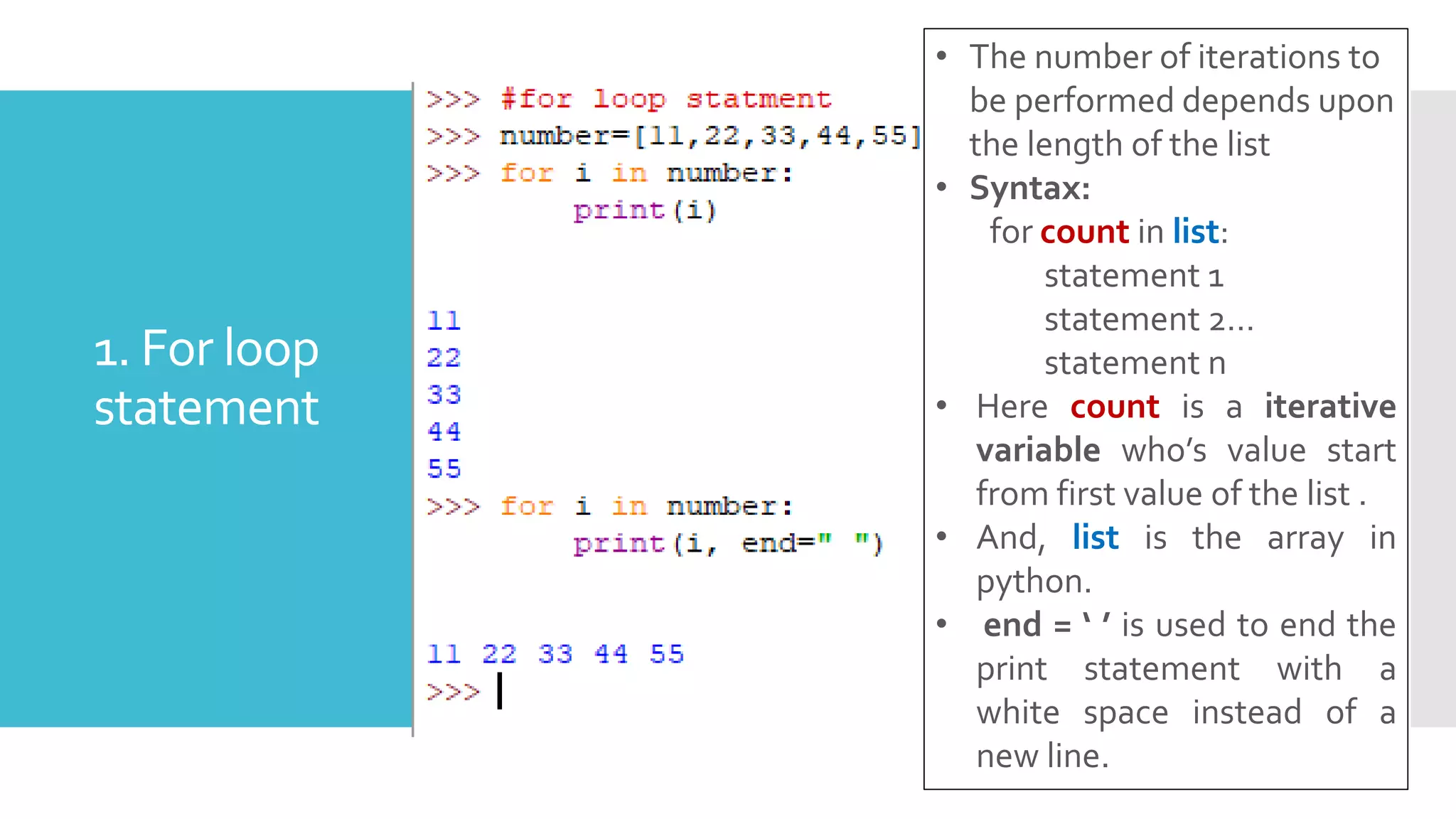
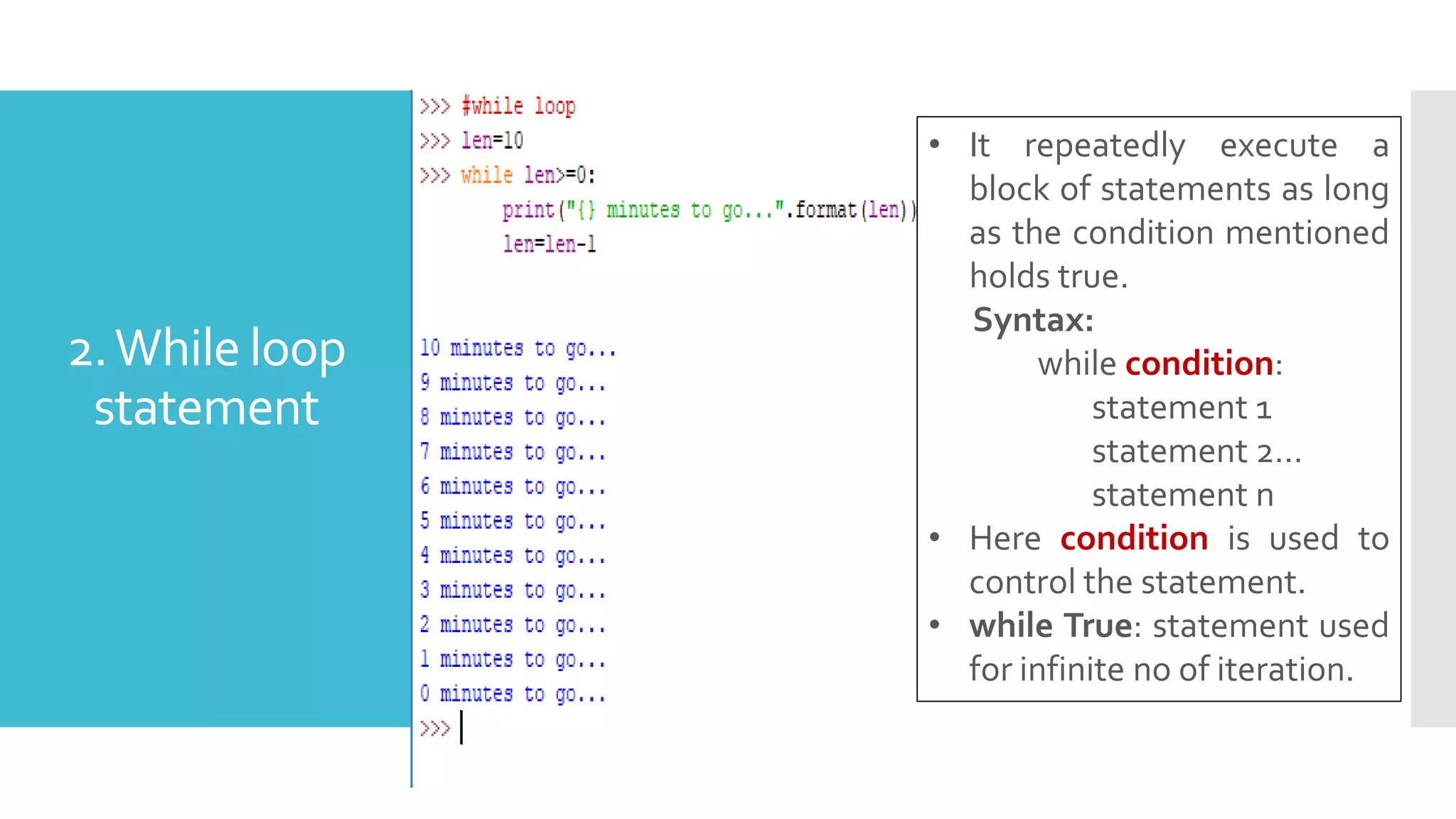
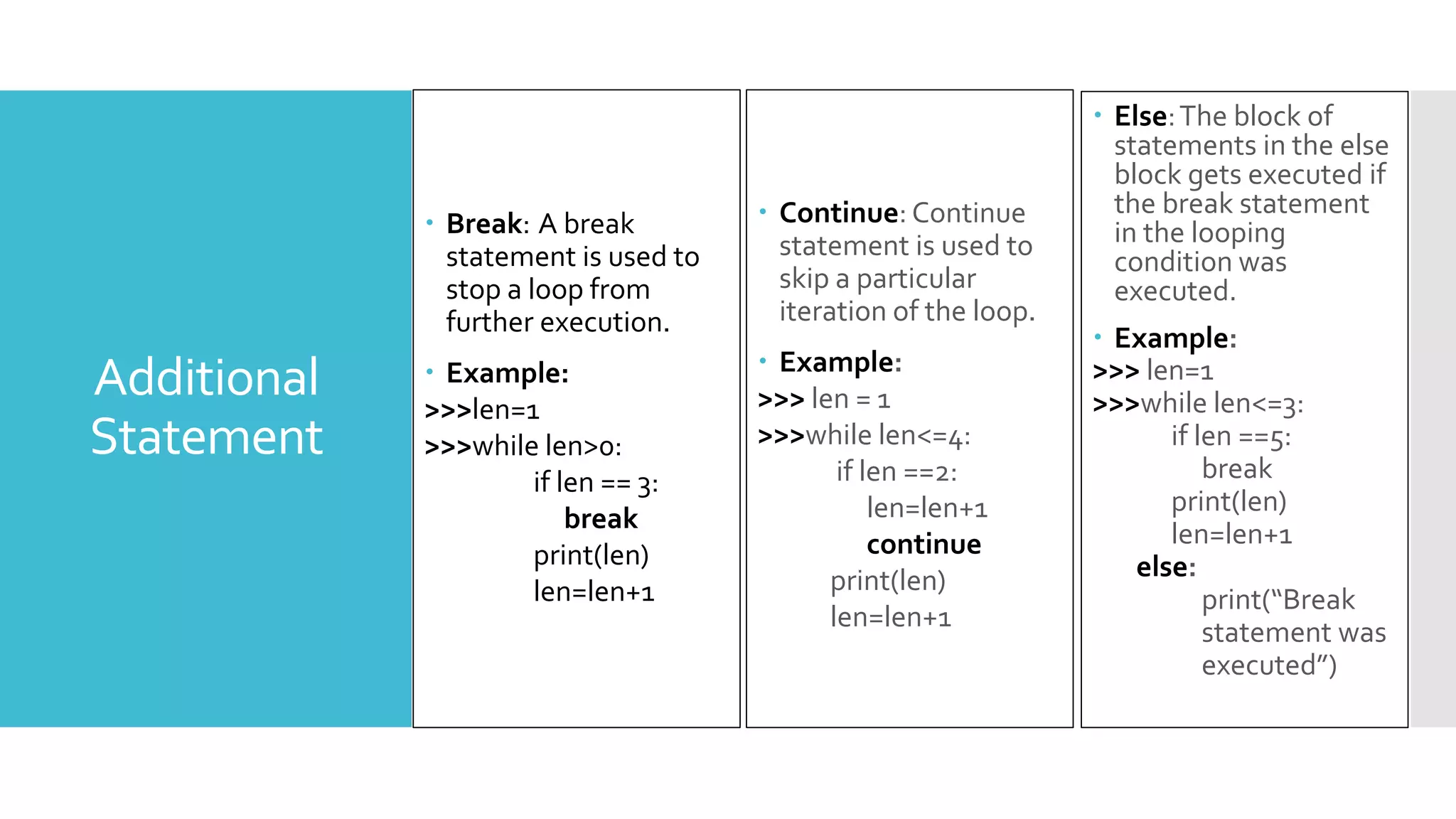
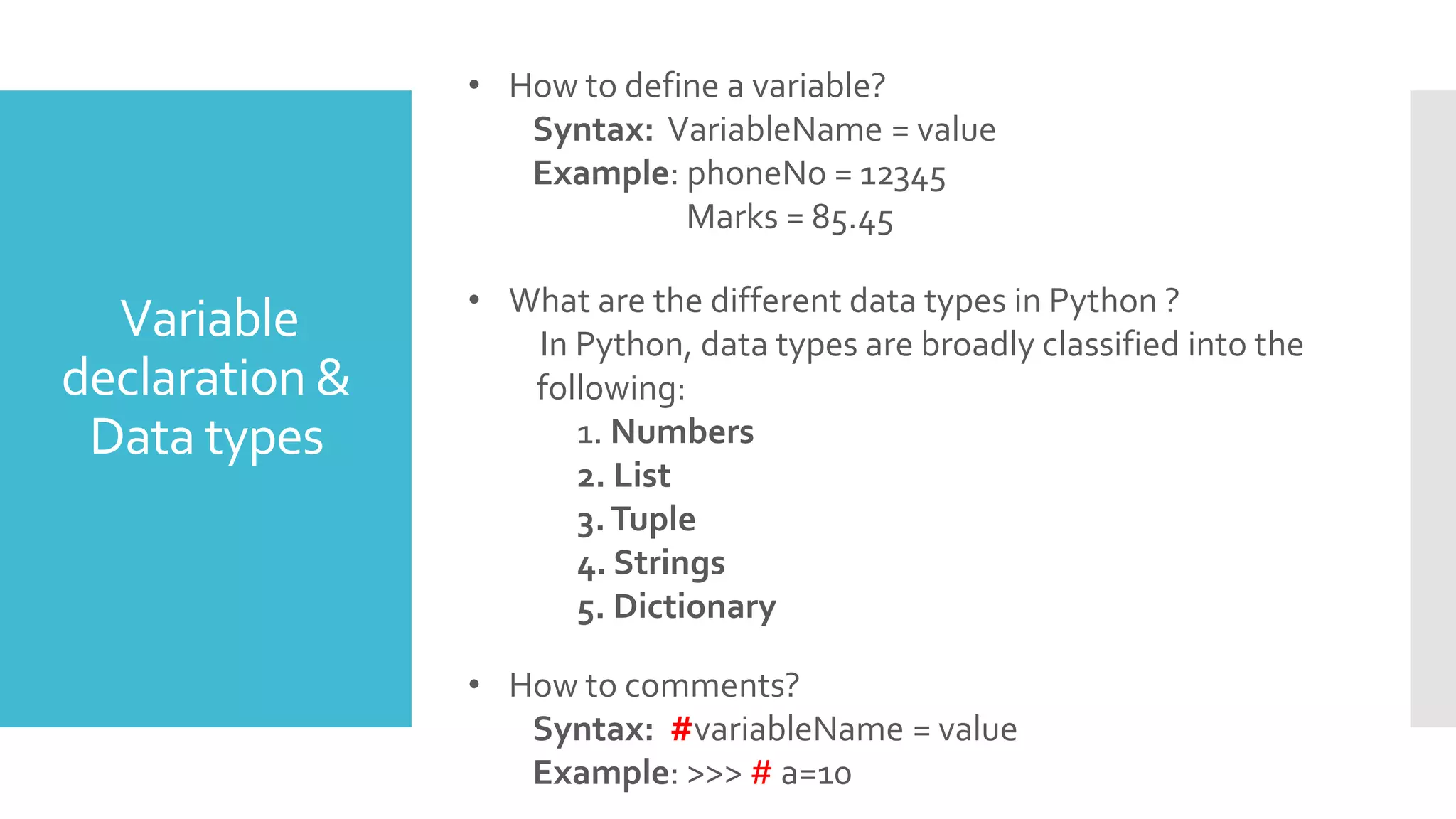
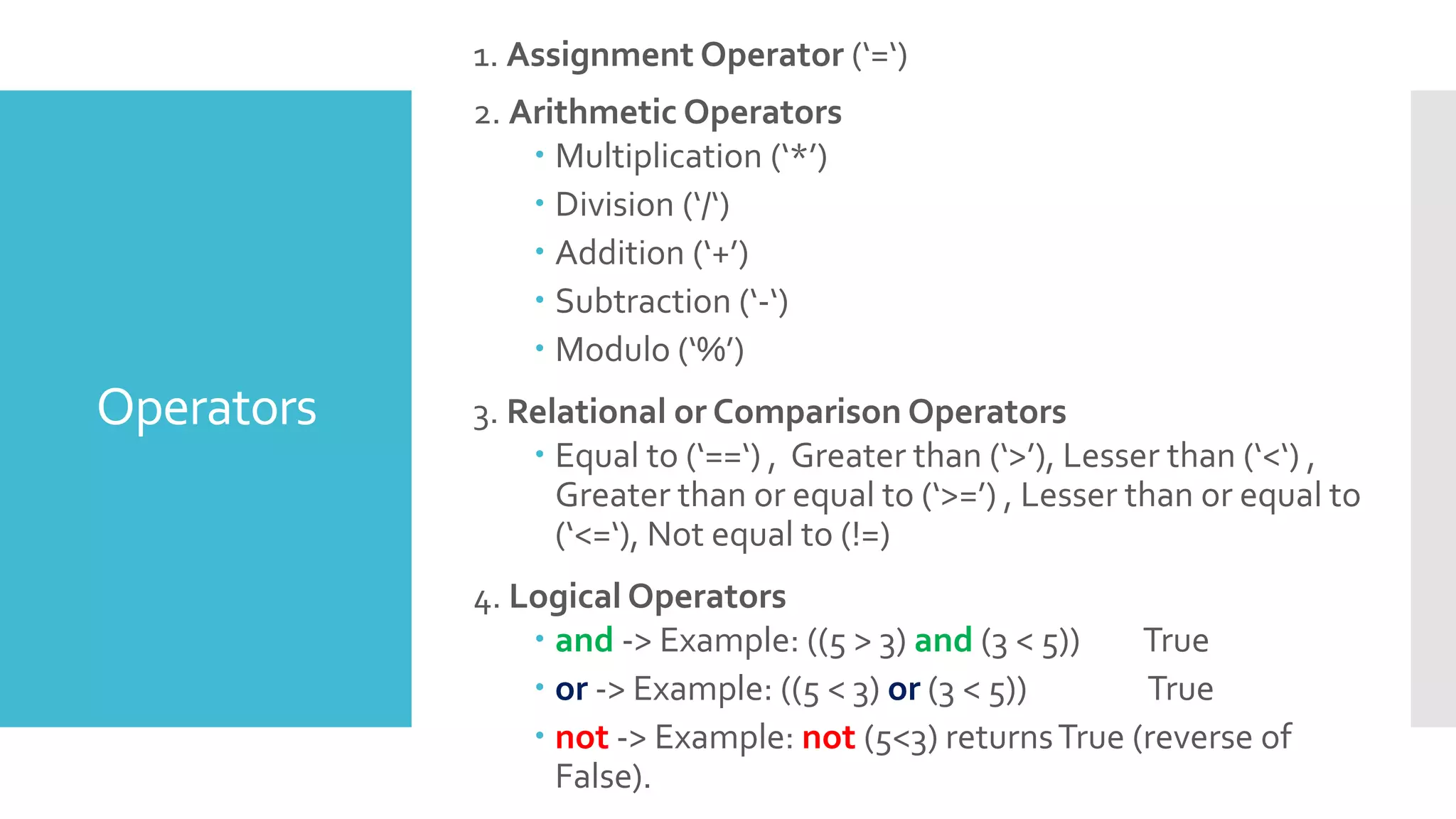
