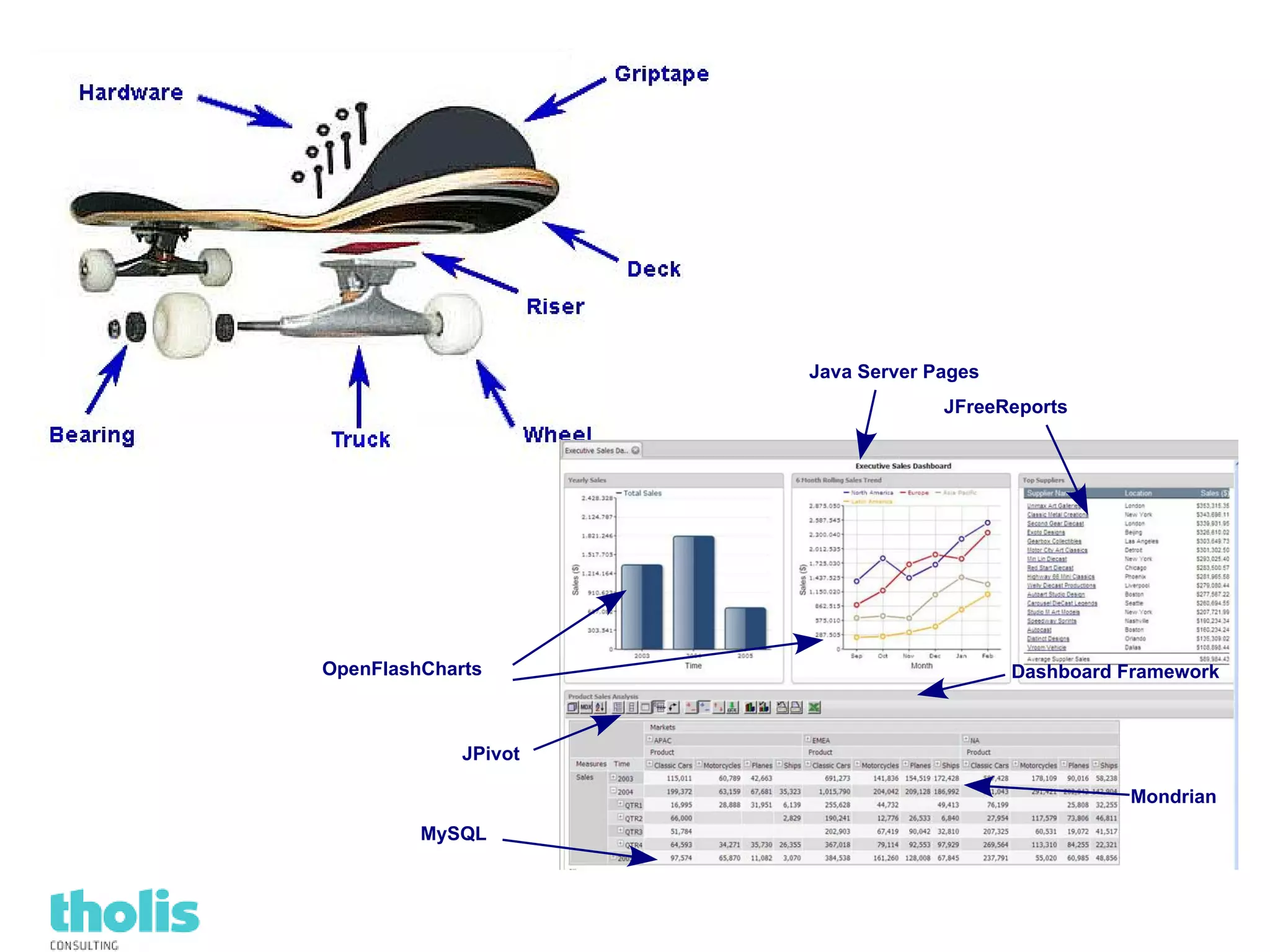
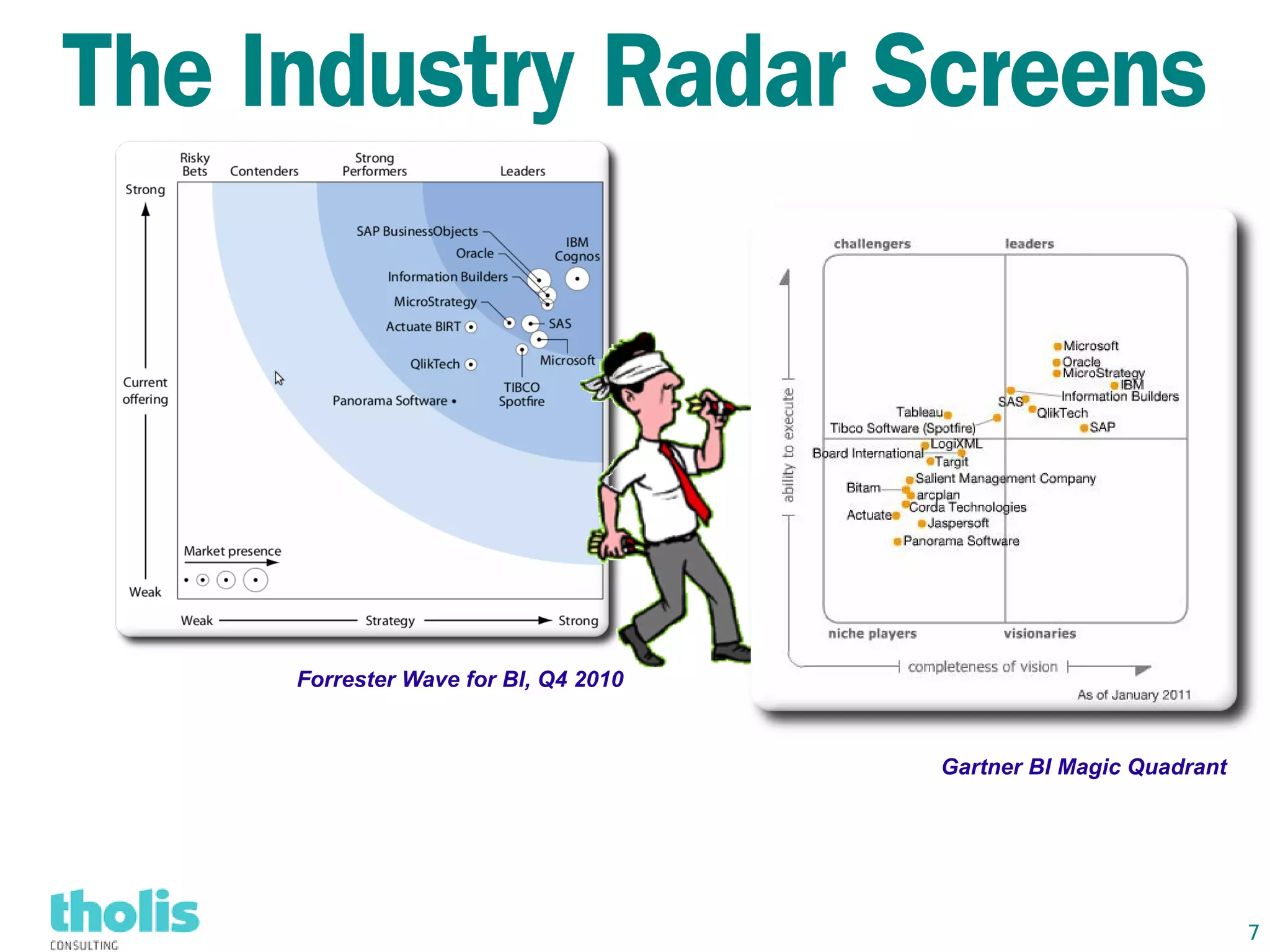
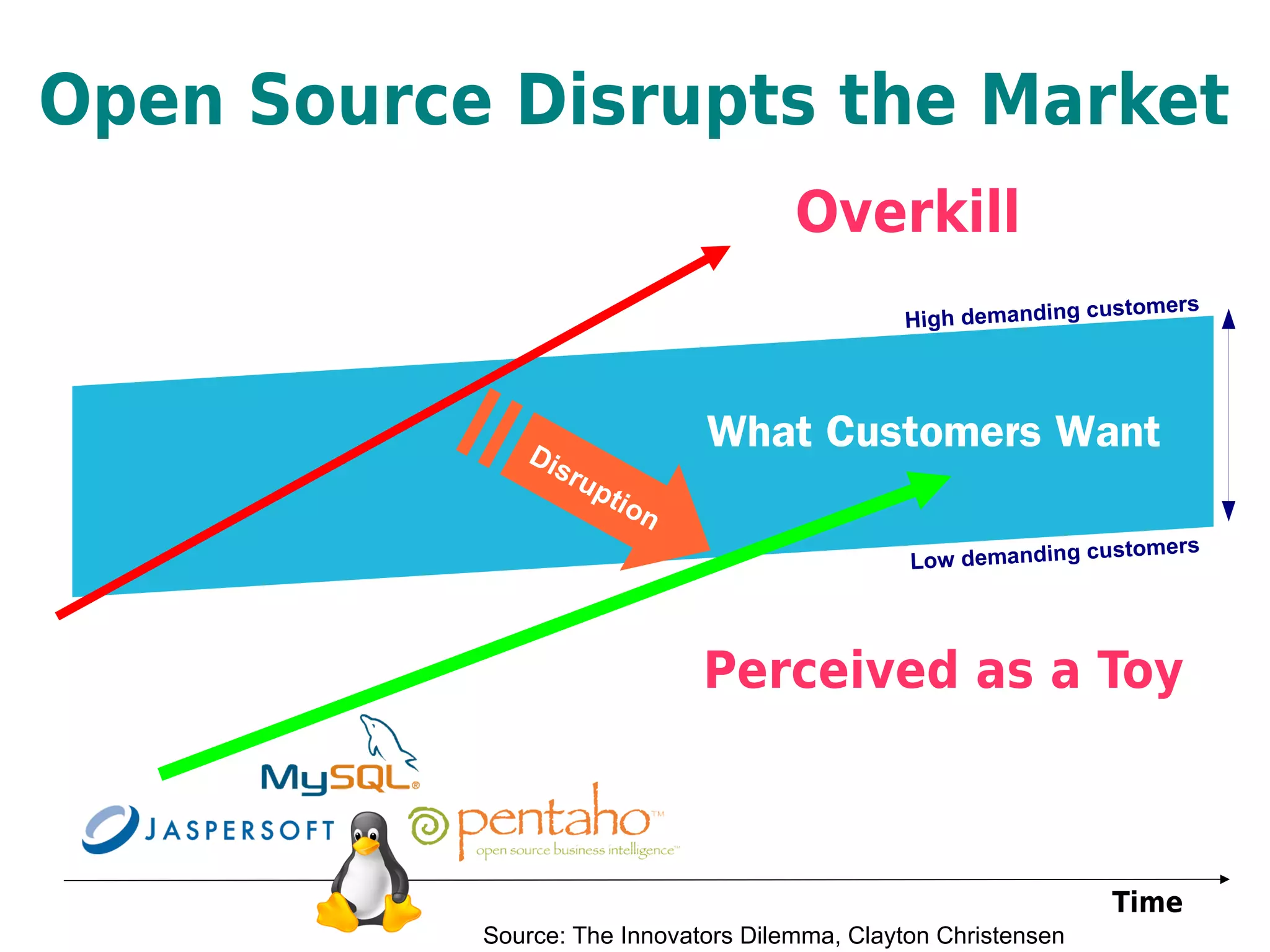
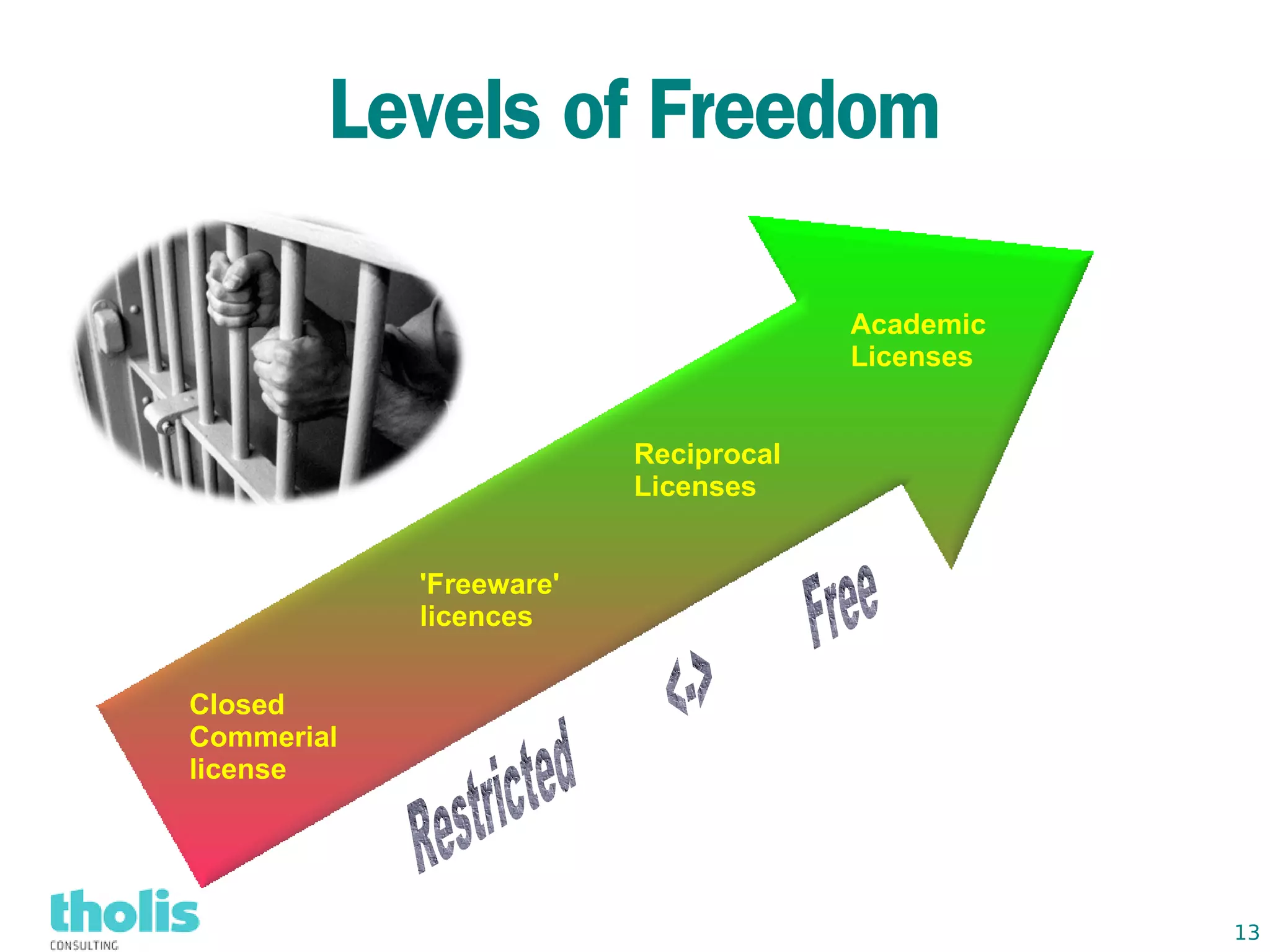
