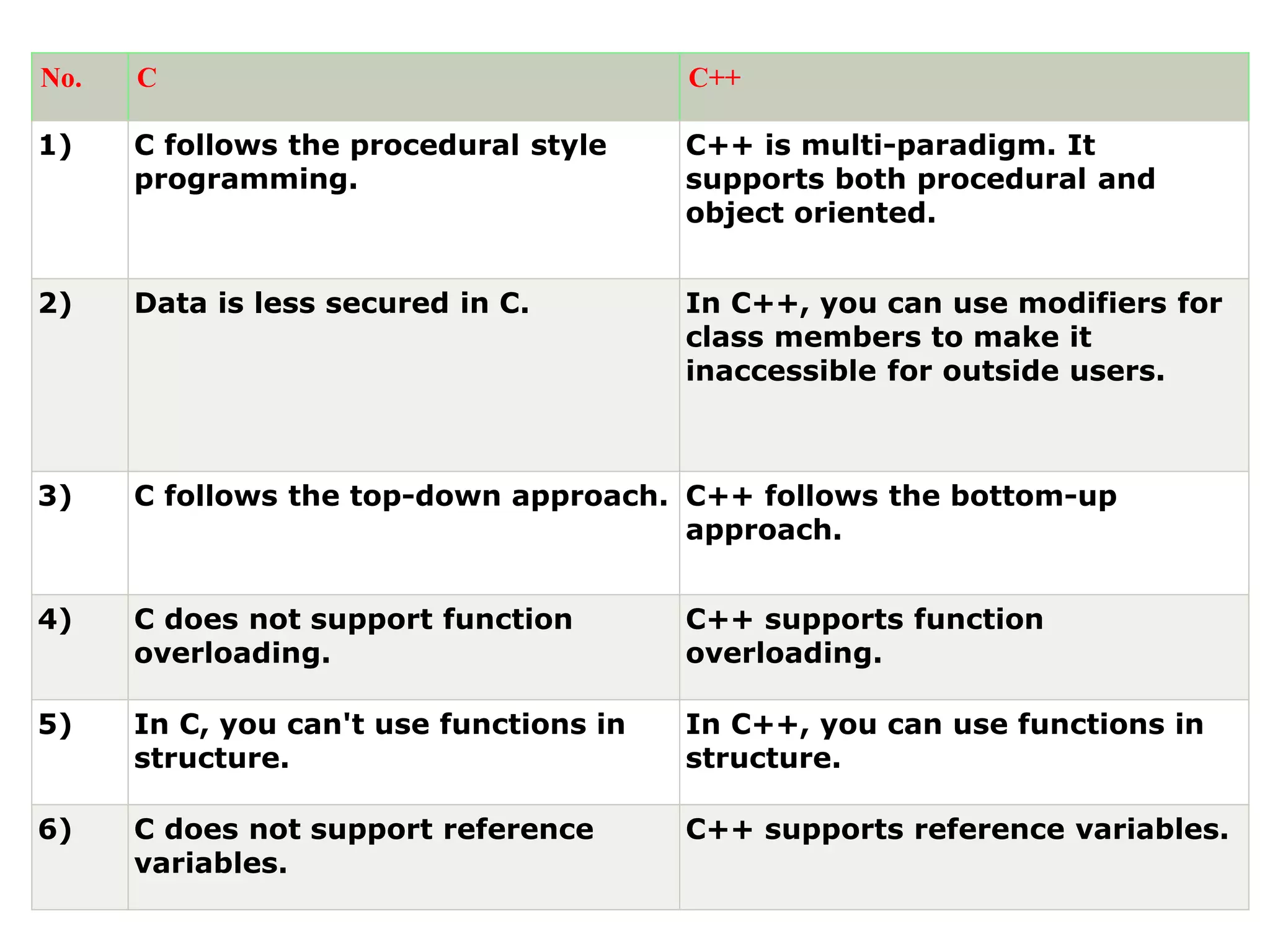
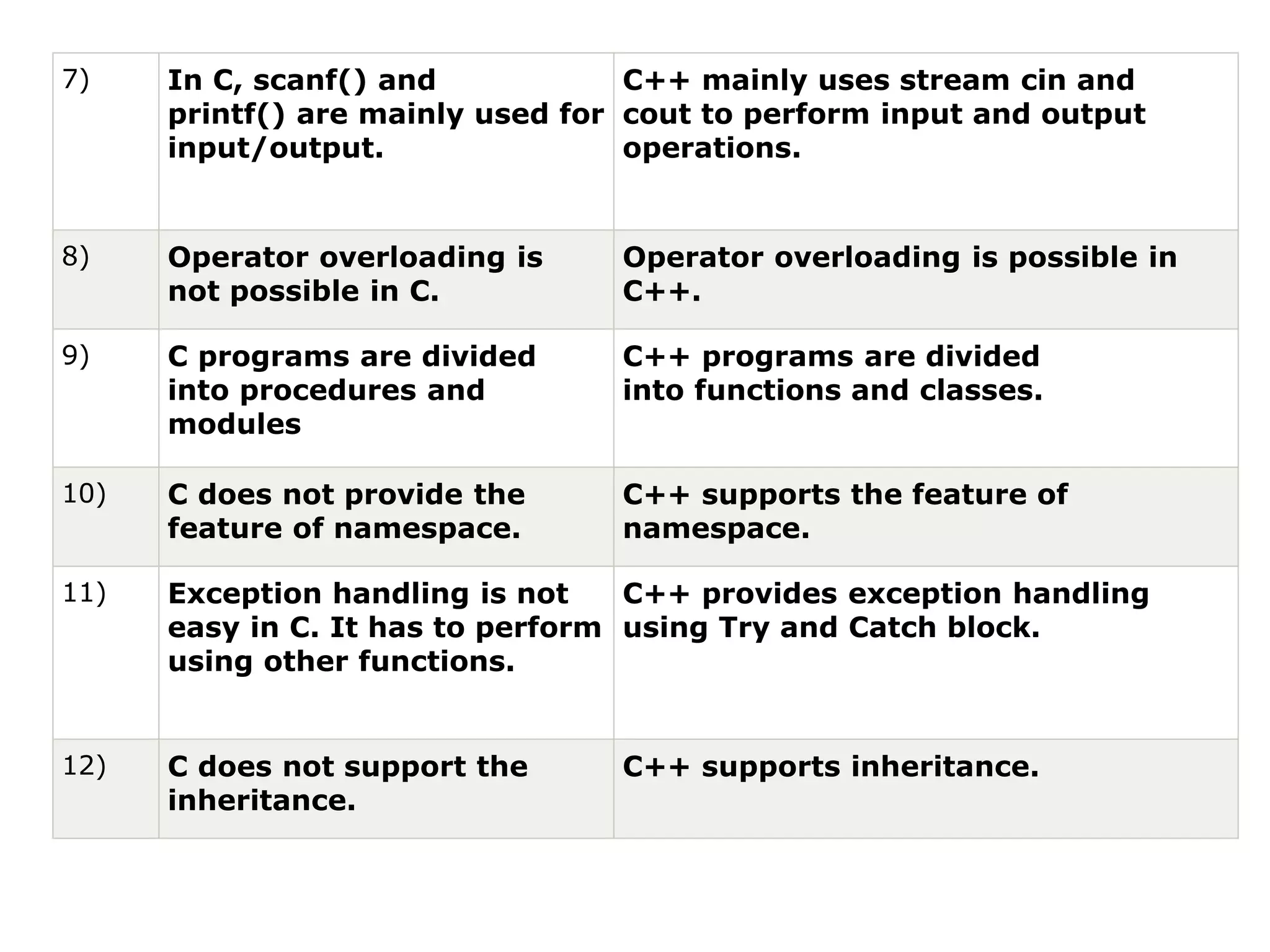
This document compares key differences between C and