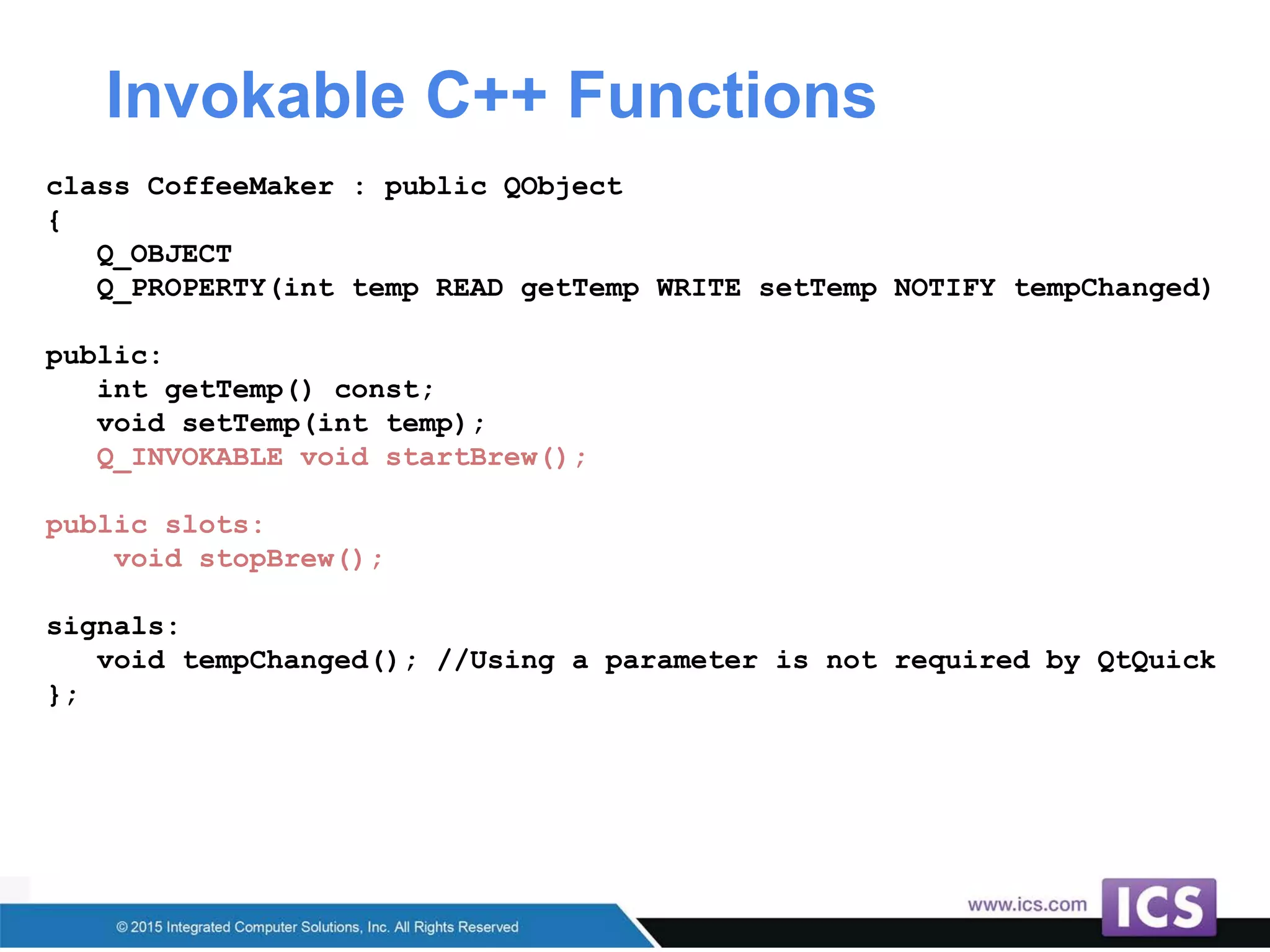
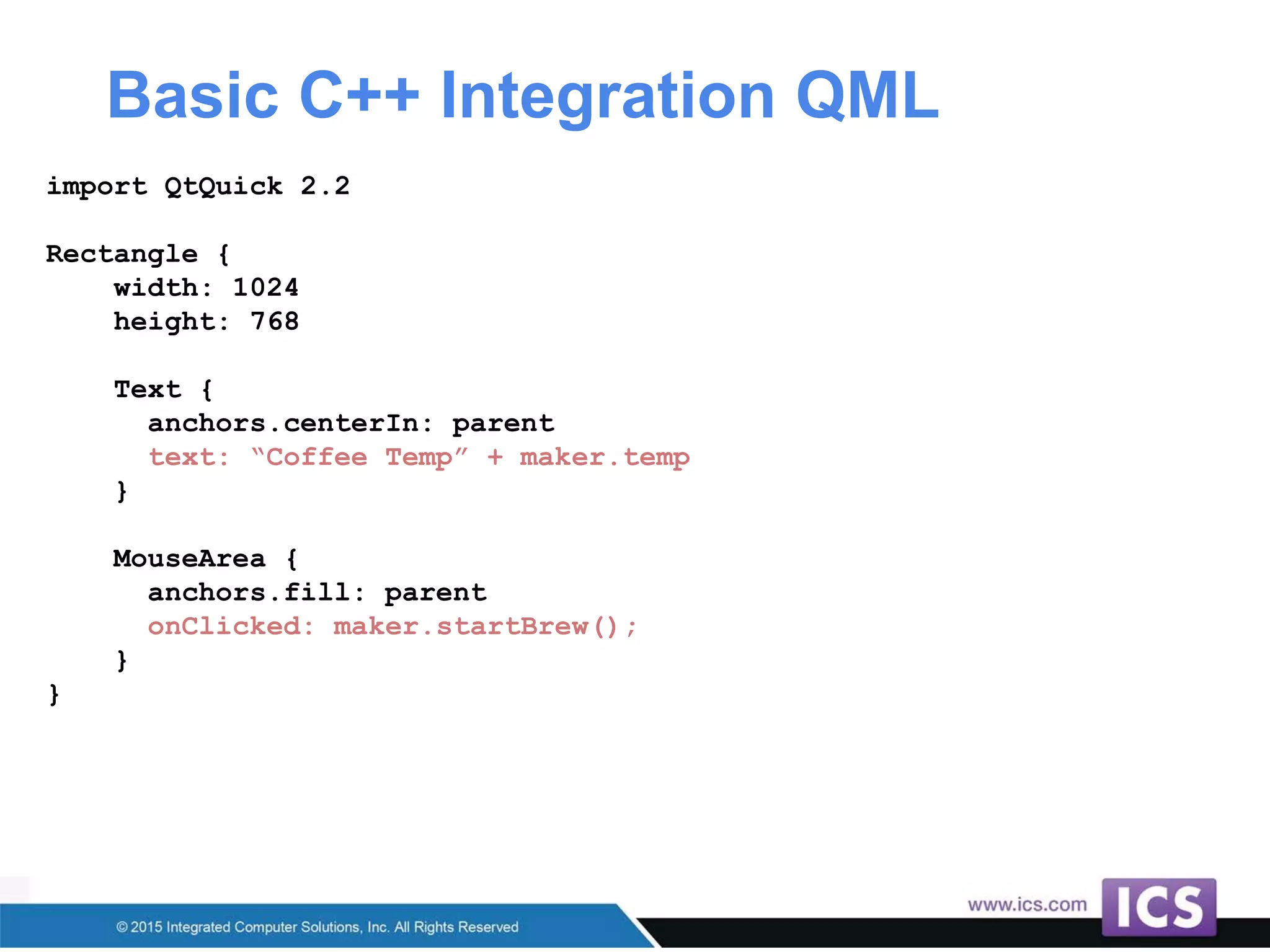
