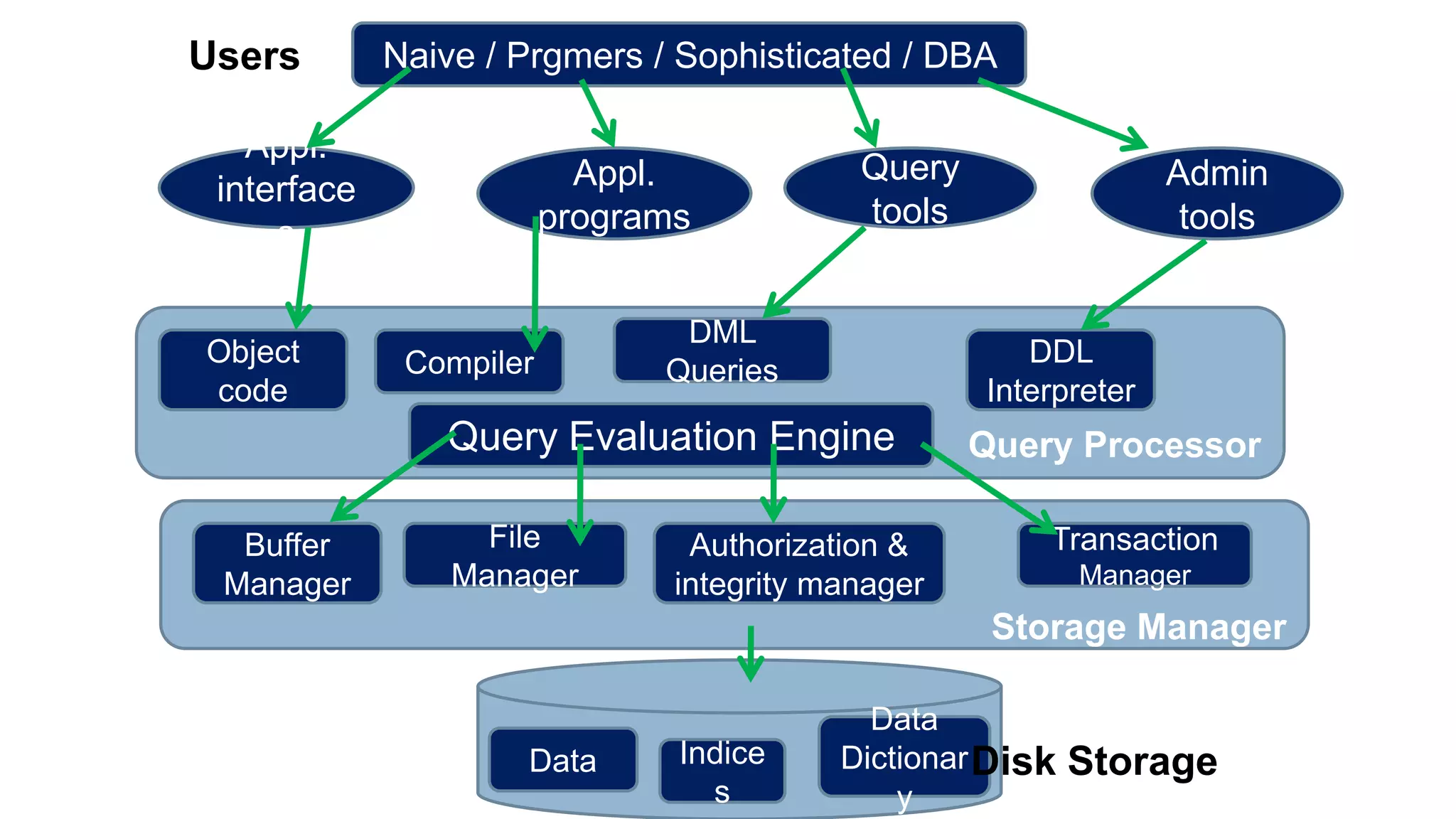
