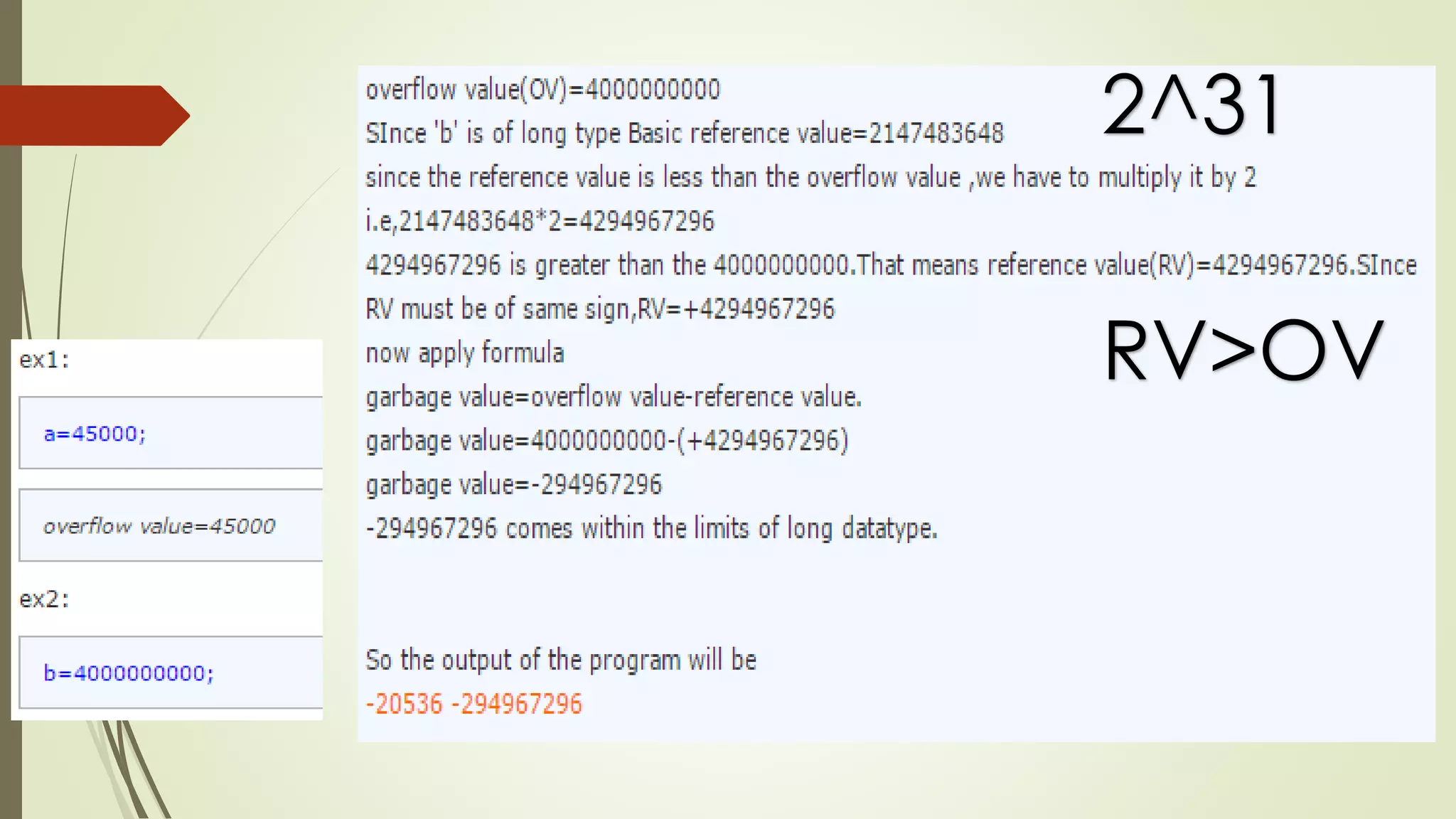
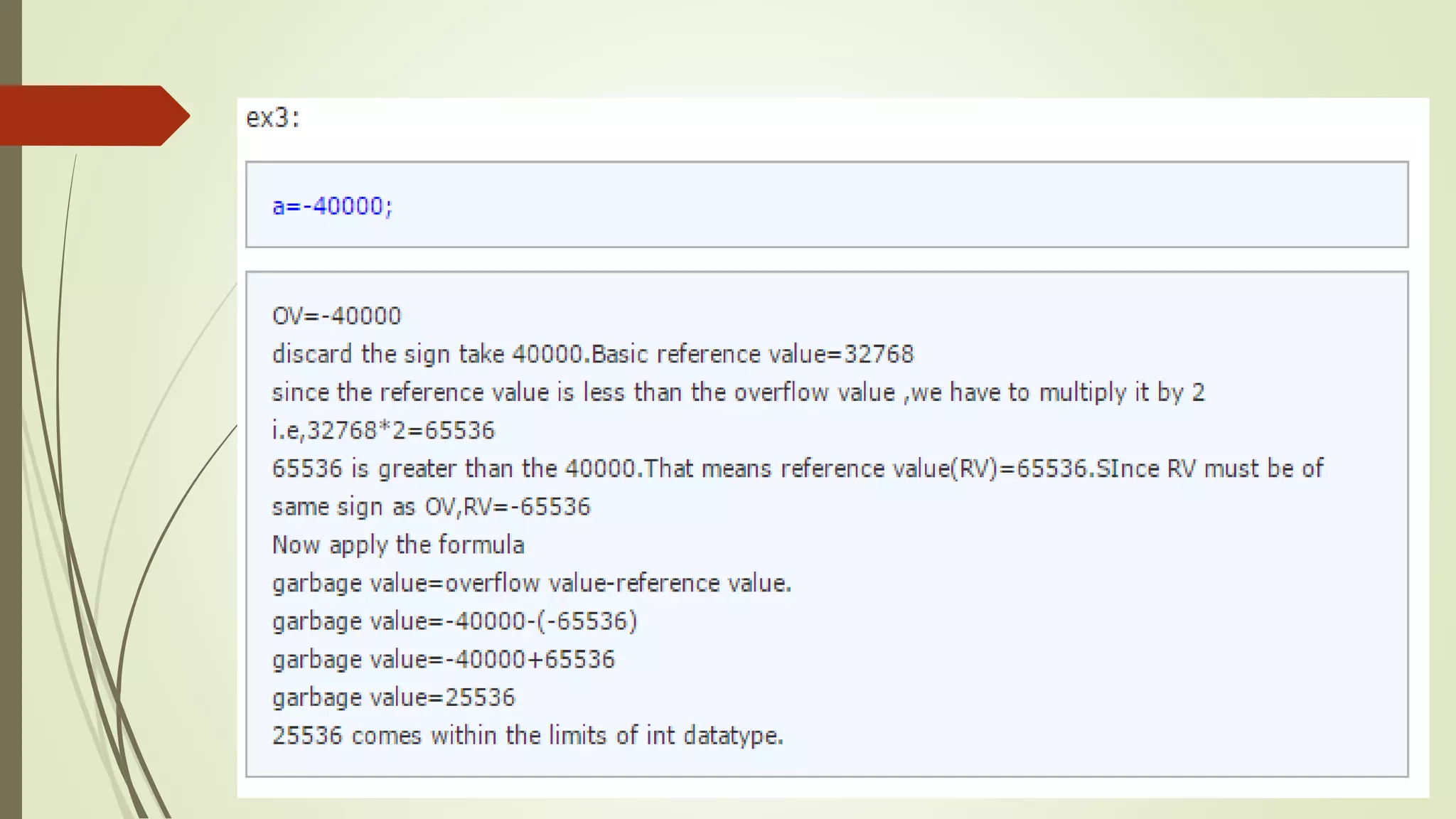
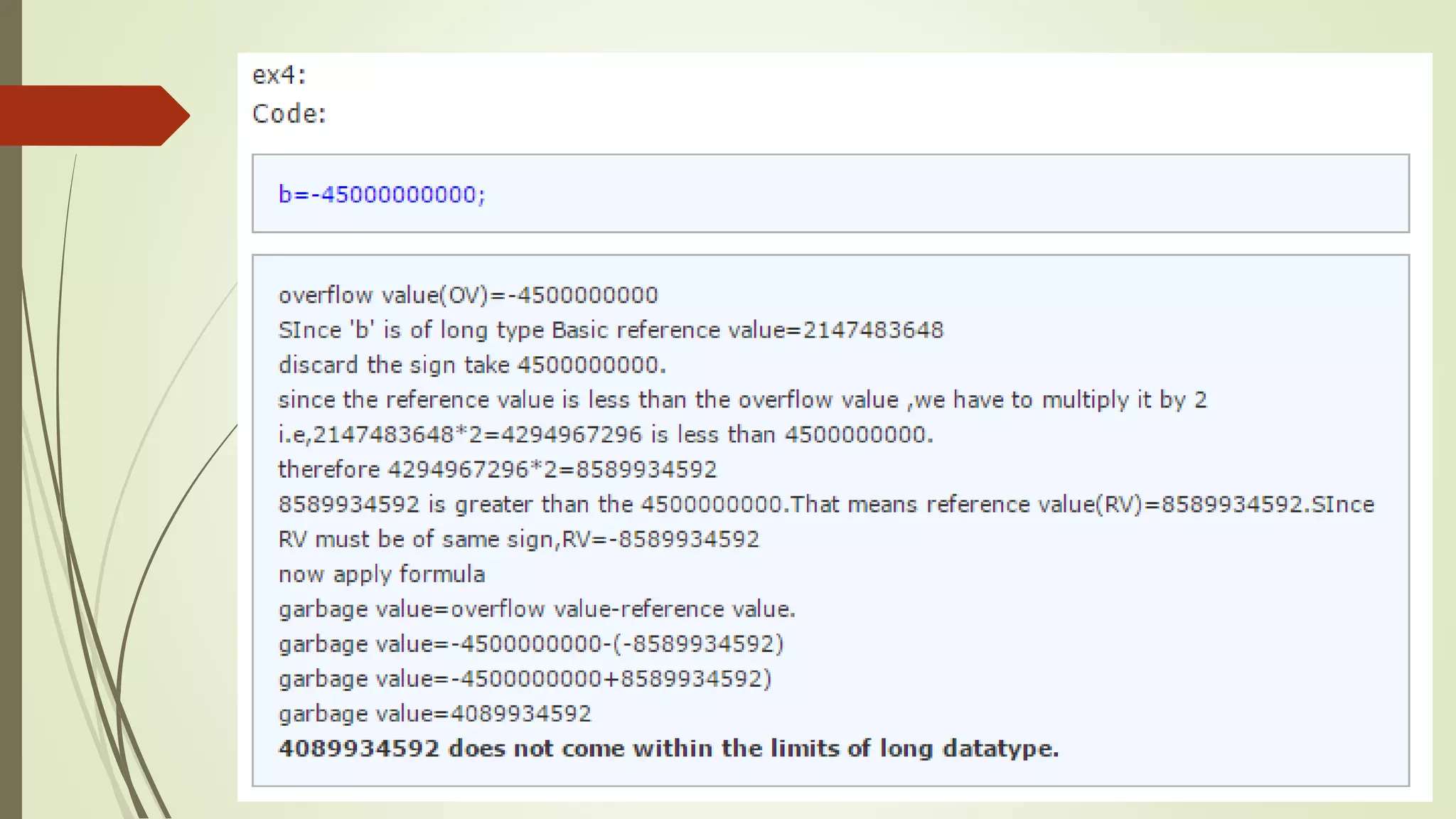
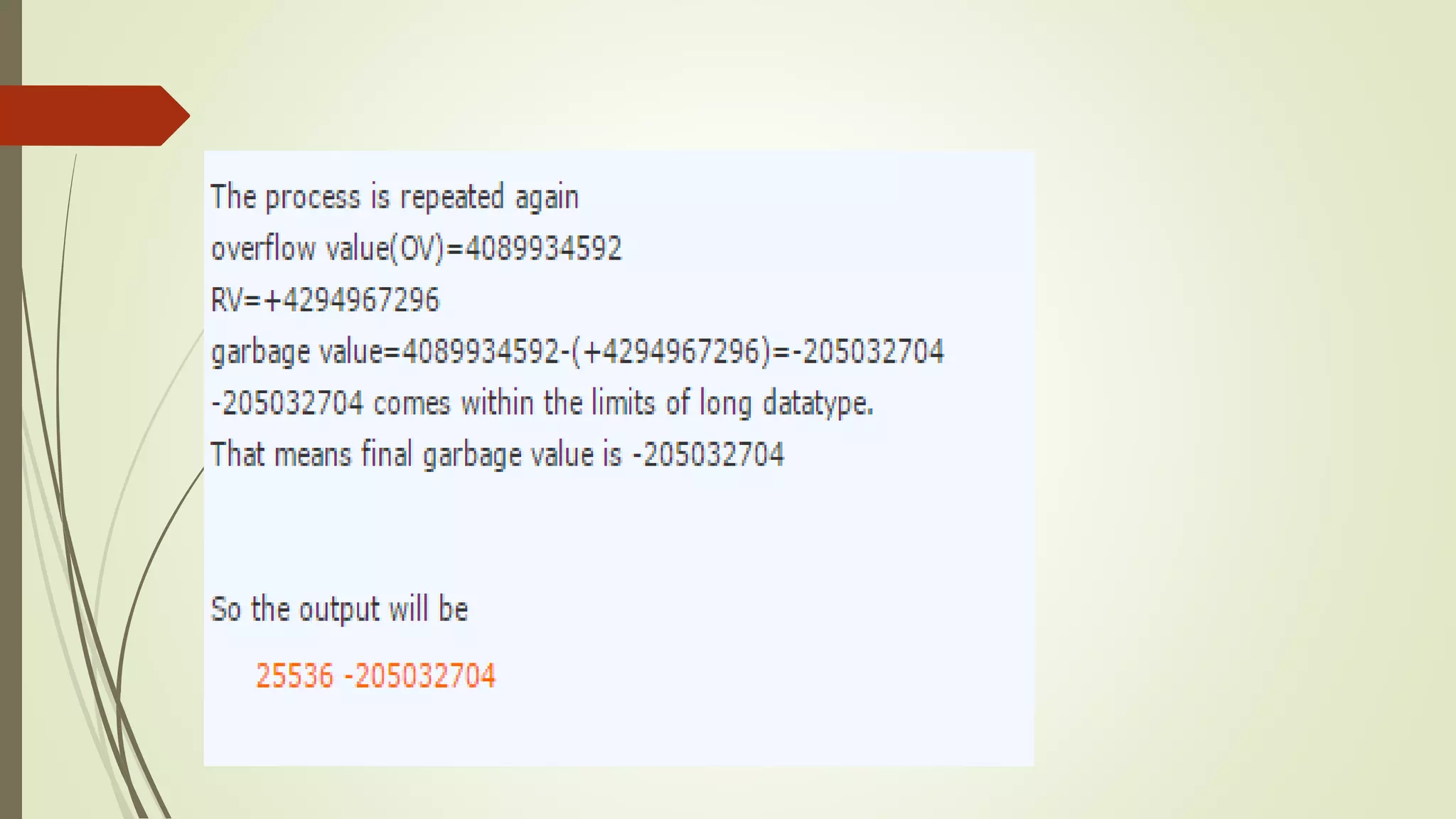
The document discusses garbage values in C programming, explaining that uninitialized variables can contain leftover values from previous operations, leading to erroneous results. It details how to avoid garbage values by properly initializing variables, and explains the bit allocation and maximum values for different data types (int, long). The concept of calculating garbage values is also covered, providing a formula and example calculations for clarity.