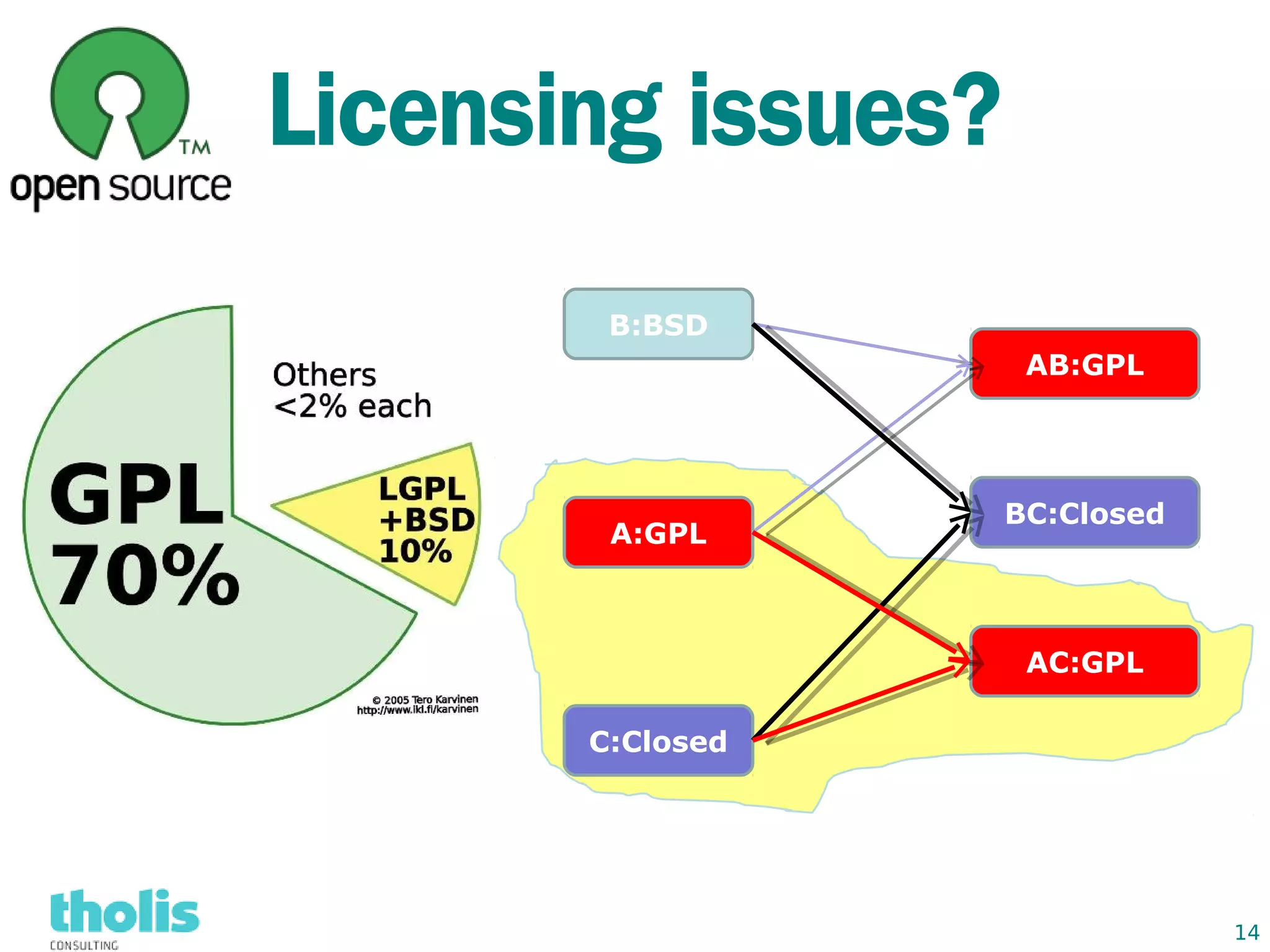
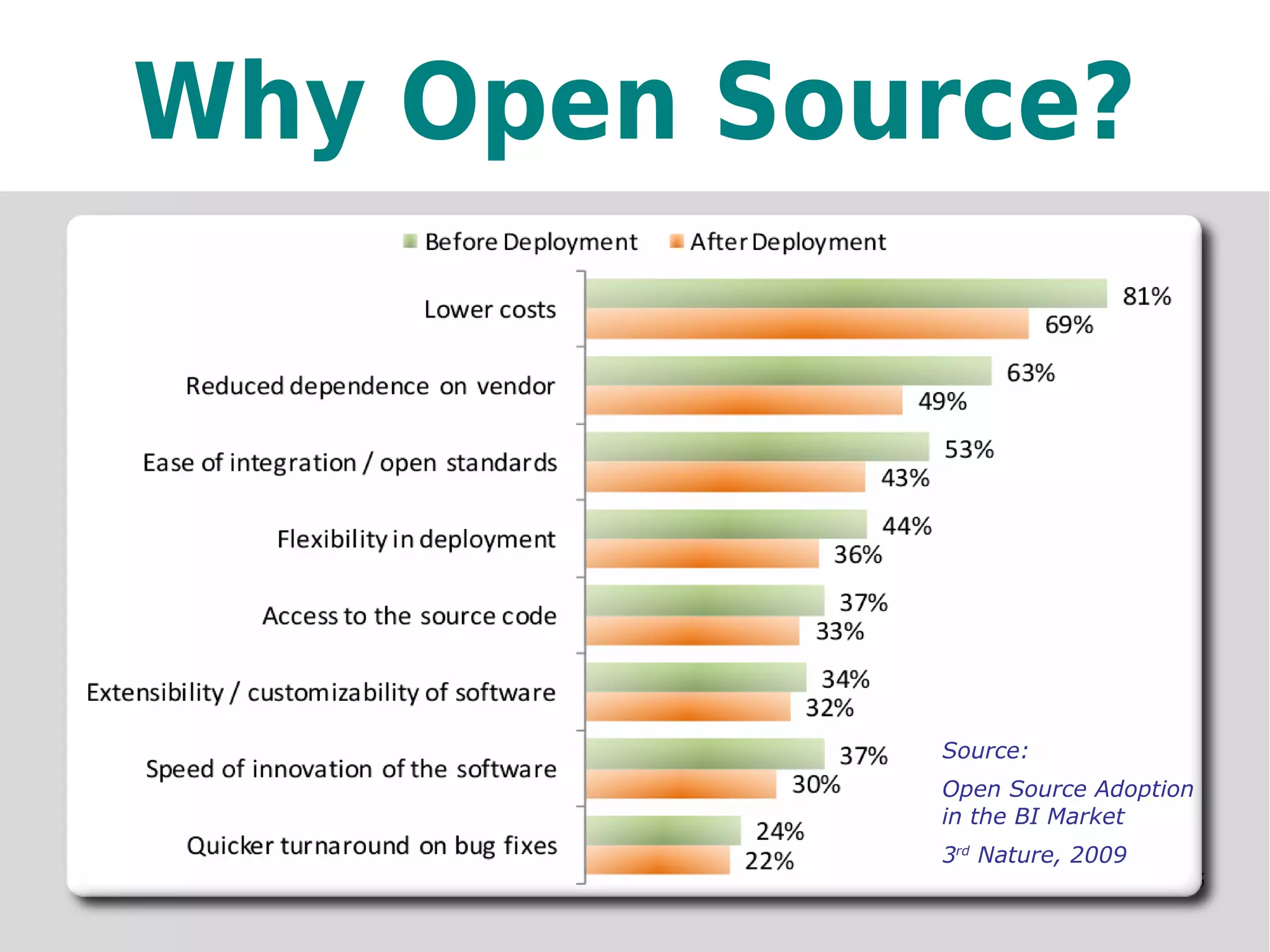
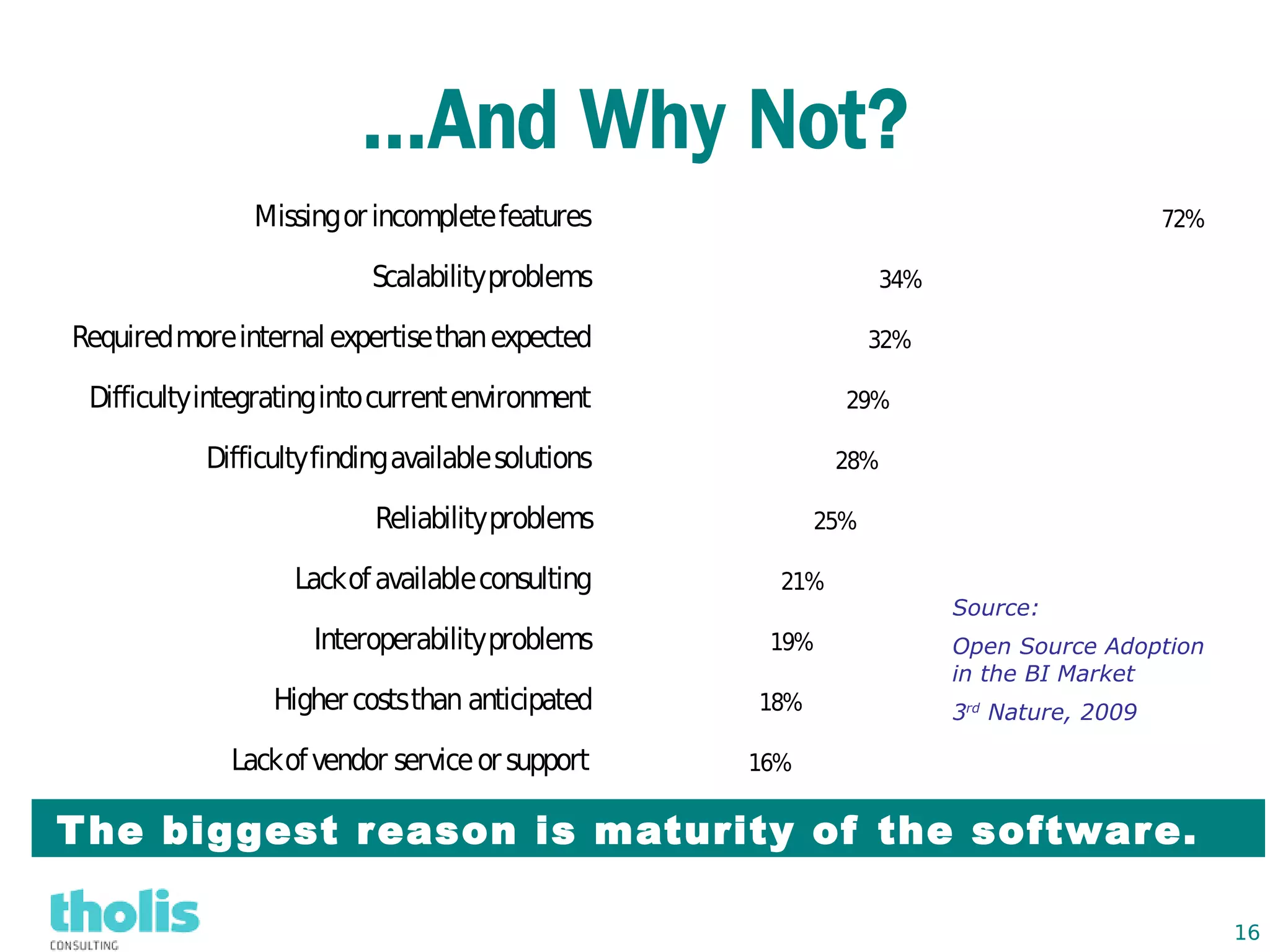
