The document provides an overview of fundamental JavaScript concepts such as variables, data types, operators, control structures, functions, and objects. It also covers DOM manipulation and interacting with HTML elements. Code examples are provided to demonstrate JavaScript syntax and how to define and call functions, work with arrays and objects, and select and modify elements of a web page.






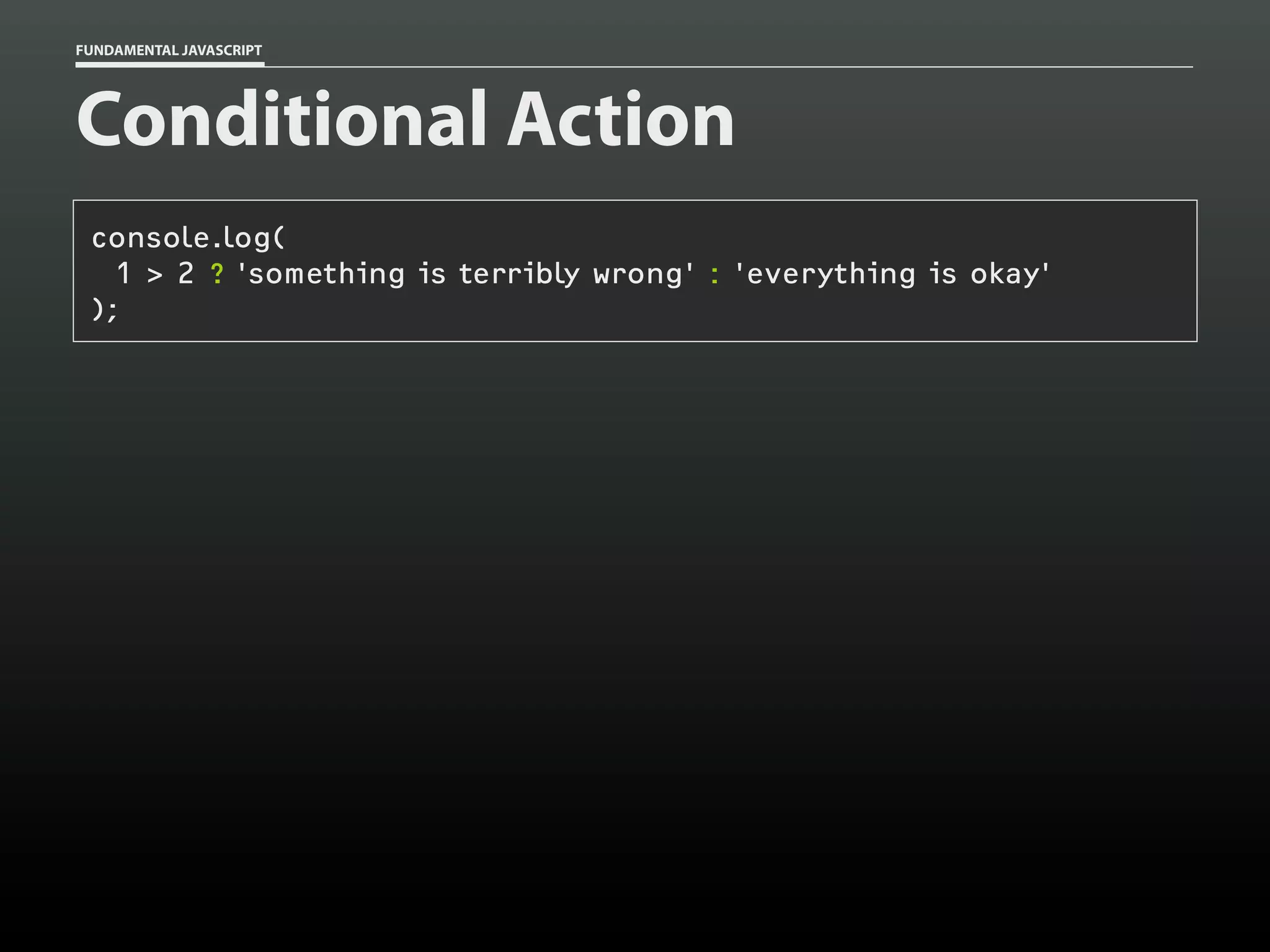
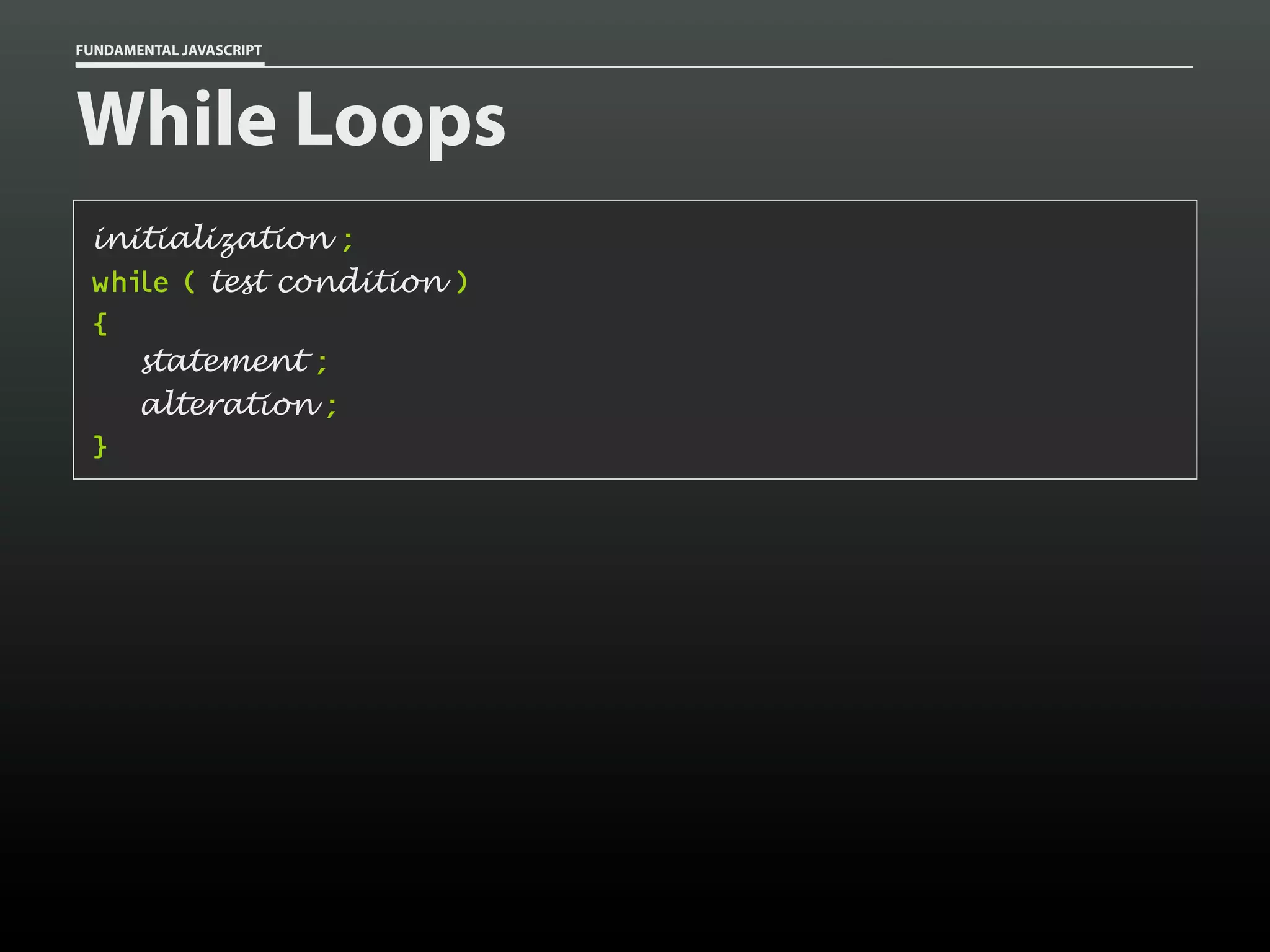
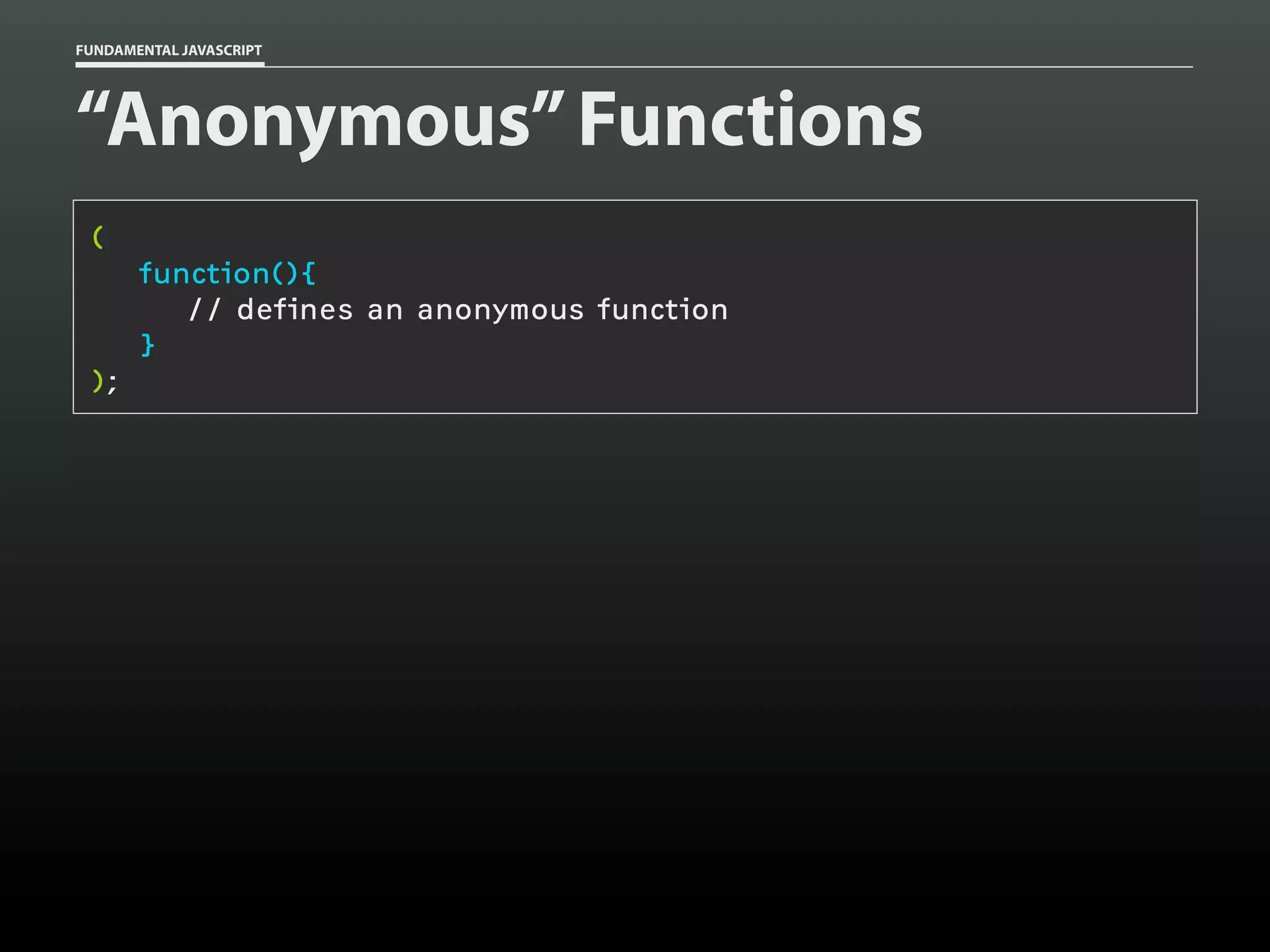
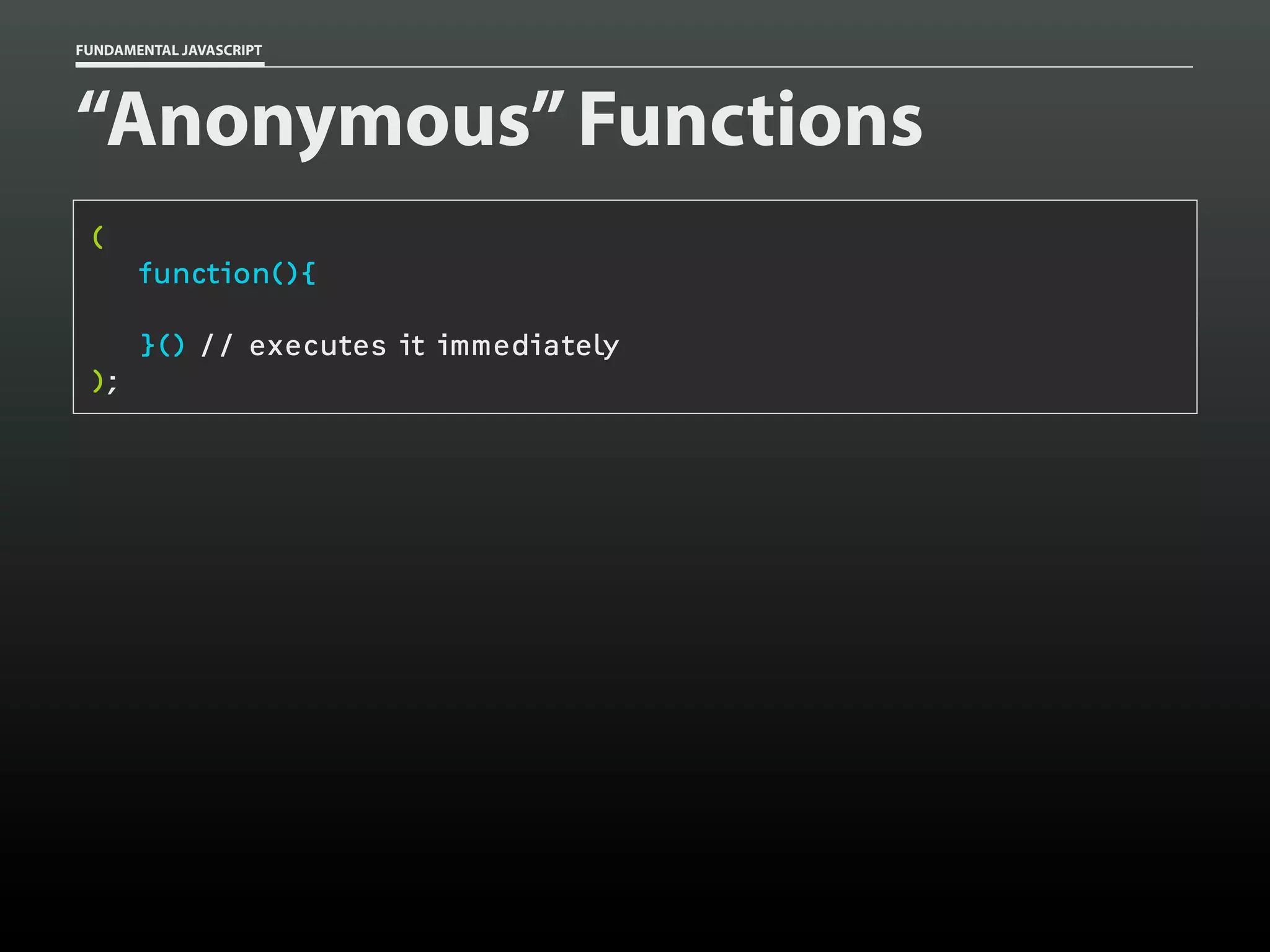
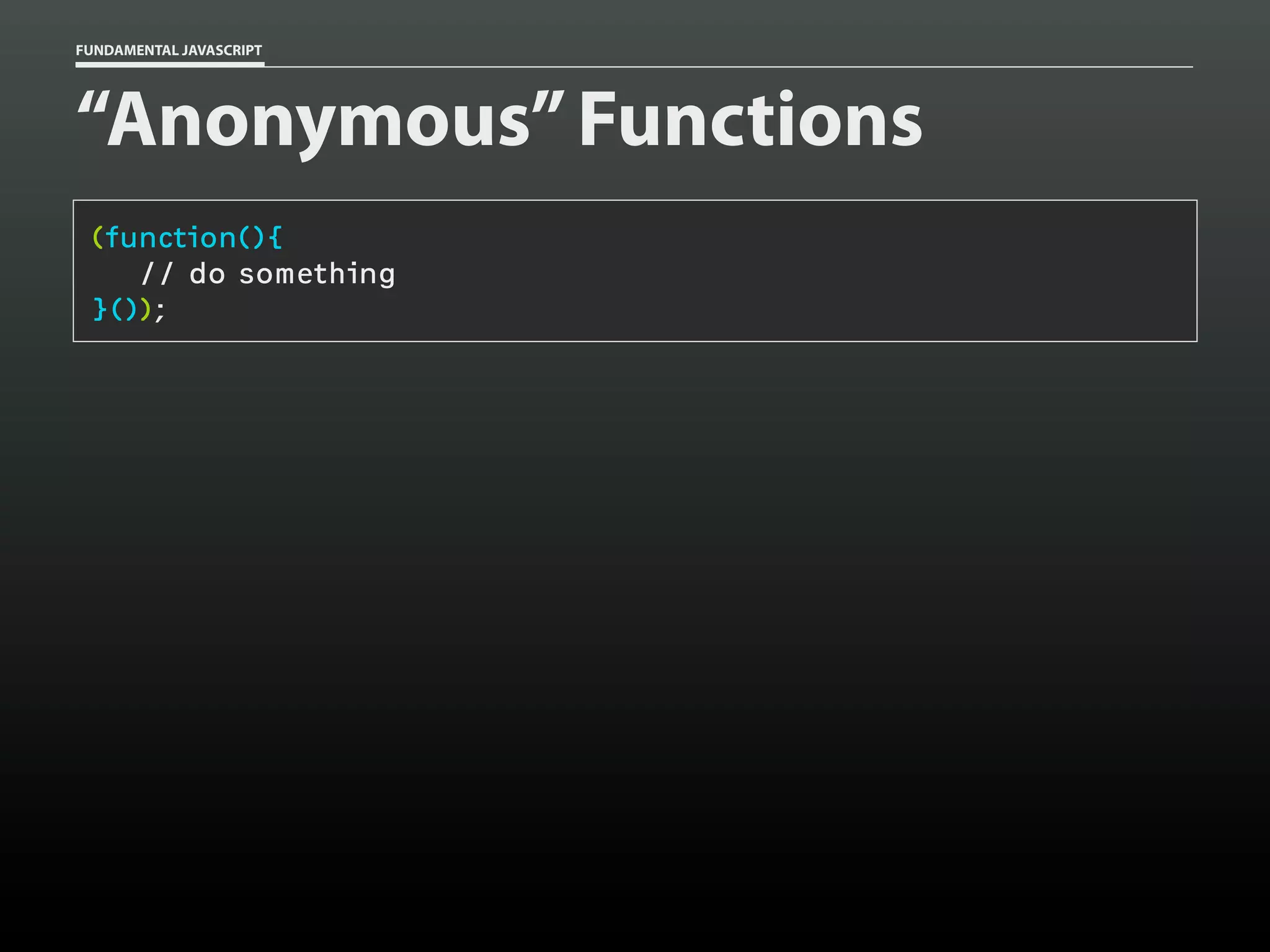
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
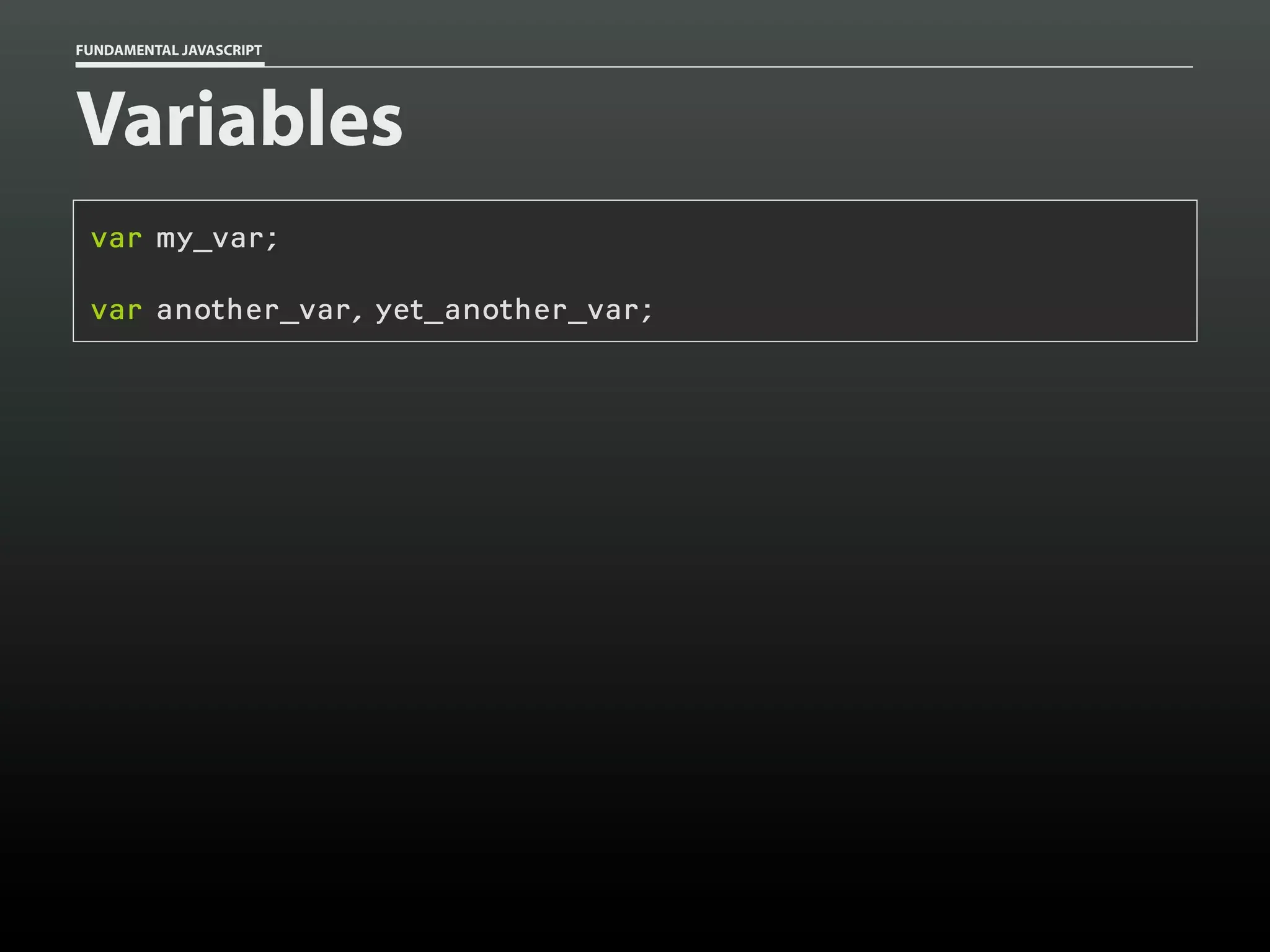
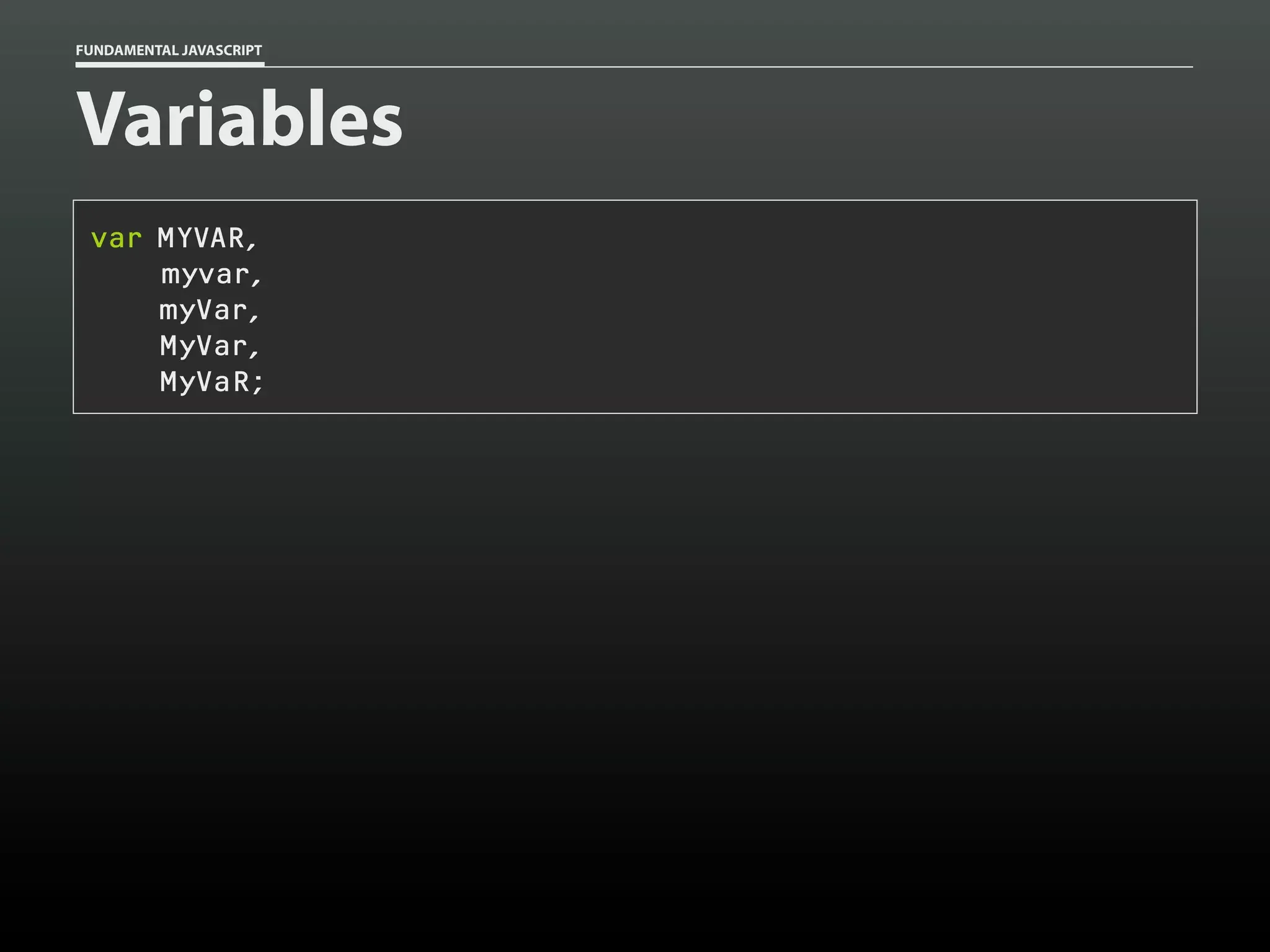
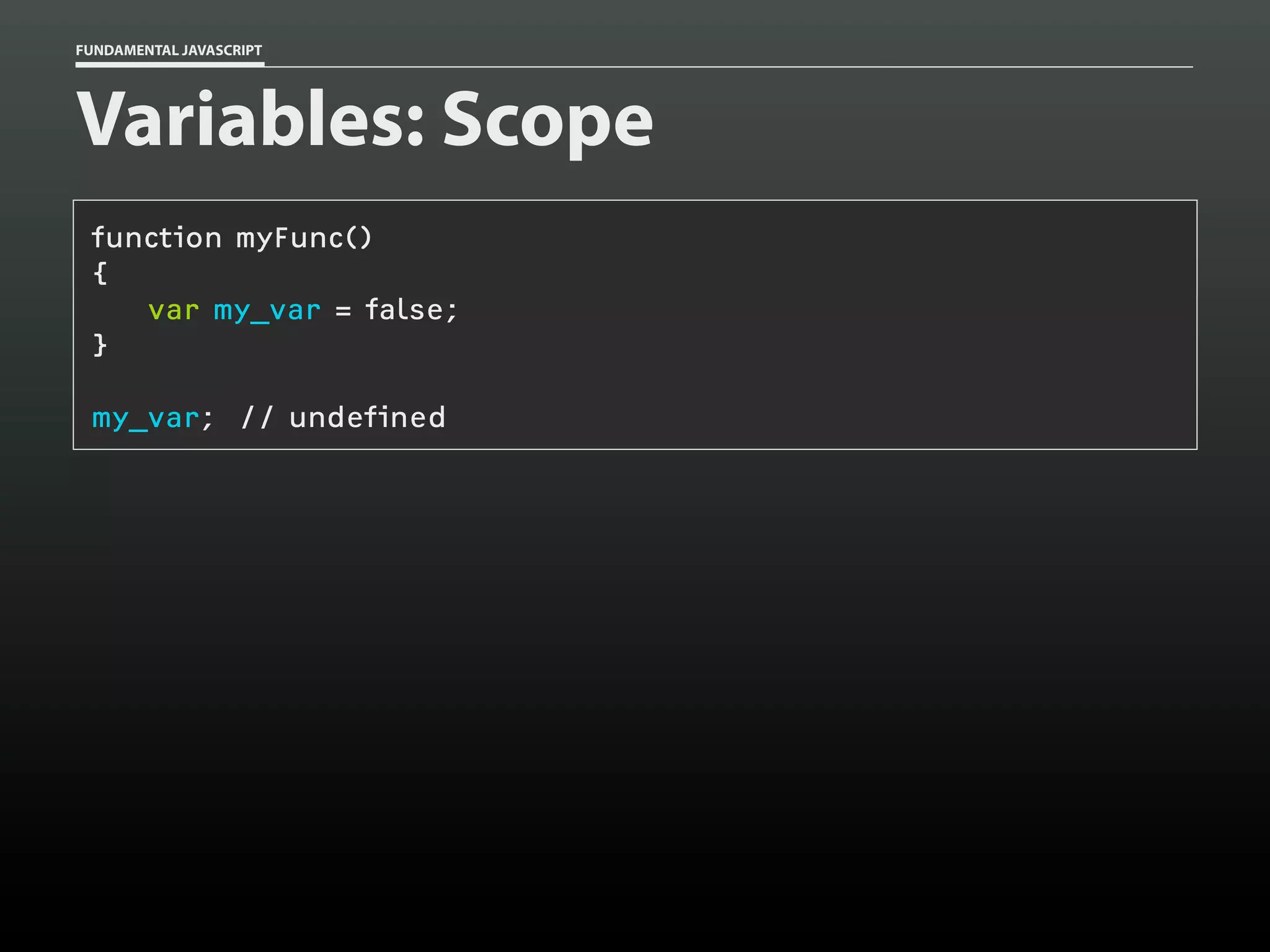
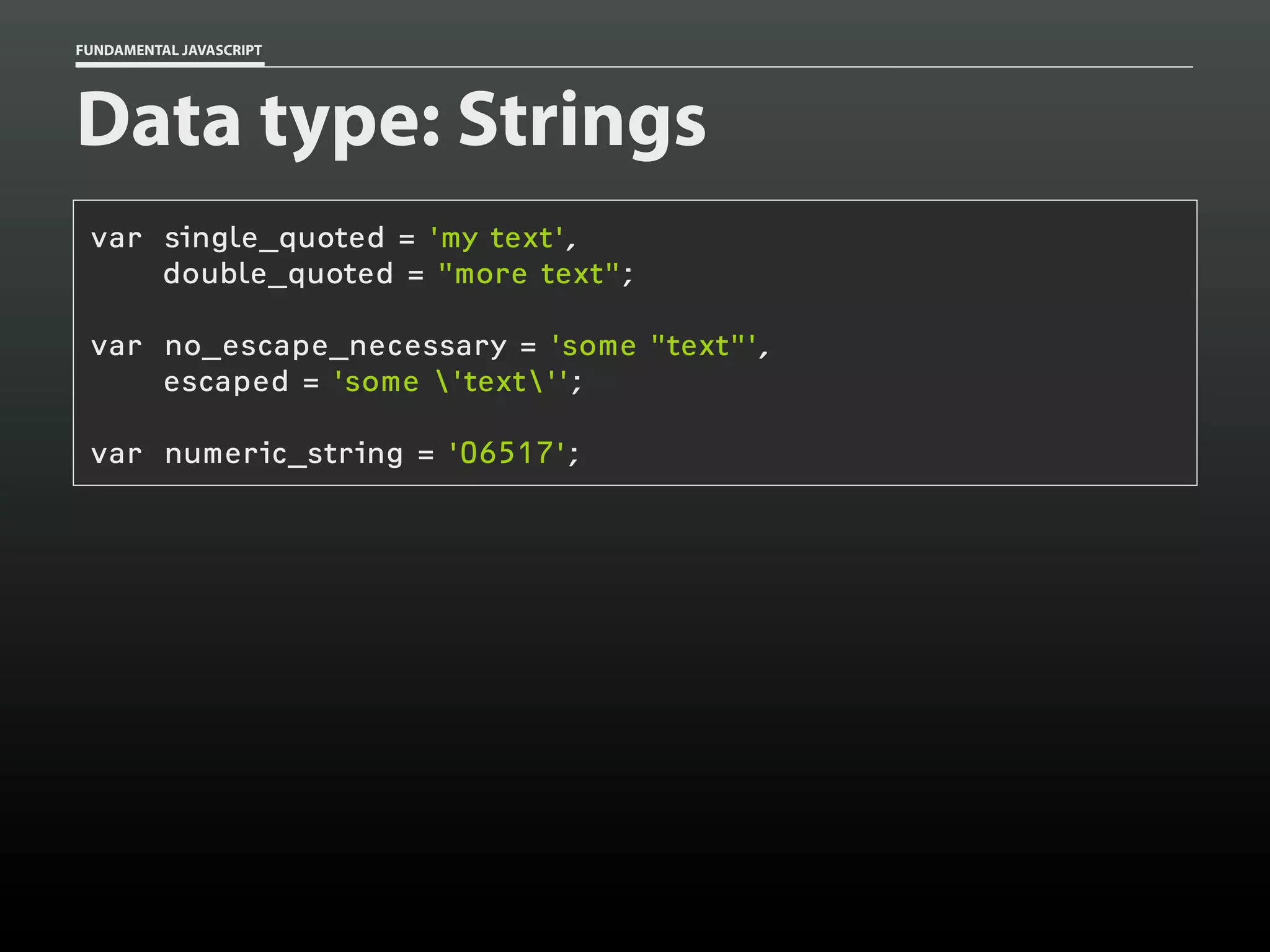
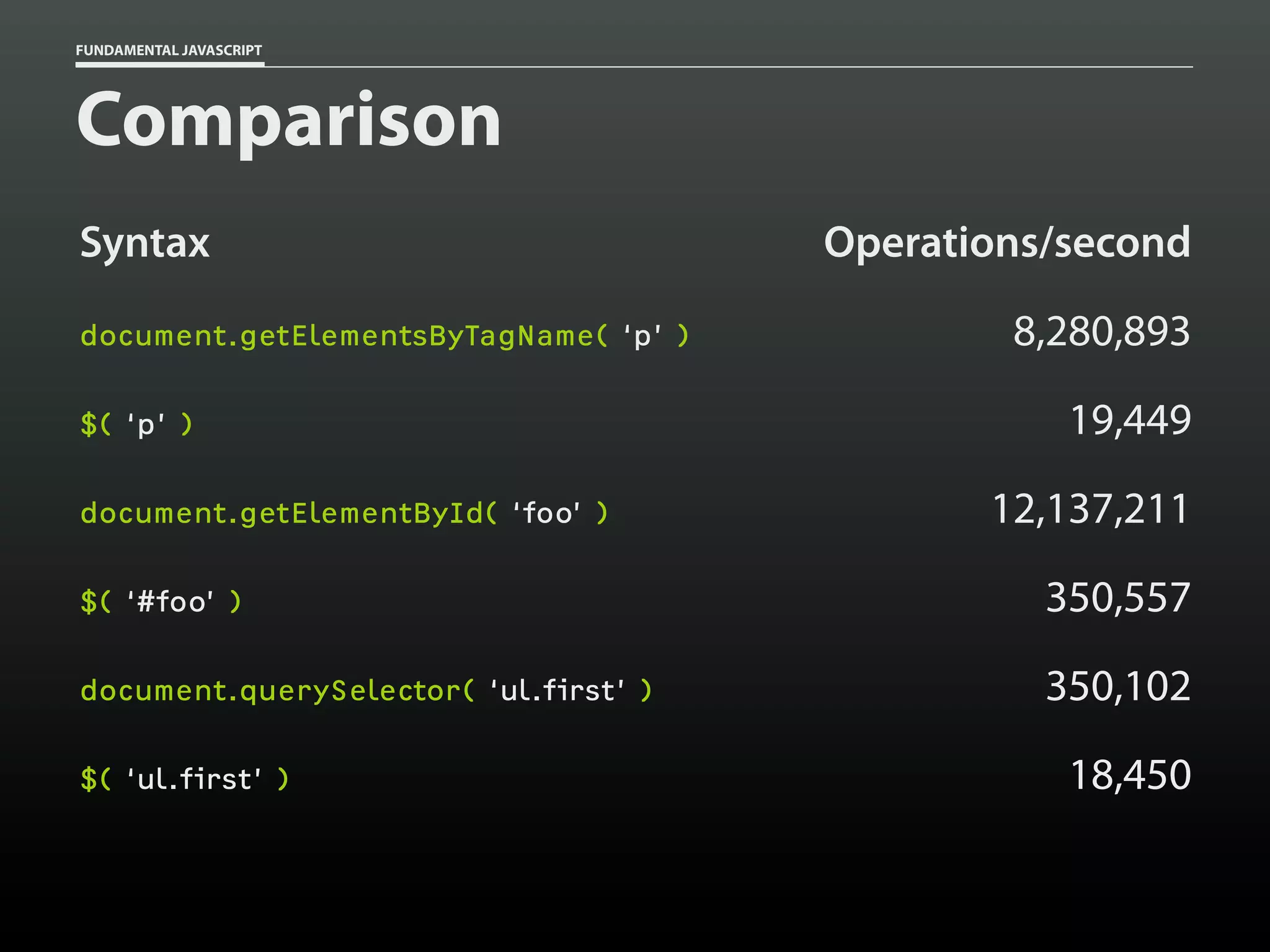
Data type: Arrays
var my_cats = [];
my_cats[0] = 'Sabine';
my_cats[1] = 'Dakota';
my_cats; // ['Sabine','Dakota']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-13-2048.jpg)
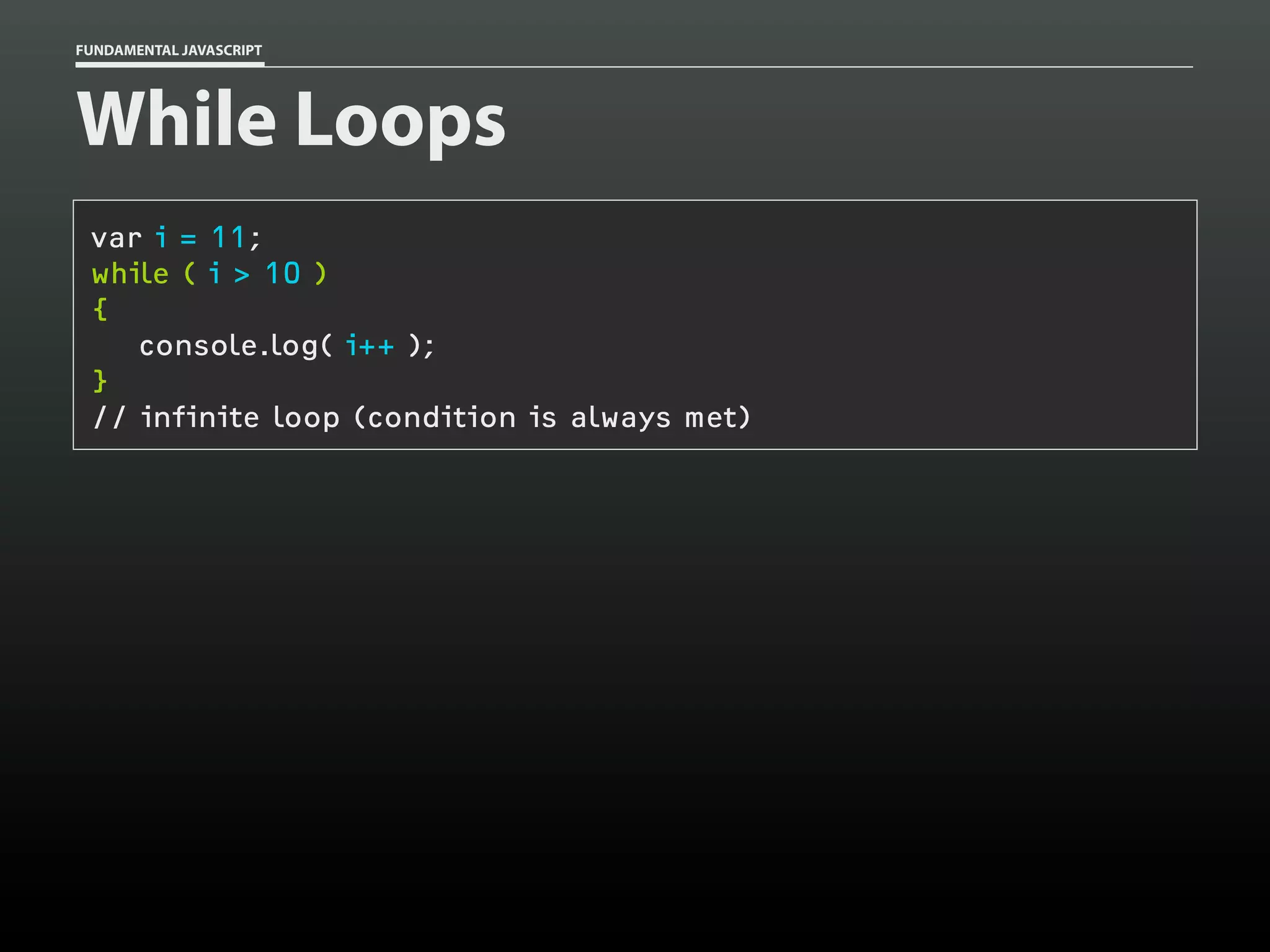
