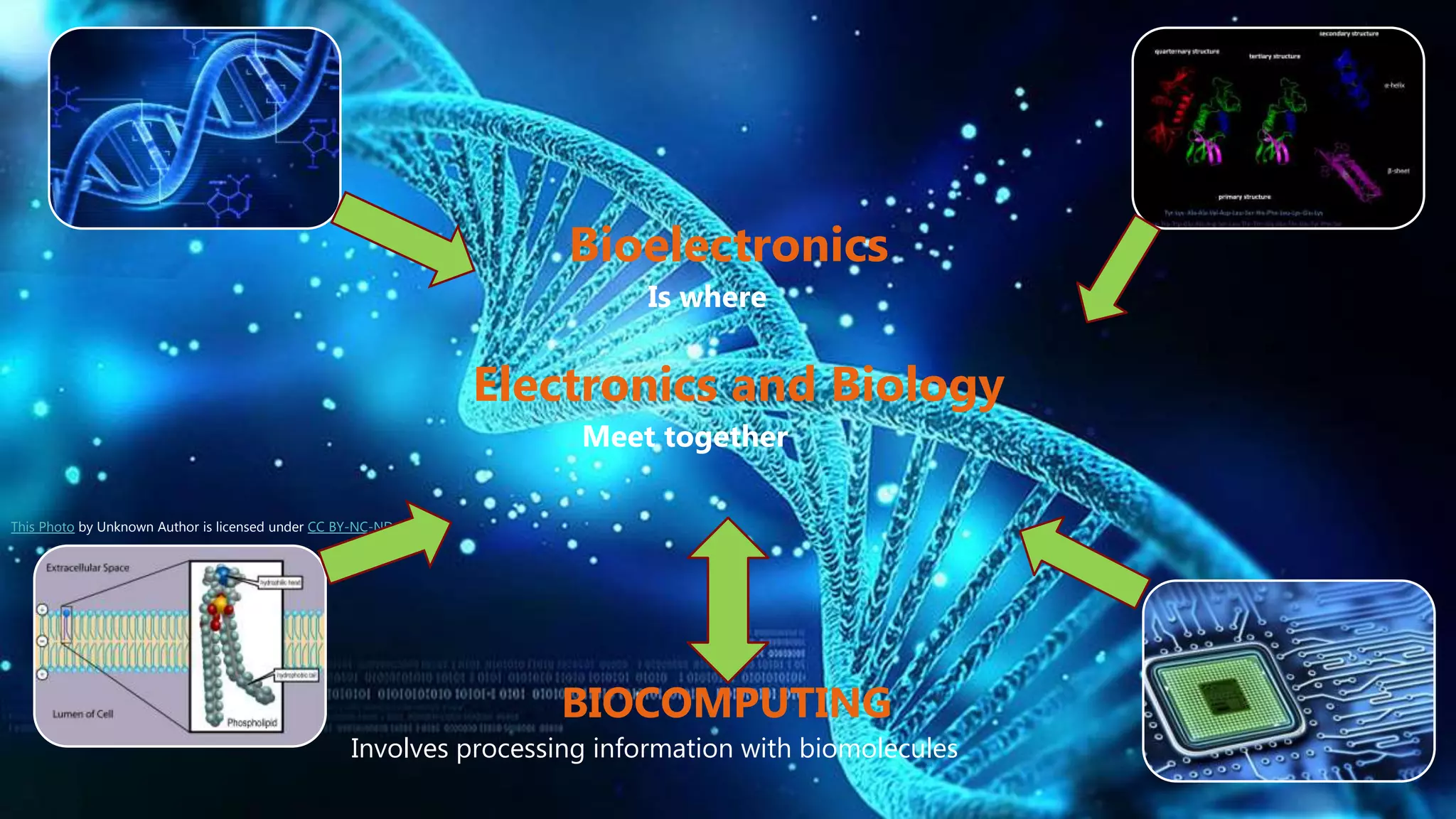
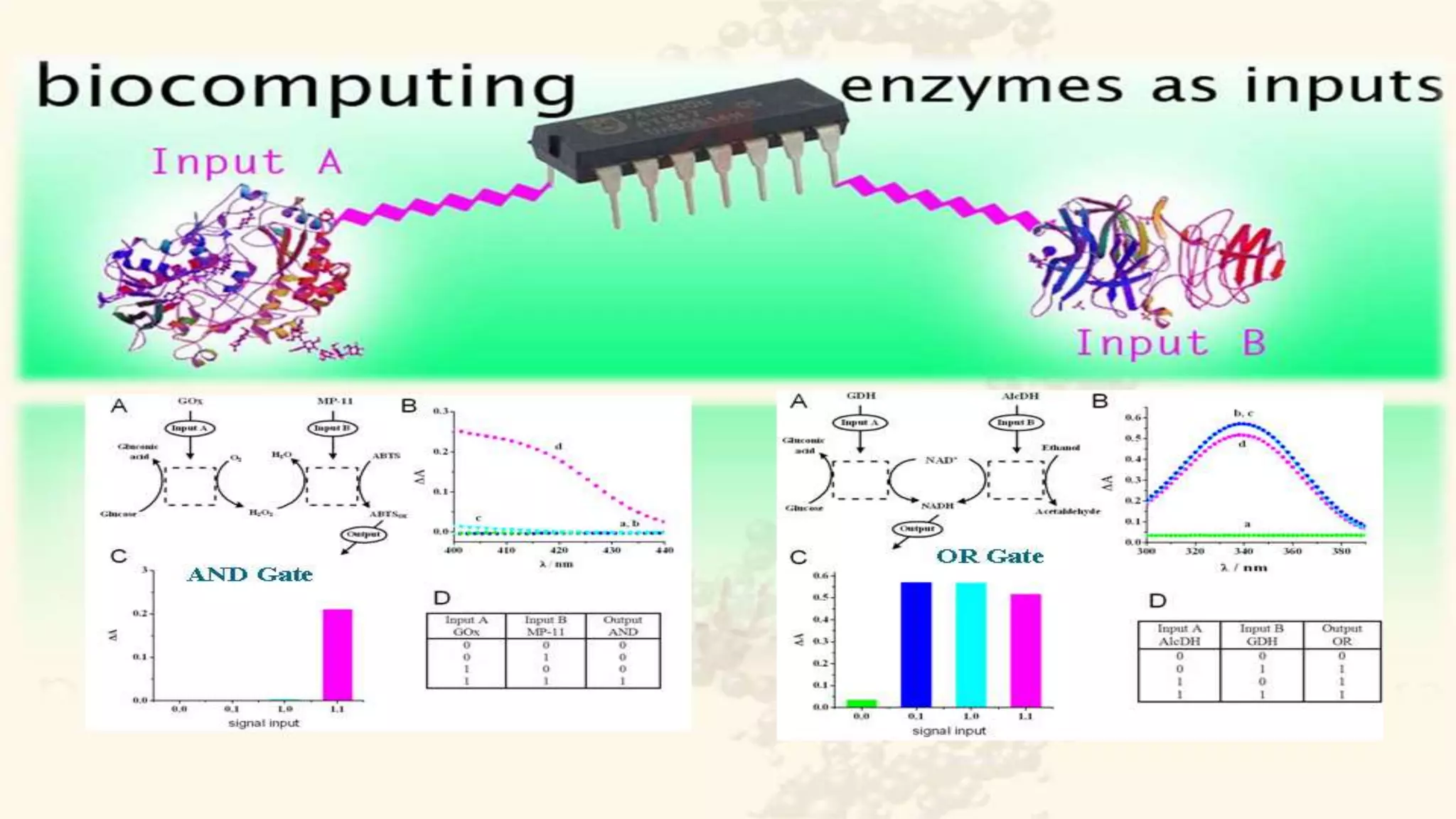
This document provides an overview of bio computers. It discusses that bio computers use biological molecules like DNA and proteins to store, retrieve, and process data, enabled by nanobiotechnology. There are three main types: biochemical computers use feedback loops in biological reactions; biomechanical computers rely on molecules adopting physical configurations under conditions; and bioelectronic computers measure electrical conductivity of designed biomolecules. While bio computers could potentially store vastly more data than silicon-based computers and be smaller, they currently operate more slowly and require human assistance. The future potential of bio computers is unknown, as capabilities have yet to surpass conventional computers, but some believe there is great potential.