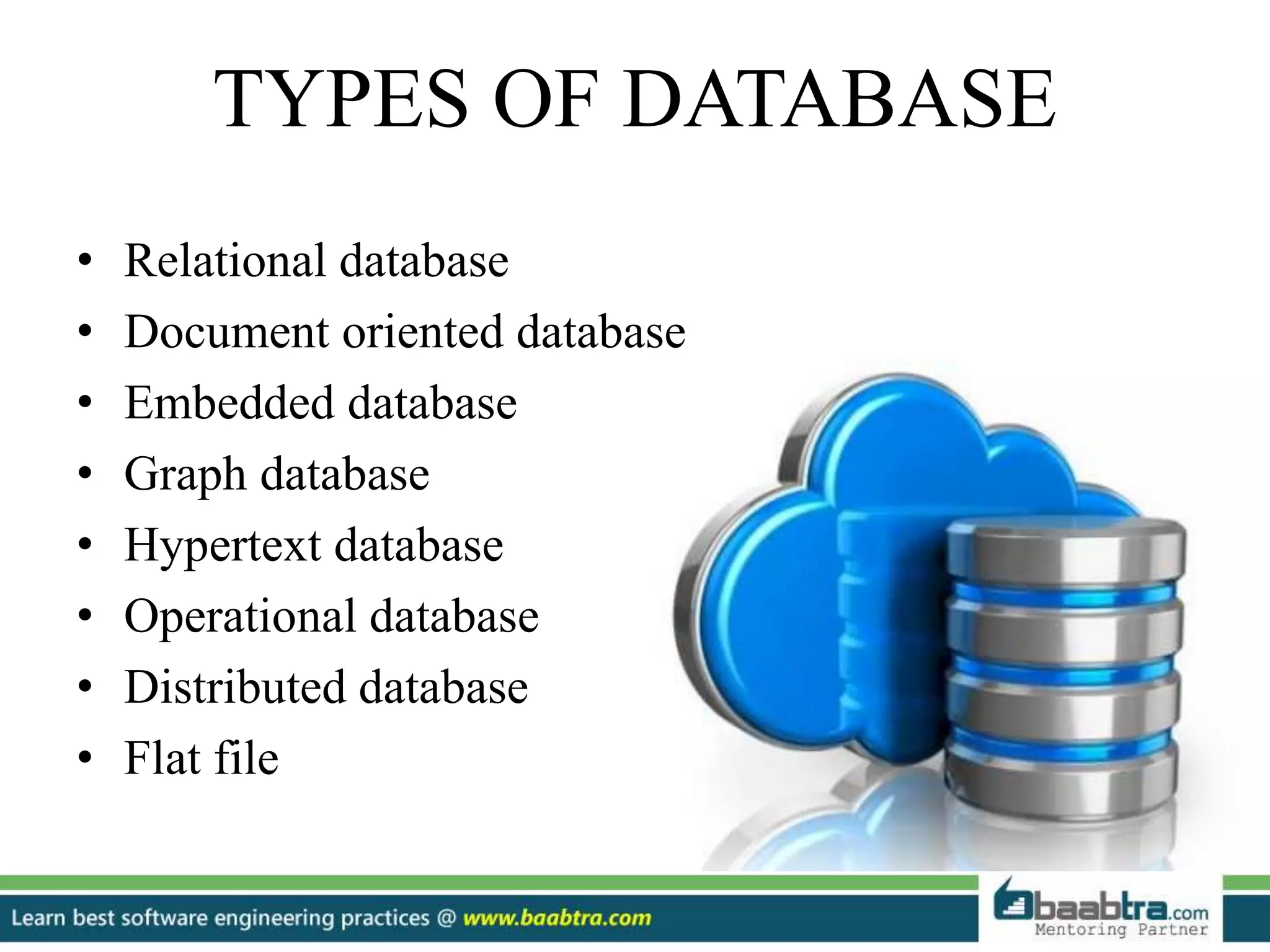
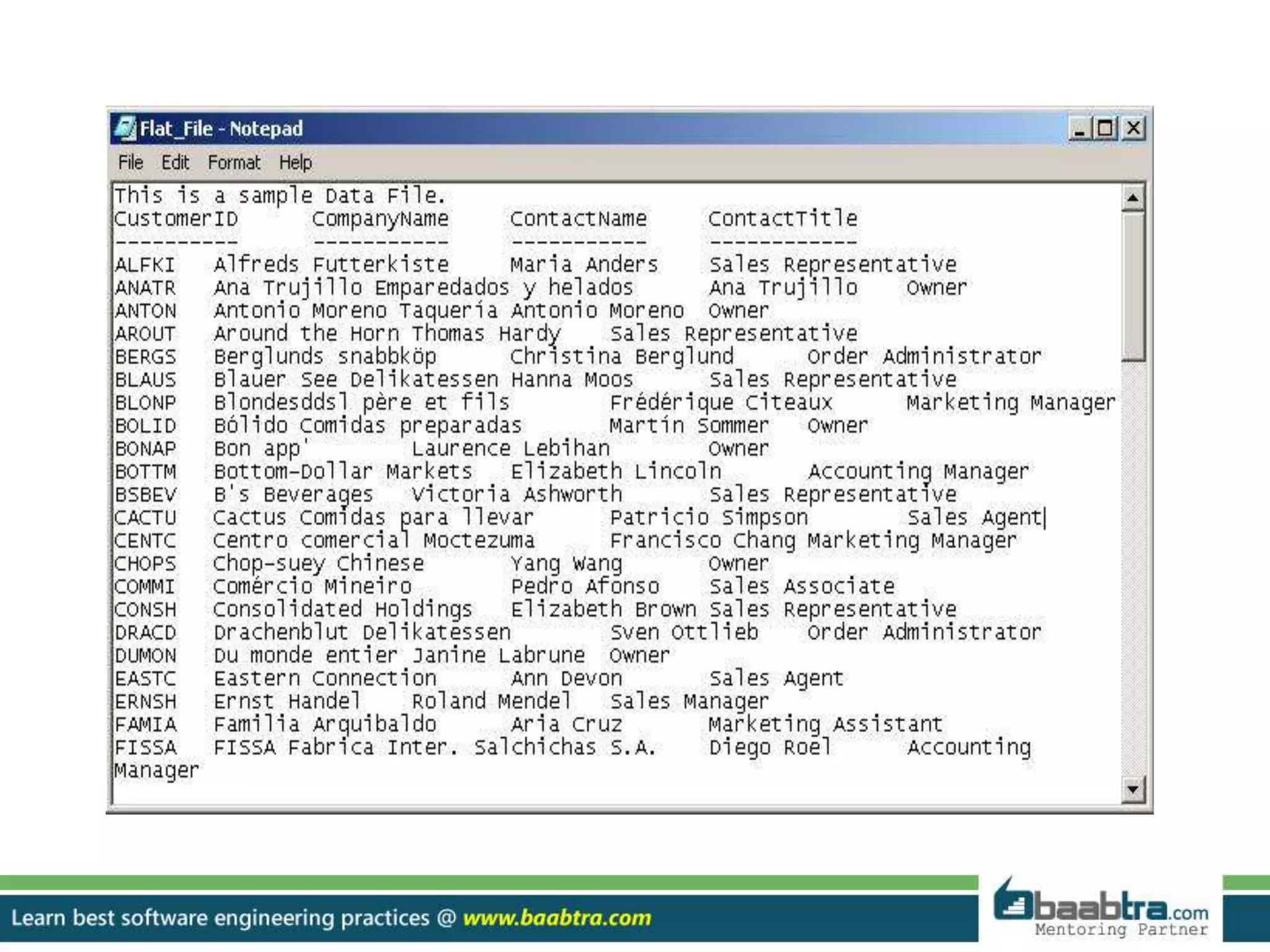
This document provides an overview of different types of