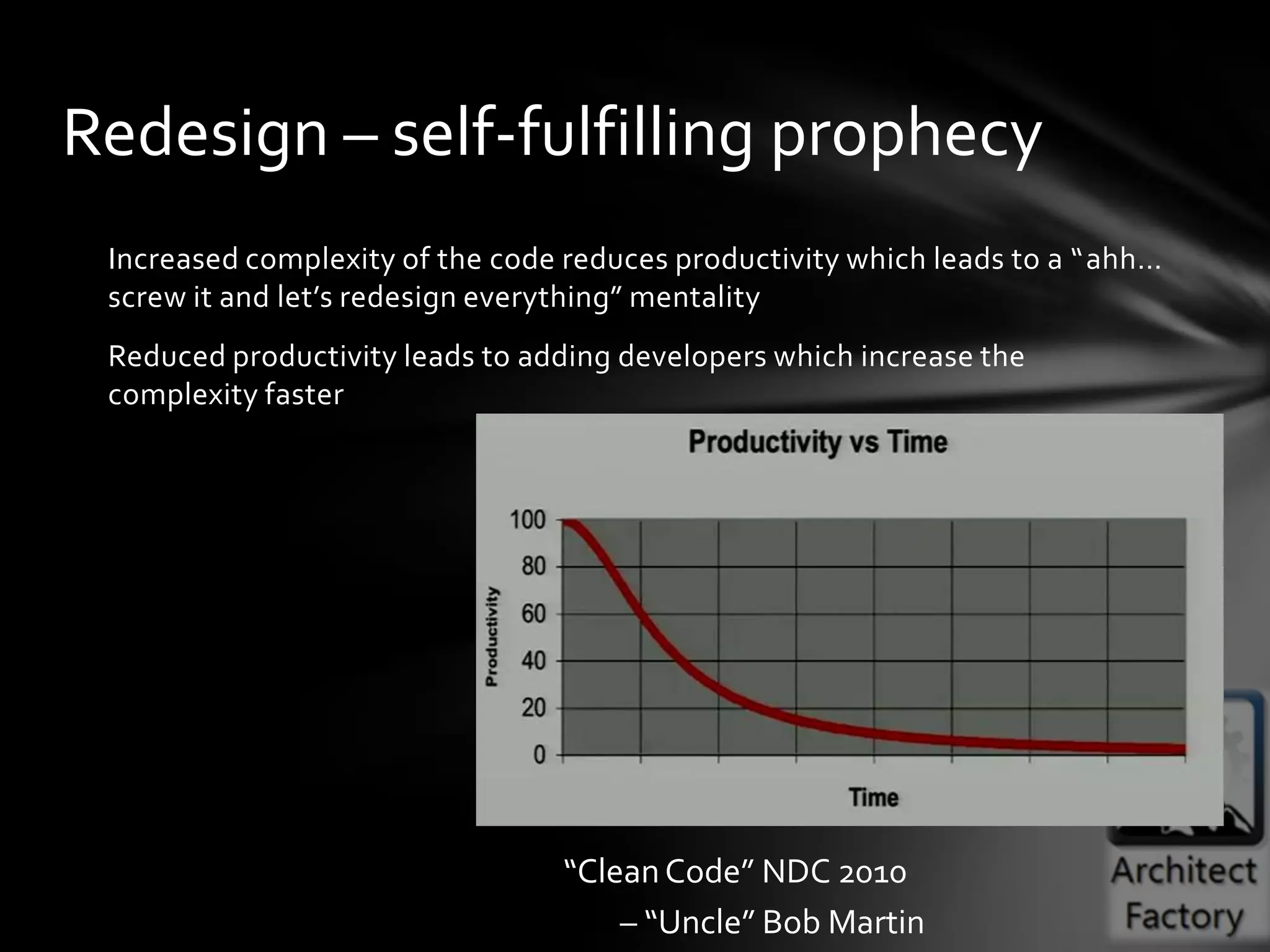
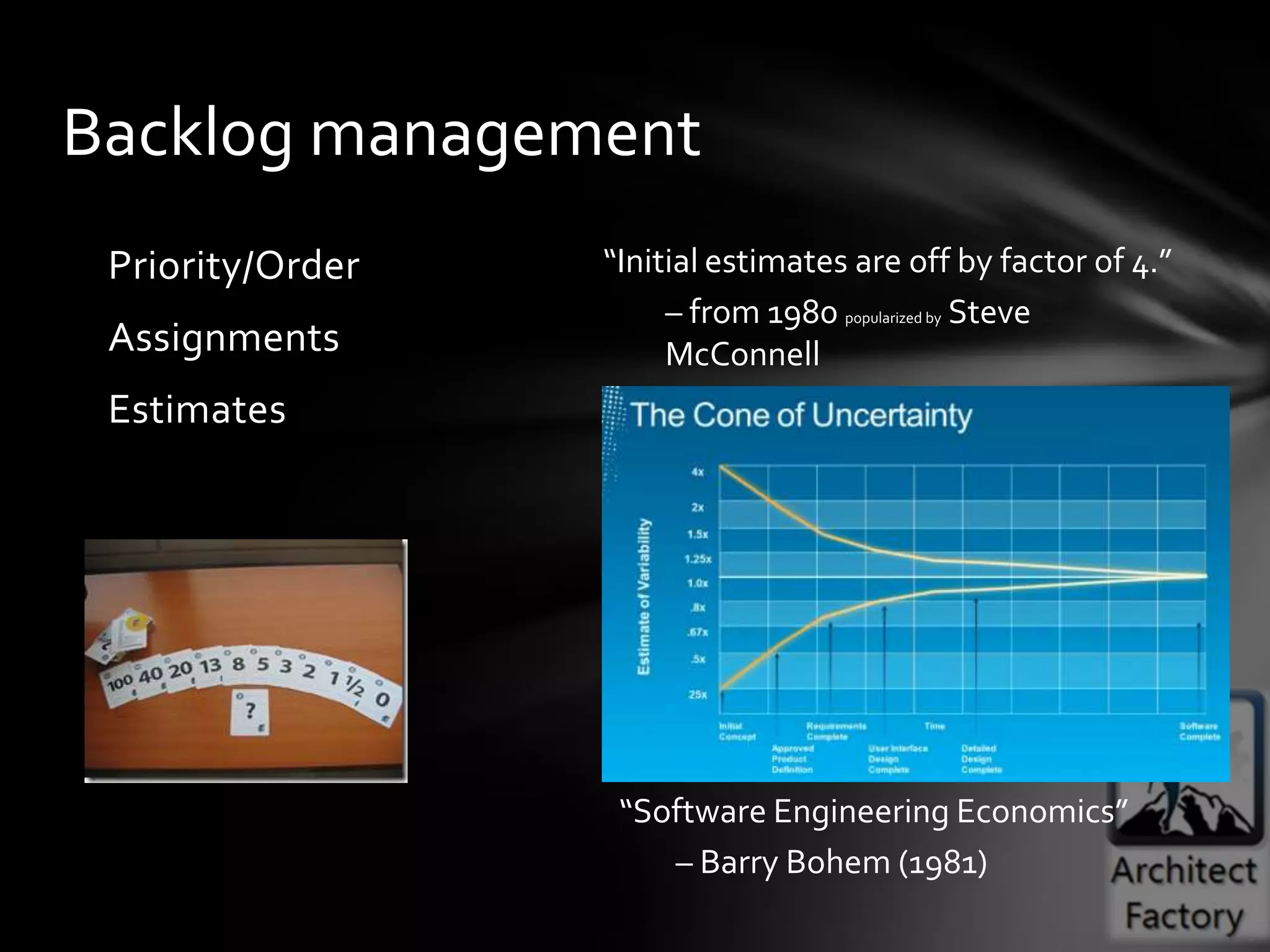
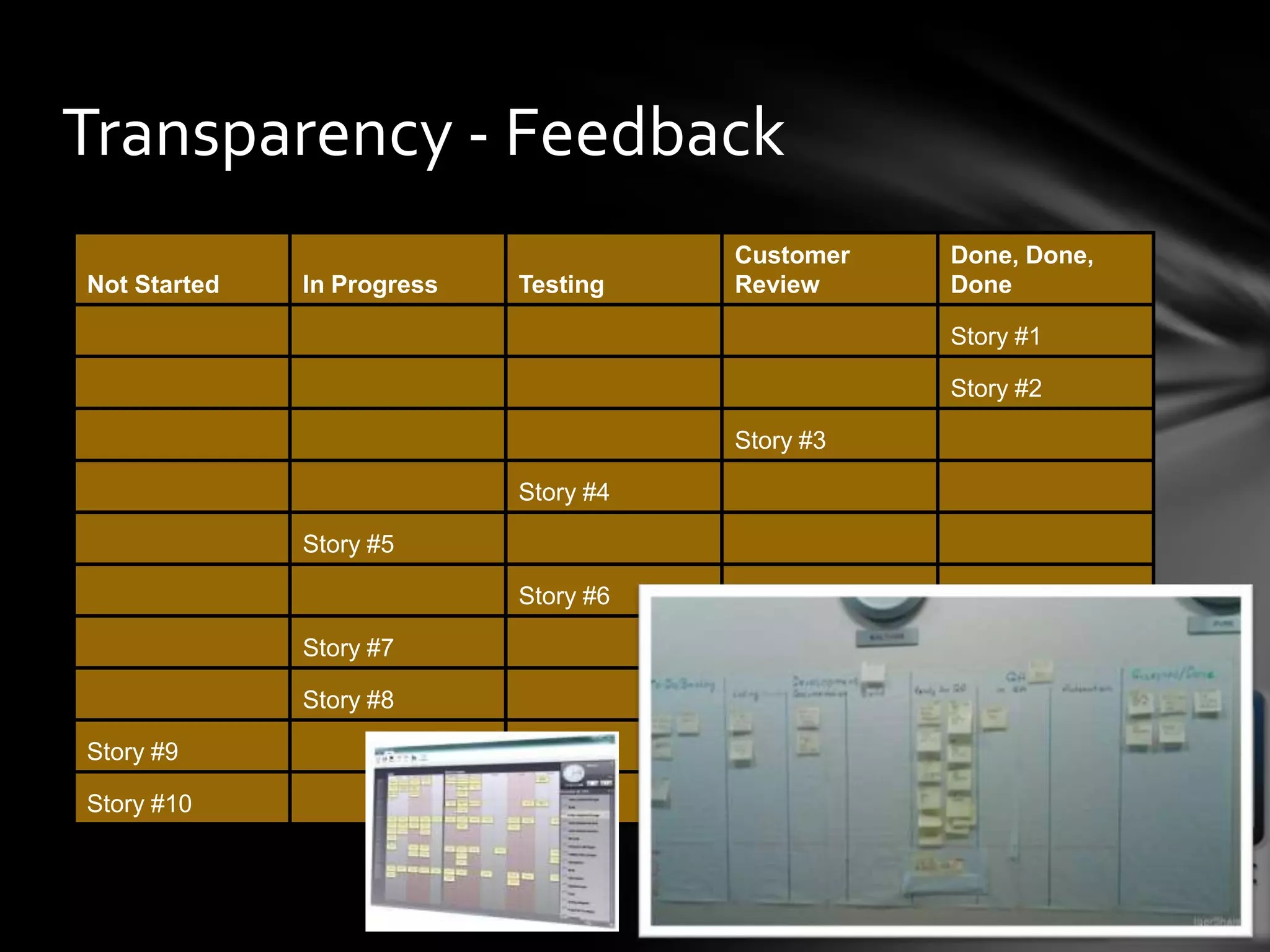
