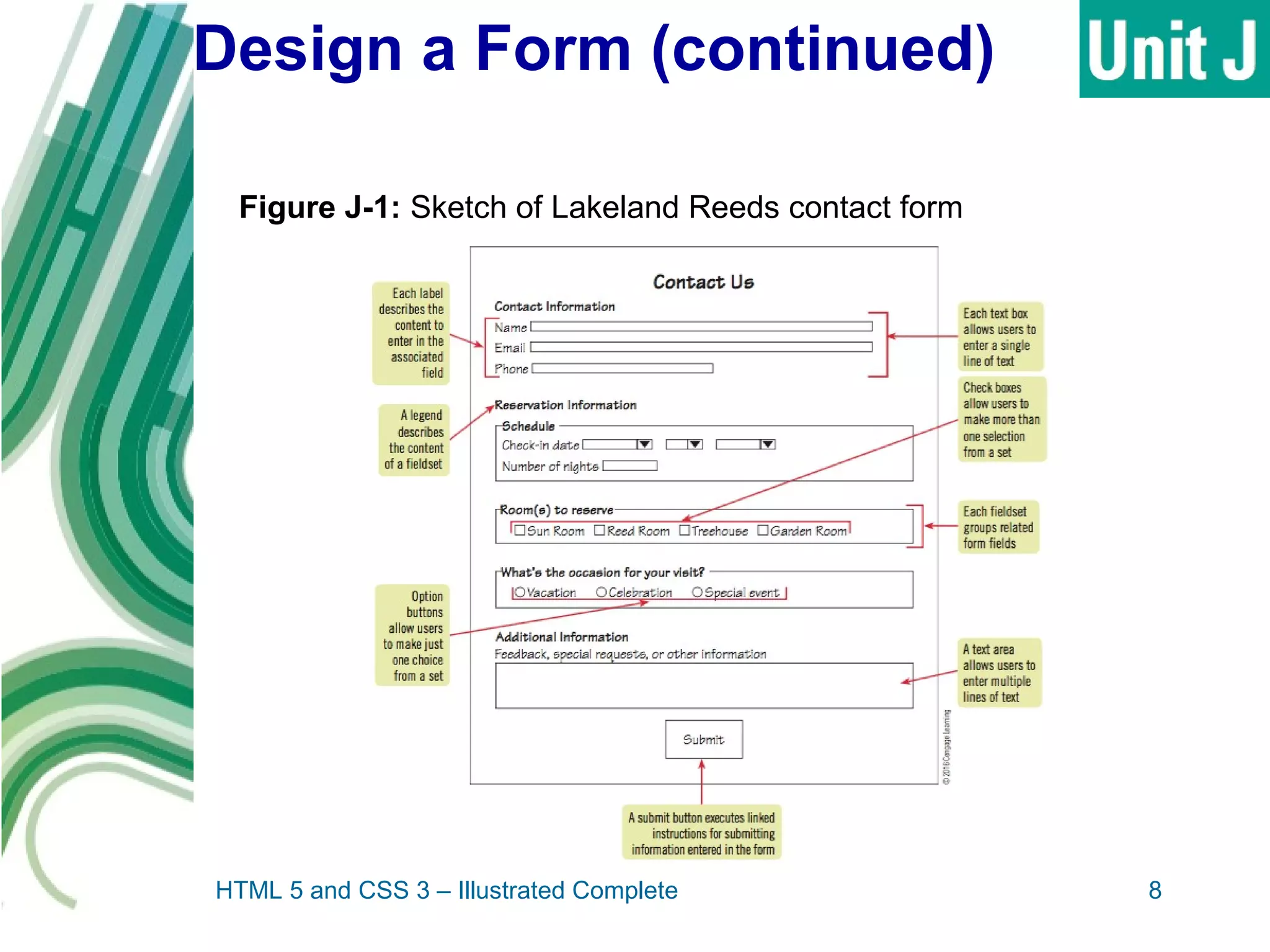
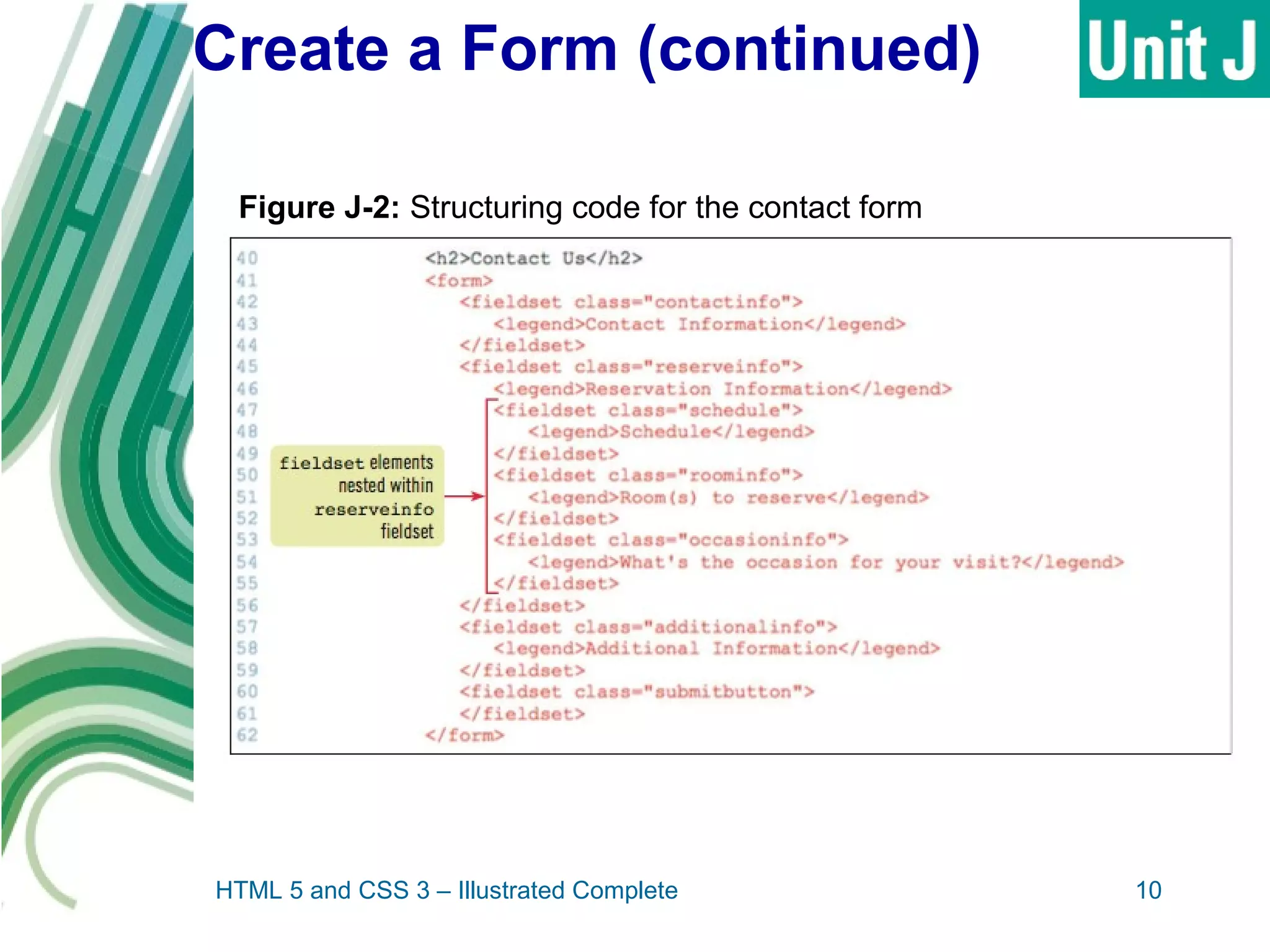
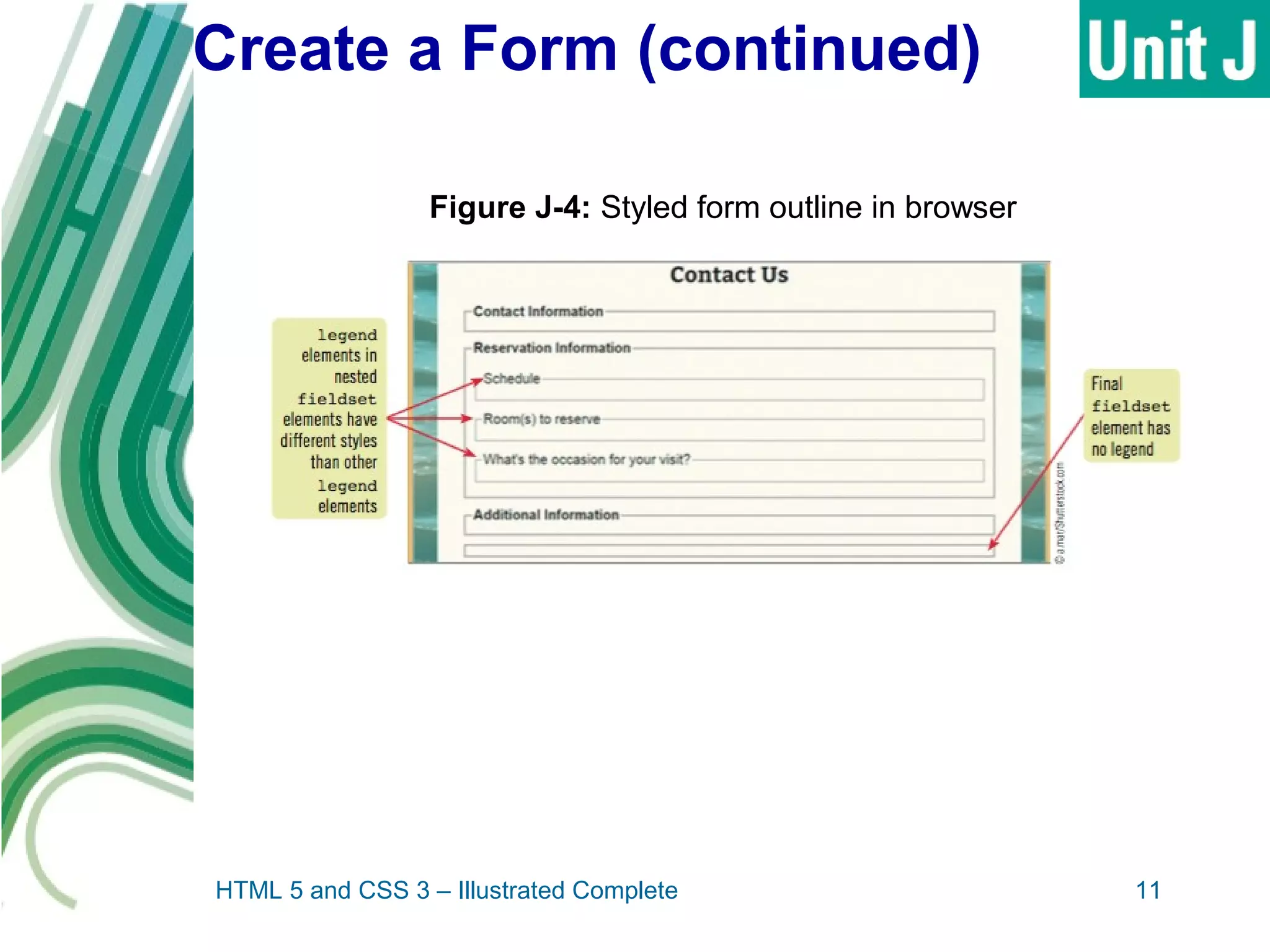