databases including relational, document oriented, embedded, graph, hypertext, operational, distributed, and flat file databases. Key points include:
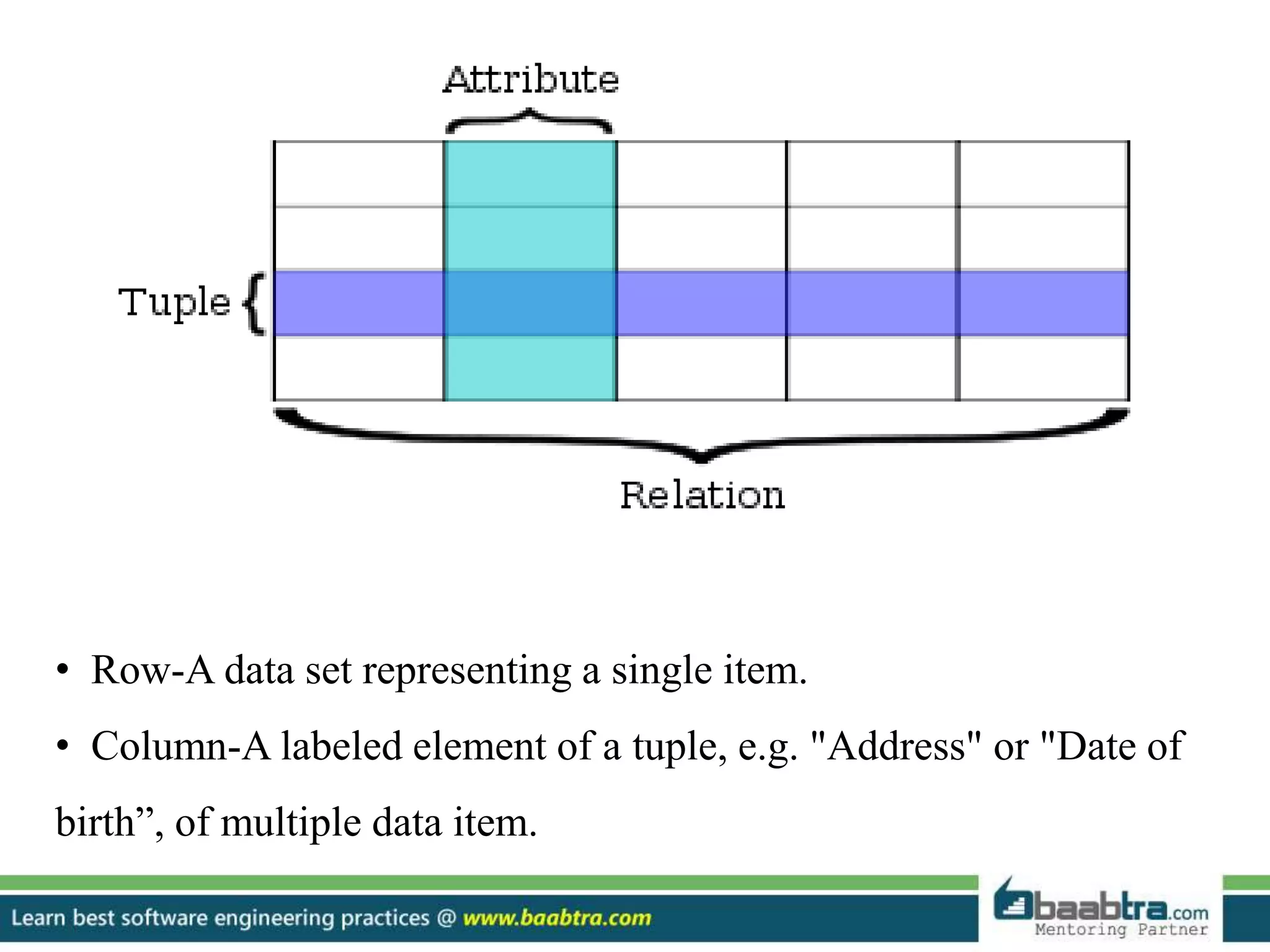
- Relational databases store data in tables with rows and columns and use primary and foreign keys.