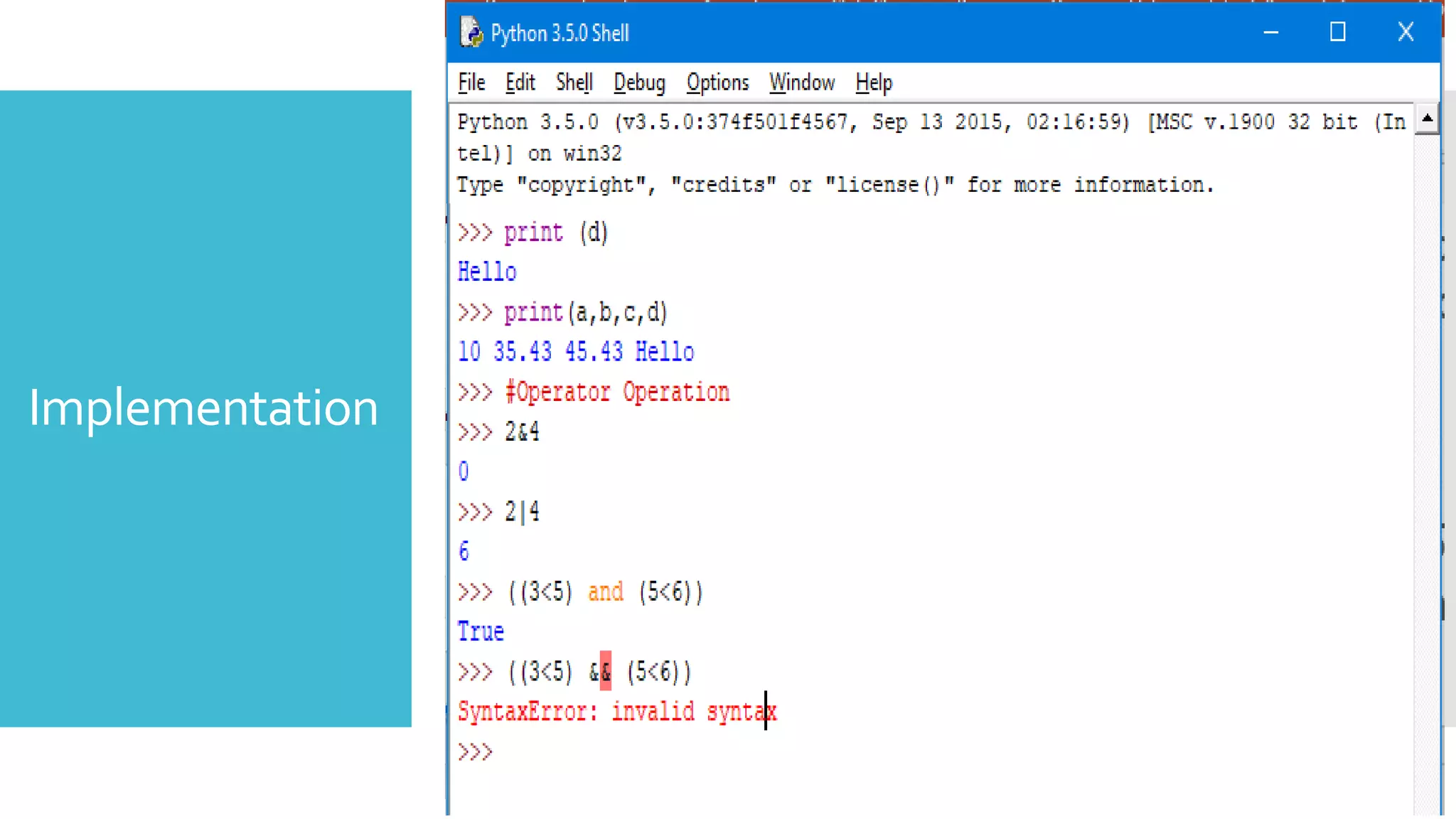
This document provides an outline and overview of a presentation on learning Python for beginners. The presentation covers what Python is, why it is useful, how to install it and common editors used. It then discusses Python variables, data types, operators, strings, lists, tuples, dictionaries, conditional statements, looping statements and real-world applications. Examples are provided throughout to demonstrate key Python concepts and how to implement various features like functions, methods and control flow. The goal is to give attendees an introduction to the Python language syntax and capabilities.







