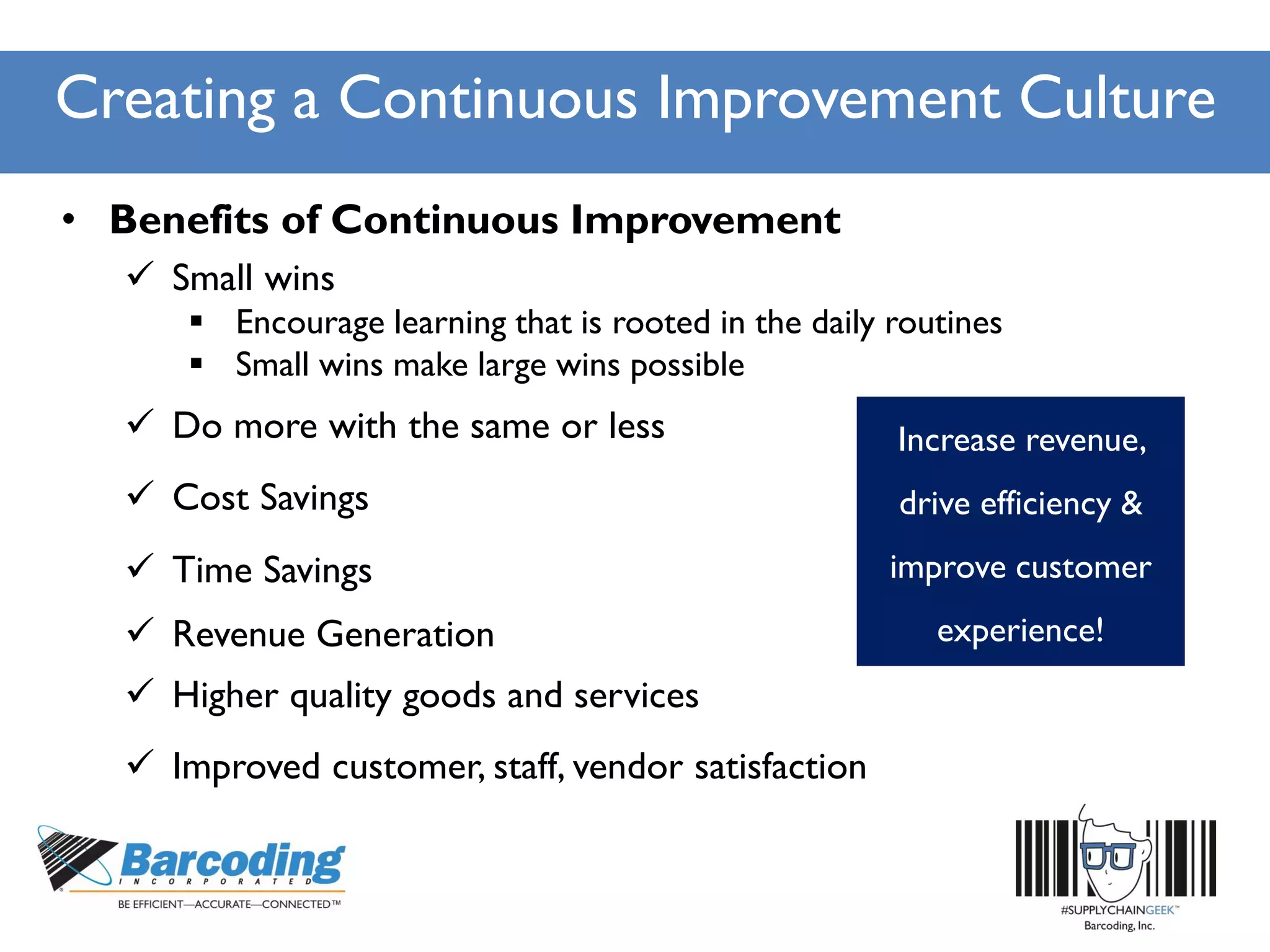
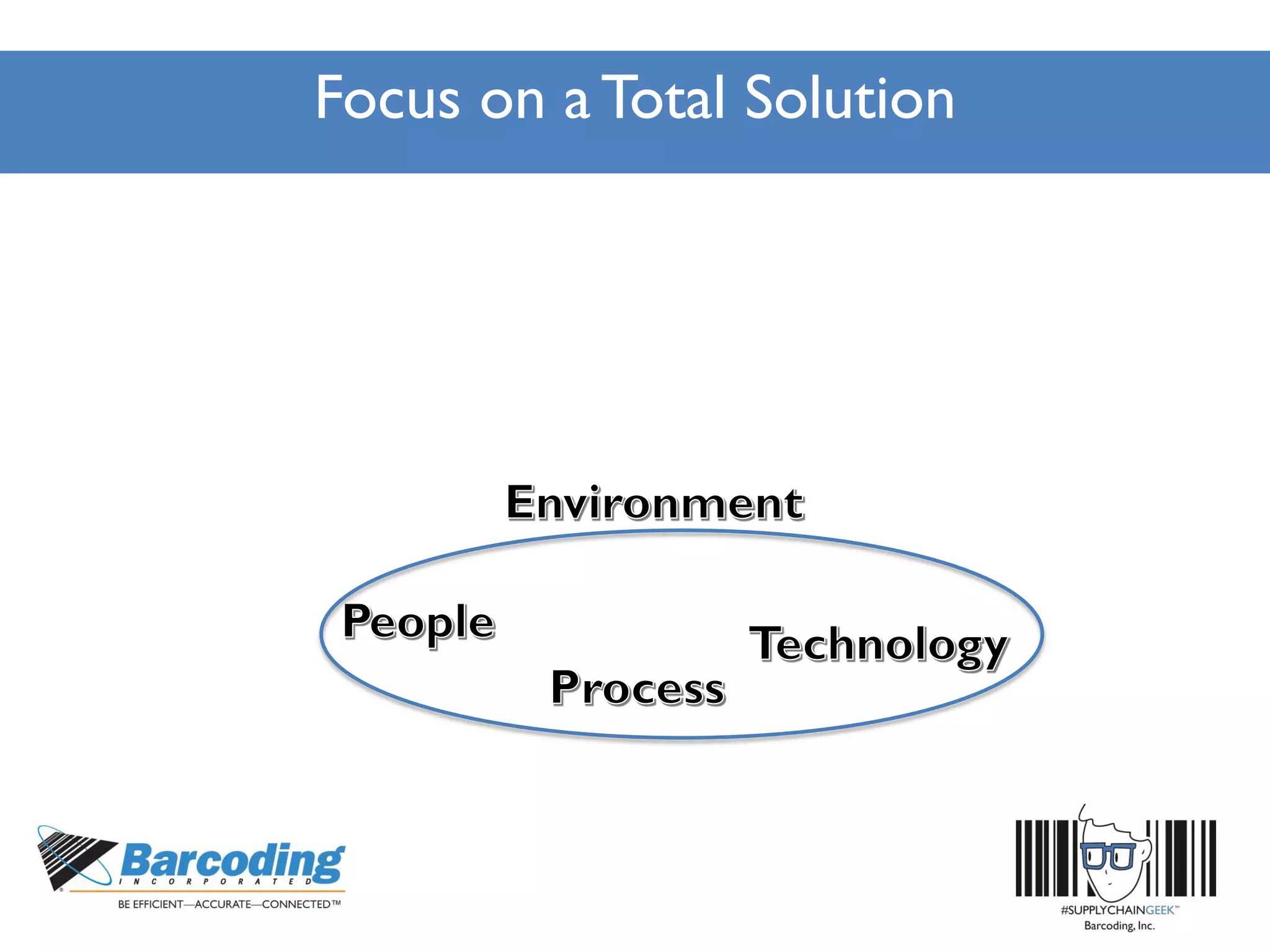
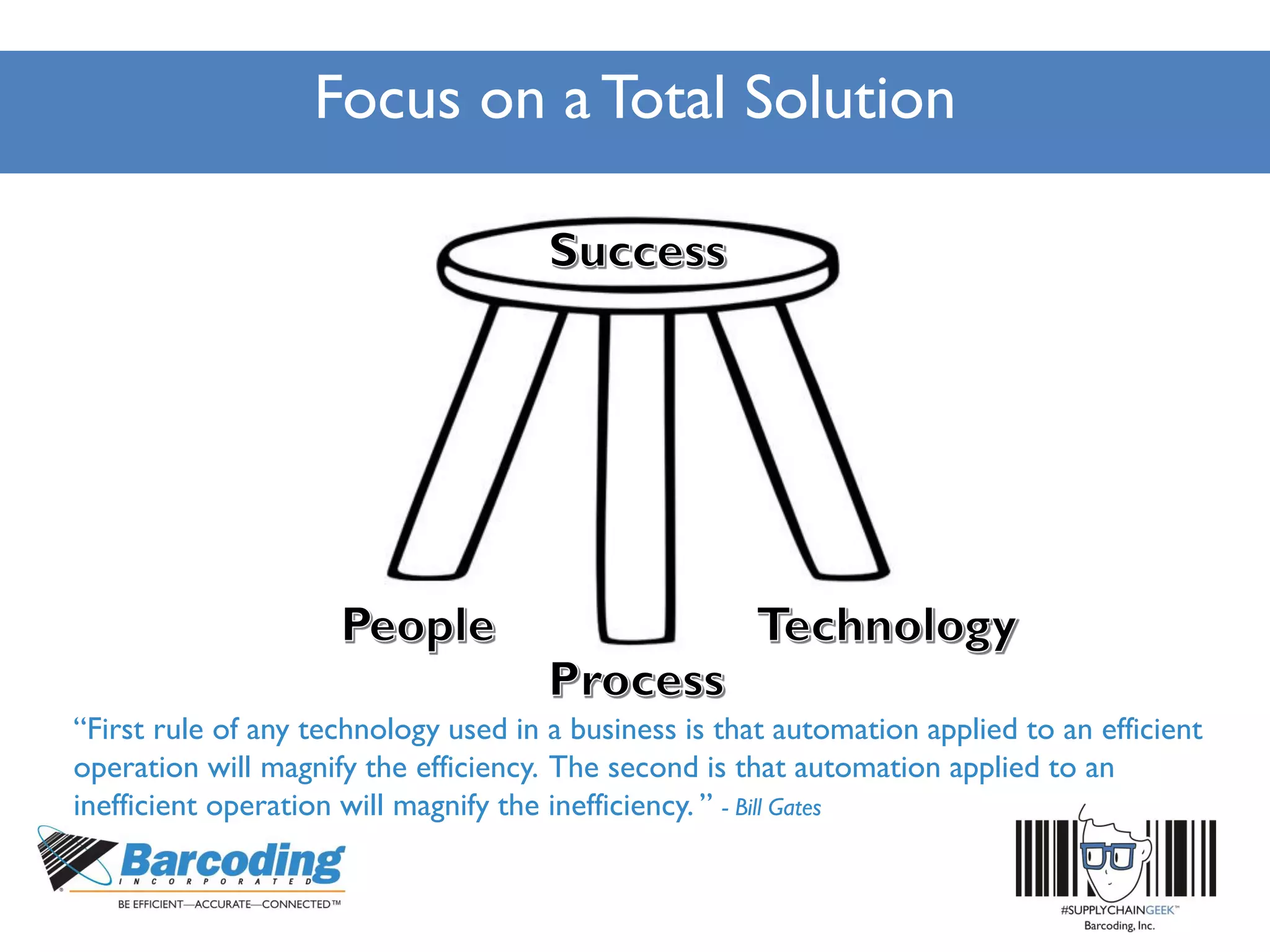
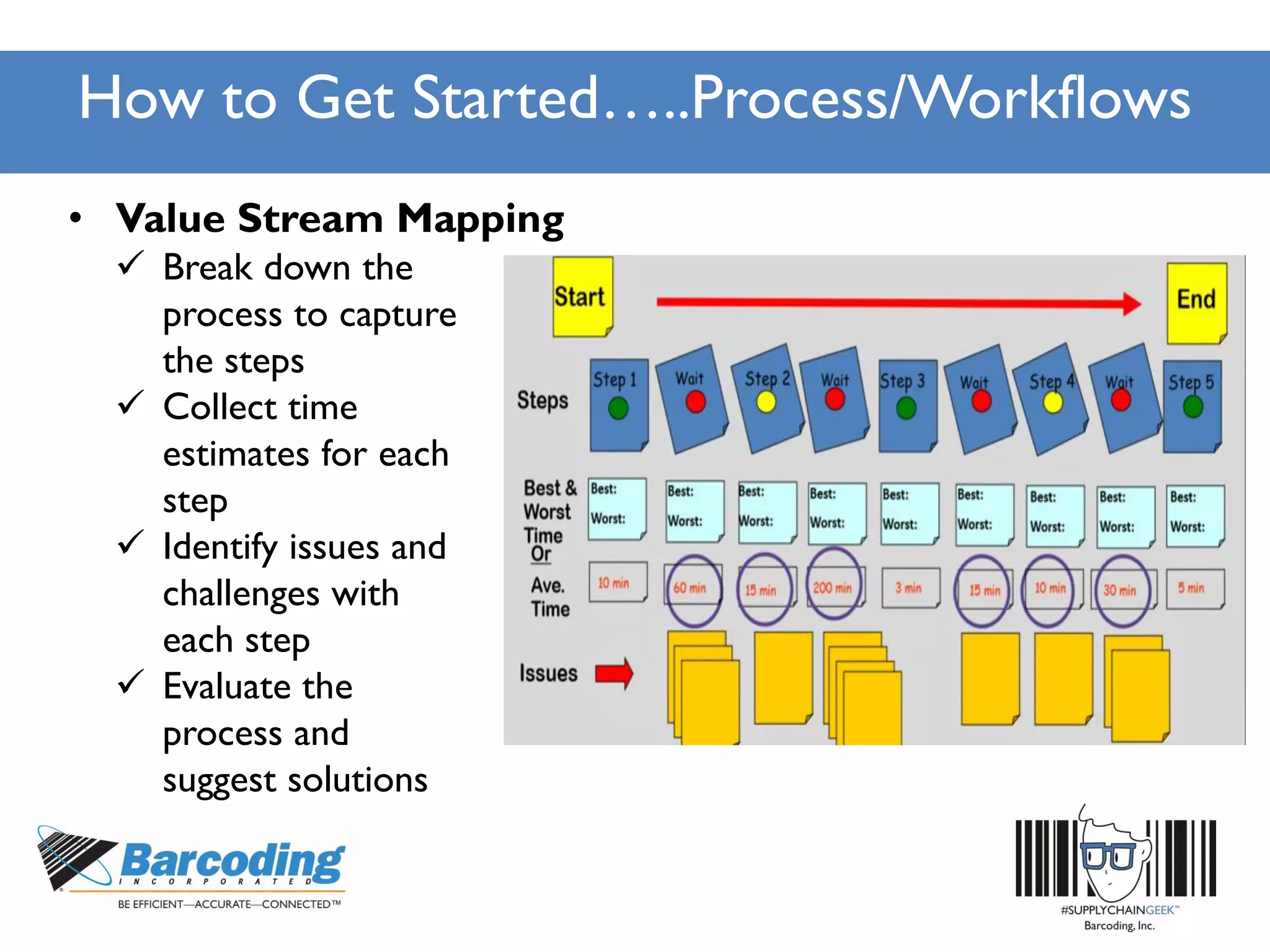