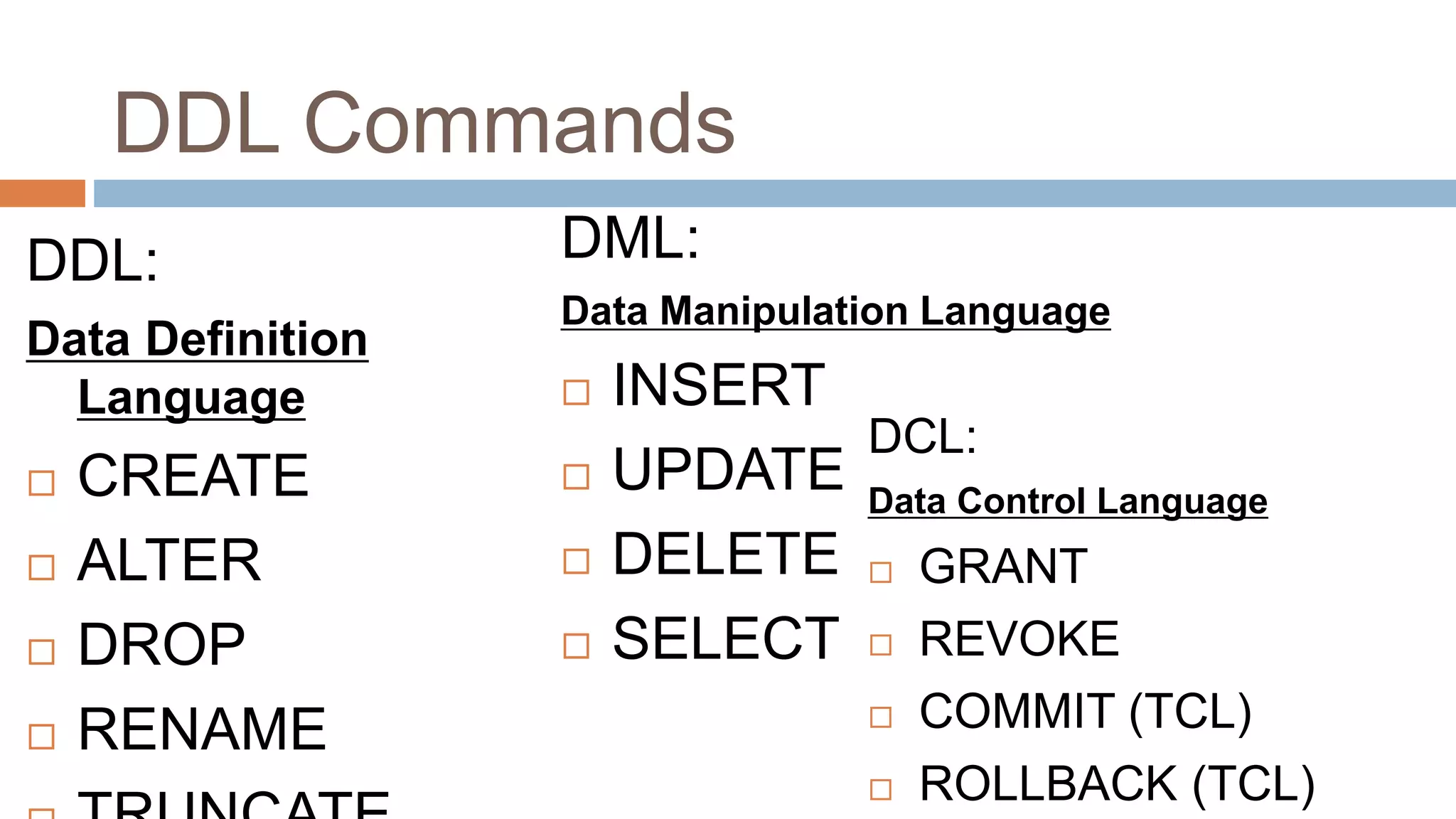