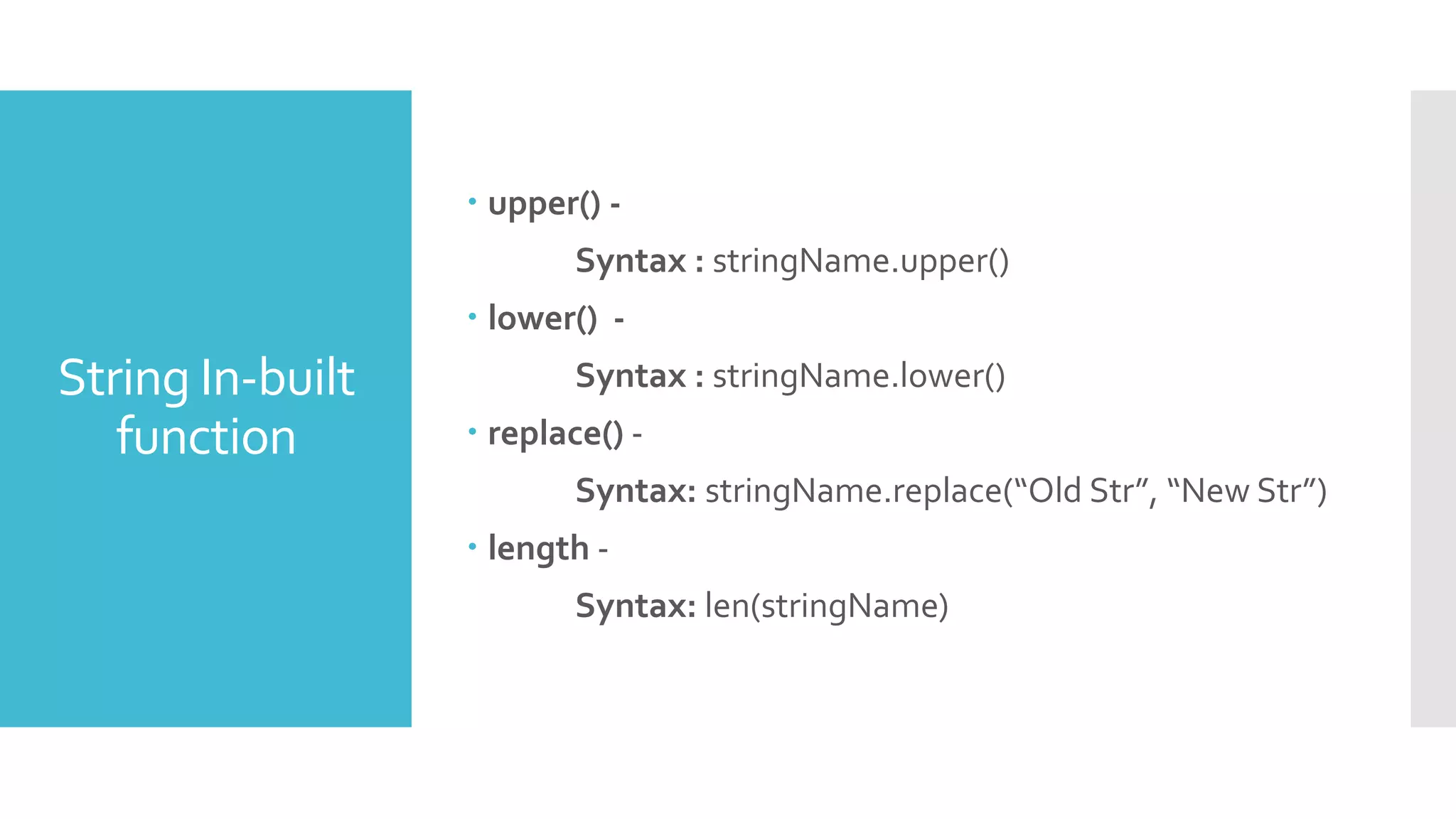
![List
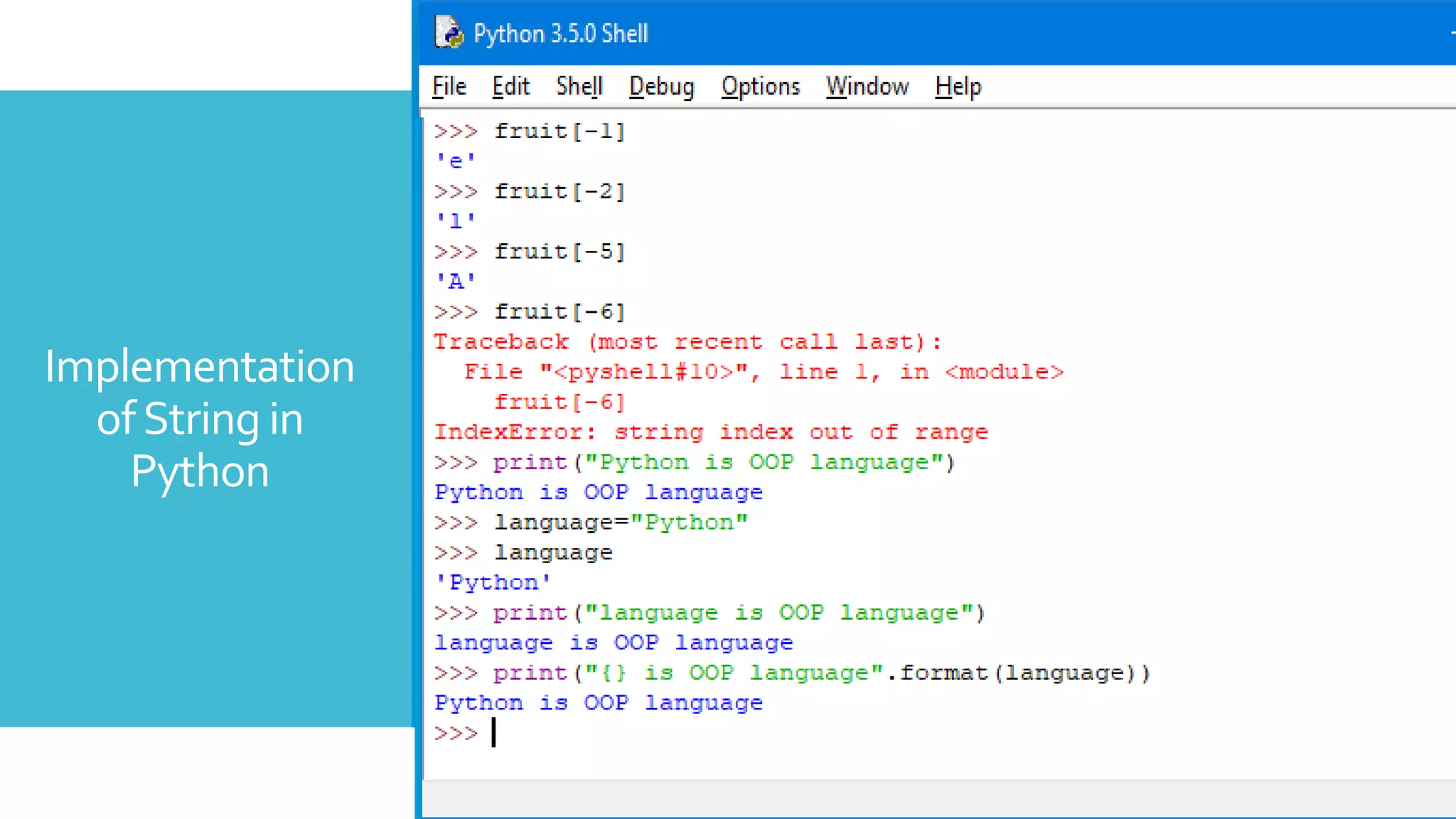
A list is a container that holds many objects under a
single name.