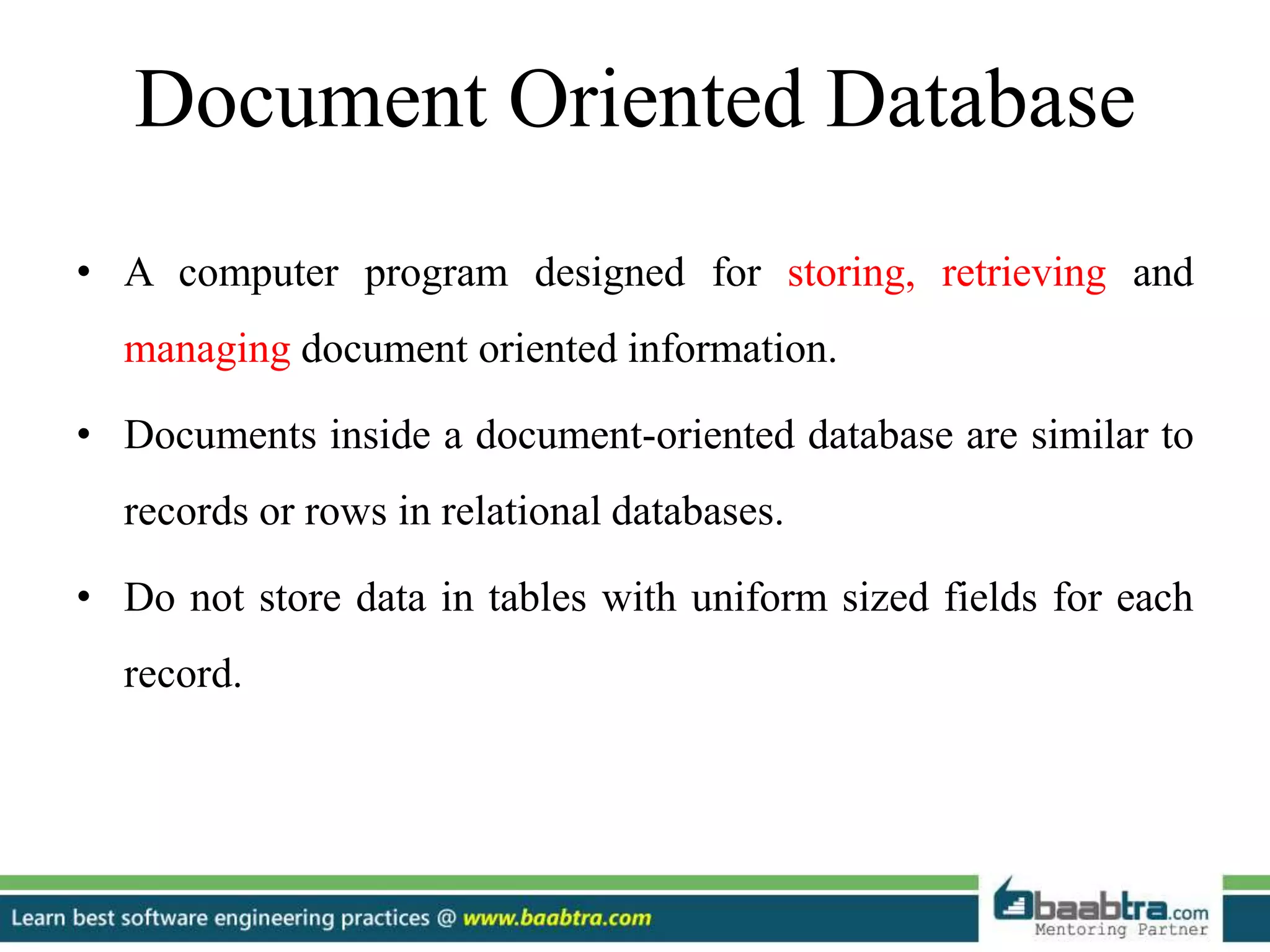
- Document oriented databases store flexible documents without uniform fields.
