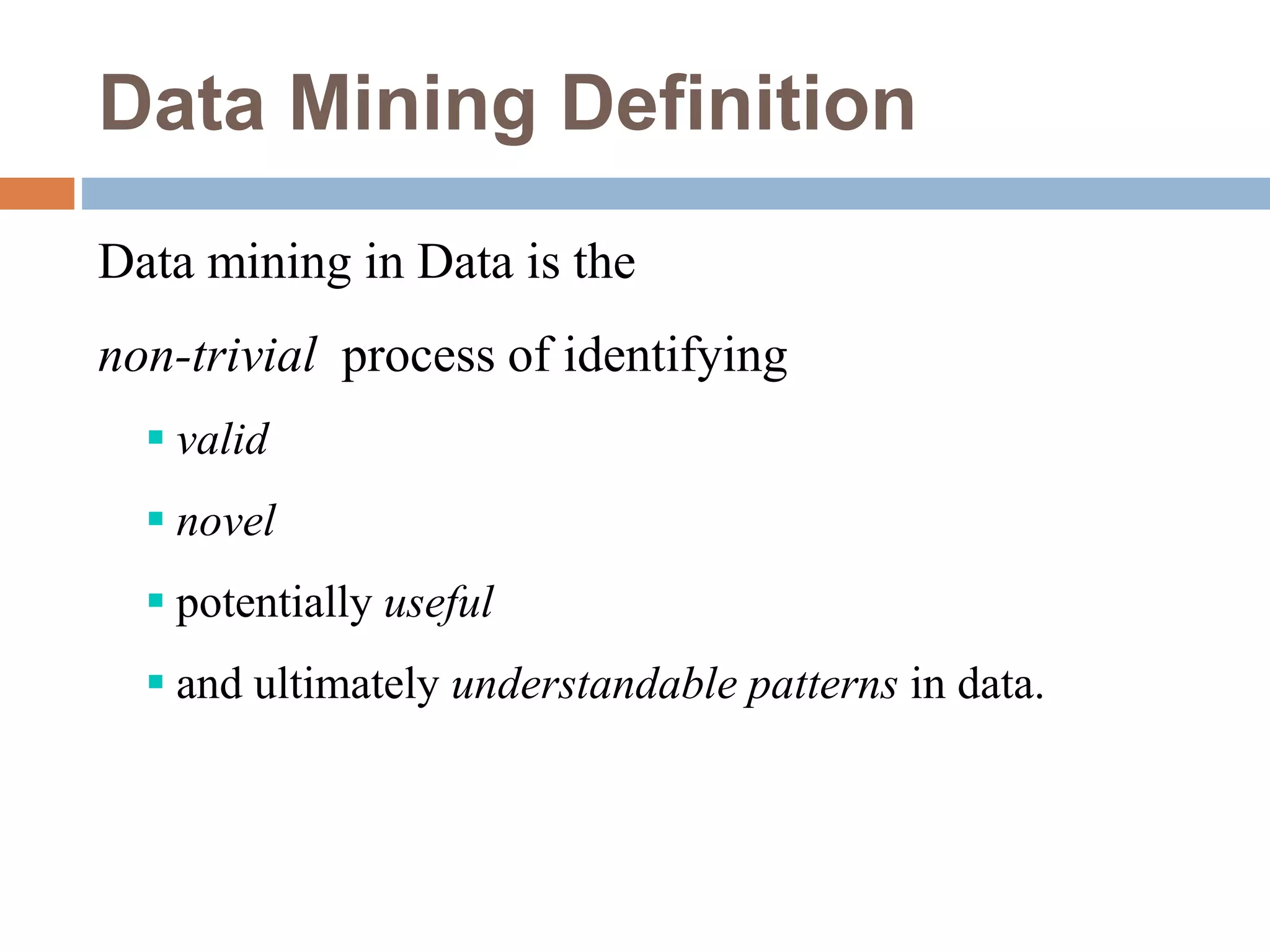
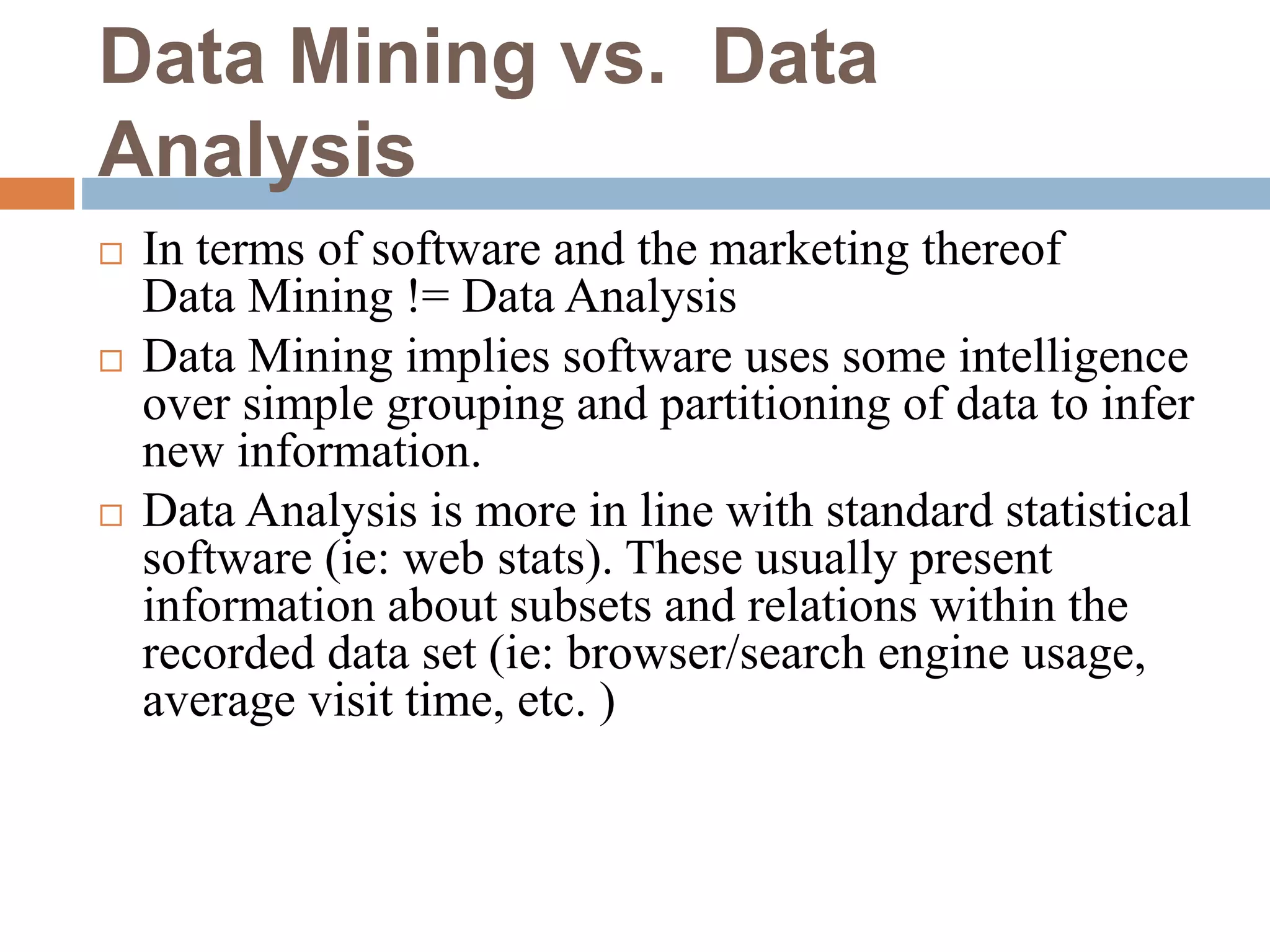
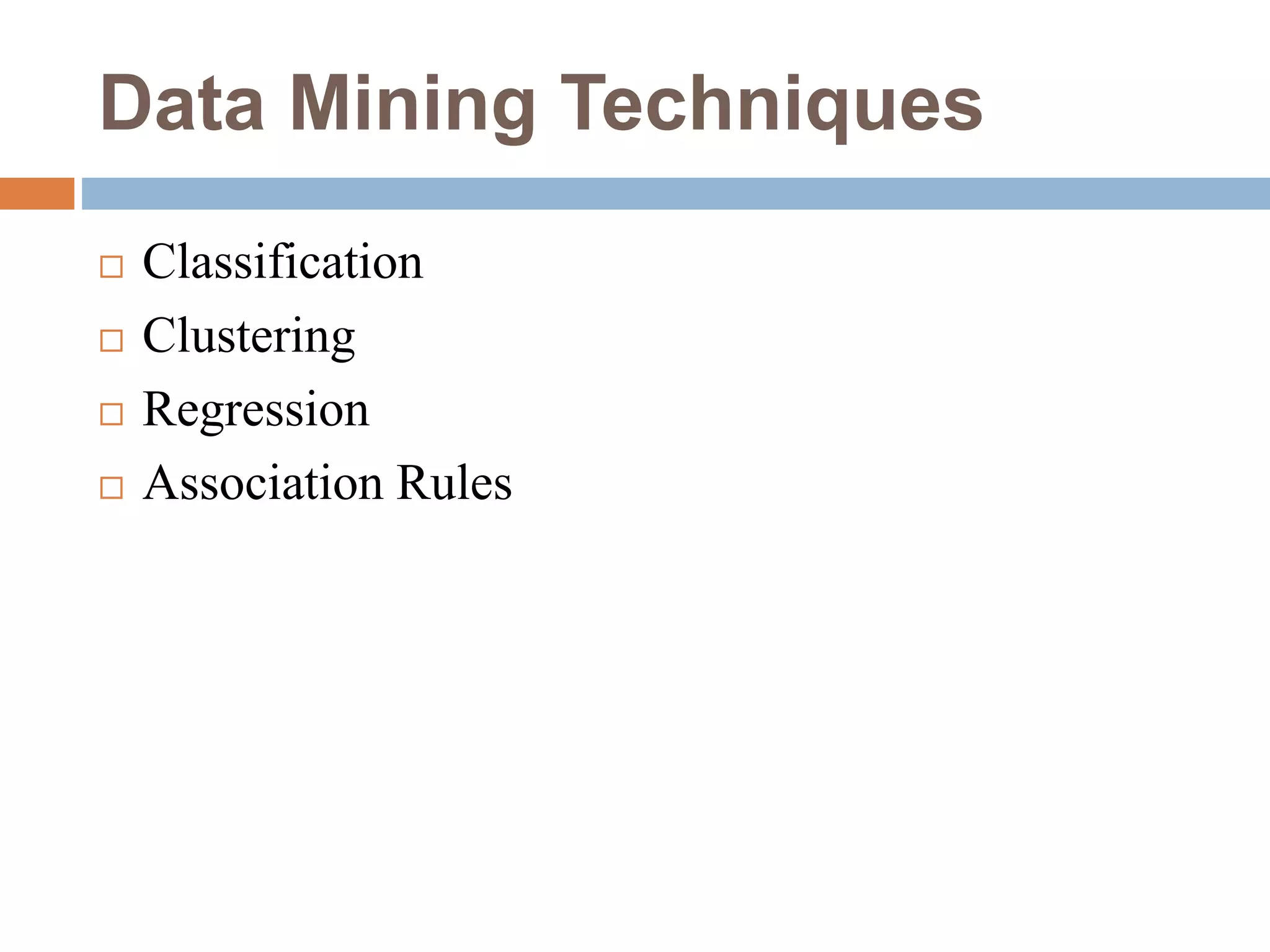
