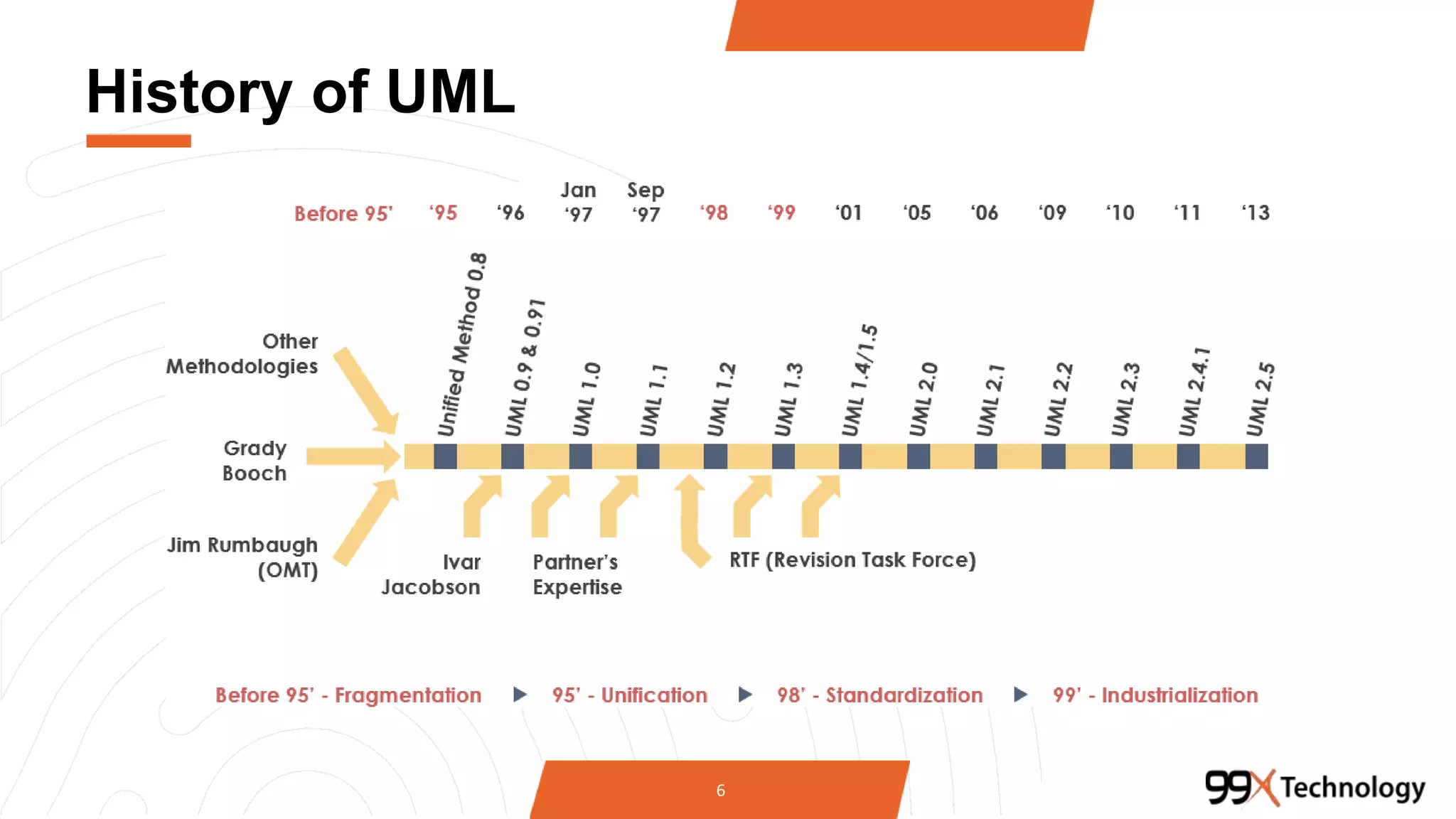
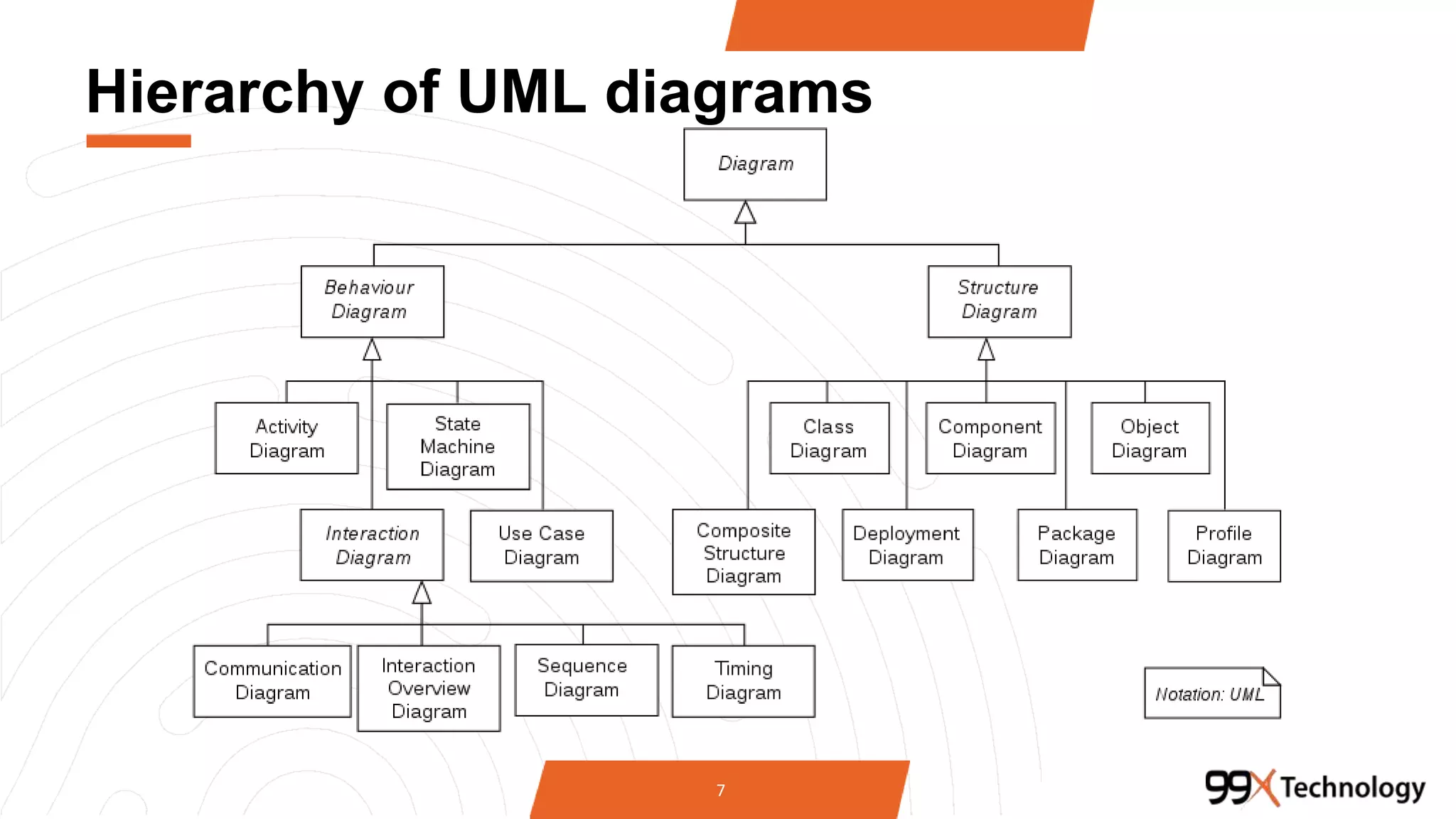