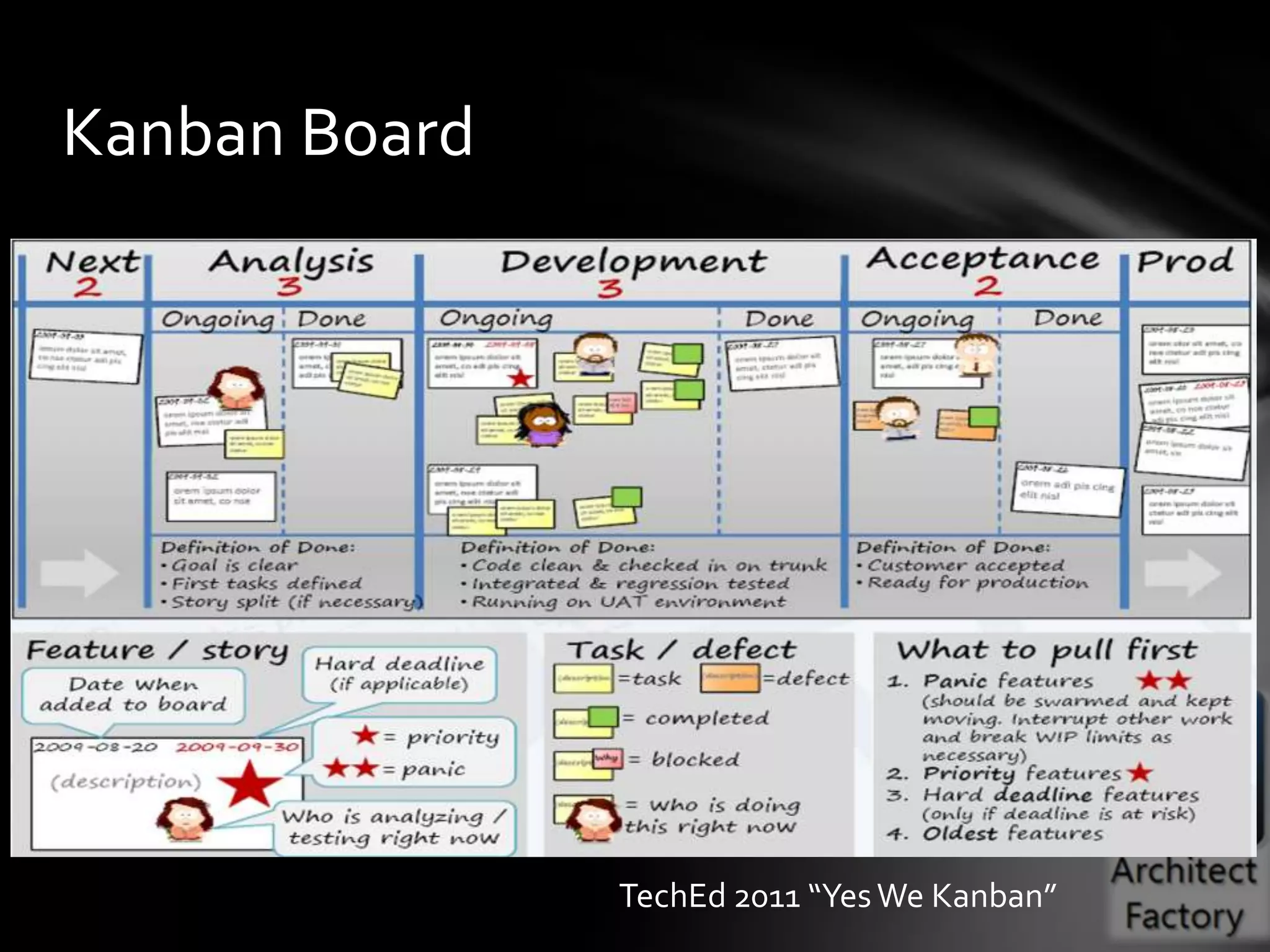
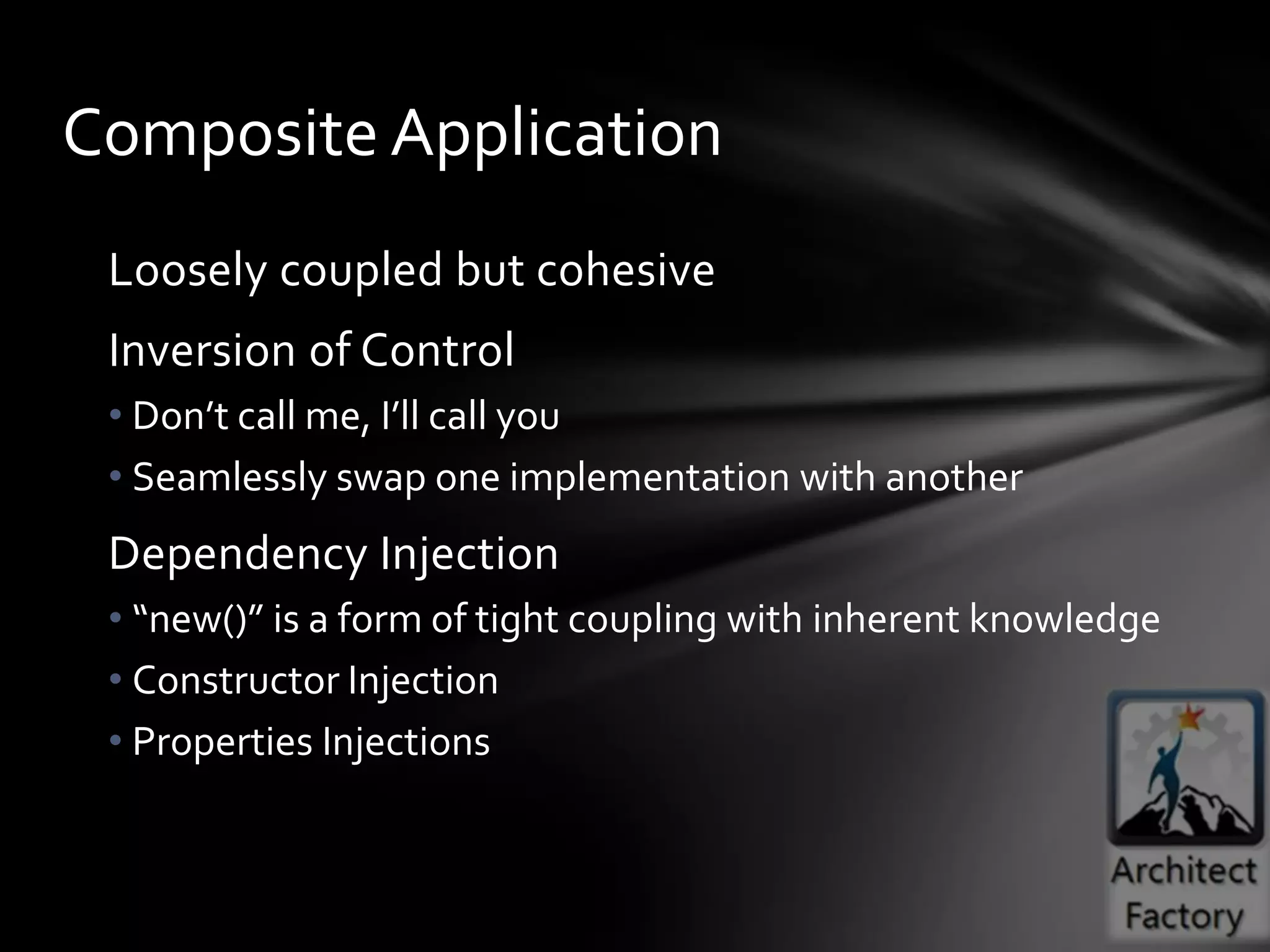
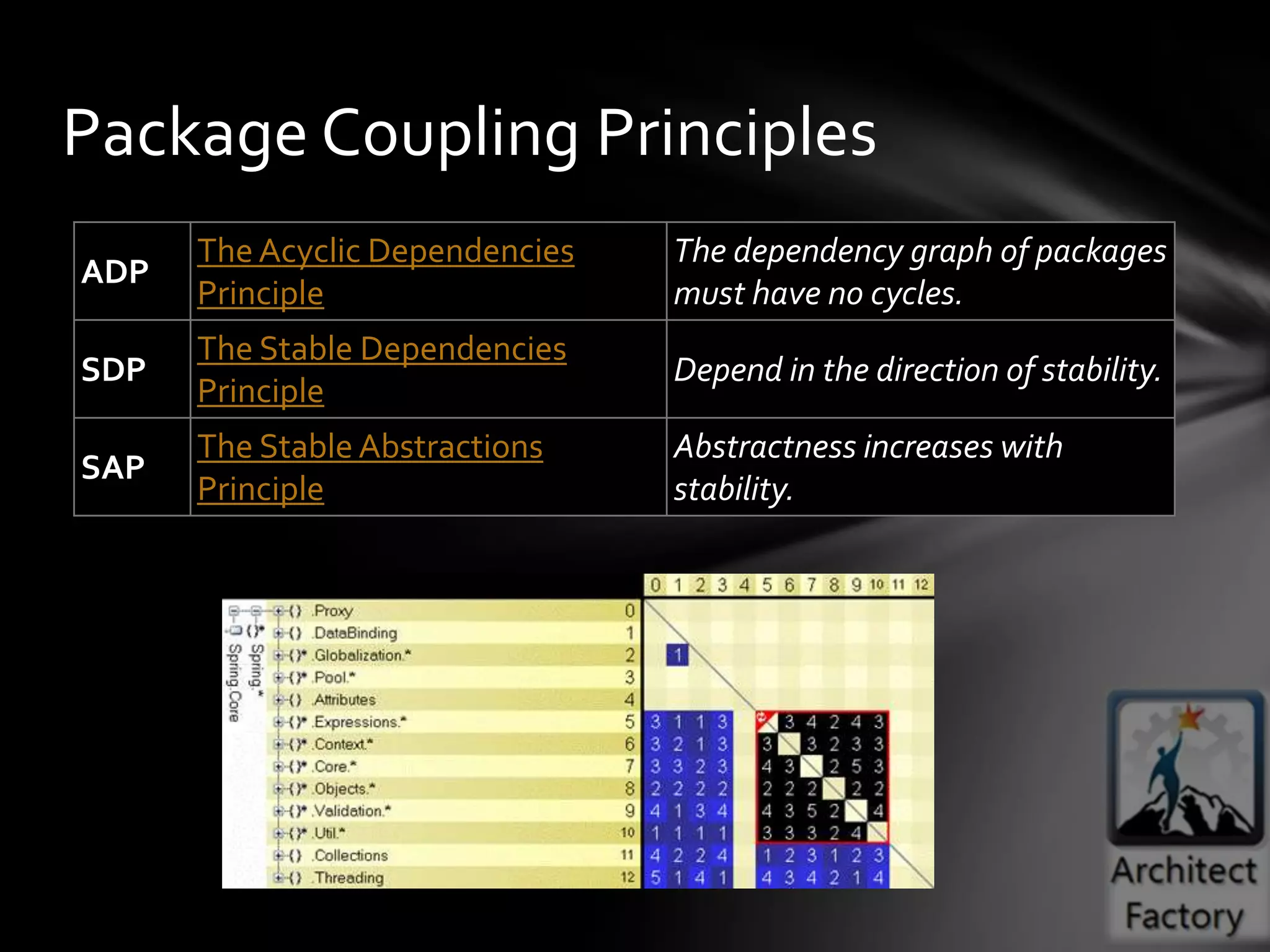