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
Data type: Arrays
var sabine = [
'Sabine',
// 0 = name
'cat',
// 1 = type
'female',
// 2 = gender
17,
// 3 = age
true
// 4 = spayed/neutered
];
sabine[2]; // 'female'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-14-2048.jpg)
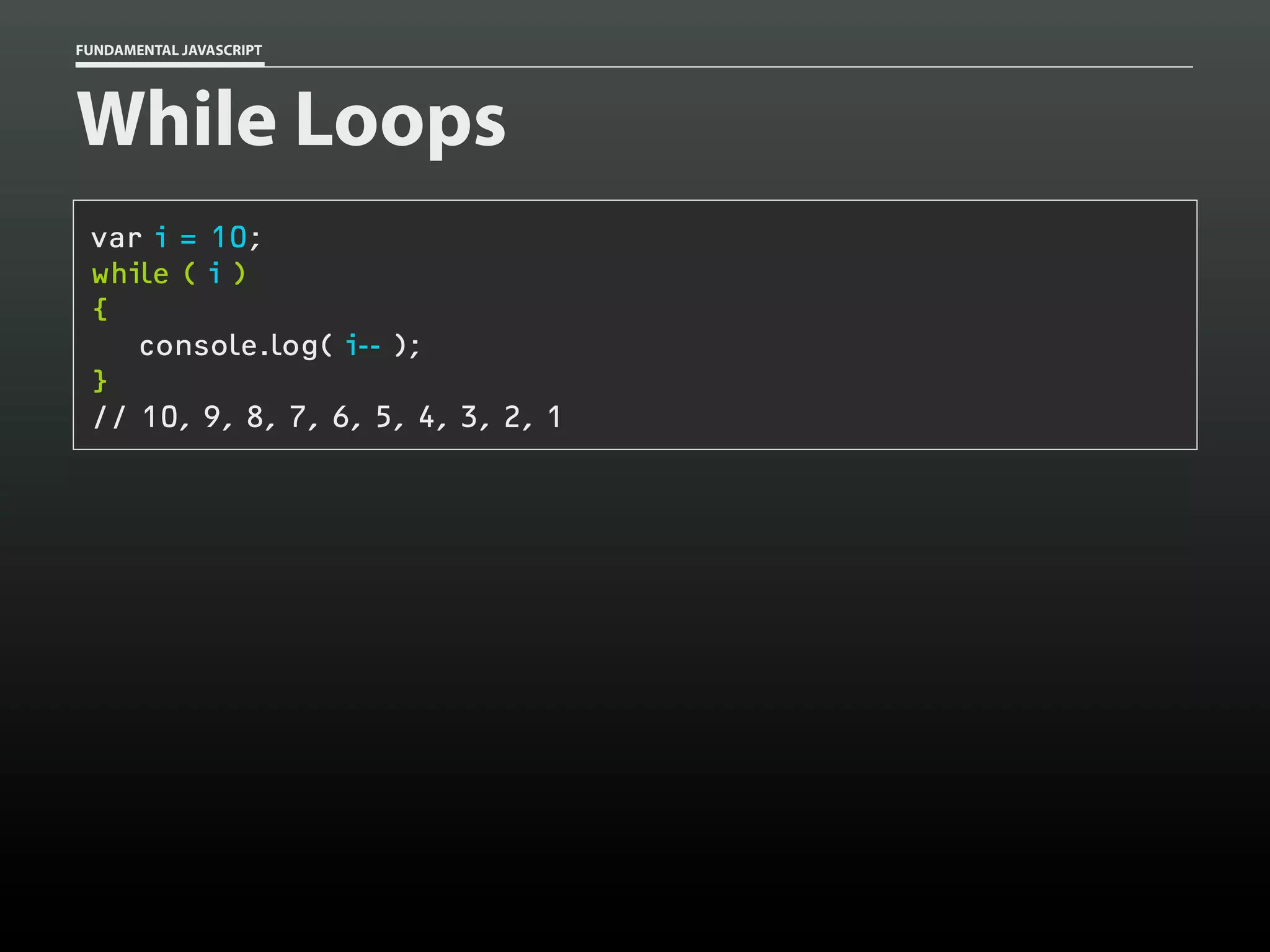
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
Data type: Arrays
var sabine = ['Sabine', 'cat', 'female', 14, true],
dakota = ['Dakota', 'cat', 'male', 13, true];
pets = [ sabine, dakota ];
pets[1][0]; // 'Dakota'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-15-2048.jpg)
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
Data type: Hashes
var sabine = [];
sabine['name'] = 'Sabine';
sabine['type'] = 'cat';
sabine['gender'] = 'female';
sabine['age'] = 14;
sabine['fixed'] = true;
sabine;
// []
sabine['name']; // 'Sabine'
sabine.name;
// 'Sabine'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-16-2048.jpg)
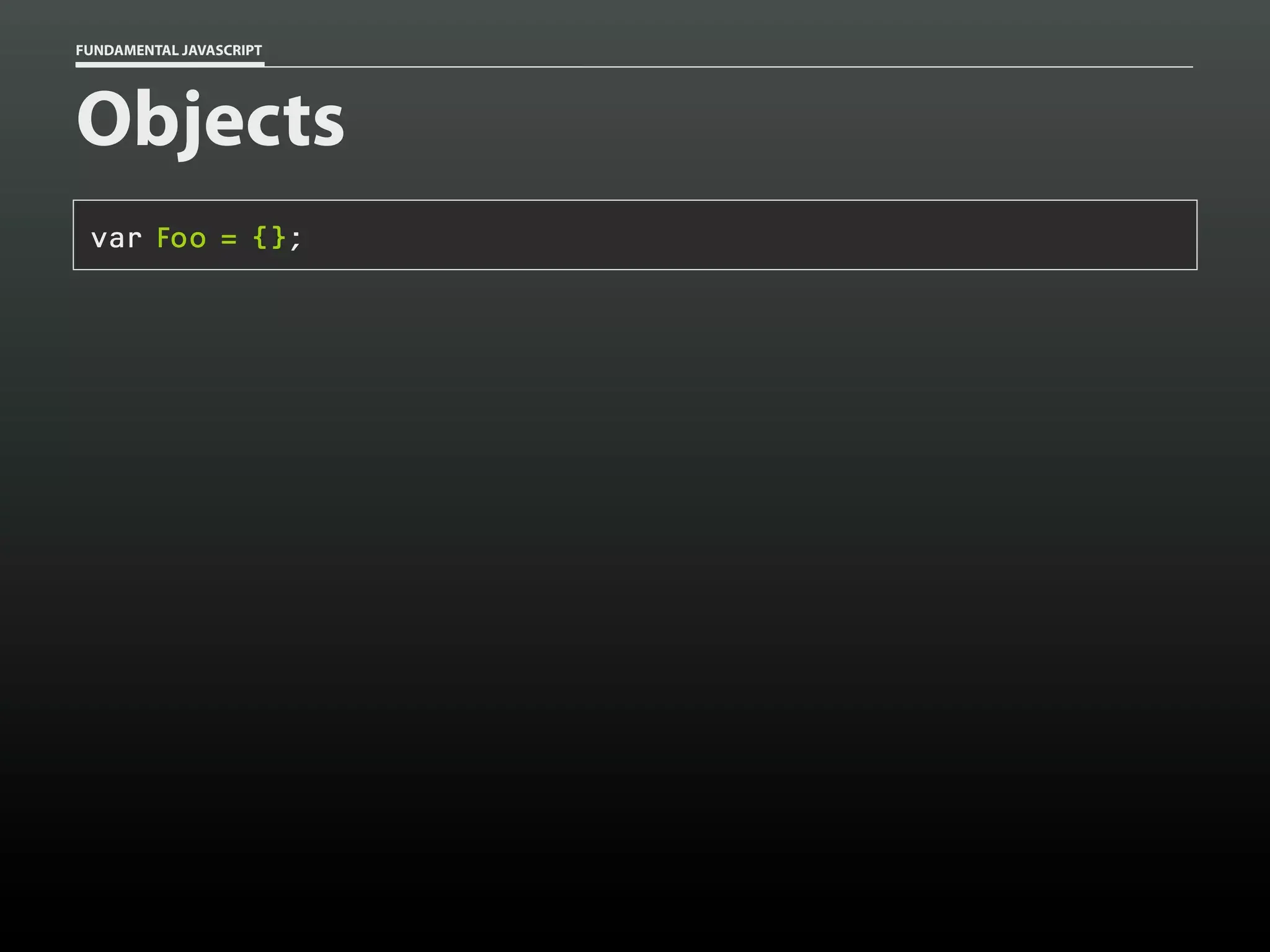
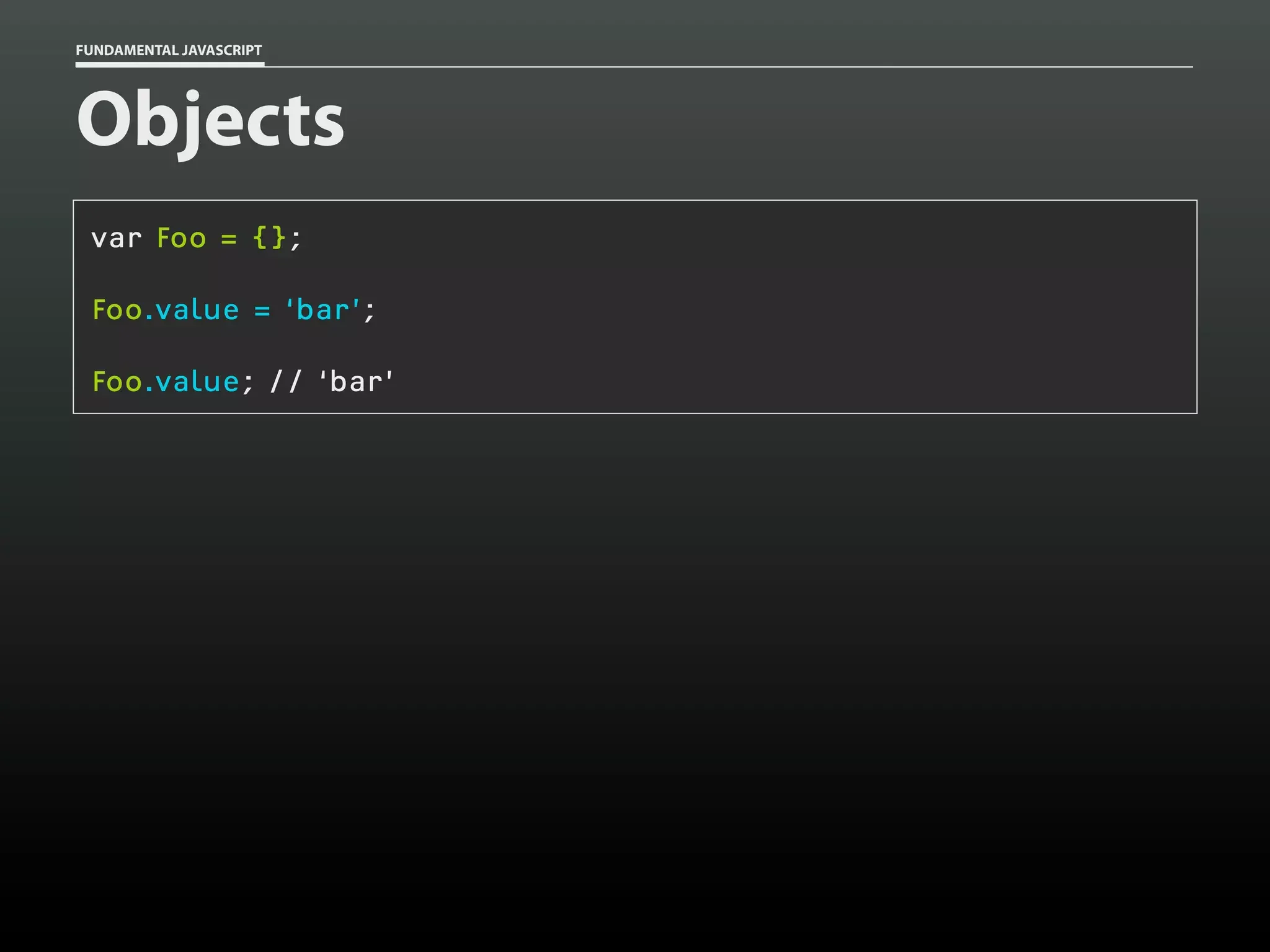
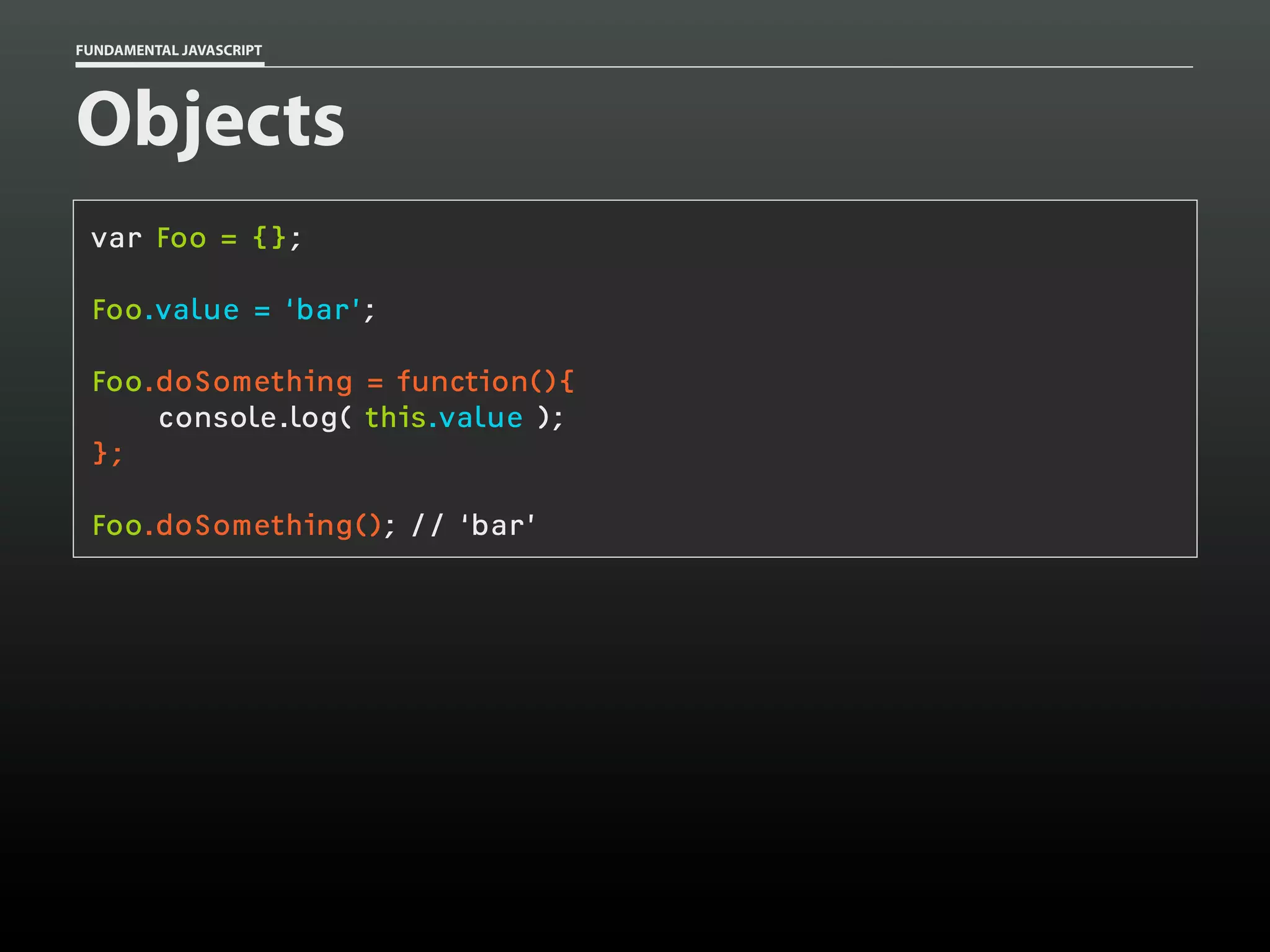
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