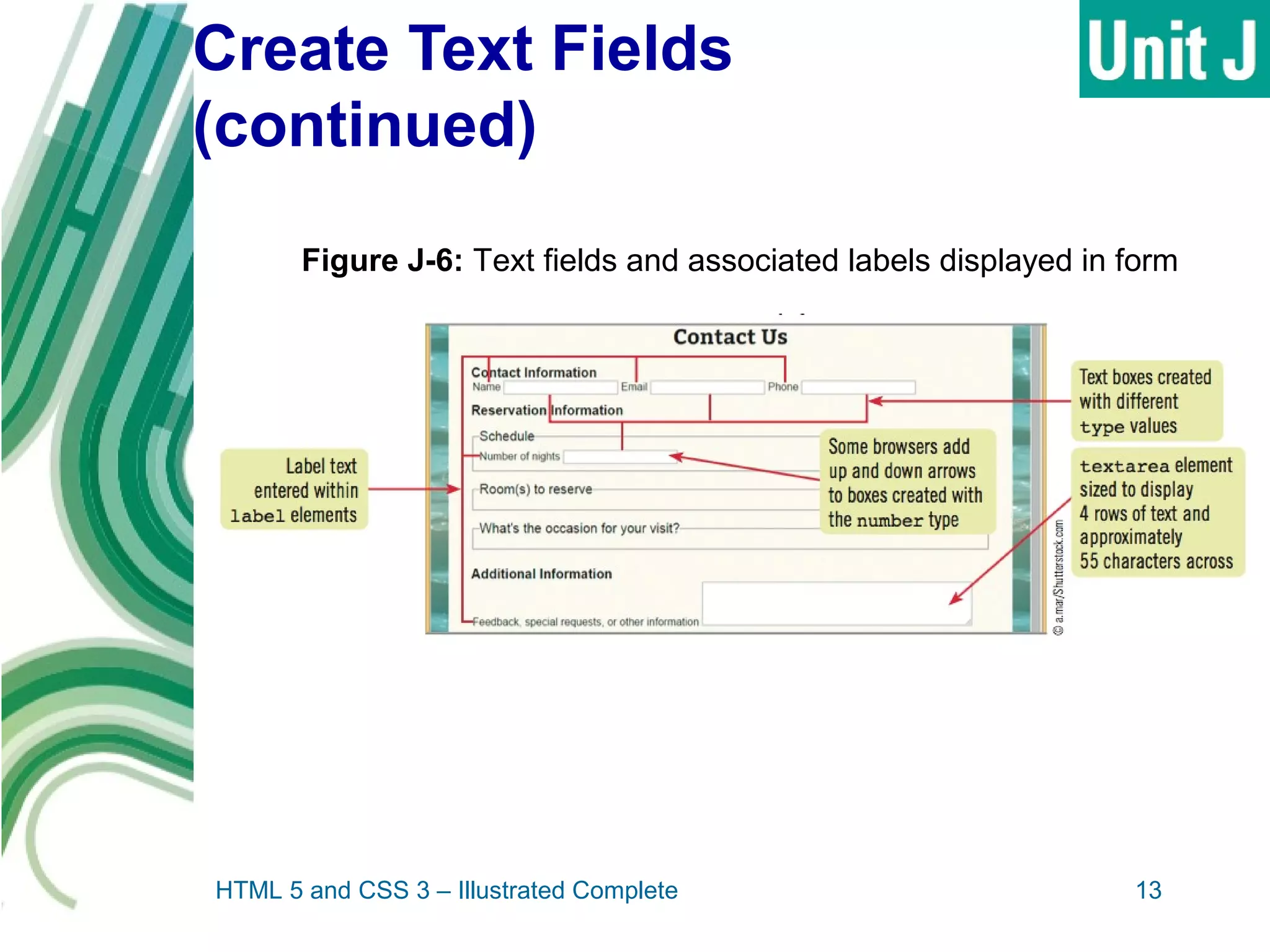
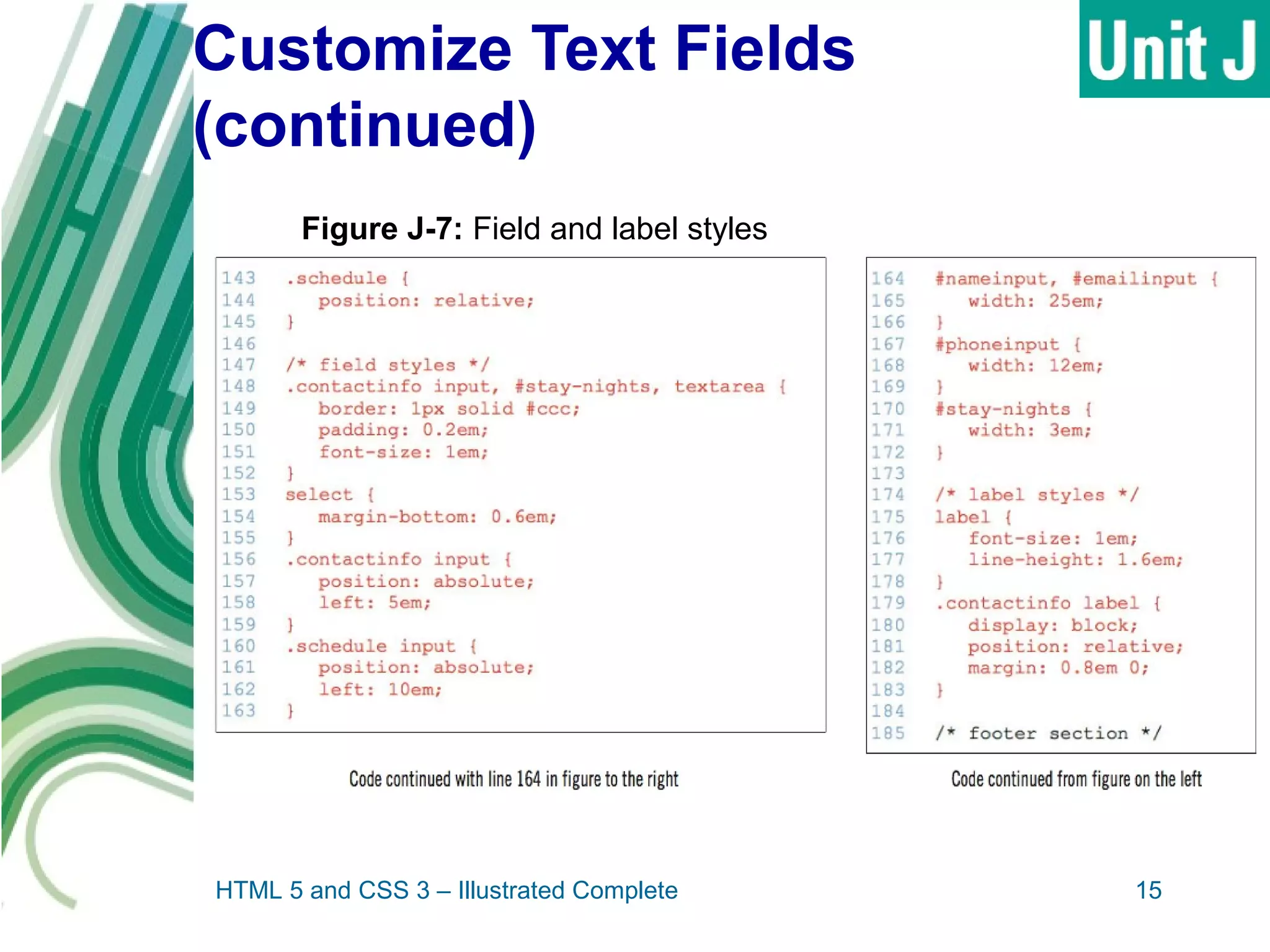
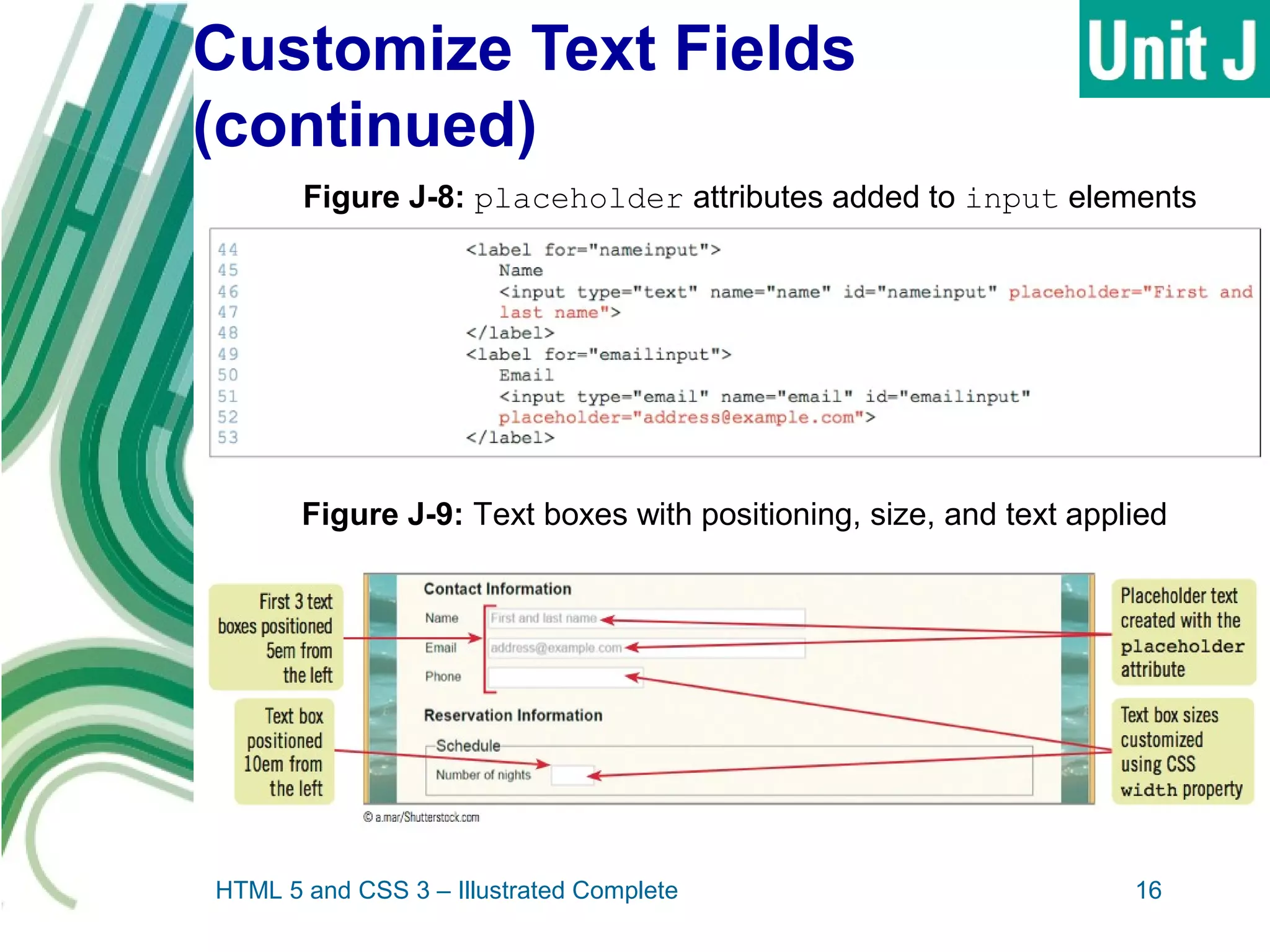
