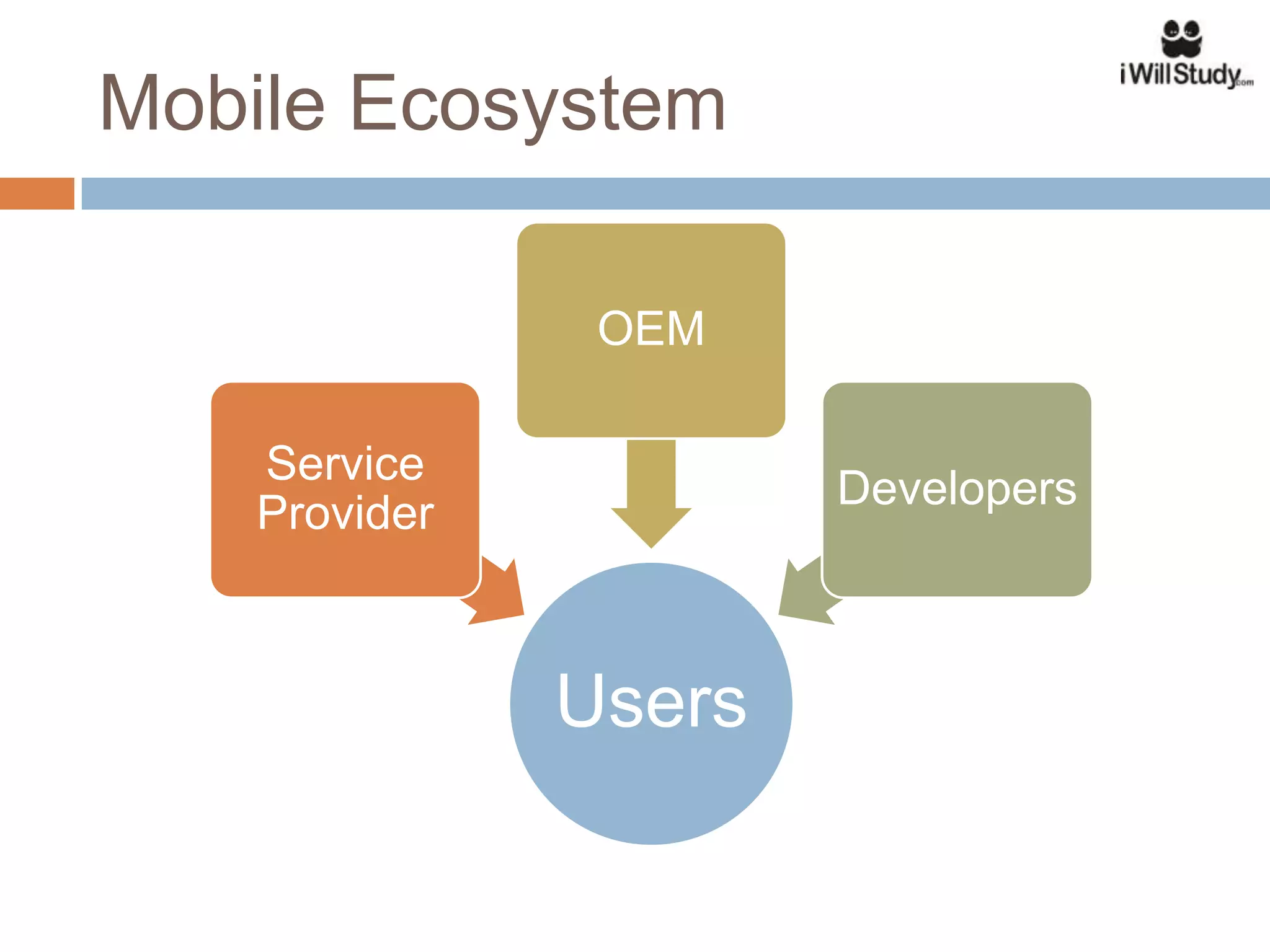
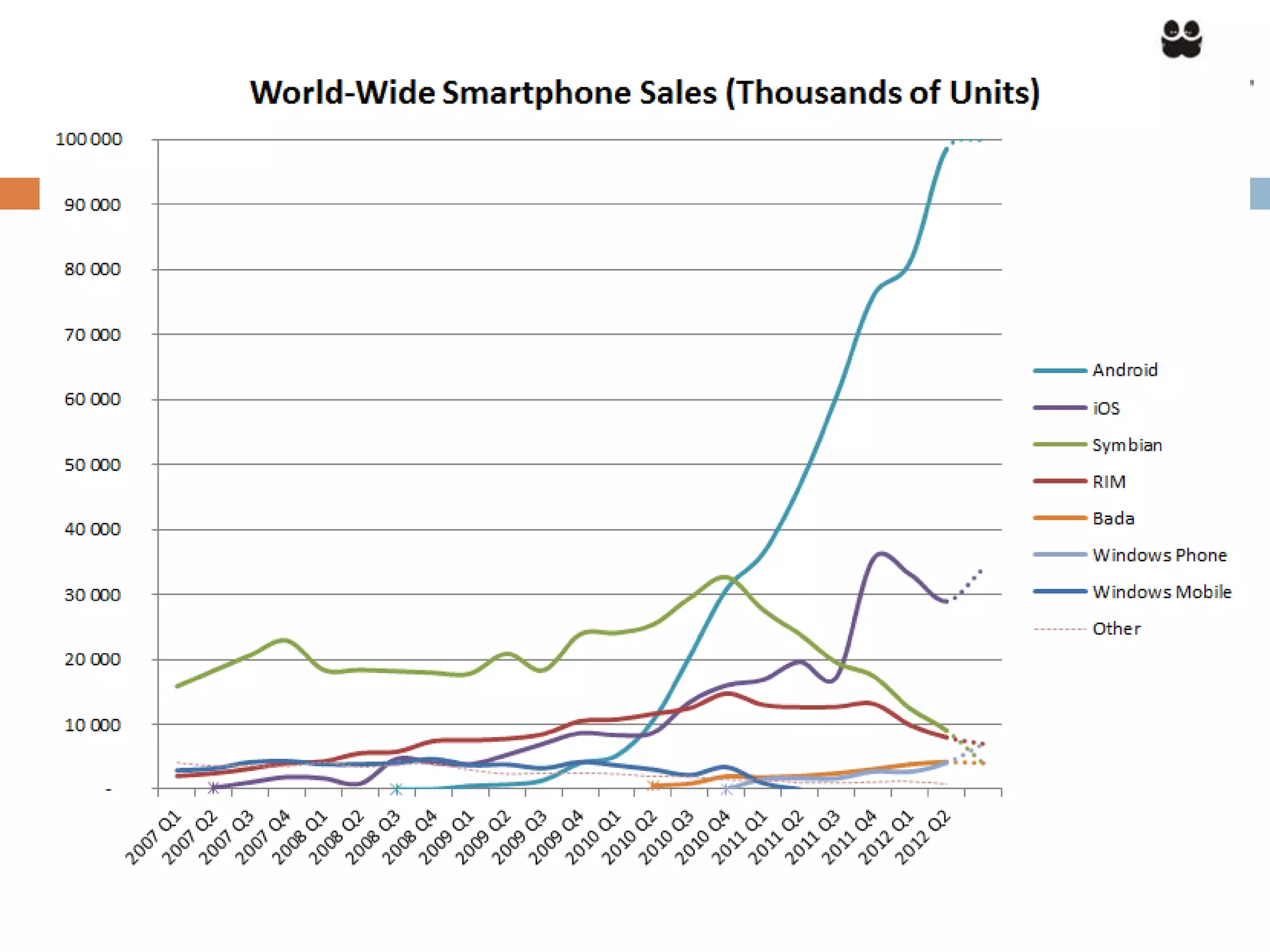
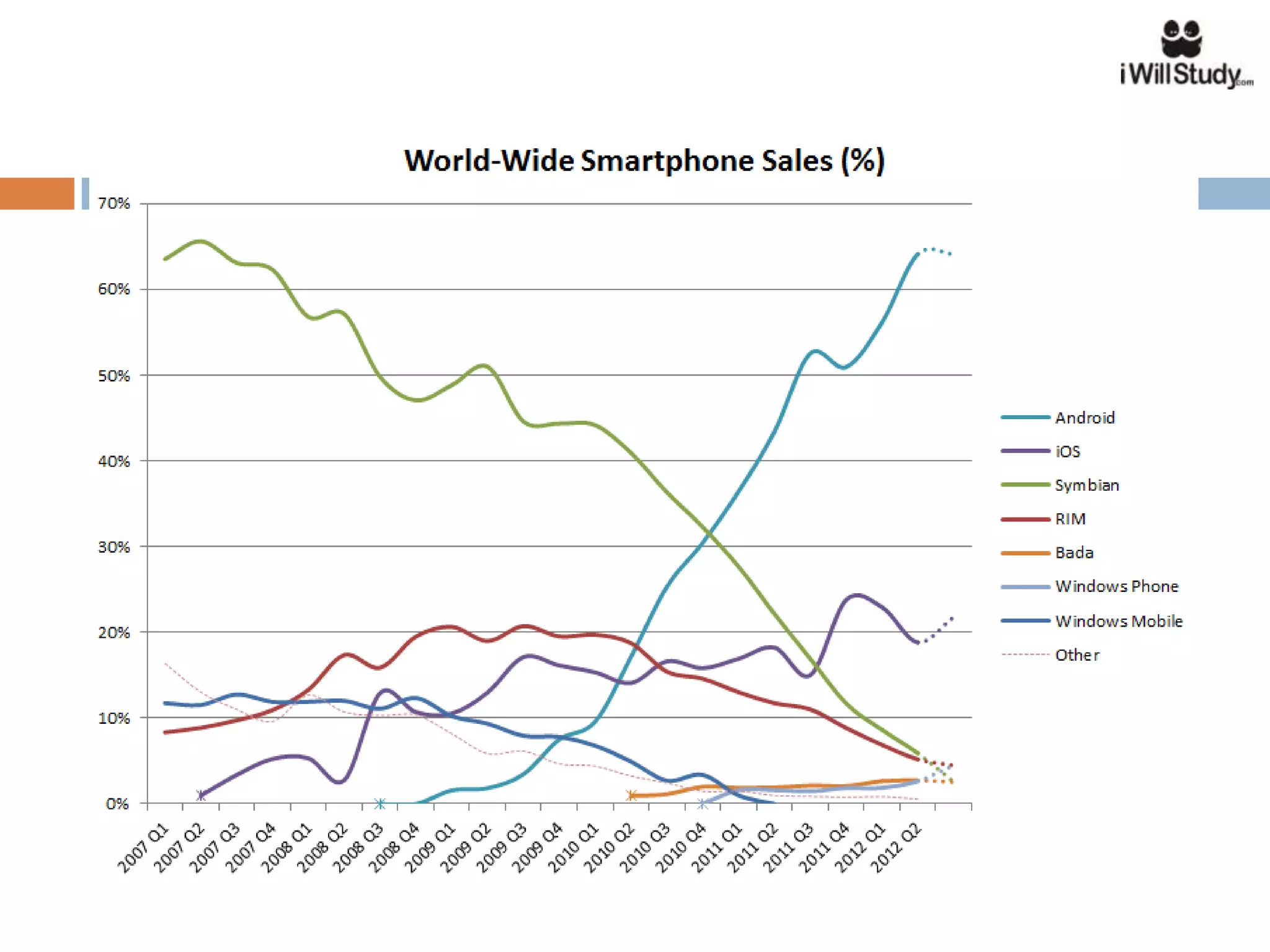
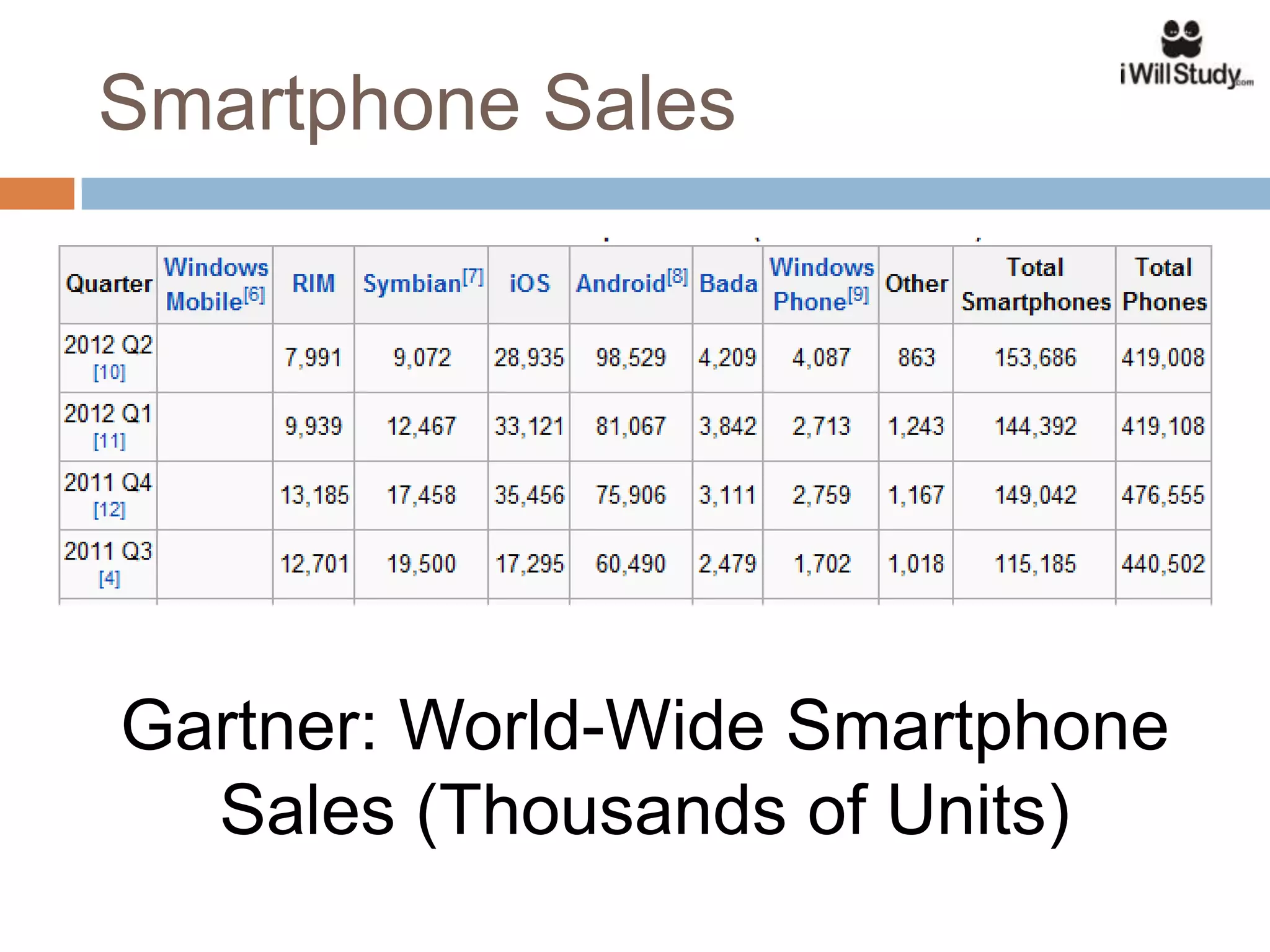
