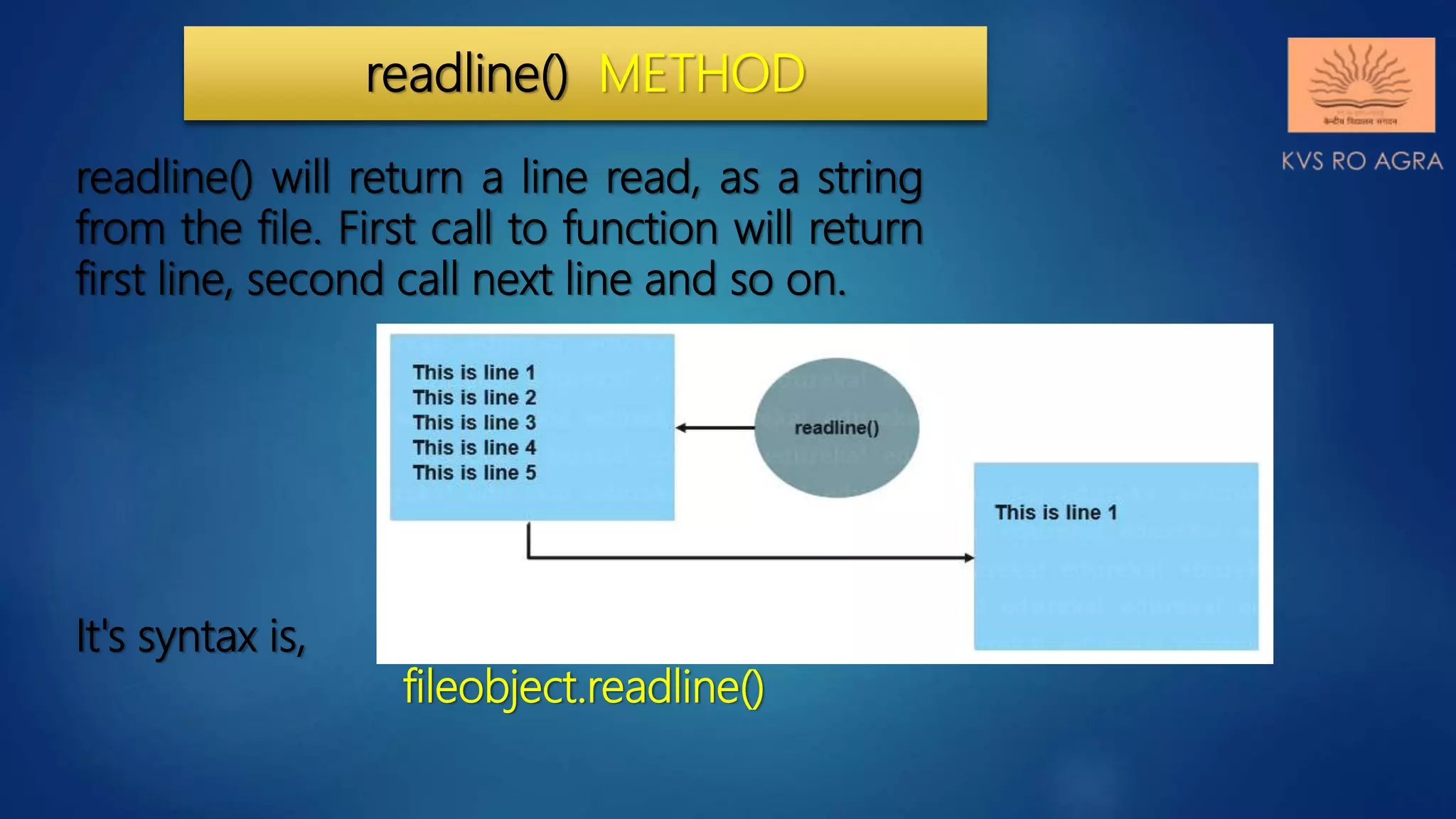
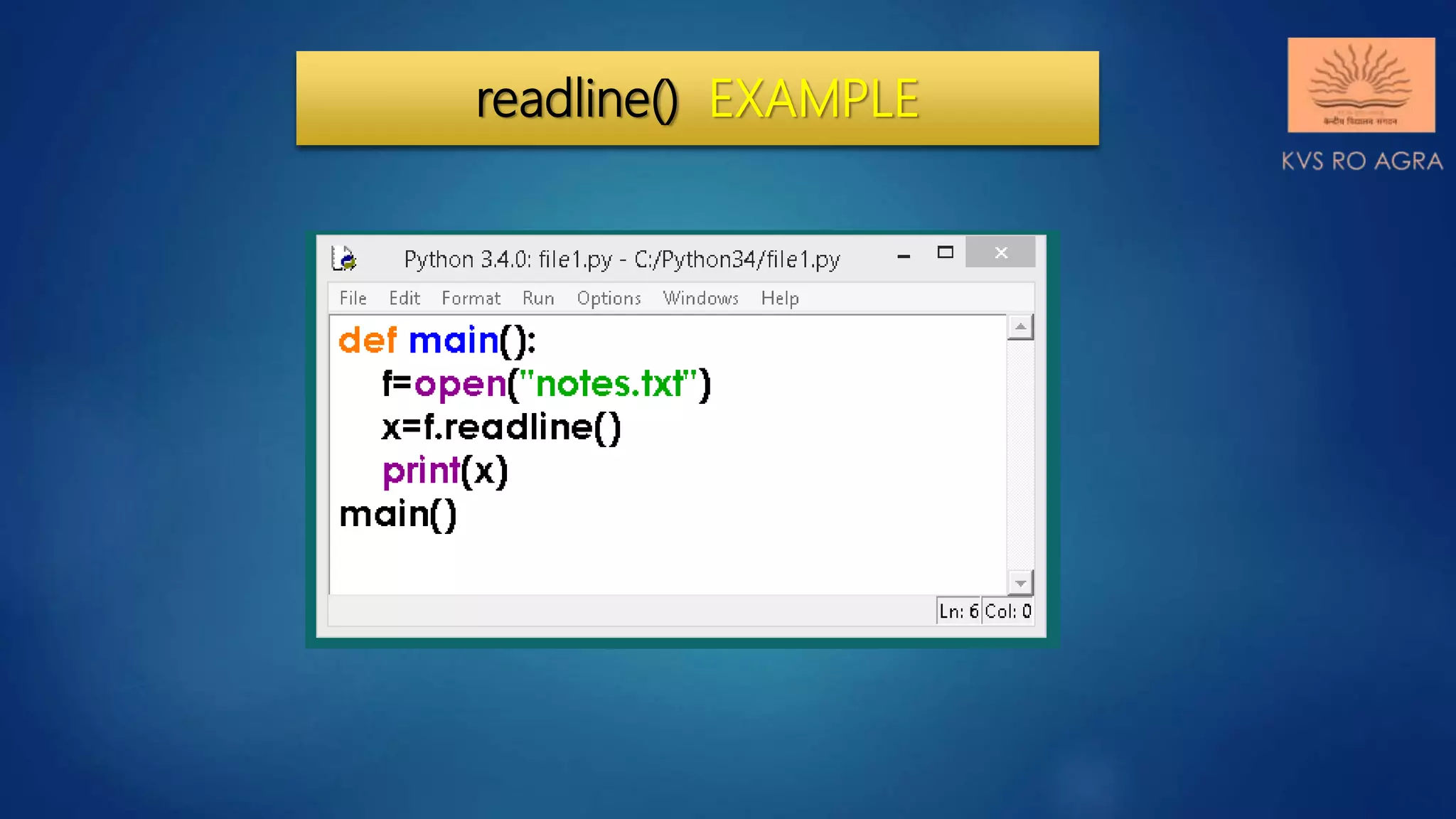
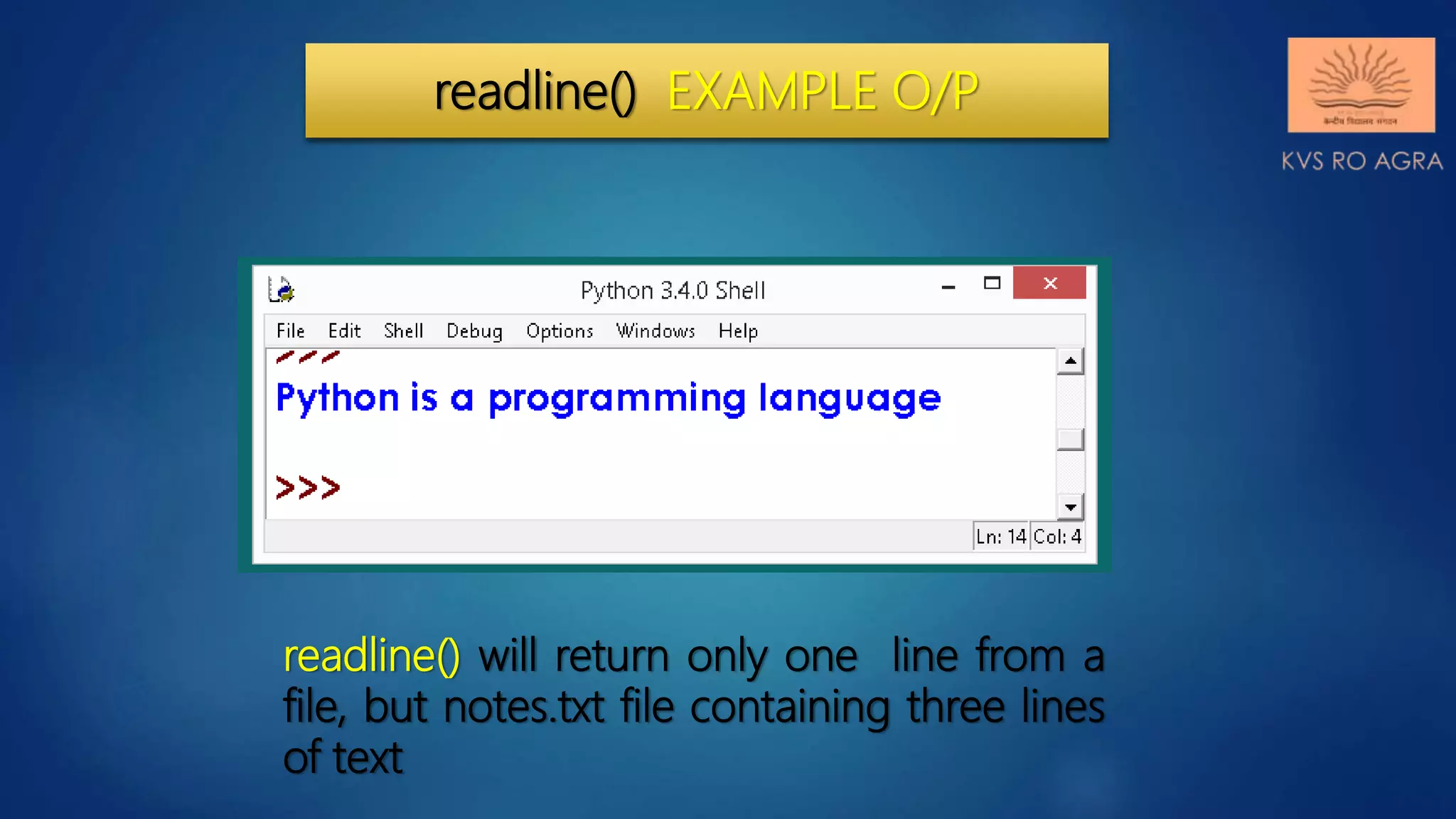
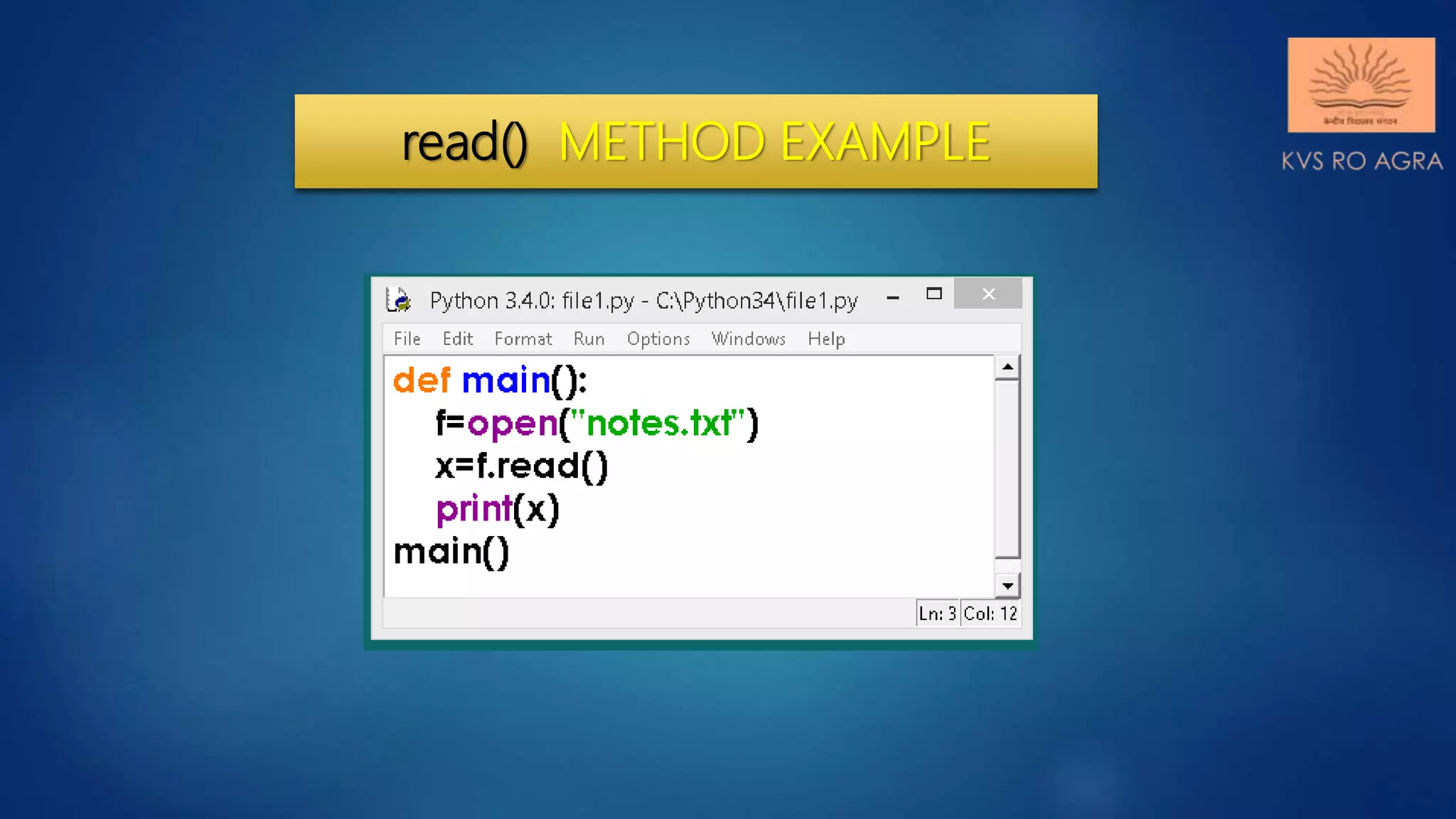
