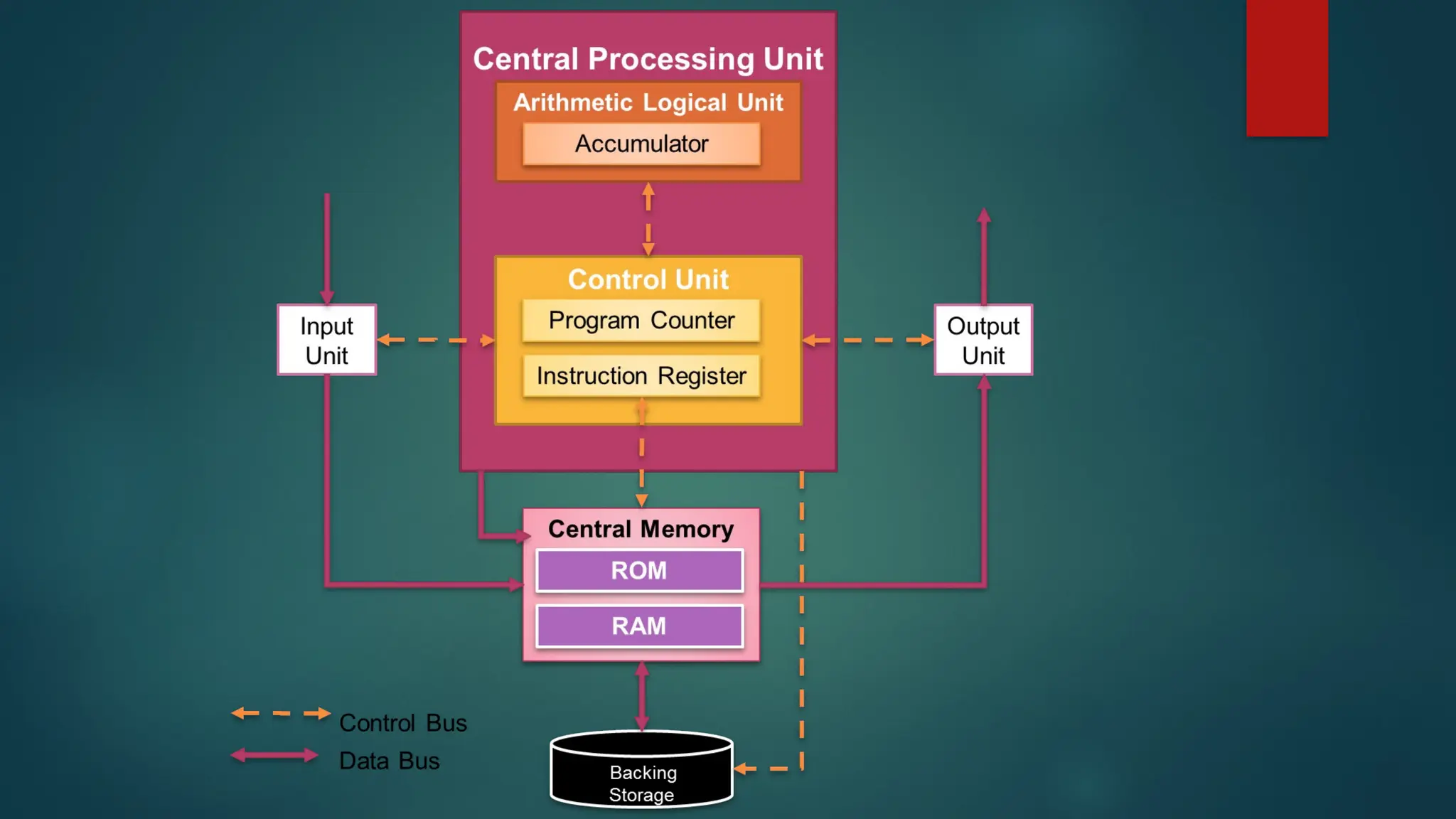
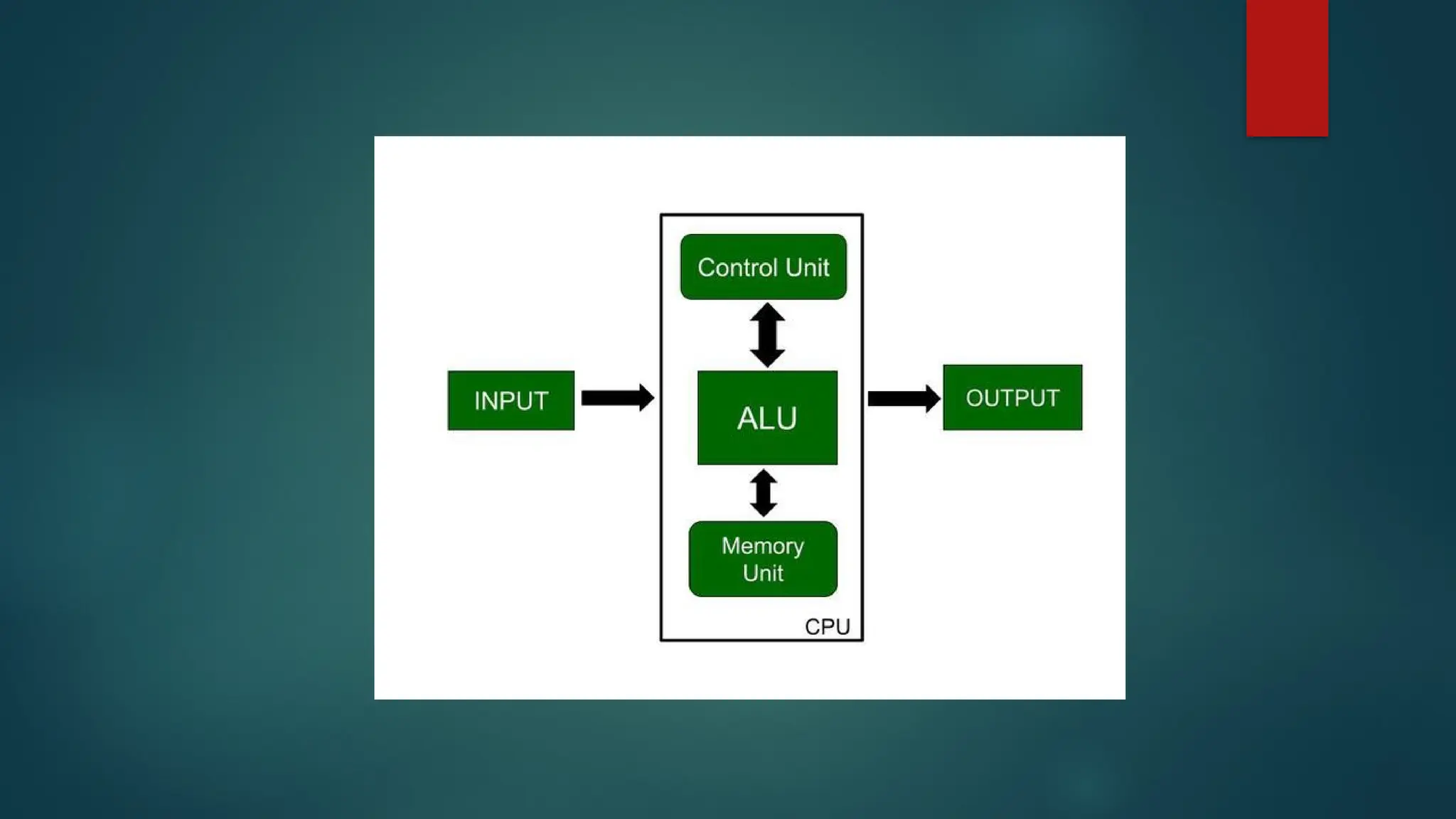
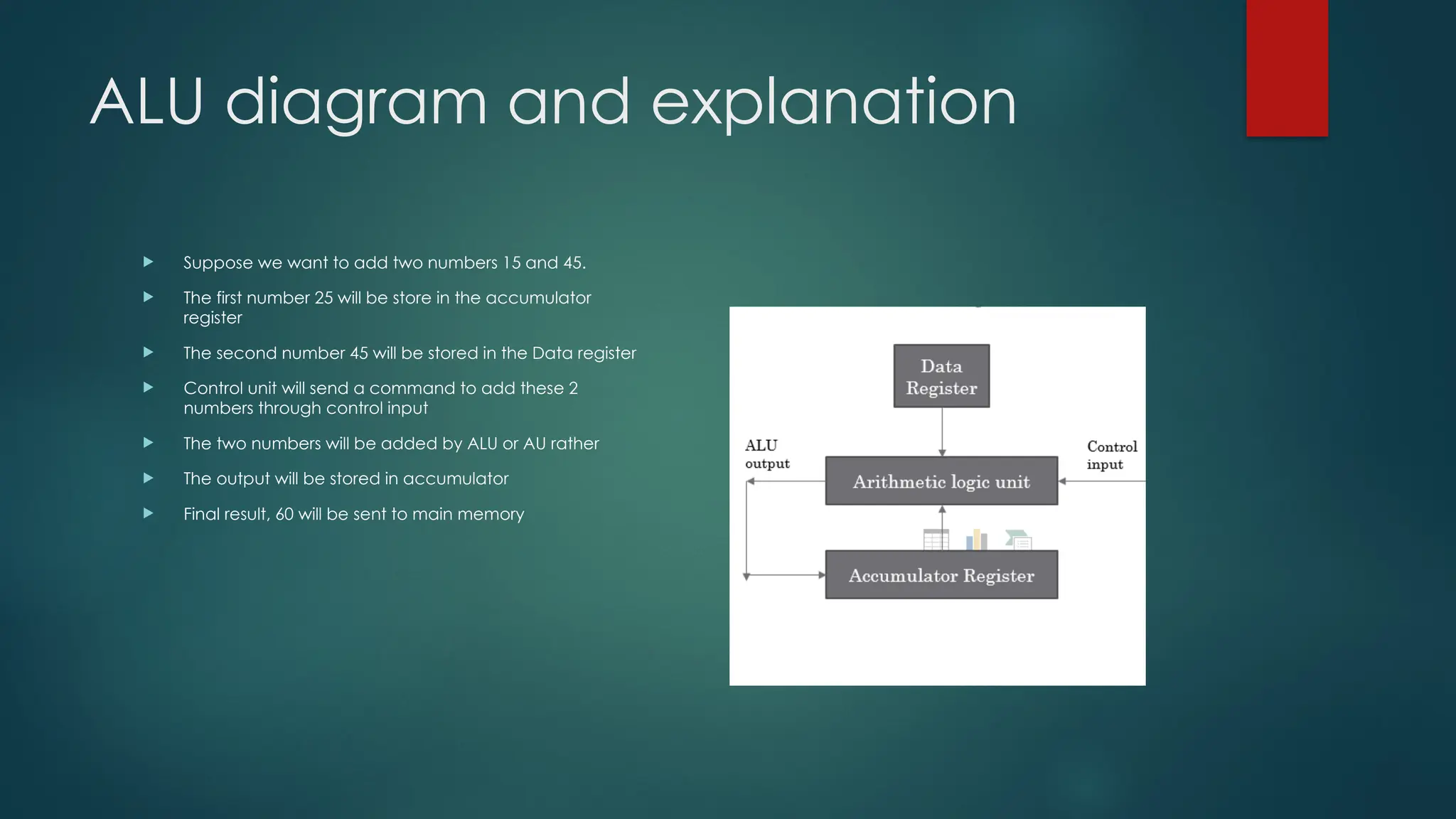
The document provides an overview of CPU architecture and functions, detailing the roles of the central processing unit as the brain of a computer, executing instructions by fetching, decoding, and executing them. It outlines various types of CPUs, including single-core, dual-core, and quad-core, along with their components like the control unit, arithmetic logic unit, registers, and buses. Additionally, it discusses computer programs, storage modes, and the advantages and disadvantages of CPUs, emphasizing their critical role in computer functionality.