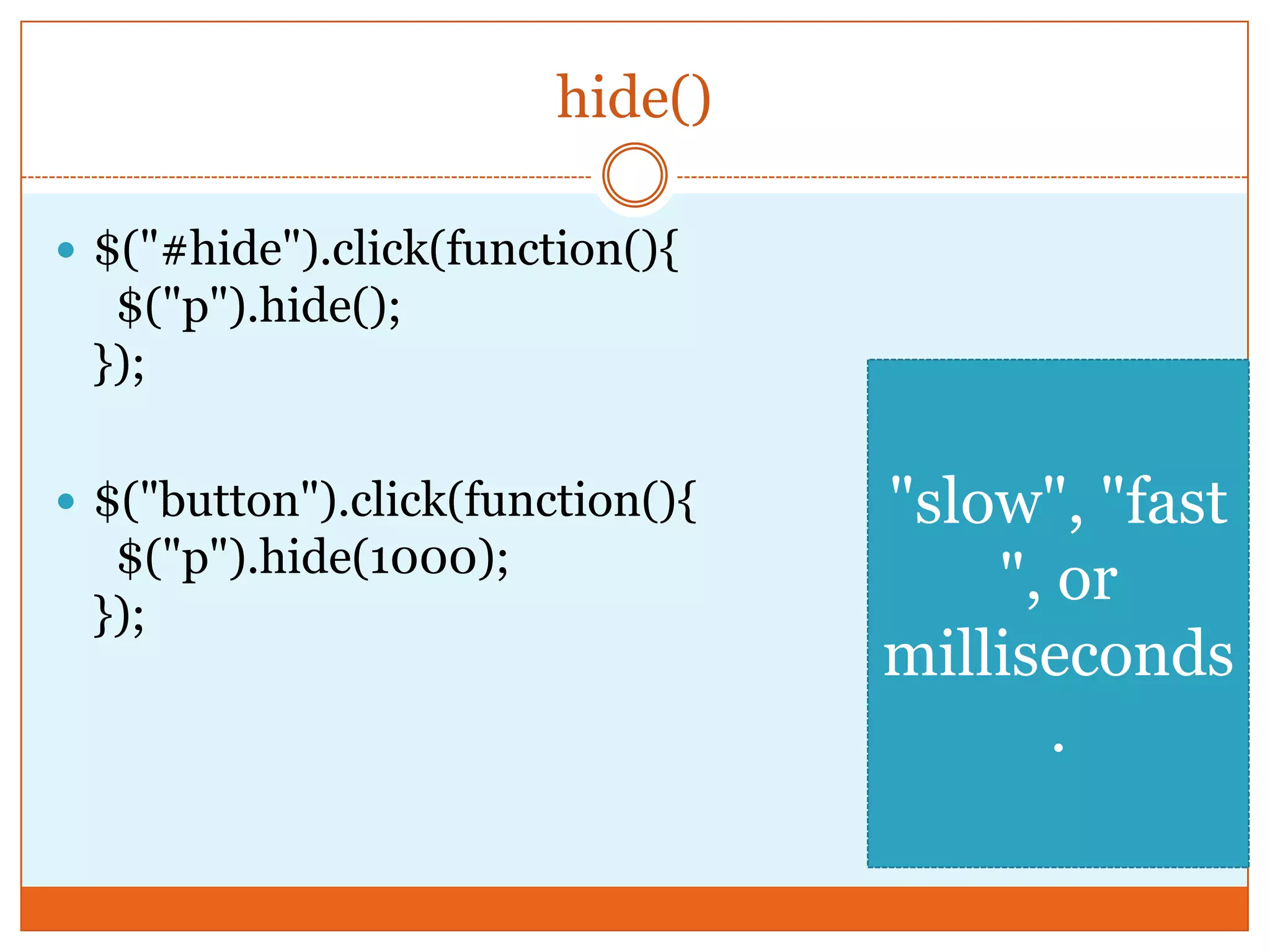
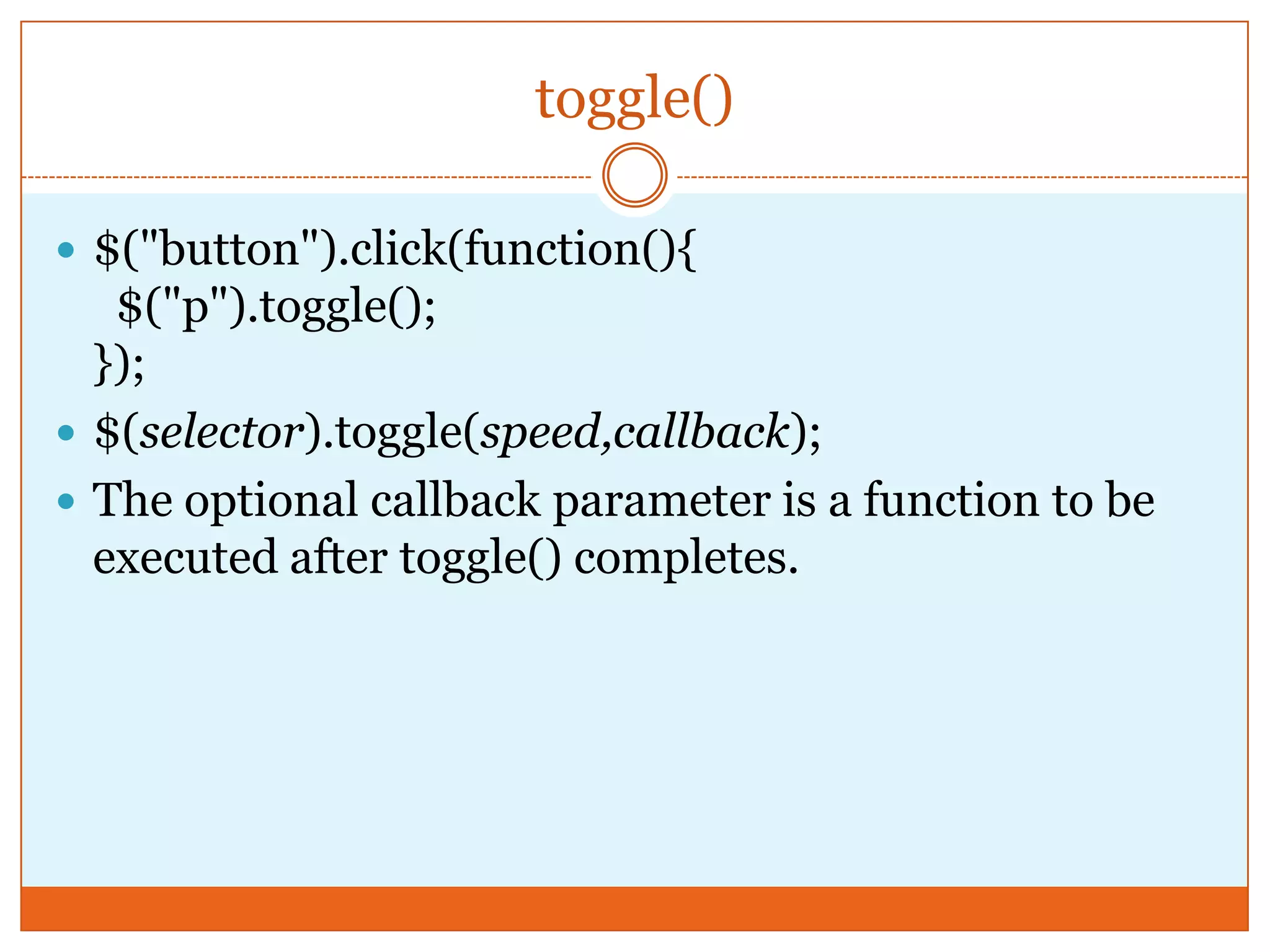
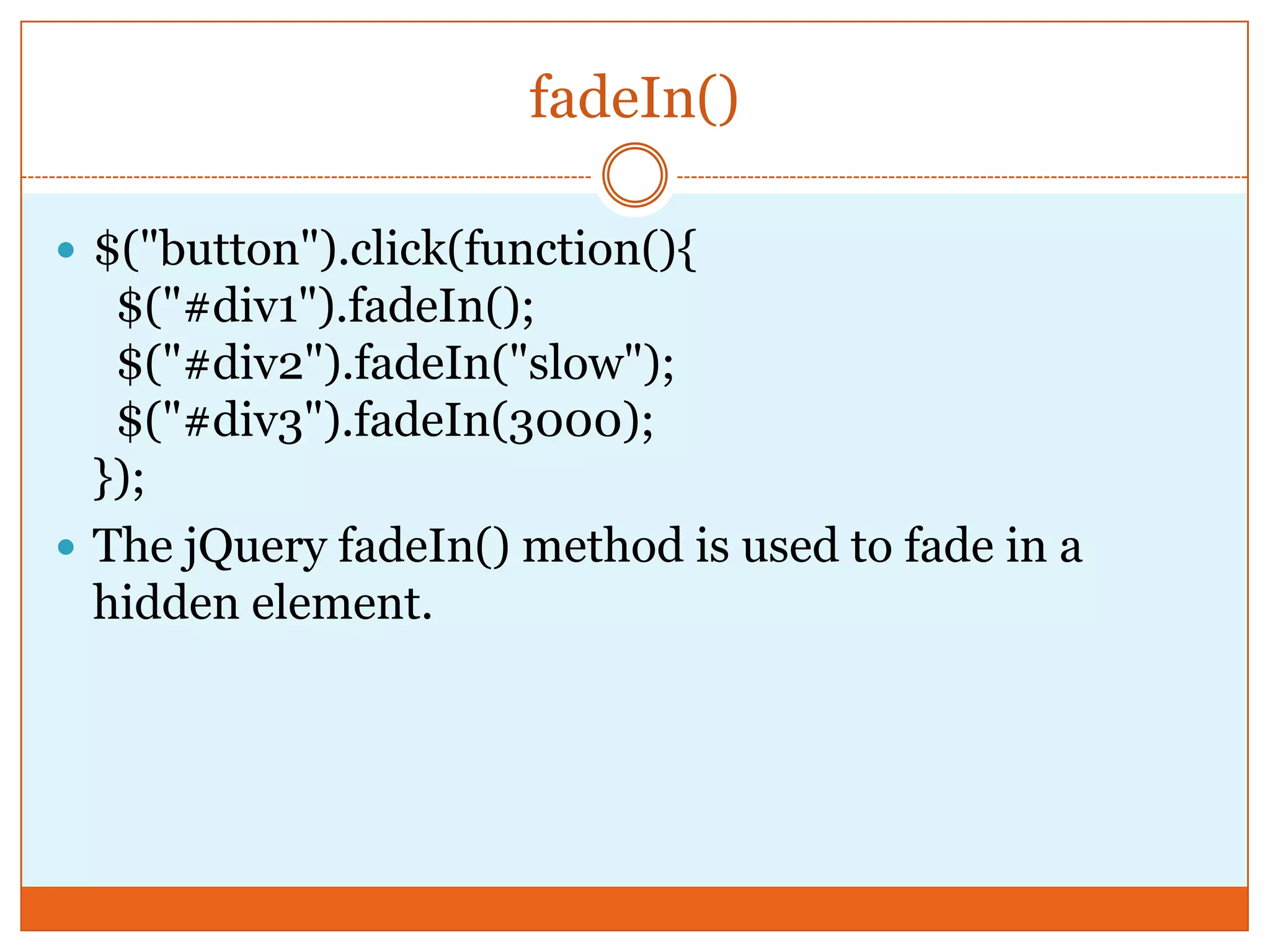
