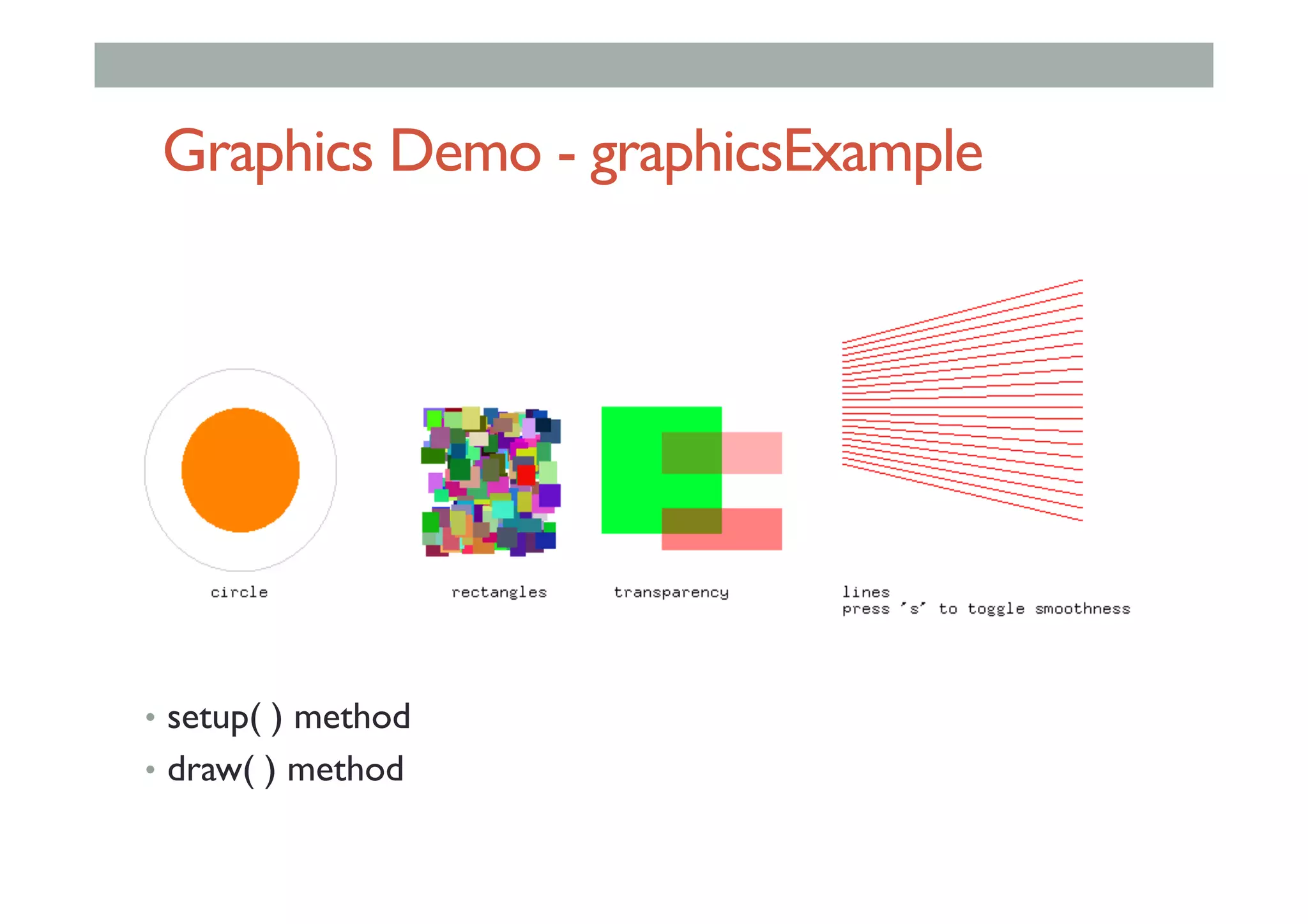
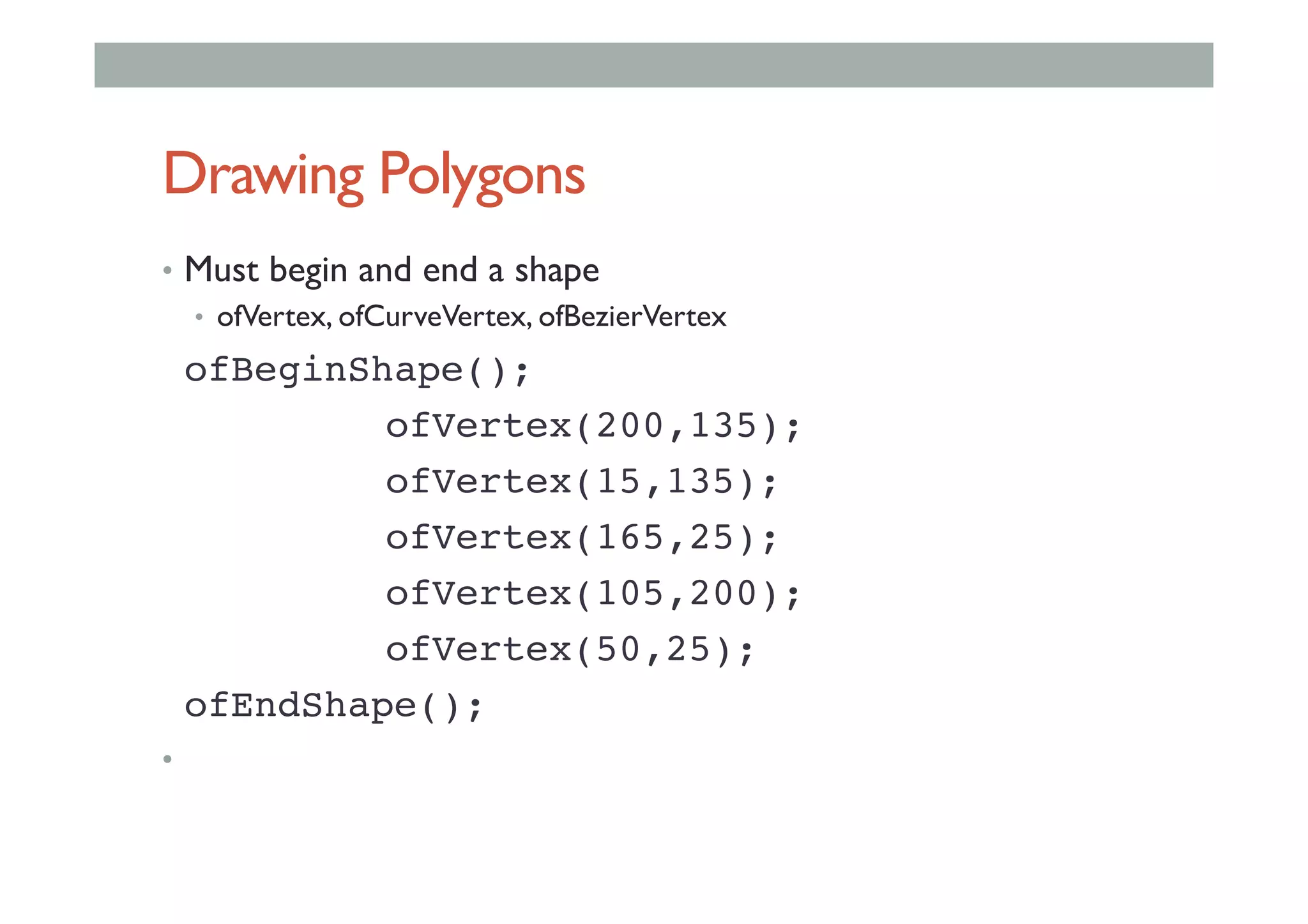
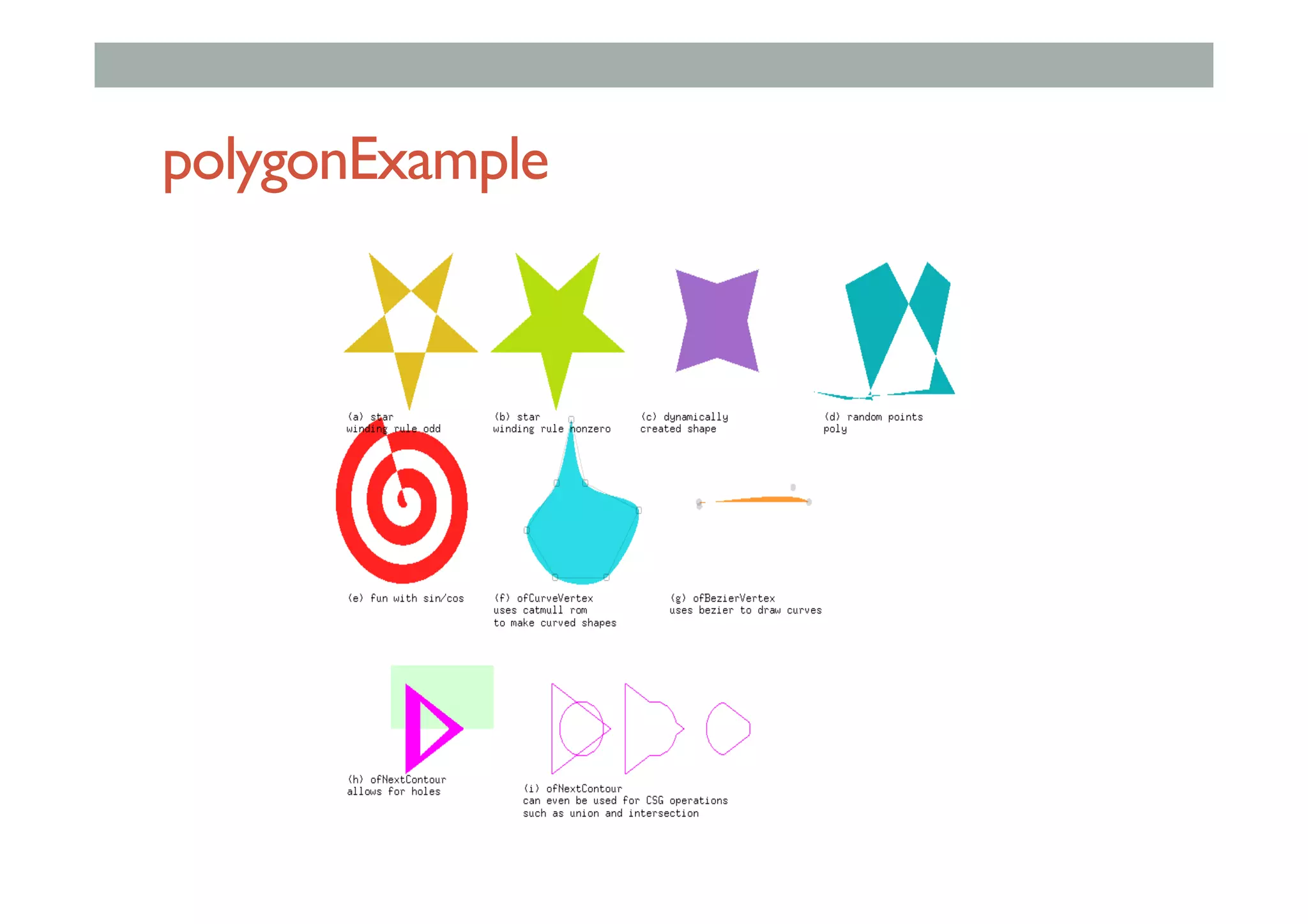
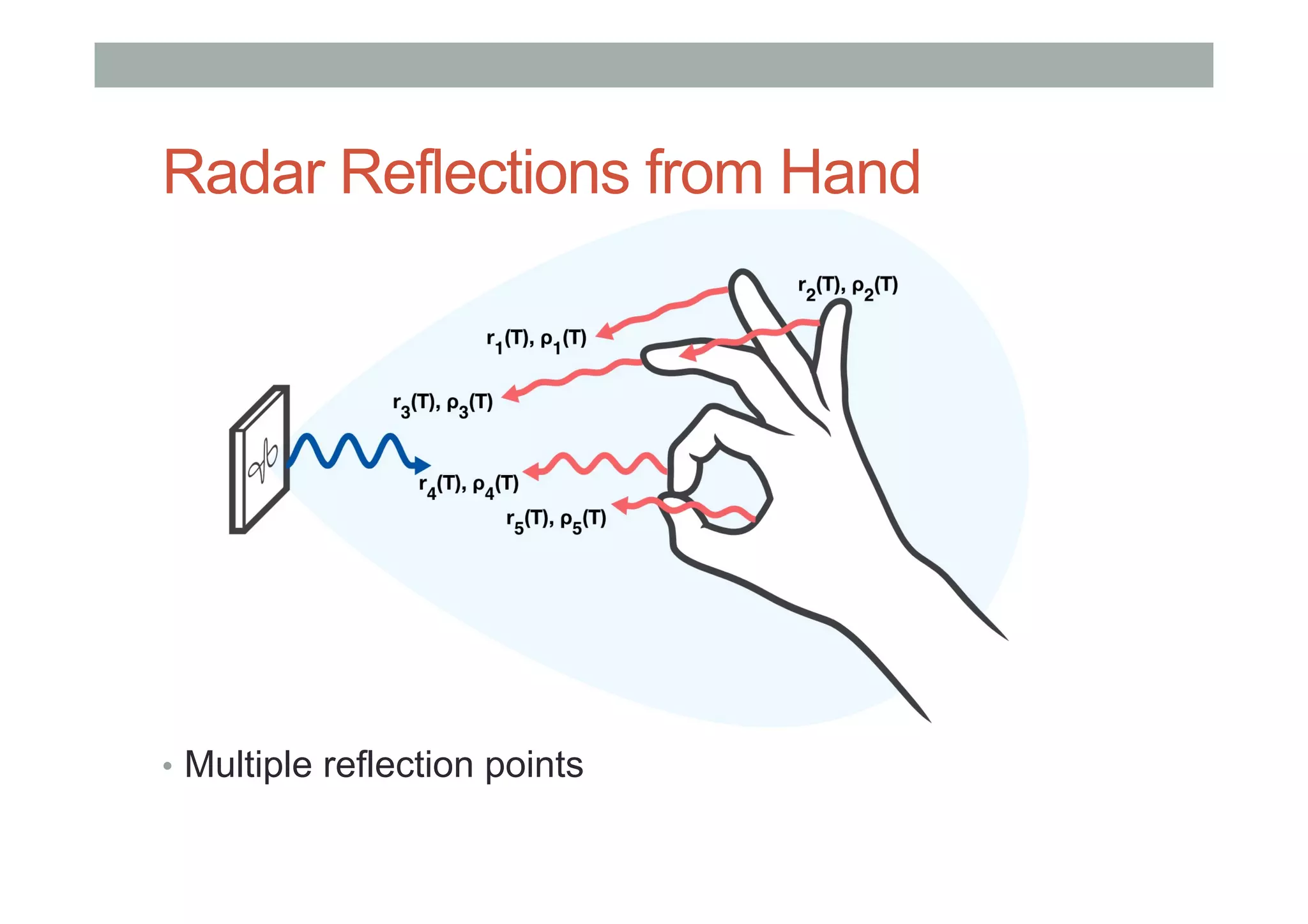
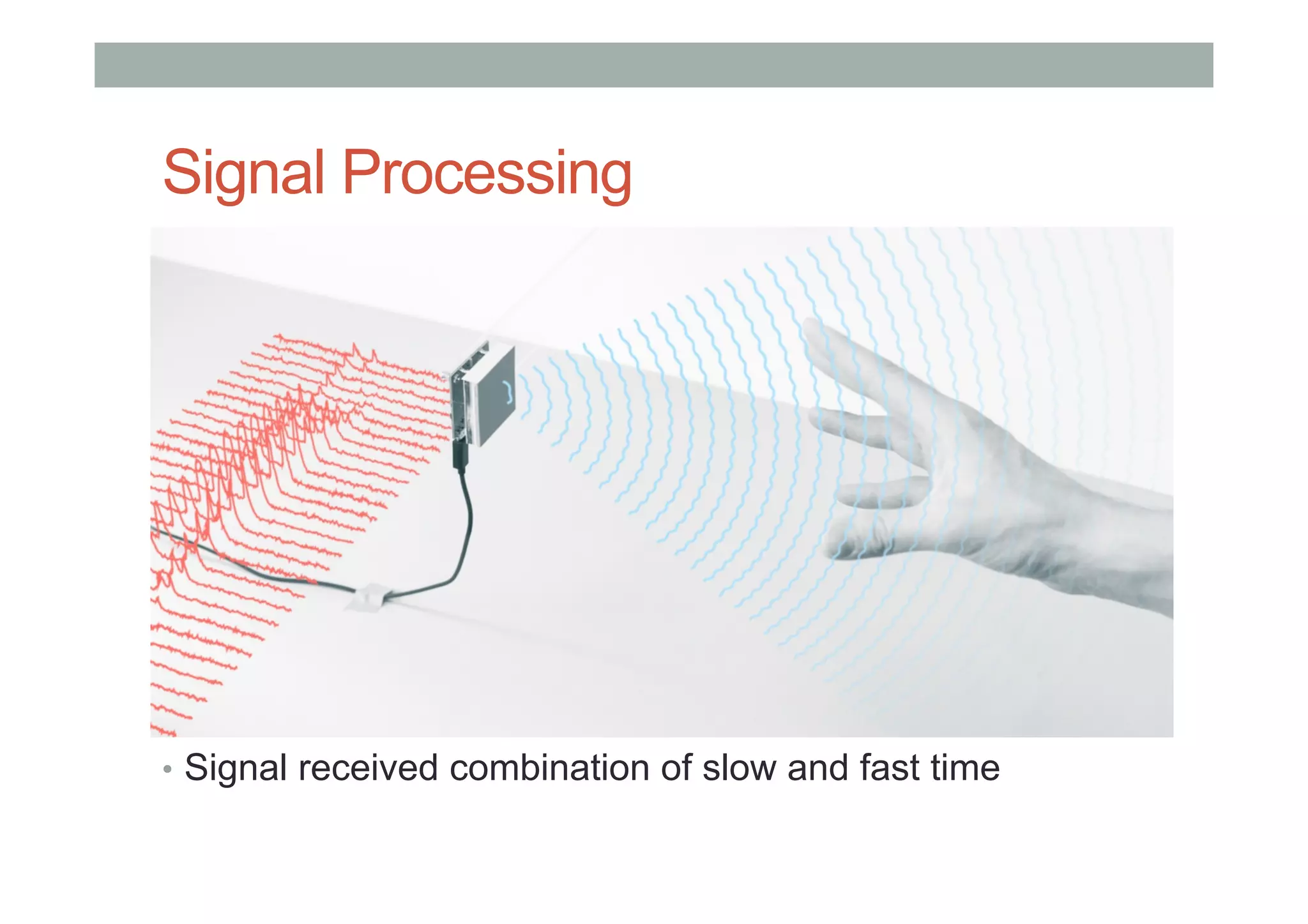
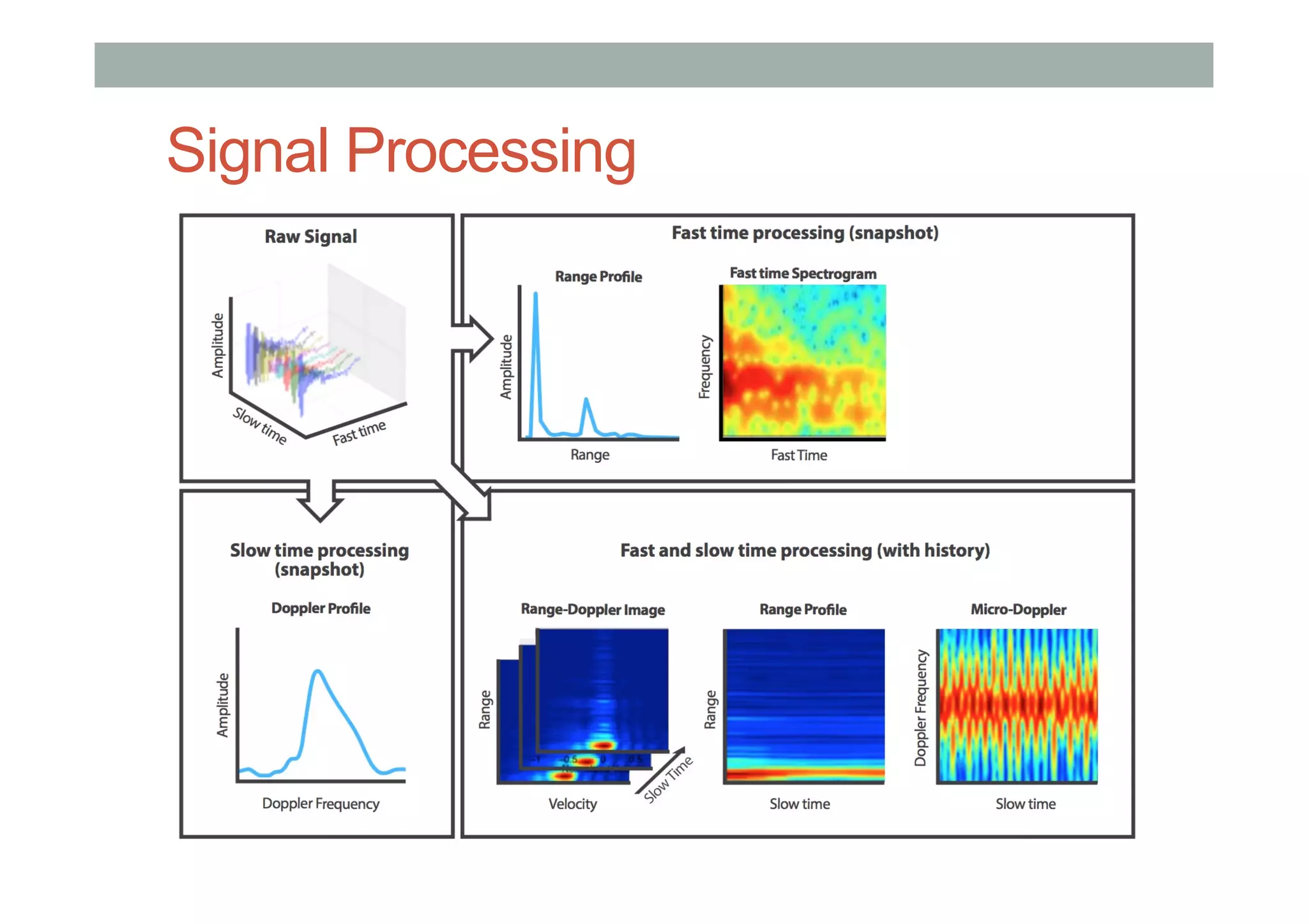