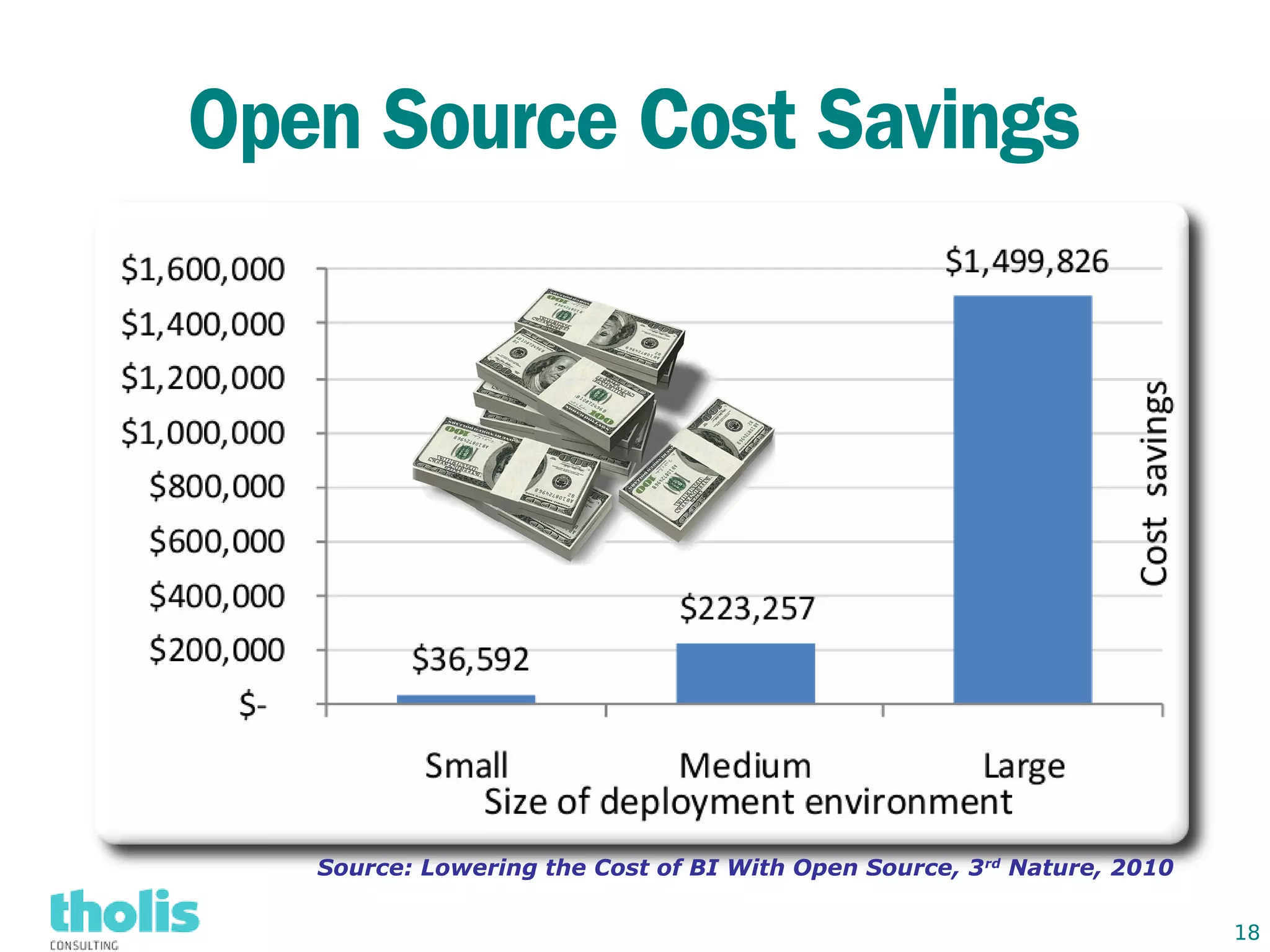
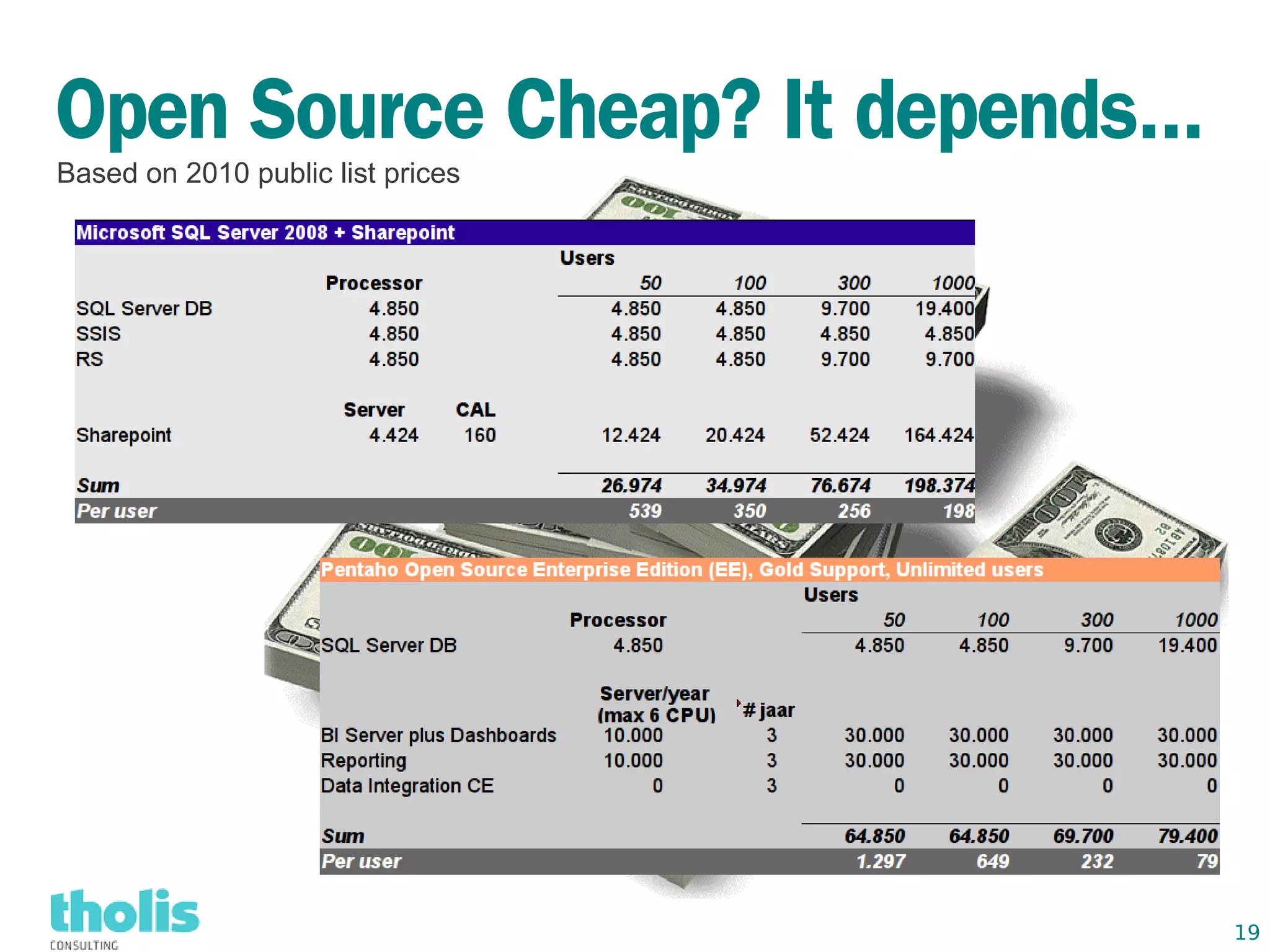
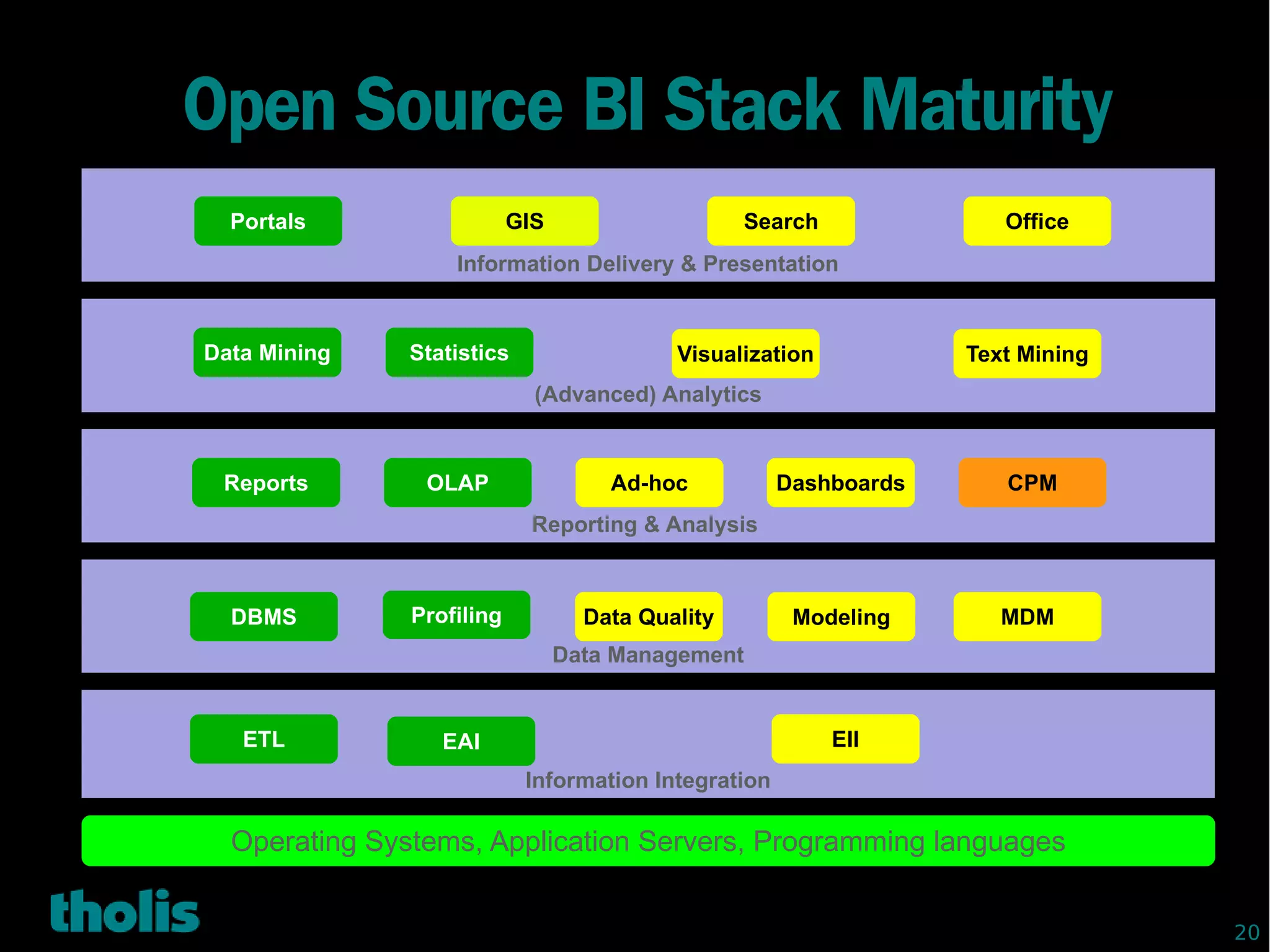
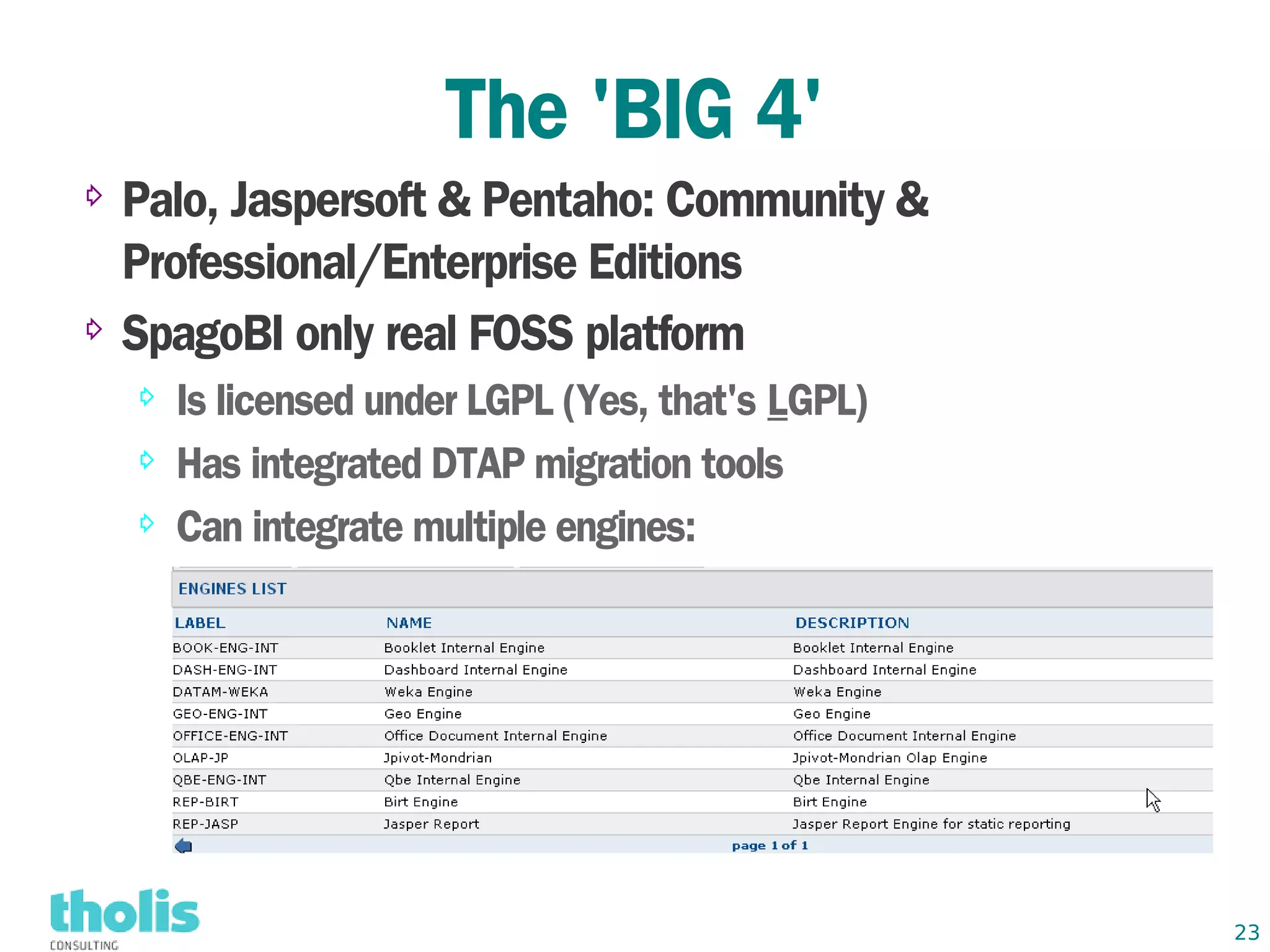