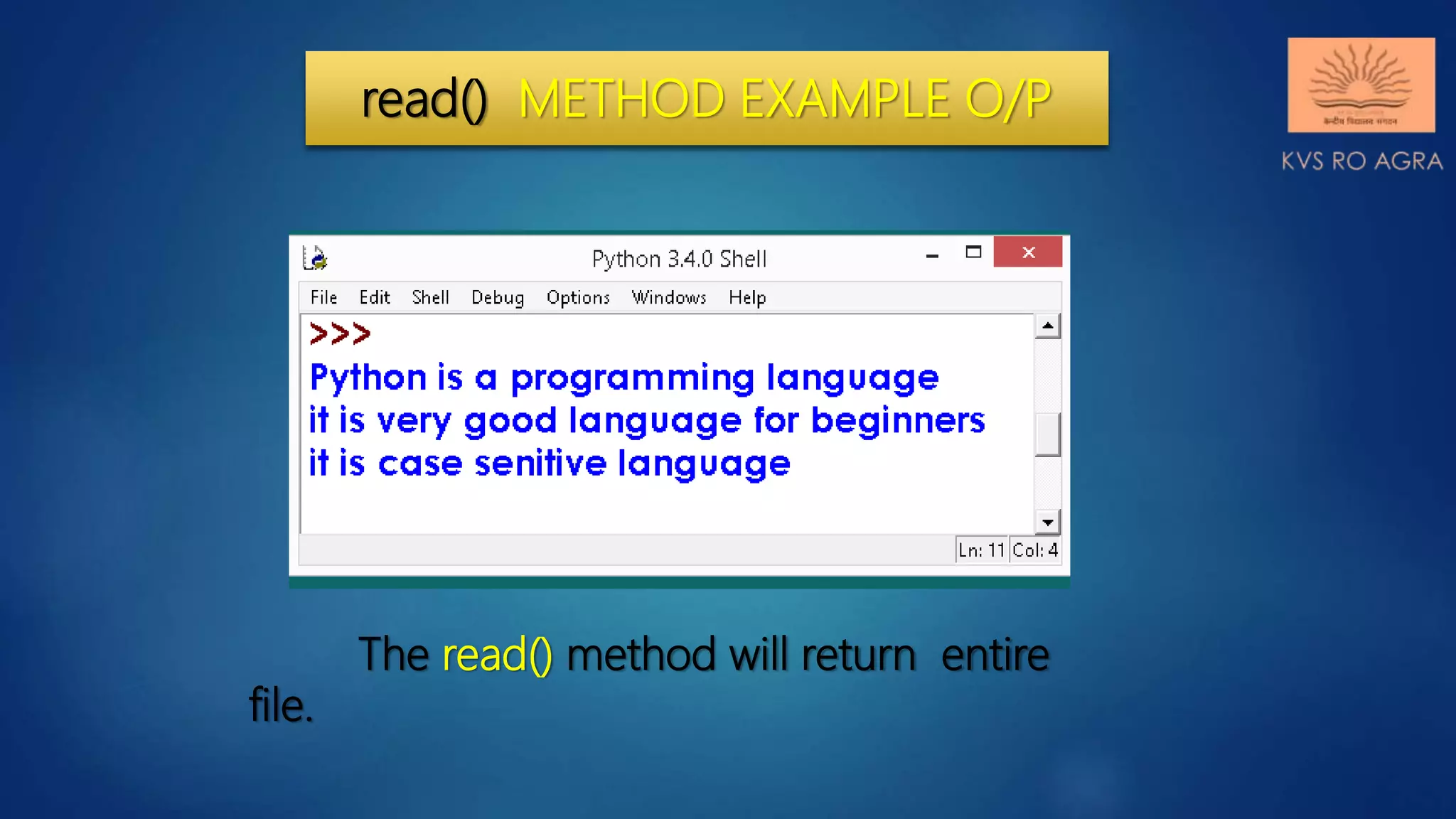
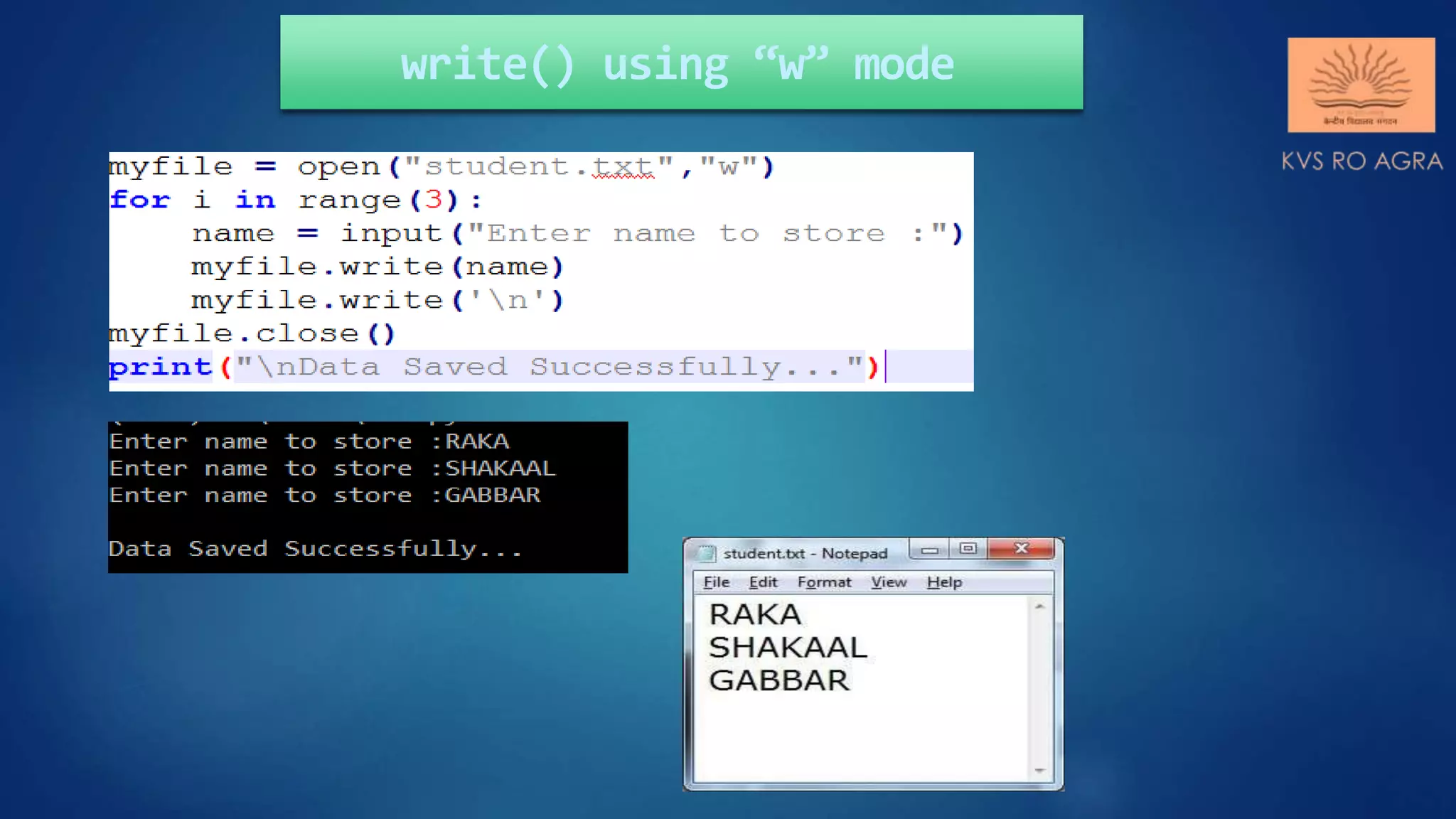
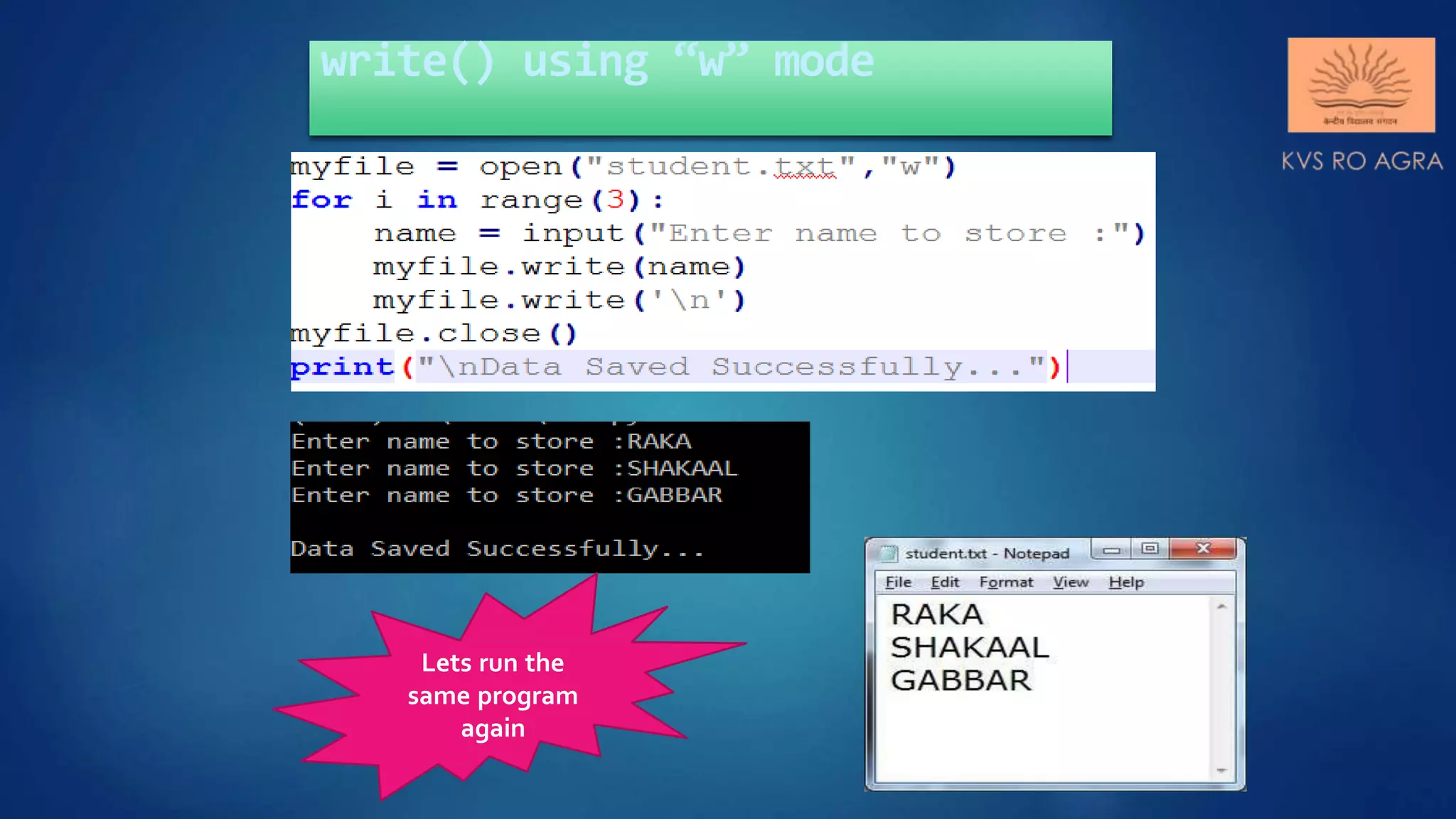