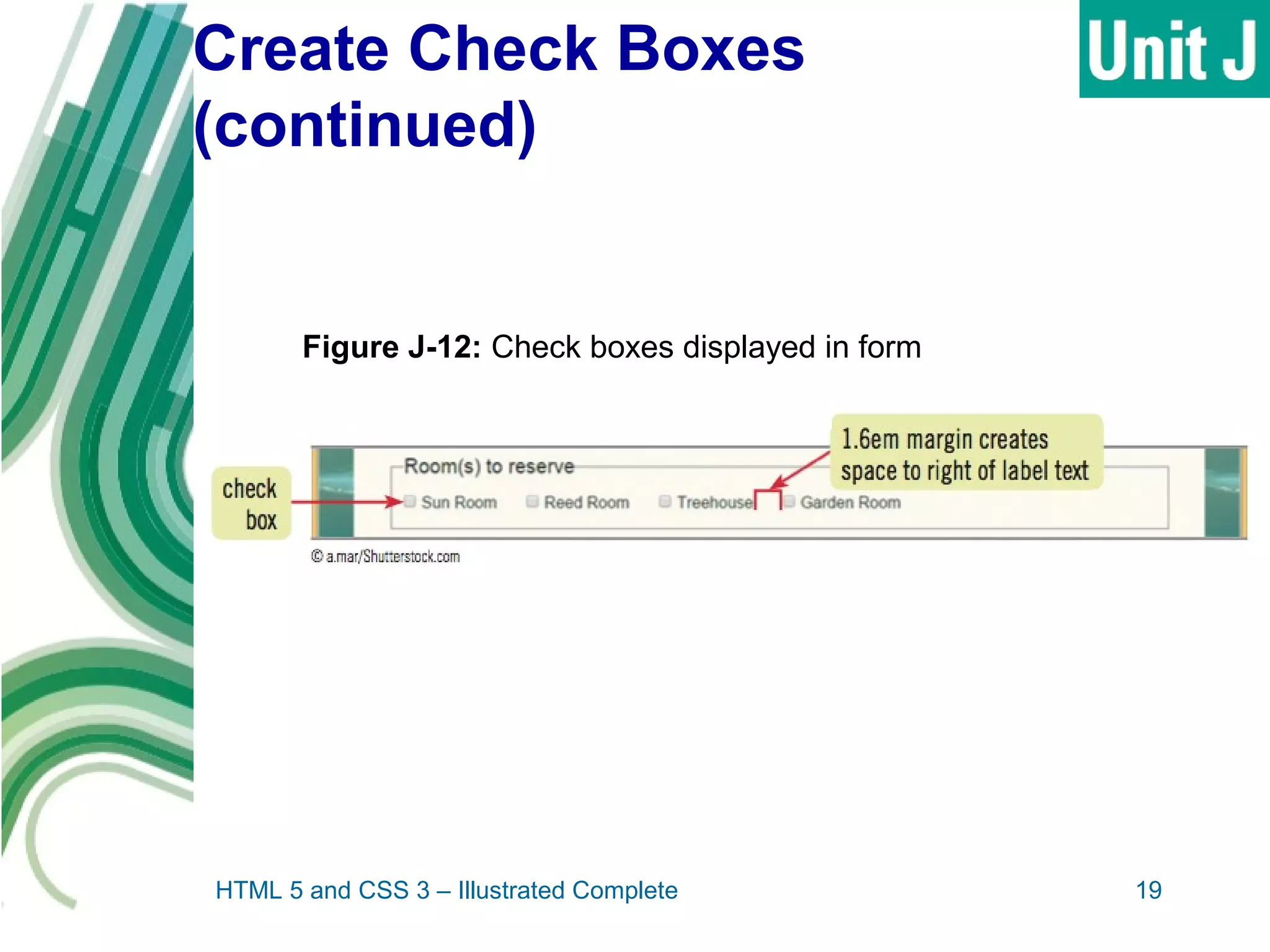
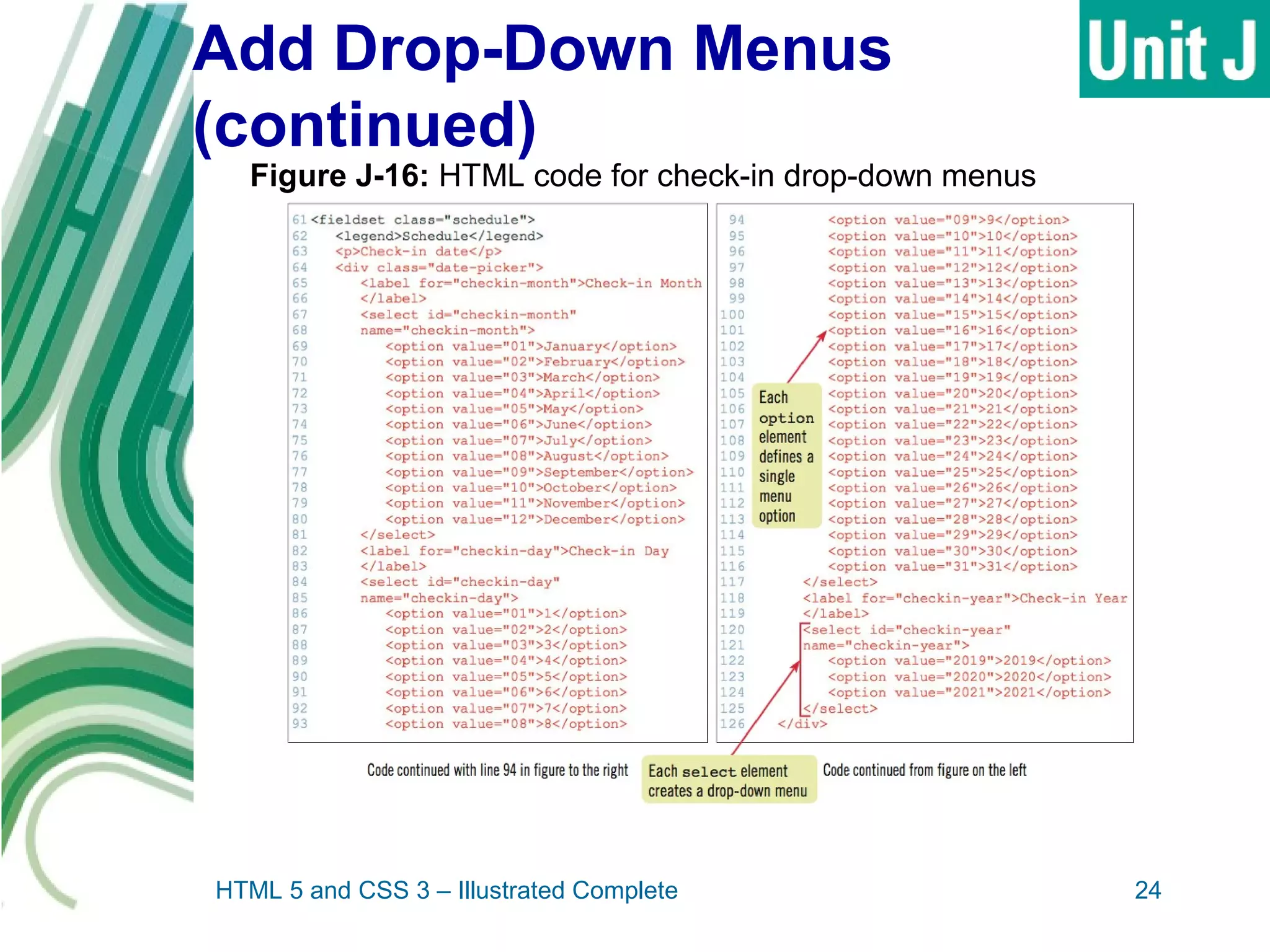