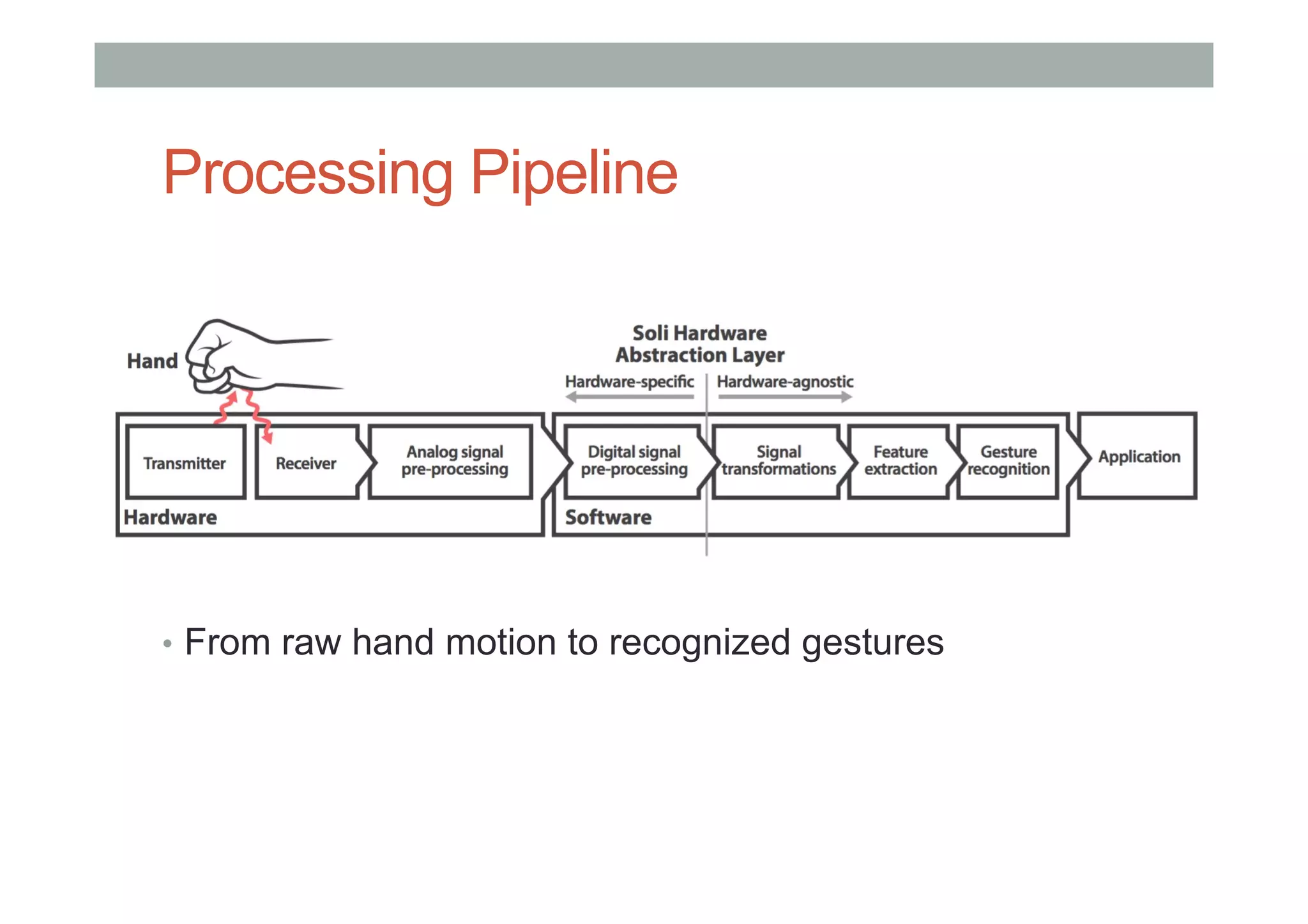
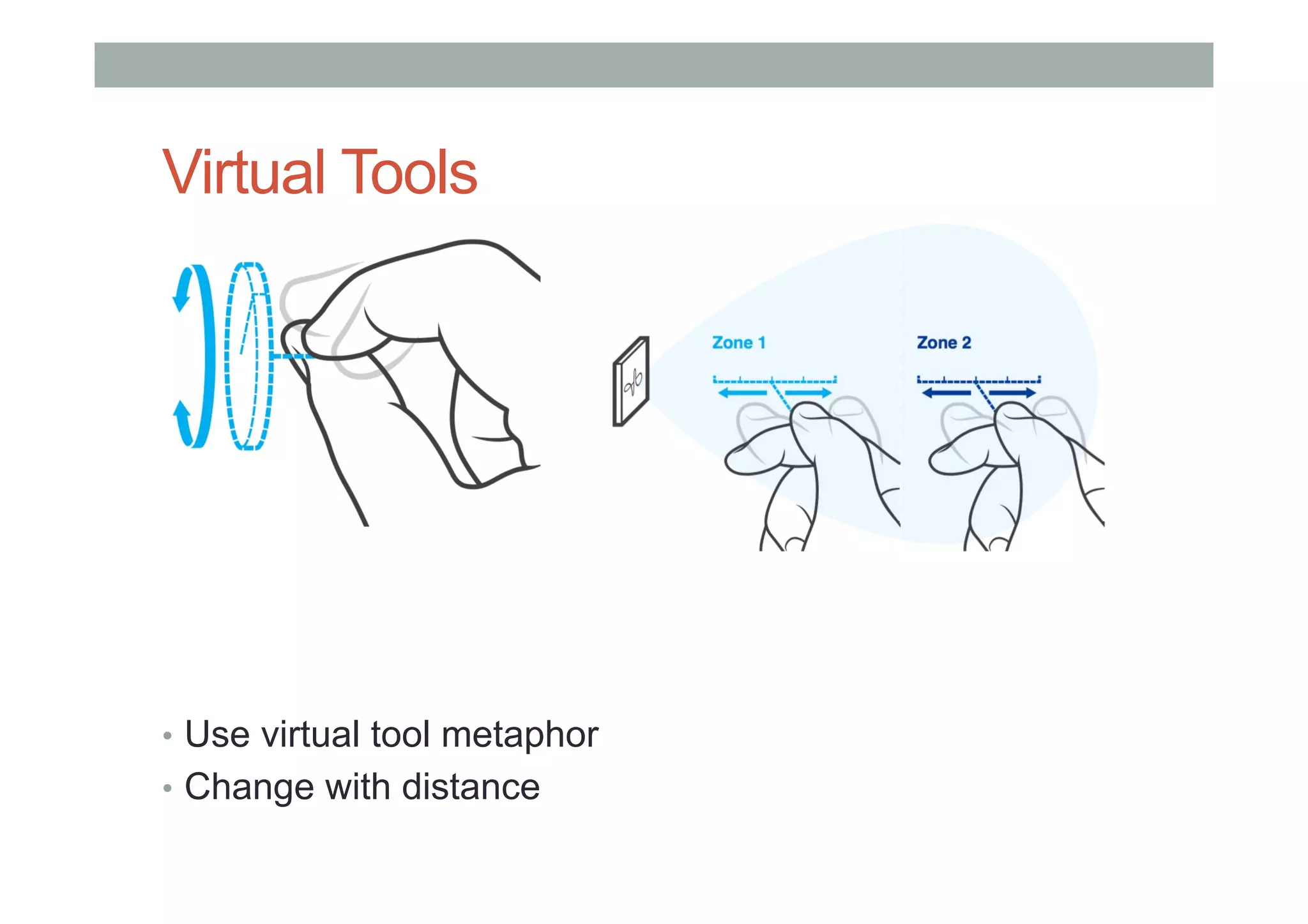
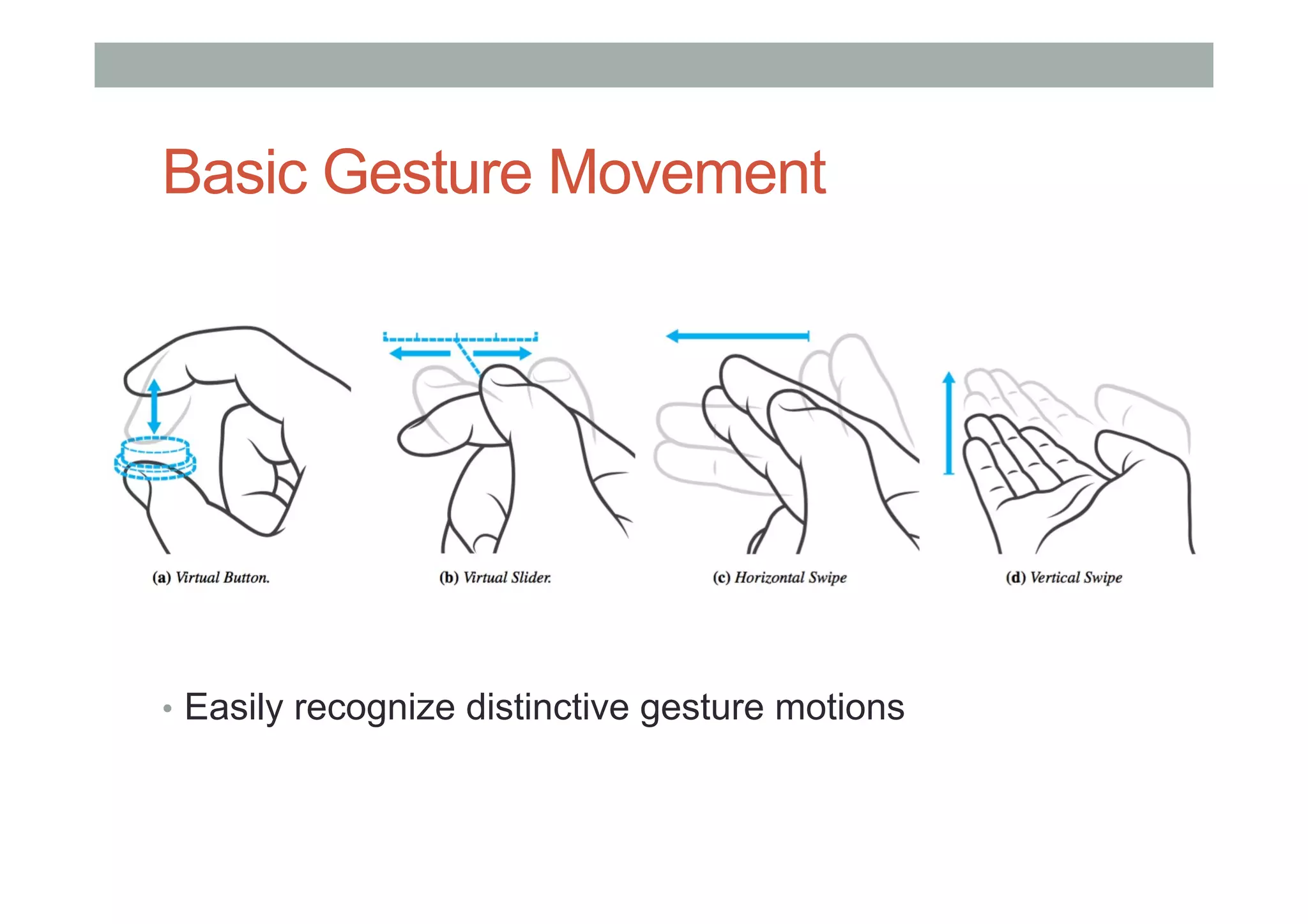
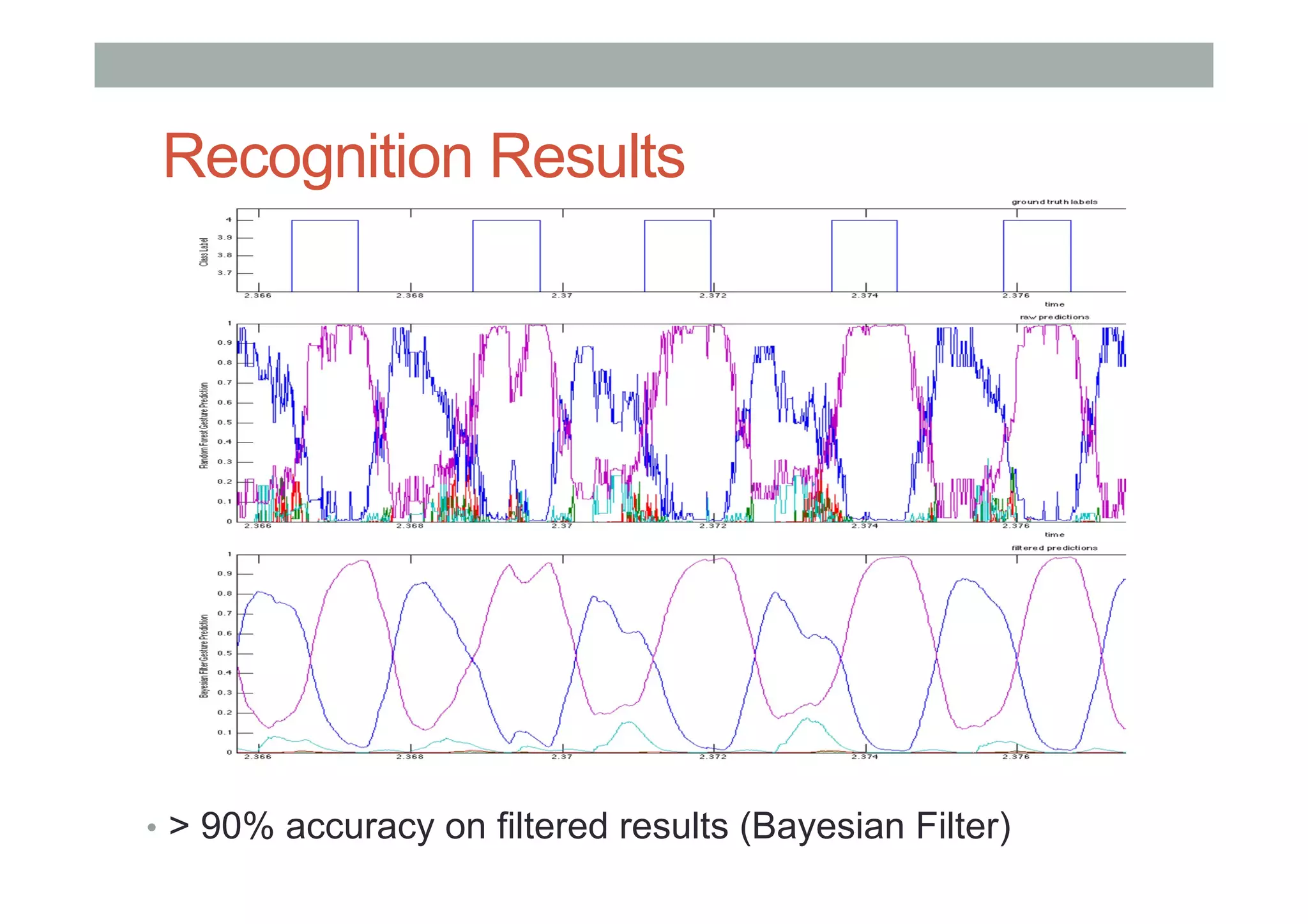
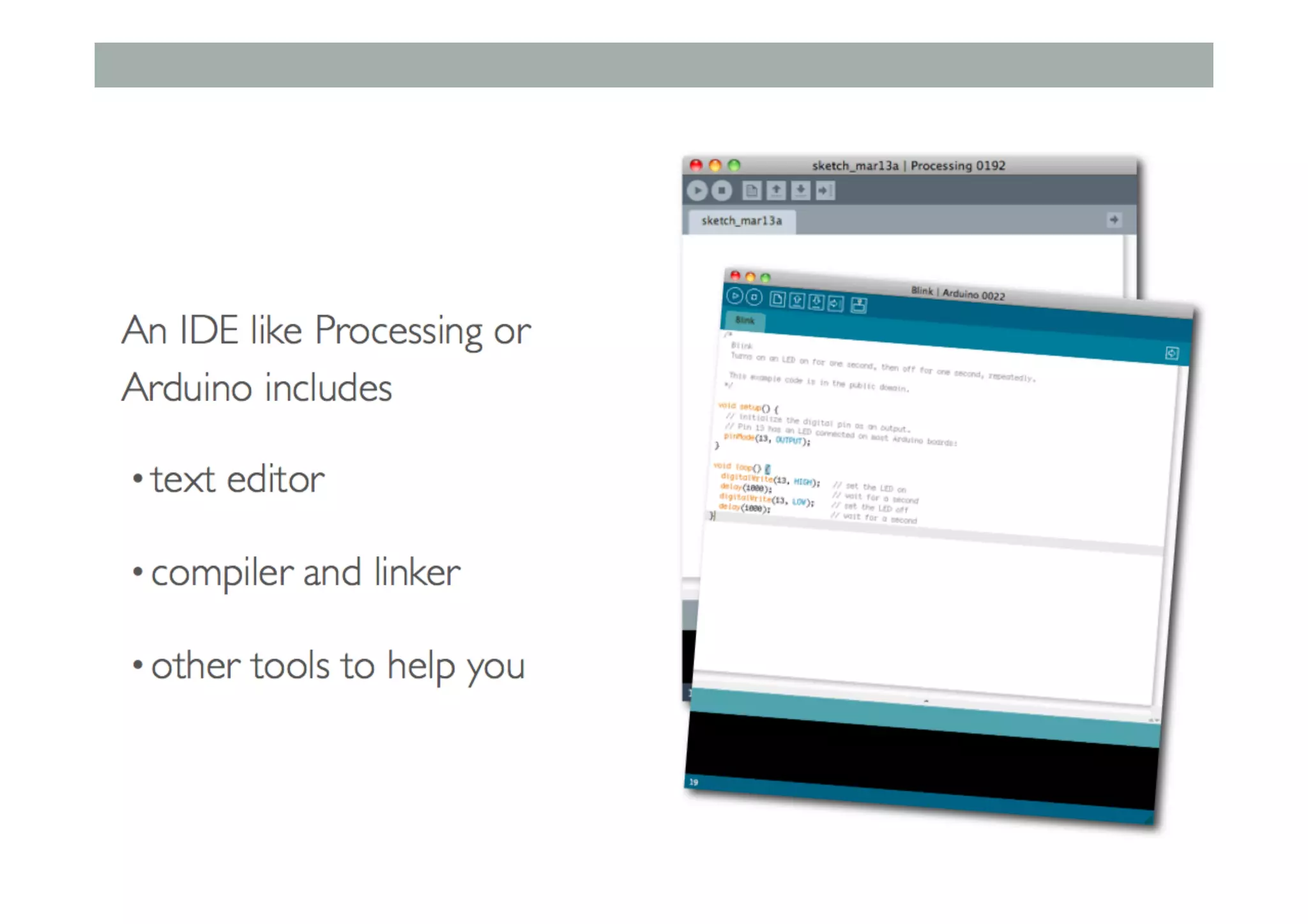
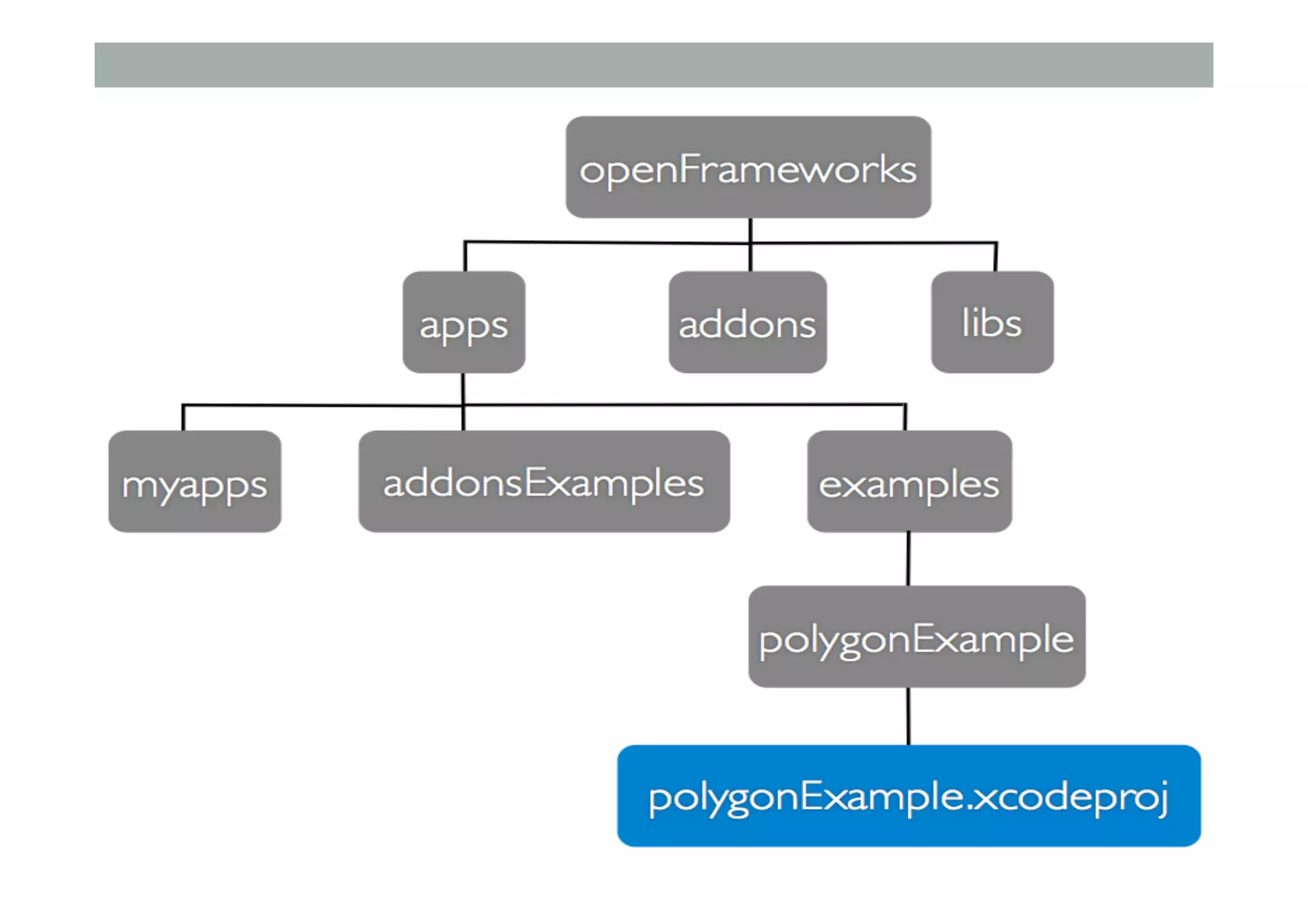
This document outlines a lecture on advanced human-computer interaction technologies, focusing on wearable computing, augmented reality, virtual reality, and the Project Soli radar-based motion sensing technology. It details the process for a class project involving advanced technology design and covers OpenFrameworks as a toolkit for creative coding in C++. Key concepts discussed include the capabilities of wearable computers, the definition of augmented reality, and the programming nuances of C++ related to OpenFrameworks.