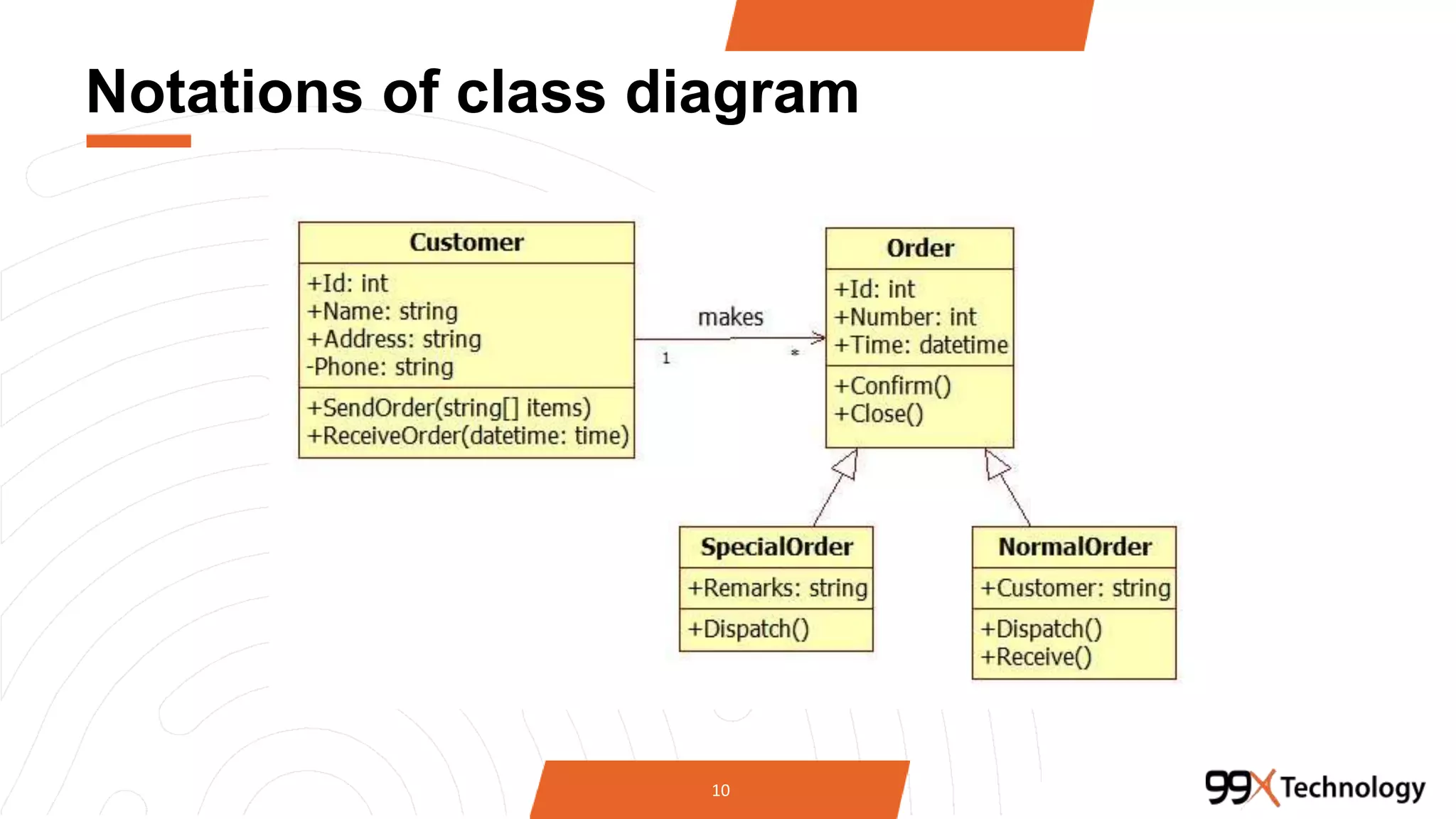
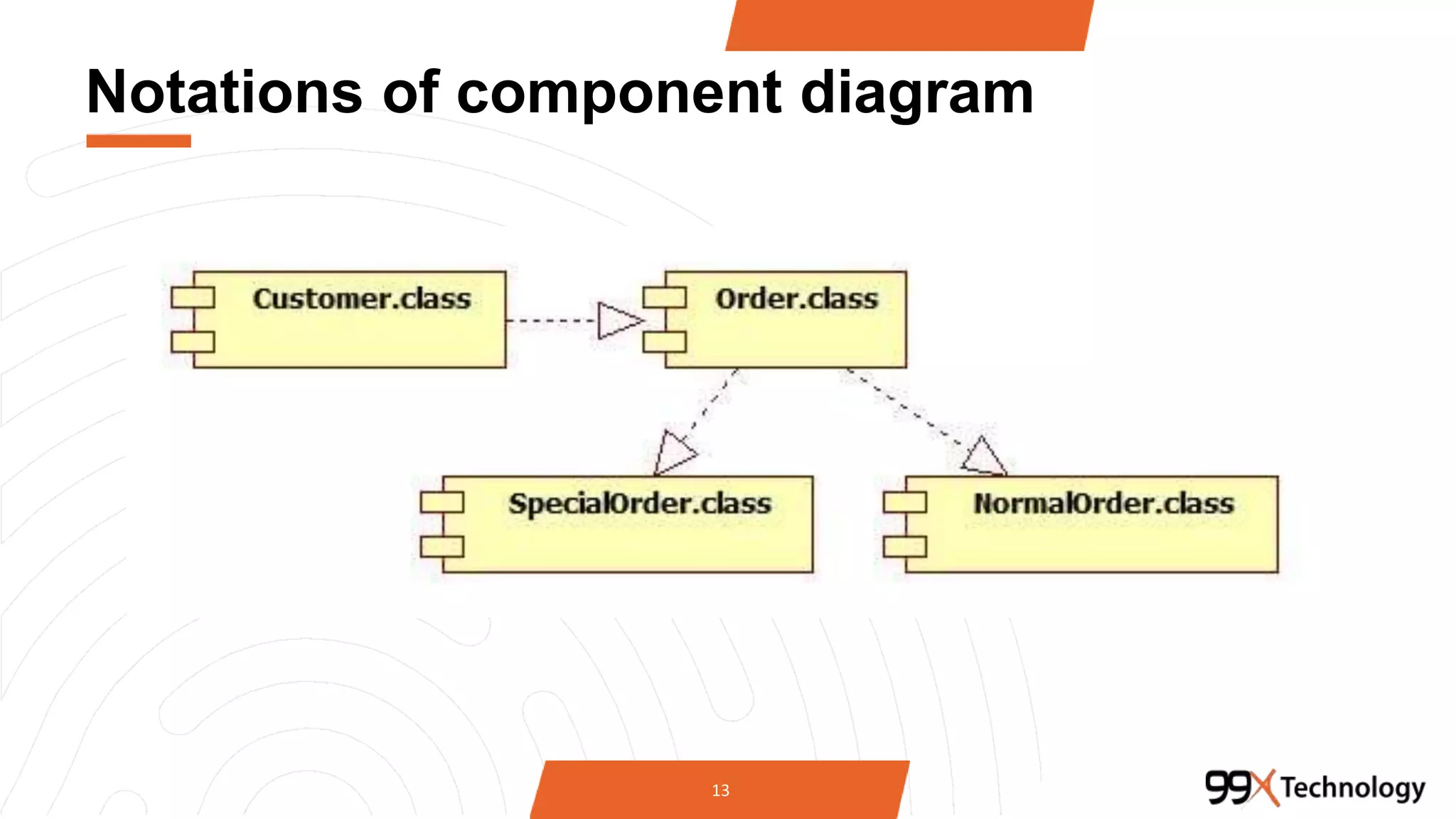
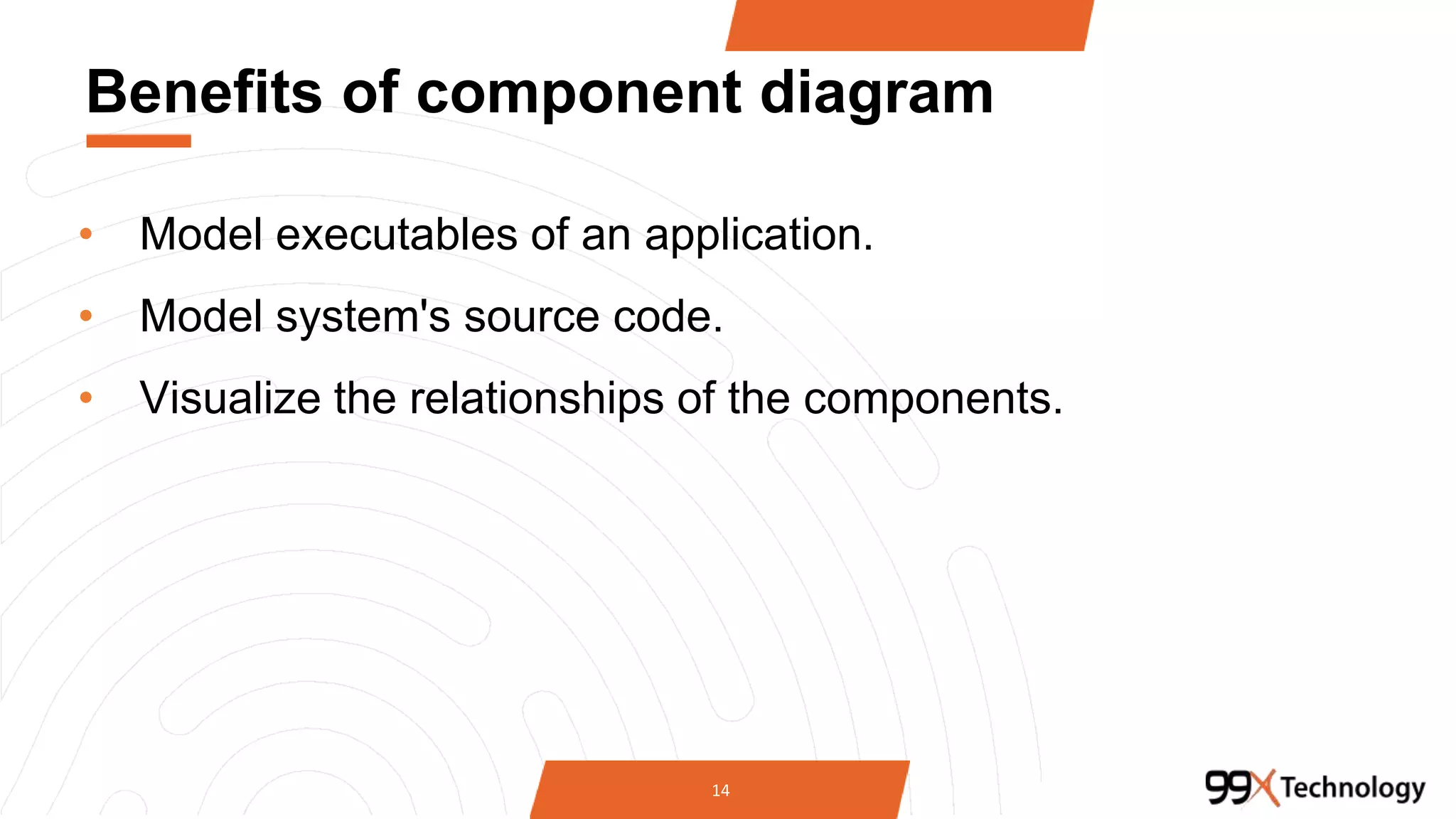