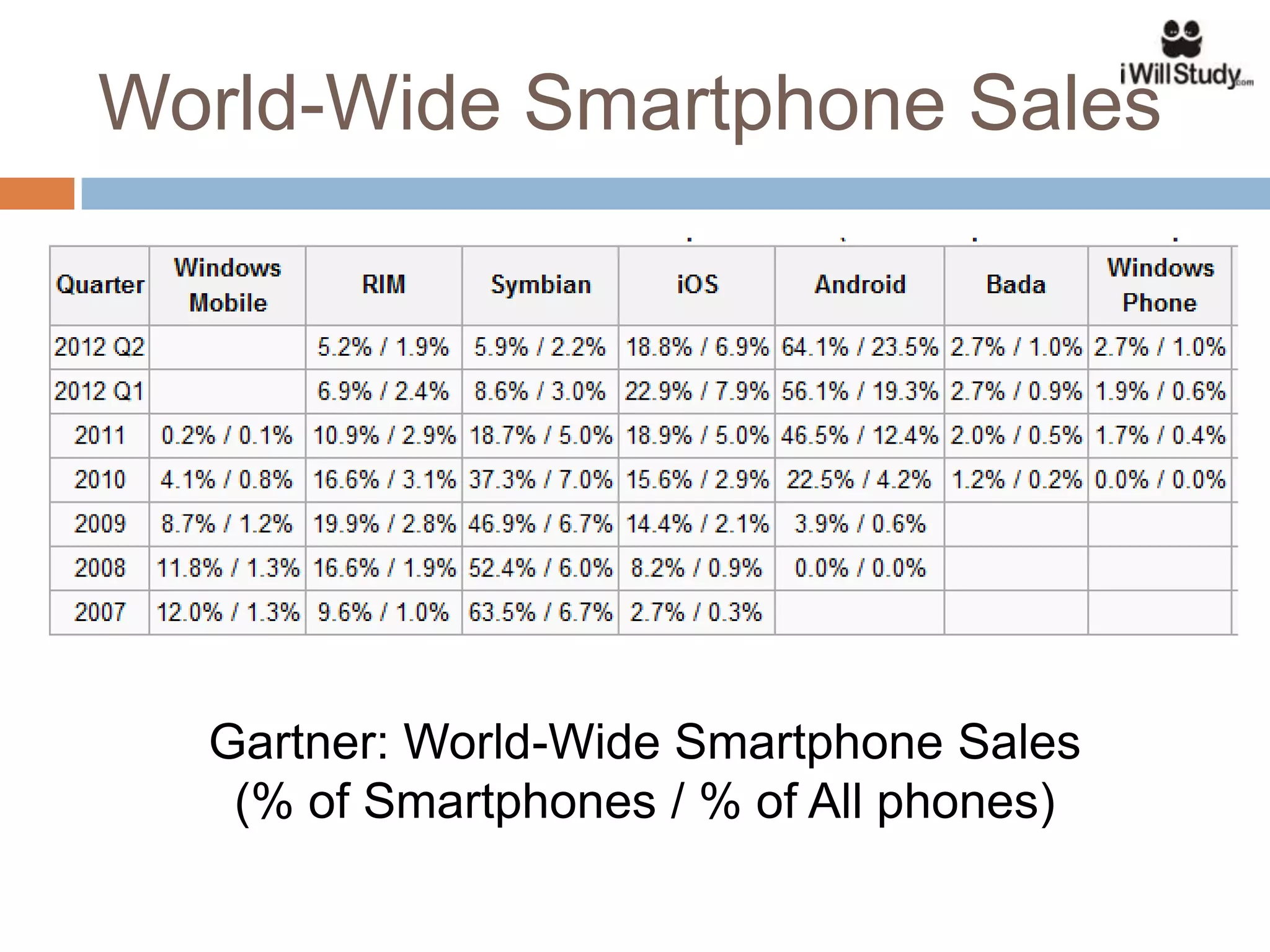
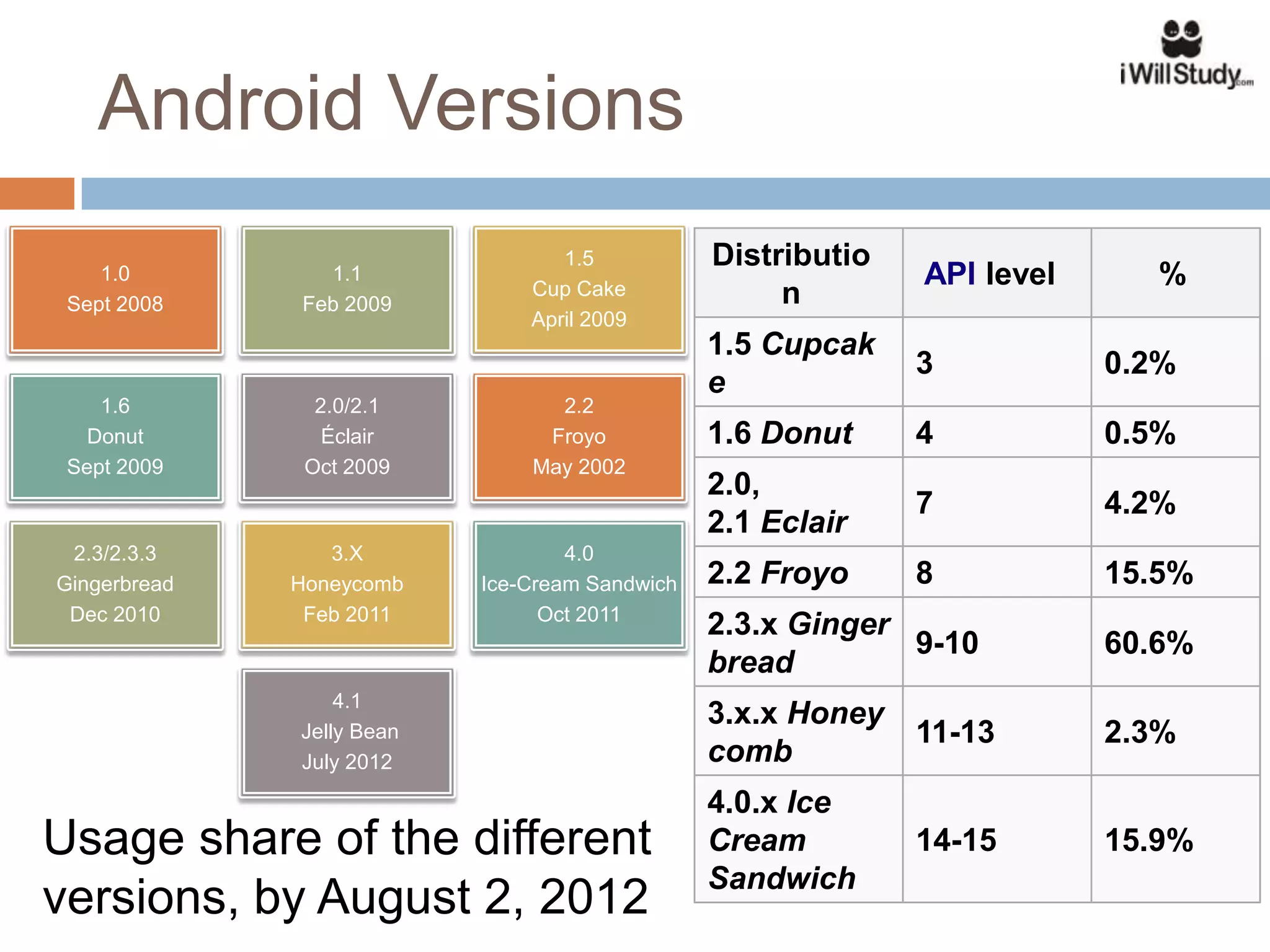
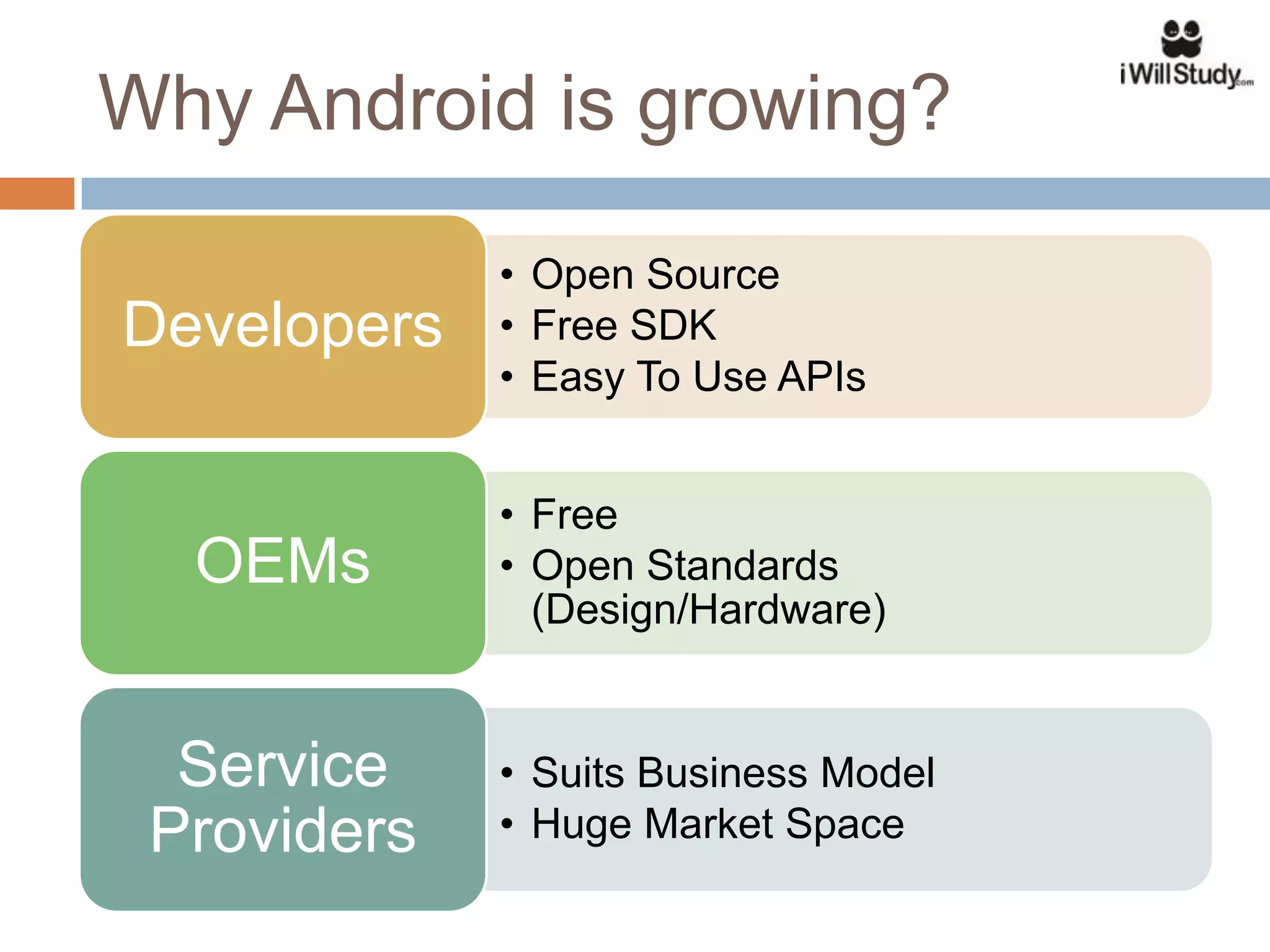
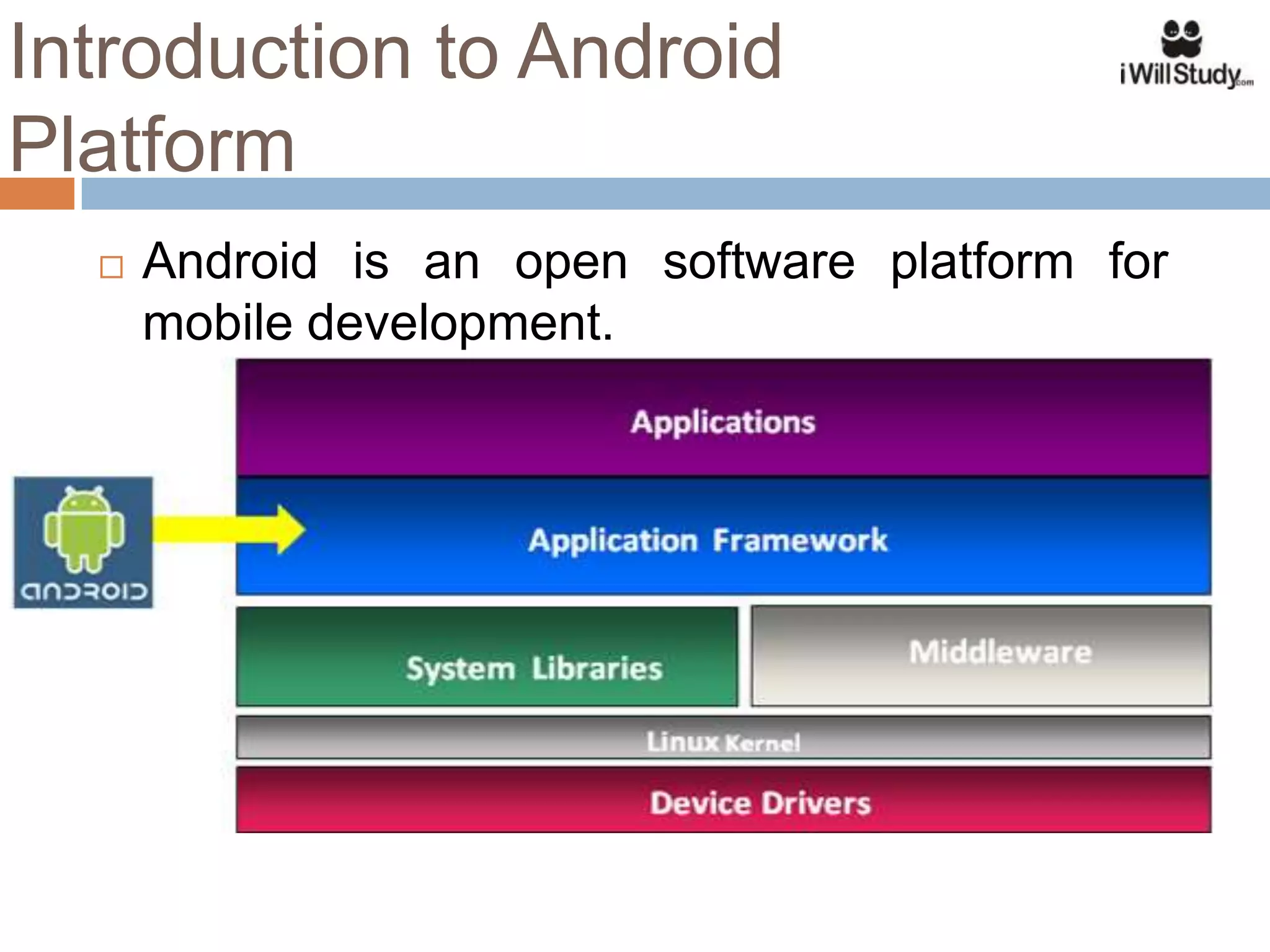
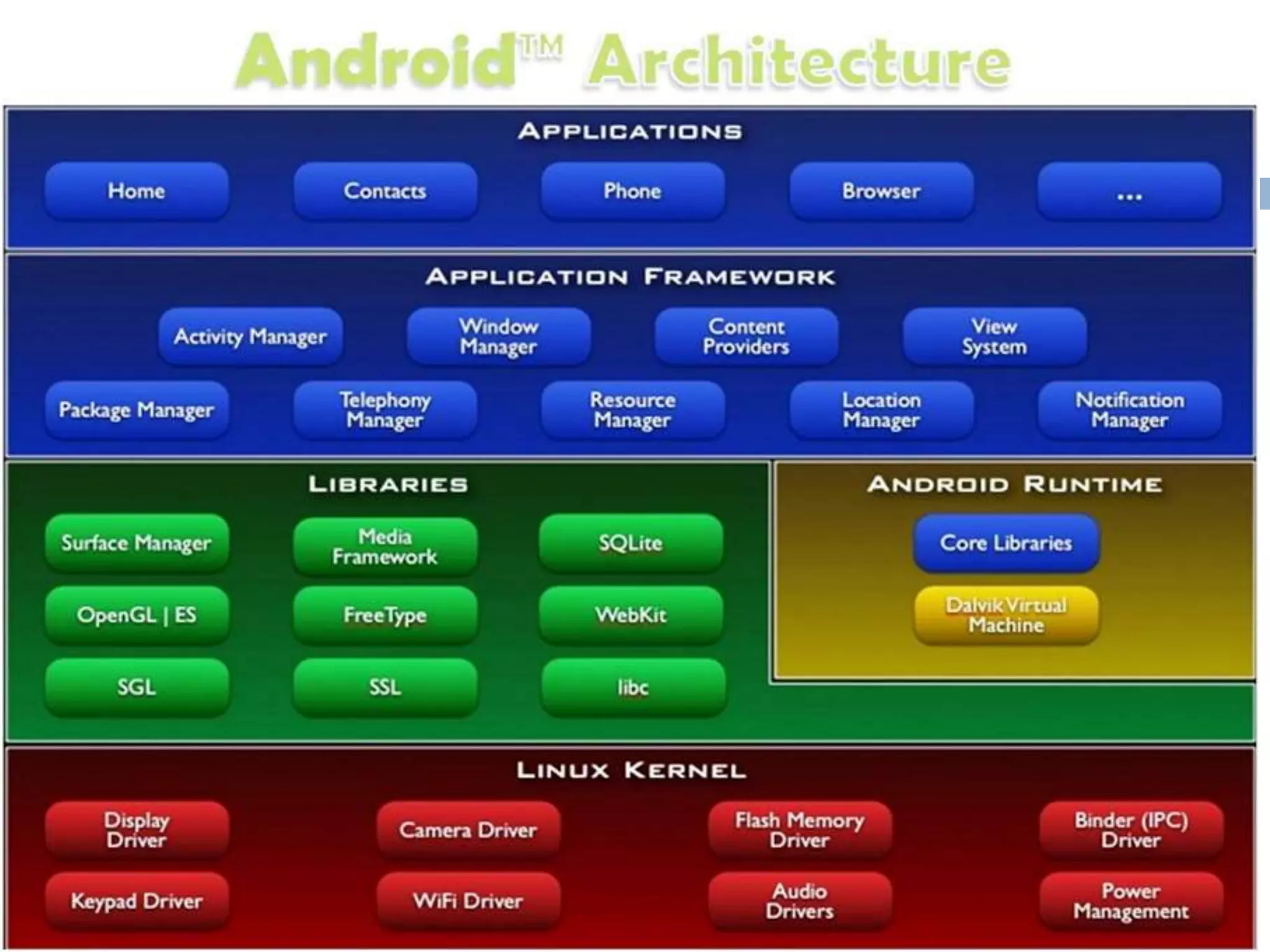