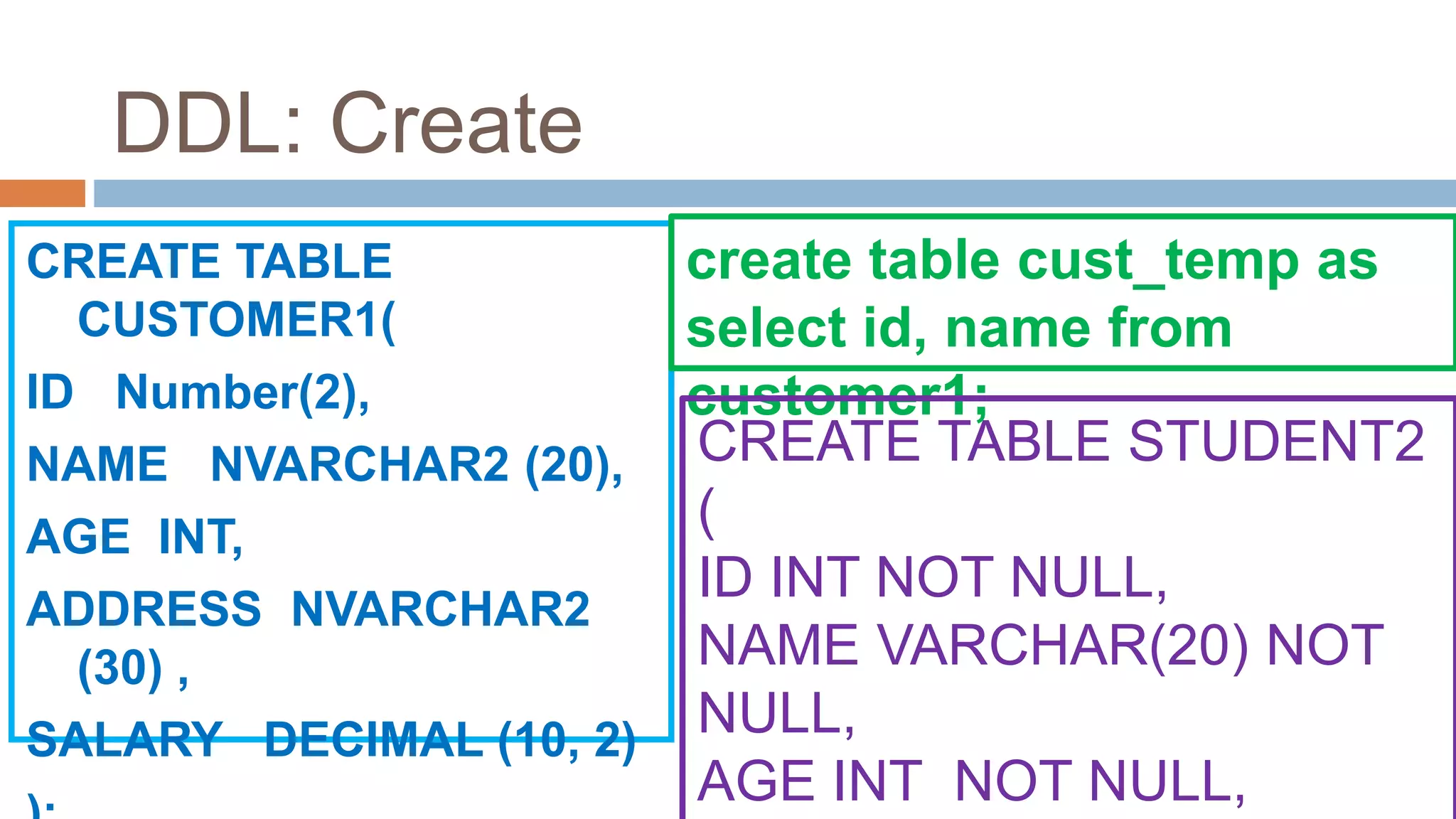
