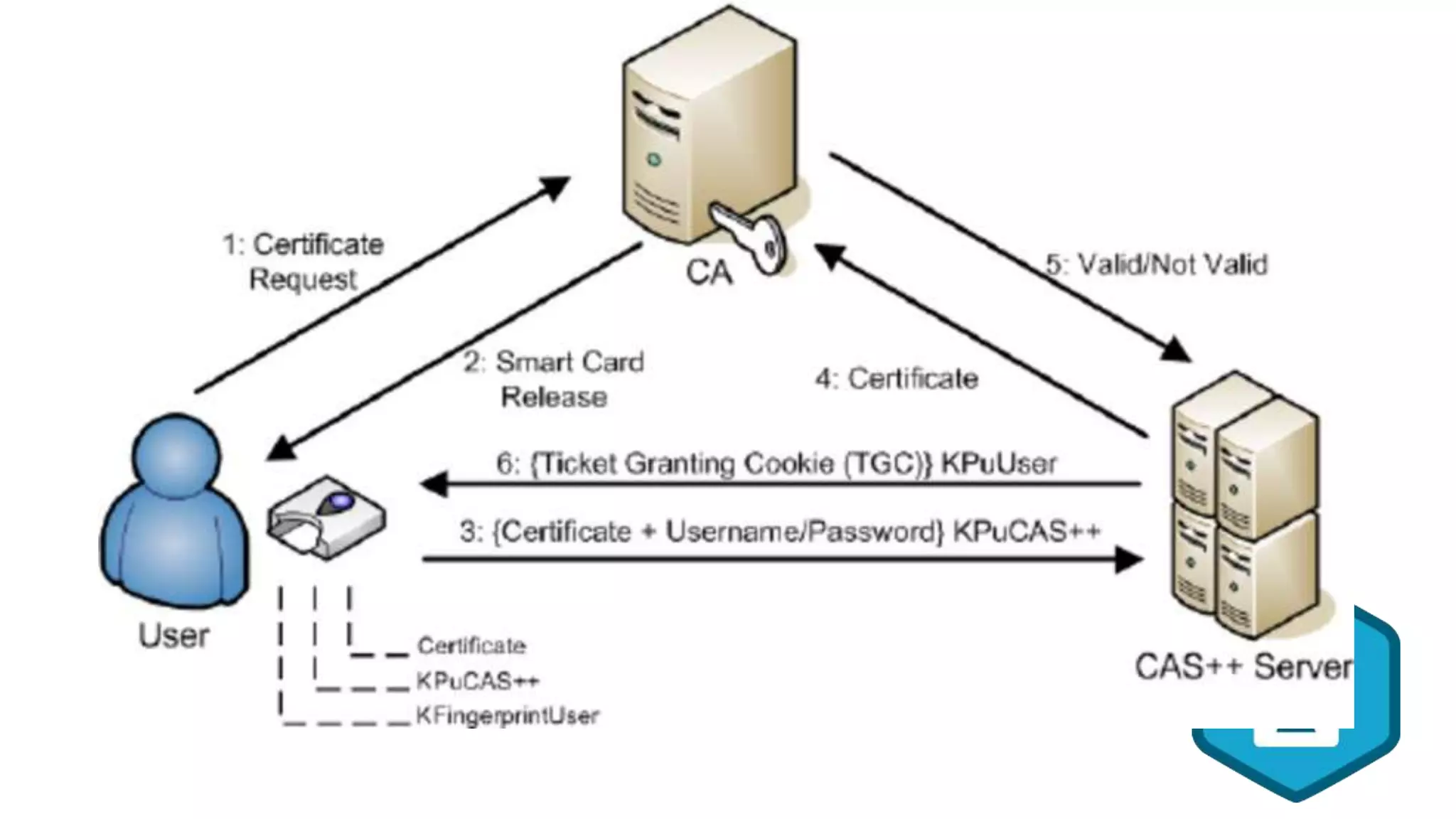
Broken authentication and authorization can occur when authentication and authorization functions are not implemented correctly, allowing attackers to compromise credentials and exploit flaws. This can lead to valuable business information being leaked, customer dissatisfaction, and financial losses. Issues can be addressed through measures like strong password policies, access control, validating users, and server-side validation. Known security incidents provide examples like personal information of millions being leaked through an API or robberies occurring due to unauthorized access to cash transit details.