C++ programming languages. It lists 12 points of comparison between the two languages. Some key differences mentioned are:
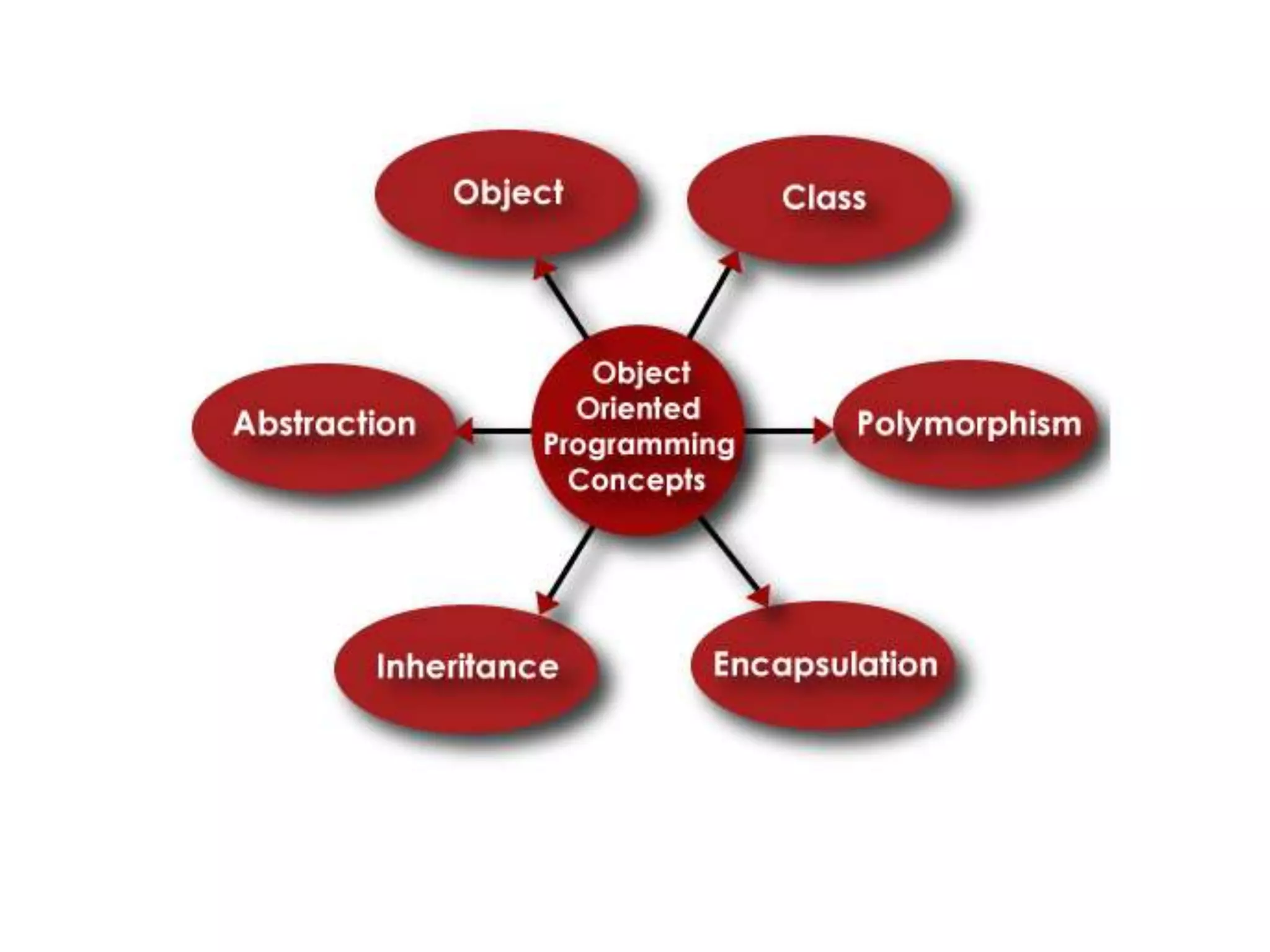
1) C follows procedural programming while C++ supports both procedural and object-oriented programming.