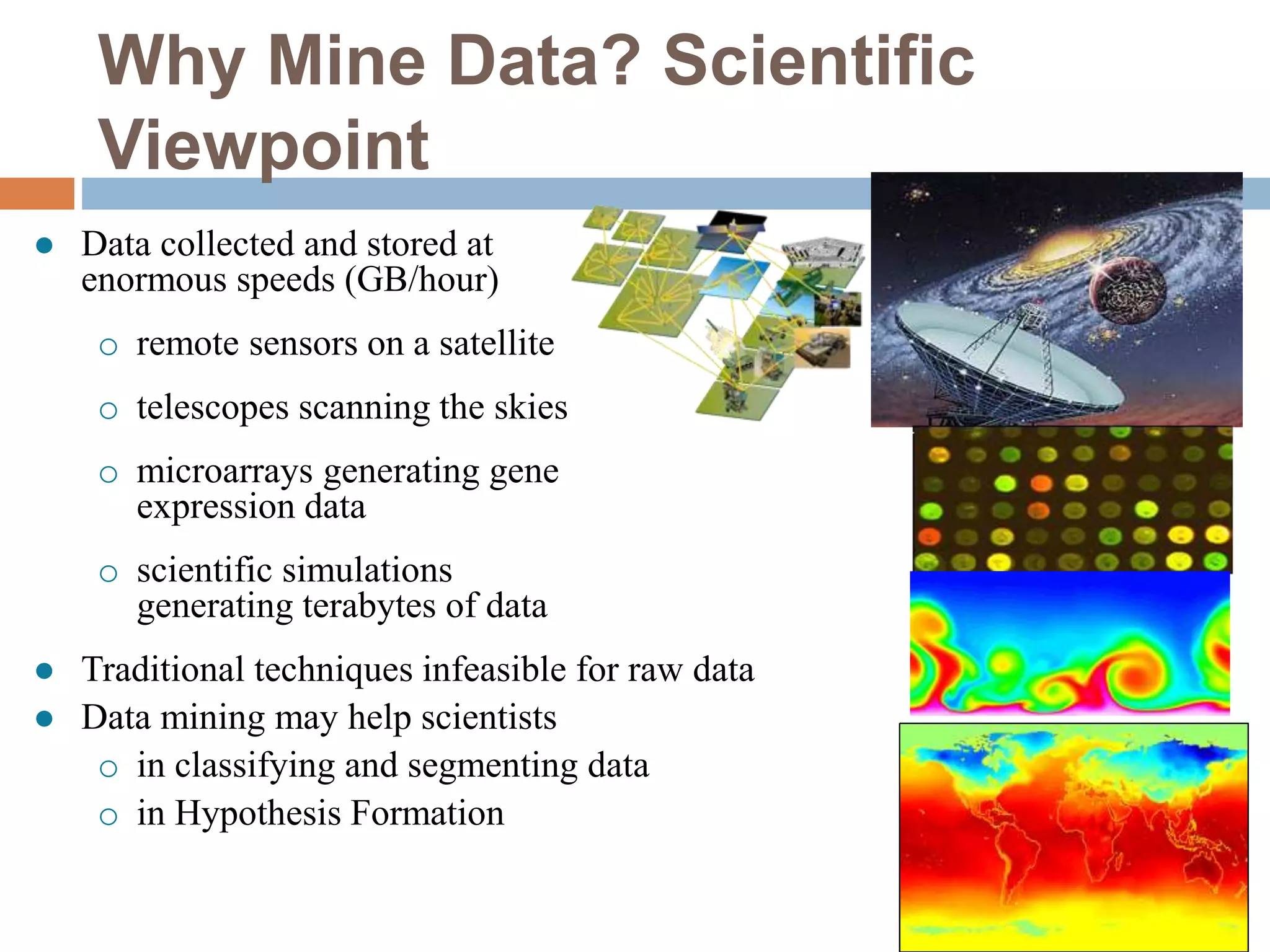
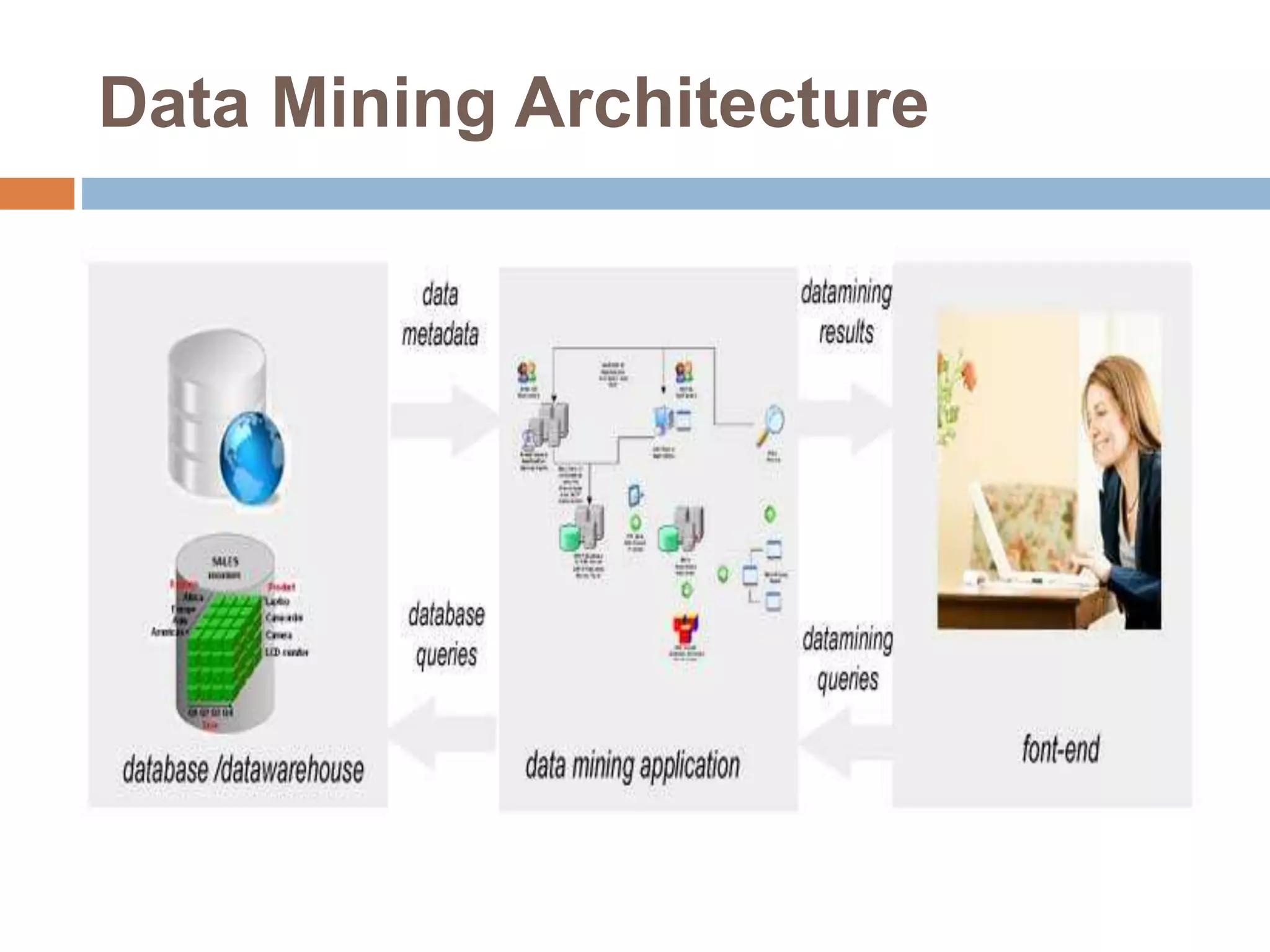
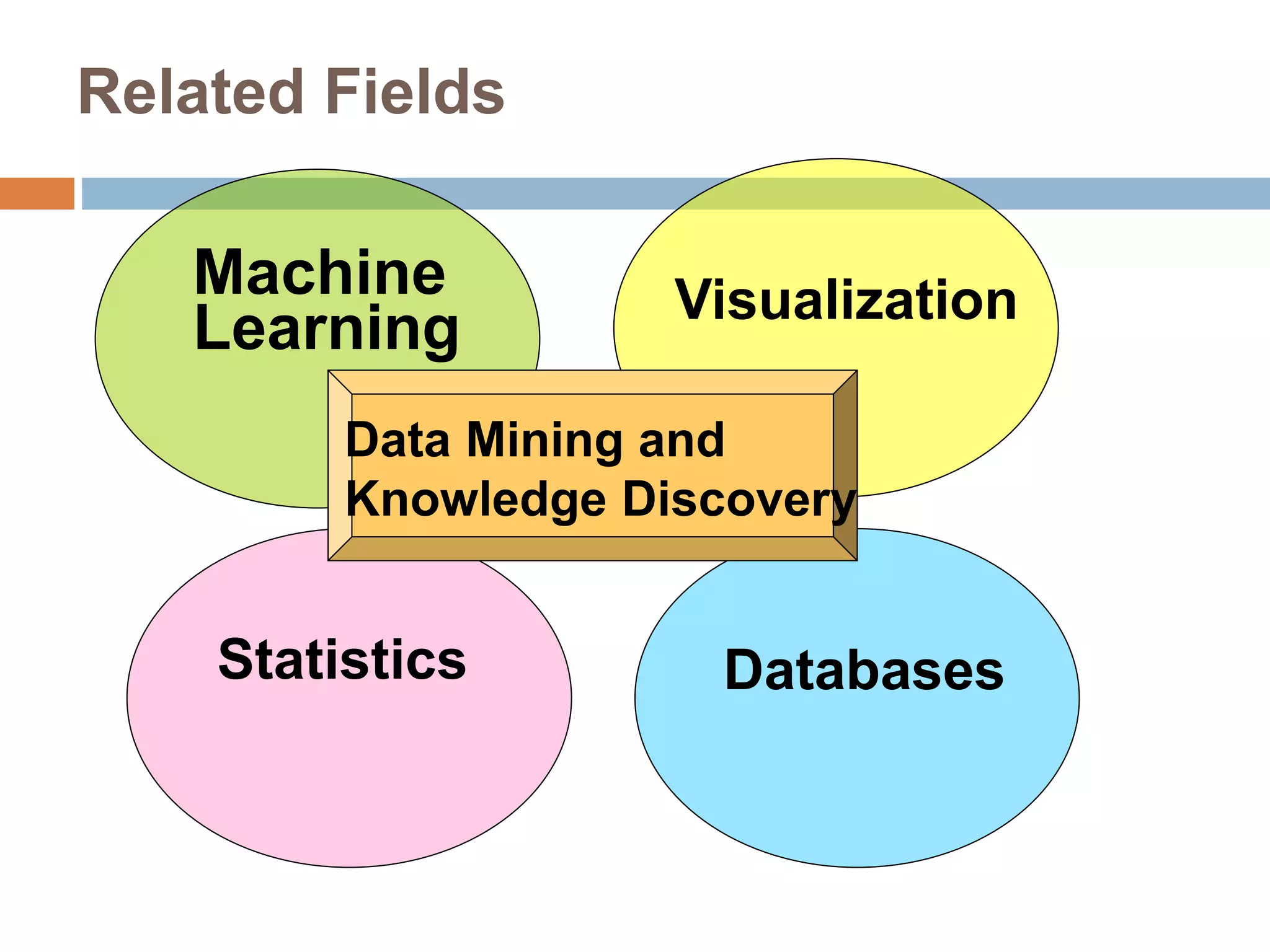