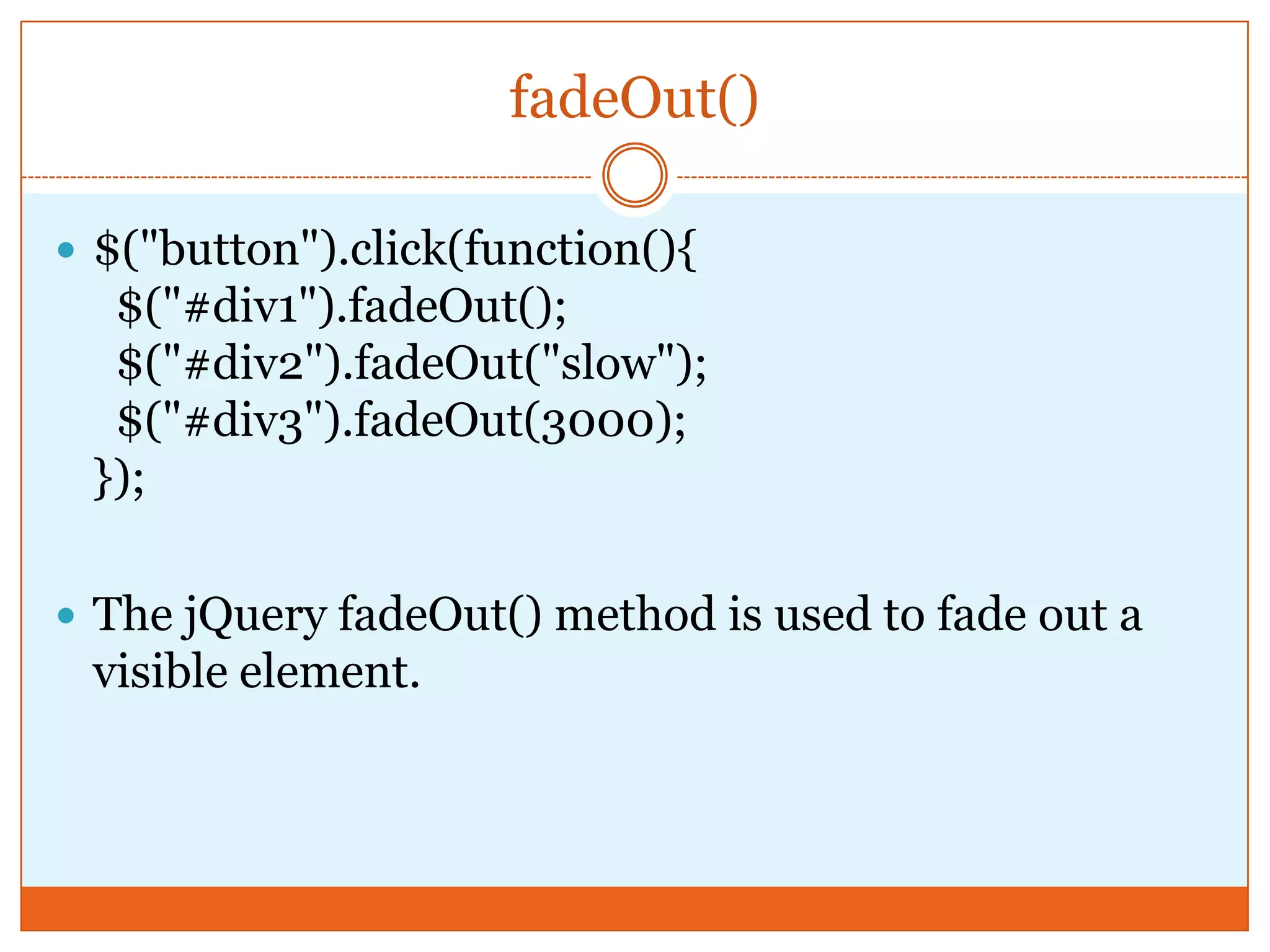
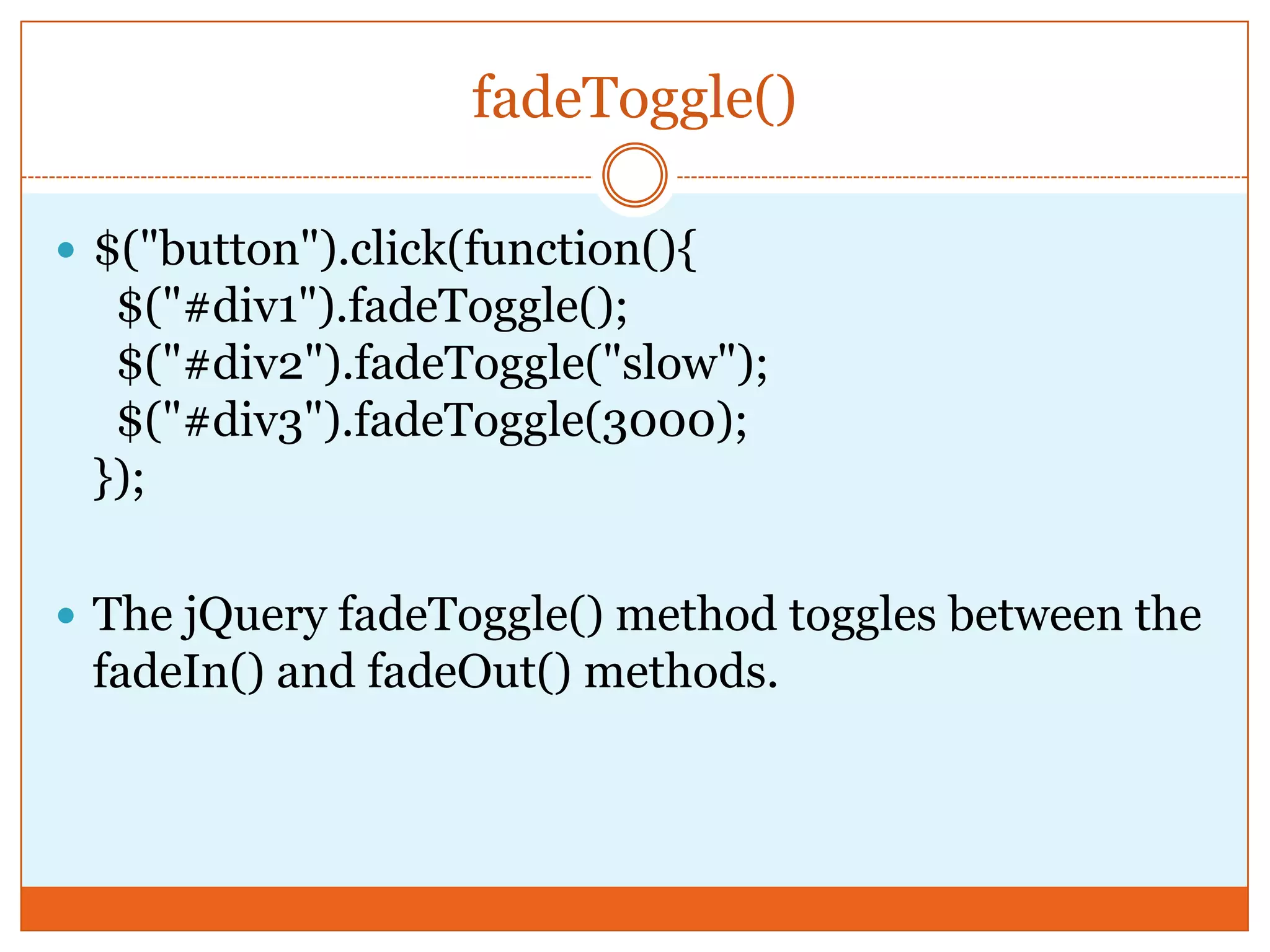
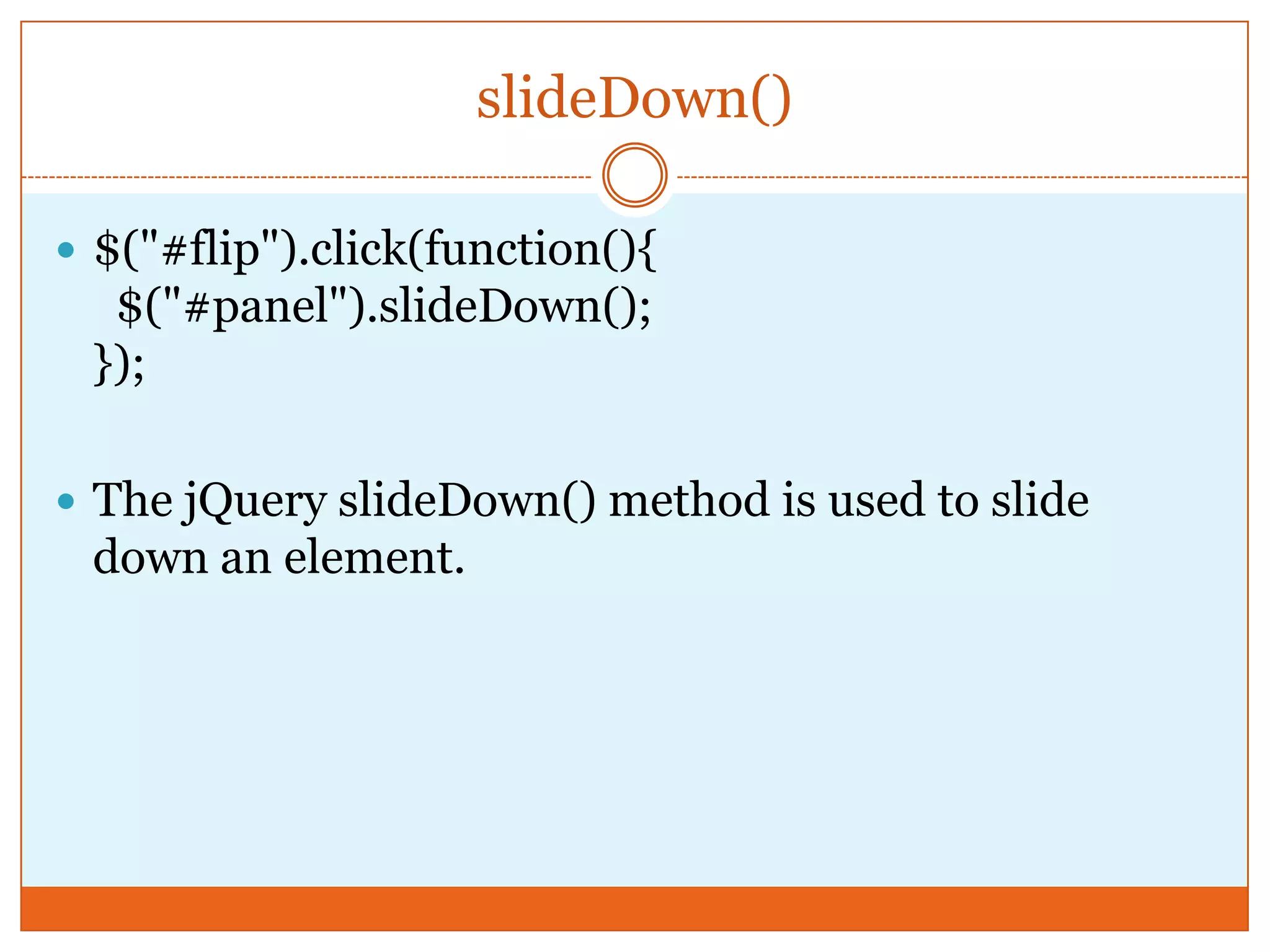