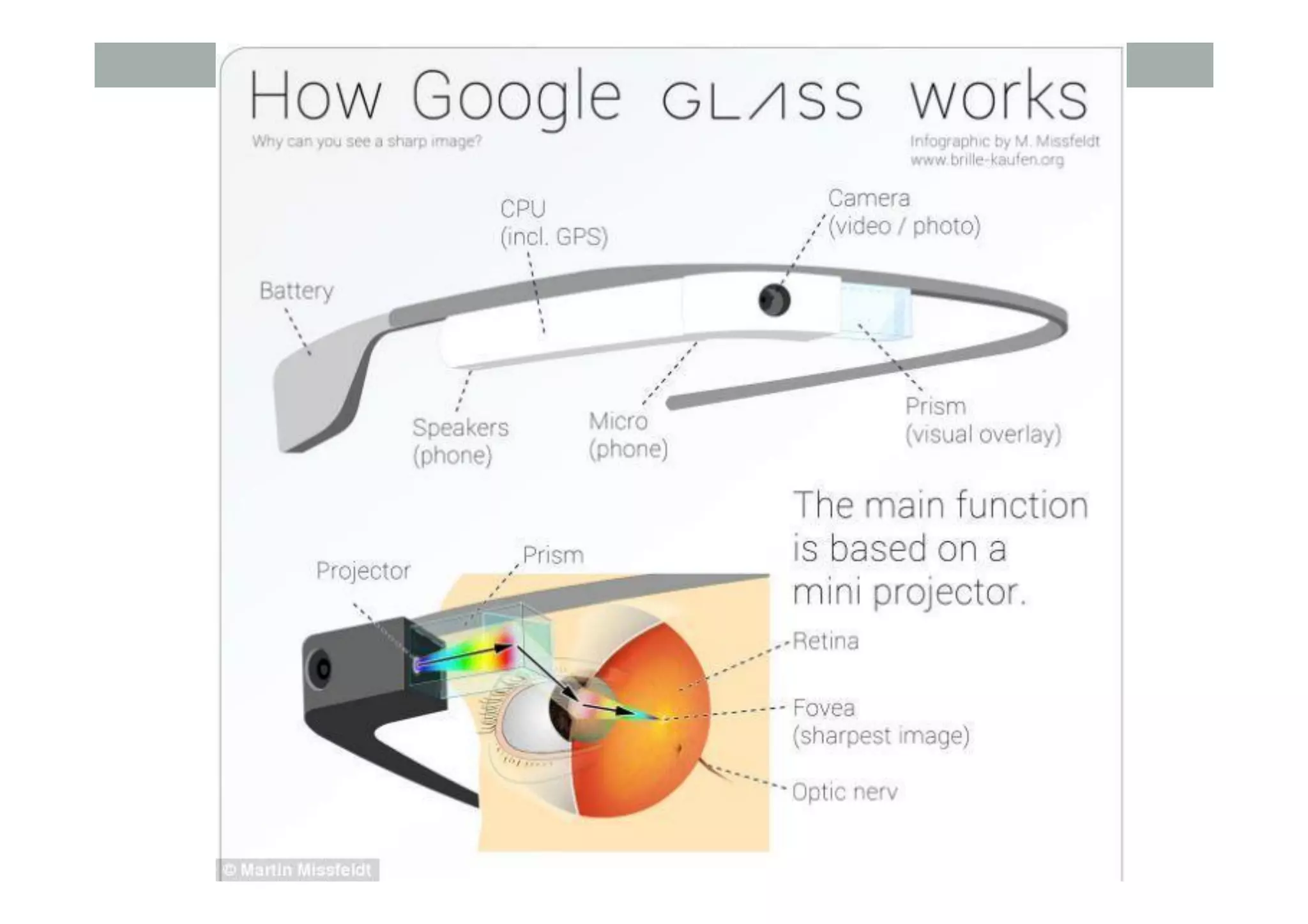
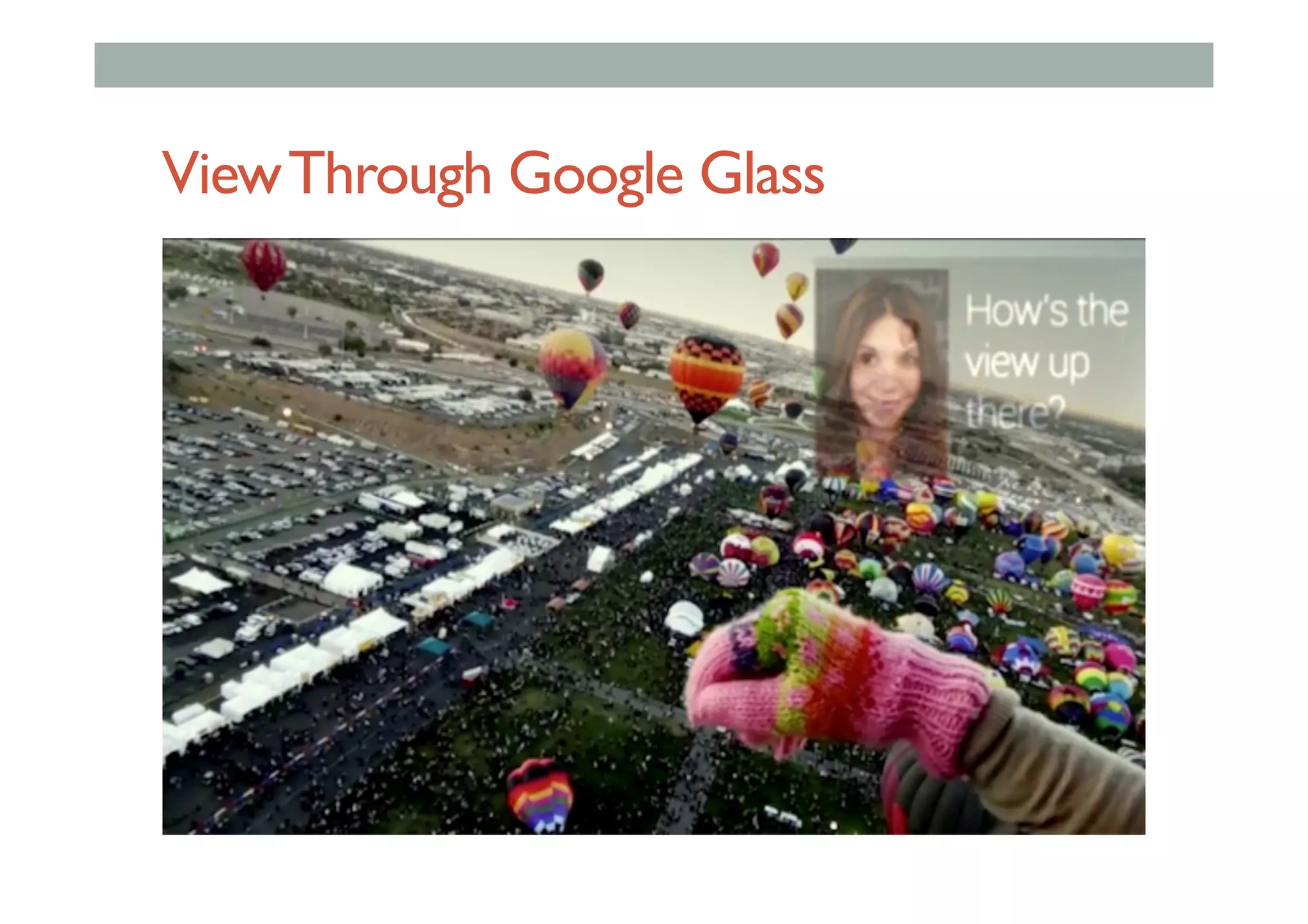

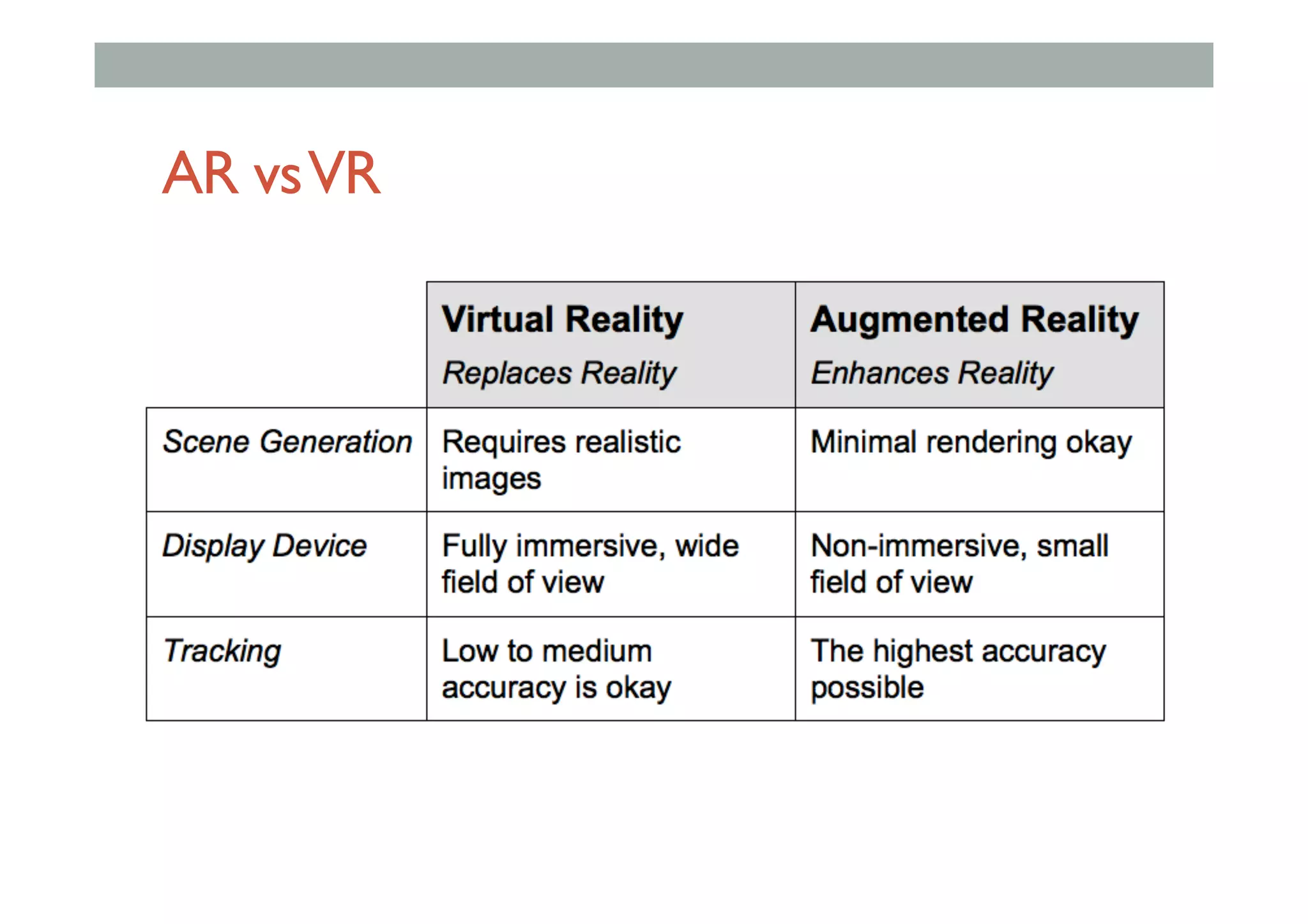
![Augmented Reality Definition
• Defining Characteristics [Azuma 97]
• Combines Real andVirtual Images
• Both can be seen at the same time
• Interactive in real-time
• The virtual content can be interacted with
• Registered in 3D
• Virtual objects appear fixed in space
Azuma, R. T. (1997). A survey of augmented reality. Presence, 6(4), 355-385.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-openframeworksfinal-160827070744/75/COMP-4026-Lecture-5-OpenFrameworks-and-Soli-11-2048.jpg)

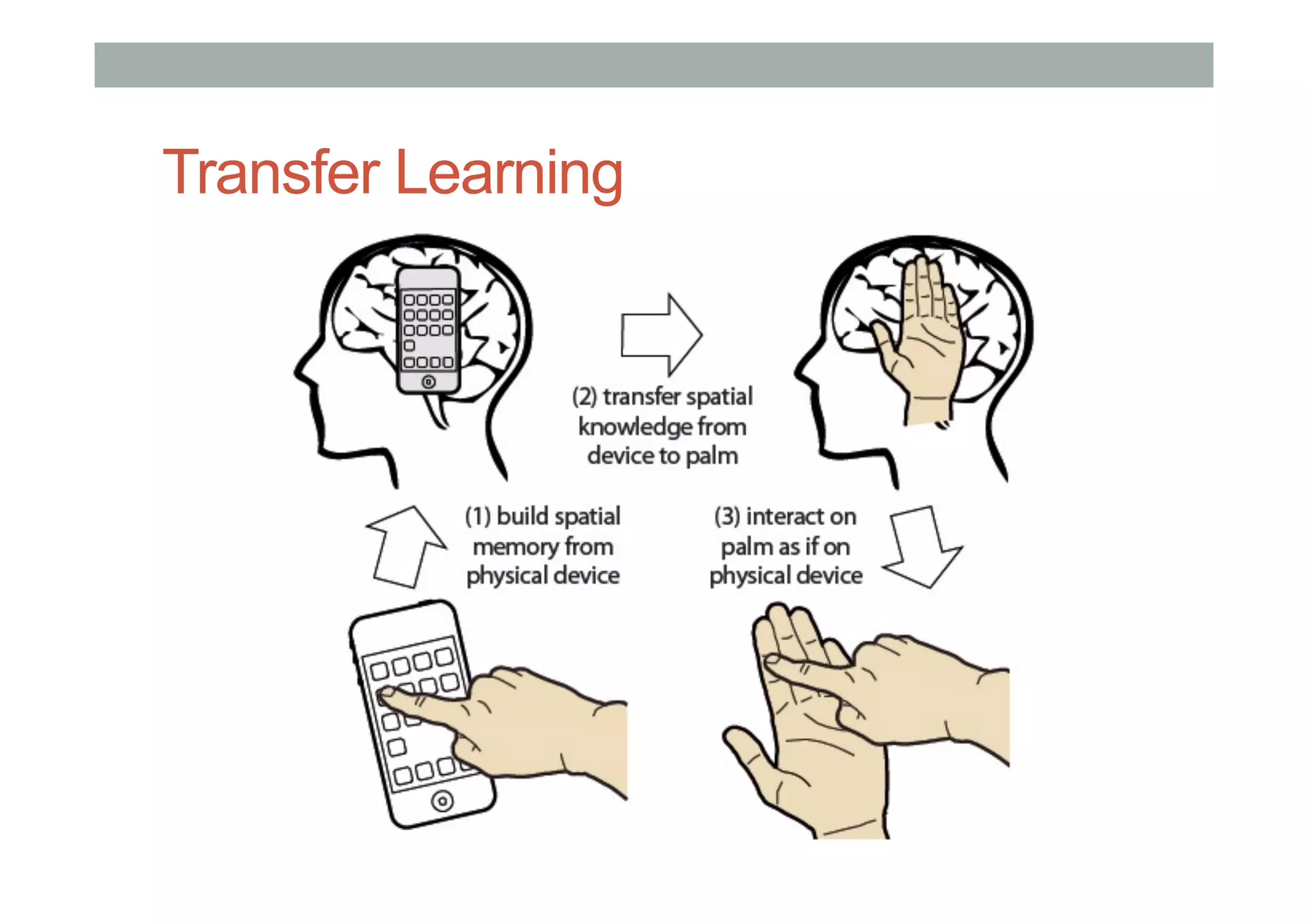
![Early Examples