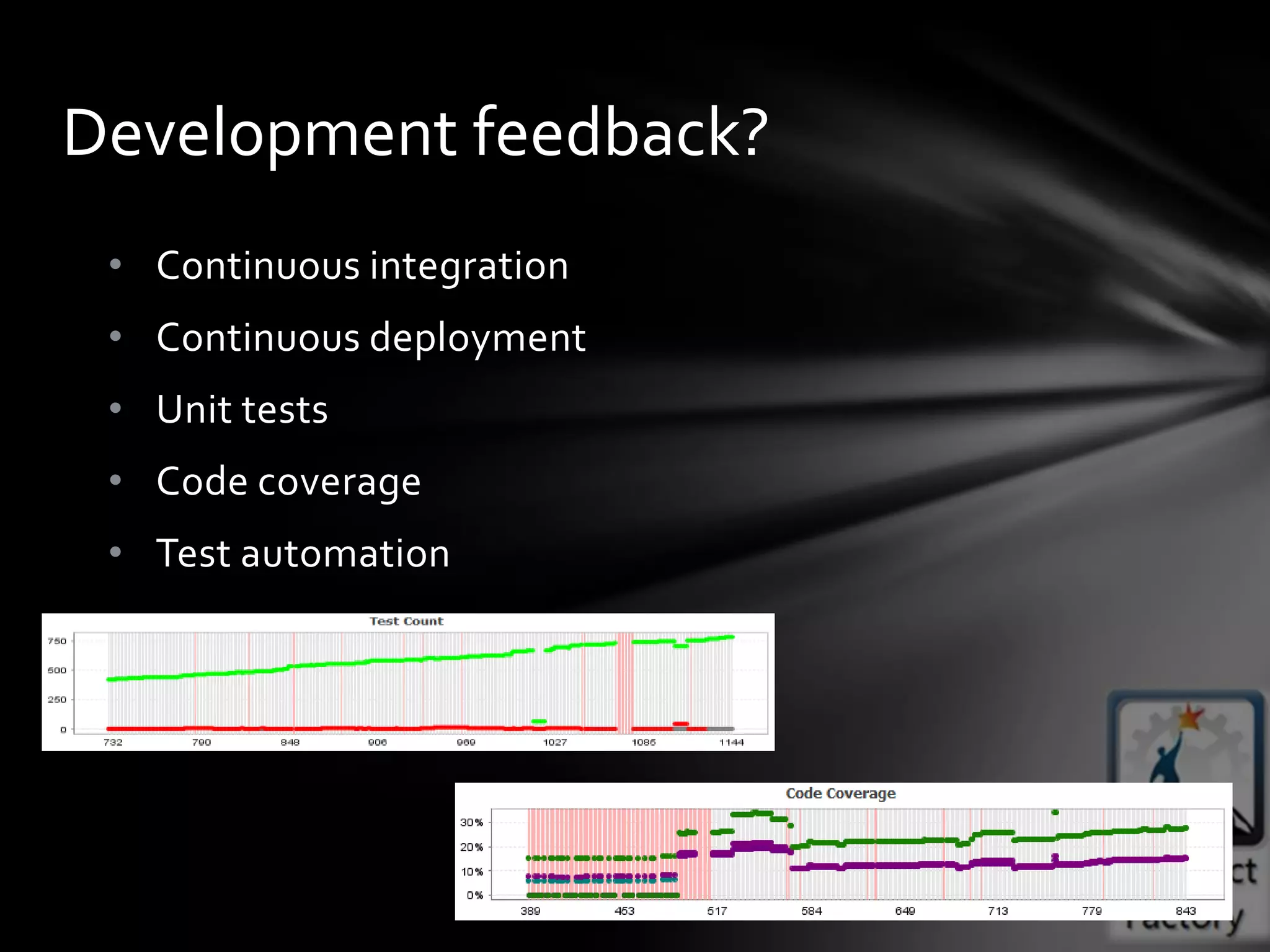
This document provides guidance on agile architecture and design principles. It emphasizes that agile design is about responding quickly to change for customers and teams through transparency, lightweight processes, and continuous learning. Key principles discussed include designing incrementally without large upfront design; getting early and continuous feedback; delaying commitment and complexity; and maximizing evolutionary design through reversibility and packaging. The document also covers topics like testing, distributed teams, and delivering frequently.