Syntax : listName = [object1, object2, object3]
Example: fruit = [‘Apple', ‘Mango', ‘Orange’]
It is same as array in C, C++ or JAVA.
To access the list :
Example : fruit[0] = Apple, fruit[1] = Mango,
fruit[2] = Orange](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofpython-ss-200509141346/75/Basic-of-Python-Hands-on-Session-15-2048.jpg)
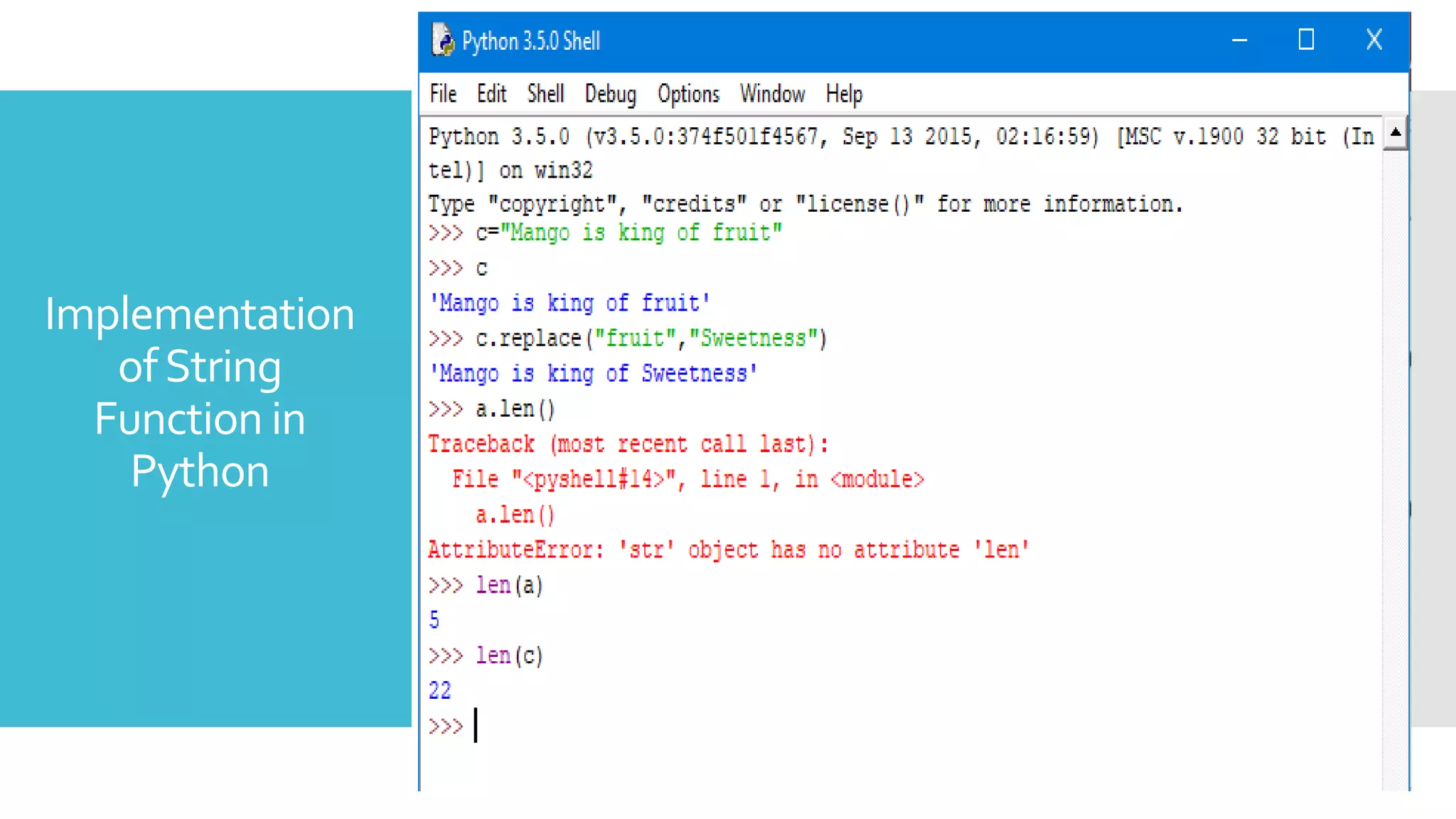
![Tuples
• A tuple is a container that holds many objects under a single
name.
• A tuple is immutable which means, a tuple once defined
cannot be modified.
Syntax : tupleName = (object1, object2, object3)
Example: ImpDate = (“11-09-1989”, “13-2-2020”)
• To access the values in a tuple
>>> ImpDate[1]
>>>13-2-2020
• To delete a tuple
Syntax: del(tupleName)
Example: del(ImpDate)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofpython-ss-200509141346/75/Basic-of-Python-Hands-on-Session-18-2048.jpg)
![Dictionary
• A dictionary is a set of key-value pairs referenced by a
single name.