Data type: Objects
var sabine = {};
sabine.name = 'Sabine';
sabine.type = 'cat';
sabine.gender = 'female';
sabine.age = 14;
sabine.fixed = true;
sabine;
// Object
sabine['name']; // 'Sabine'
sabine.name;
// 'Sabine'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-17-2048.jpg)




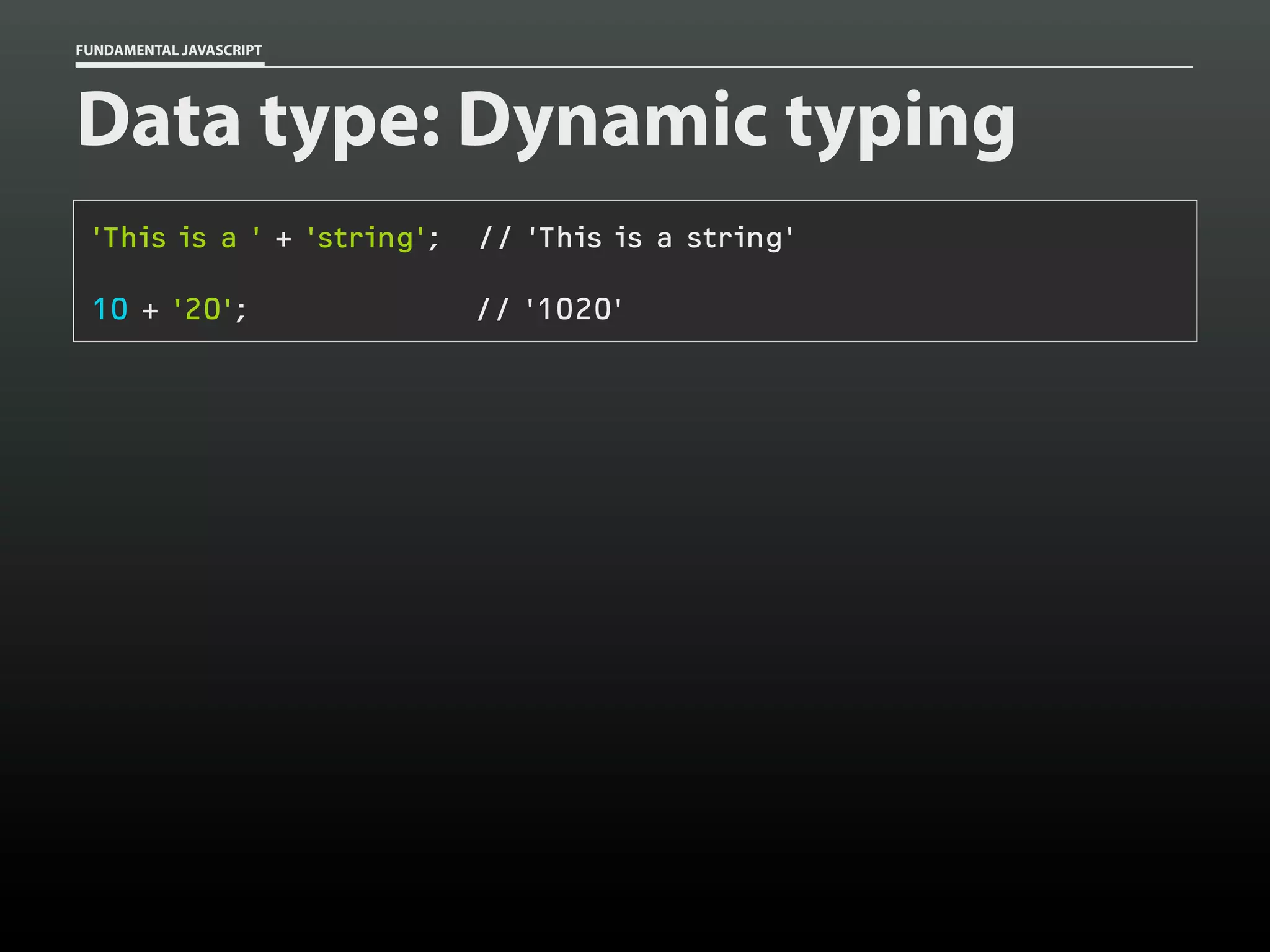
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
Data type: Dynamic typing
var my_var = false;
// boolean
my_var = 14;
// number
my_var = "test";
// string
my_var = [];
// array
my_var = {};
// object
my_var = function(){}; // function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-27-2048.jpg)




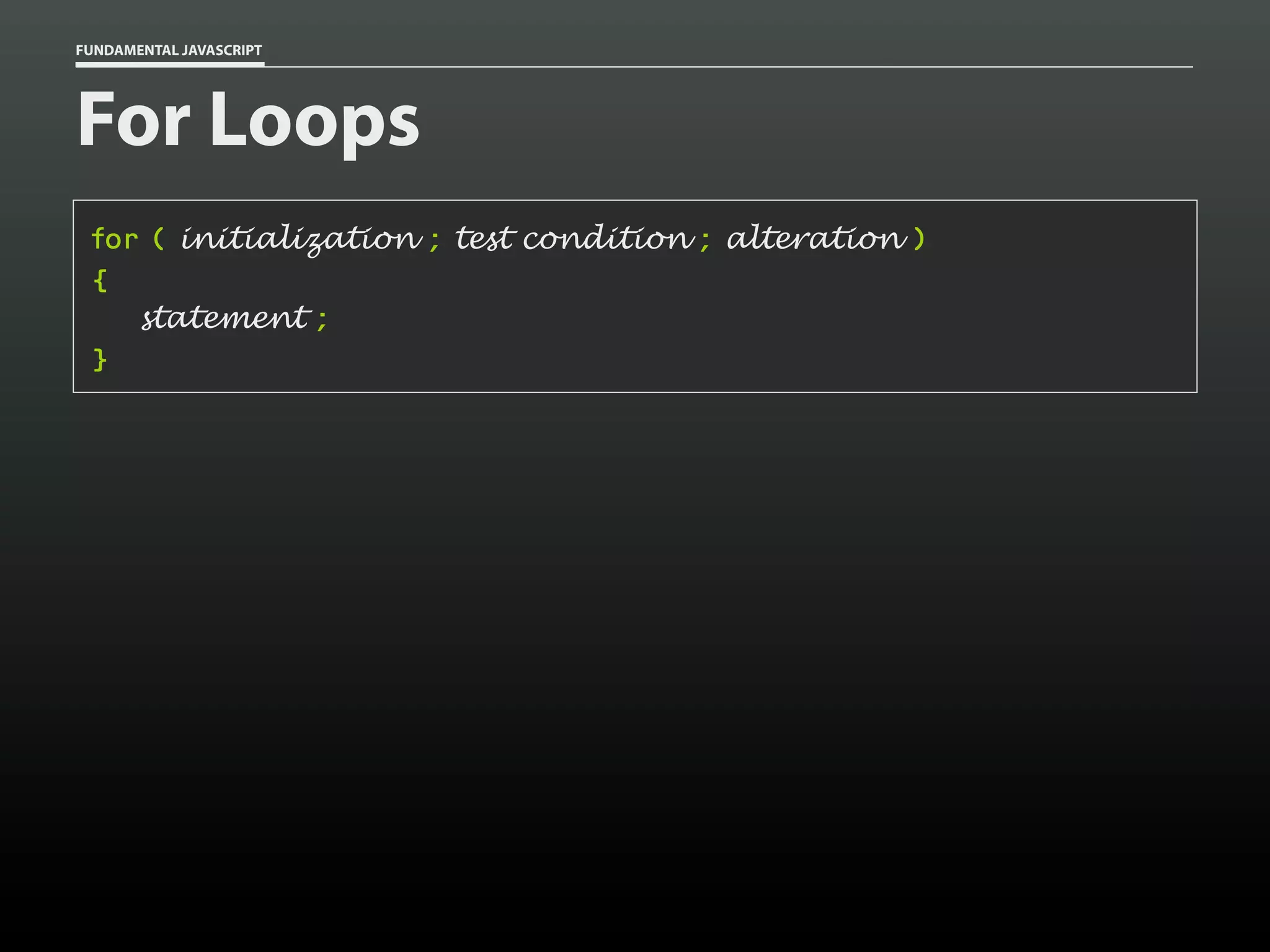
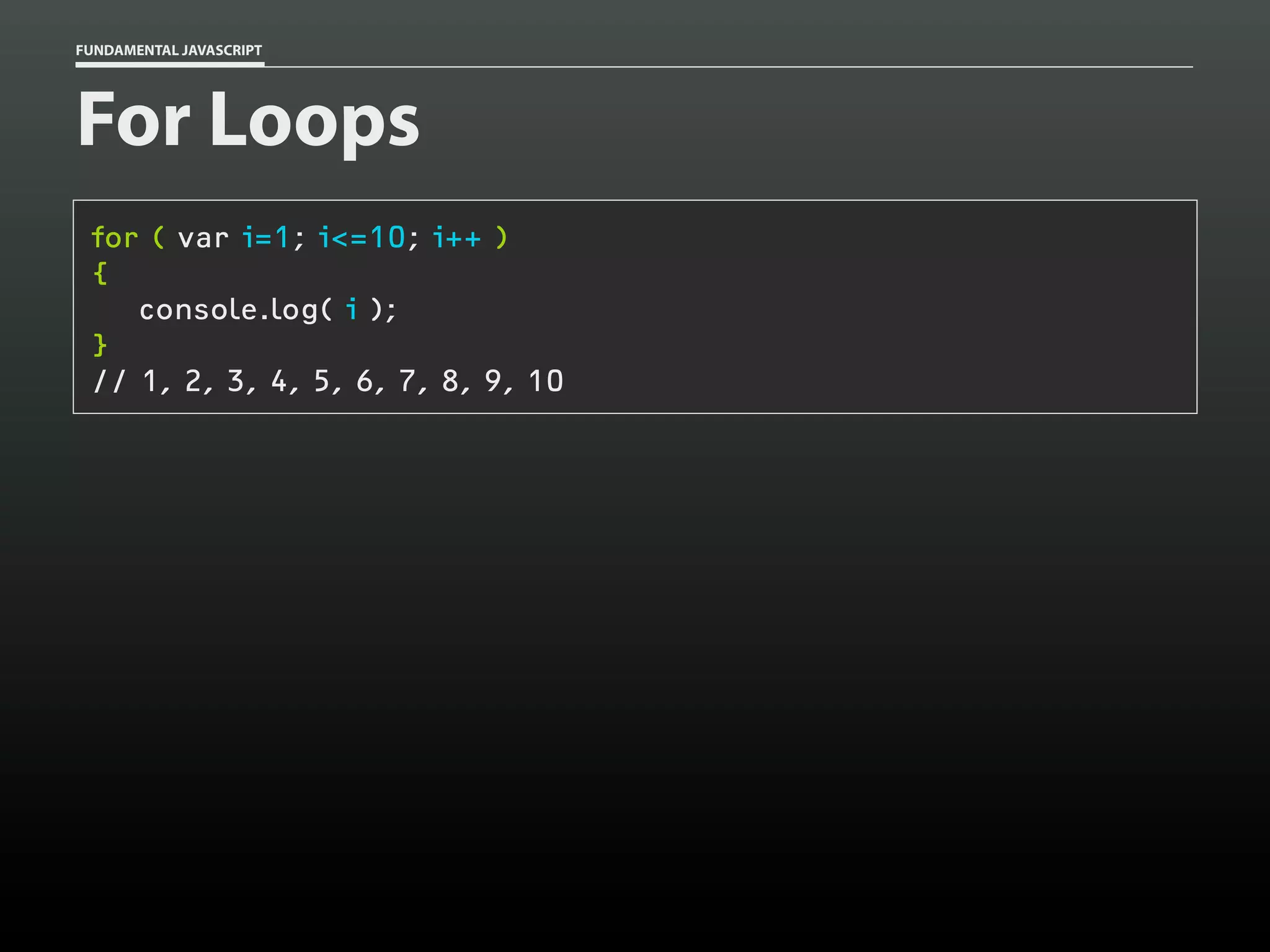



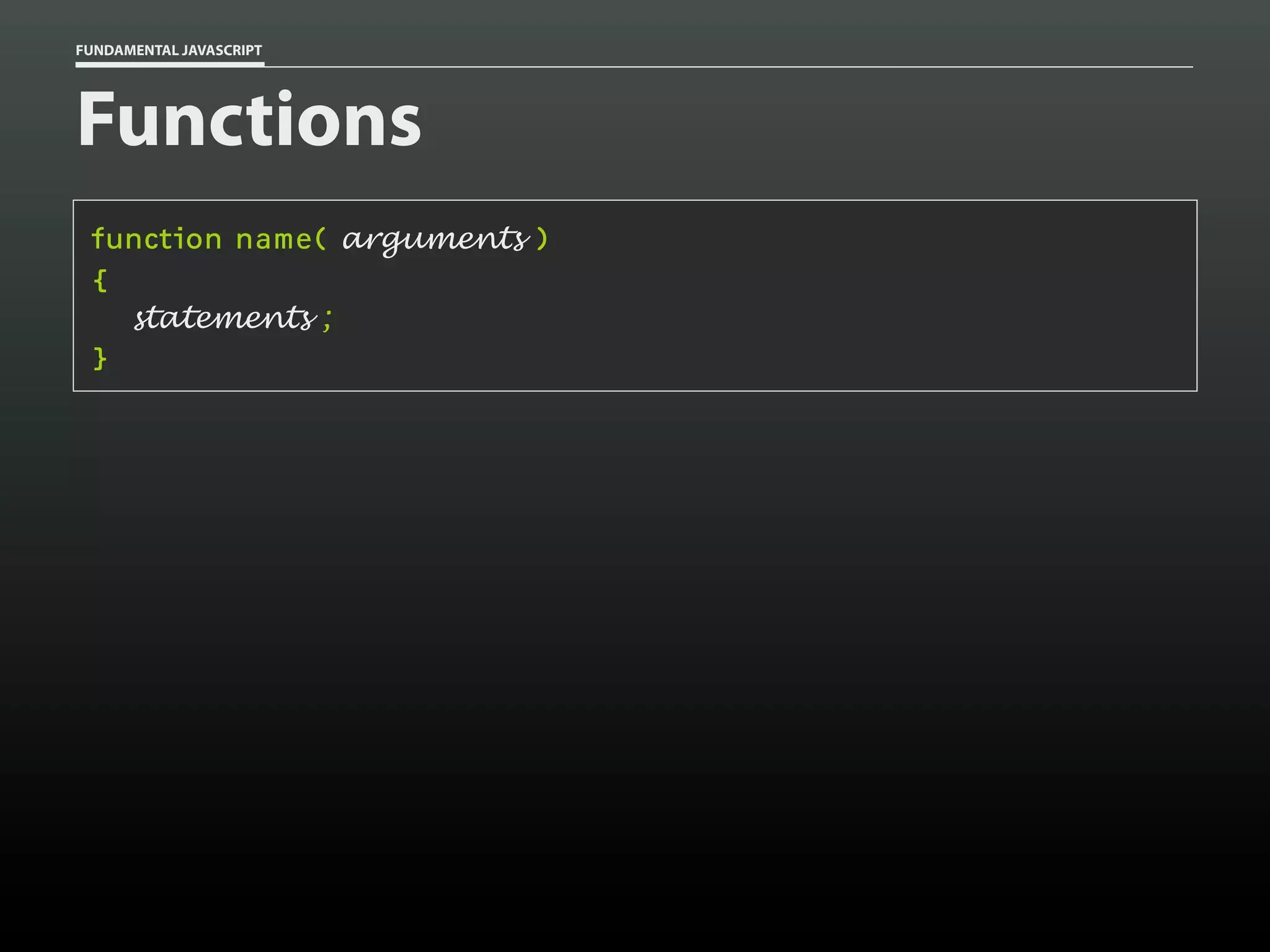
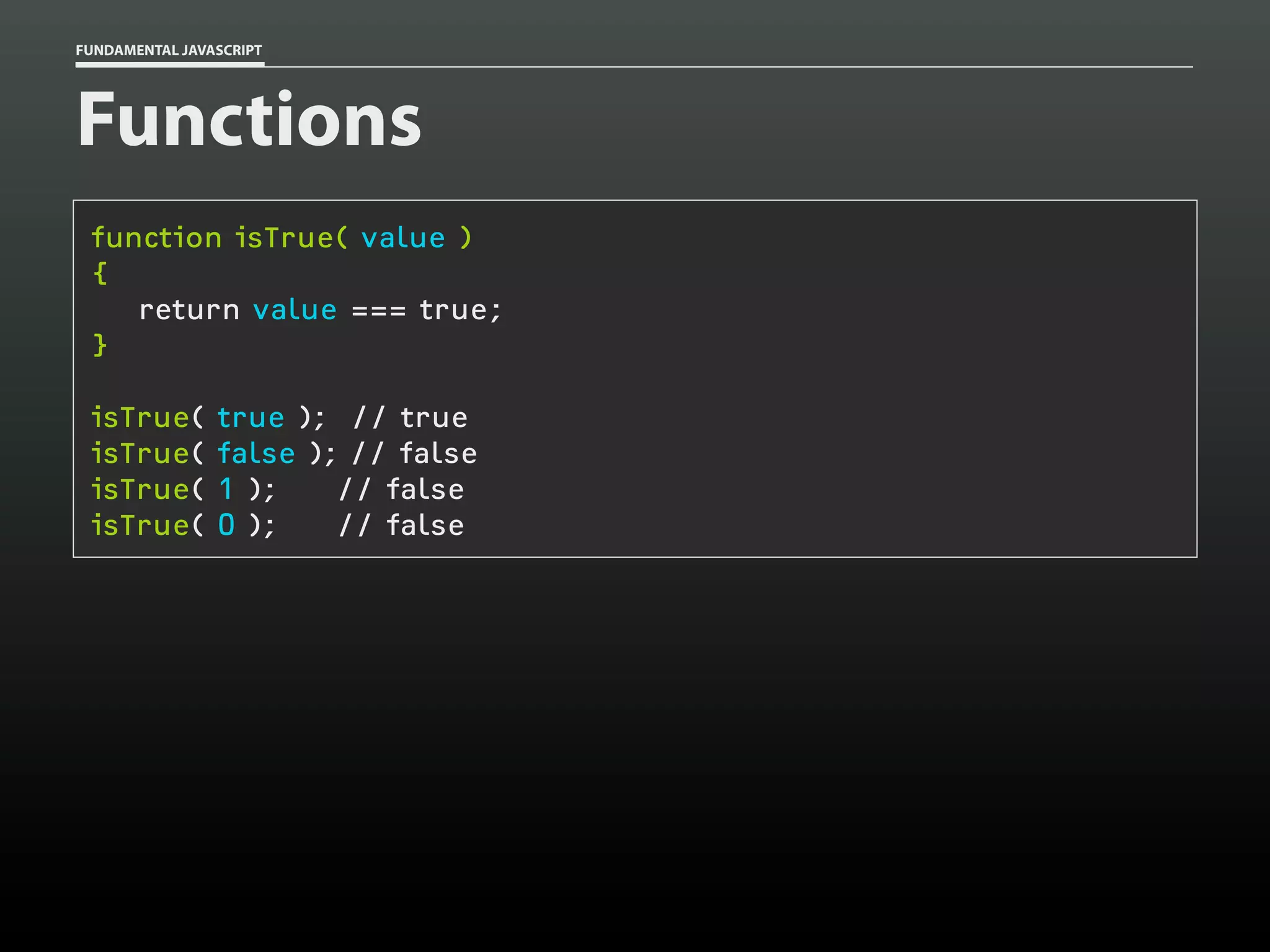
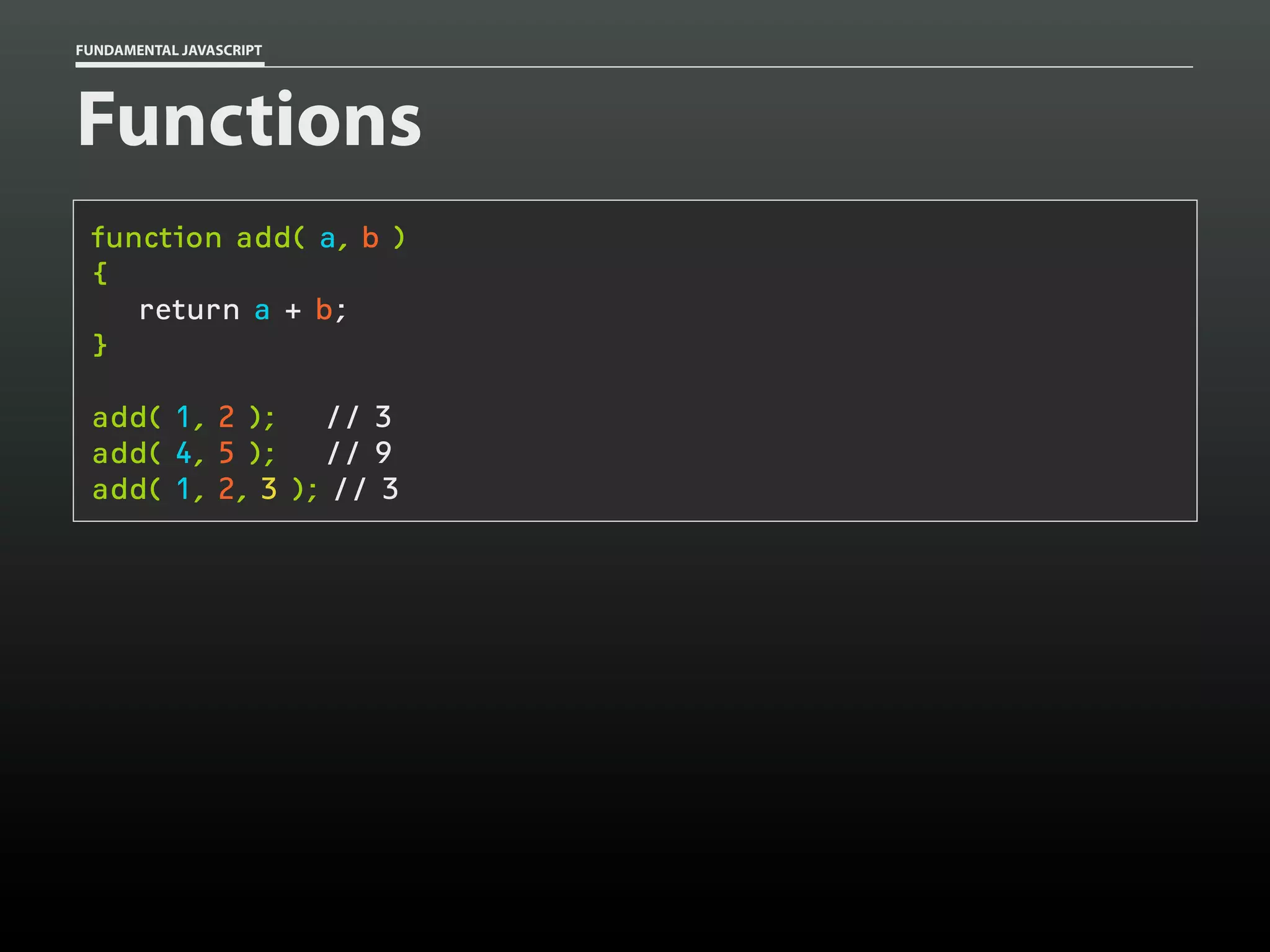
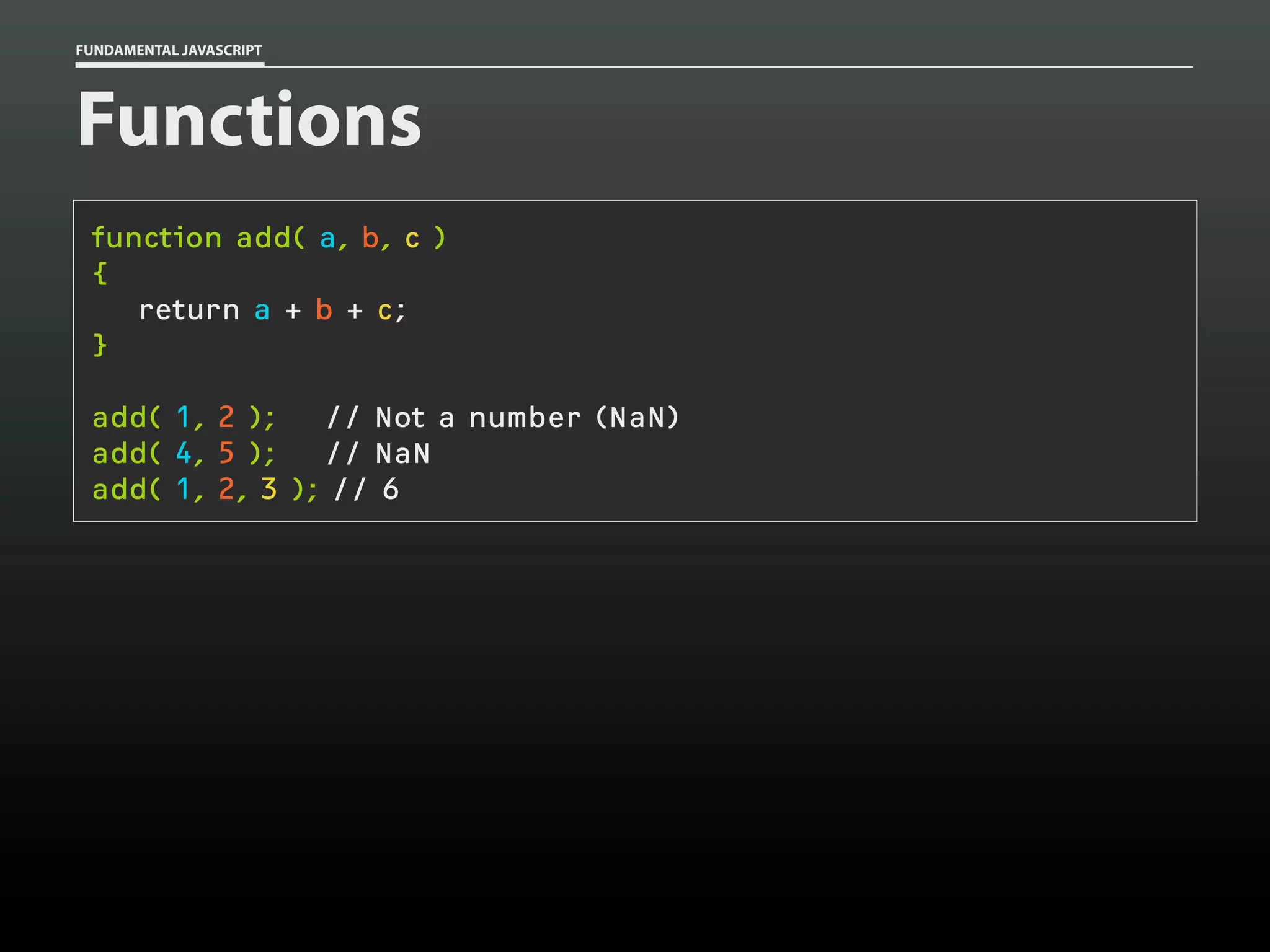
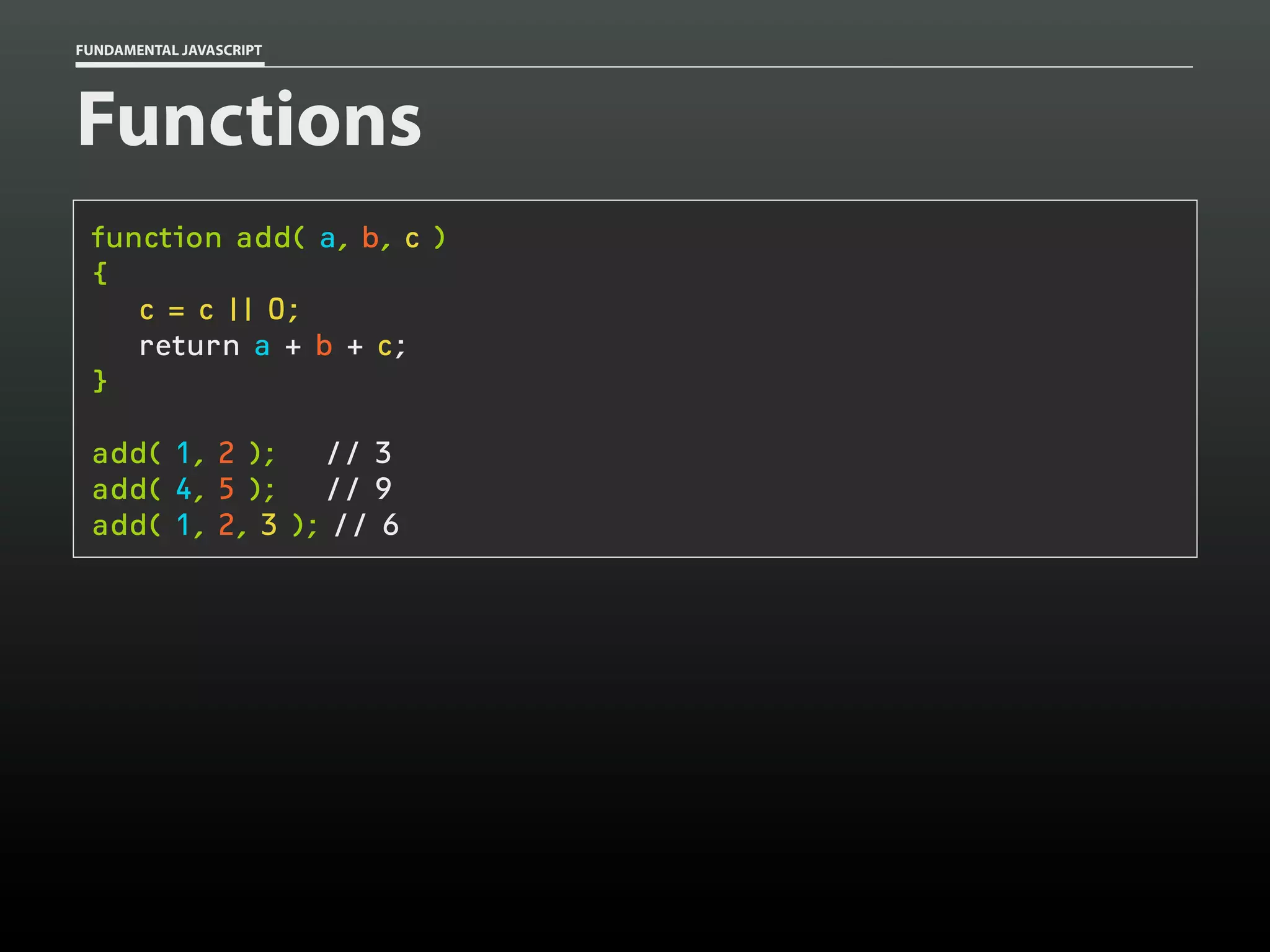
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
Functions
function add()
{
var total = 0,
i = 0;
while ( arguments[i] )
{
total += arguments[i++];
}
return total;
}
add( 1, 2 );
