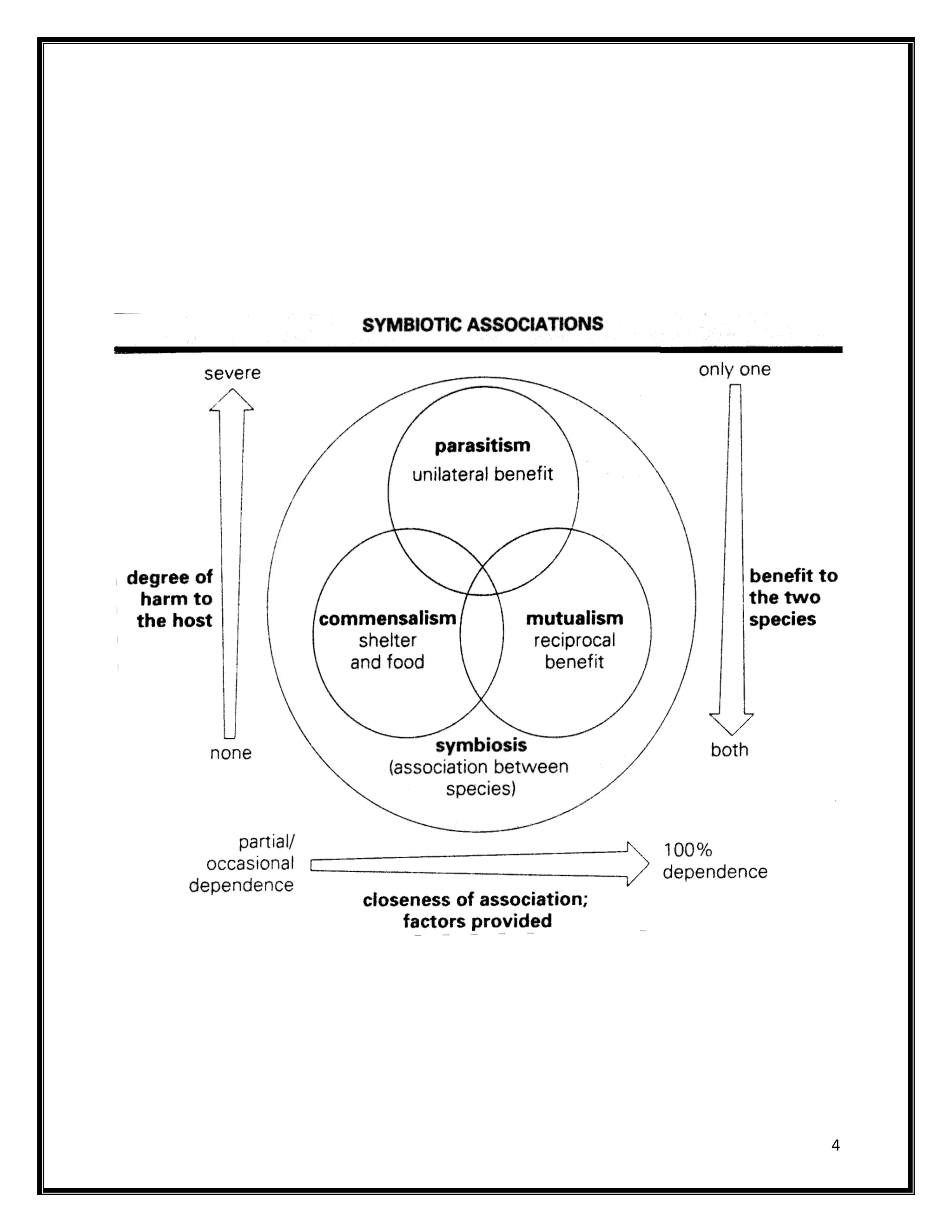
1. Microbial associations refer to the close relationships between microorganisms, which can include mutualism, commensalism, and antagonism. Mutualism benefits both microorganisms, commensalism benefits one without affecting the other, and antagonism involves predation or parasitism where one benefits at the expense of the other.
2. Examples of microbial associations include nitrogen-fixing bacteria that live symbiotically in plant root nodules, fungi and algae that form lichens, and microbes in animal digestive systems that aid in breaking down food.
3. These associations play important roles in the environment, from nutrient cycling to industrial applications like producing antibiotics and fermented foods