Syntax : dictionaryName = {“keyOne” : “valueOne”,
“keyTwo”: “valueTwo”}
Example:>>> colorOfFruits = {“apple”: “red”,
“mango”: “yellow”, “orange”: “orange”}
• To Retrieve the value of dictionary
Syntax: dictionaryName[“key”]
Example: >>>colorOfFruits[“mango”]
>>>yellow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofpython-ss-200509141346/75/Basic-of-Python-Hands-on-Session-19-2048.jpg)
![Dictionary
inbuilt
Functions
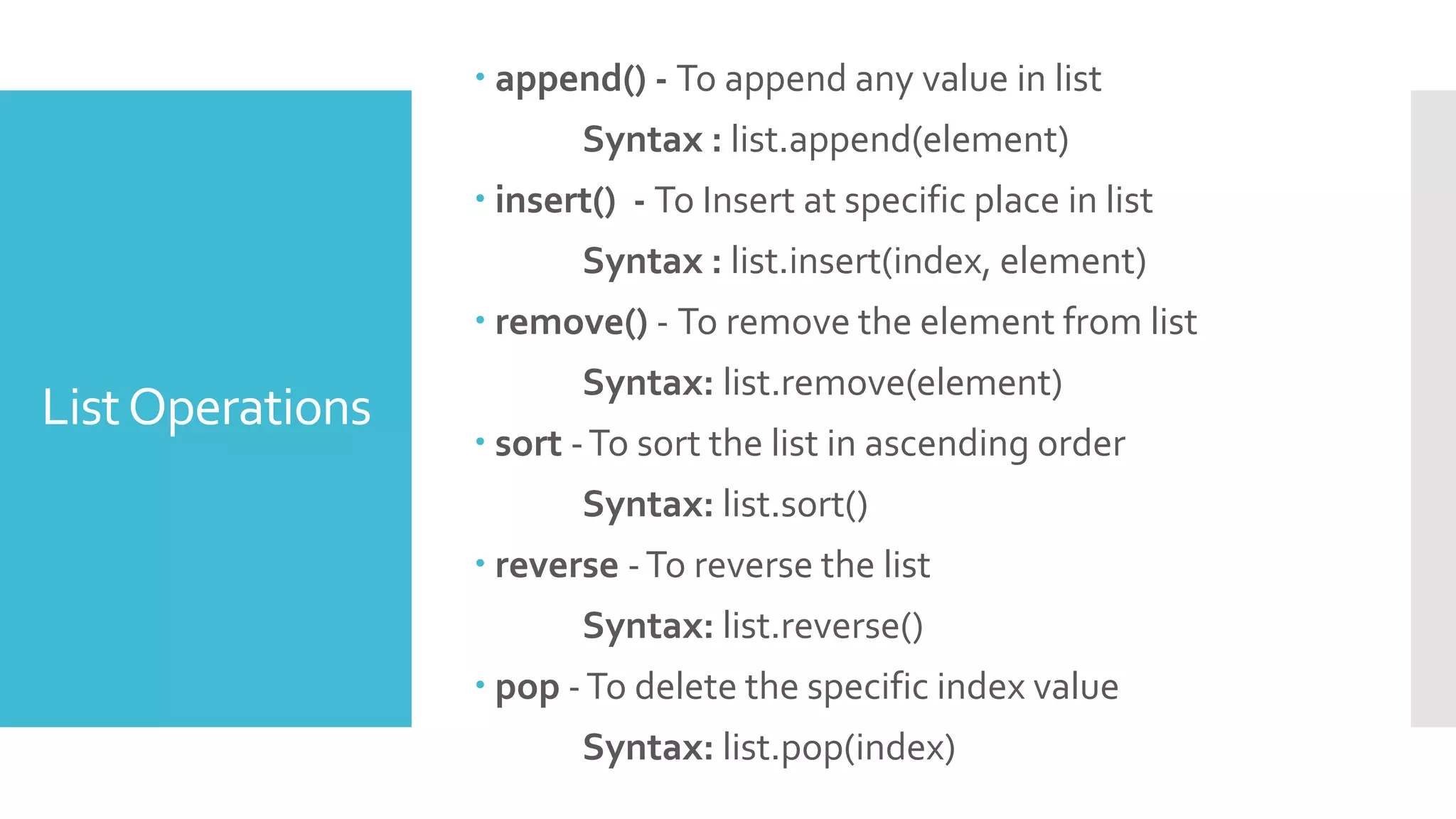
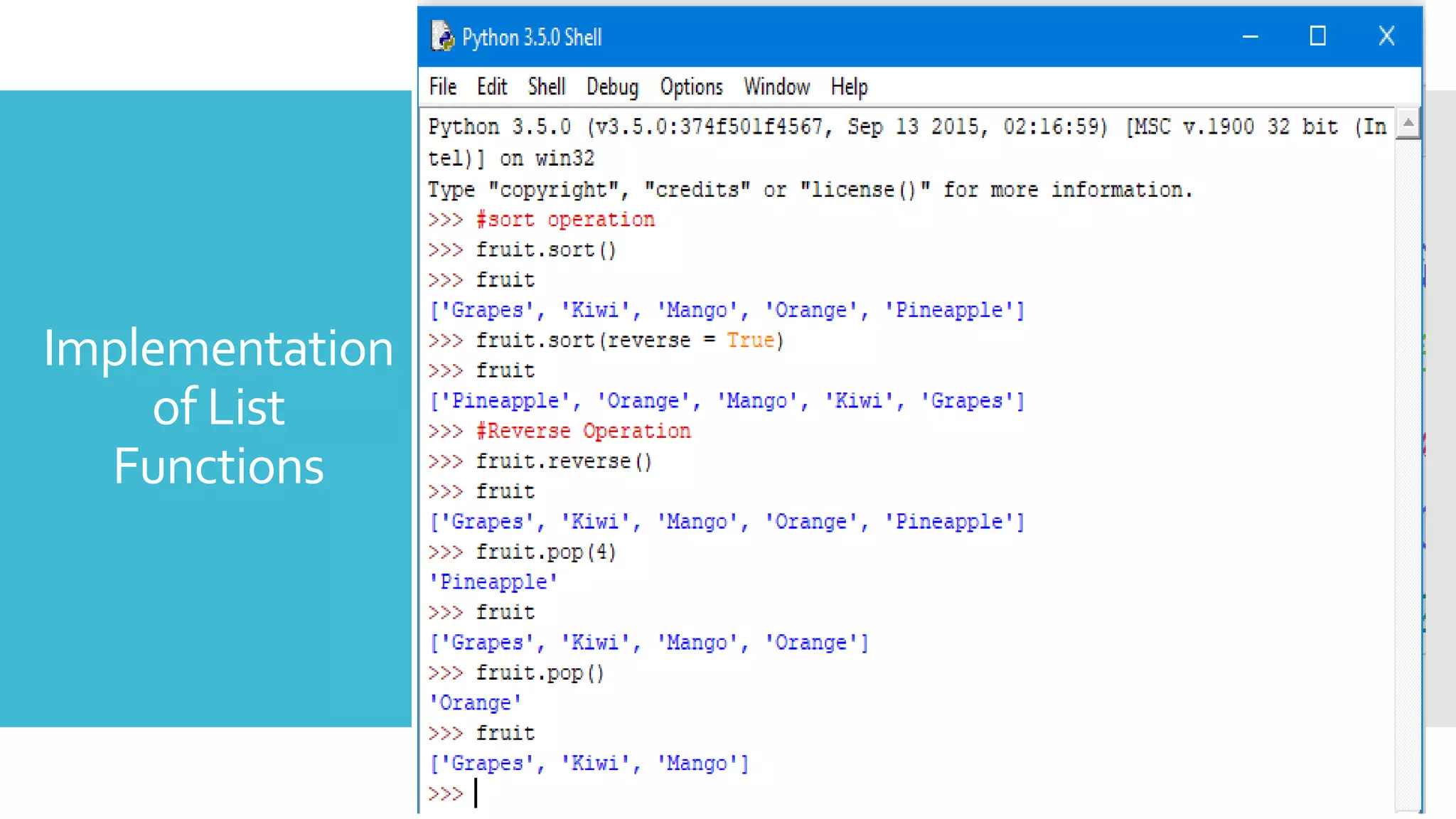
List all keys : keys() is used to list all the keys in a dictionary.