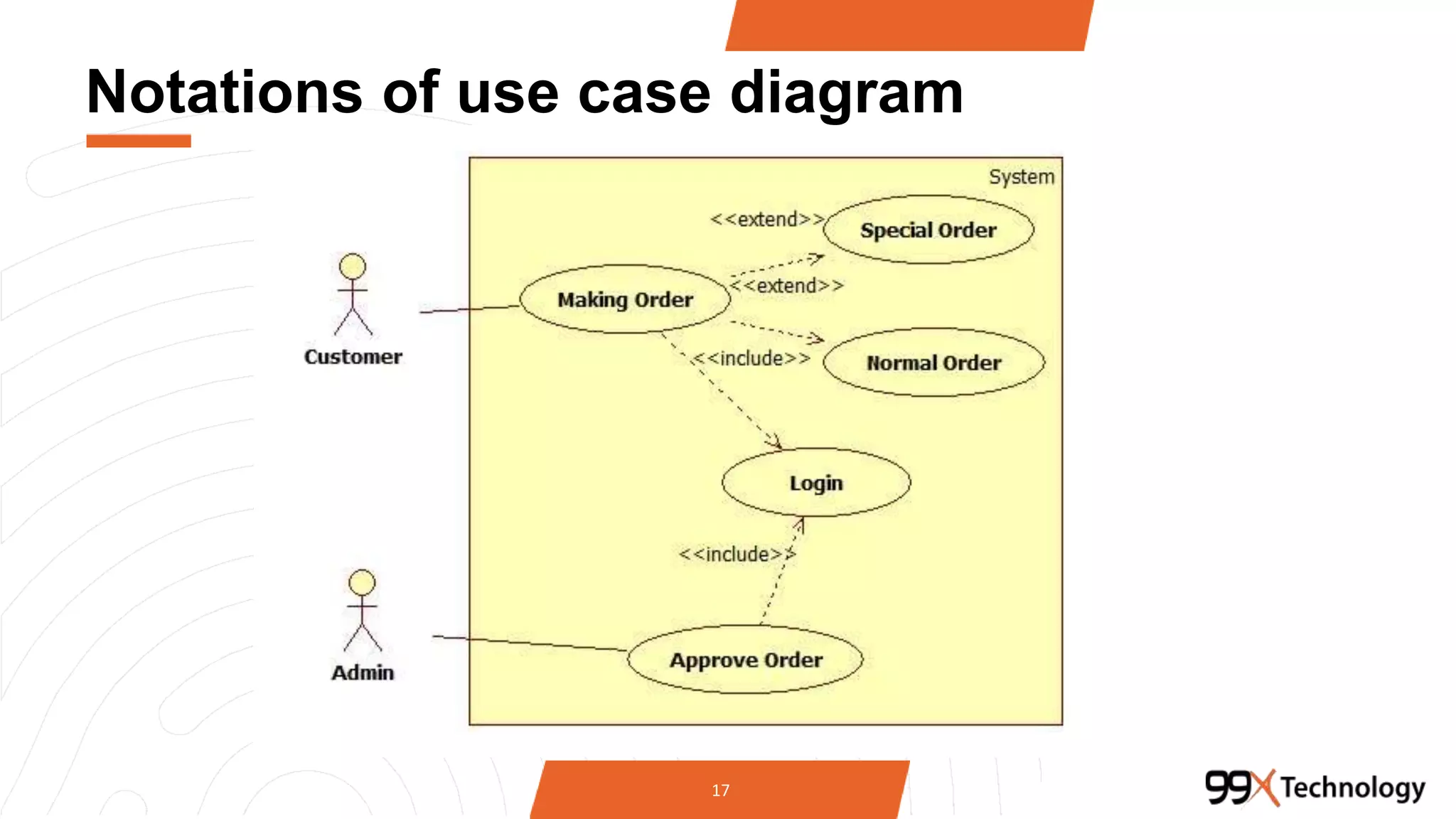
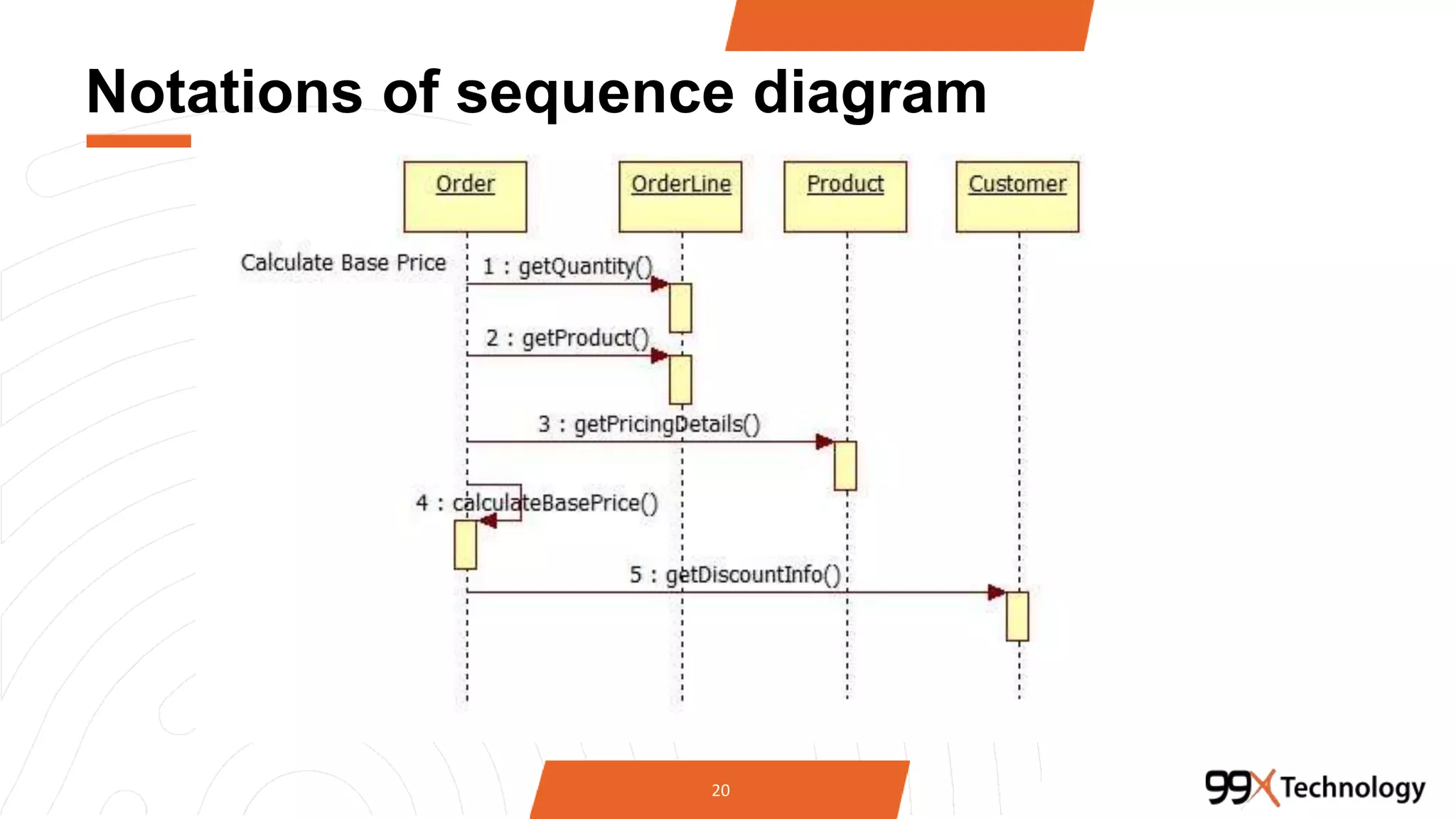