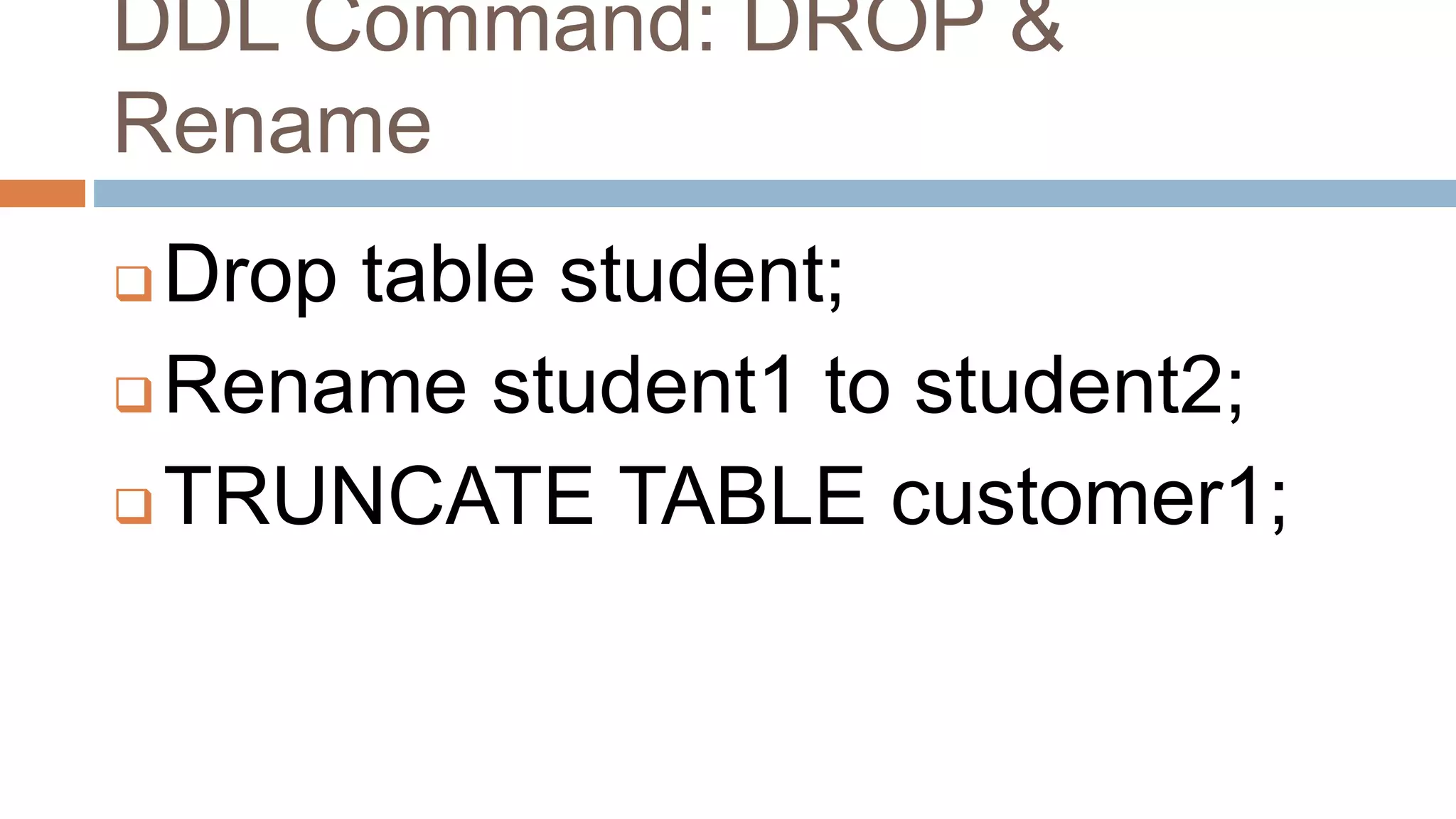