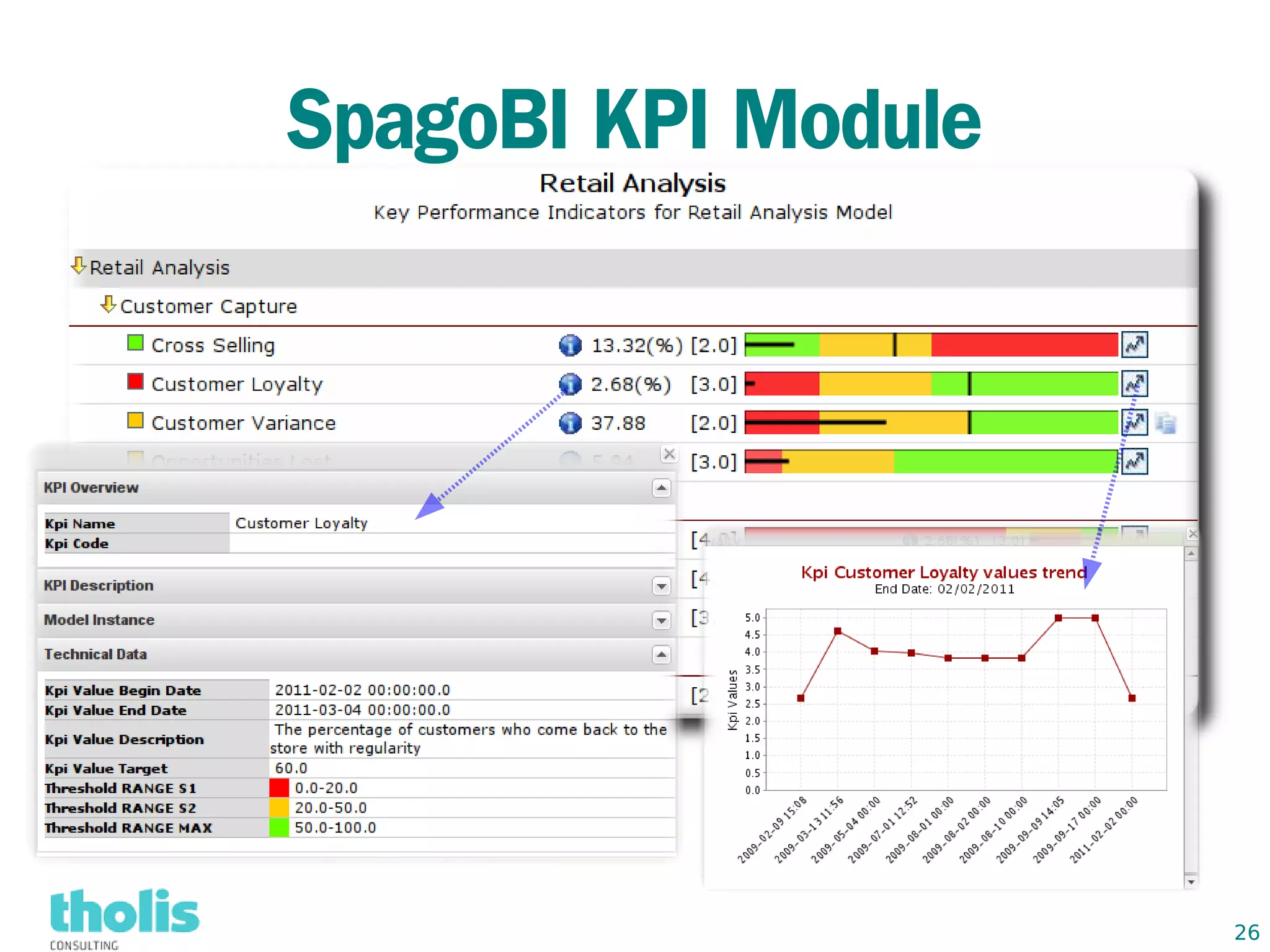
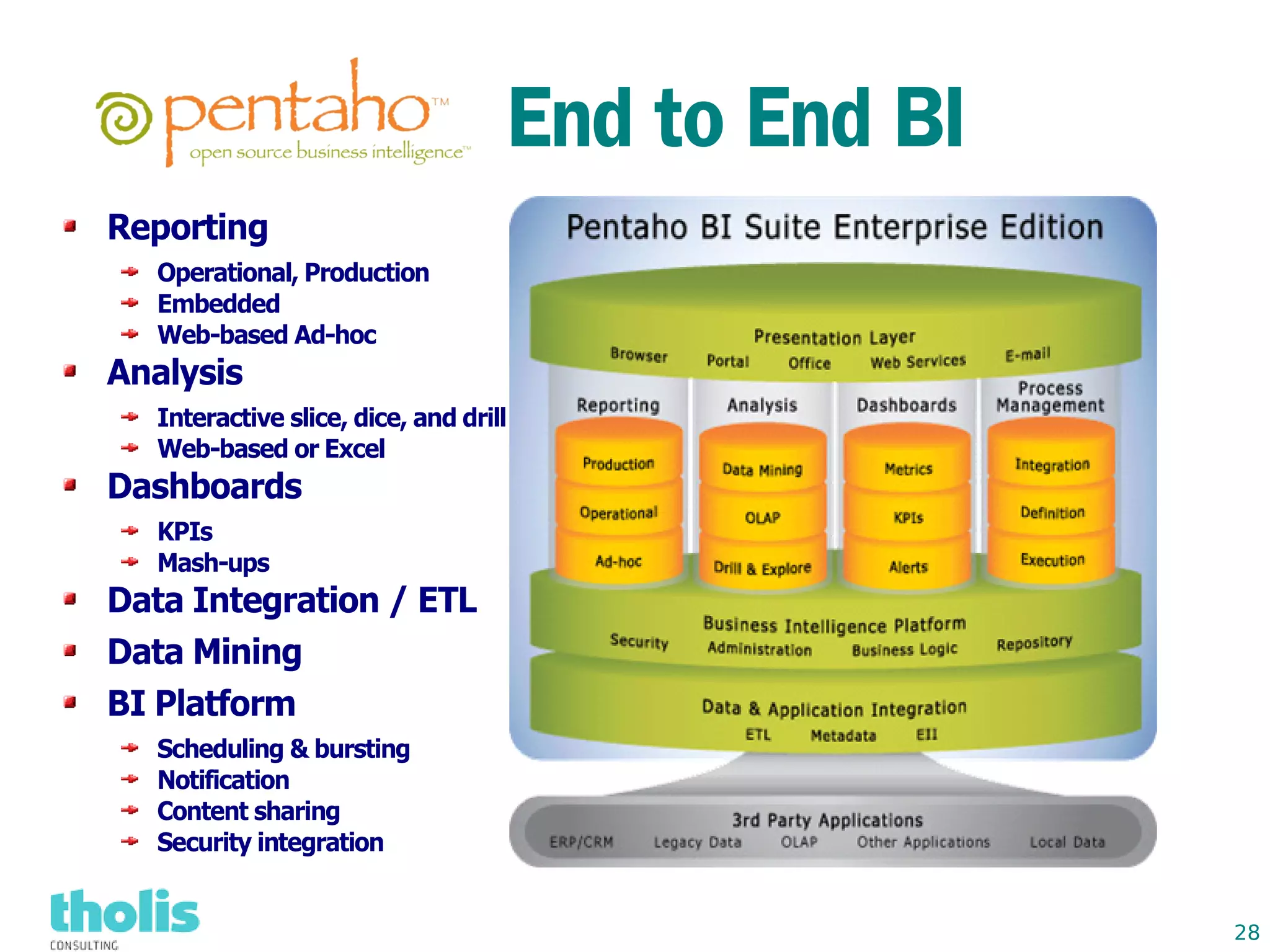
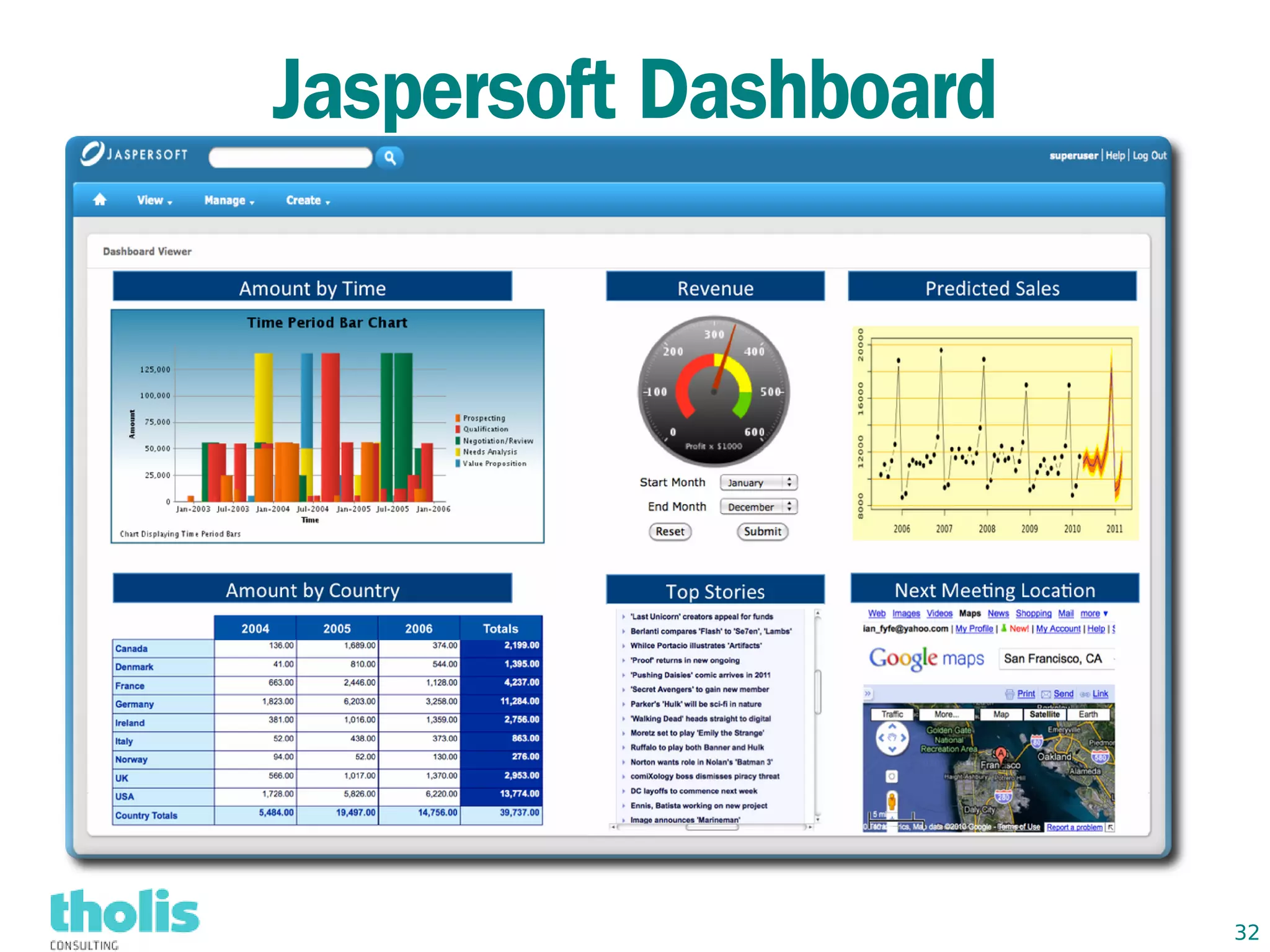
