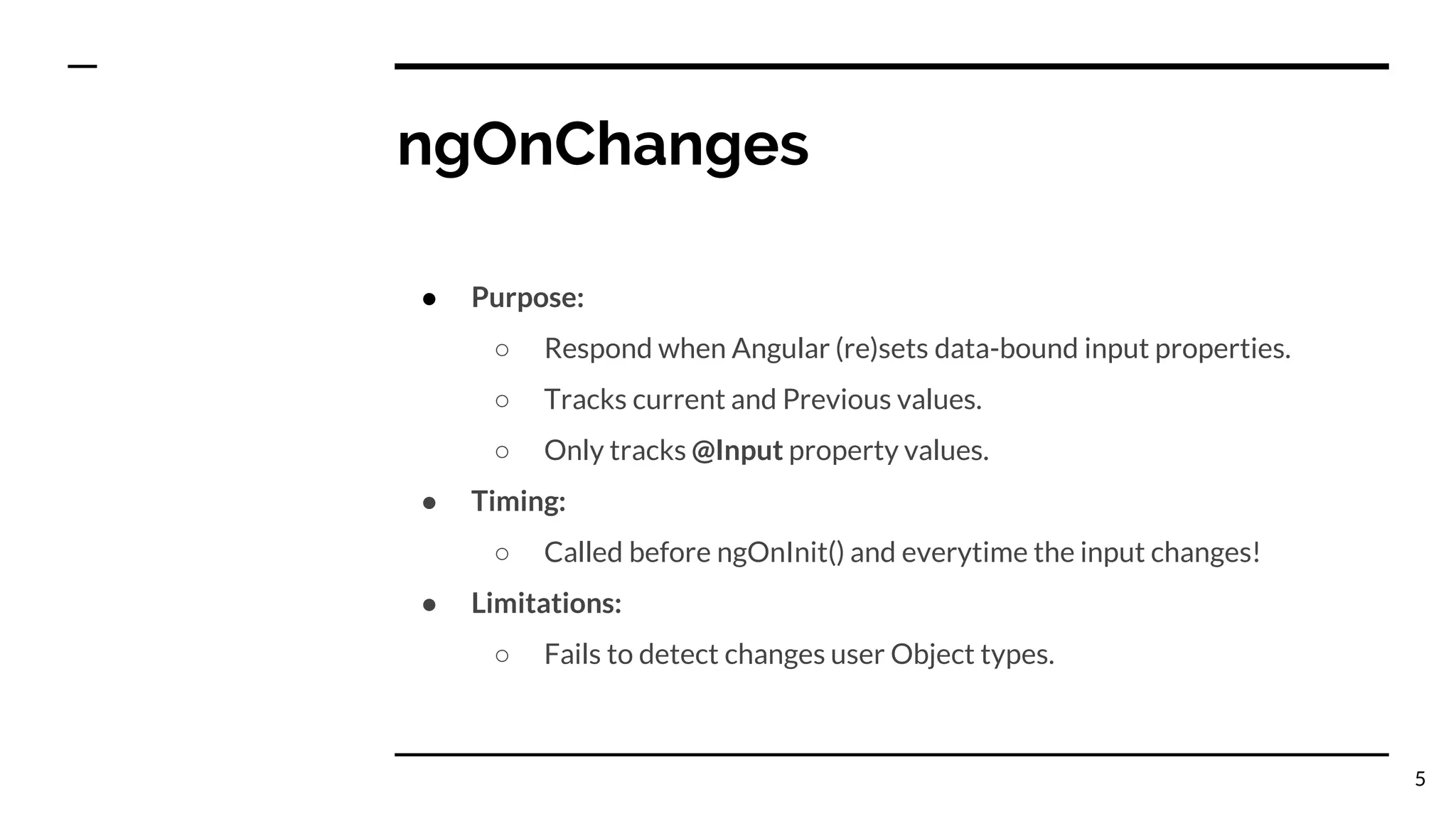
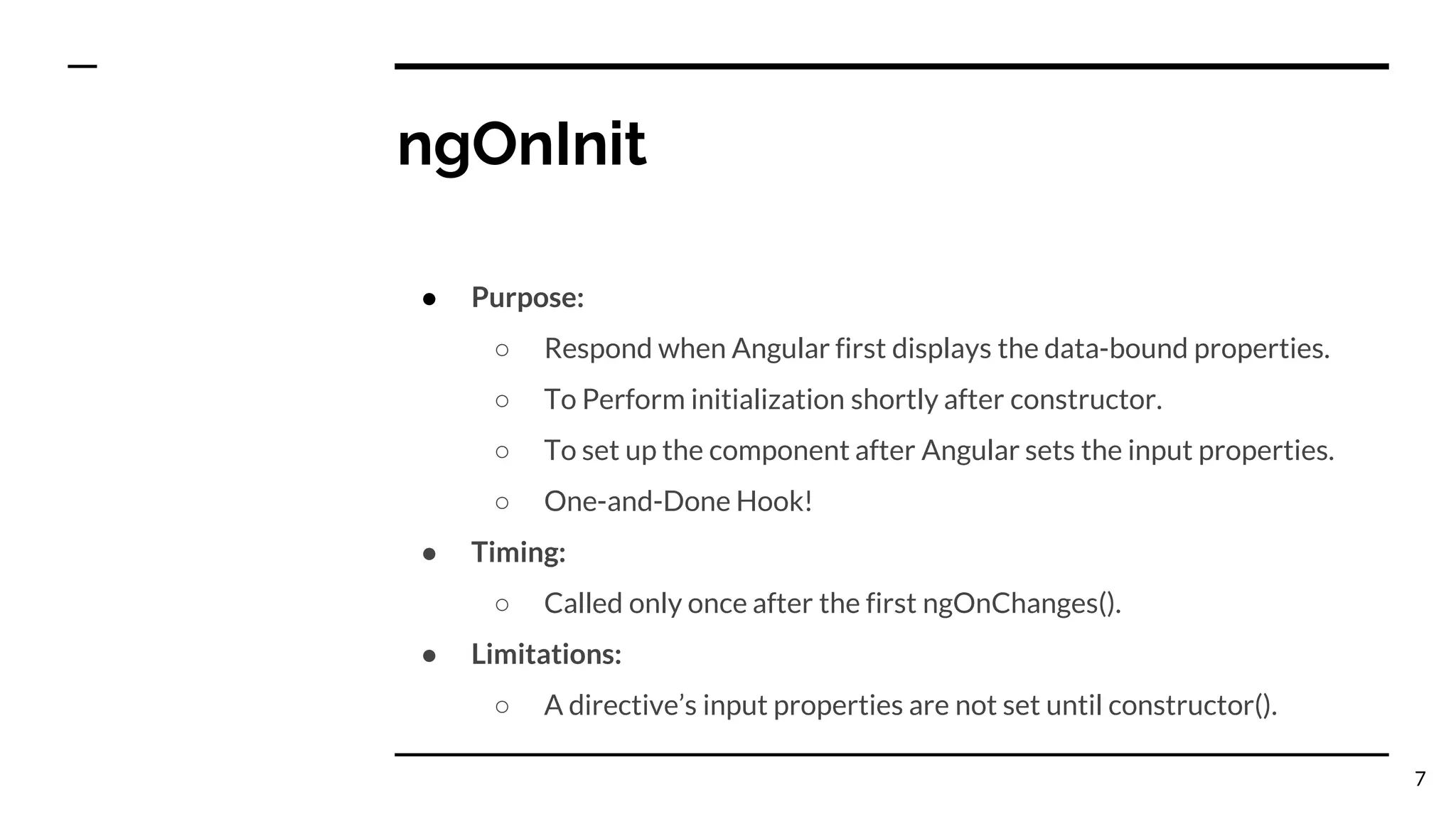
