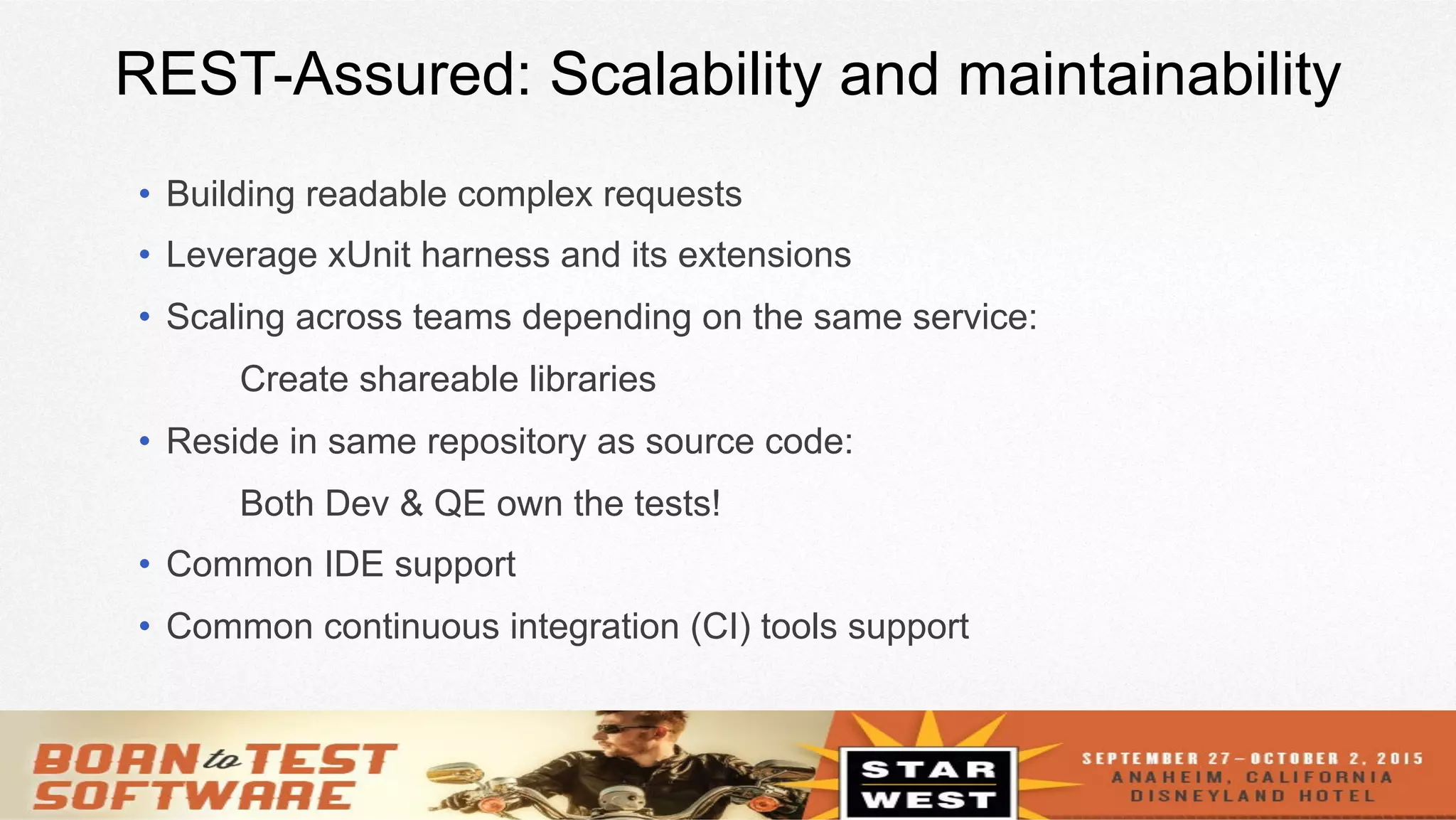
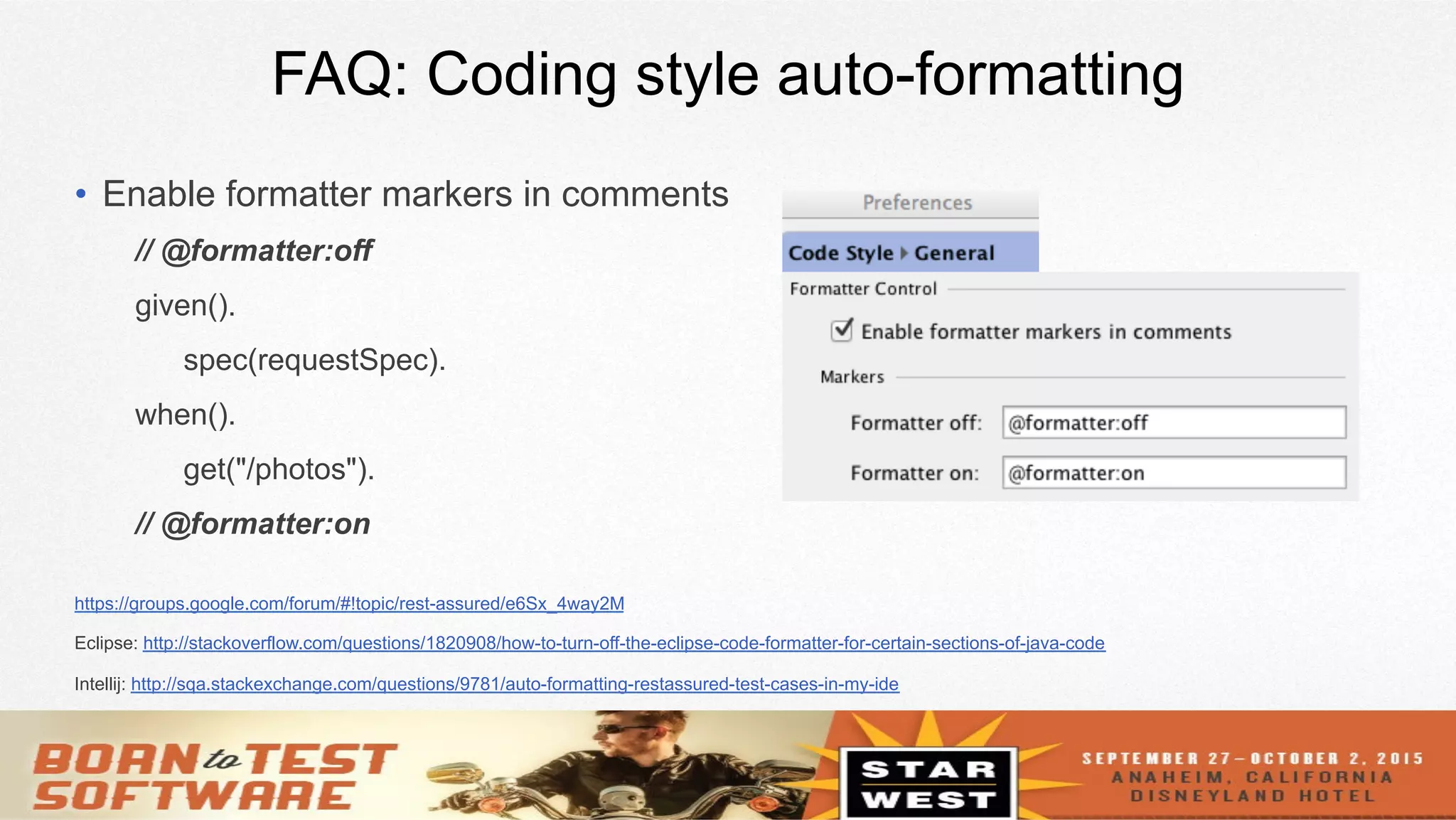
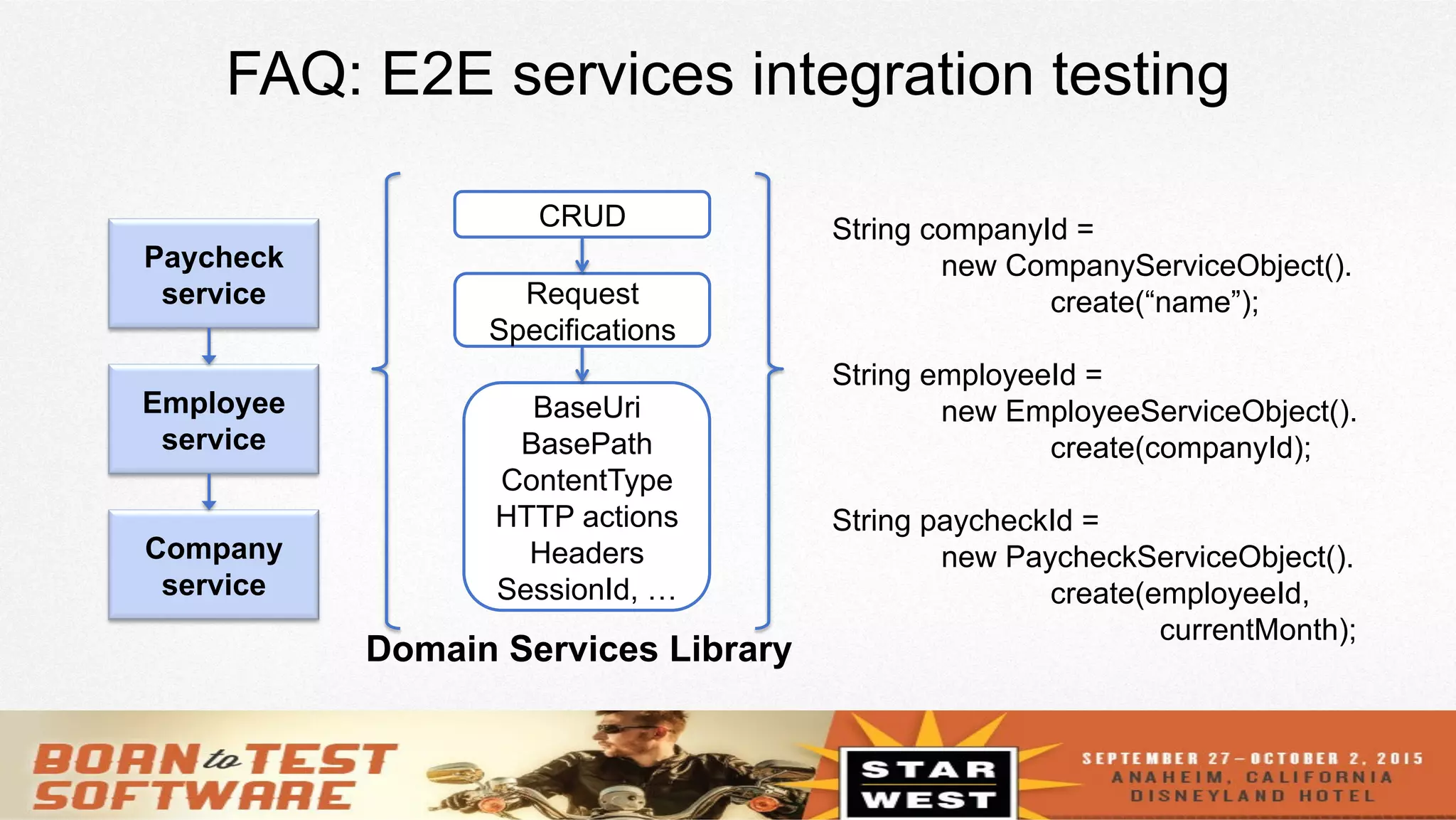
The document provides an overview of using REST-assured for testing REST services, discussing its features such as Java DSL, support for various HTTP methods, and reusability of requests and responses. It includes a session outline, demos, and real examples of how to implement authentication, serialization, and response verification. Additionally, it addresses FAQs regarding SOAP support, asynchronous responses, and coding style for test cases.















![16
REST-Assured: Complex assertions made easy
{
"firstName": ”J”, "lastName": ”D",
”phone": [
{ "type": ”work”,
"number”: "6501234566” },
{ "type": ”work”,
"number”: "6501234567” },
{ "type": "fax”,
"number": "6501234568” }
]
}
1. when().
get("/customers/1").
then().
body("phone.type", hasItems("work", "fax"));
2. List<HashMap> phones = JsonPath.
from(resp).getList("phone", HashMap.class);
3. List<Map> workphones =
from(resp).get("phone.findAll {
phone-> phone.type == "work" }");
4. What about XML?
• Use XmlPath](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/t9-151213233633/75/Automate-REST-Services-Testing-with-RestAssured-16-2048.jpg)