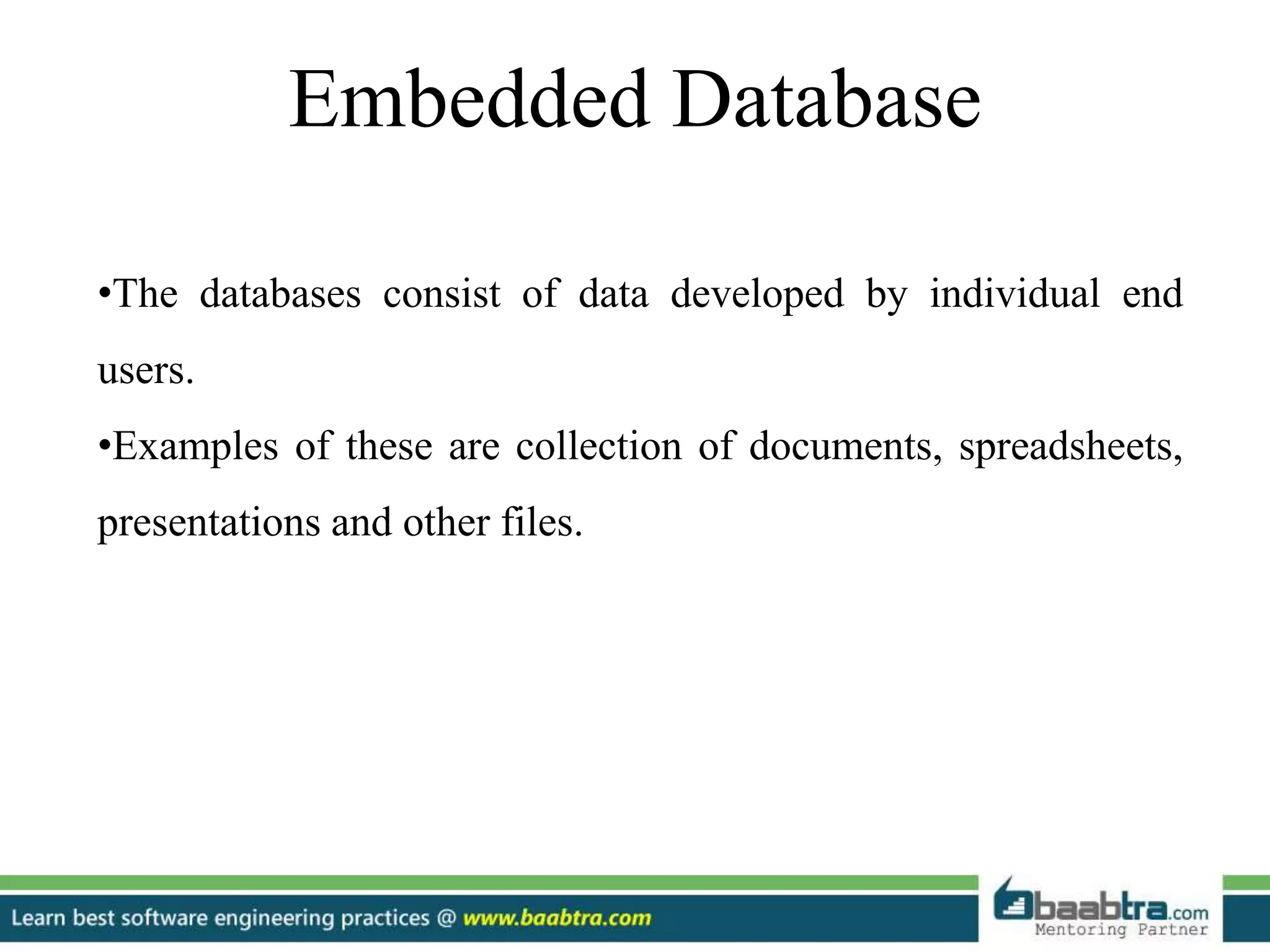
- Embedded databases consist of end-user files like documents and spreadsheets.