add( 1, 2, 3 );
add( 1, 2, 3, 8 );
// 3
// 6
// 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-52-2048.jpg)
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
Functions
function add()
{
var total = 0,
i = 0;
while ( arguments[i] )
{
total += arguments[i++];
}
return total;
}
add(
add(
add(
add(
1,
1,
1,
1,
2 );
2, 3 );
2, 3, 8 );
2, ‘foo’, 8 );
// 3
// 6
// 14
// 3foo8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-53-2048.jpg)
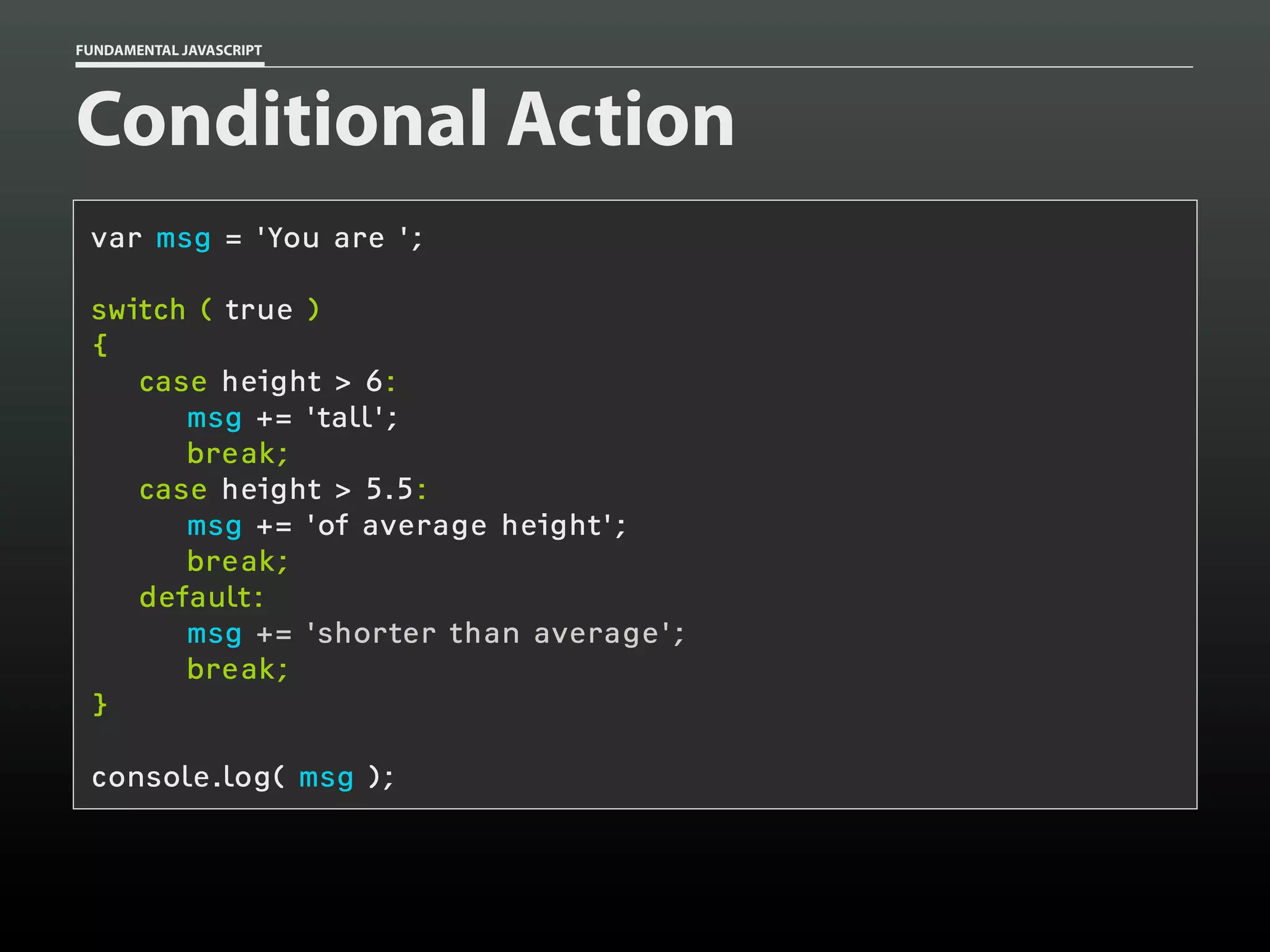
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
Functions
function add()
{
var total = 0,
i = 0;
while ( arguments[i] )
{
if ( typeof arguments[i] == 'number' )
{
total += arguments[i];
}
i++;
}
return total;
}
add(
add(
add(
add(
1,
1,
1,
1,
2 );
2, 3 );
2, 3, 8 );
2, ‘foo’, 8 );
// 3
// 6
// 14
// 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-54-2048.jpg)


![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
Almost everything’s an object
var arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
arr.length;
arr.join( ' ' );
// 5
// '1 2 3 4 5'
arr.pop();
arr;
// 5