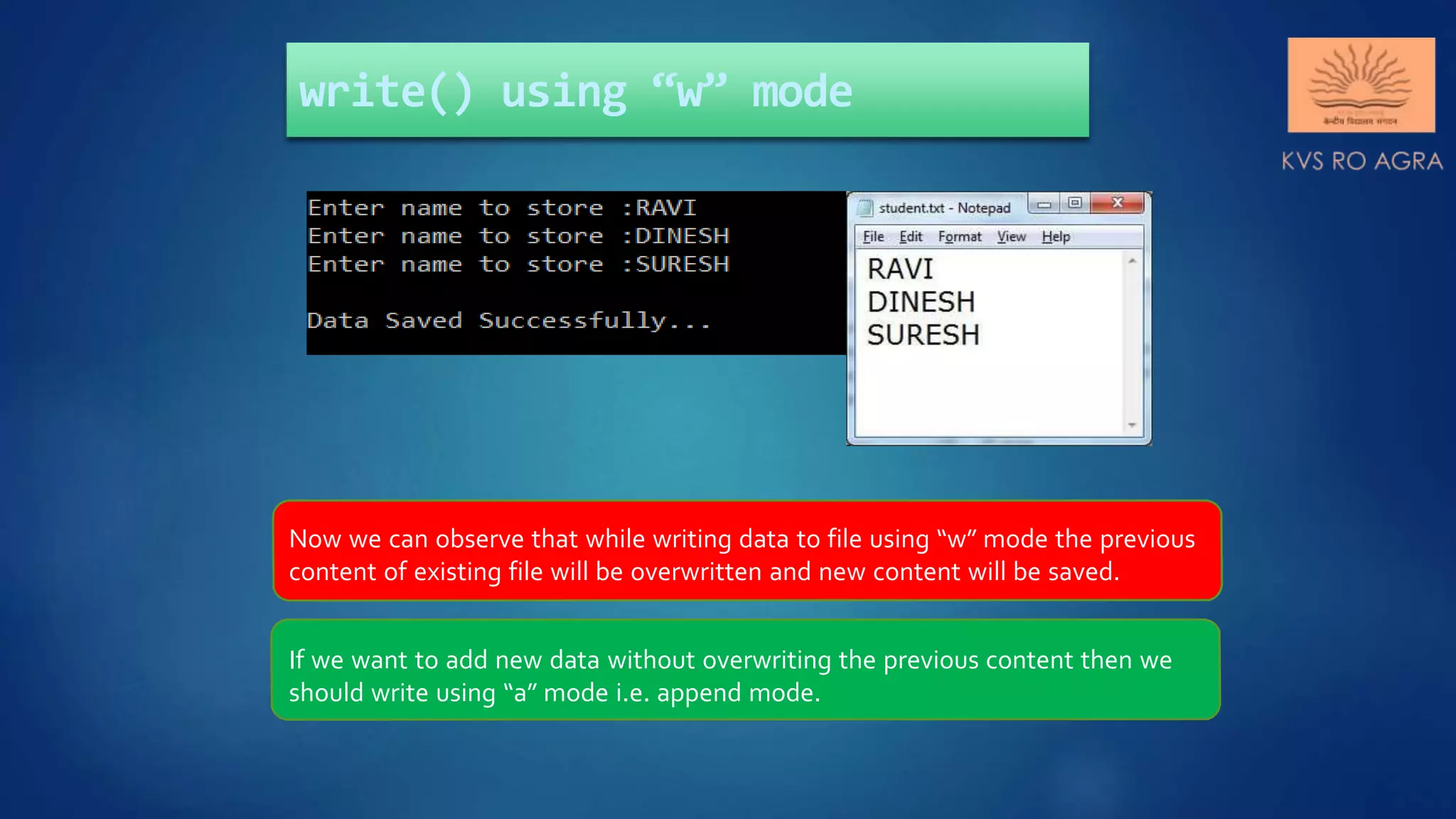
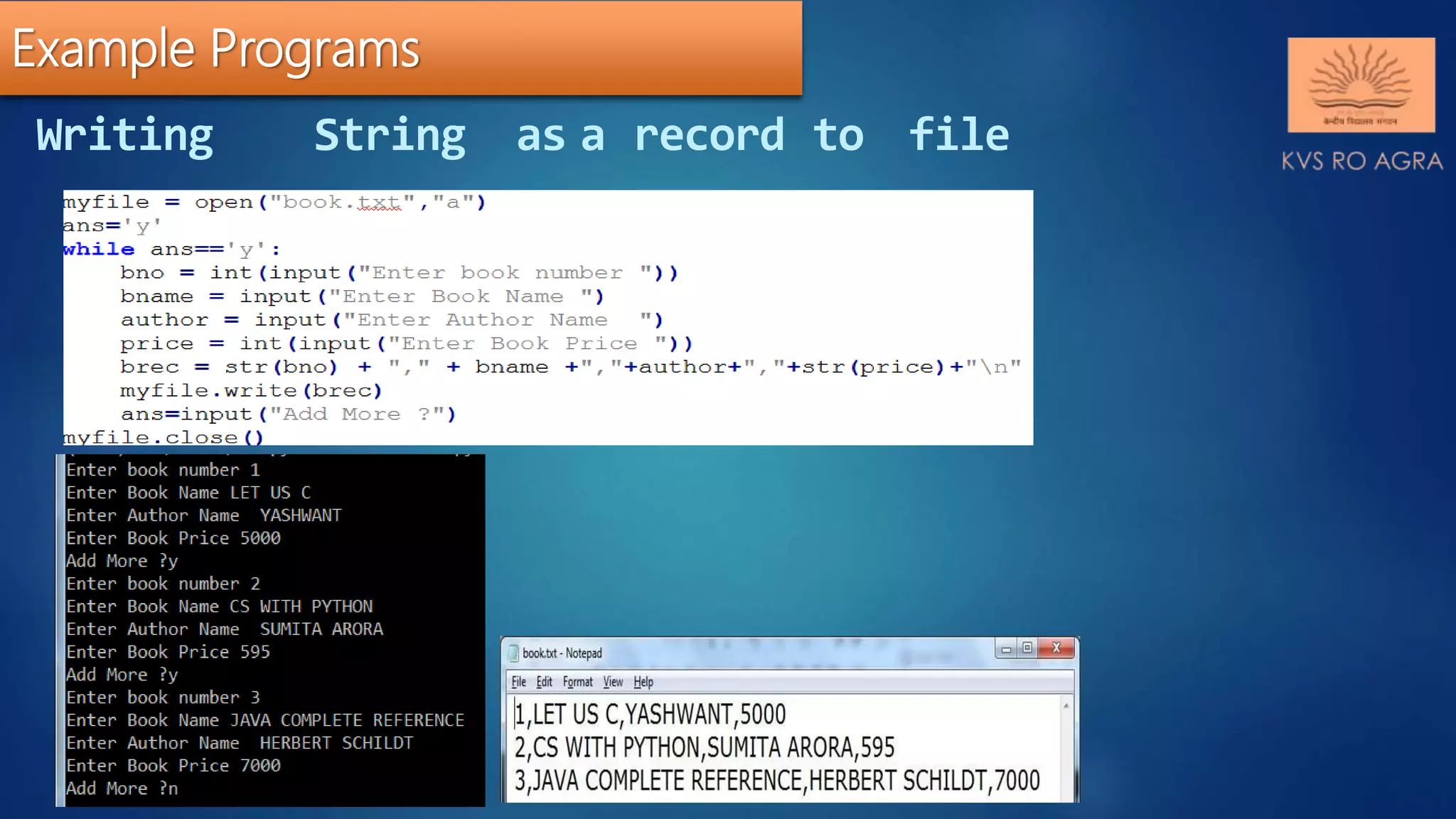
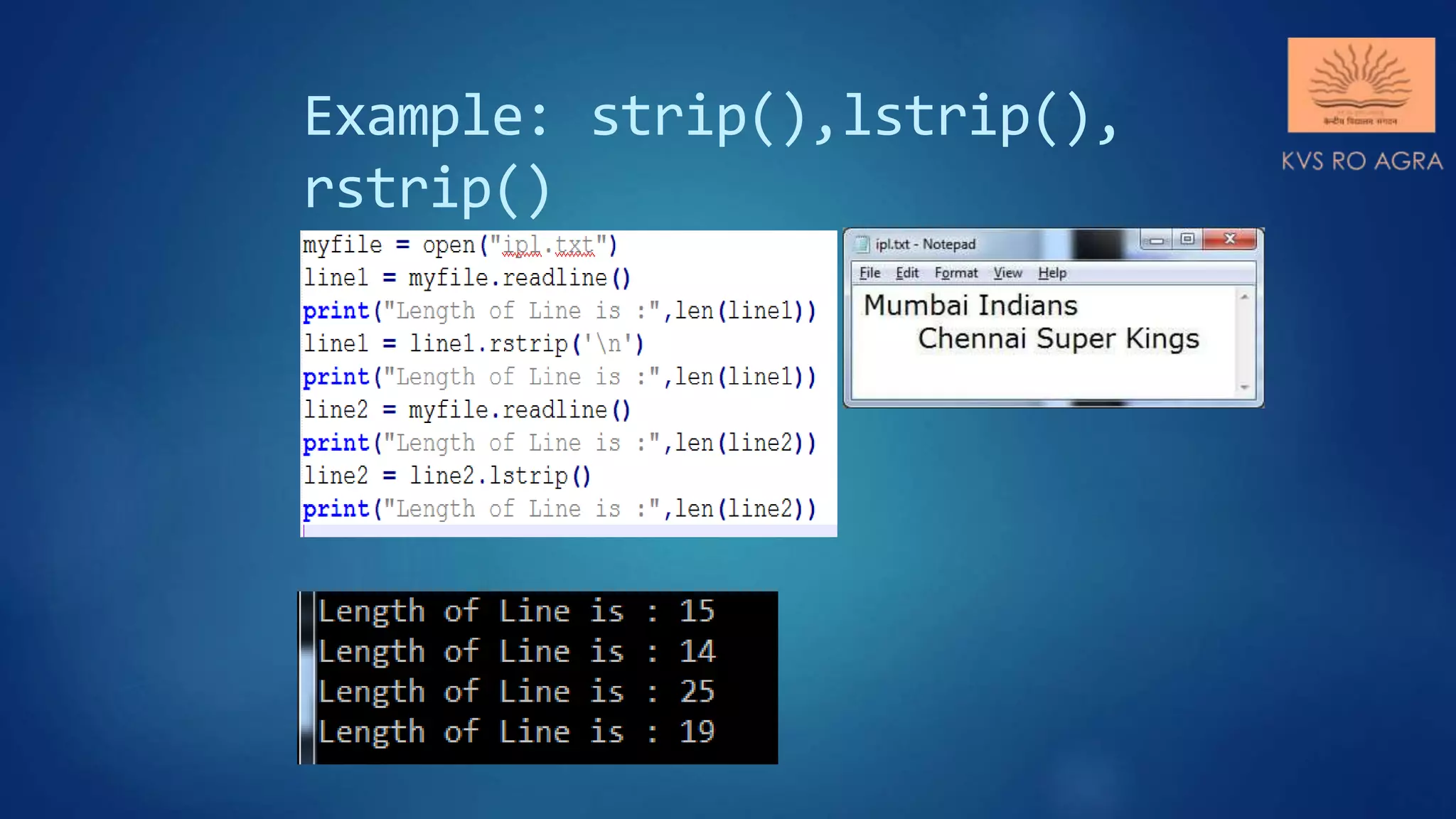
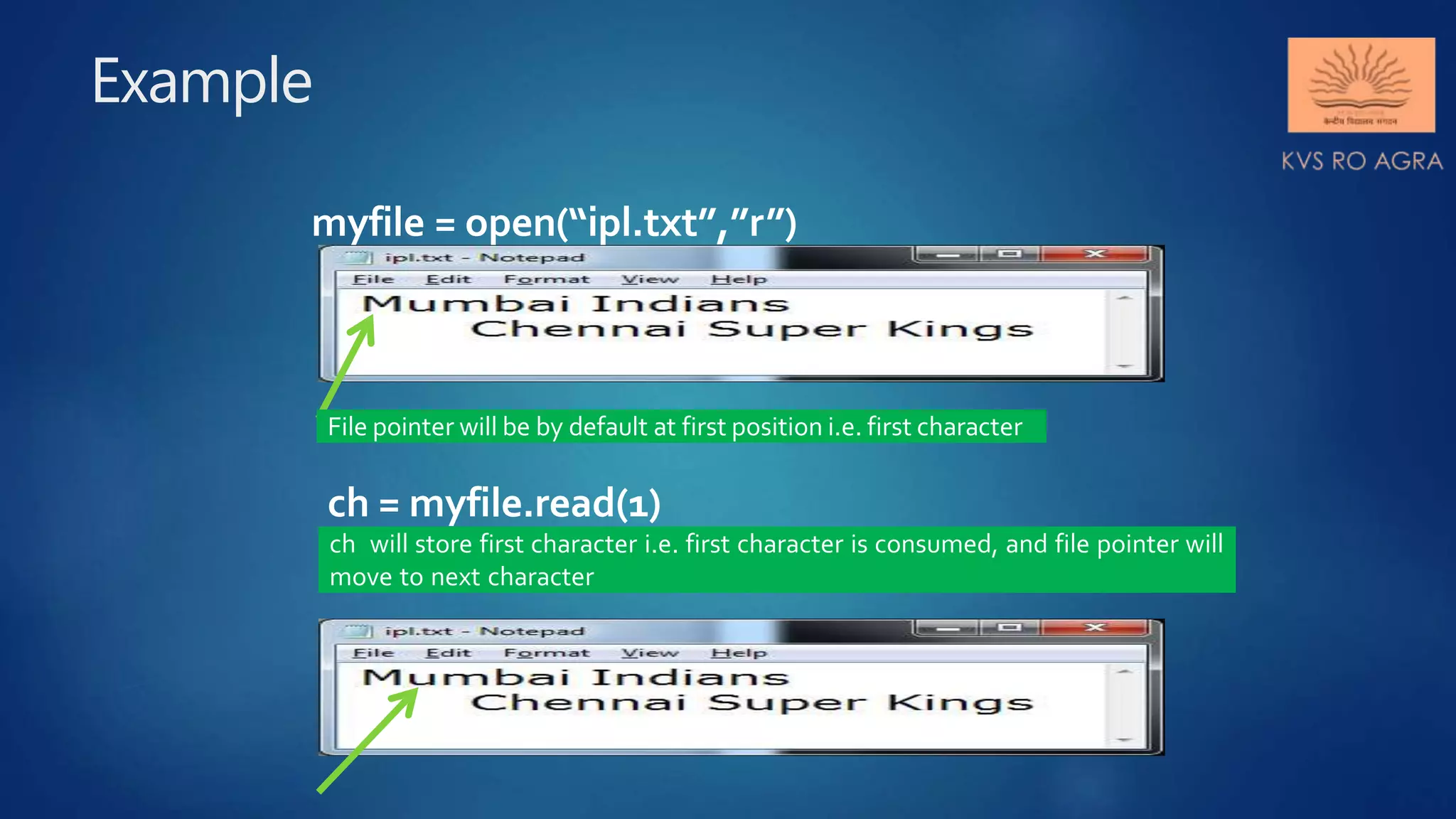
This document discusses various methods for reading and writing files in Python. It describes readline(), readlines(), and read() methods for reading files line-by-line or in full. It also covers write() and writelines() methods for writing strings or lists to files, and discusses opening files in different modes and manipulating the file pointer position. Standard input, output, and error streams are also briefly explained.