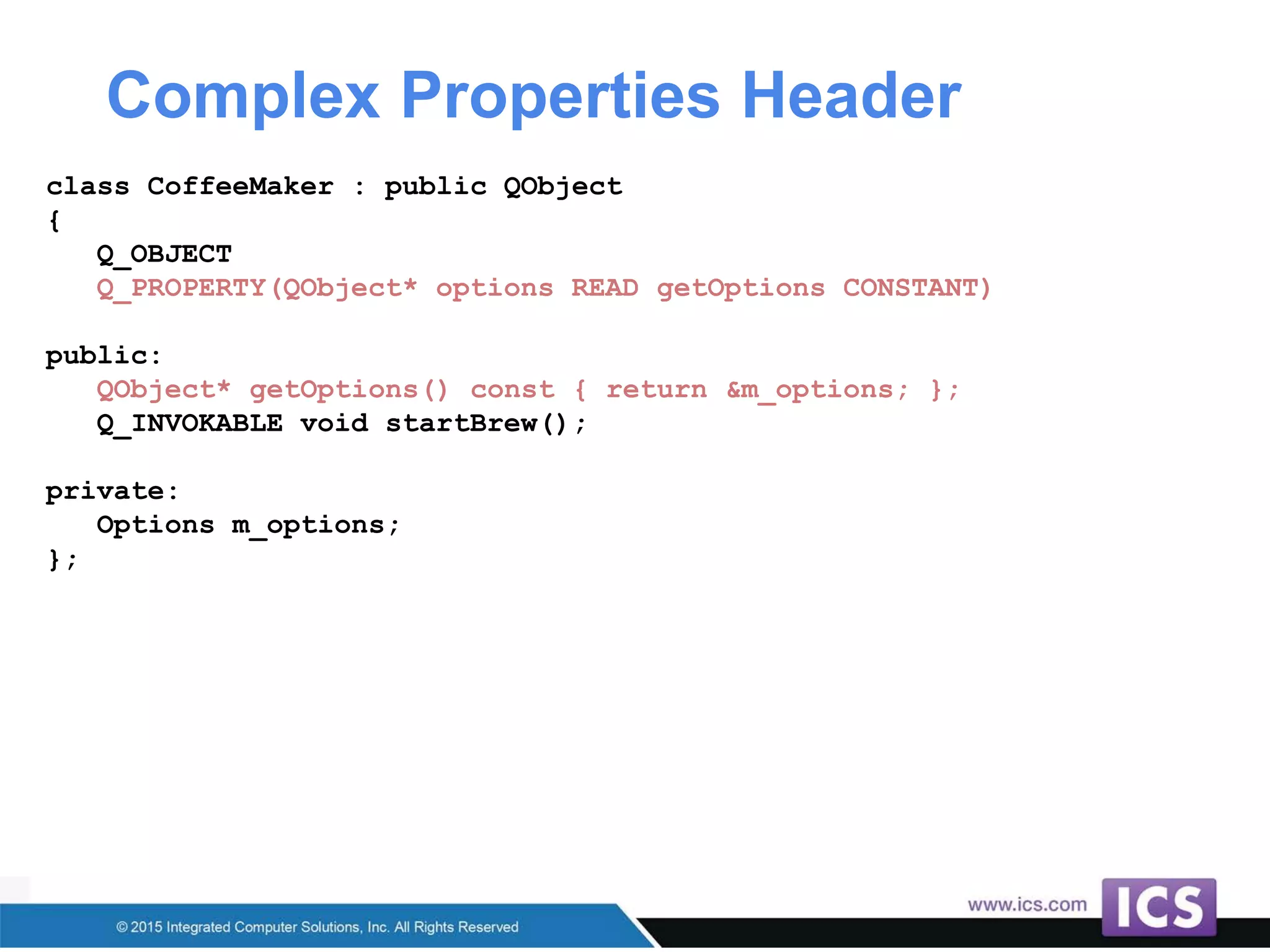
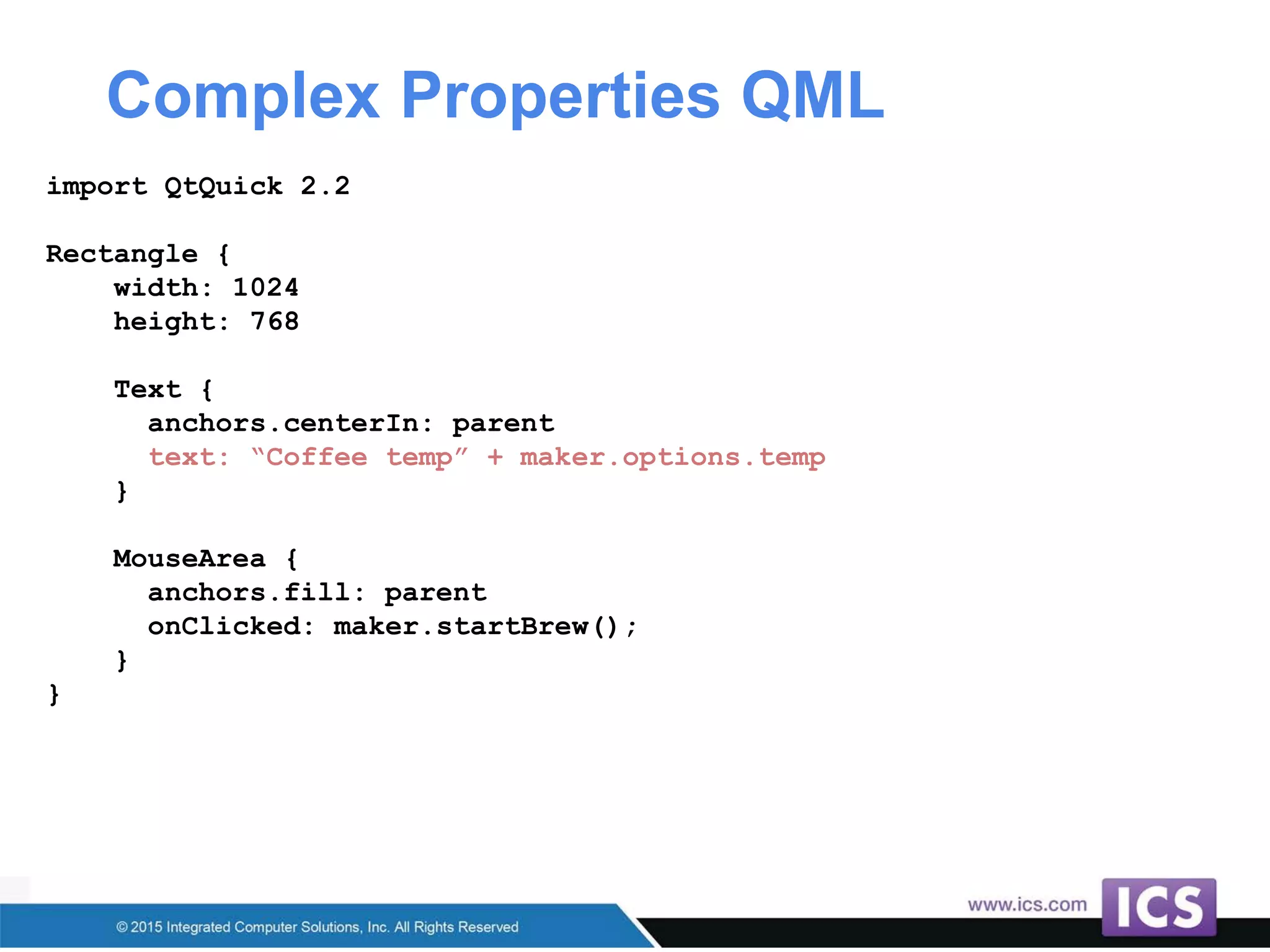
