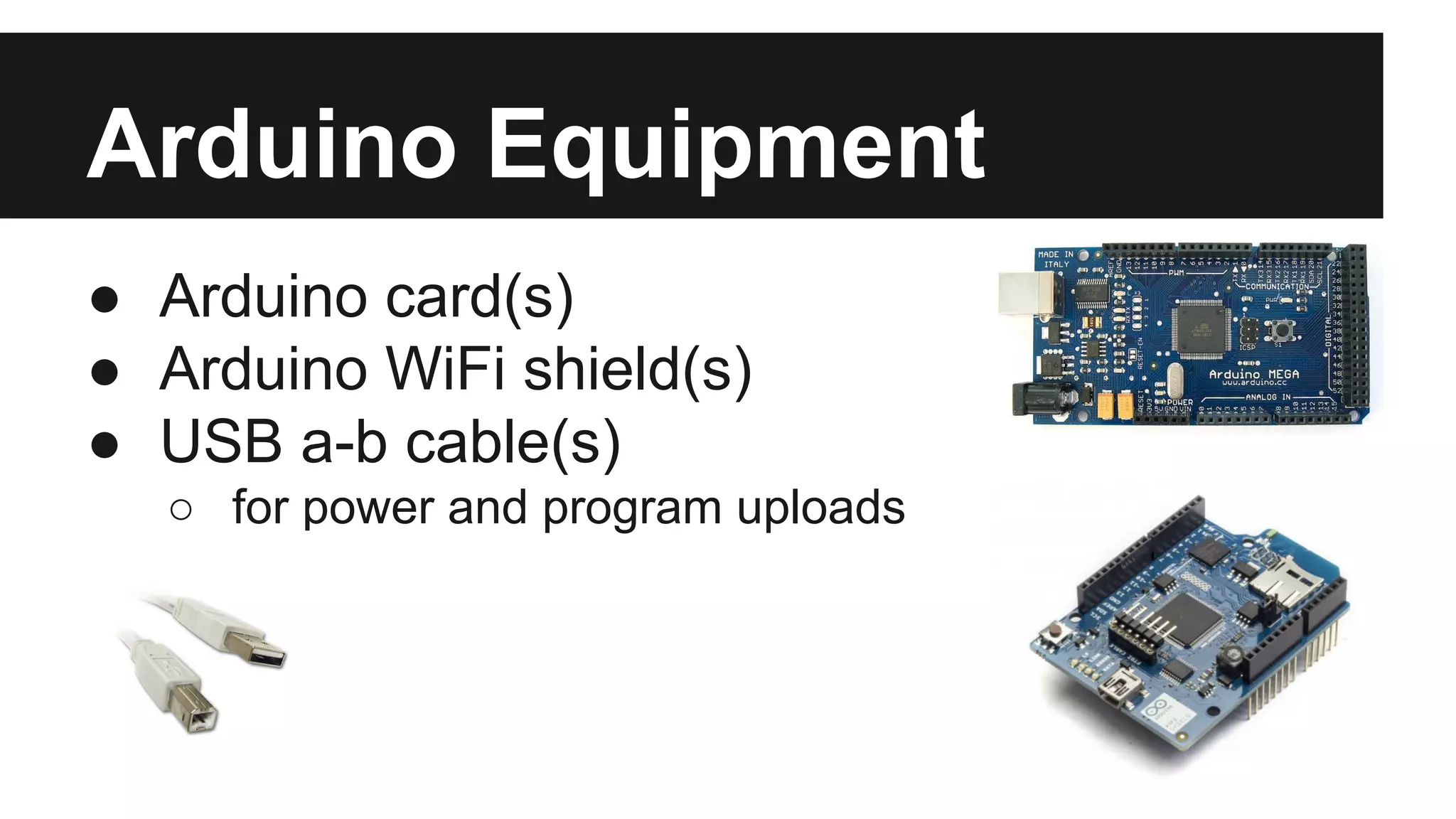
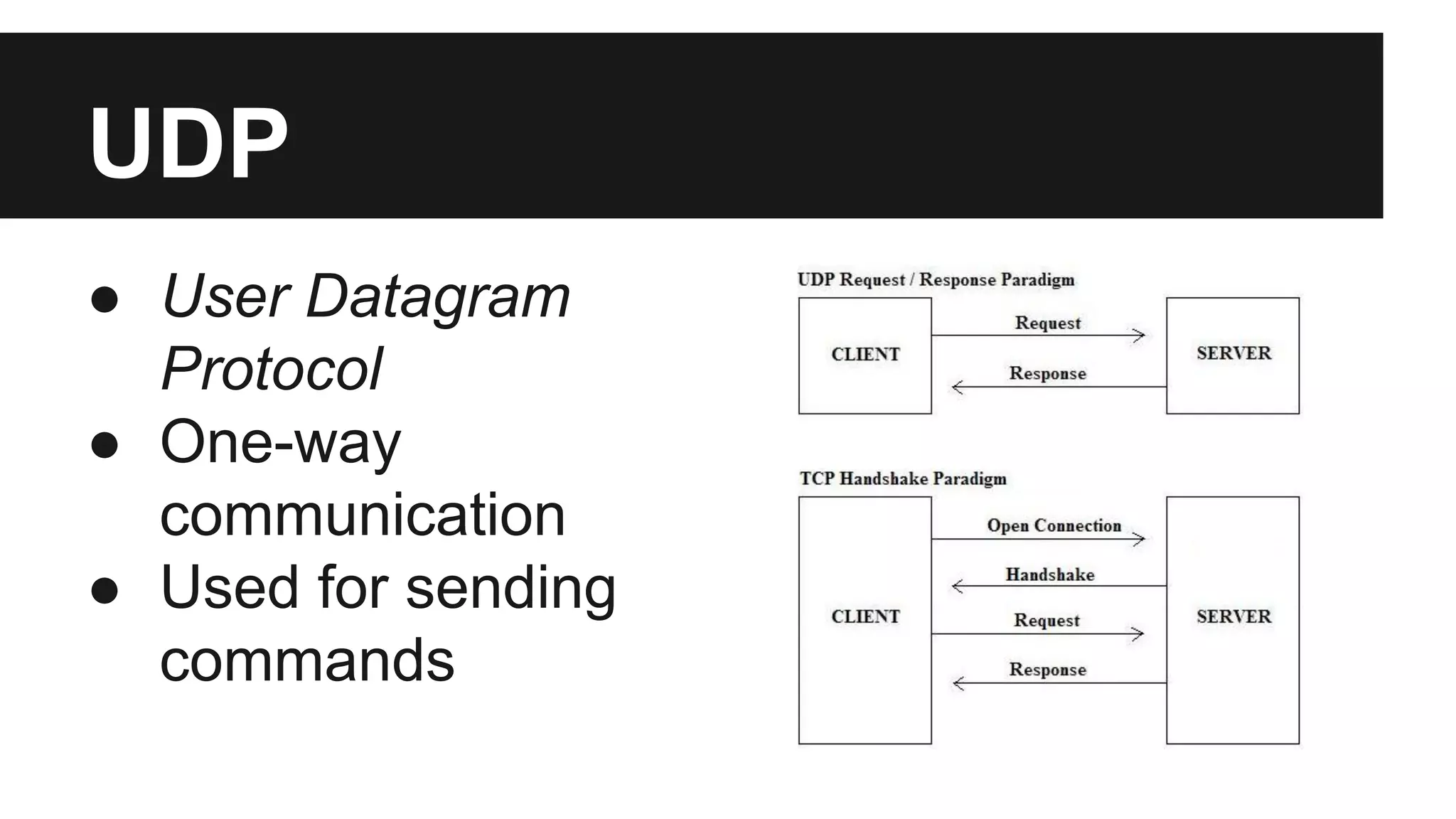
The document outlines the communication process between Android devices and Arduino boards, detailing the setup and programming requirements for both platforms. It covers the necessary hardware, software options, and networking methods, including the use of a portable Wi-Fi hotspot and protocols like UDP. The document also highlights the simplicity of Arduino programming and the complexities of Android development, encouraging further exploration and collaboration through provided GitHub links.