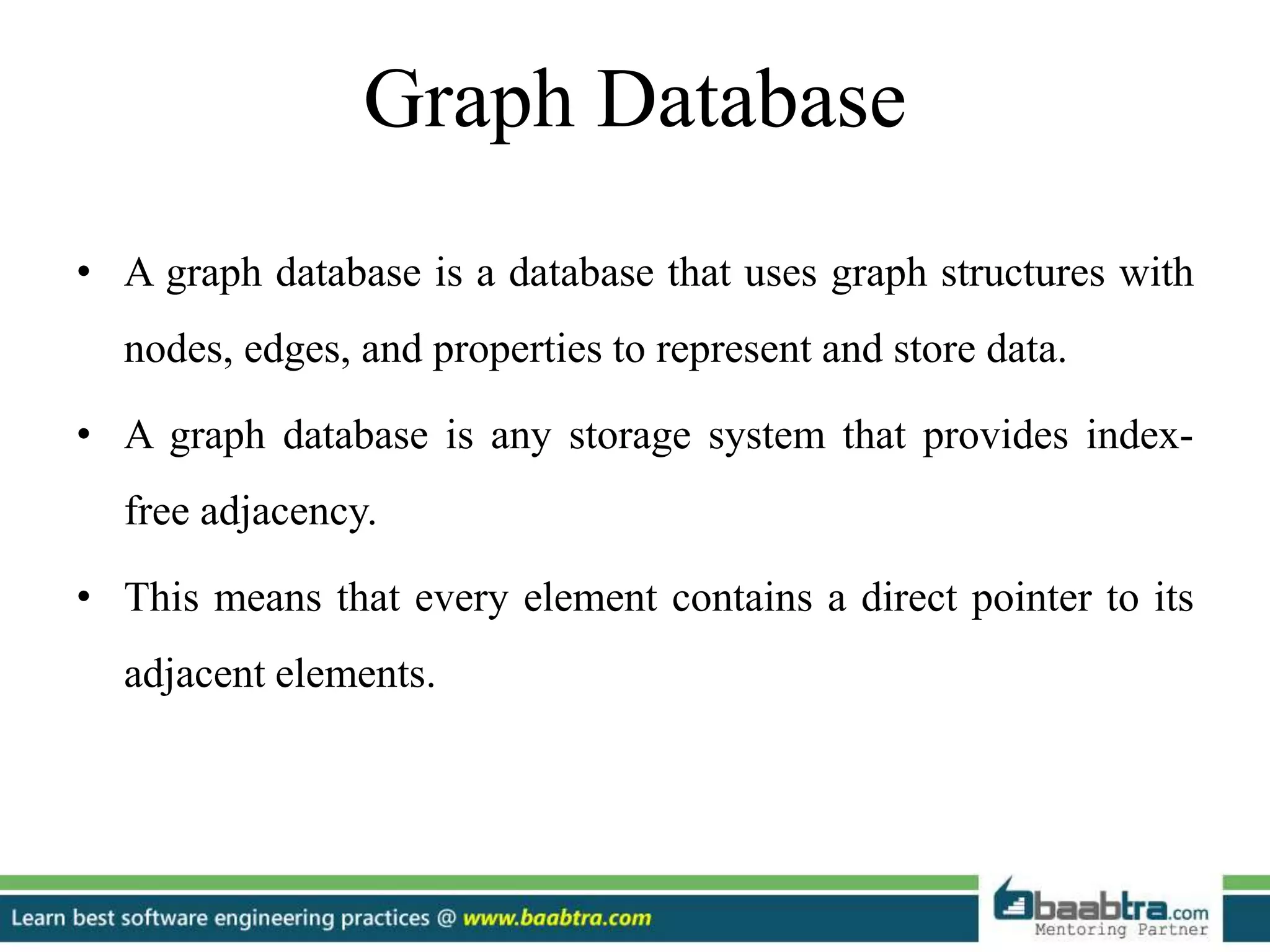
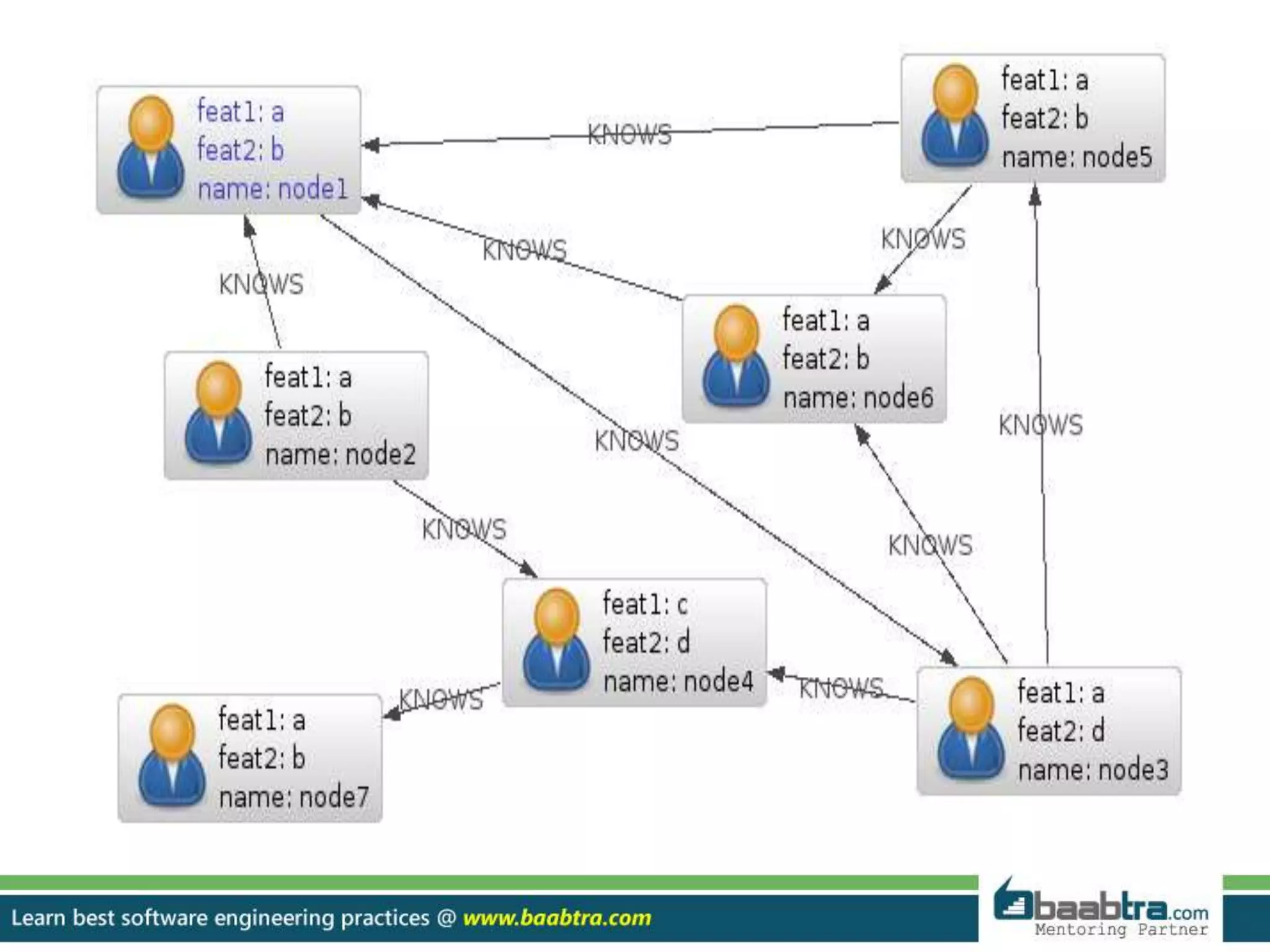
- Graph databases represent data through nodes and edges to show relationships.
- The document also provides contact information for Baabtra, a company that offers online courses and mentoring for software development.