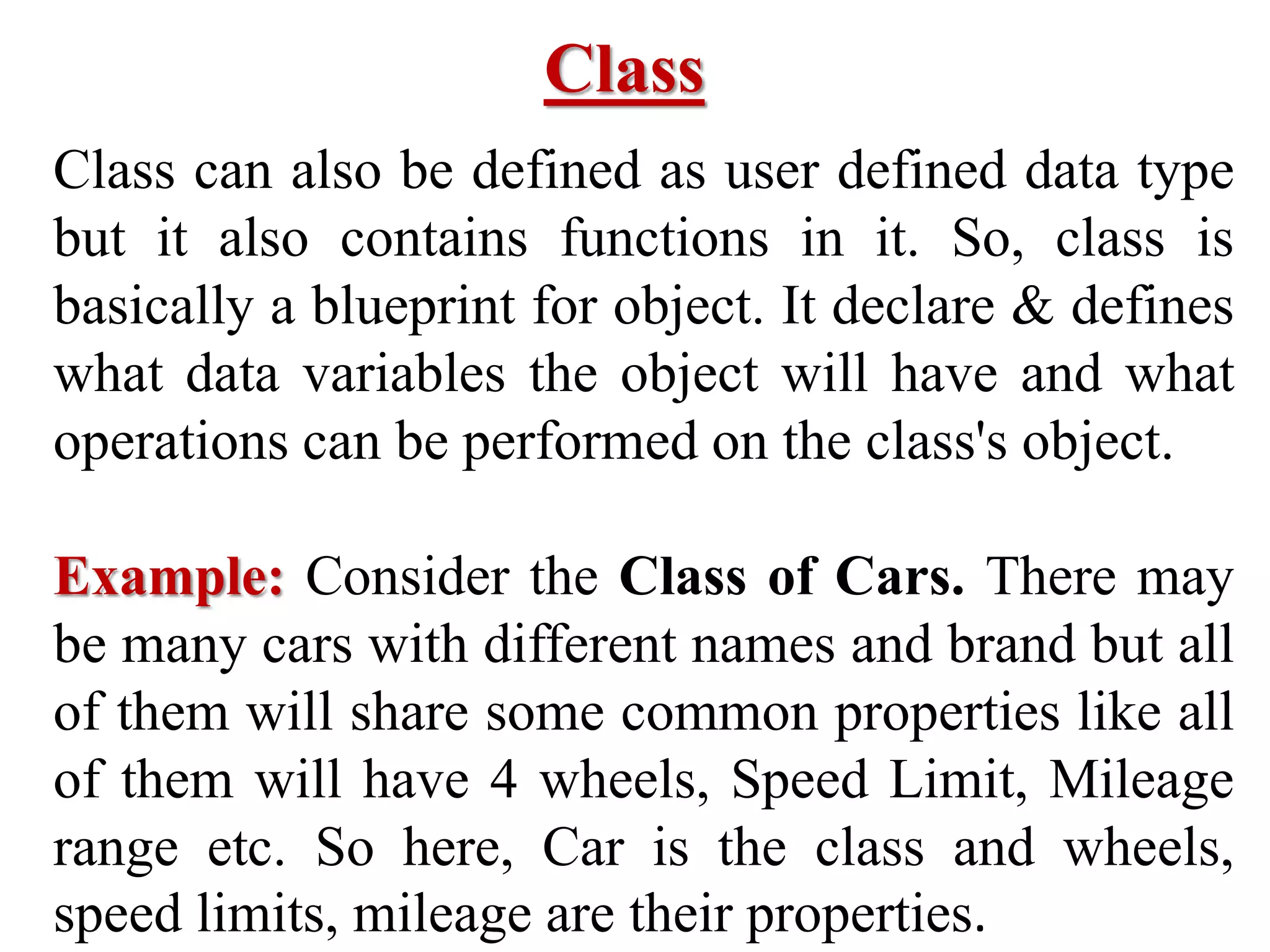
2) C++ allows for better data encapsulation and security through access modifiers for class members.
