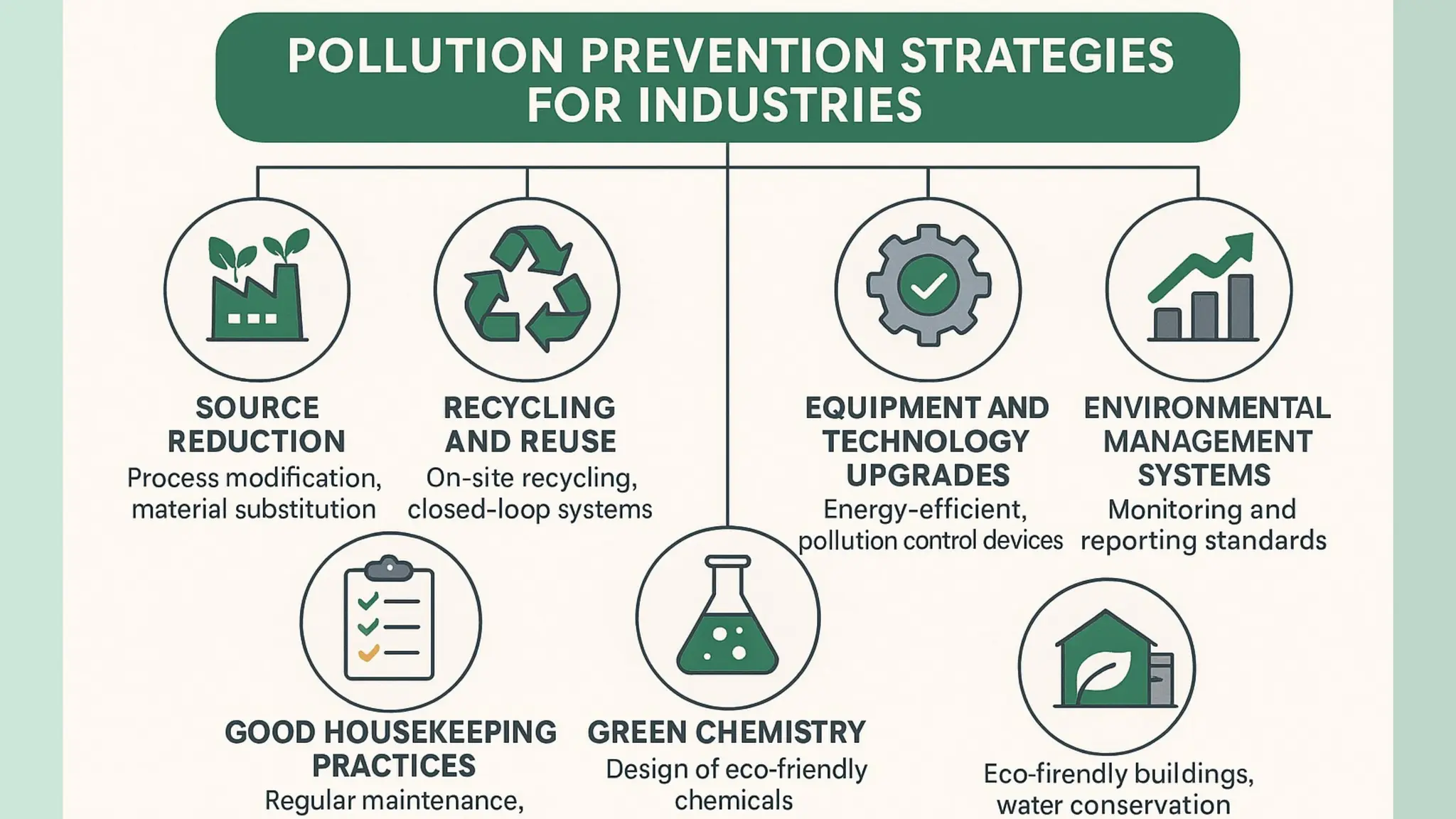
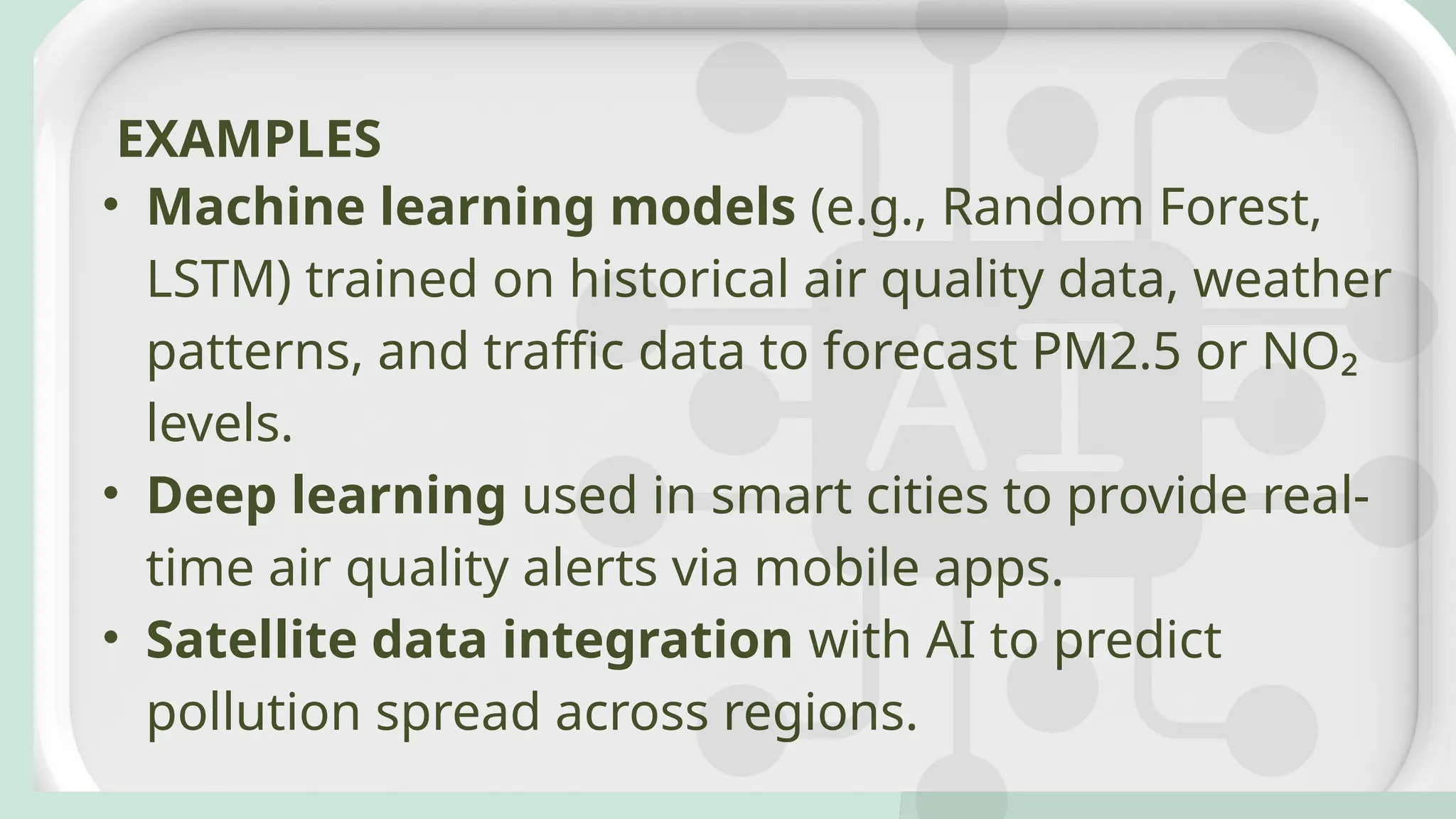
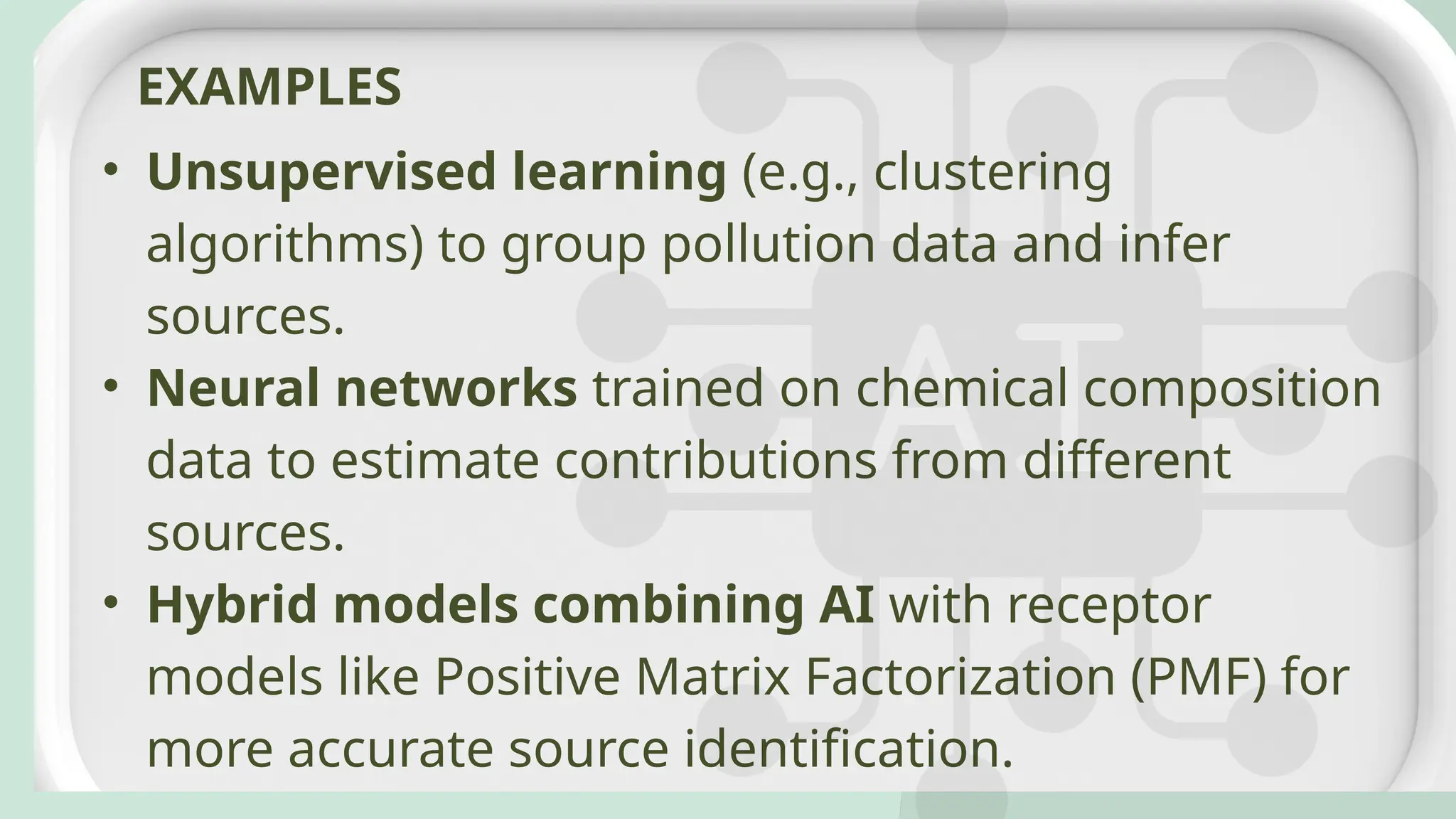
Air pollution control devices help reduce harmful emissions from industries and vehicles. Common examples include electrostatic precipitators, baghouse filters, scrubbers, and catalytic converters—each designed to capture or neutralize pollutants like dust, gases, and chemicals before they reach the atmosphere.