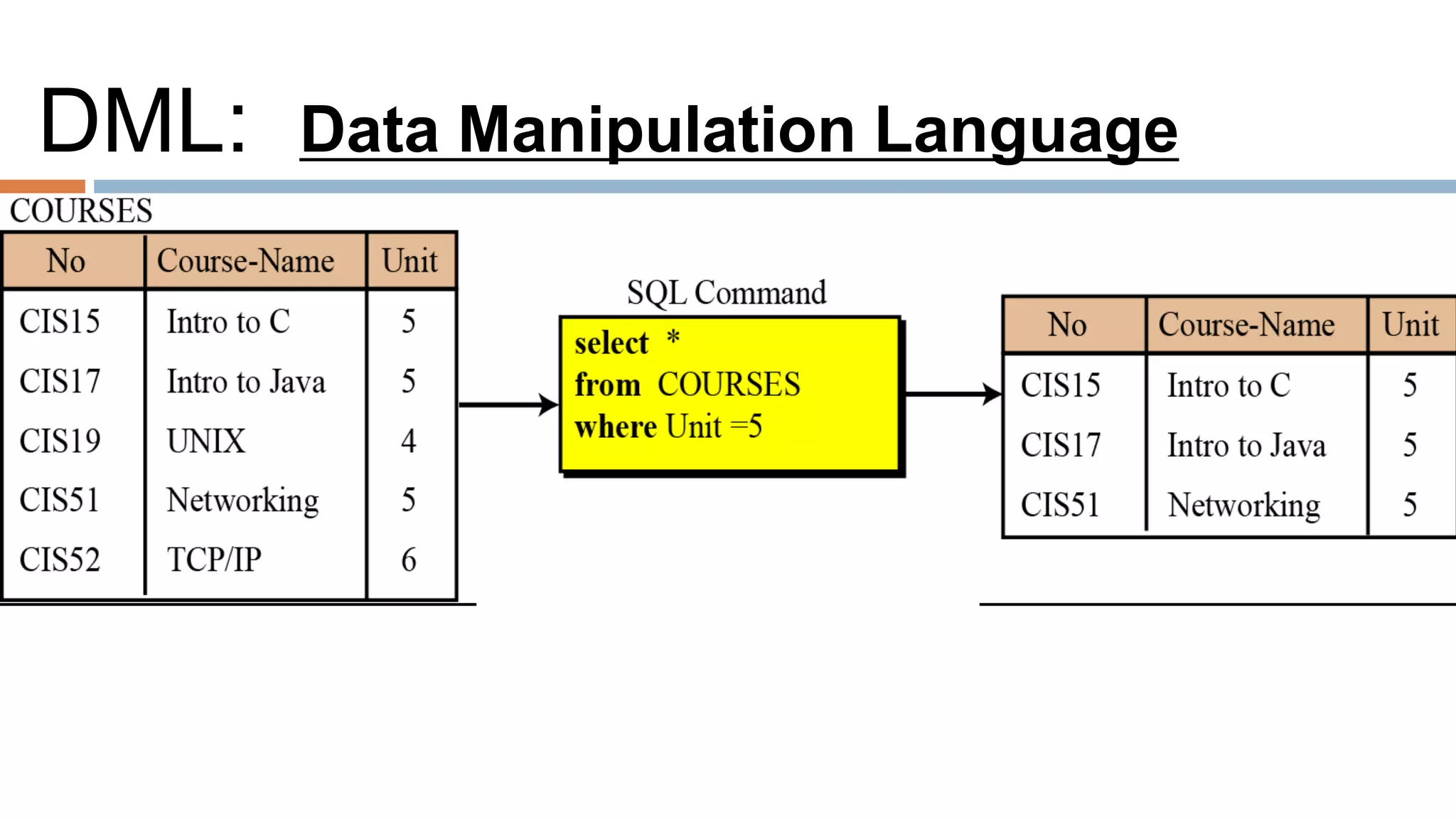
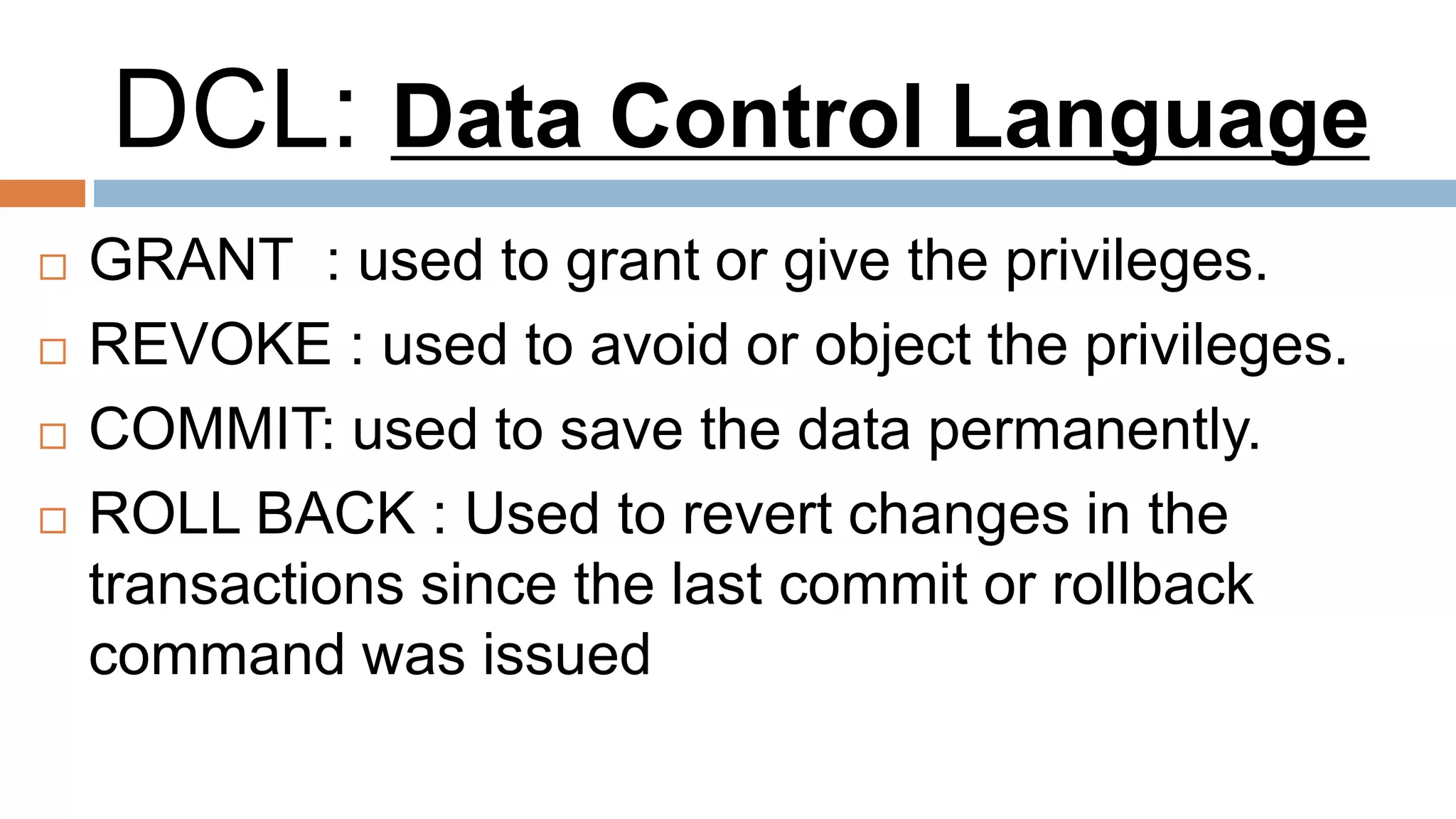
