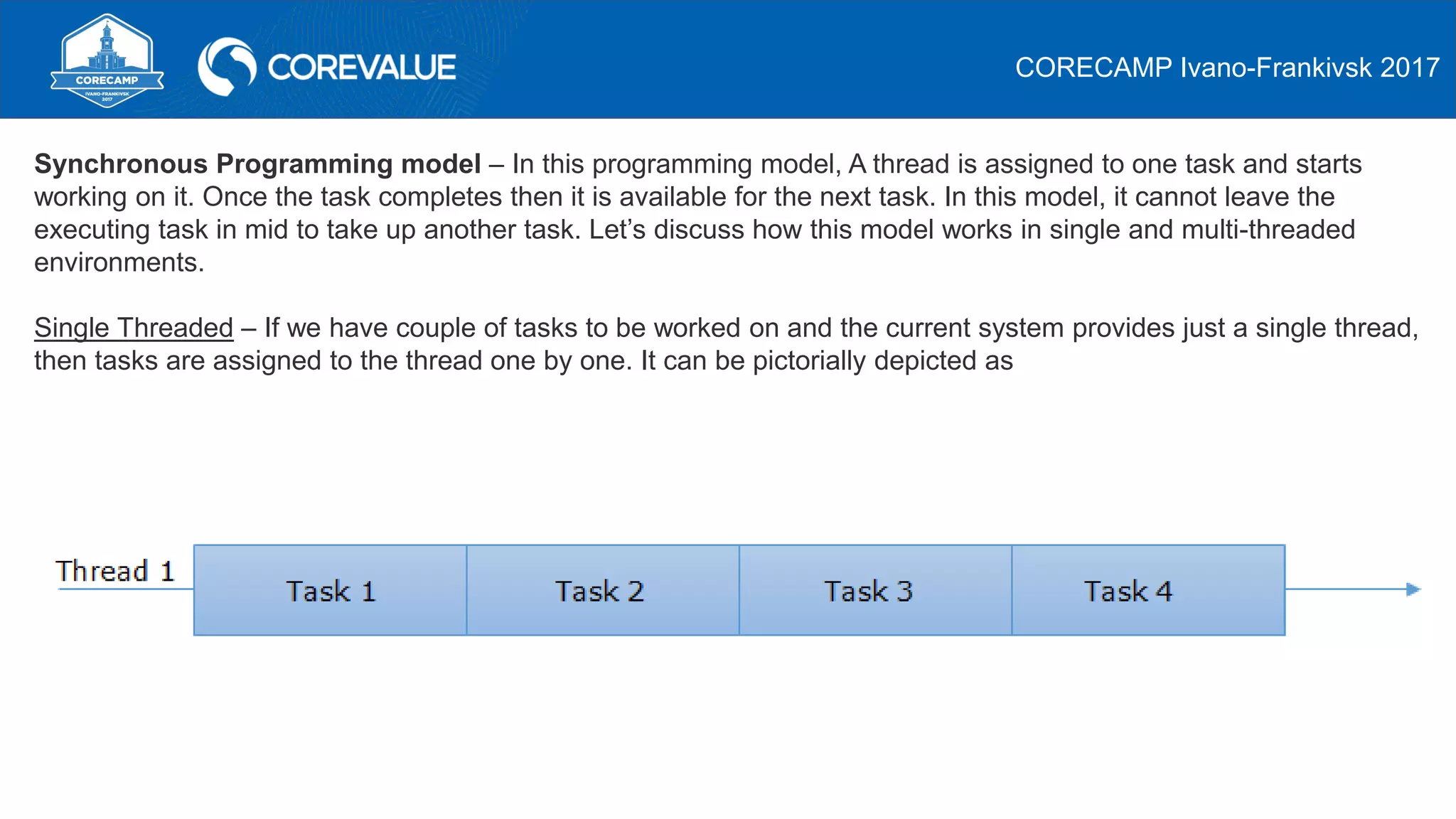
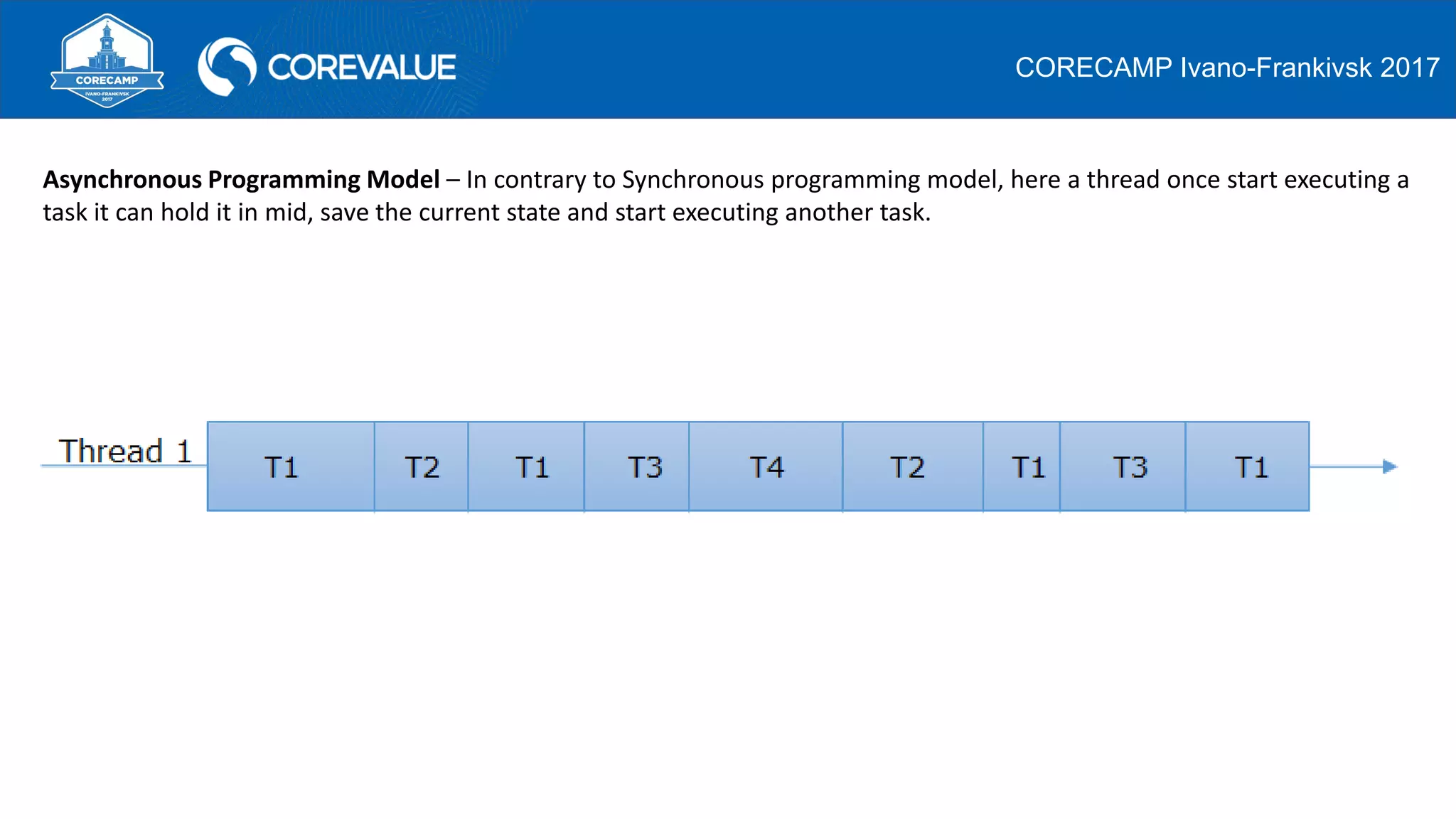
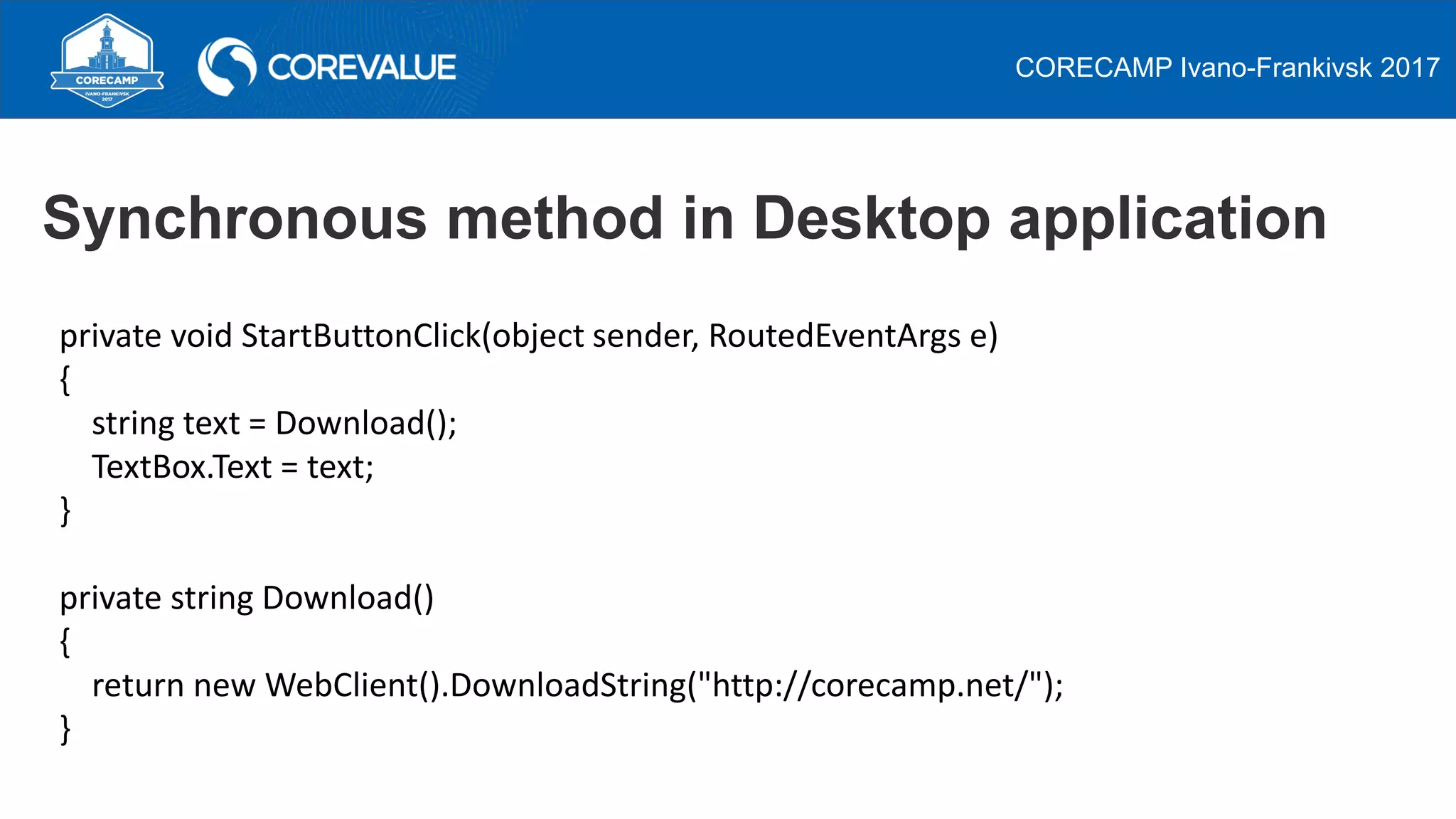
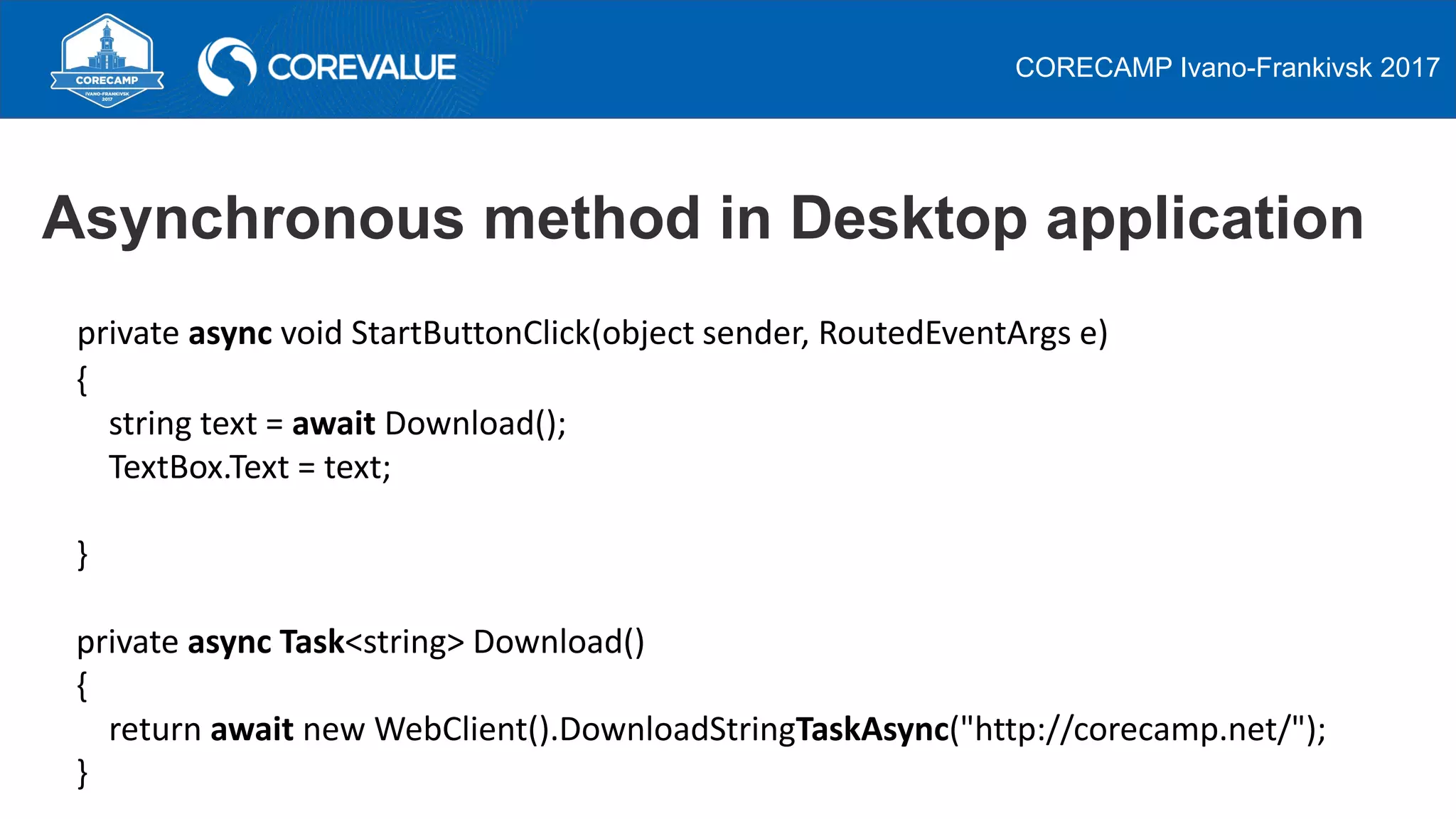
This document discusses asynchronous programming in C# and compares it to synchronous programming. It explains that asynchronous programming allows a thread to pause its execution of a task and switch to another task, while synchronous programming requires a thread to fully complete a task before moving to the next one. It also discusses how asynchronous and synchronous programming can be used in both single-threaded and multi-threaded environments. The document then provides examples of asynchronous programming using the Asynchronous Programming Model, Event-based Asynchronous Pattern, and Task-based Asynchronous Pattern in .NET.