![read(size) METHOD
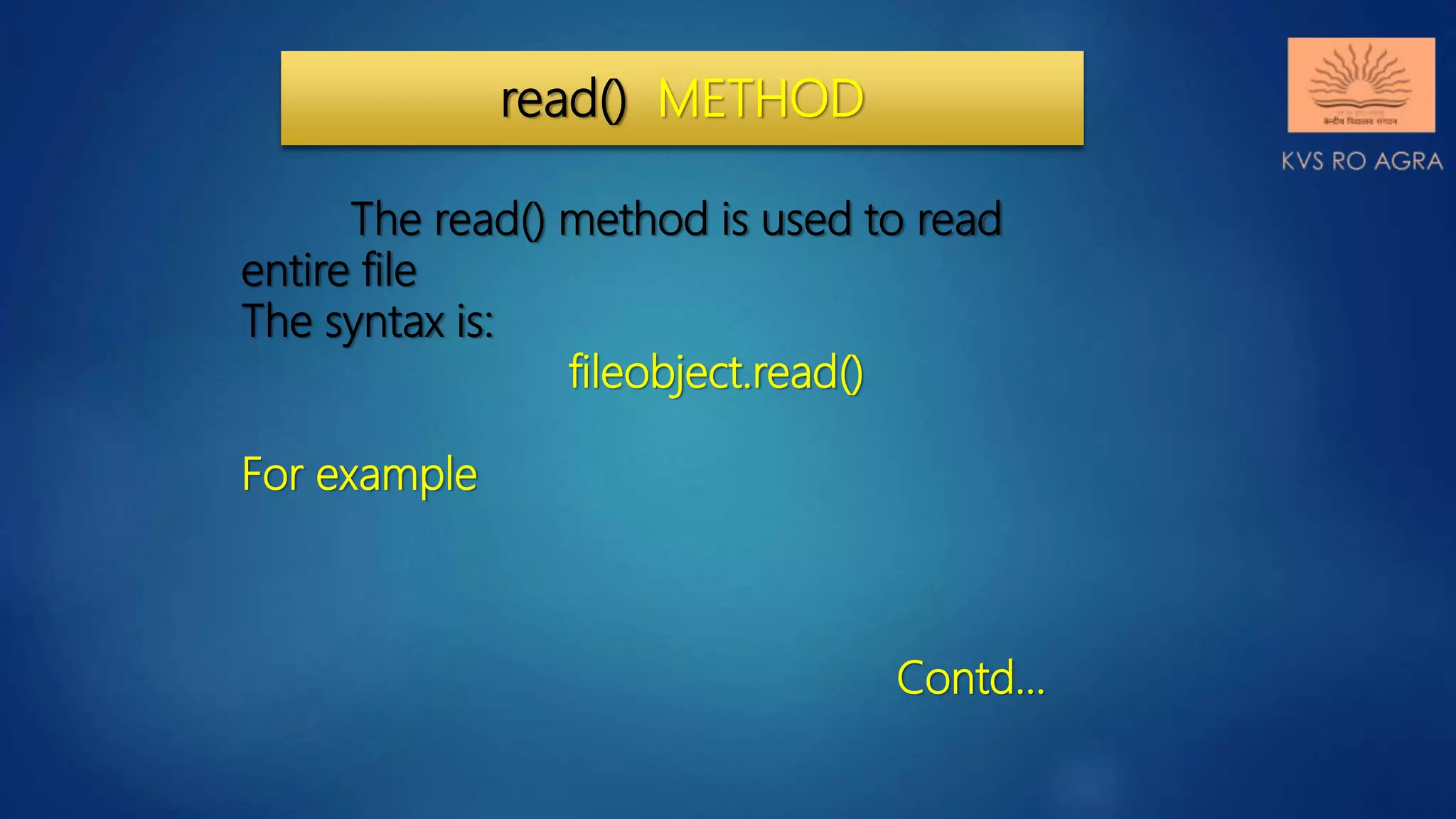
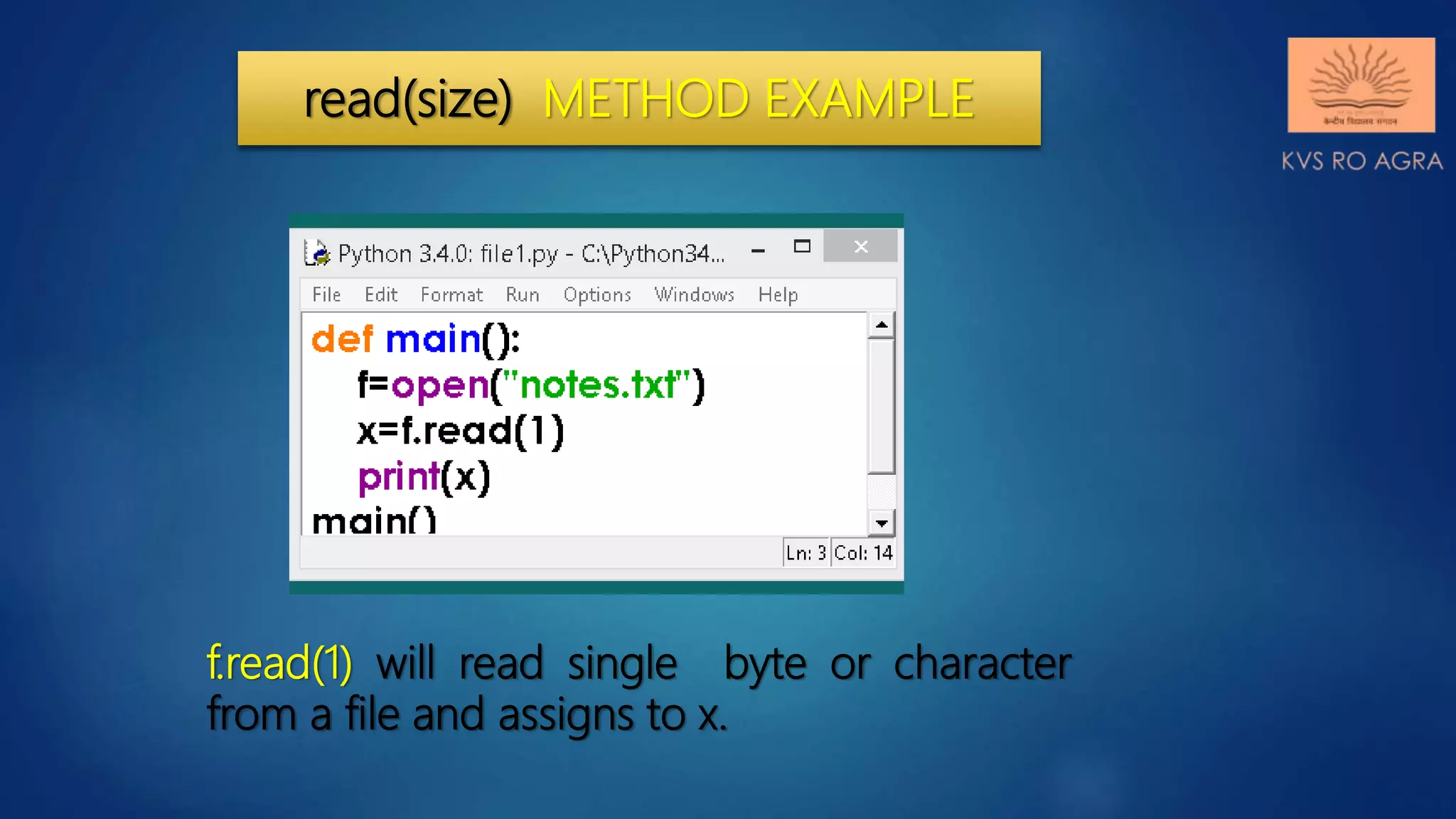
read() can be used to read specific
size string from file. This function also
returns a string read from the file.