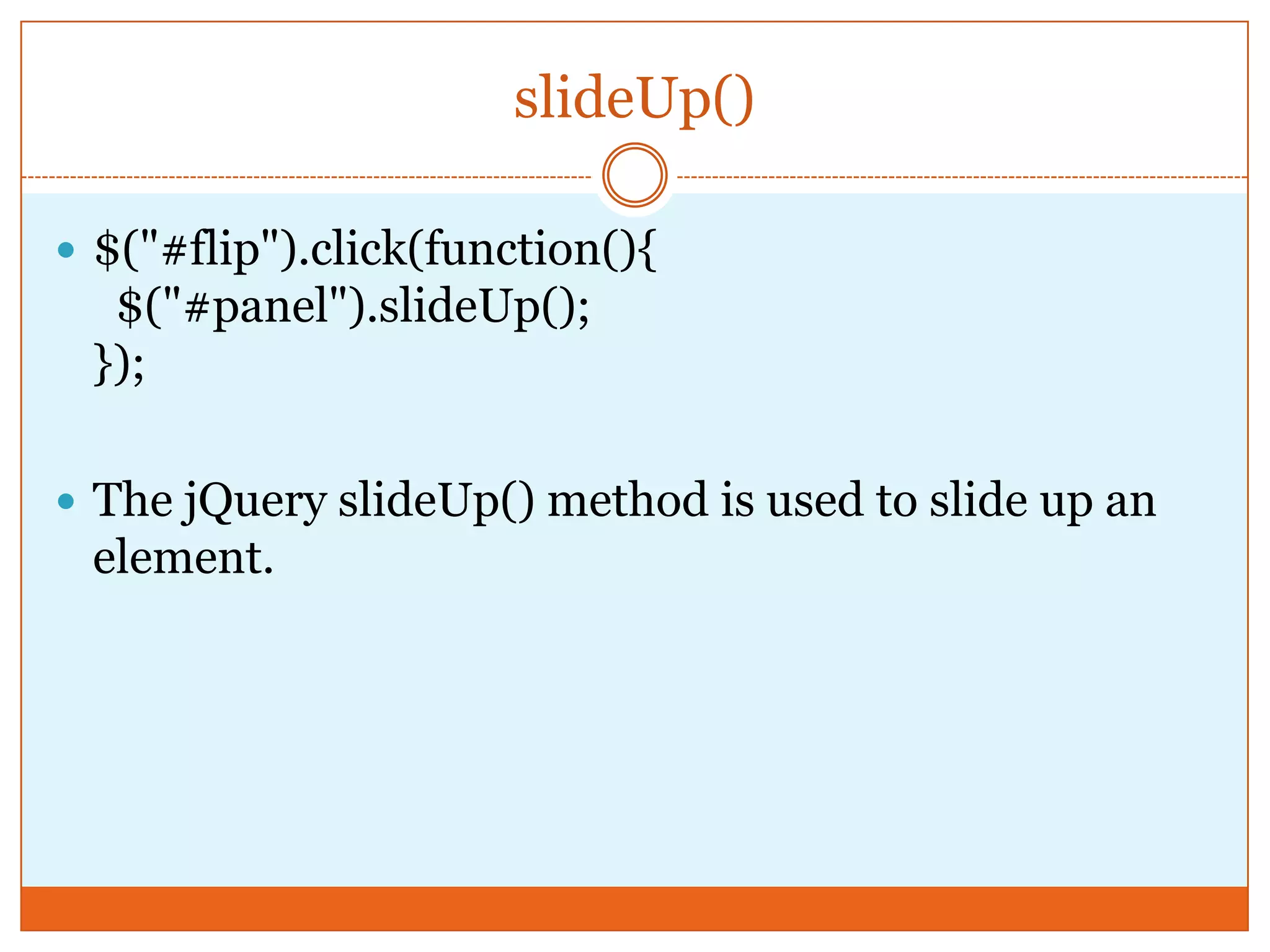
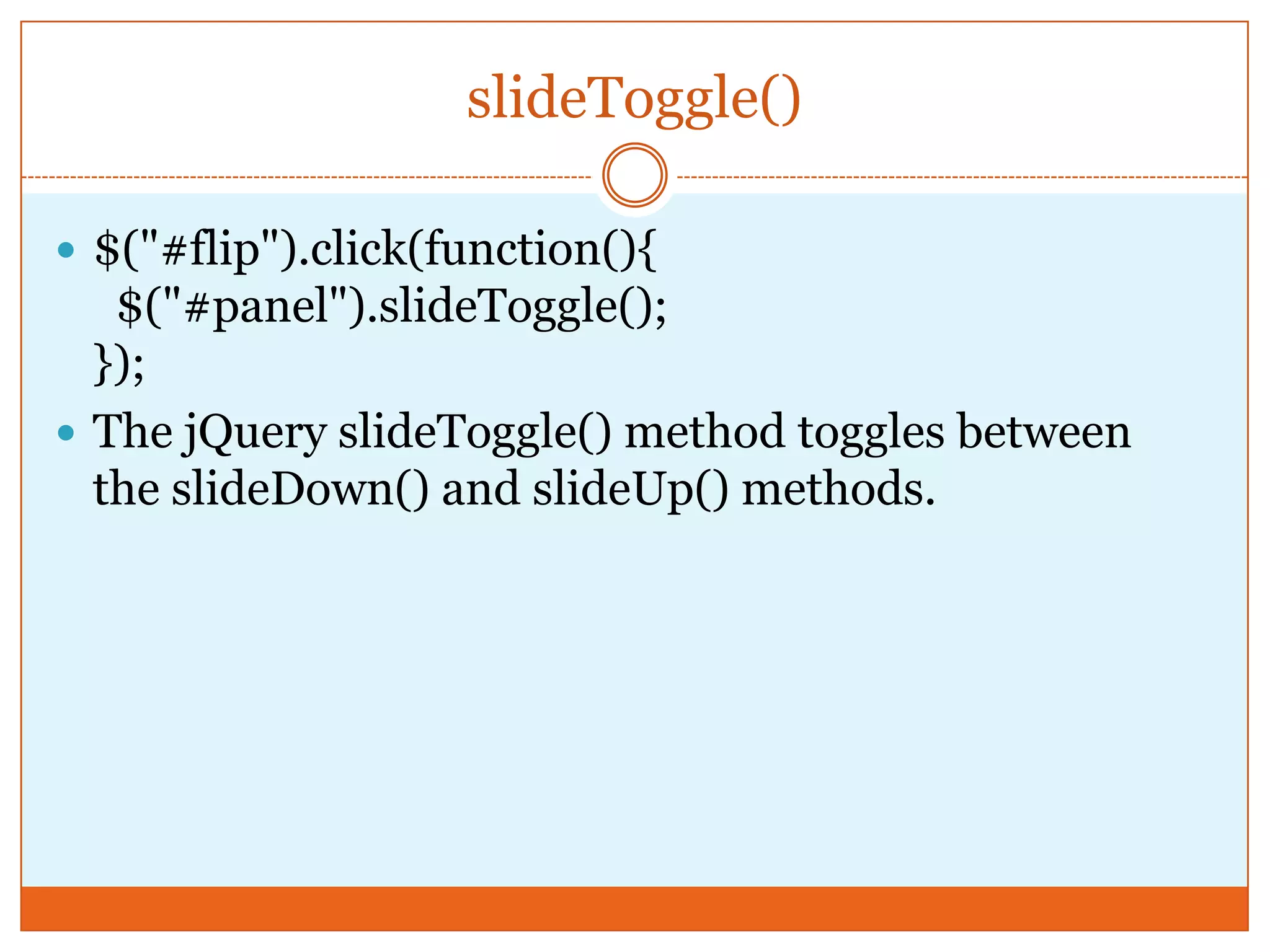
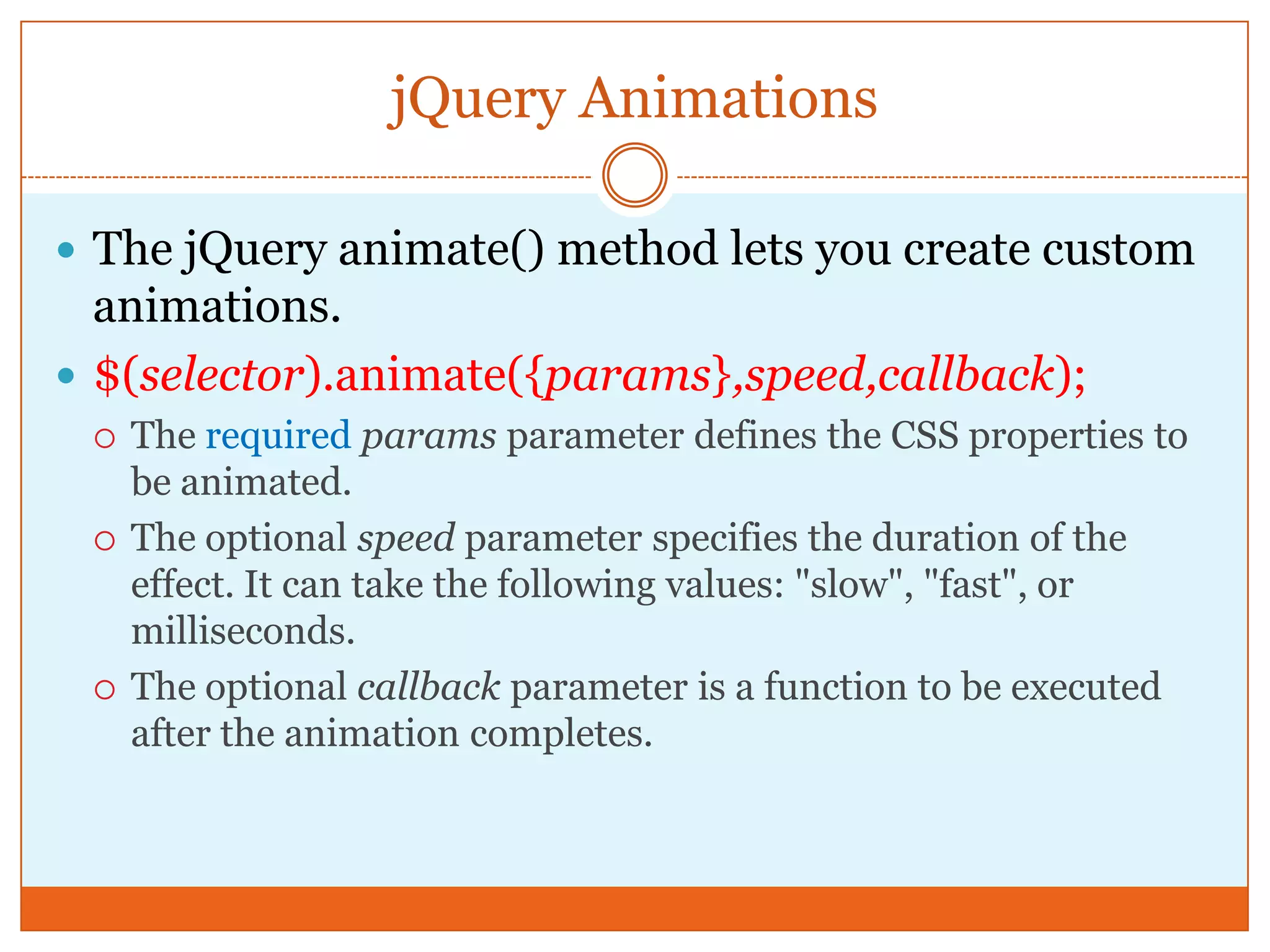