// [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
arr.push( 6 );
arr;
// 5 (the new length)
// [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 ]
arr.reverse();
arr;
// [ 6, 4, 3, 2, 1 ]
arr.shift();
arr.unshift( 5 );
arr;
// 6
// 5 (the new length)
// [ 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-71-2048.jpg)


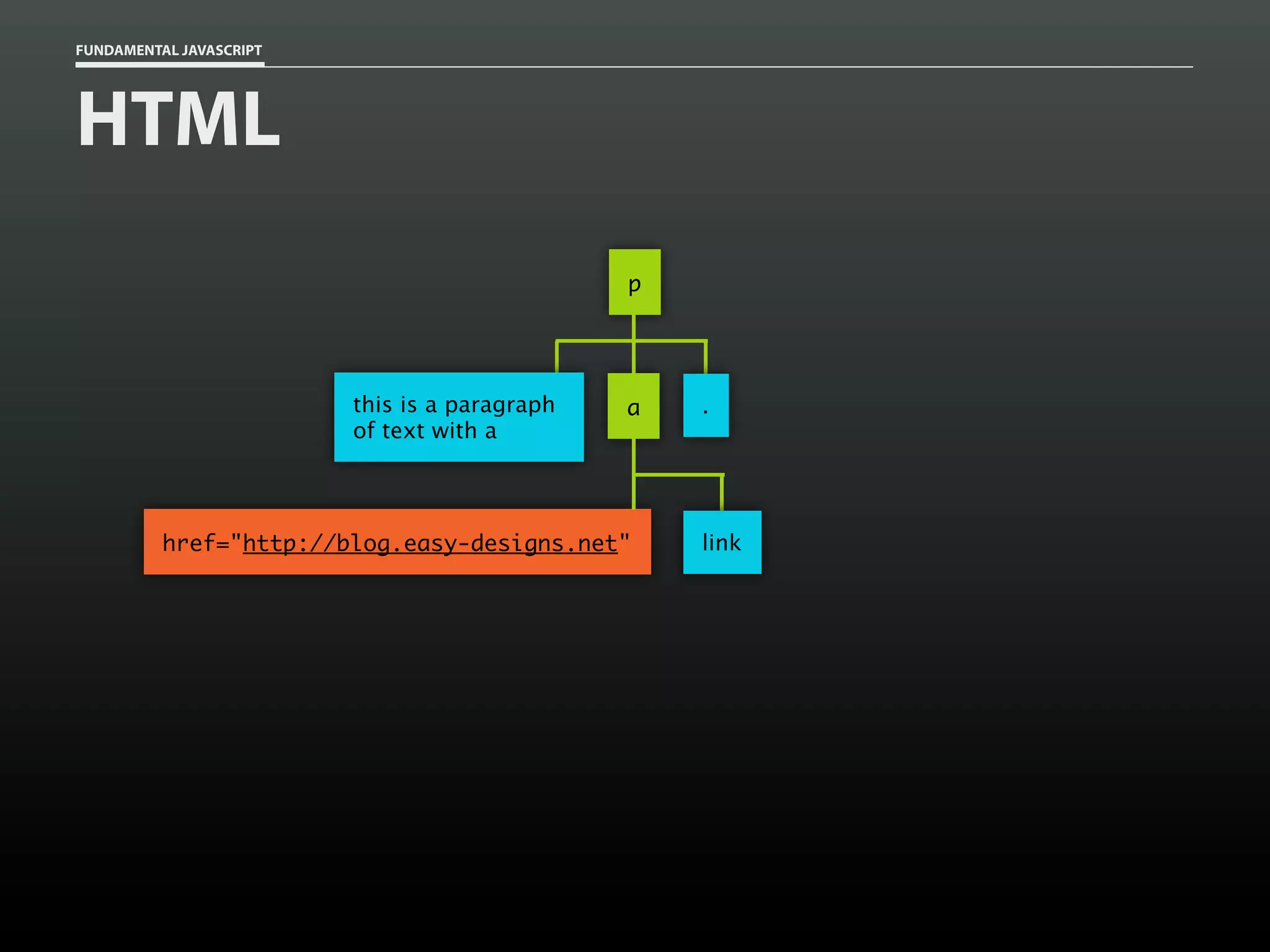

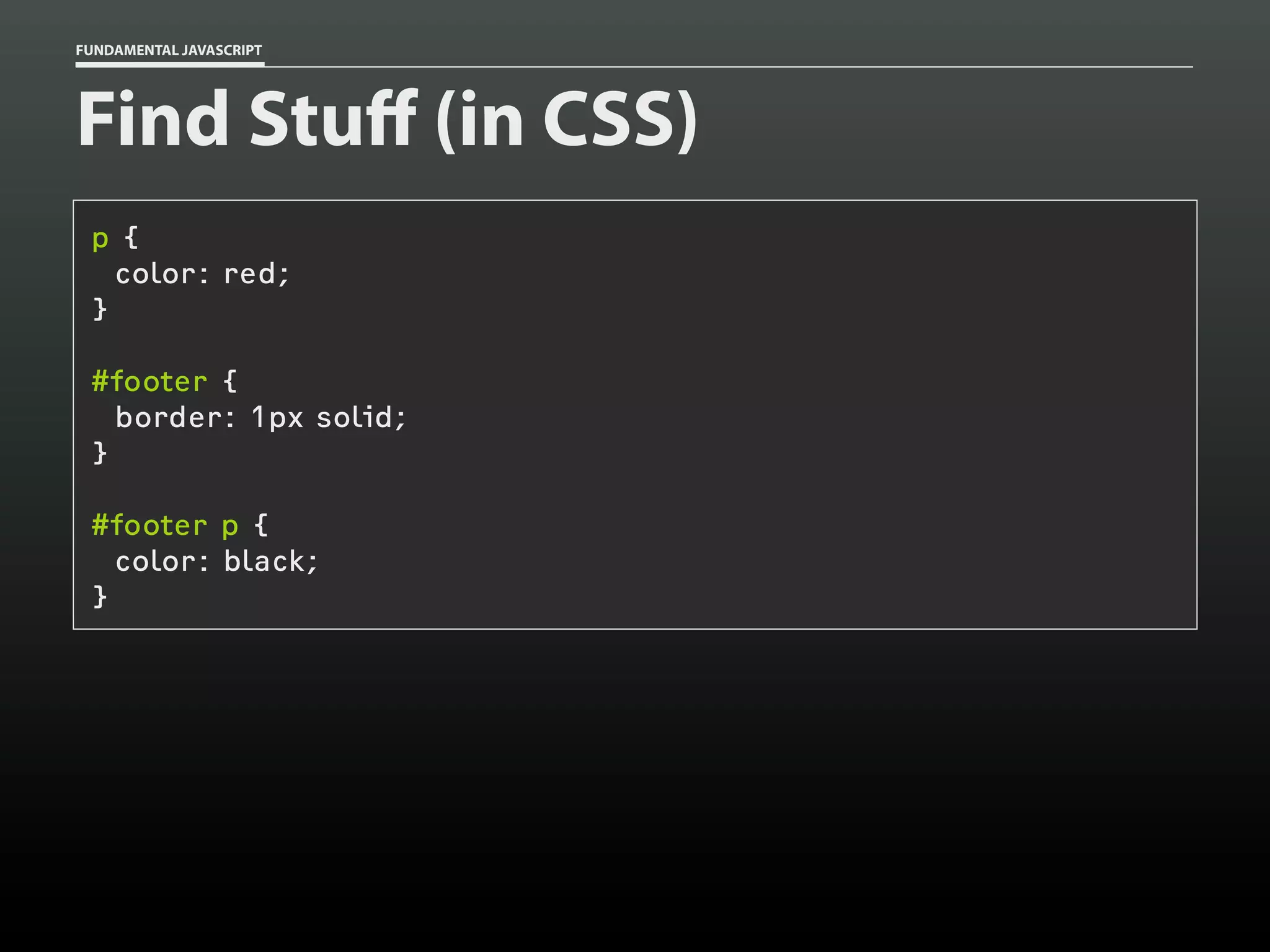
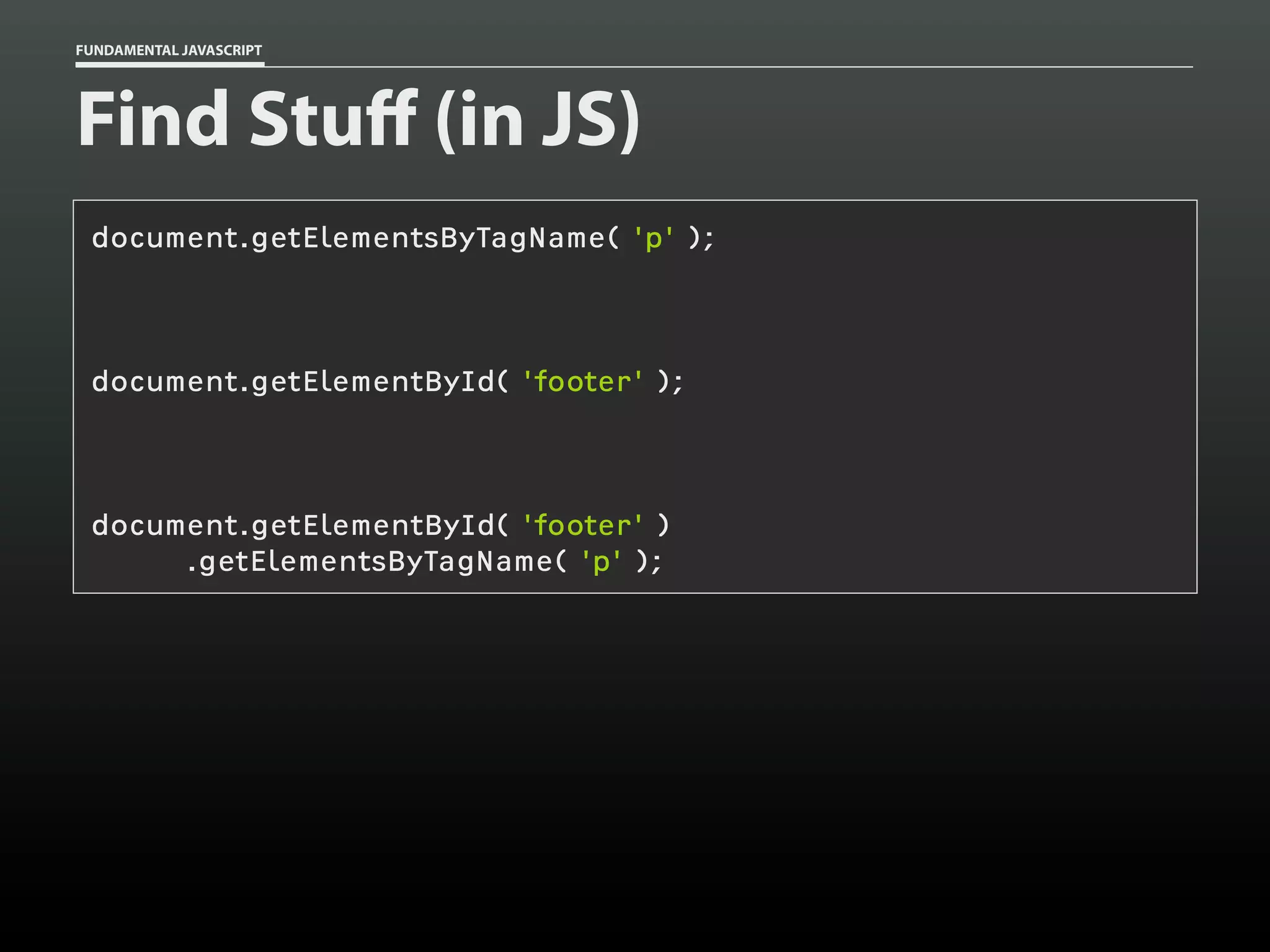
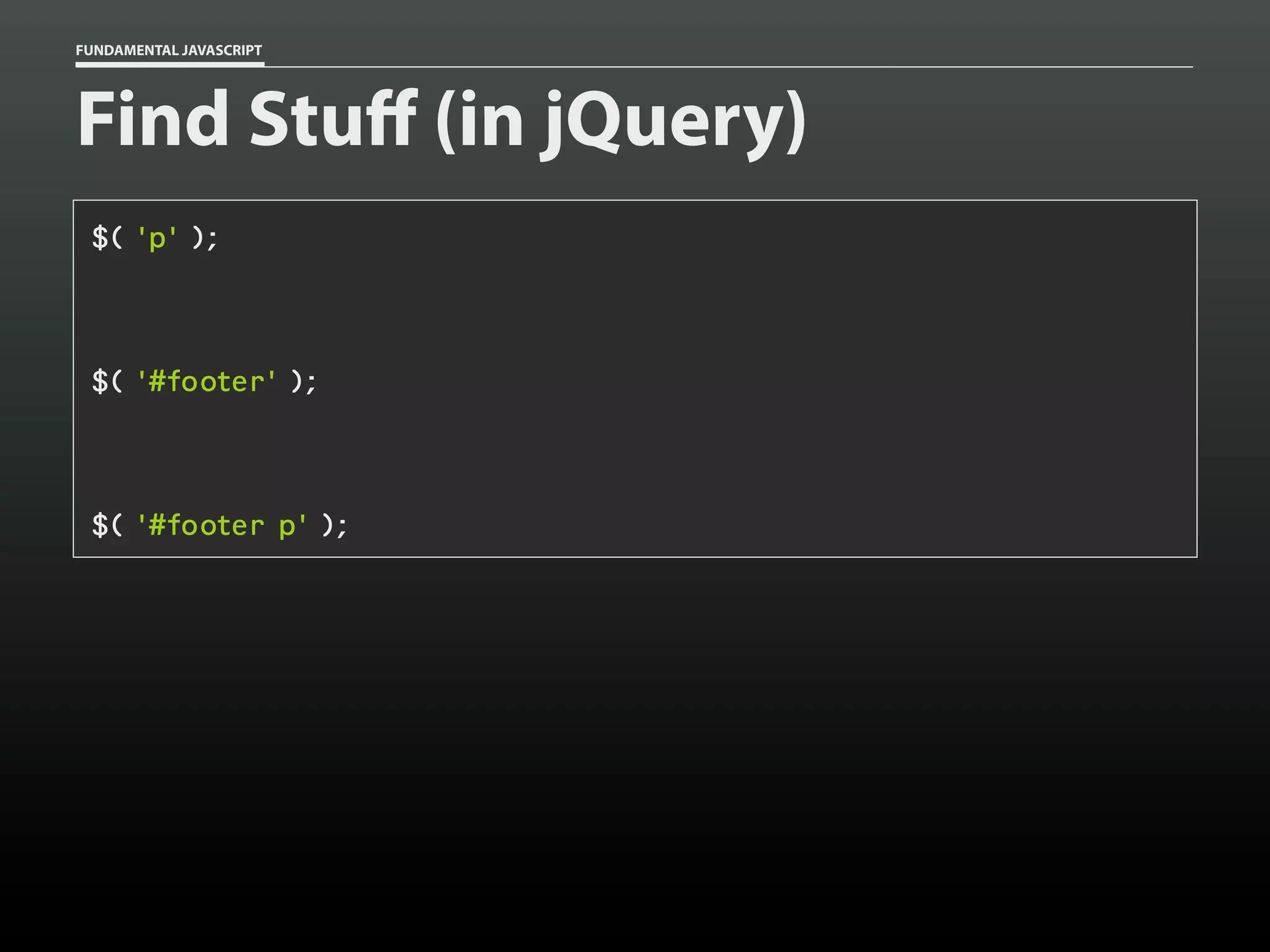
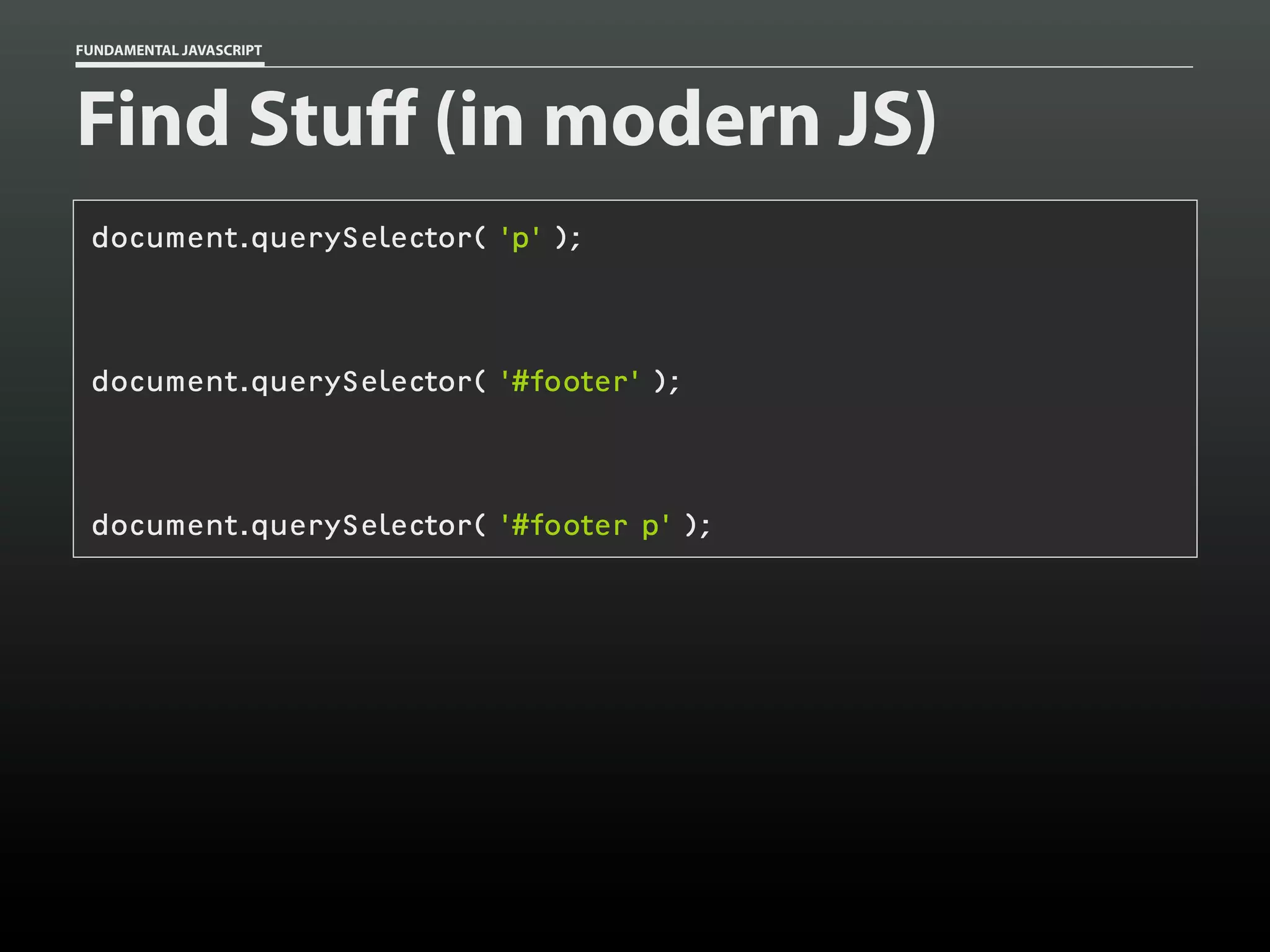


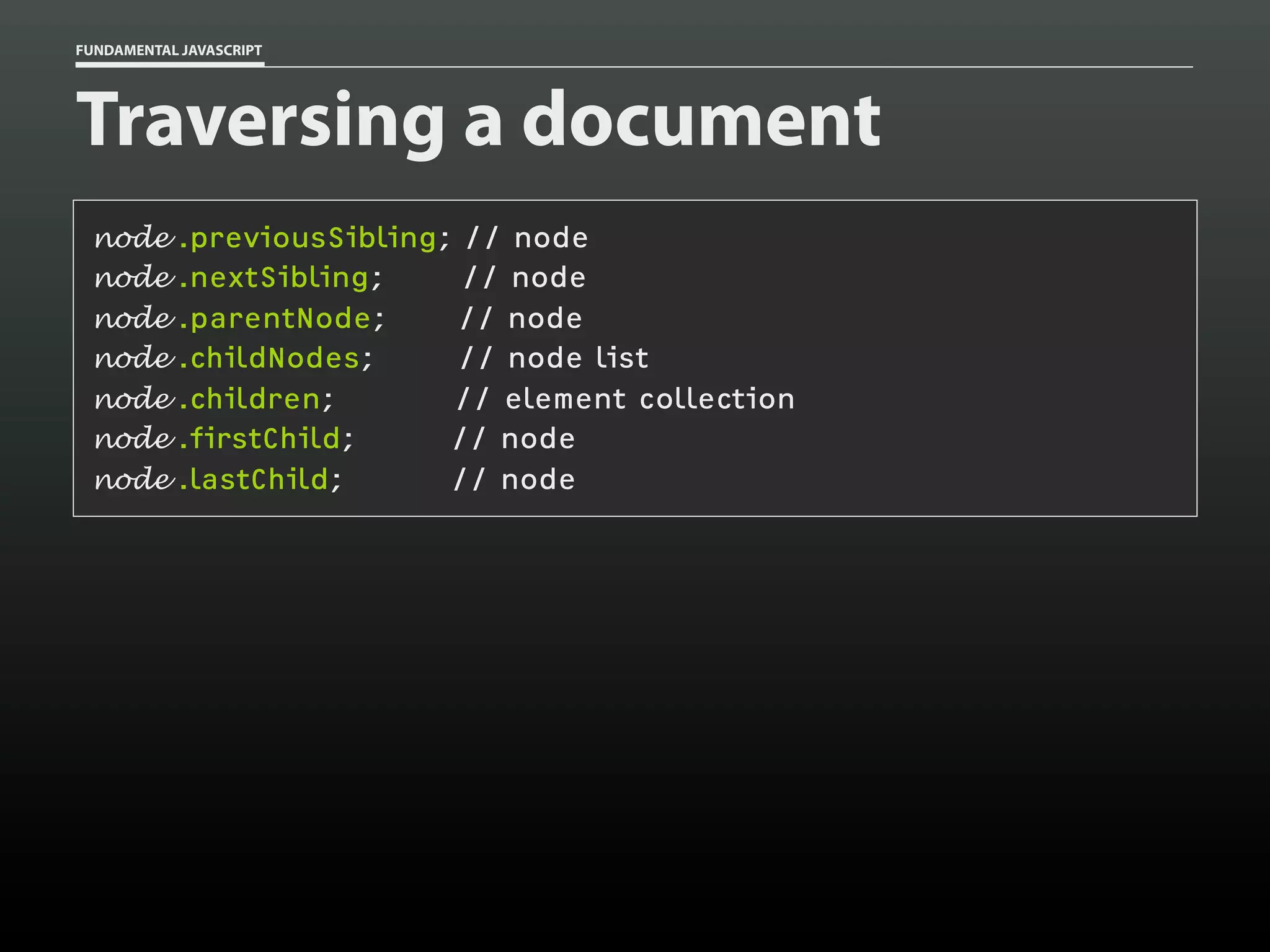
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
Traversing a document
var a = document.getElementsByTagName( 'a' ),
a_len = a.length,
i,
title;
for ( i=0; i < a_len; i++ )
{
title = a[i].getAttribute( 'title' );
if ( title )
{
console.log( title );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-85-2048.jpg)
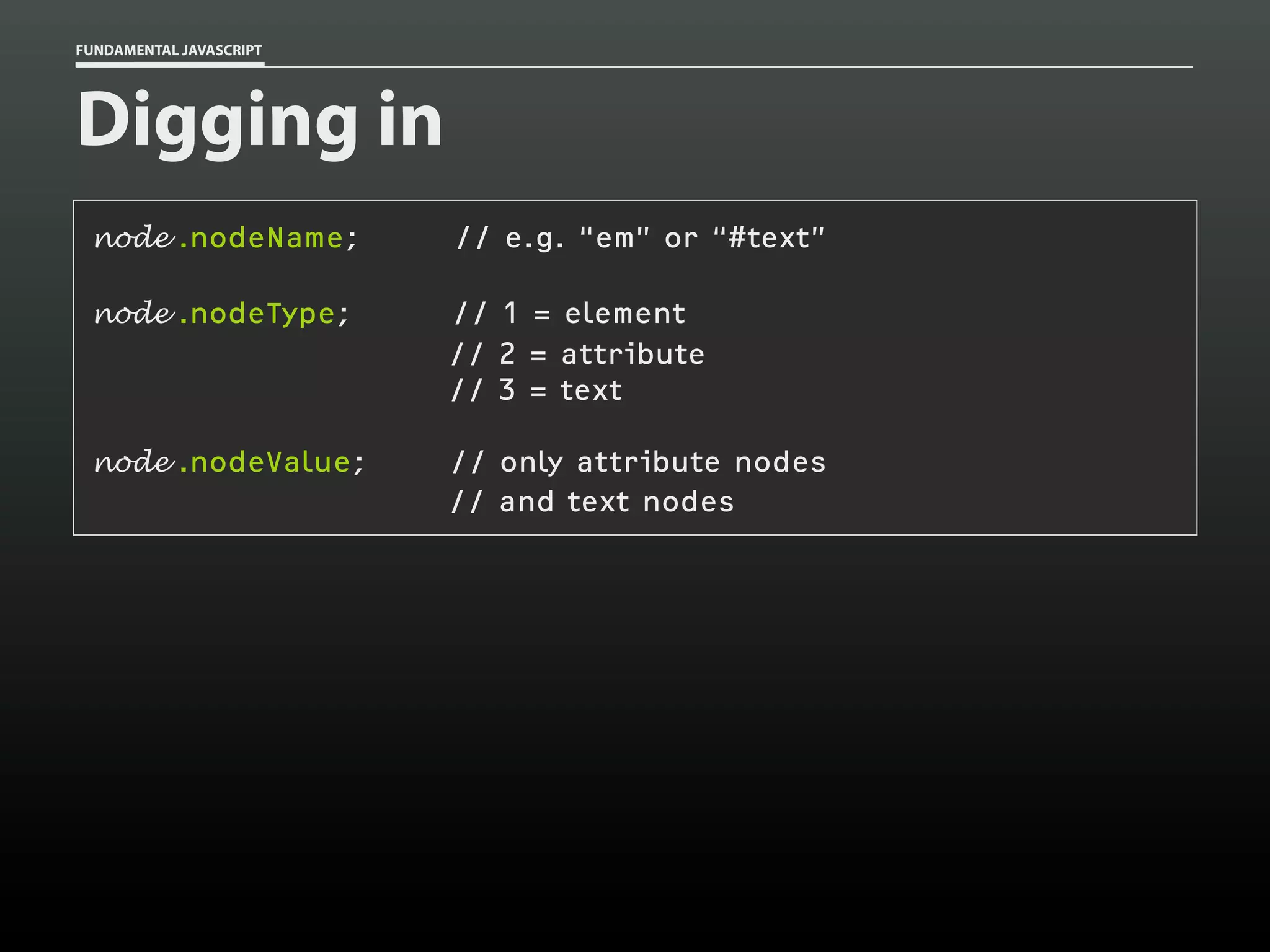

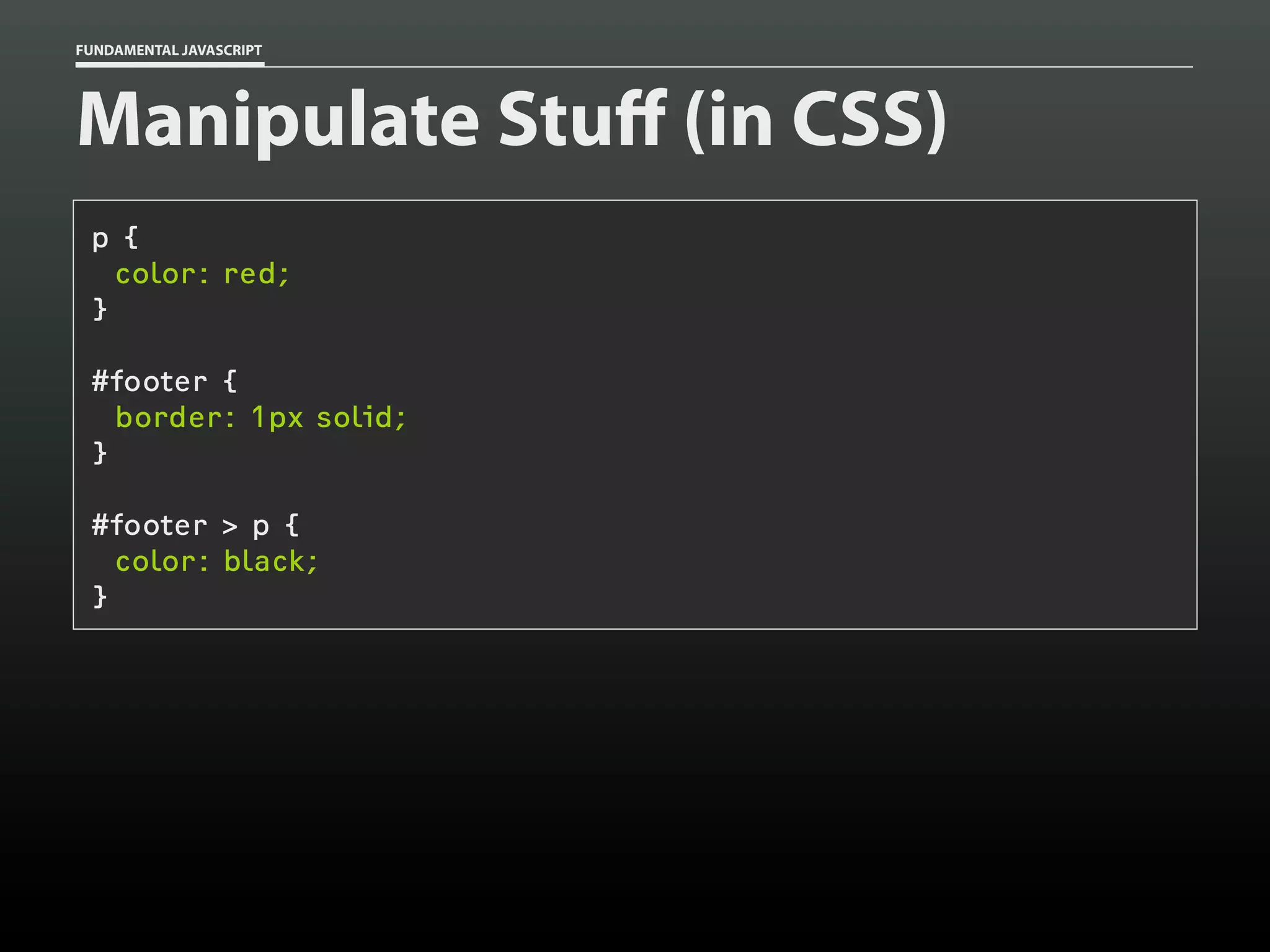
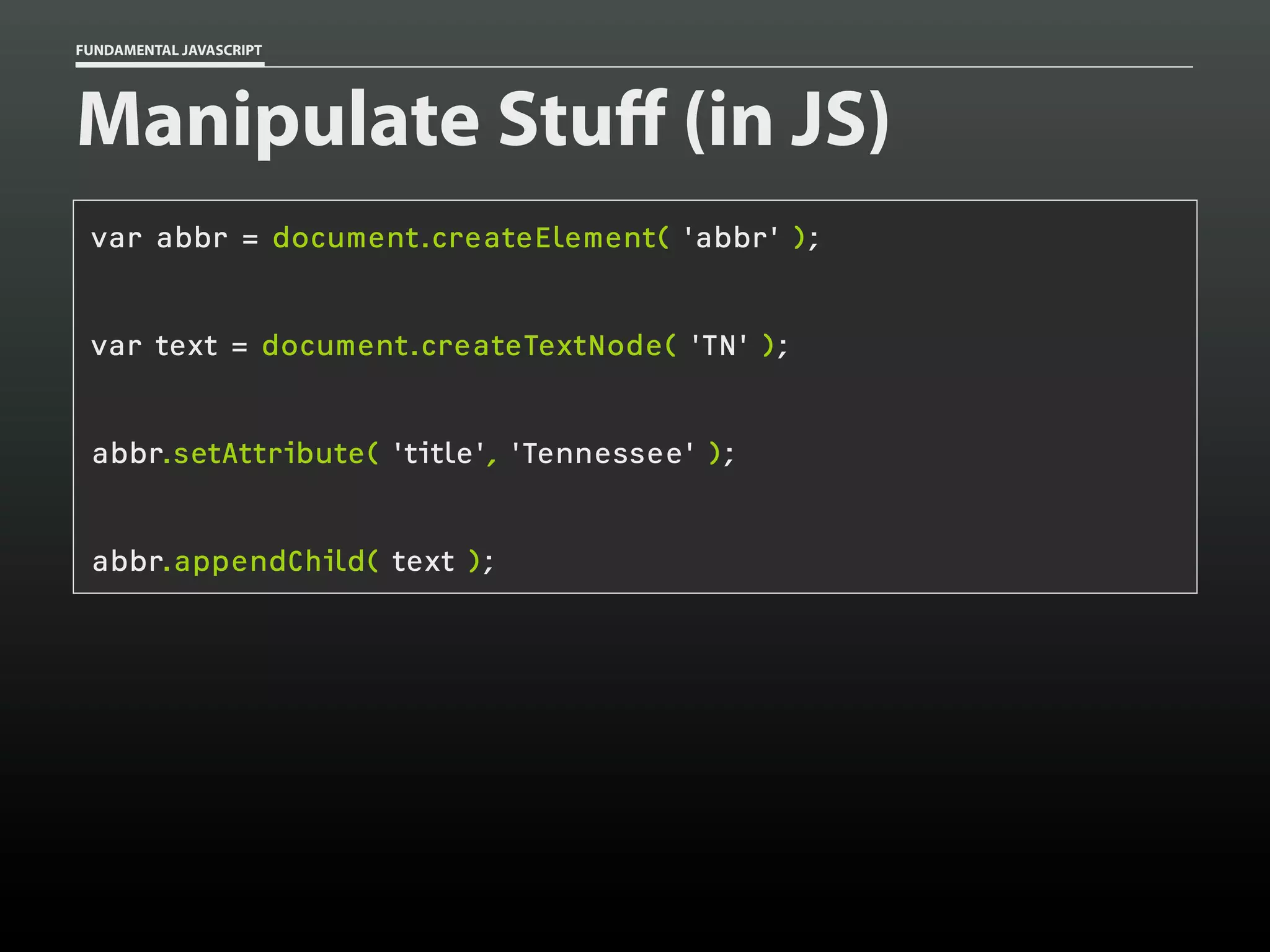
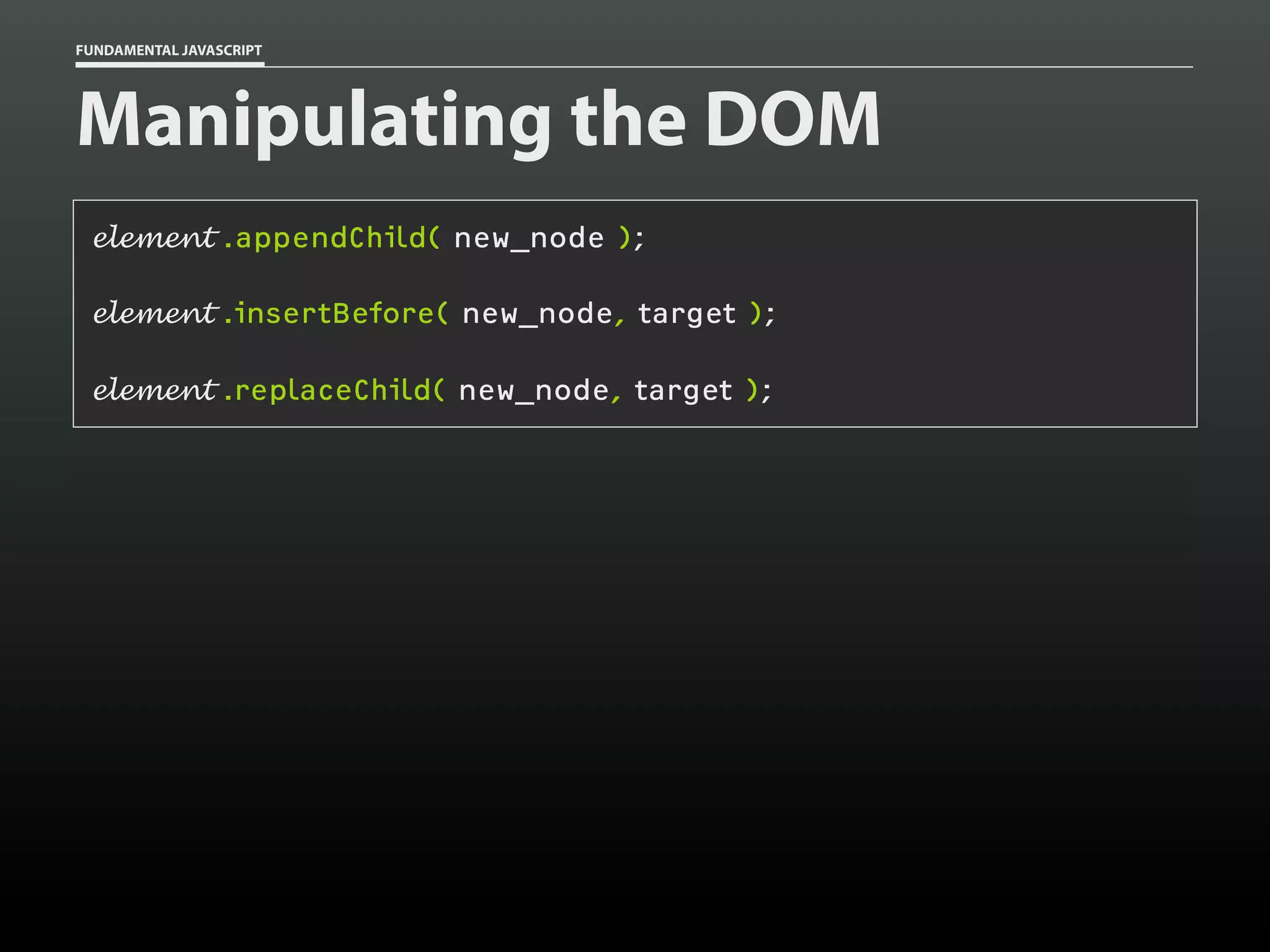
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