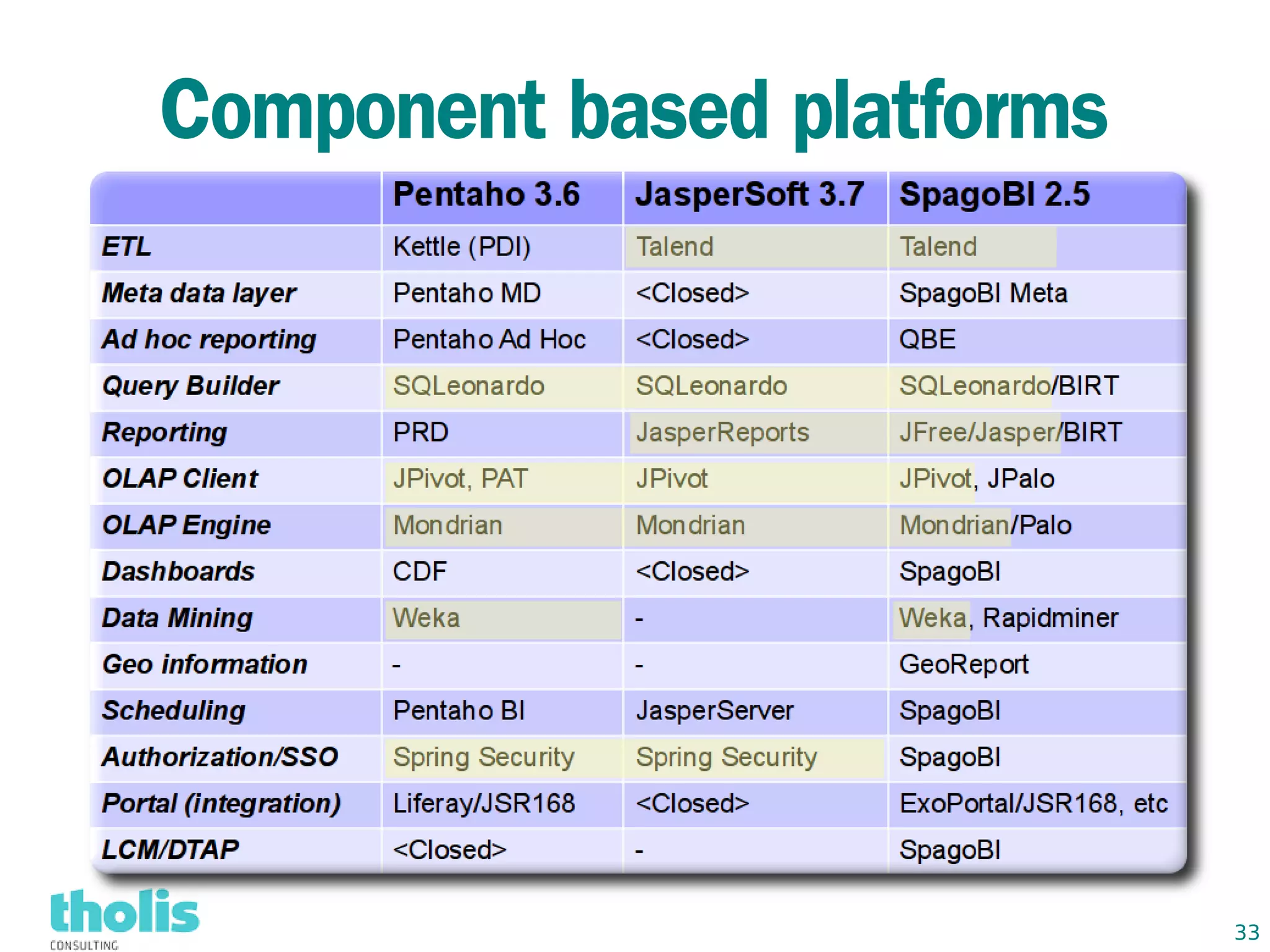
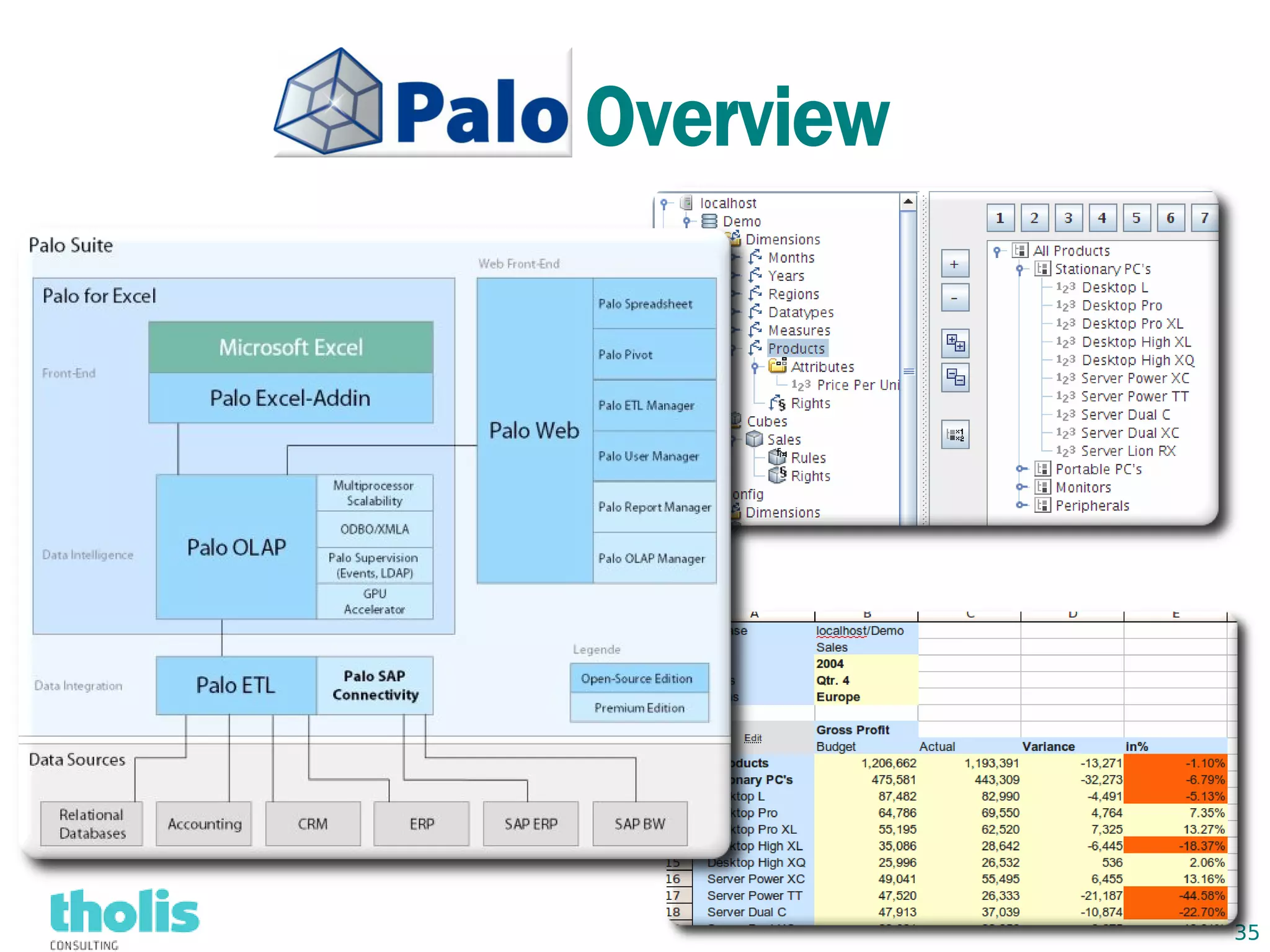
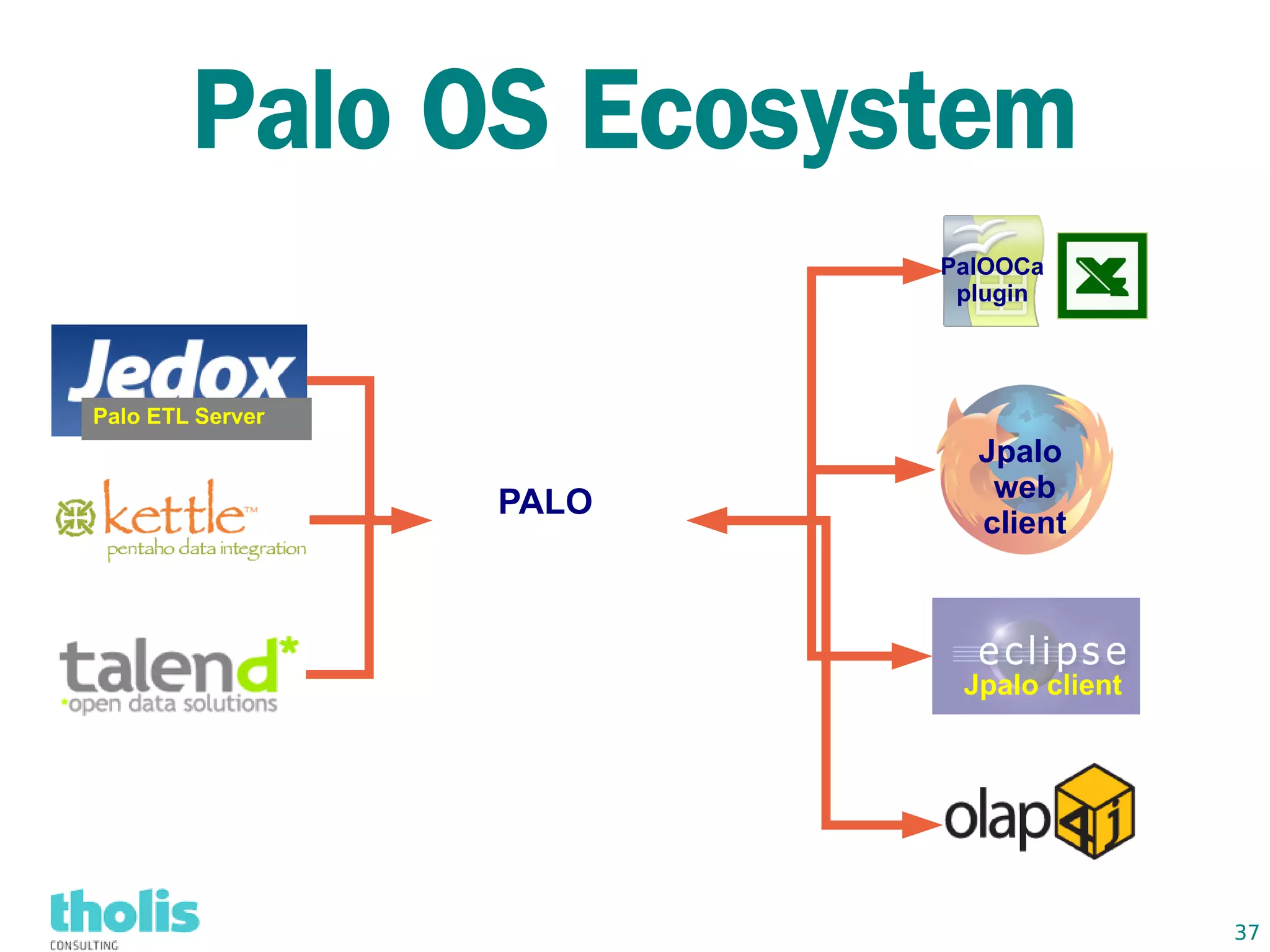
This document provides an overview of open source business intelligence. It discusses key open source BI platforms like Pentaho, SpagoBI, Jaspersoft, and Palo. It outlines the history and components of each platform. The document also covers topics like open source cost savings, licensing issues, and the maturity of different open source BI technologies. Overall, the document serves as a guide to the major players and concepts in the open source BI landscape.