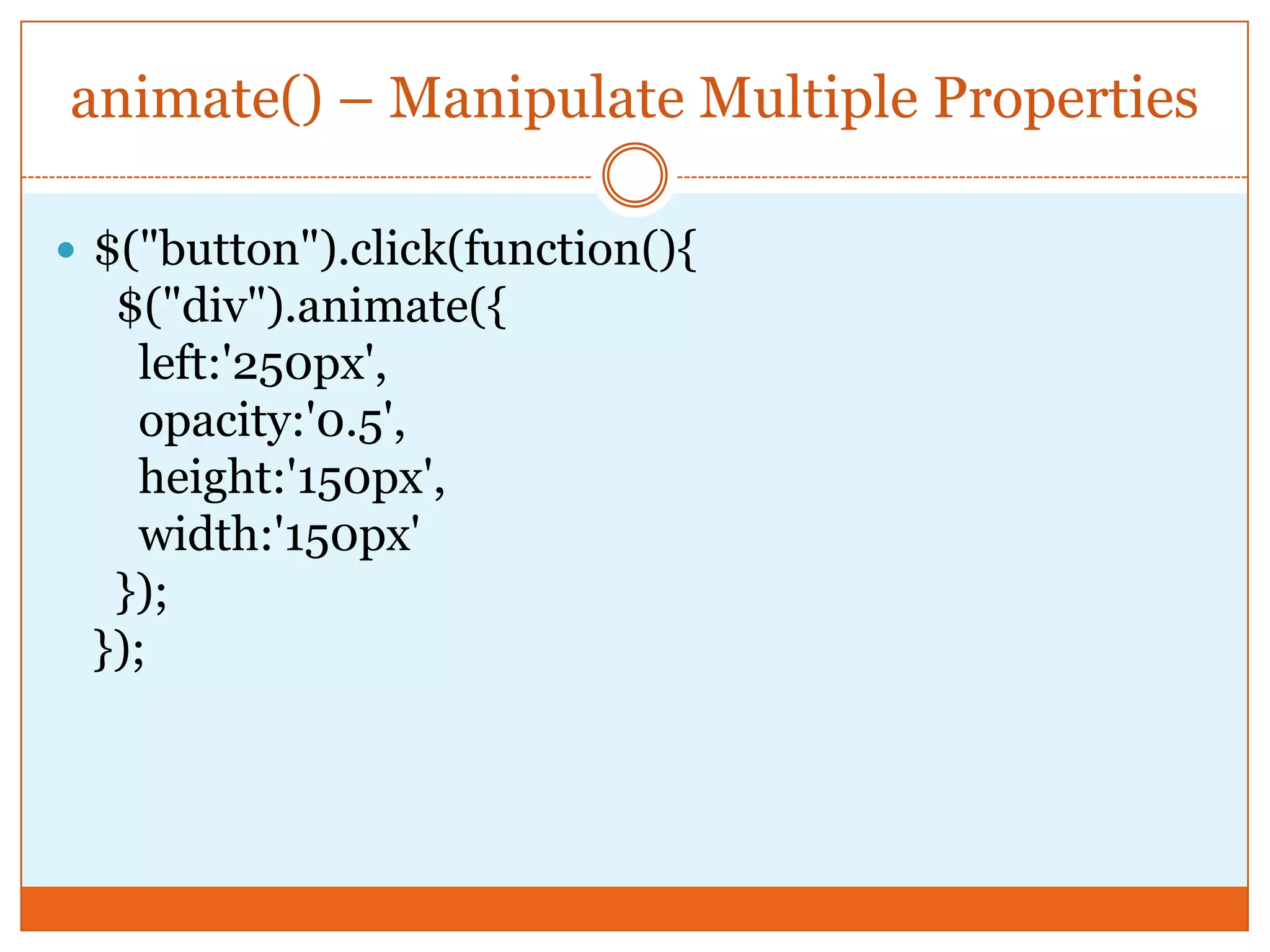
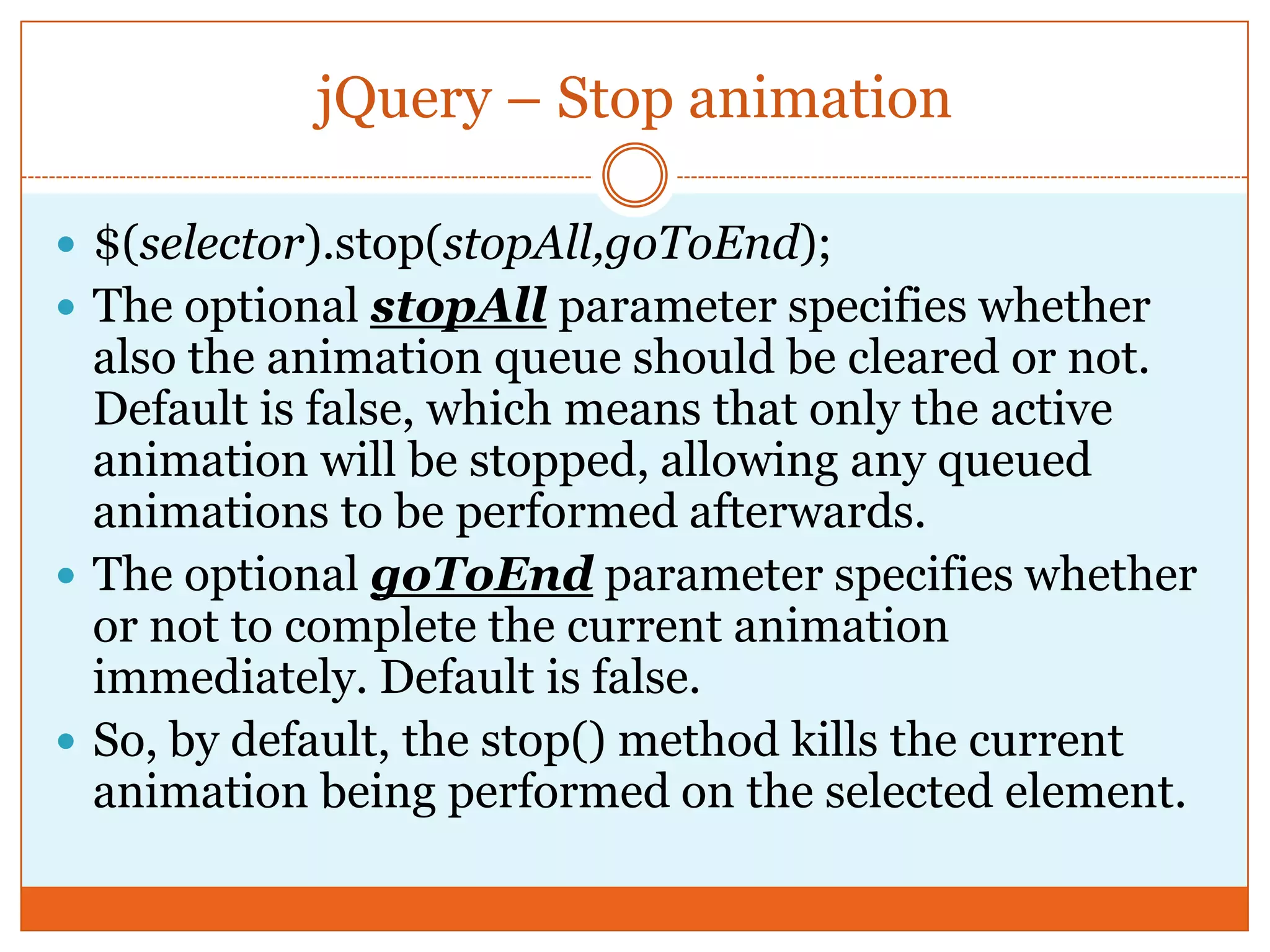
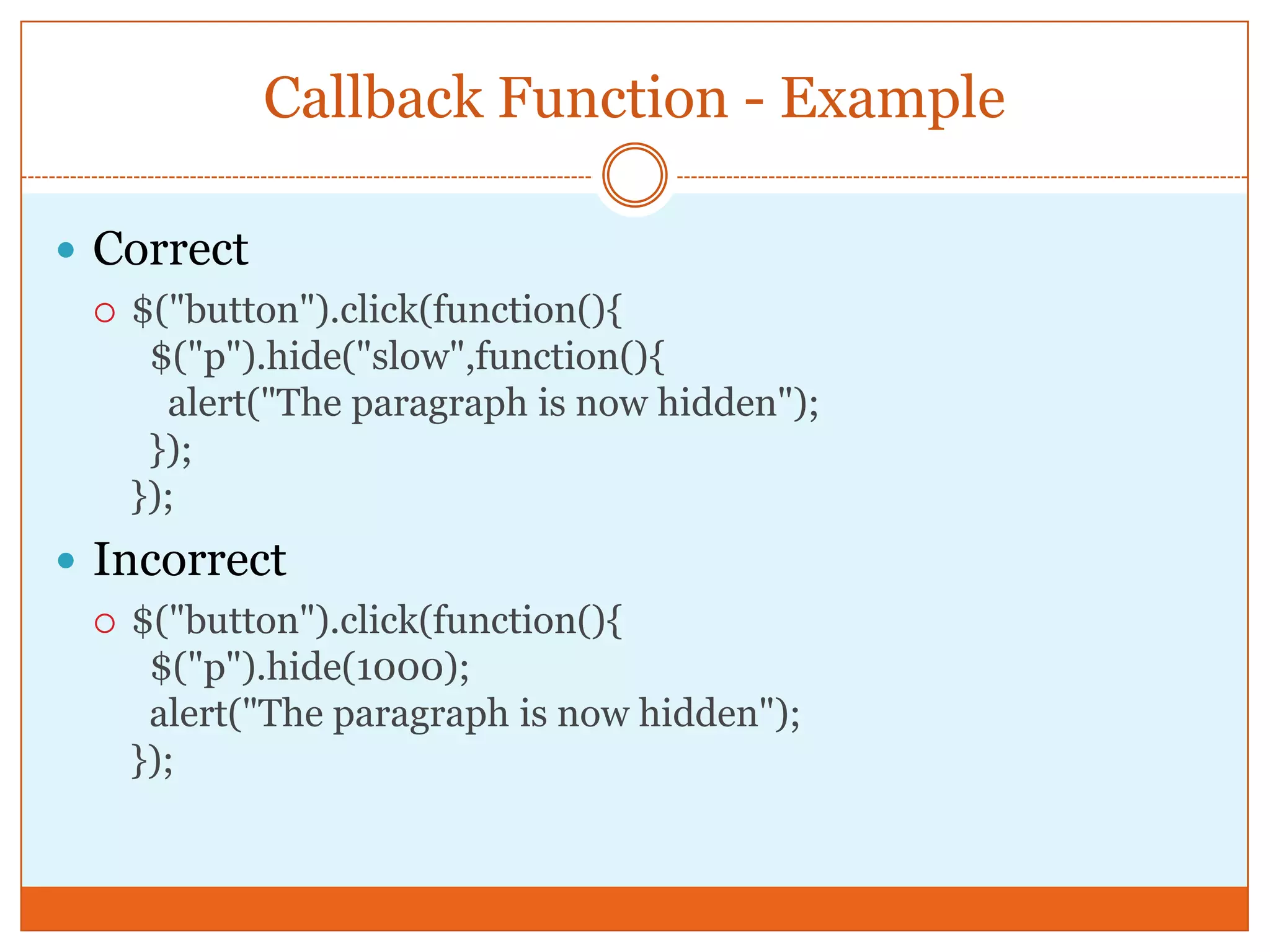
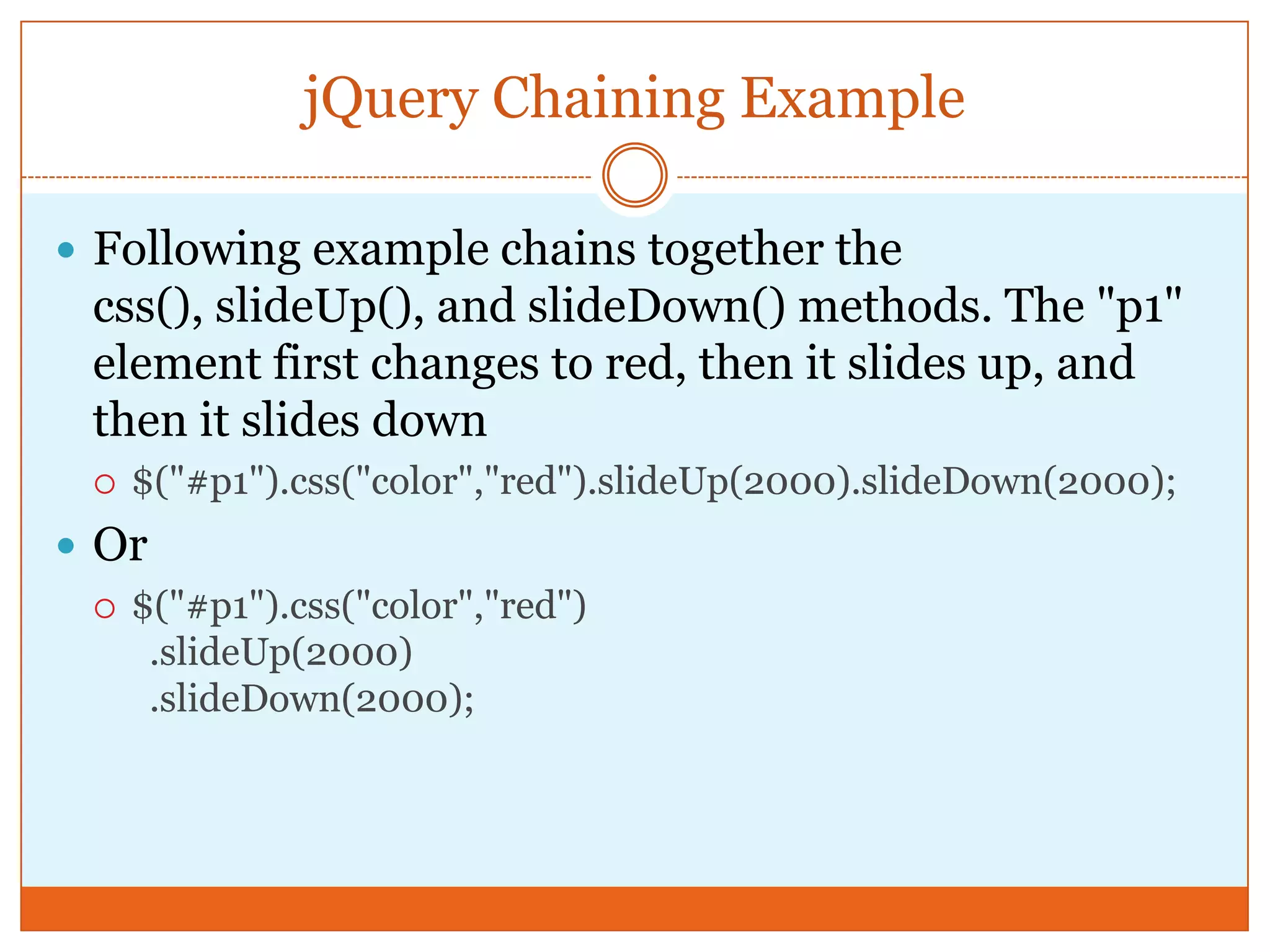