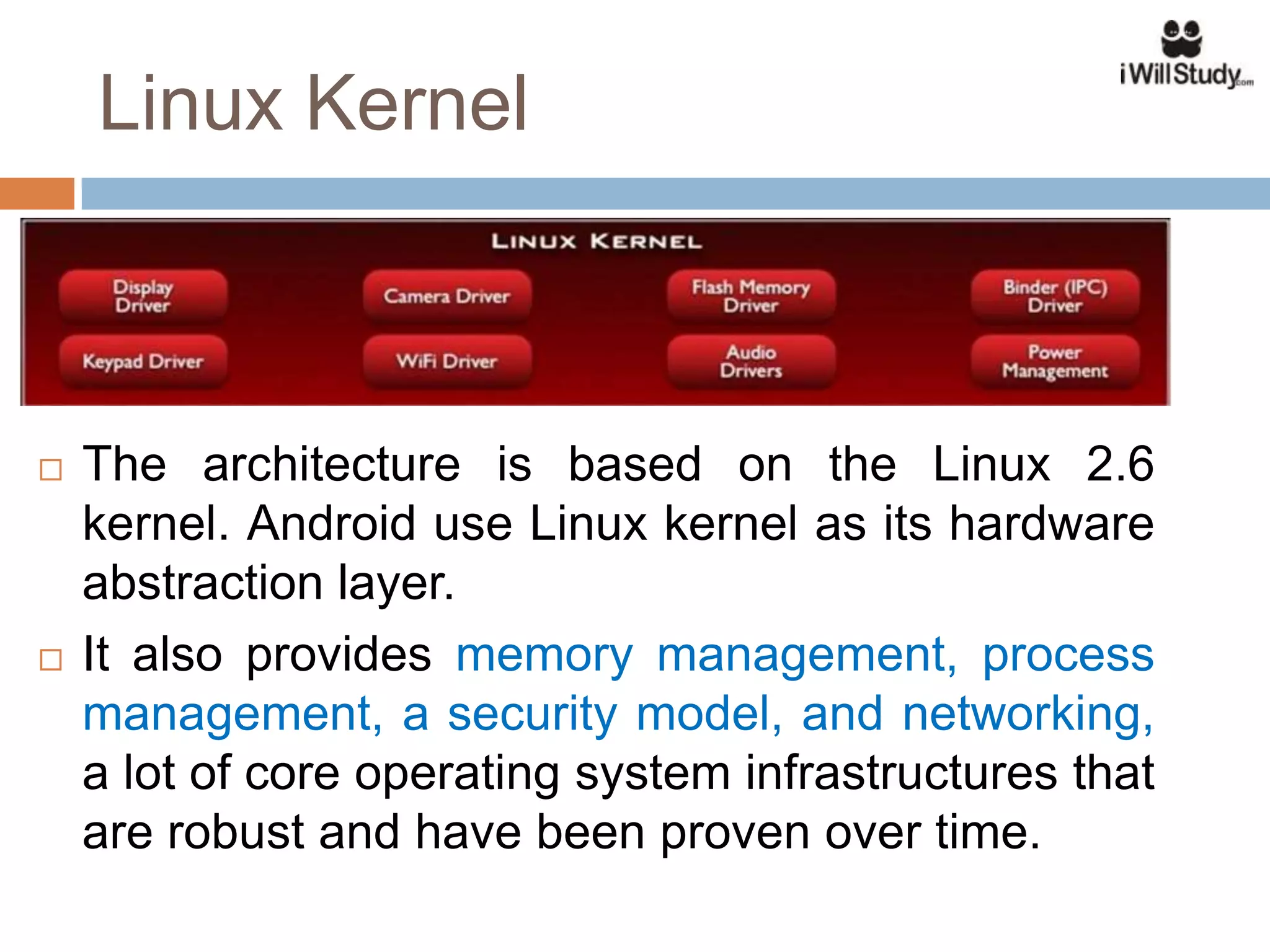
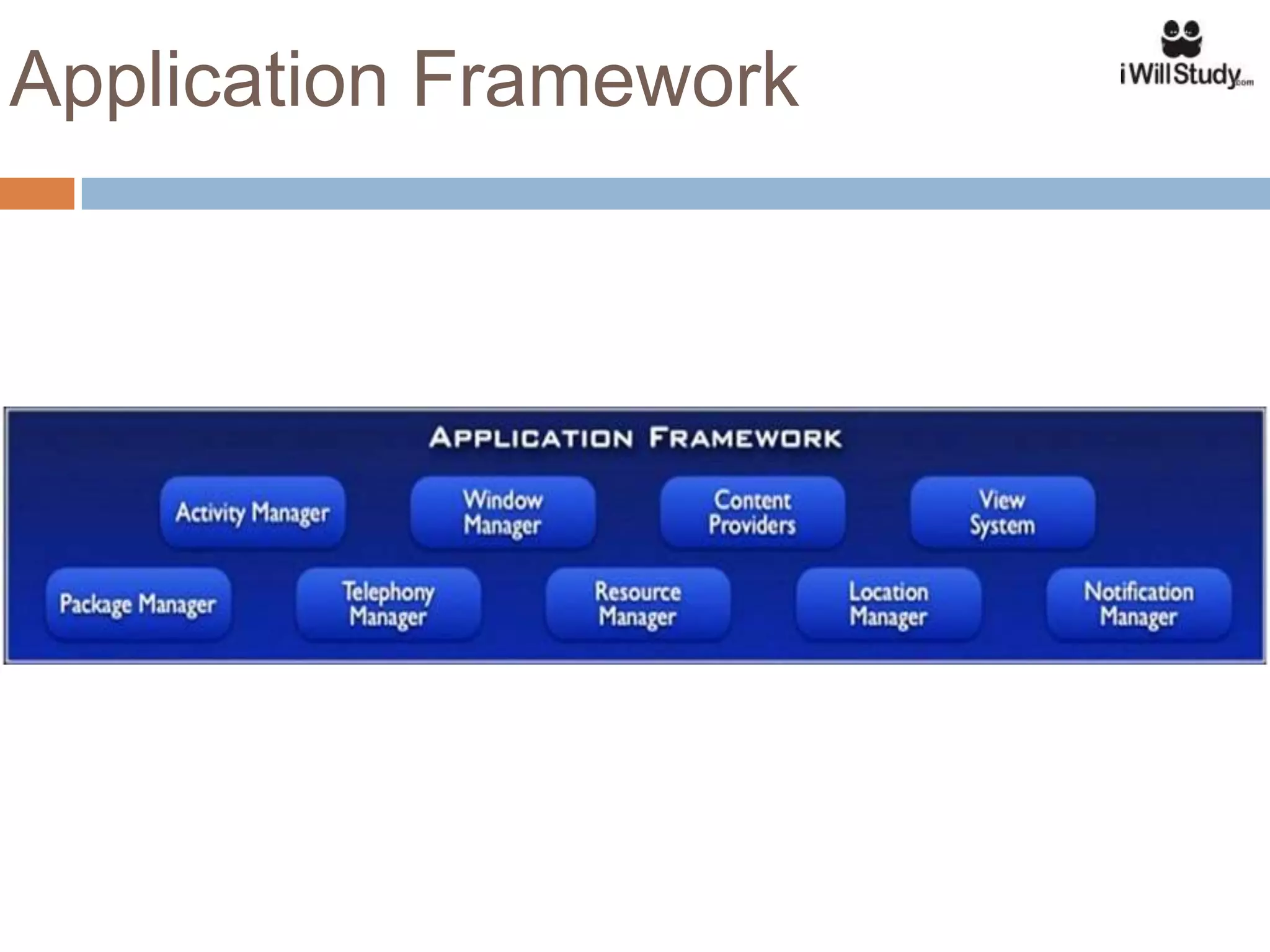
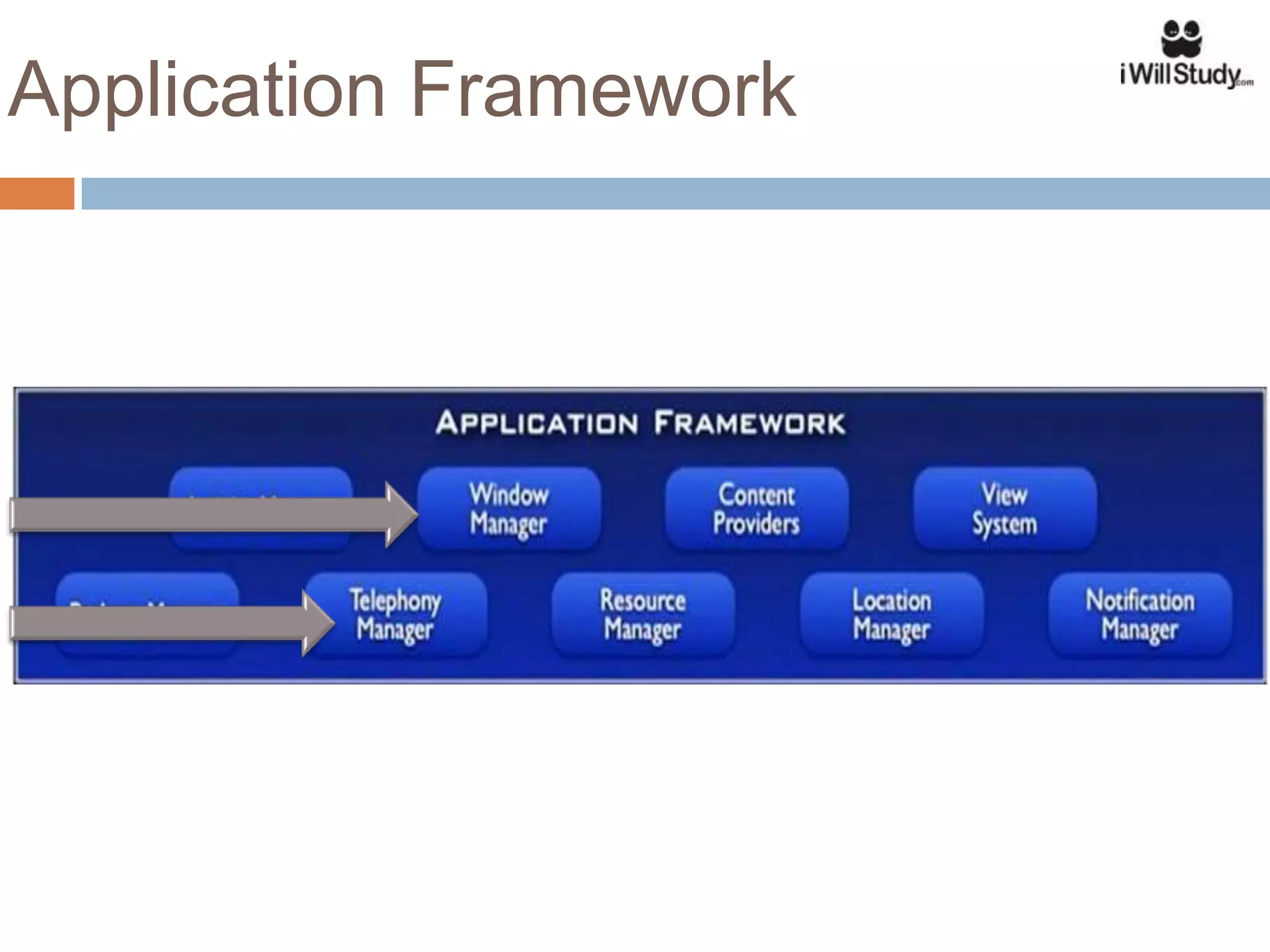
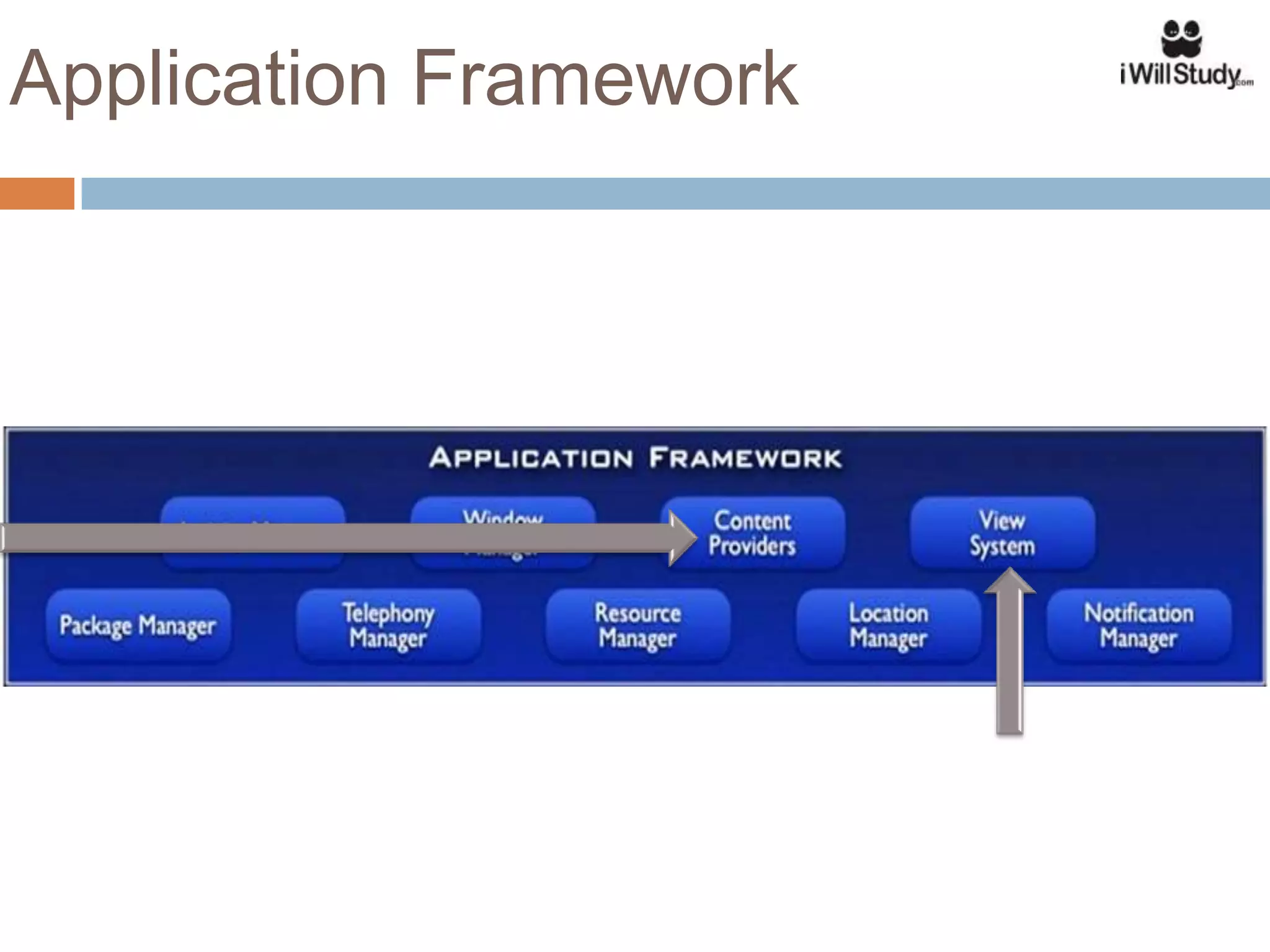