• Interaction without devices:
• BodySpace [Strachan 2007]: Functions to body position
• Abracadabra [Harrison 2007]: Magnets on finger tips
• GesturePad [Rekimoto 2001]: Capacitive sensing in clothing
• Palm-based Interaction
• Haptic Hand [Kohli 2005]: Using non-dominant hand in VR
• Sixth Sense [Mistry 2009]: Projection on hand
• Brainy Hand [Tamaki 2009]: Head worn projector/camera](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-openframeworksfinal-160827070744/75/COMP-4026-Lecture-5-OpenFrameworks-and-Soli-14-2048.jpg)
![ImaginaryPhone
• Gustafson, S., Holz, C., & Baudisch, P. [2011]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-openframeworksfinal-160827070744/75/COMP-4026-Lecture-5-OpenFrameworks-and-Soli-15-2048.jpg)
![Invisible Interfaces – Gestures in Space
• Gustafson, S., Bierwirth, D., & Baudisch, P. [2010]
• Using a non-dominant hand stabilized interface.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-openframeworksfinal-160827070744/75/COMP-4026-Lecture-5-OpenFrameworks-and-Soli-17-2048.jpg)







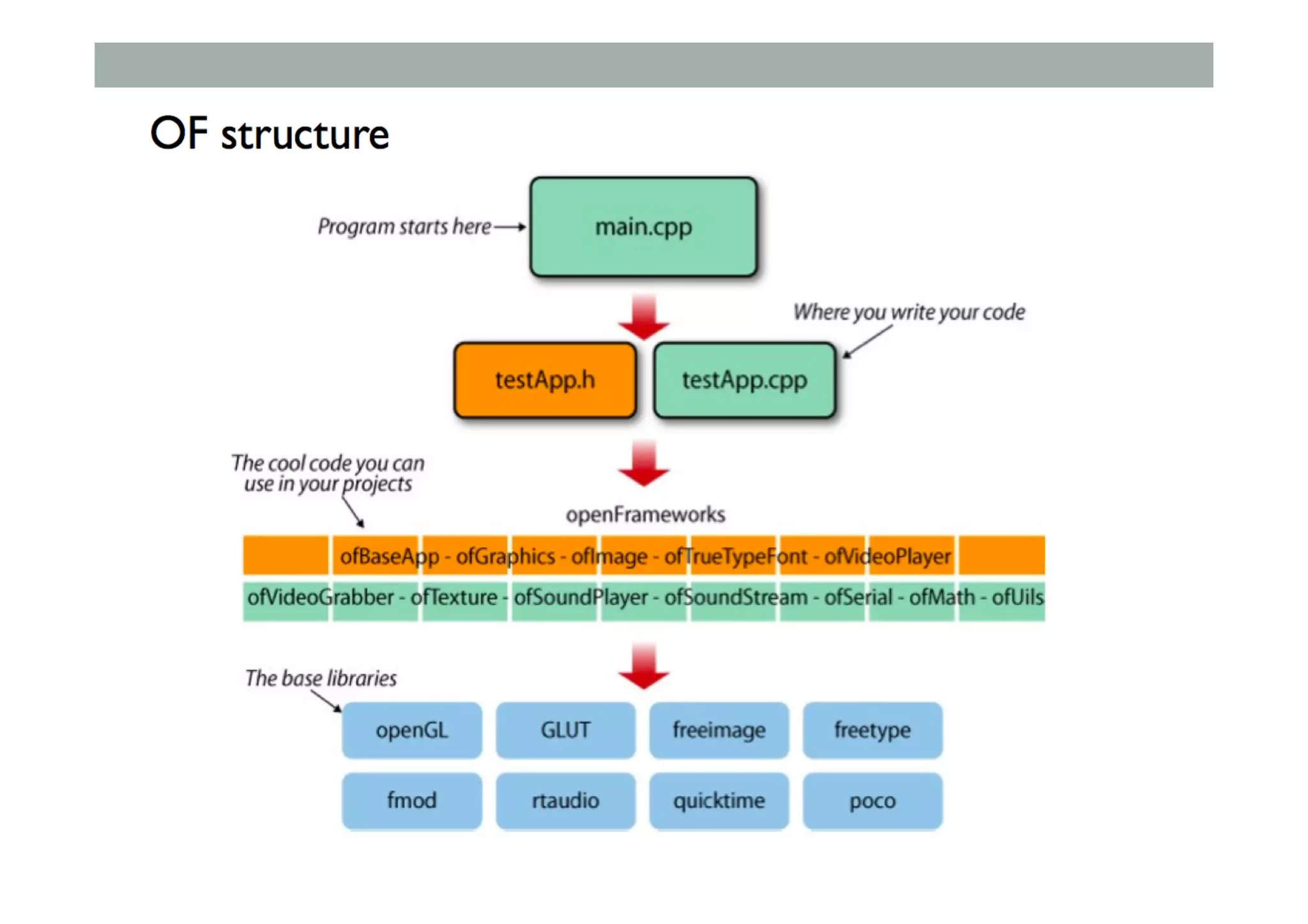
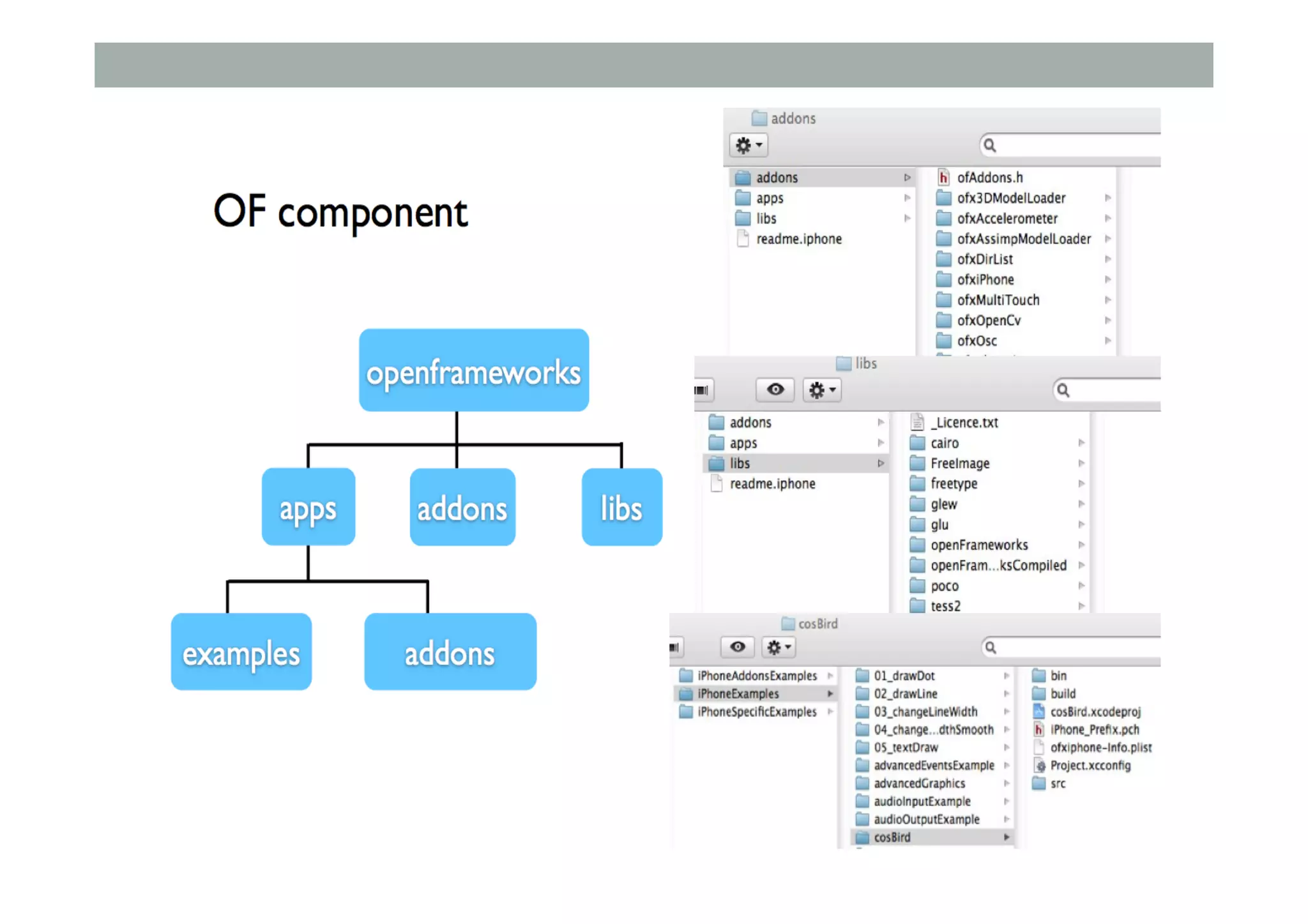
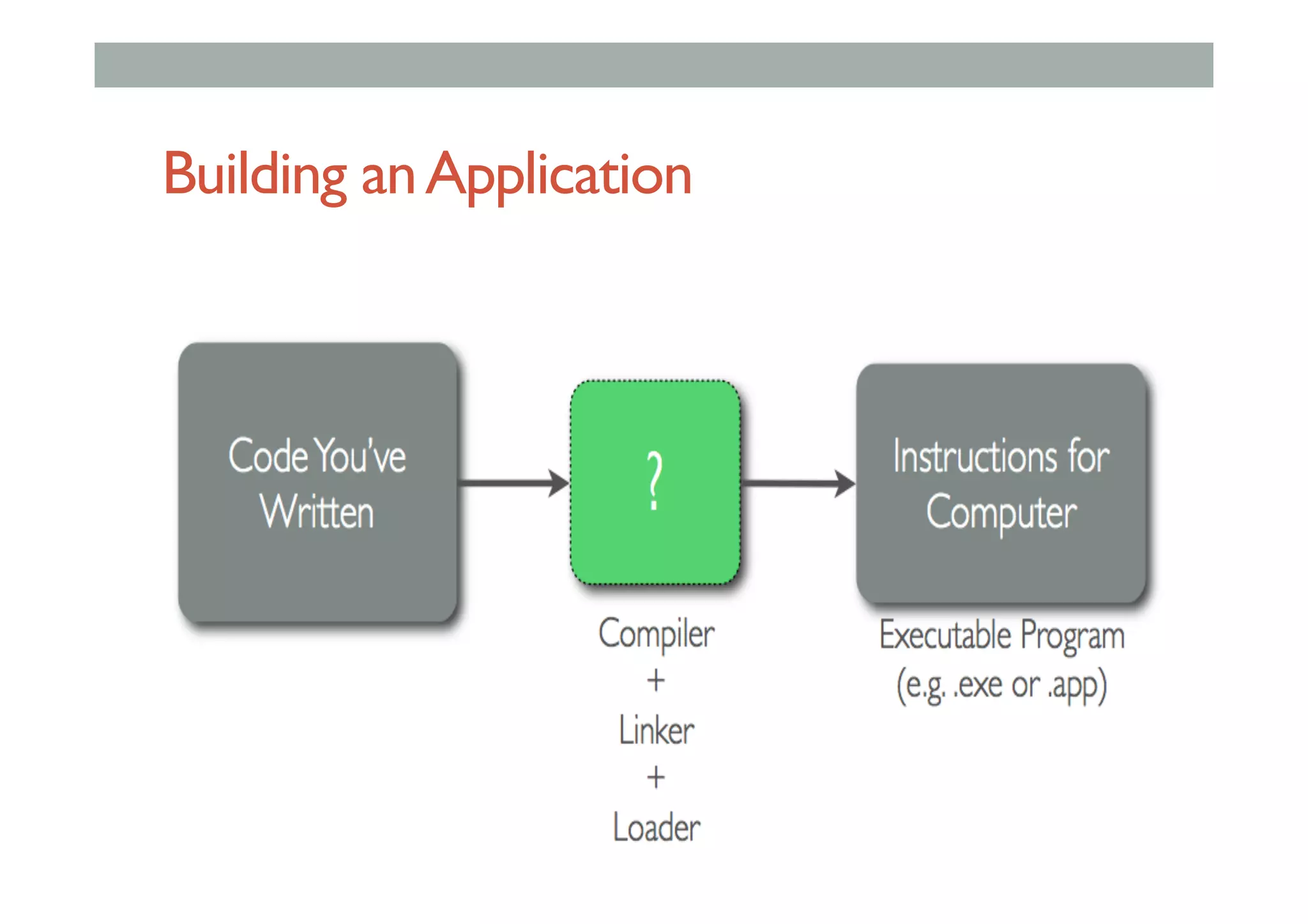
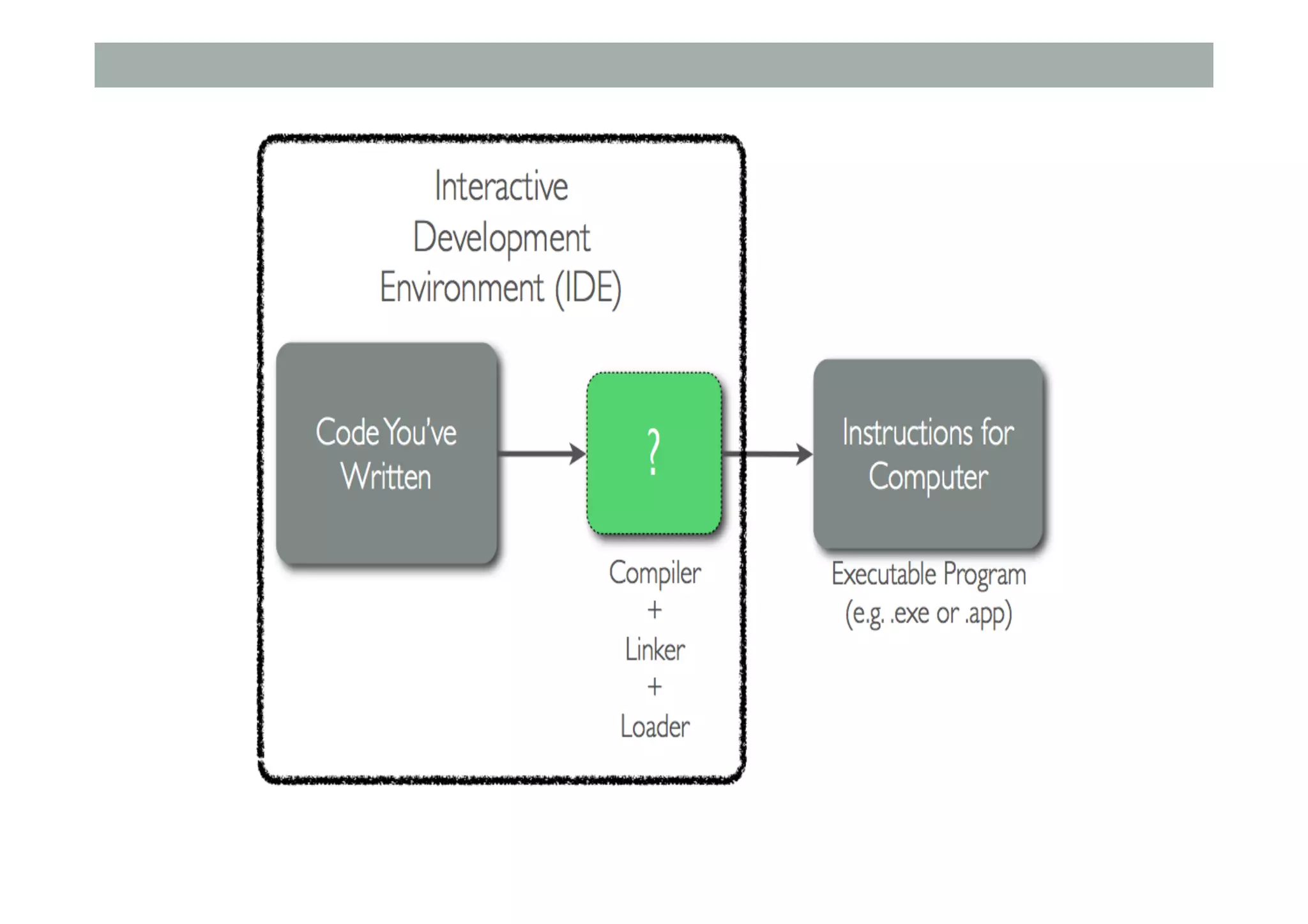



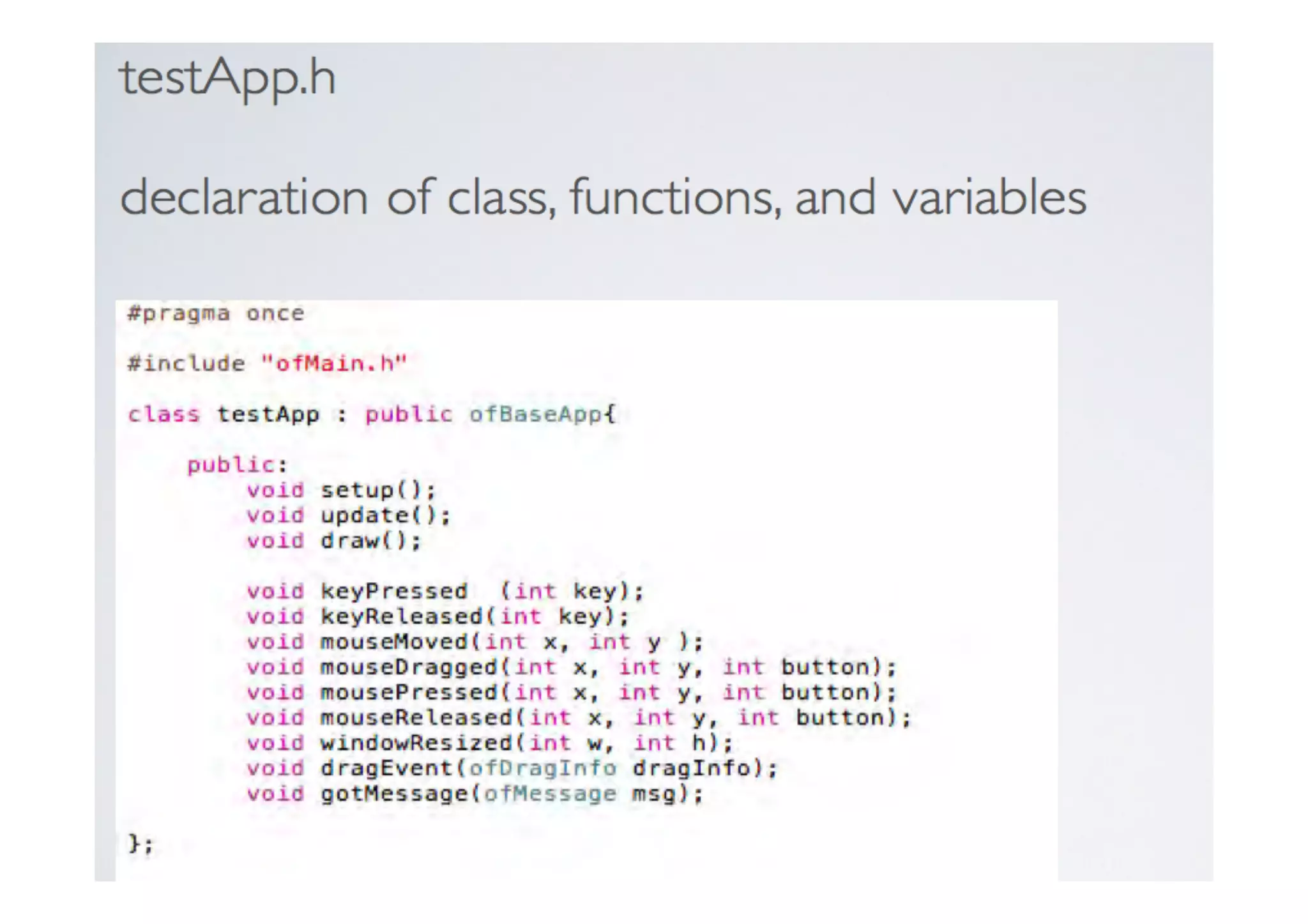
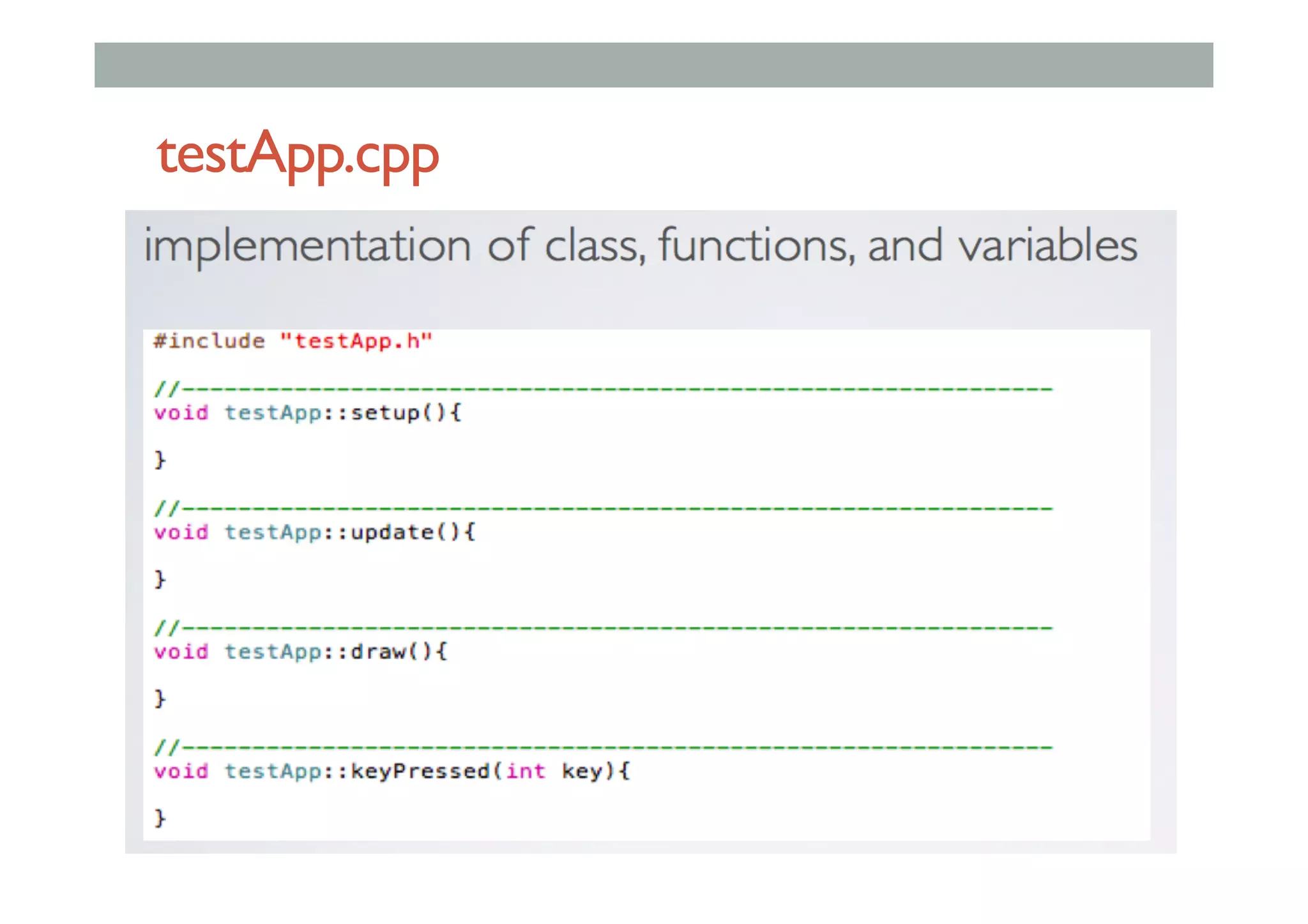
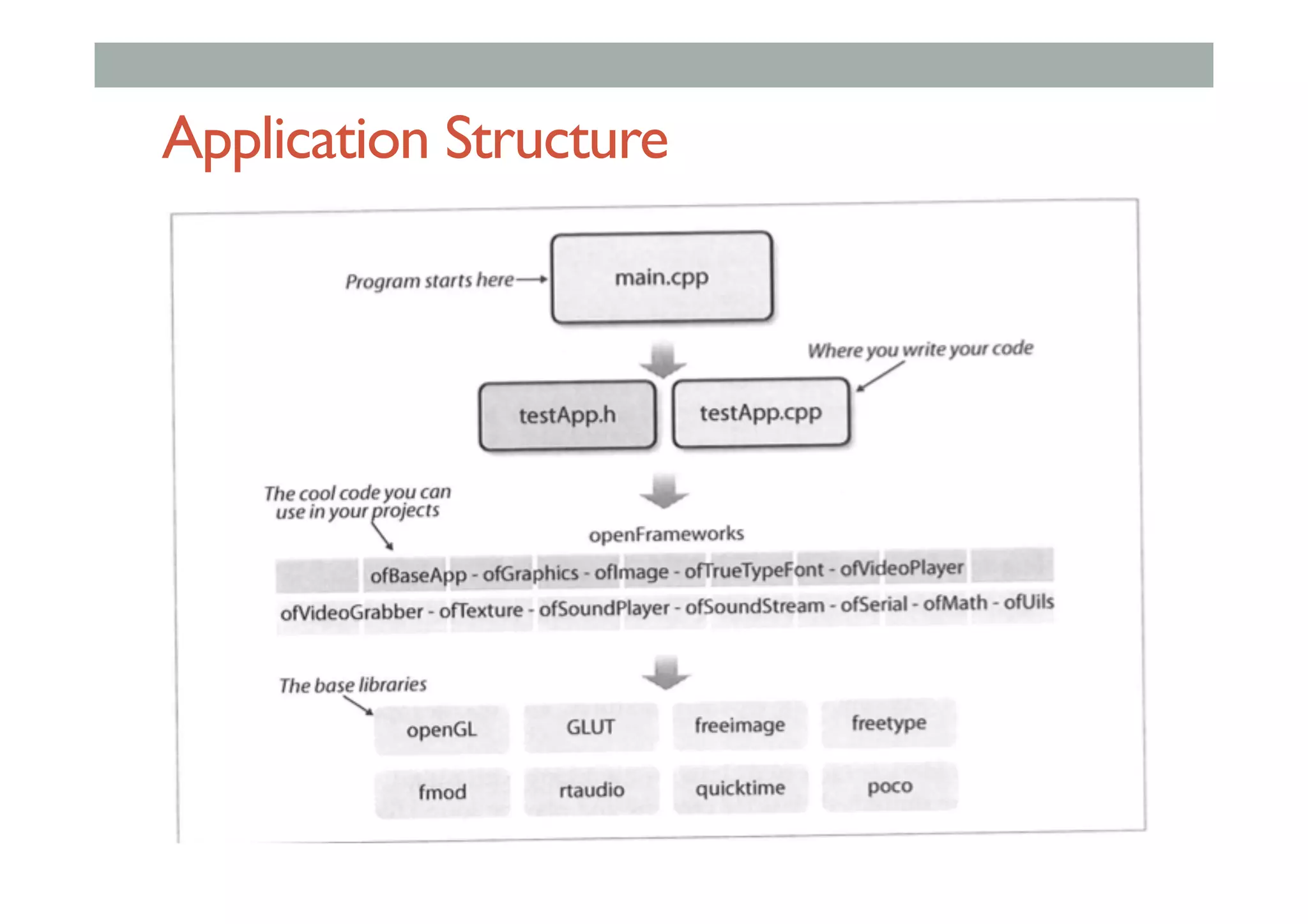


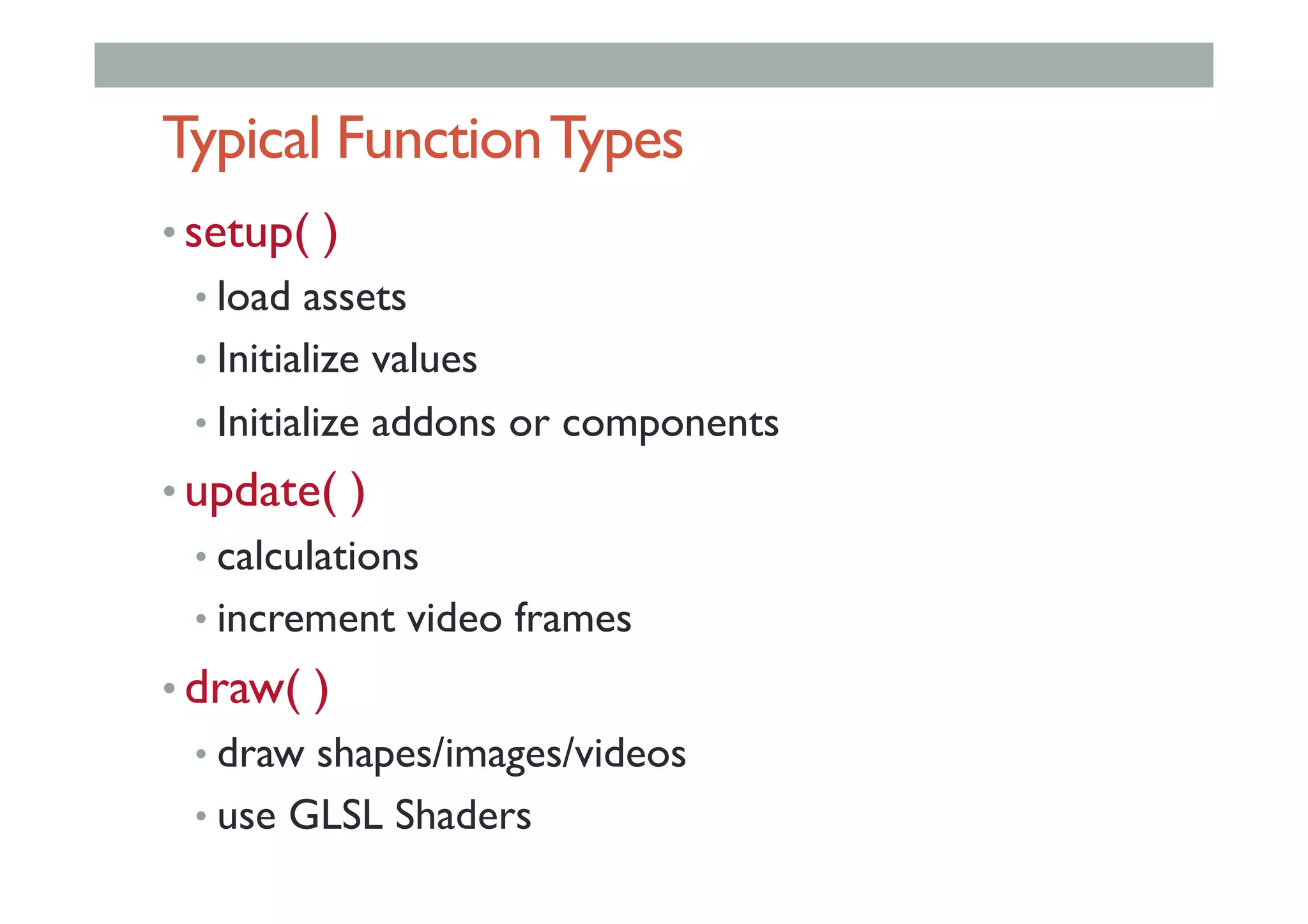



![Class Extending
• Take one class and add functionality to it with a new class
• Eg enemy class for video game
!class Enemy {!
! !int x, y; //position!
! !.. .. !
! !public void draw() {!
! !//draw my picture to the screen at the proper location }!
!}!
• Want to draw enemy twice – create new class
!//on a "DoubleEnemy.h" file!
!class DoubleEnemy: public Enemy // class[className]:[privacy][extended Class]{}!
!{!
! !public void draw();//the actual code inthe "DoubleEnemy.cpp" file!
!}; // note the ";" at the end of the class statement!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture5-openframeworksfinal-160827070744/75/COMP-4026-Lecture-5-OpenFrameworks-and-Soli-48-2048.jpg)