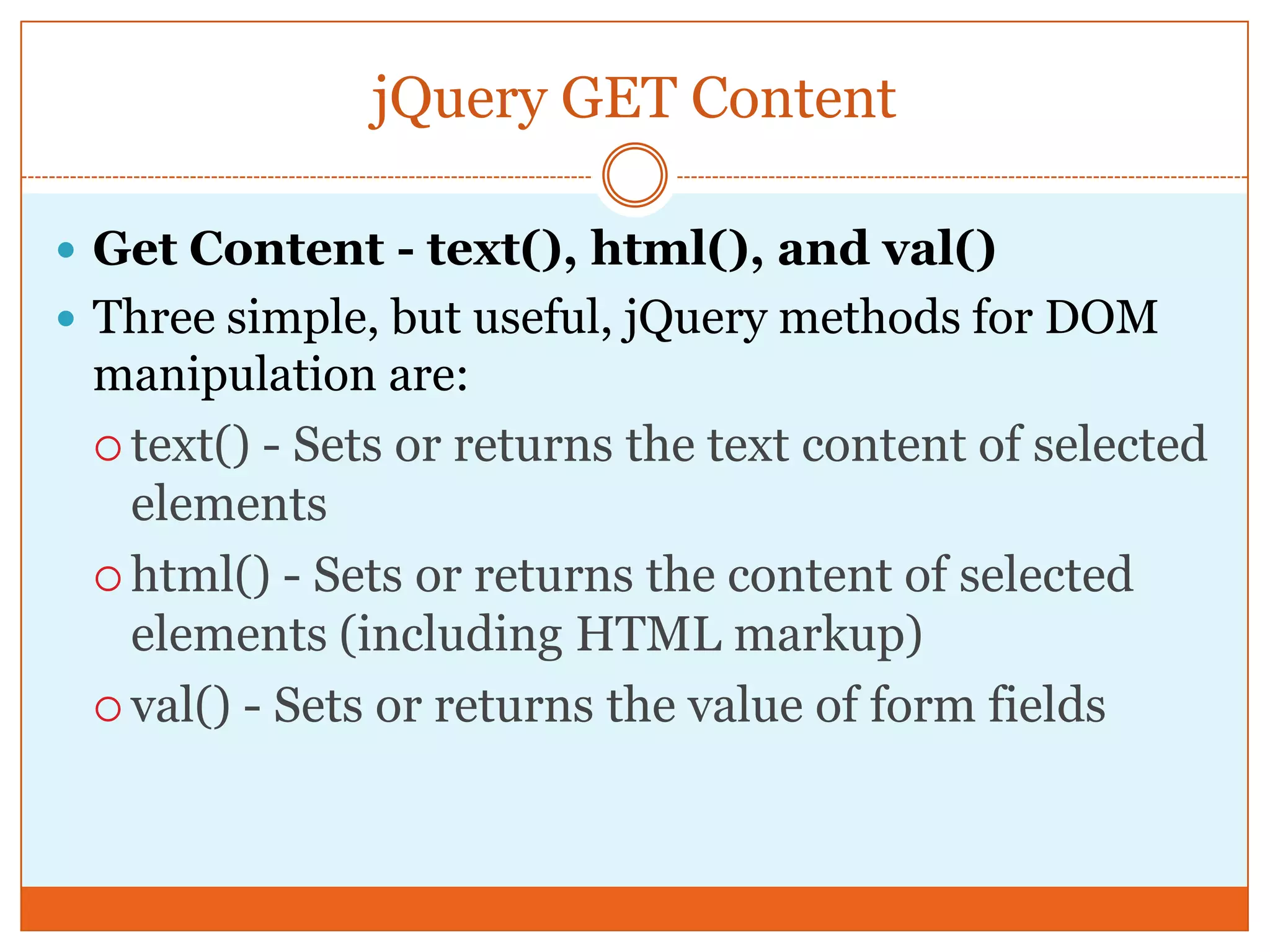
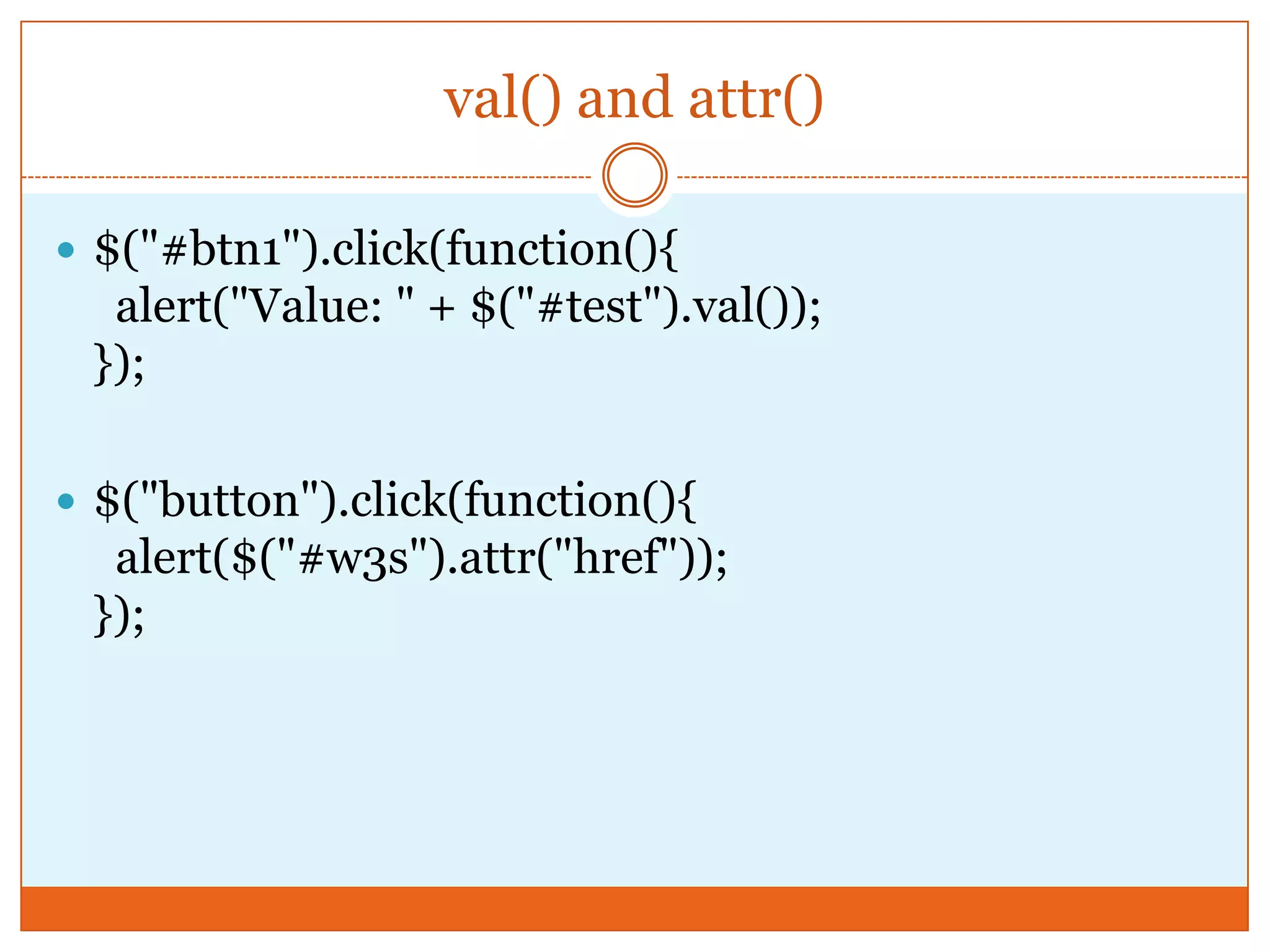
The document provides a comprehensive overview of basic jQuery methods for manipulating the visibility and effects of HTML elements, such as hide(), show(), fadeIn(), and slideUp(). It also covers jQuery animations, including custom animation with the animate() method and chaining multiple jQuery commands. Additionally, the document discusses how to get and set content using text(), html(), and val() methods.