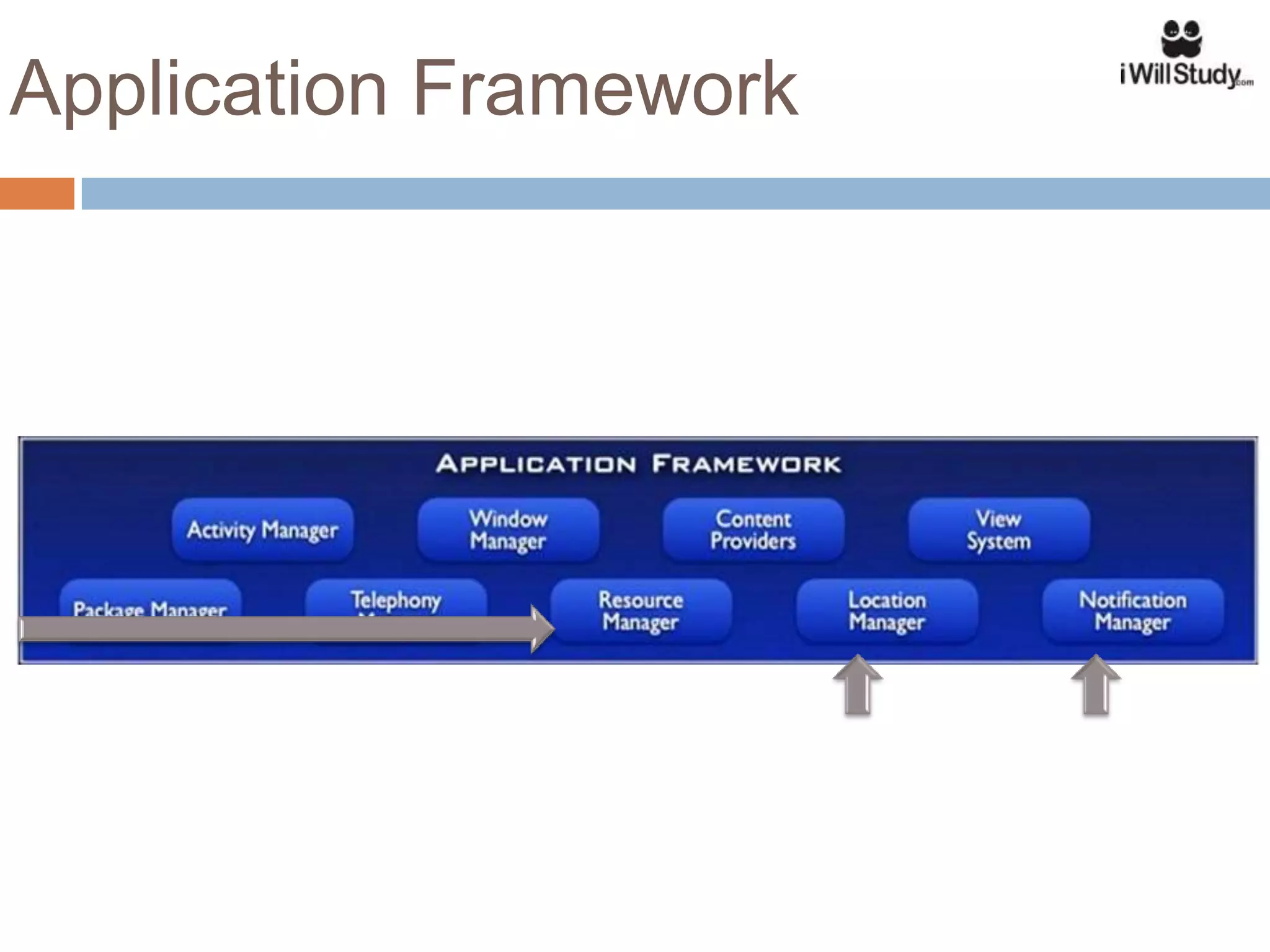
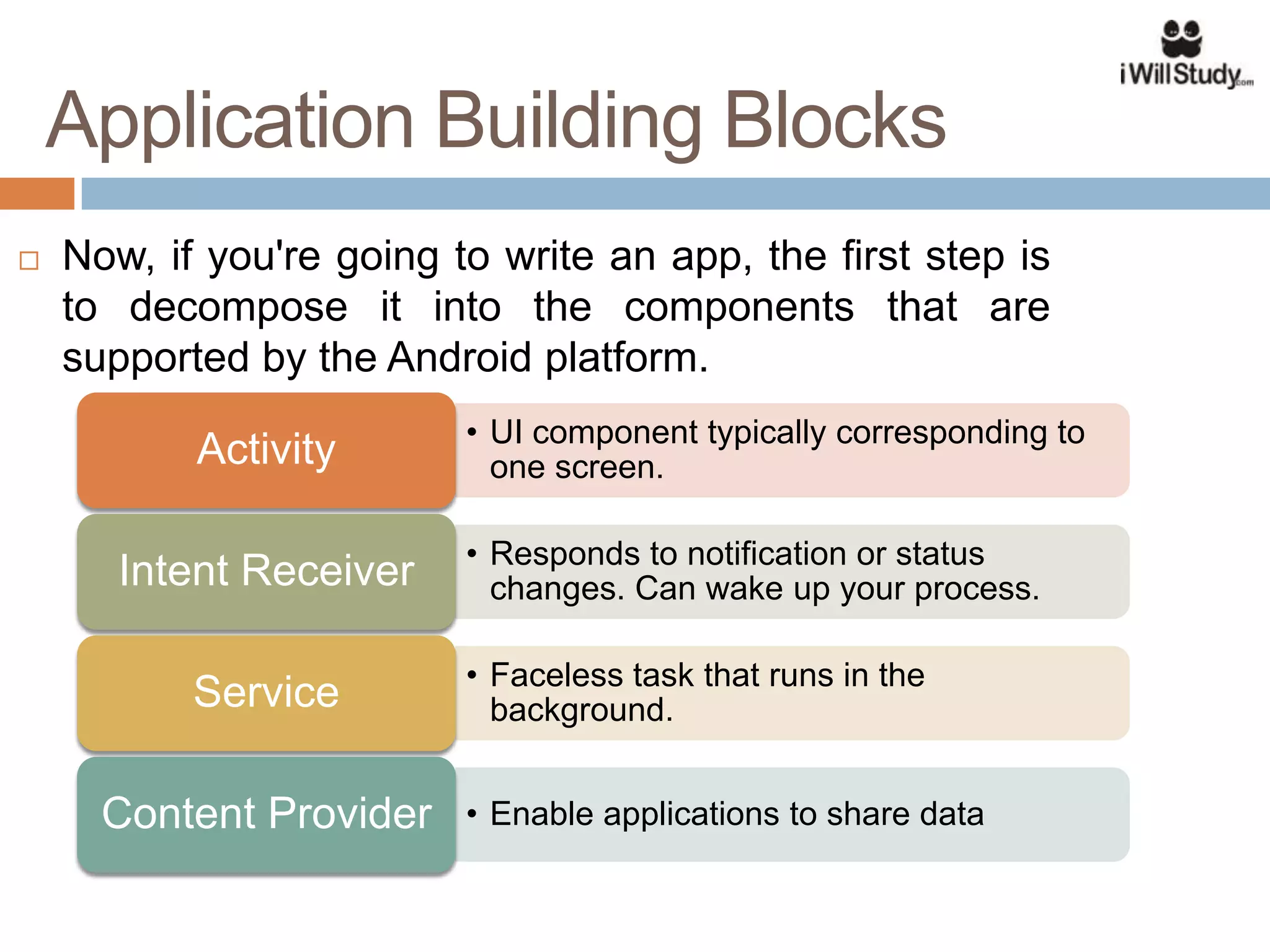
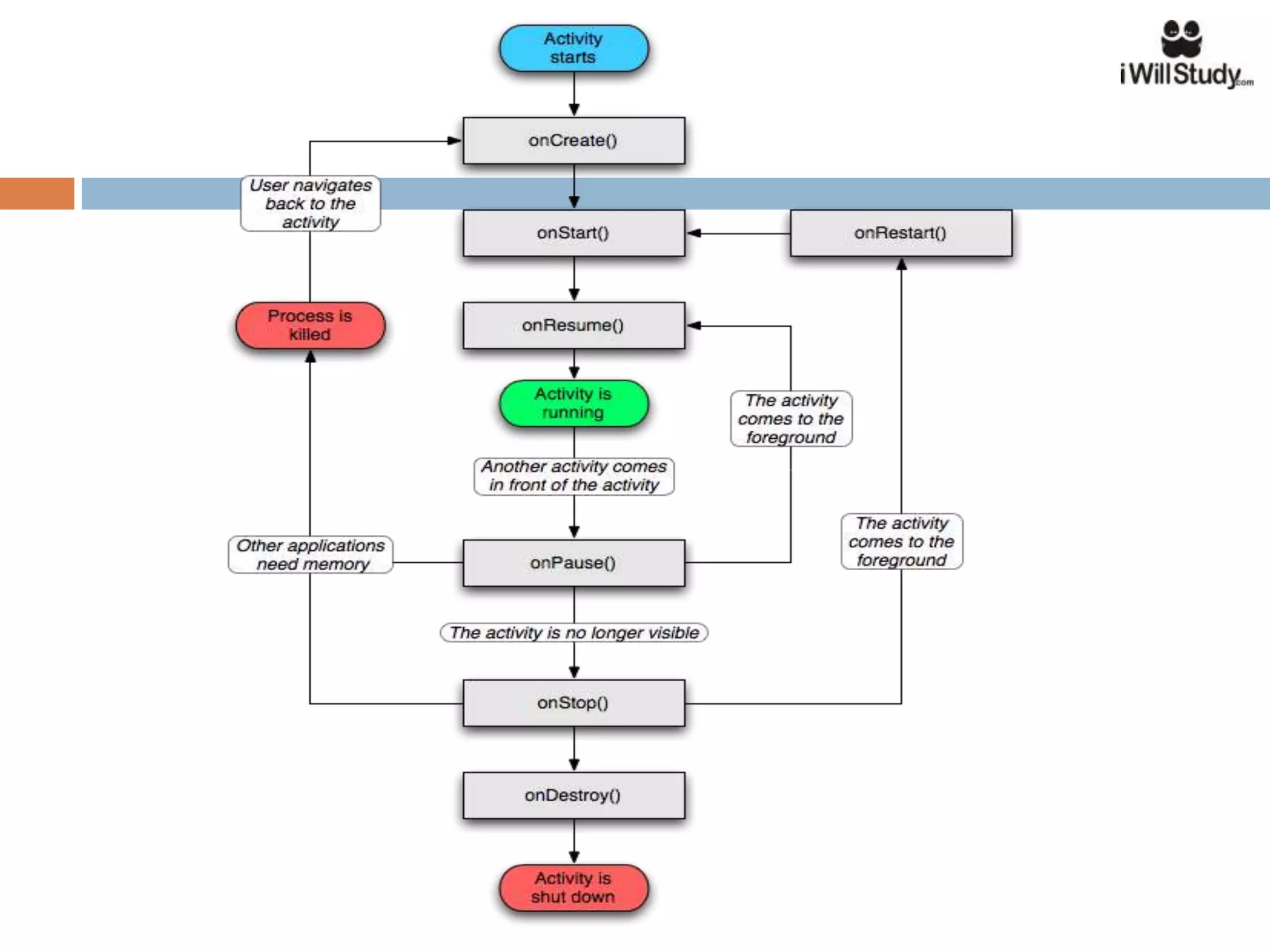
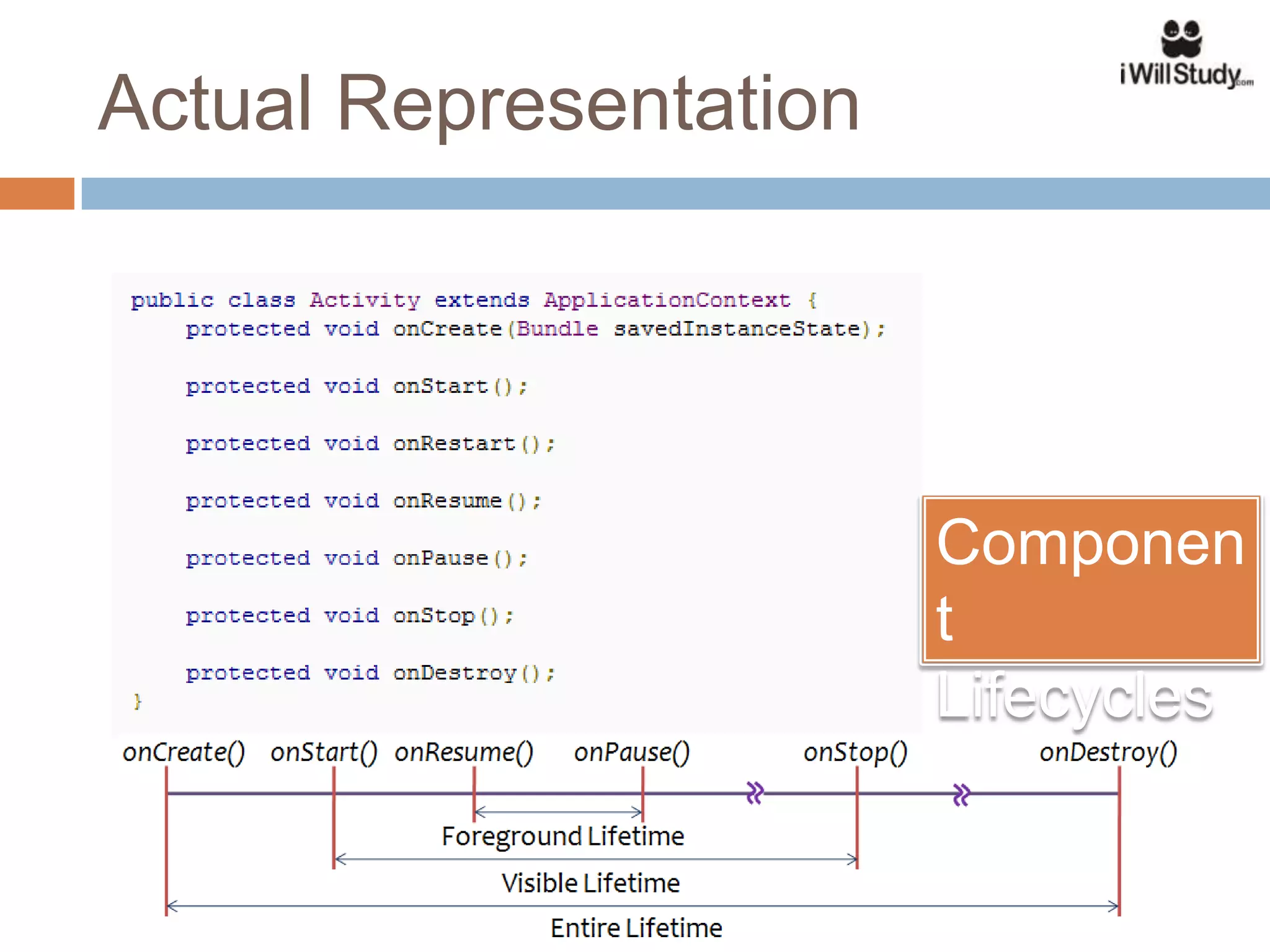