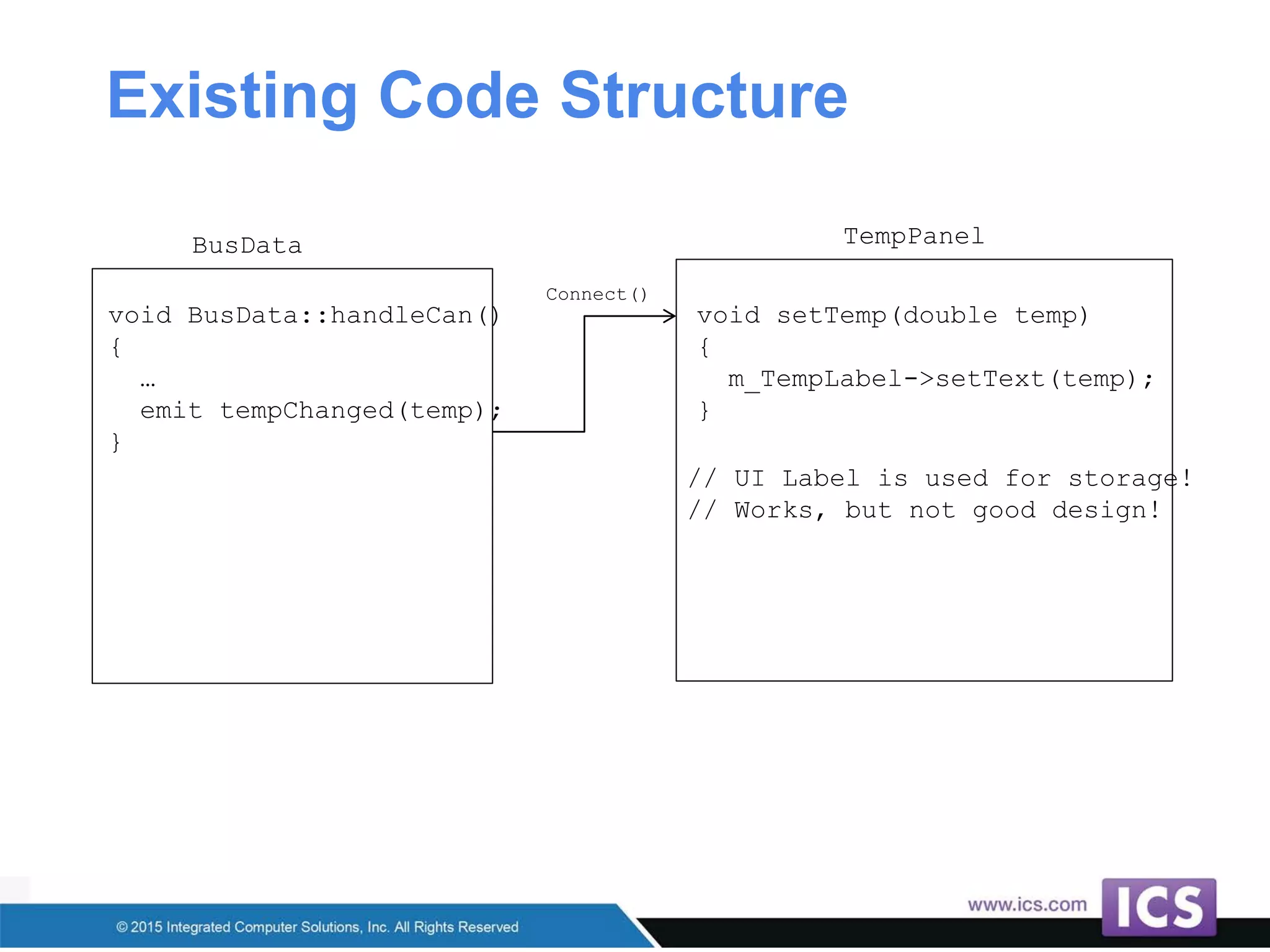
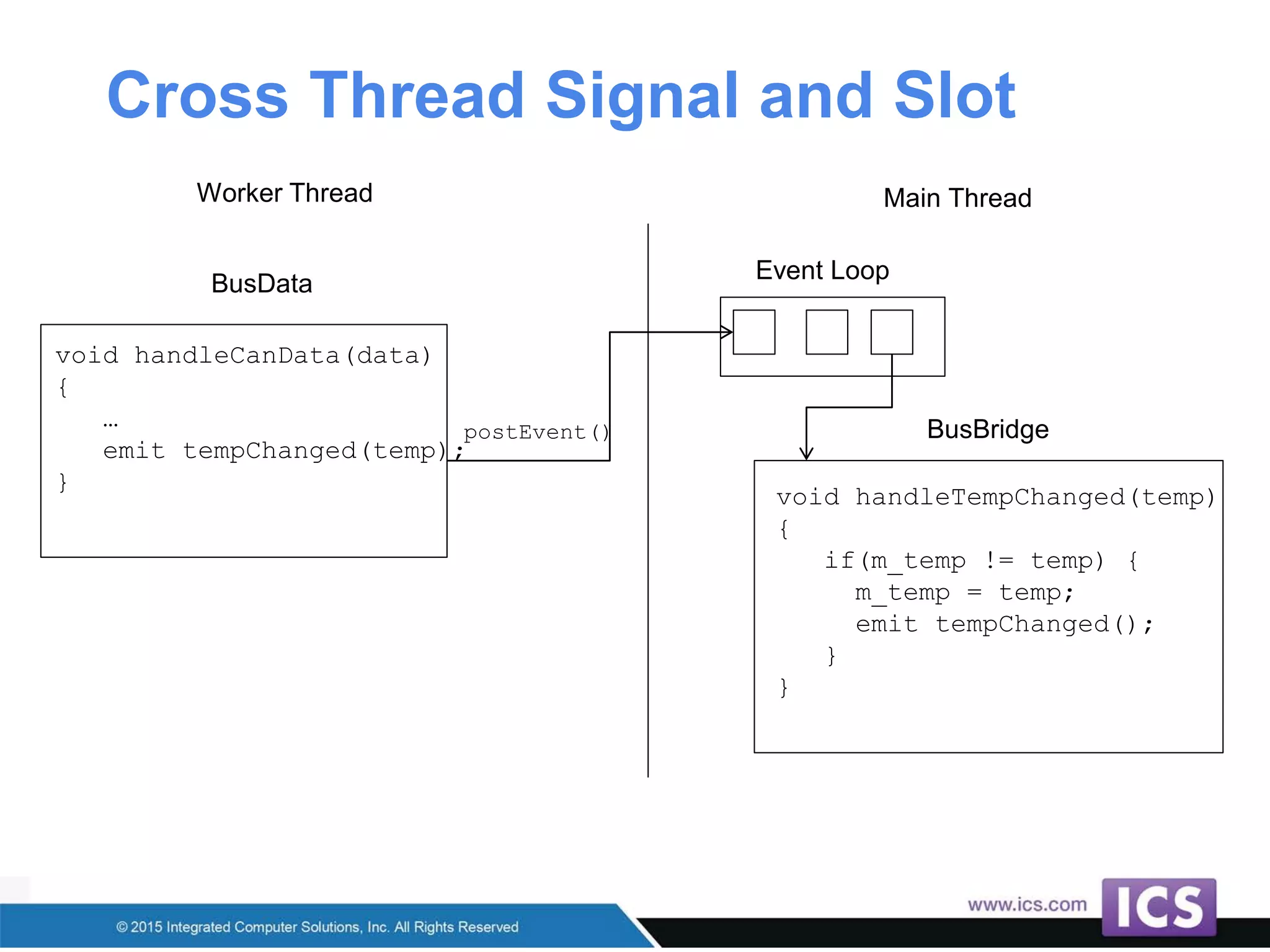
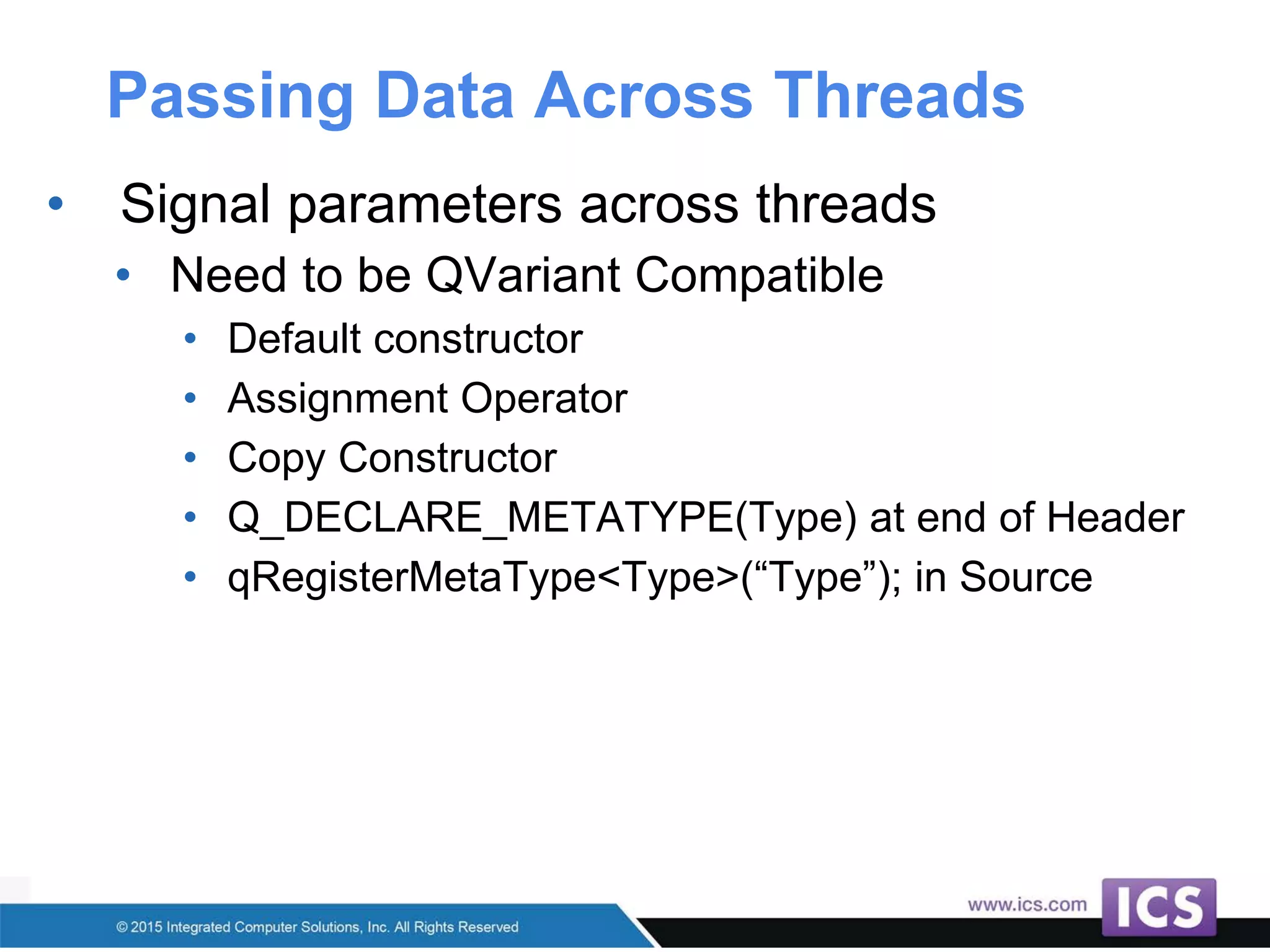