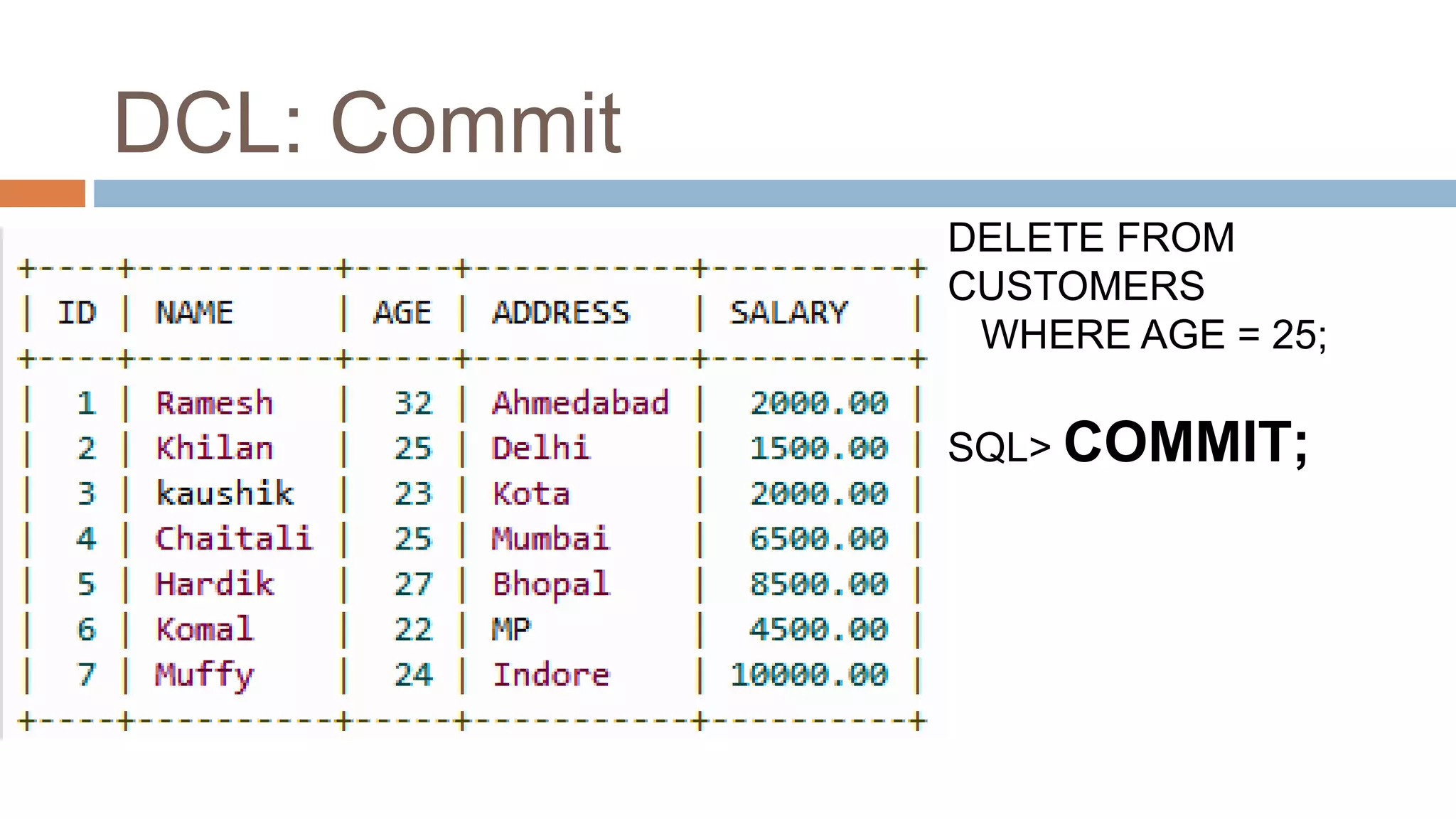