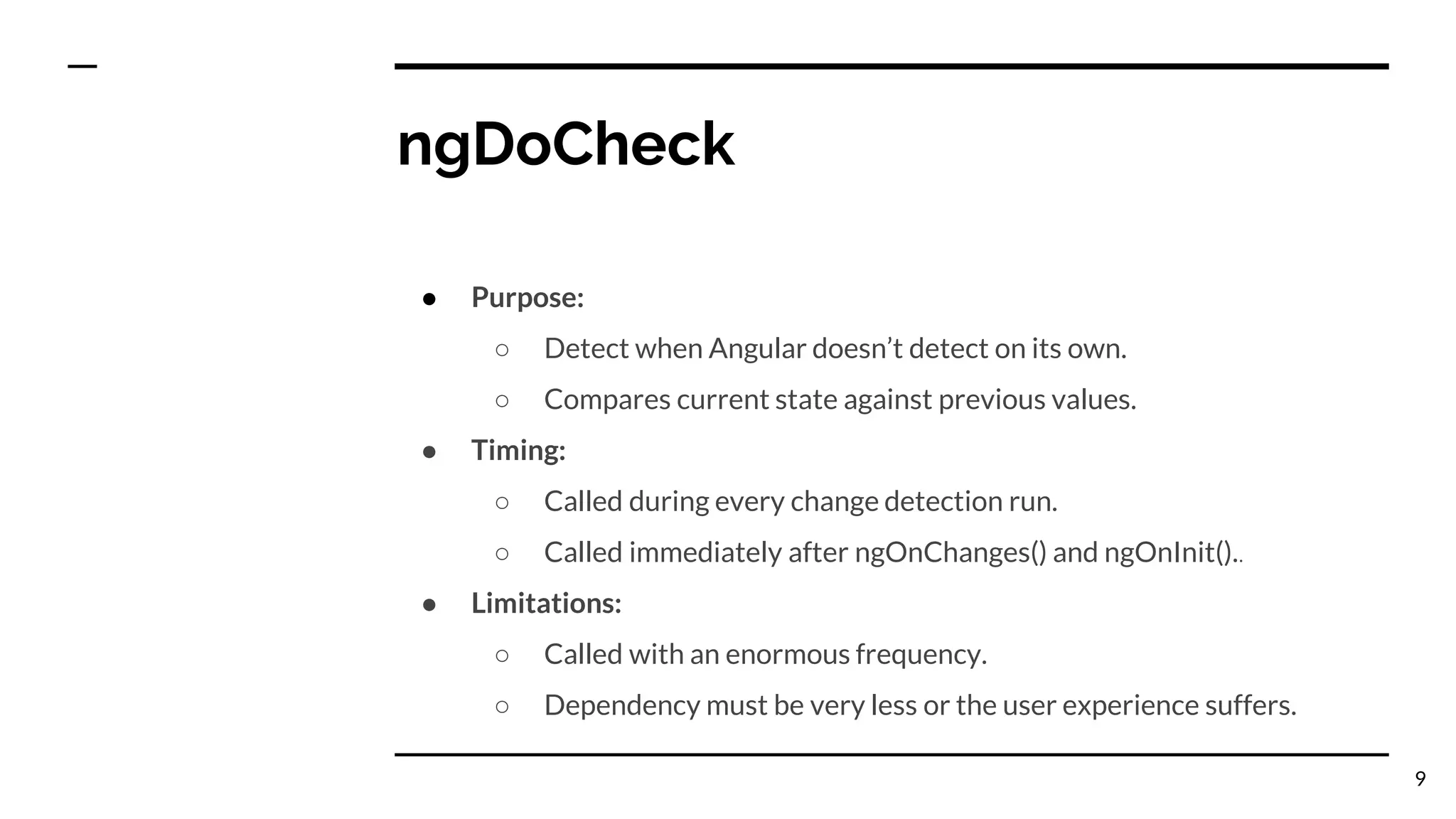
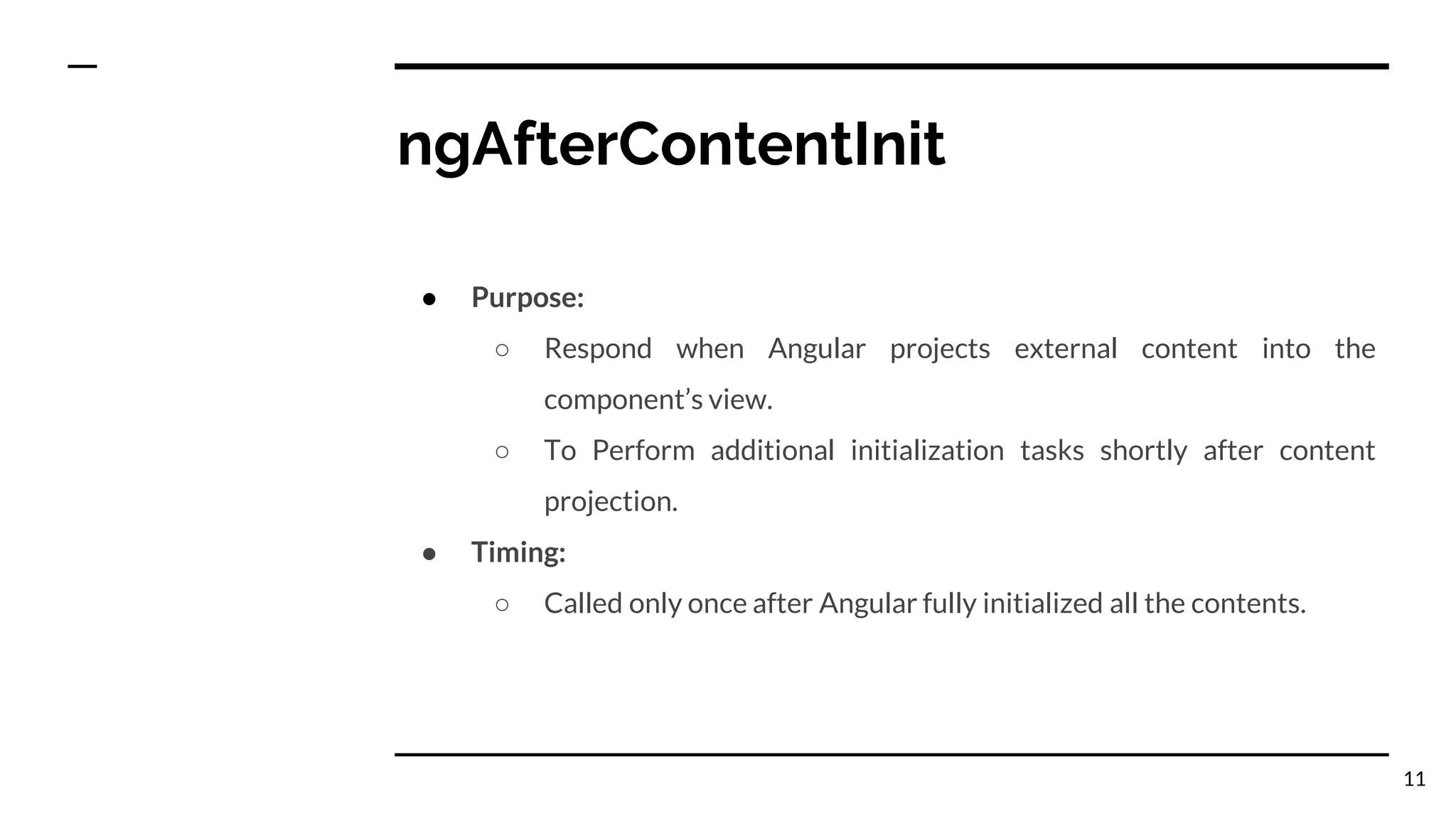