Manipulating elements
var p = document.getElementsByTagName( 'p' )[0],
// collect
abbr = document.createElement( 'abbr' ),
text = document.createTextNode( 'TN' );
// generate
abbr.setAttribute( 'title', 'Tennessee' );
abbr.appendChild( text );
p.appendChild( abbr );
// combine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-92-2048.jpg)
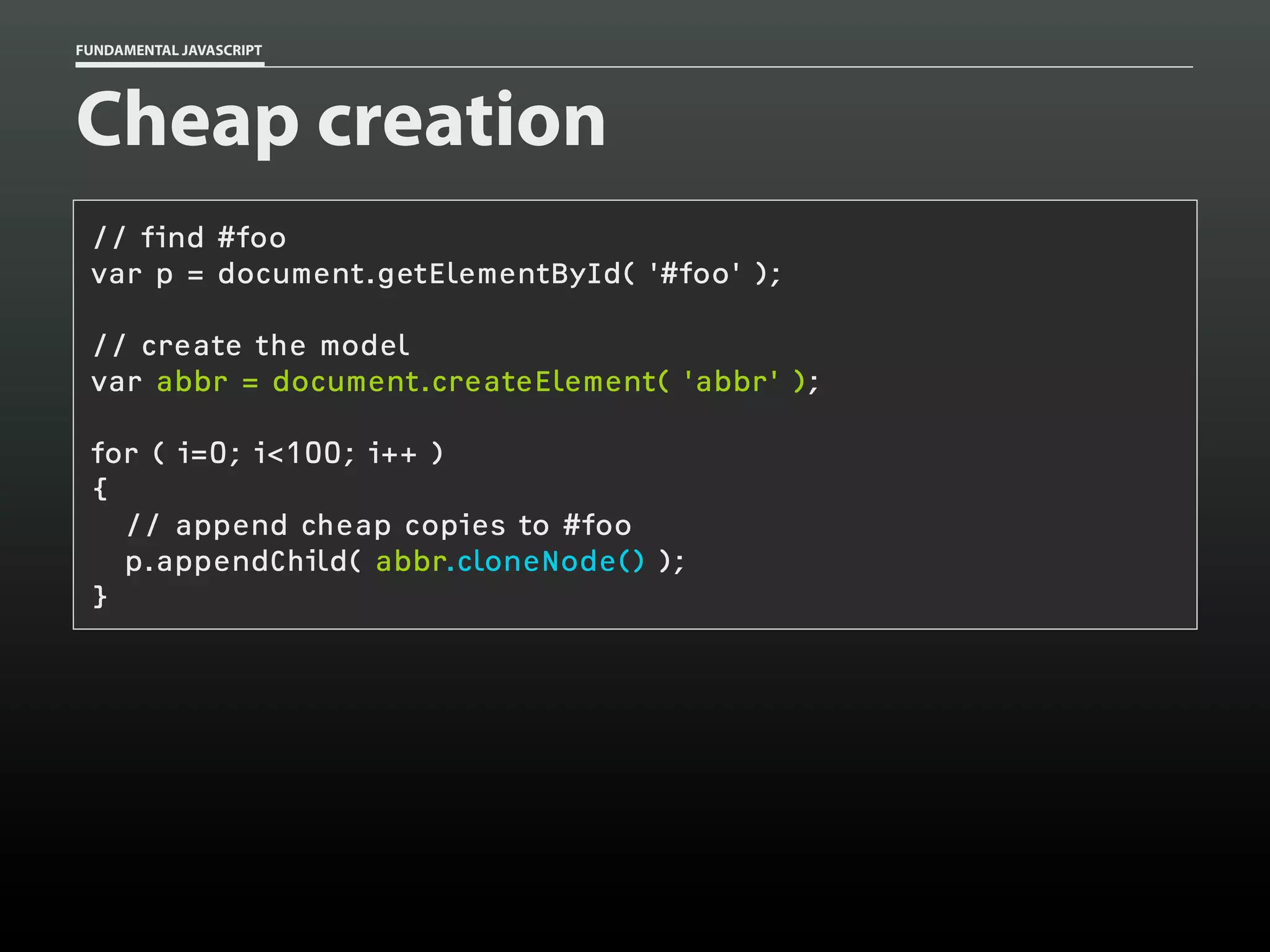
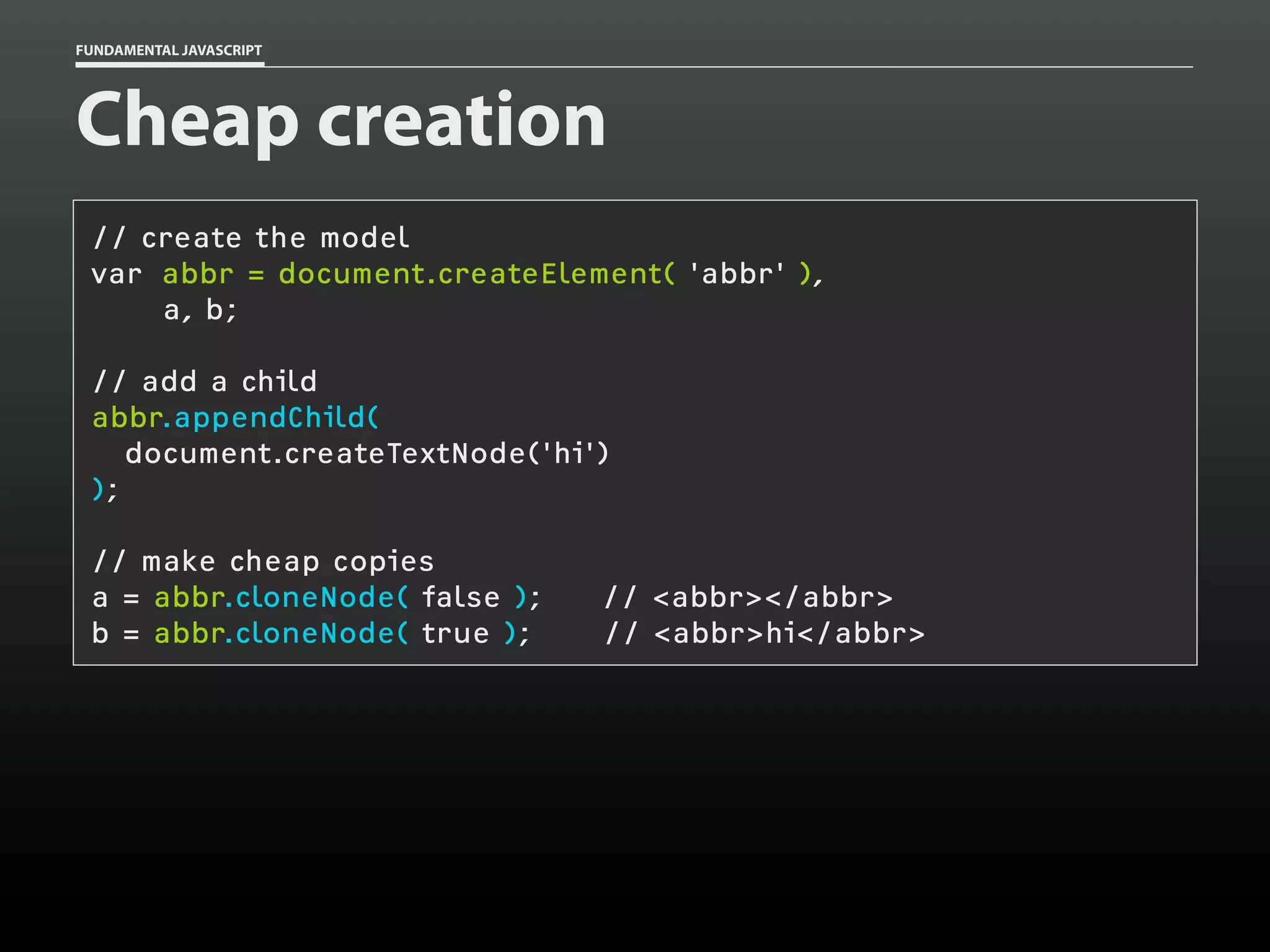
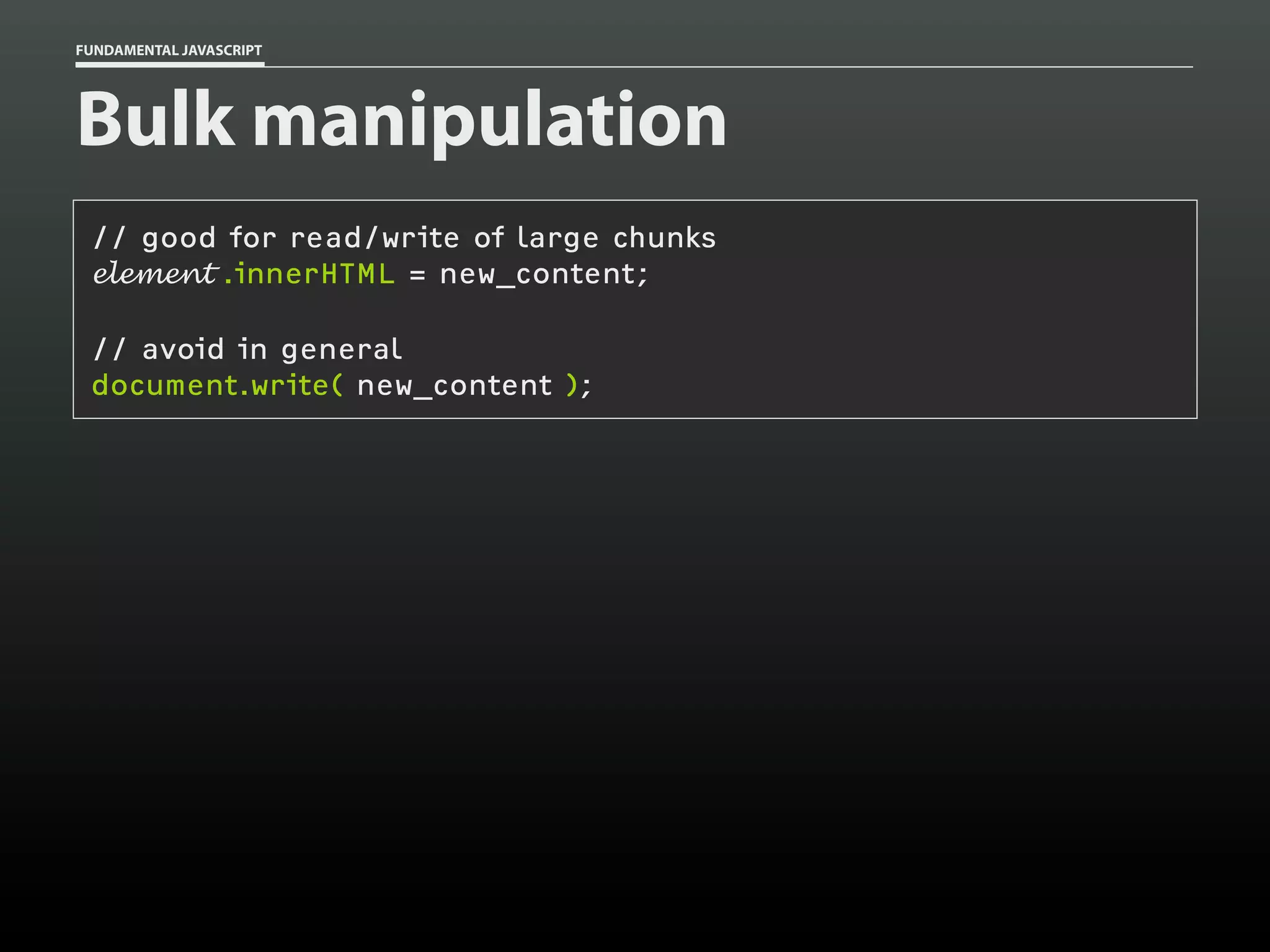


![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
My take
var quotes = document.getElementsByTagName( 'blockquote' );
for ( var i=0; i < quotes.length; i++ )
{
var source = quotes[i].getAttribute( 'cite' );
if ( source )
{
var link = document.createElement( 'a' );
link.setAttribute( 'href', source );
var text = document.createTextNode( 'source' );
link.appendChild( text );
quotes[i].appendChild( link );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-100-2048.jpg)

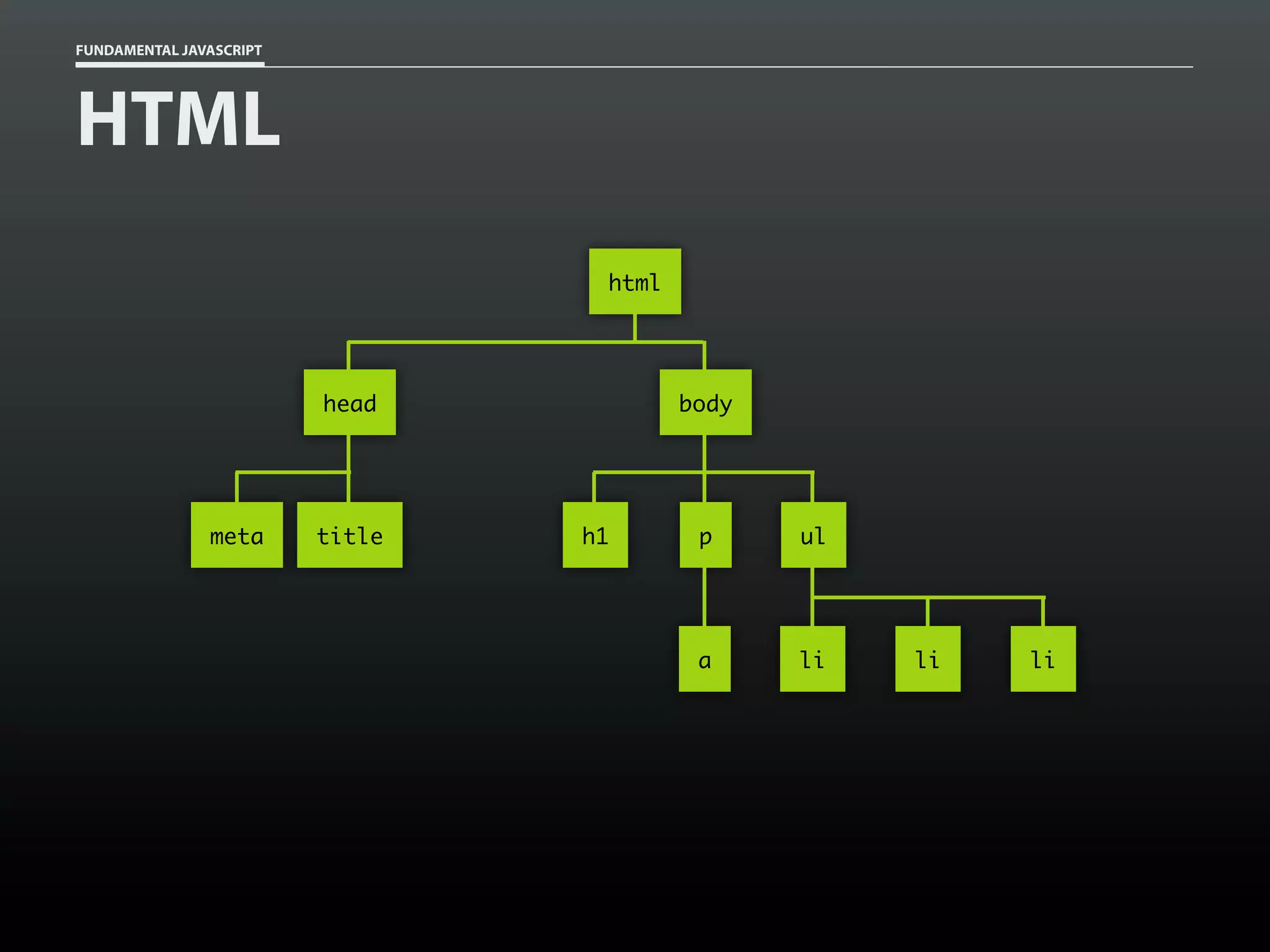
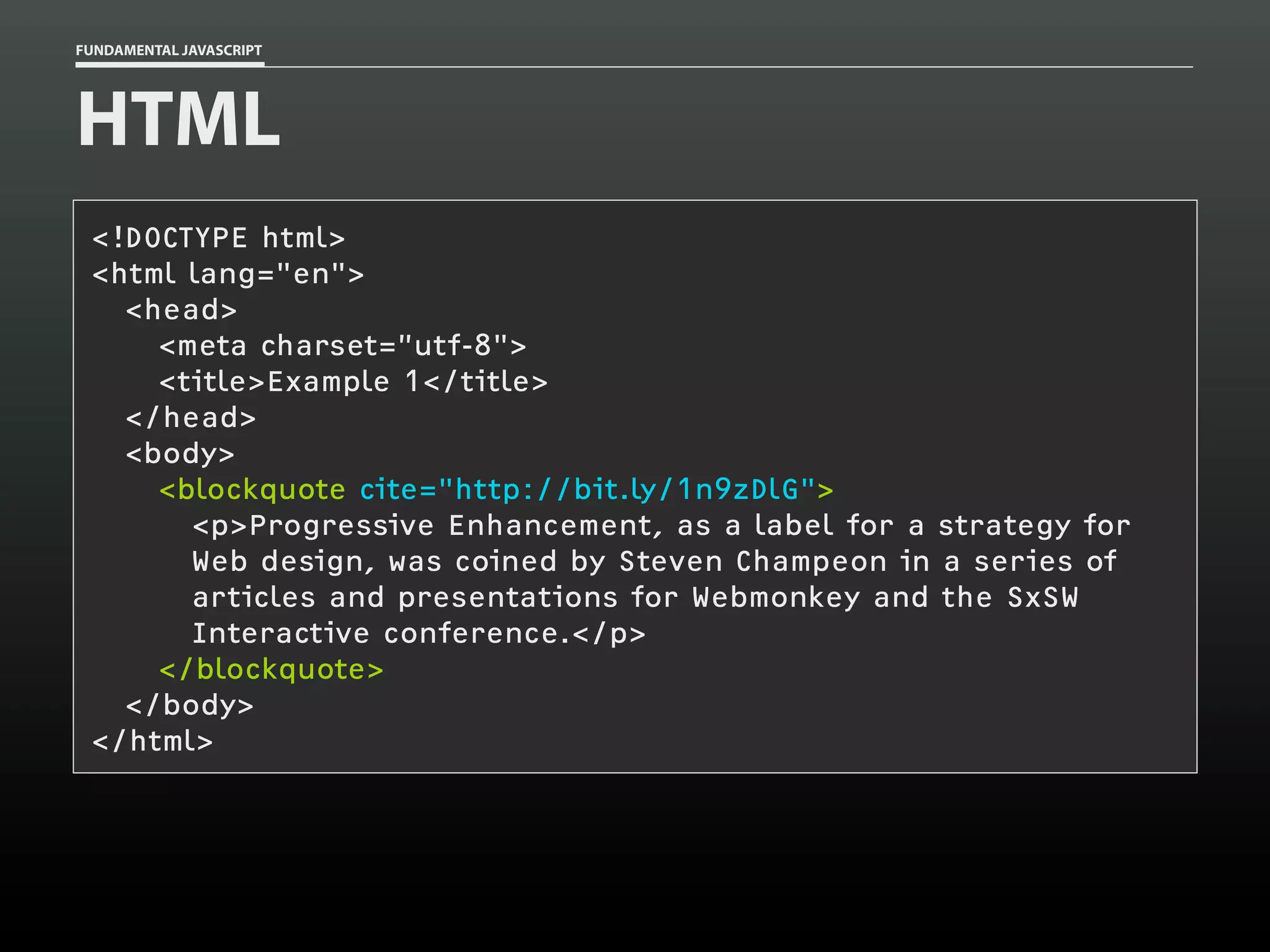
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset=”utf-8">