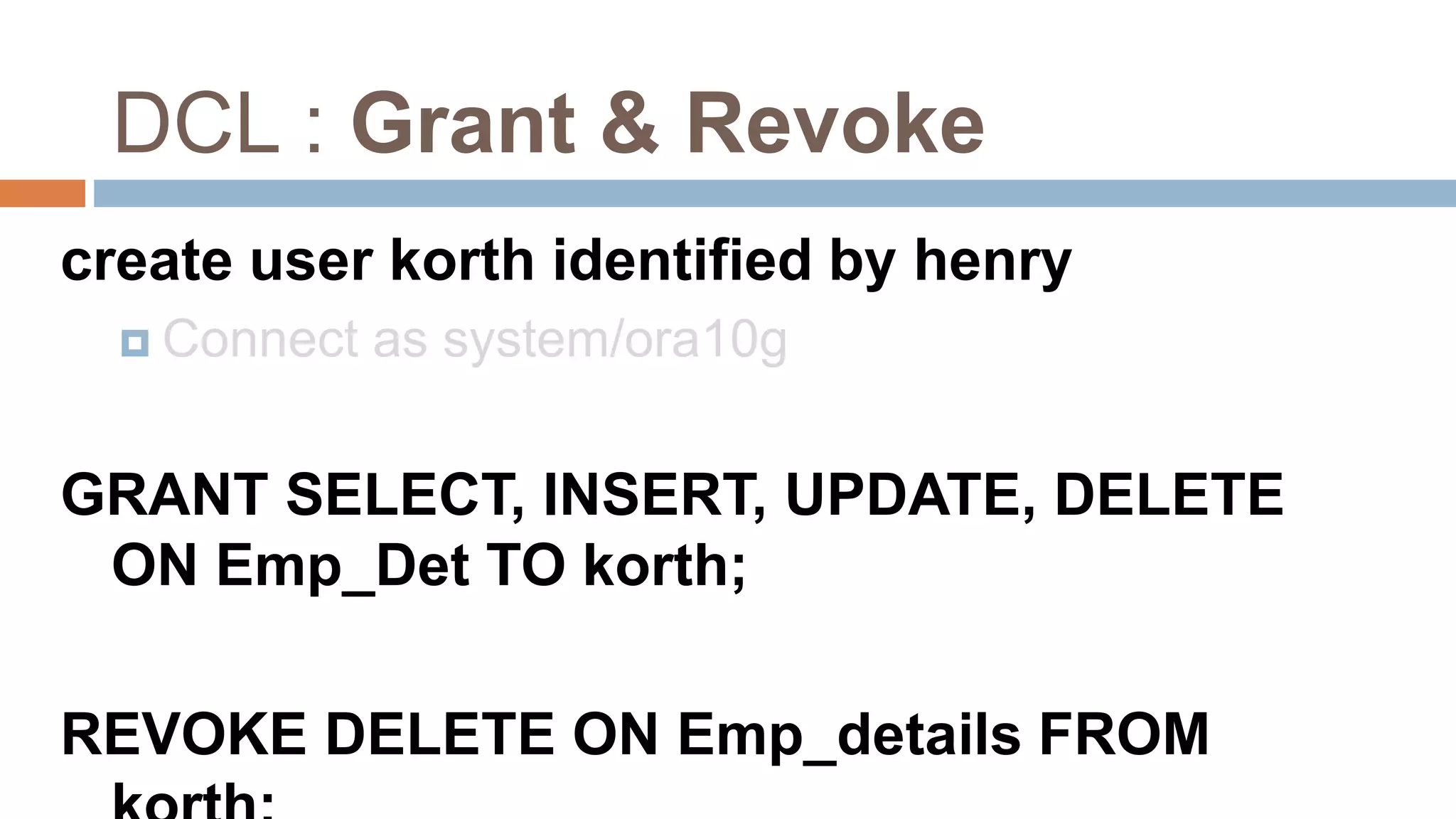