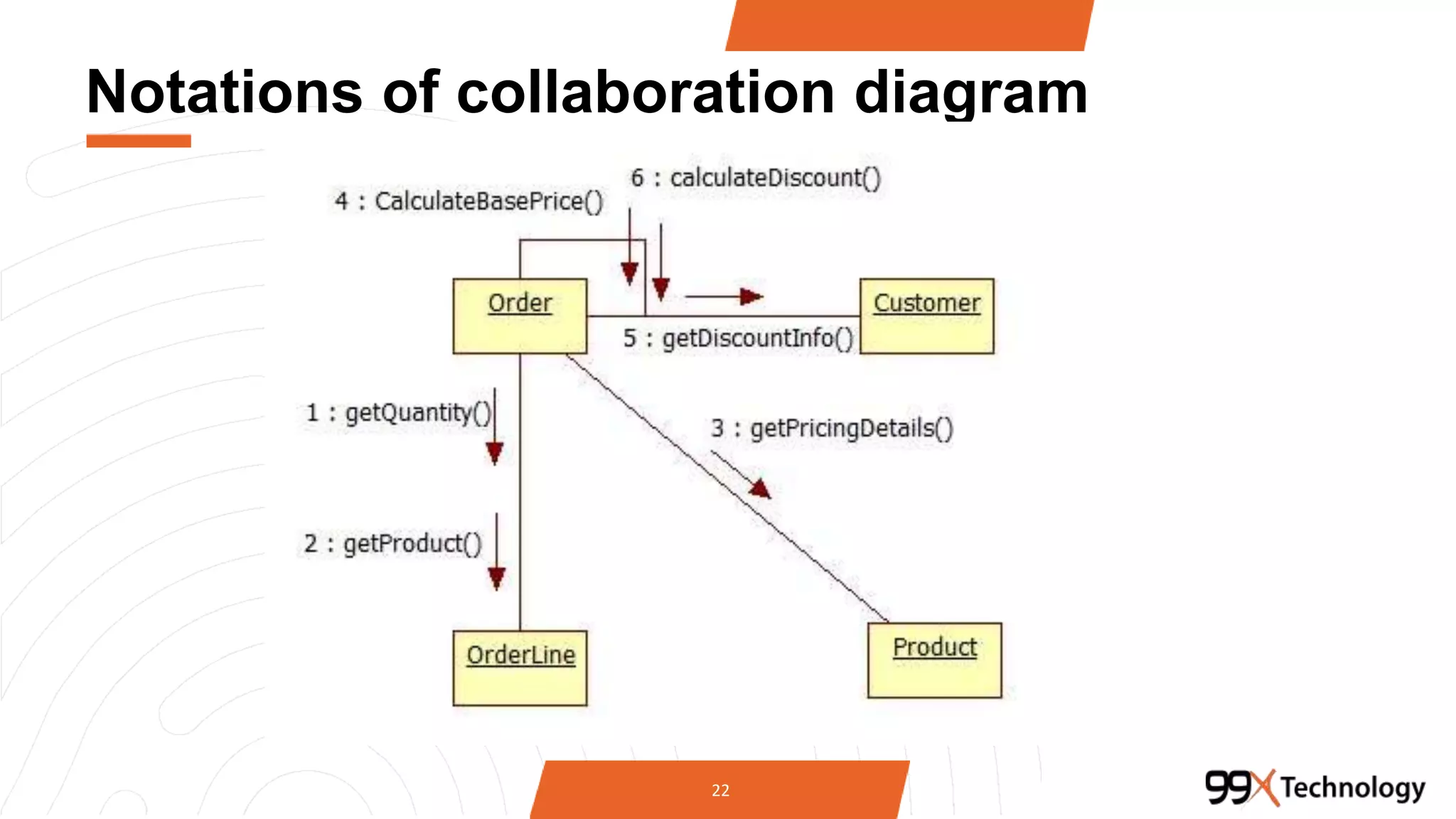
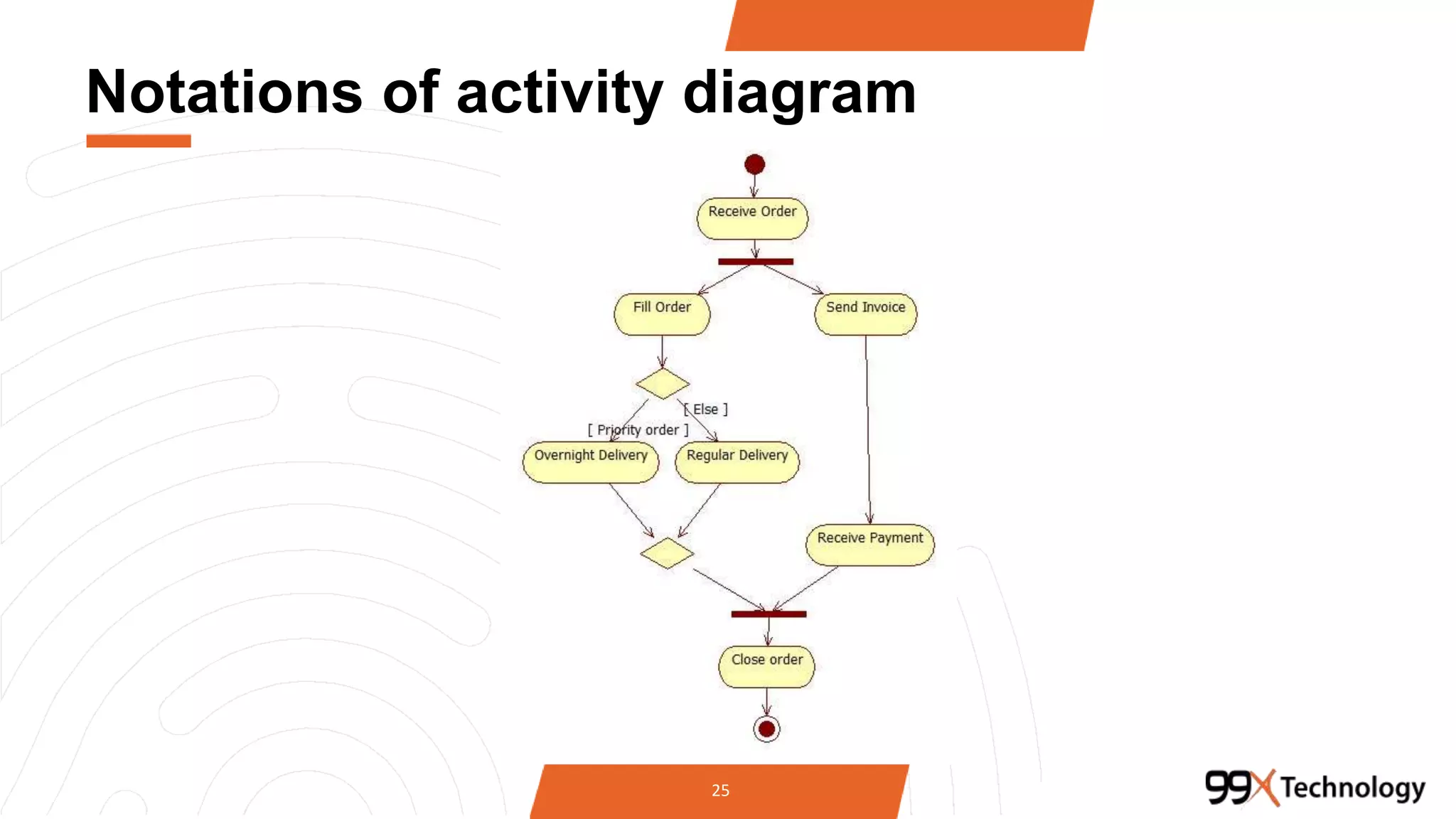
The document discusses the importance and applications of Unified Modeling Language (UML) in software engineering. It outlines various types of UML diagrams, including class diagrams, component diagrams, use case diagrams, sequence diagrams, collaboration diagrams, and activity diagrams, highlighting their functions and benefits in modeling systems. Additionally, it provides insights on using StarUML for modeling projects.