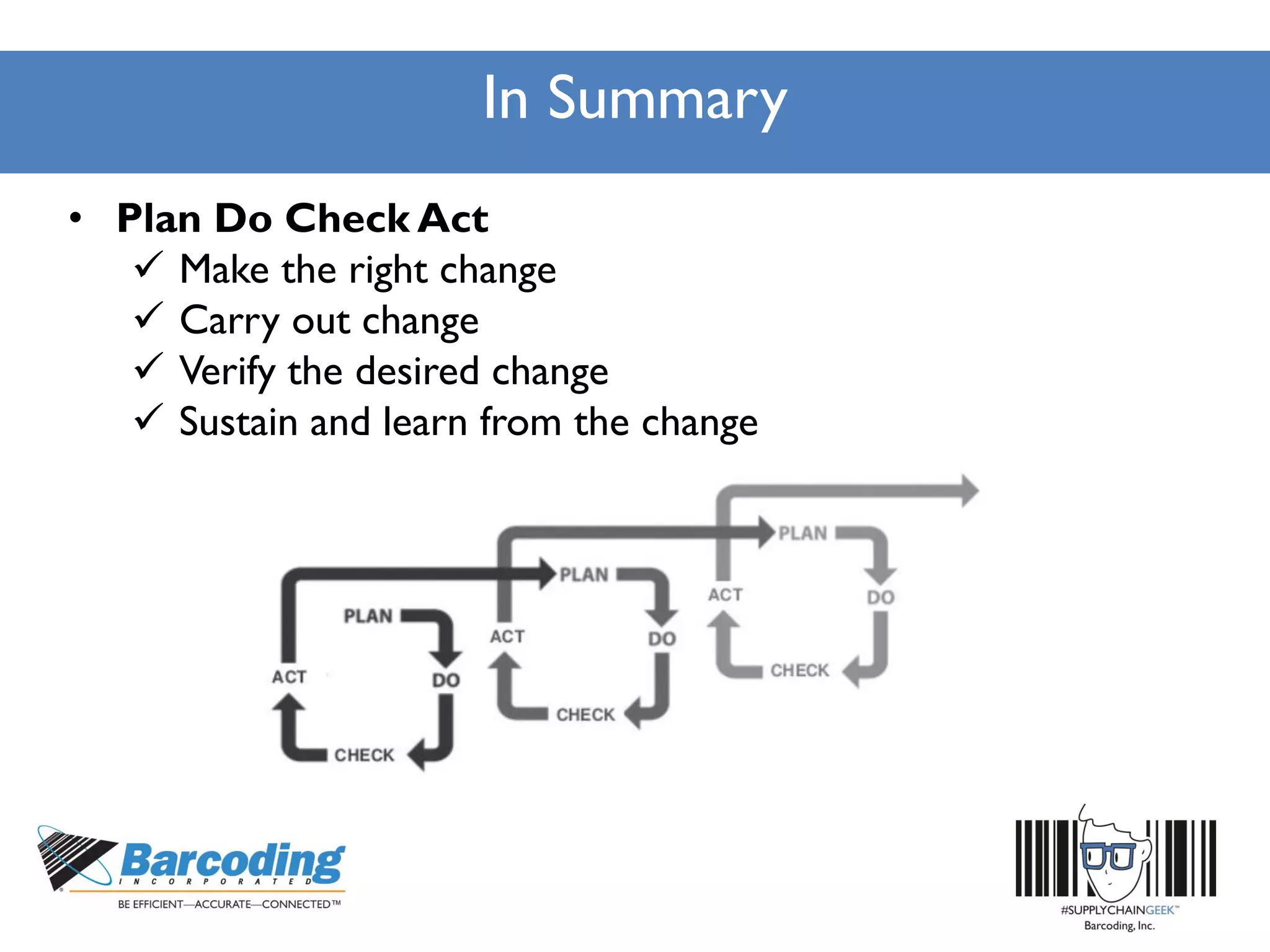
The document outlines a continuous improvement workshop led by Chase Sowden from Barcoding Inc., emphasizing the importance of fostering a culture of continuous improvement within organizations. It discusses the benefits of such a culture, common misconceptions, and practical steps for implementation, including leadership buy-in and employee engagement. Key concepts include identifying waste in supply chains, leveraging feedback, and recognizing the role of technology and communication in enhancing operational efficiency.