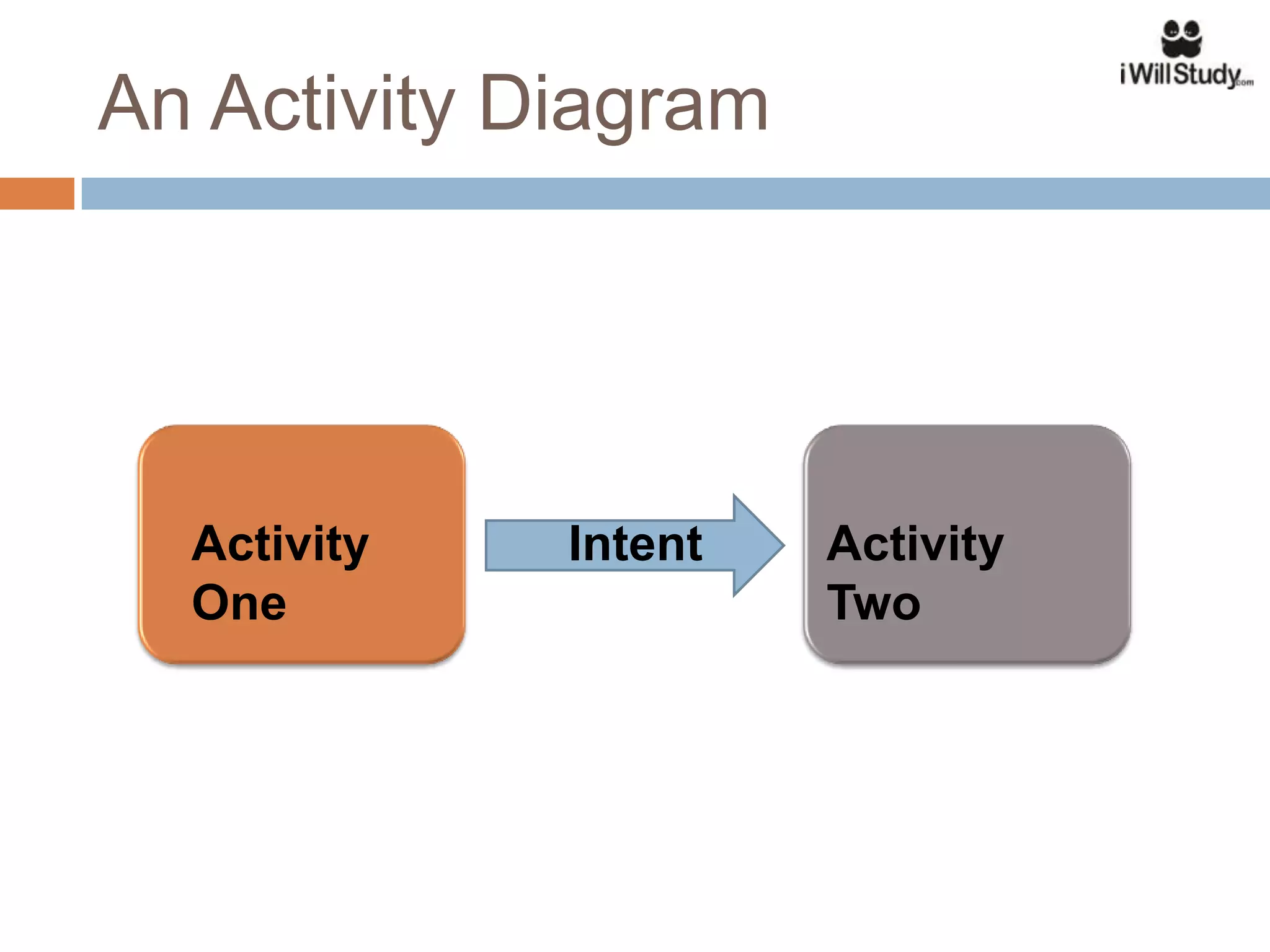
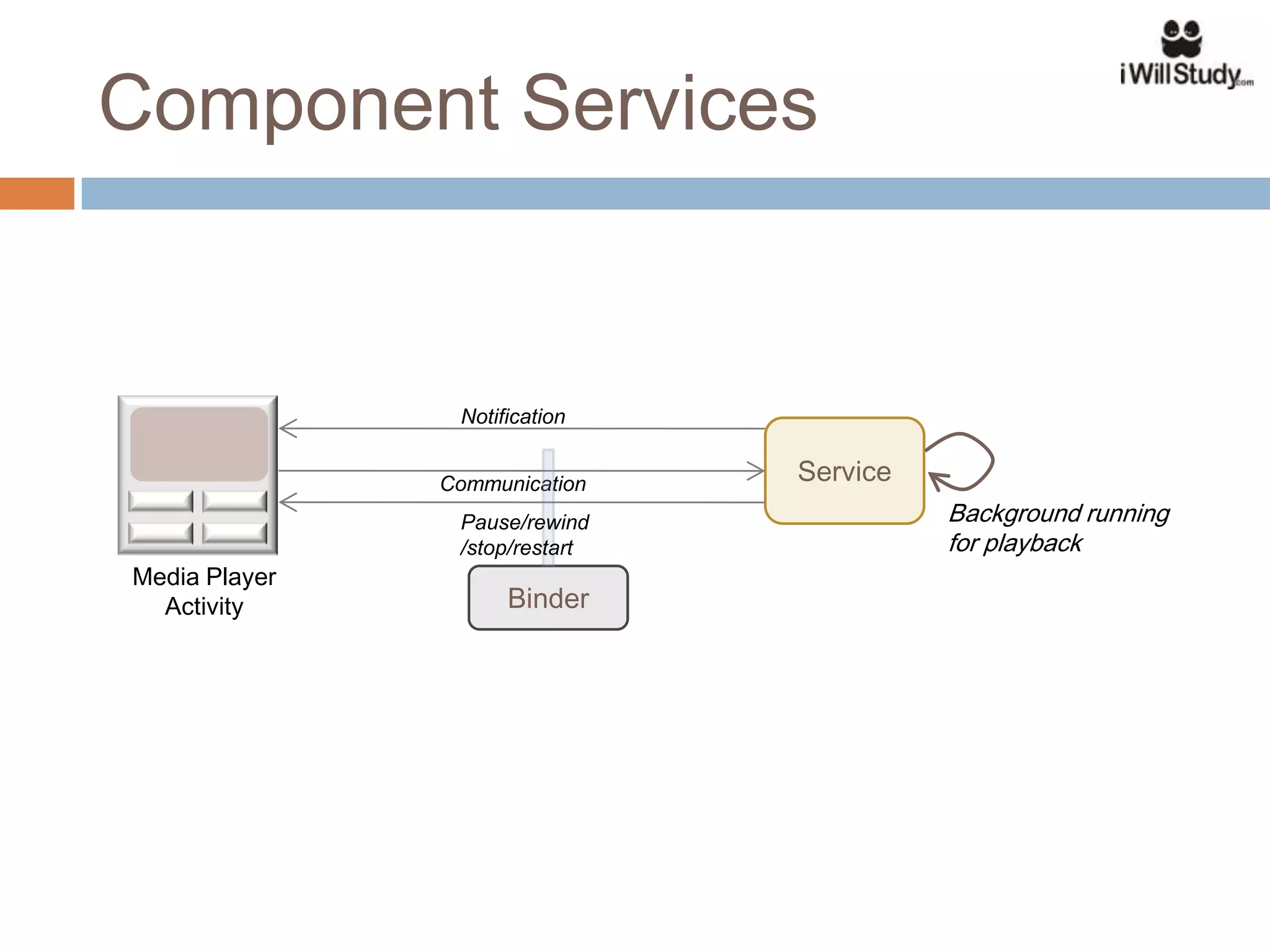
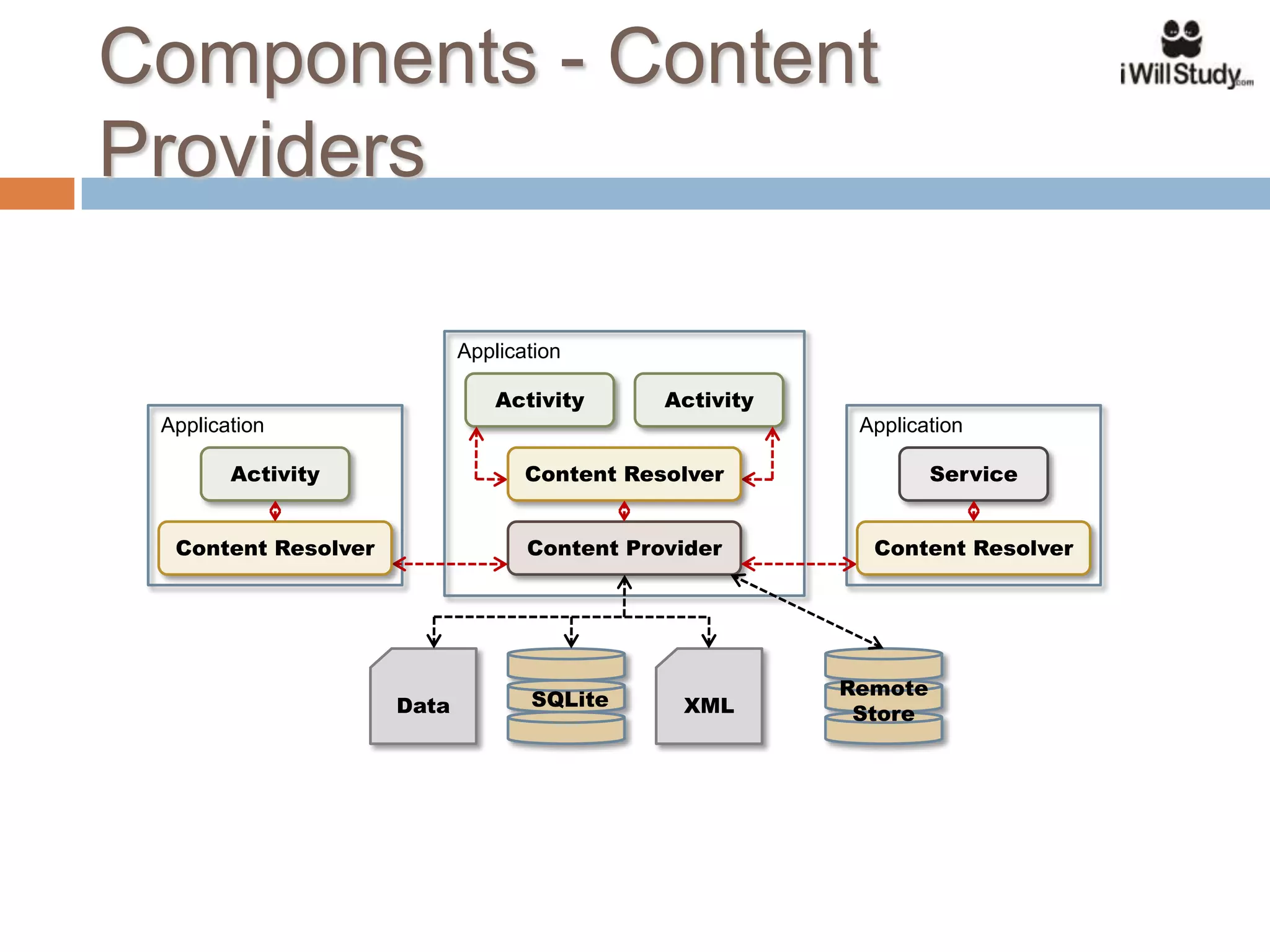
This document provides an overview of the Android mobile ecosystem and operating system. It discusses the key players in the ecosystem including OEMs, service providers, and developers. It also summarizes Android's history and growth in the mobile market. The document then describes the architecture and core components of the Android operating system including its Linux kernel, native libraries, application framework, and building blocks like activities, services, content providers, and intents. It provides examples of how these components work together in applications.