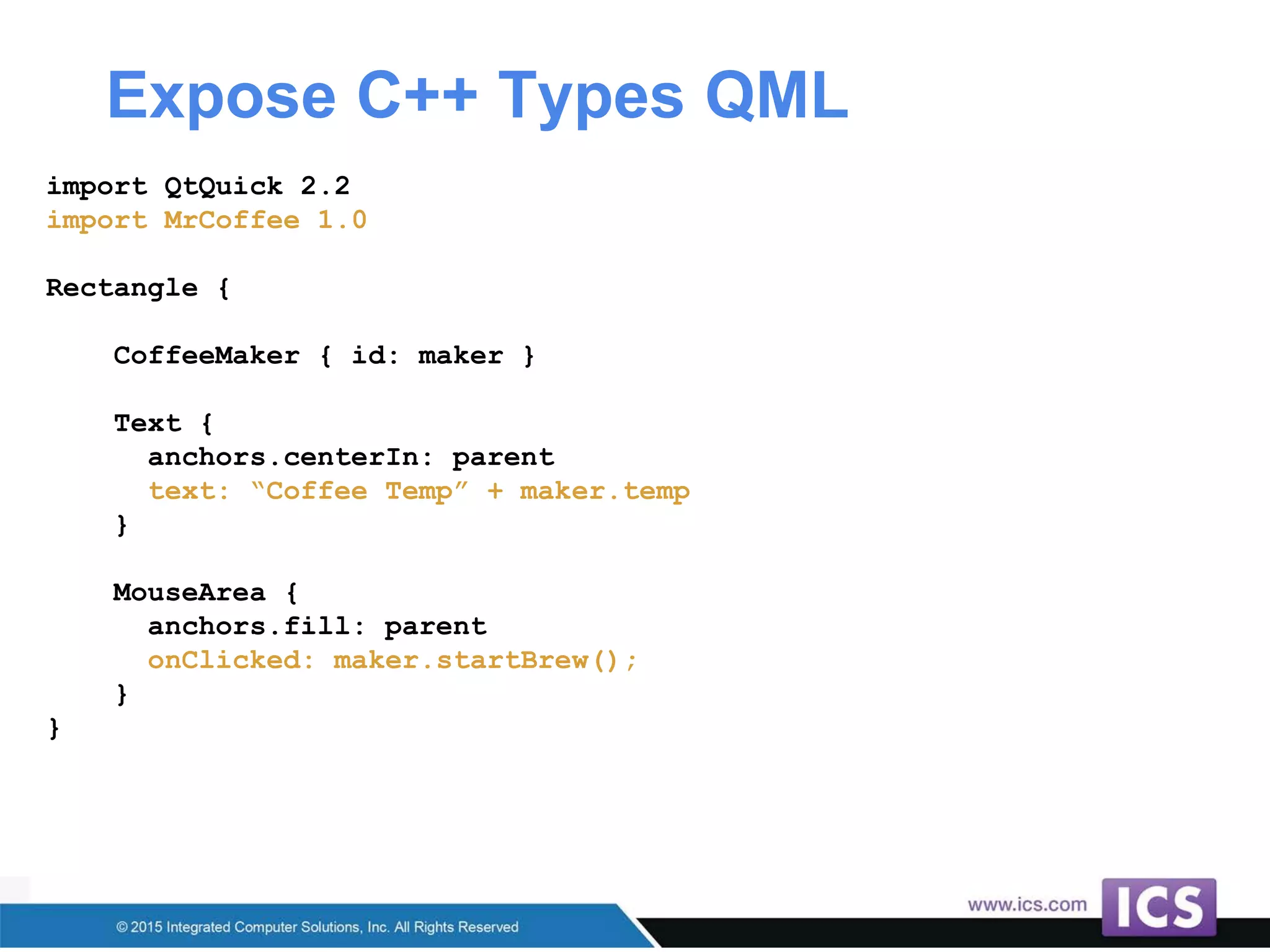
The document outlines best practices for integrating C++ with QML in Qt, emphasizing the model-view pattern, property creation, and invokable methods. It provides guidance on reusing existing C++ code, managing complex properties, and threading considerations when working with QObject instances. Techniques for exposing C++ types to QML and ensuring clean design without UI dependencies are also discussed.