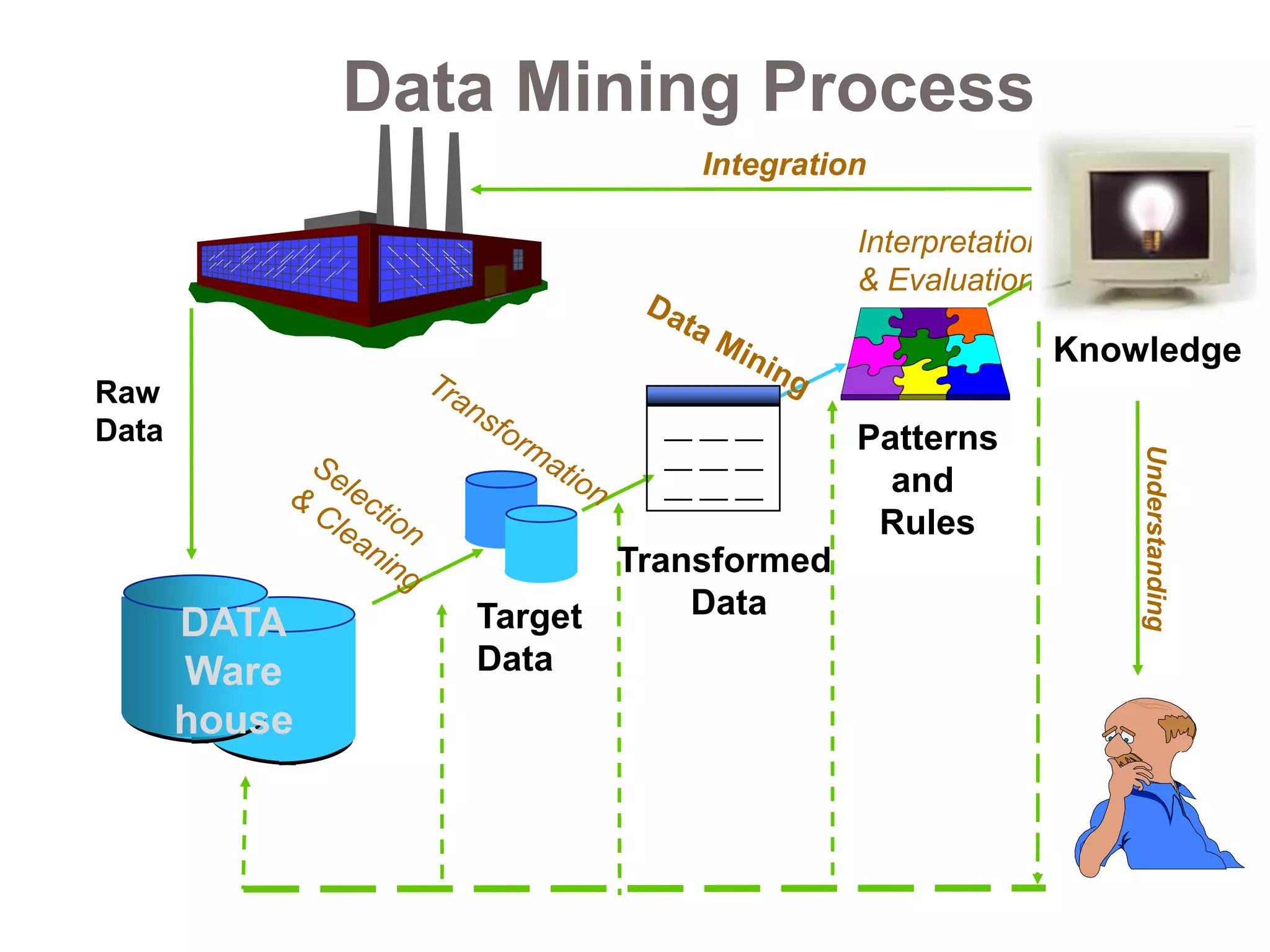
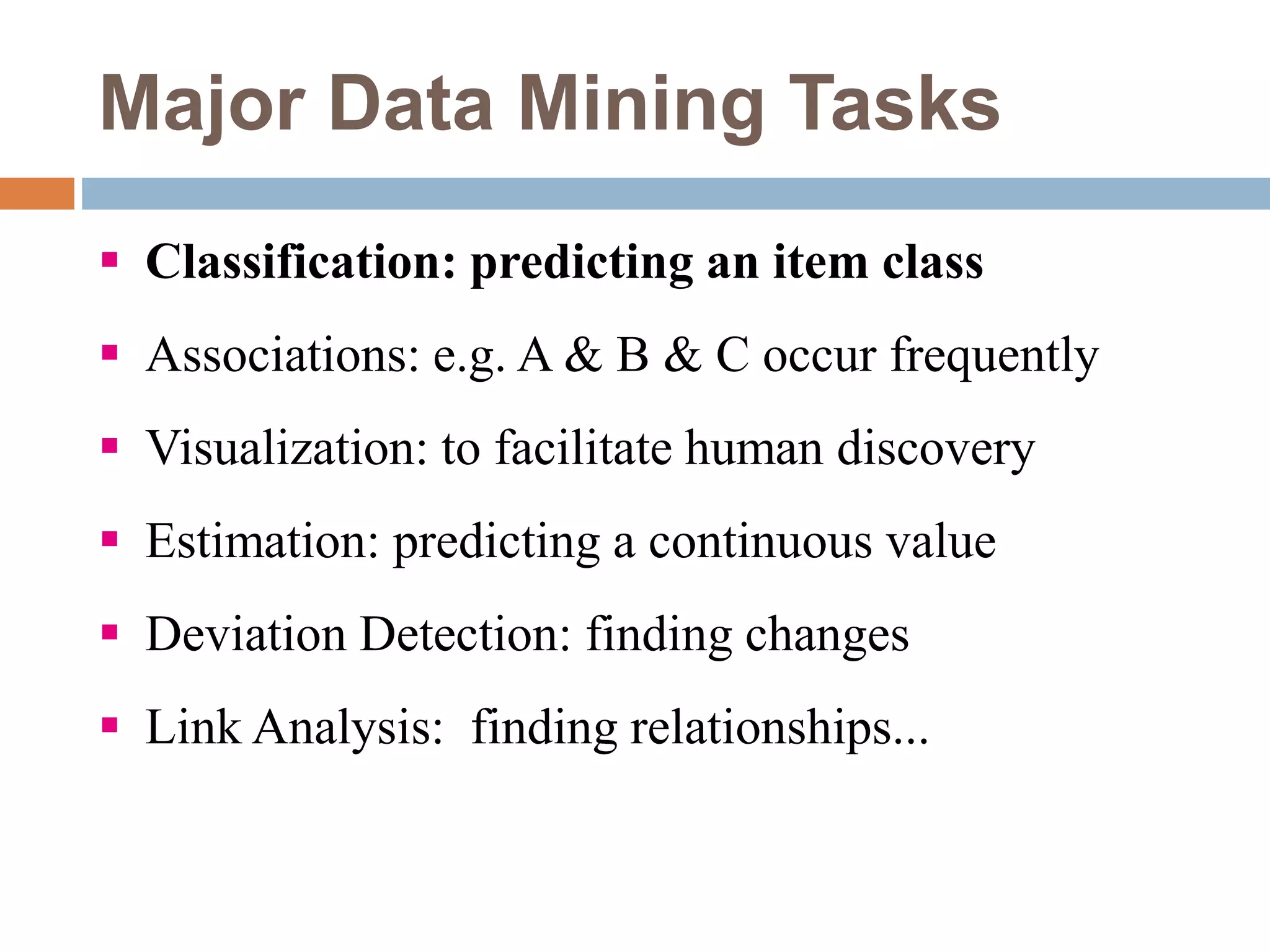