3) C follows a top-down approach while C++ follows a bottom-up approach.
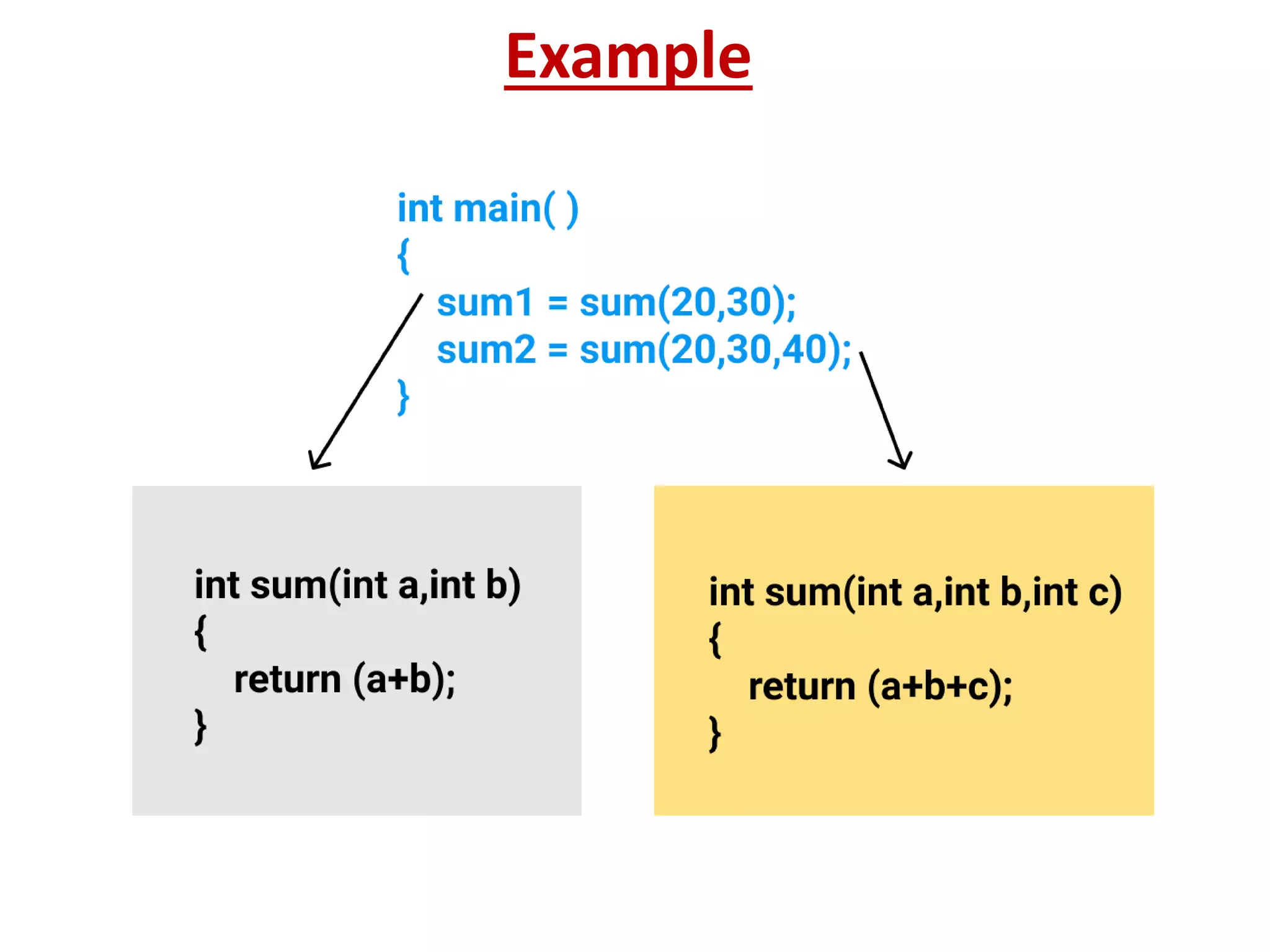
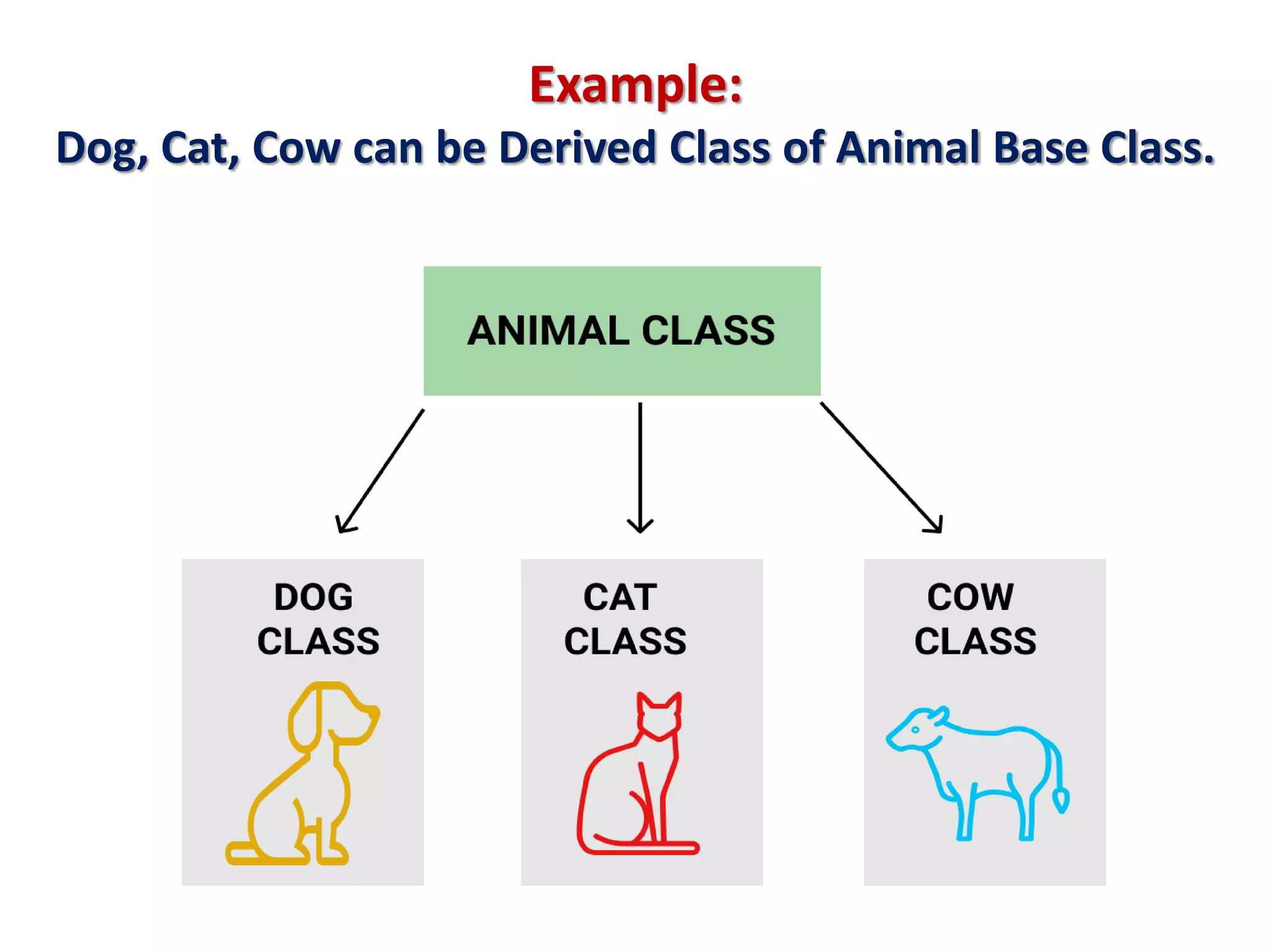
4) C++ supports features like function overloading, inheritance, exception handling, and namespaces that are not present in C.