<title>Example 2</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a <em>test</em> of a simple email obfuscation
technique. It relies on an obfuscated email address placed in
an emphasis element (<code>em</code>) and replaces it with a
<code>mailto:</code> link for the valid email address.</p>
<p>For example, this email address—<em>aaron [at]
easy [dash] designs [dot] net</em>— should be
converted.</p>
</body>
</html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-102-2048.jpg)
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
The plan
1. Find all the em elements in a document
2. Make sure the content passes our obfuscation test (e.g. contains “[at]”)
3. Grab the content and convert bracketed terms to their equivalents to
reveal the email address (e.g. “[at]” to “@”)
4. Create a new anchor
5. Set the content to be the email address
6. Set the mailto: href
7. Replace the em with the anchor
102](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-103-2048.jpg)
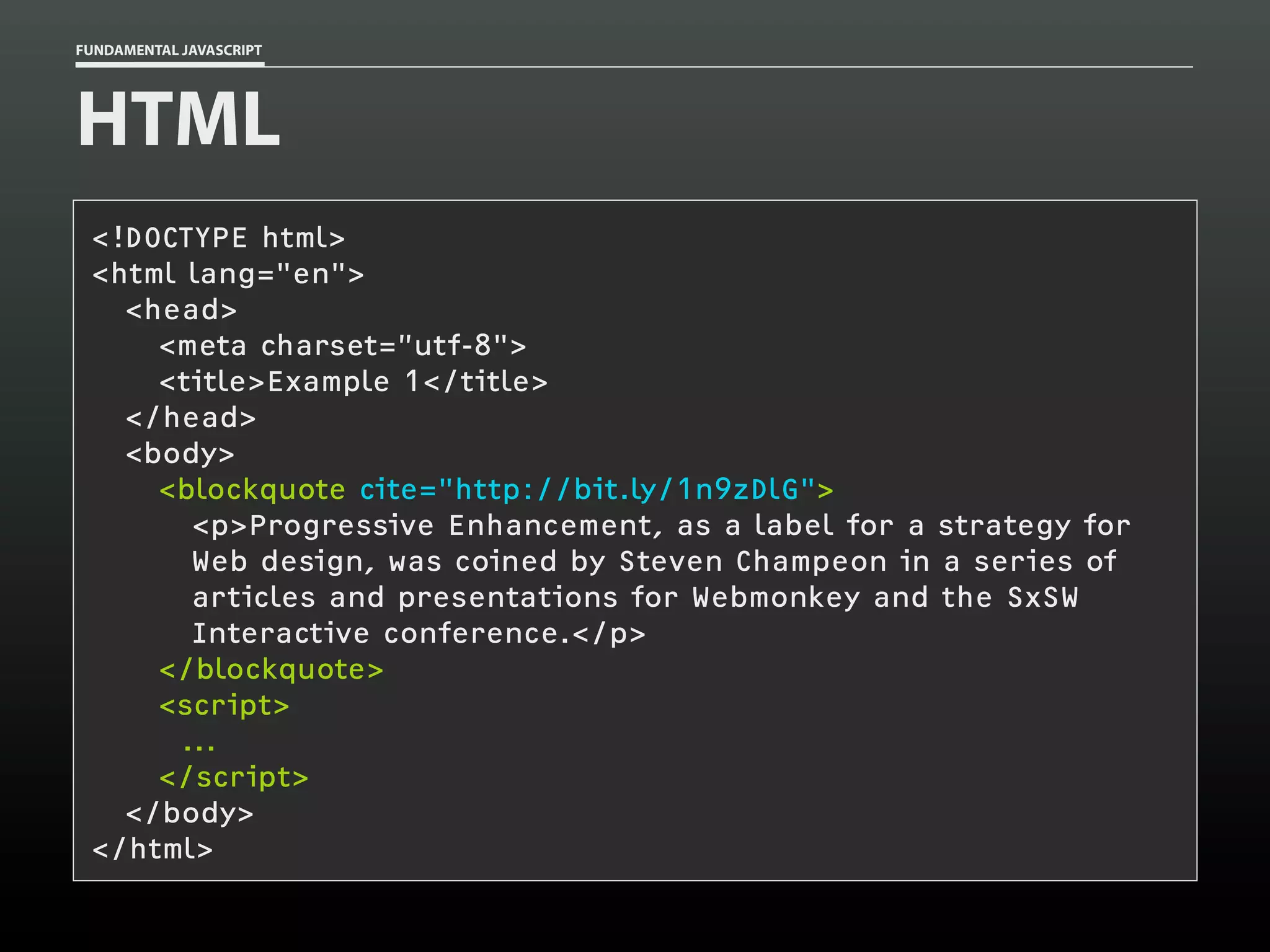
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset=”utf-8">
<title>Example 2</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a <em>test</em> of a simple email obfuscation
technique. It relies on an obfuscated email address placed in
an emphasis element (<code>em</code>) and replaces it with a
<code>mailto:</code> link for the valid email address.</p>
<p>For example, this email address—<em>aaron [at]
easy [dash] designs [dot] net</em>— should be
converted.</p>
</body>
</html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-104-2048.jpg)
![FUNDAMENTAL JAVASCRIPT
My take
var ems = document.getElementsByTagName('em'),
i = ems.length, str, a;
while ( i-- )
{
if ( ems[i].firstChild &&
ems[i].firstChild.nodeValue.match( /s*[at]s*/g ) )
{
str = ems[i].firstChild.nodeValue
.replace( /s*[dot]s*/g, '.' )
.replace( /s*[at]s*/g, '@' )
.replace( /s*[dash]s*/g, '-' );
a = document.createElement( 'a' );
a.setAttribute( 'href', 'mailto:' + str );
a.appendChild( document.createTextNode( str ) );
ems[i].parentNode.replaceChild( a, ems[i] );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fundamentaljavascriptutcmarch2014-140305104047-phpapp01/75/Fundamental-JavaScript-UTC-March-2014-105-2048.jpg)