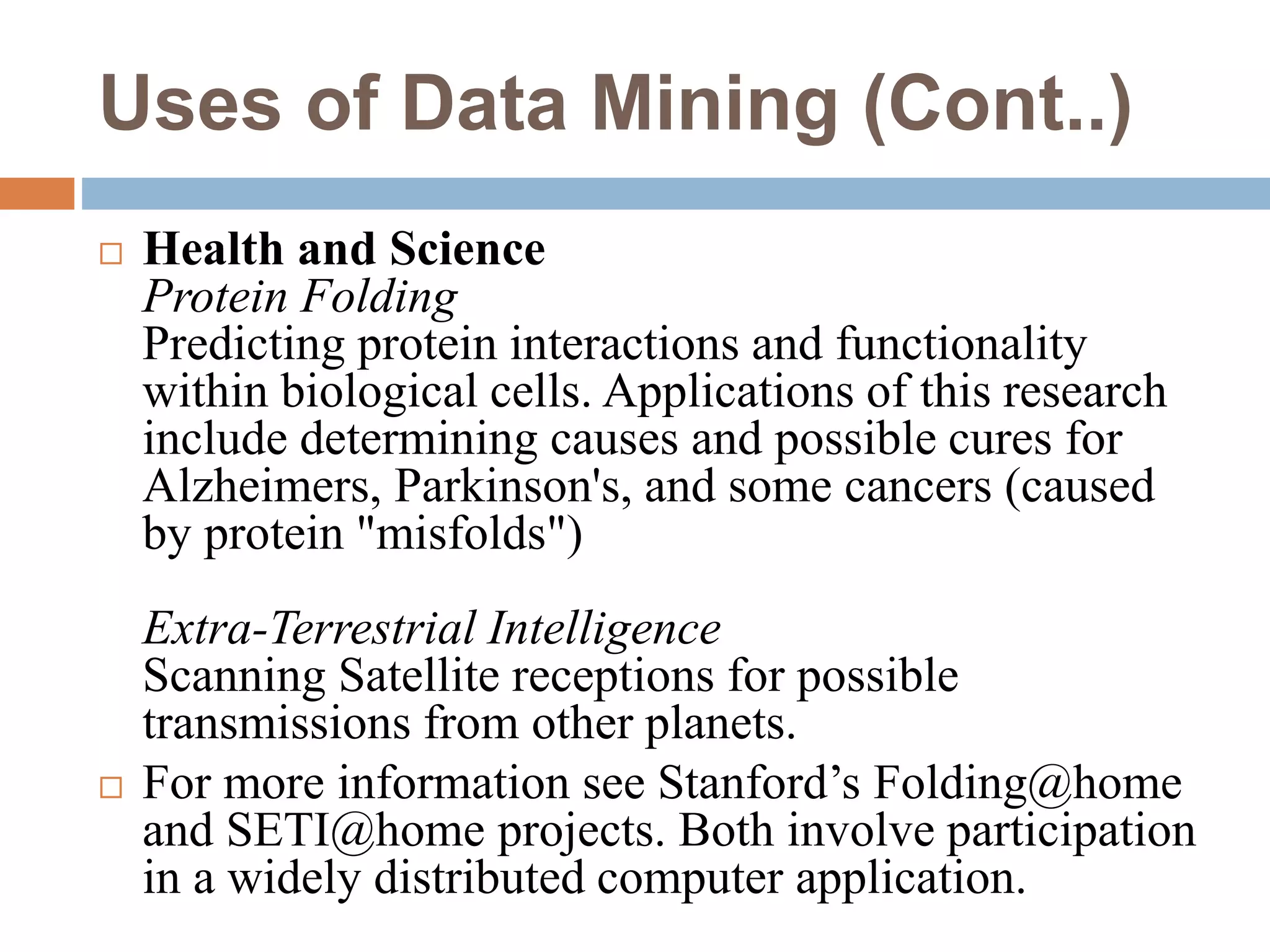
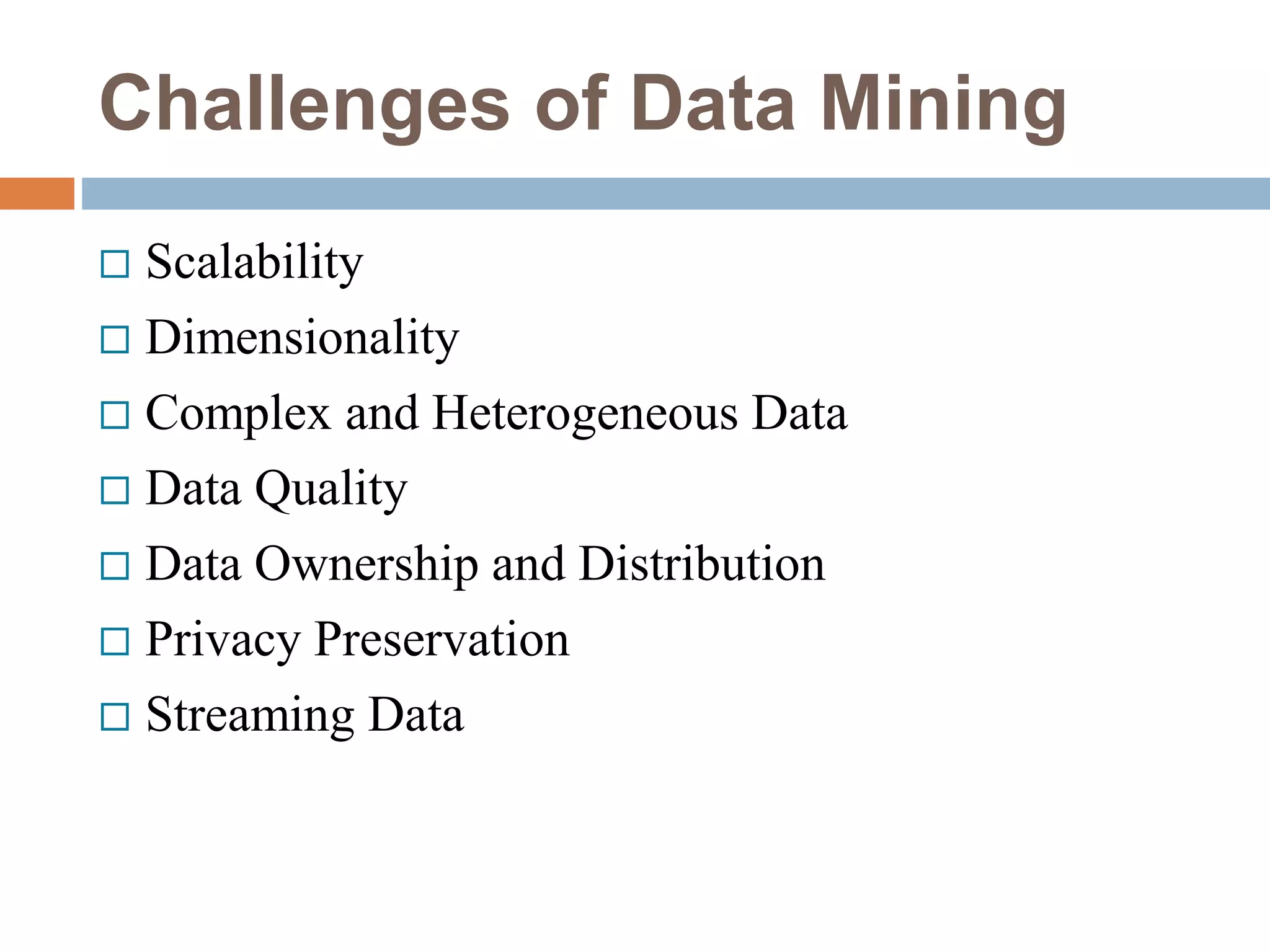
This document provides an overview of data mining. It defines data mining as the process of discovering novel and useful patterns from large amounts of data. The document outlines the main components of data mining, distinguishing it from regular data analysis. It also discusses the data mining process, major data mining techniques like classification and clustering, sources of data, challenges, and advantages. The goal of data mining is to extract useful knowledge from vast amounts of data.