Syntax: dictionaryName.keys()
List all values : values() is used to list all the values in a dictionary
Syntax: dictionaryName.values()
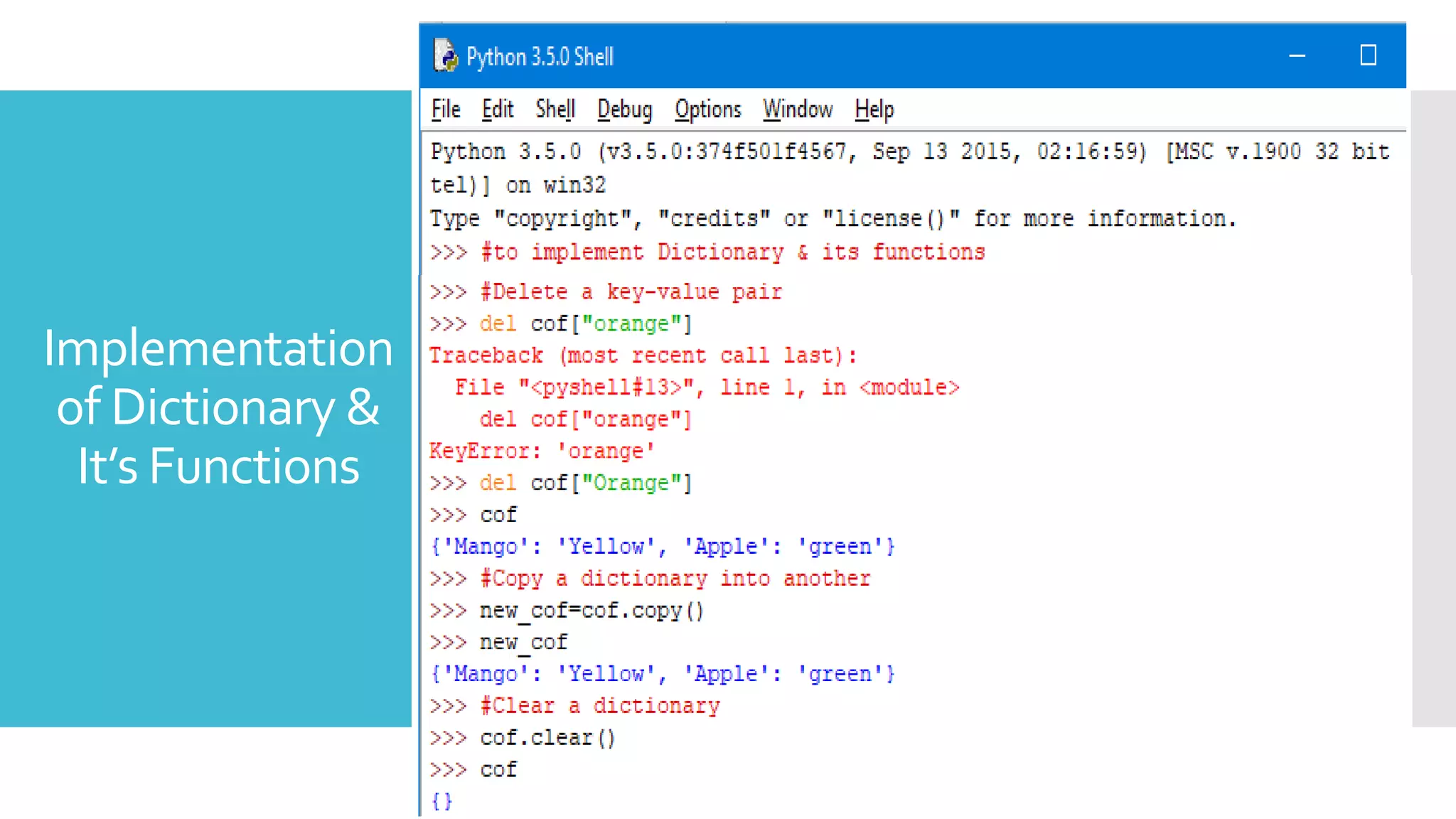
Delete a key-value pair : del keyword is used to delete a key-
value pair from a dictionary
Syntax: del dictionaryName[“key”]
Copy a dictionary into another : is used to copy the contents of
one dictionary to another
Syntax: dictionaryTwo = dictionaryOne.copy()
Clear a dictionary: is used to clear the contents of a dictionary
and make it empty .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofpython-ss-200509141346/75/Basic-of-Python-Hands-on-Session-20-2048.jpg)