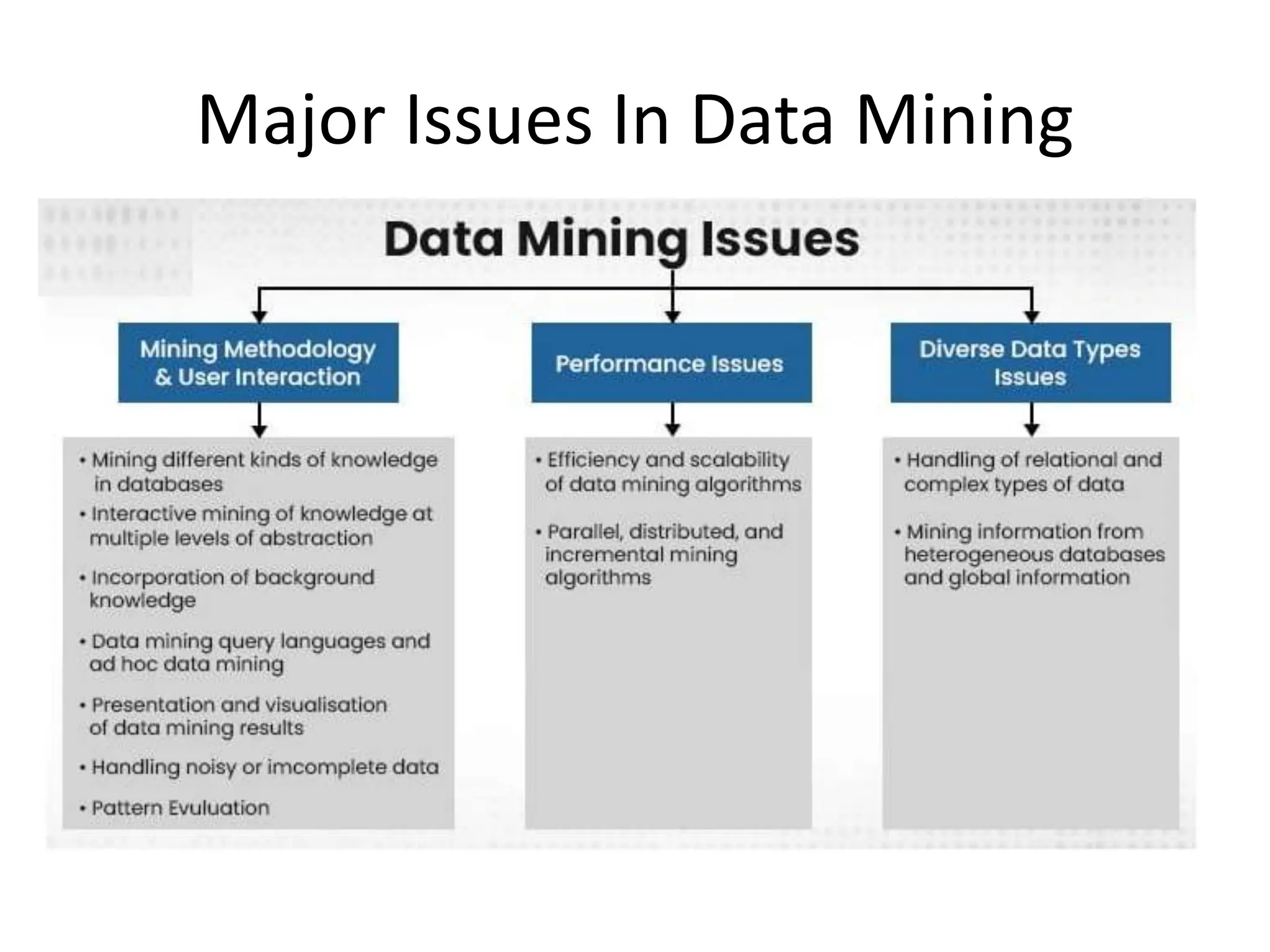
Data mining is the process of extracting knowledge from large data sets, emphasizing computational discovery of patterns through methods in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and statistics. It encompasses descriptive tasks that characterize data properties and predictive tasks that forecast outcomes, with systems designed to accommodate various patterns and user expectations. Major challenges include ensuring efficiency and scalability of algorithms, handling diverse data types, and mining from heterogeneous databases.