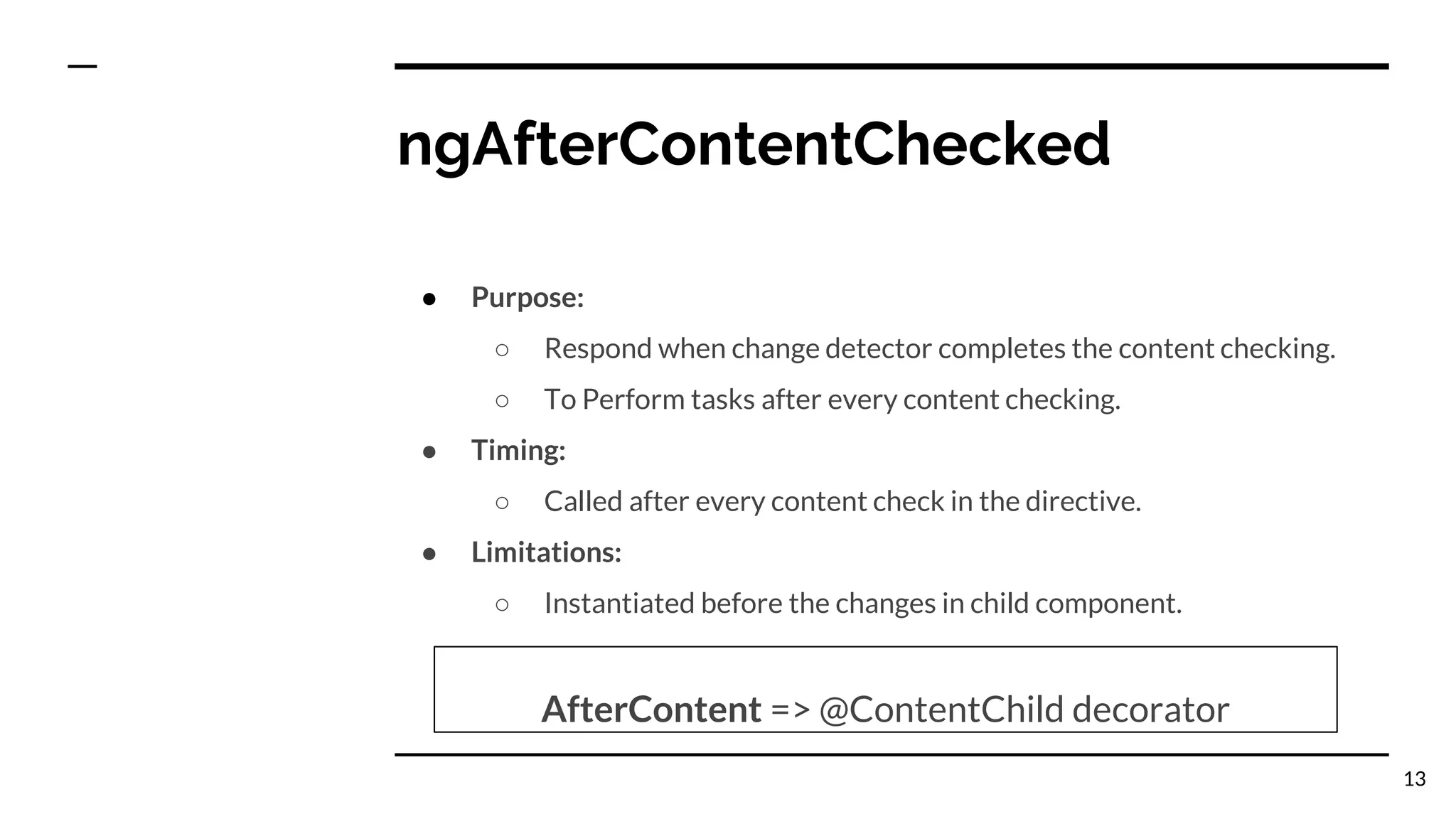
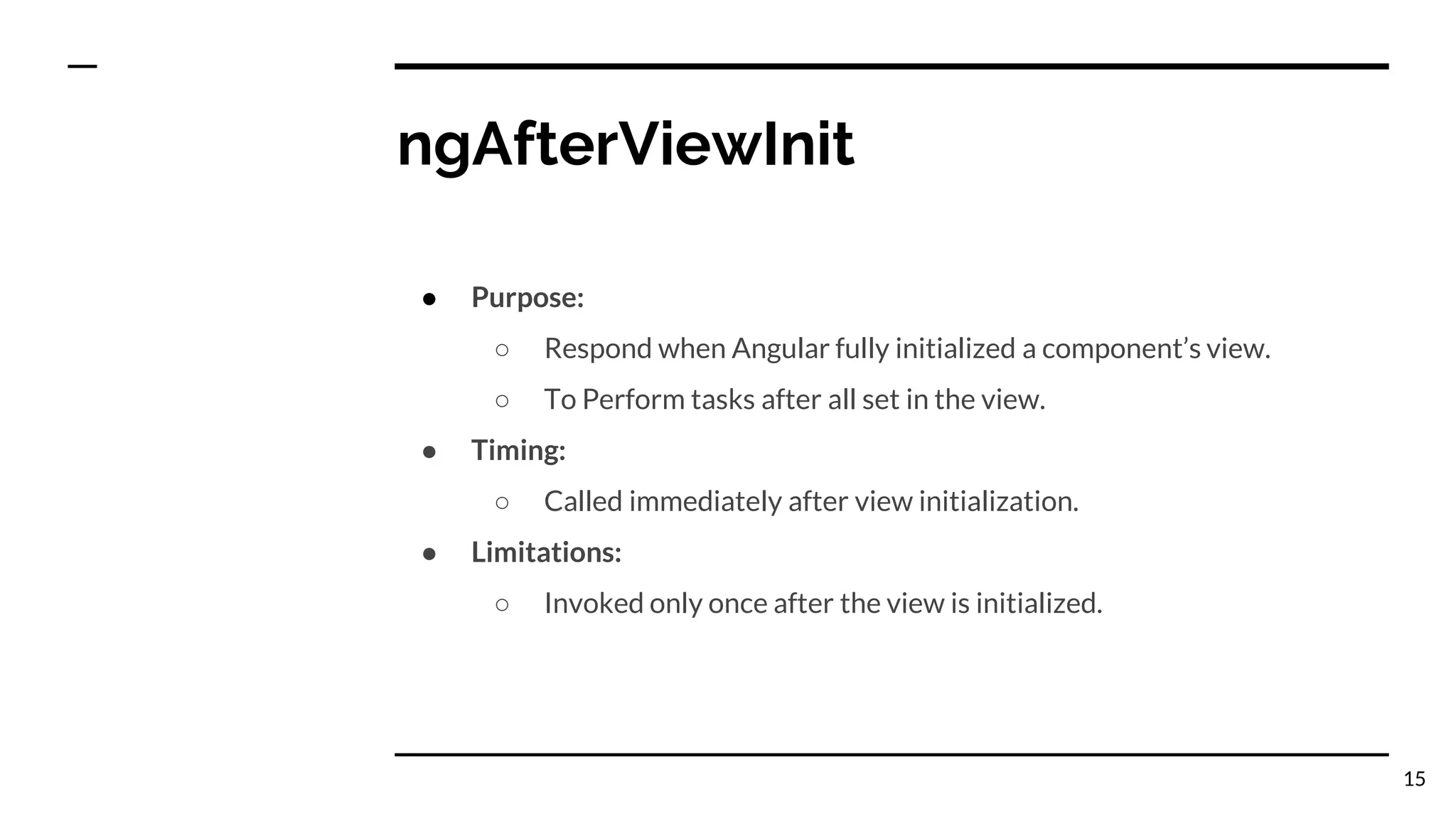
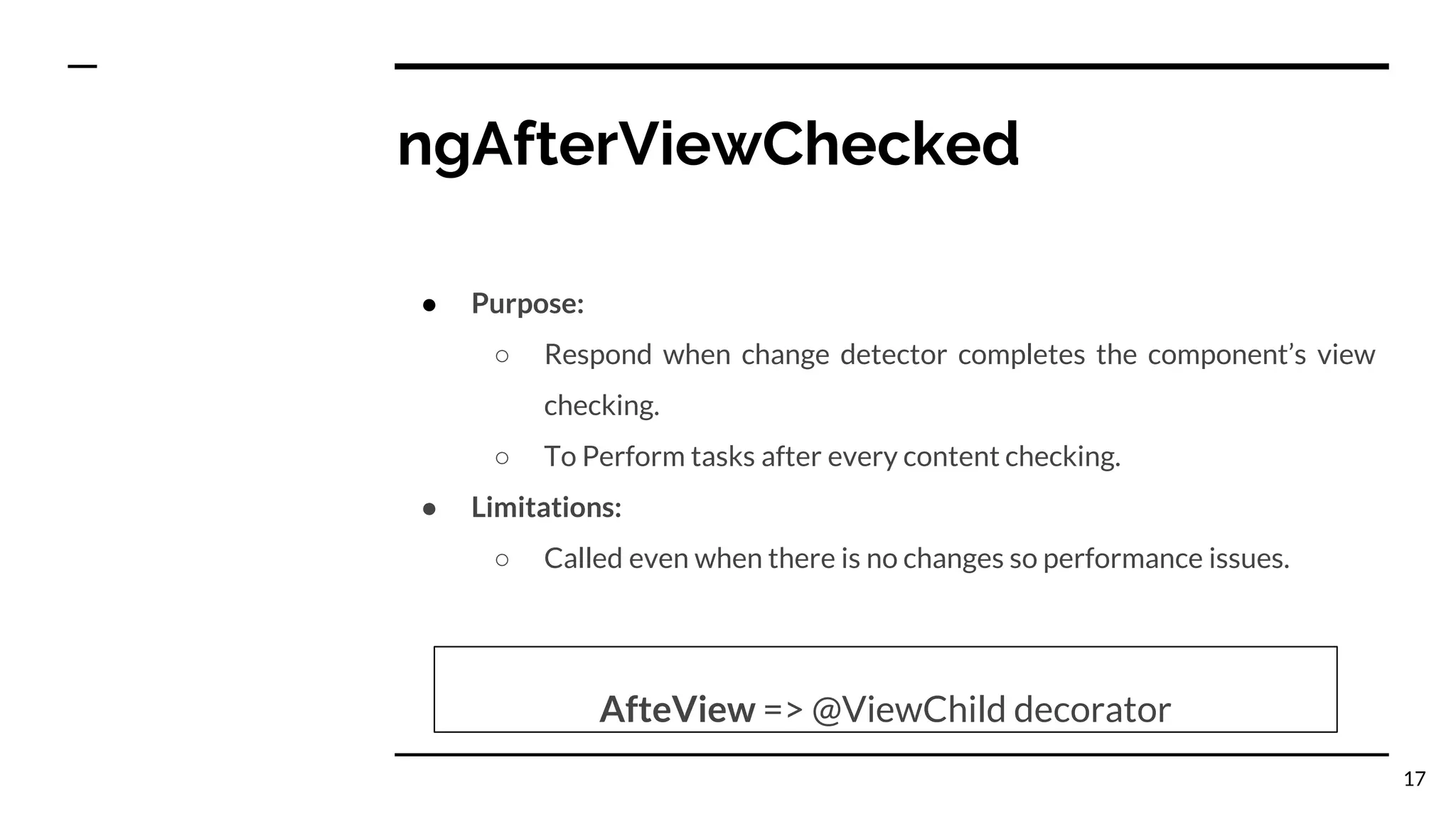
The document outlines the lifecycle hooks in Angular, detailing their order of execution and specific purposes. It explains each hook's timing, limitations, and how they respond to changes in the component's state. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding the purpose and timing of these hooks for effective component management.