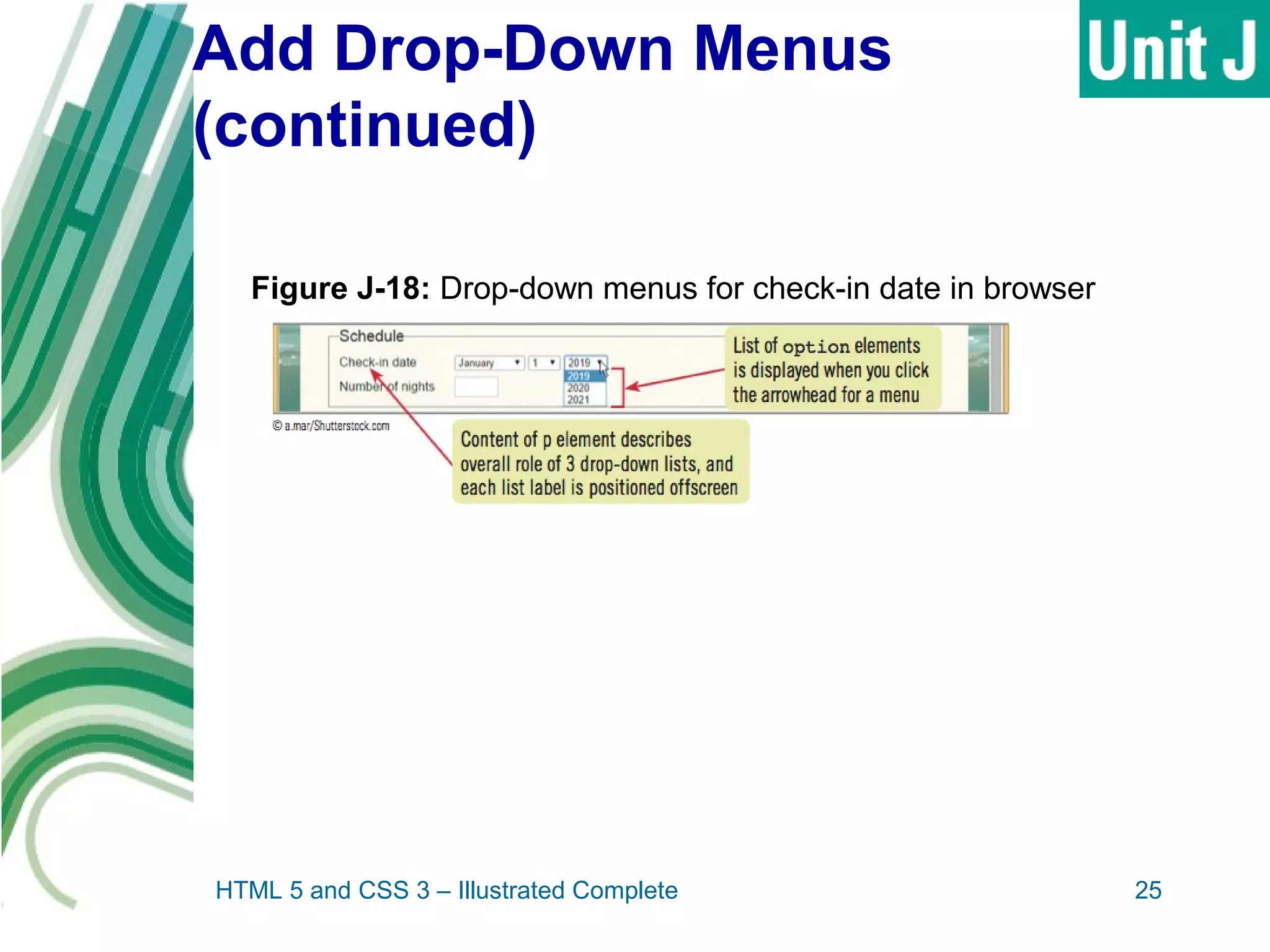
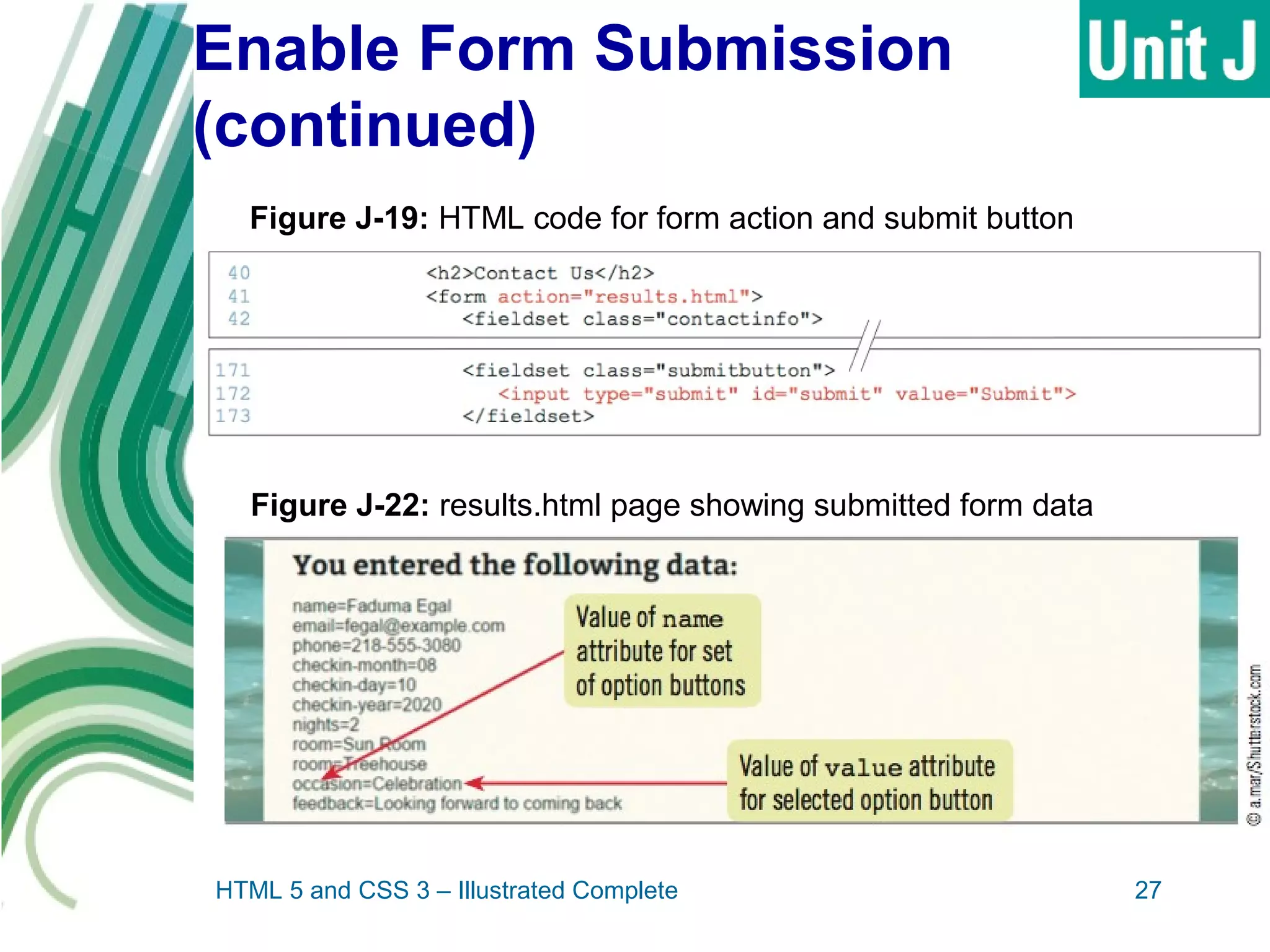
The document discusses designing and creating web forms. It explains that forms need to be planned to identify required information and logical field organization. A form is created with HTML using the form, fieldset, and label elements. Text boxes, text areas, checkboxes, option buttons, and drop-down menus can then be added as form controls using appropriate input elements and attributes. Styling the layout improves usability, and a submit button allows submitting the completed form data.