Syntax of read() function is:
fileobject.read([size])
For Example:
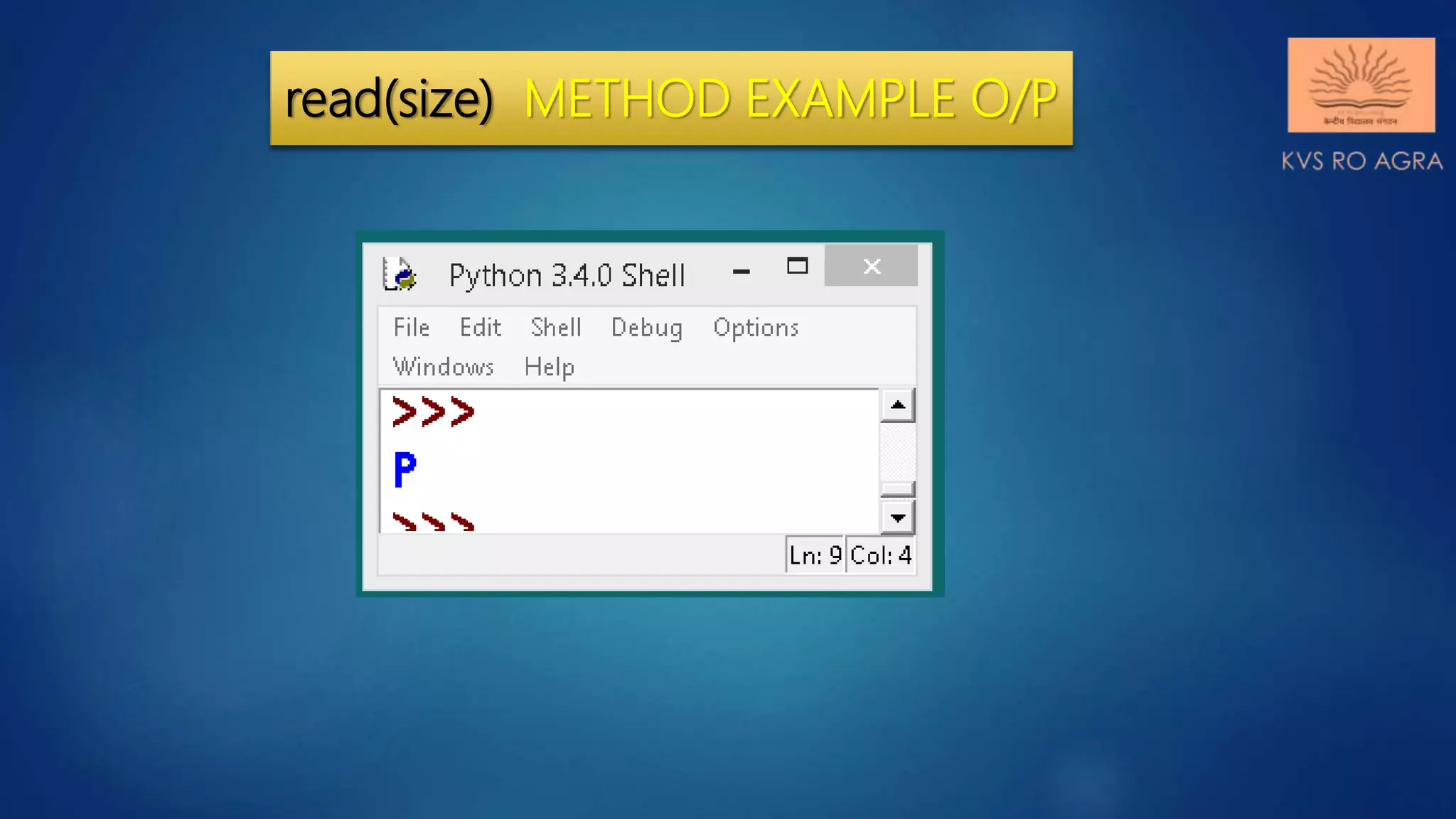
f.read(1) will read single
byte or character from a file.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datafilehandlinginpython-readingwritingmethods-200804122139/75/Data-file-handling-in-python-reading-writing-methods-15-2048.jpg)











![Set File offset in Python
Tell() Method
This method gives you the current offset of the file pointer in a file.
Syntax:
file.tell()
The tell() method doesn’t require any argument.
Seek() Method
This method can help you change the position of a file pointer in a file.
Syntax:
file.seek(offset[, from])
The <offset> argument represents the size of the displacement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datafilehandlinginpython-readingwritingmethods-200804122139/75/Data-file-handling-in-python-reading-writing-methods-35-2048.jpg)
![file.seek(offset[, from])
The <from> argument indicates the start point.
If from is 0, then the shift will start from the root level.
If from is 1, then the reference position will become the current position.
It from is 2, then the end of the file would serve as the reference position.
Example: Setting offsets in Python
with open('app.log', 'w', encoding = 'utf-8') as f:
#first line
f.write('It is my first filen')
#second line
f.write('This filen')
#third line
f.write('contains three linesn')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datafilehandlinginpython-readingwritingmethods-200804122139/75/Data-file-handling-in-python-reading-writing-methods-36-2048.jpg)