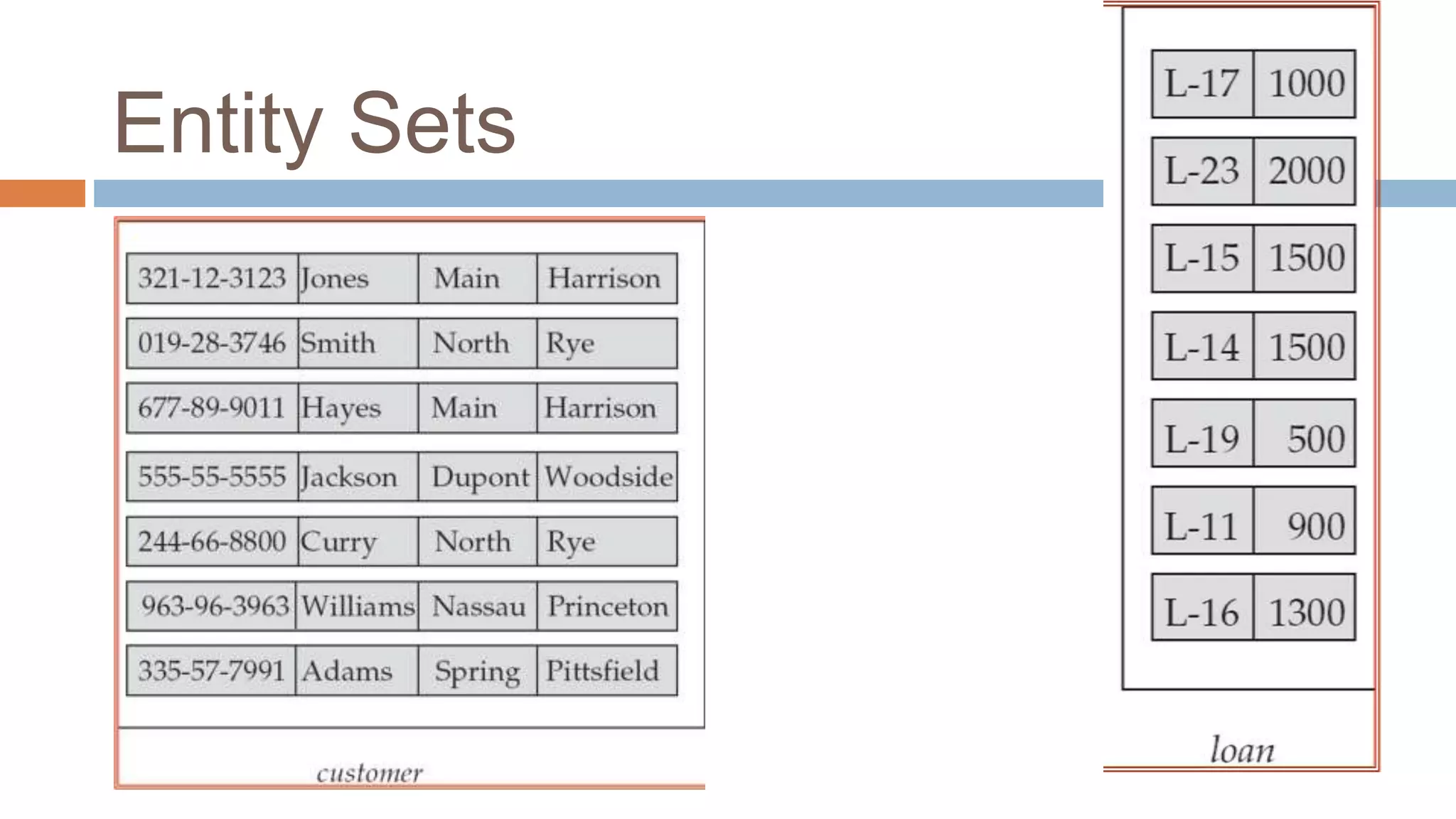
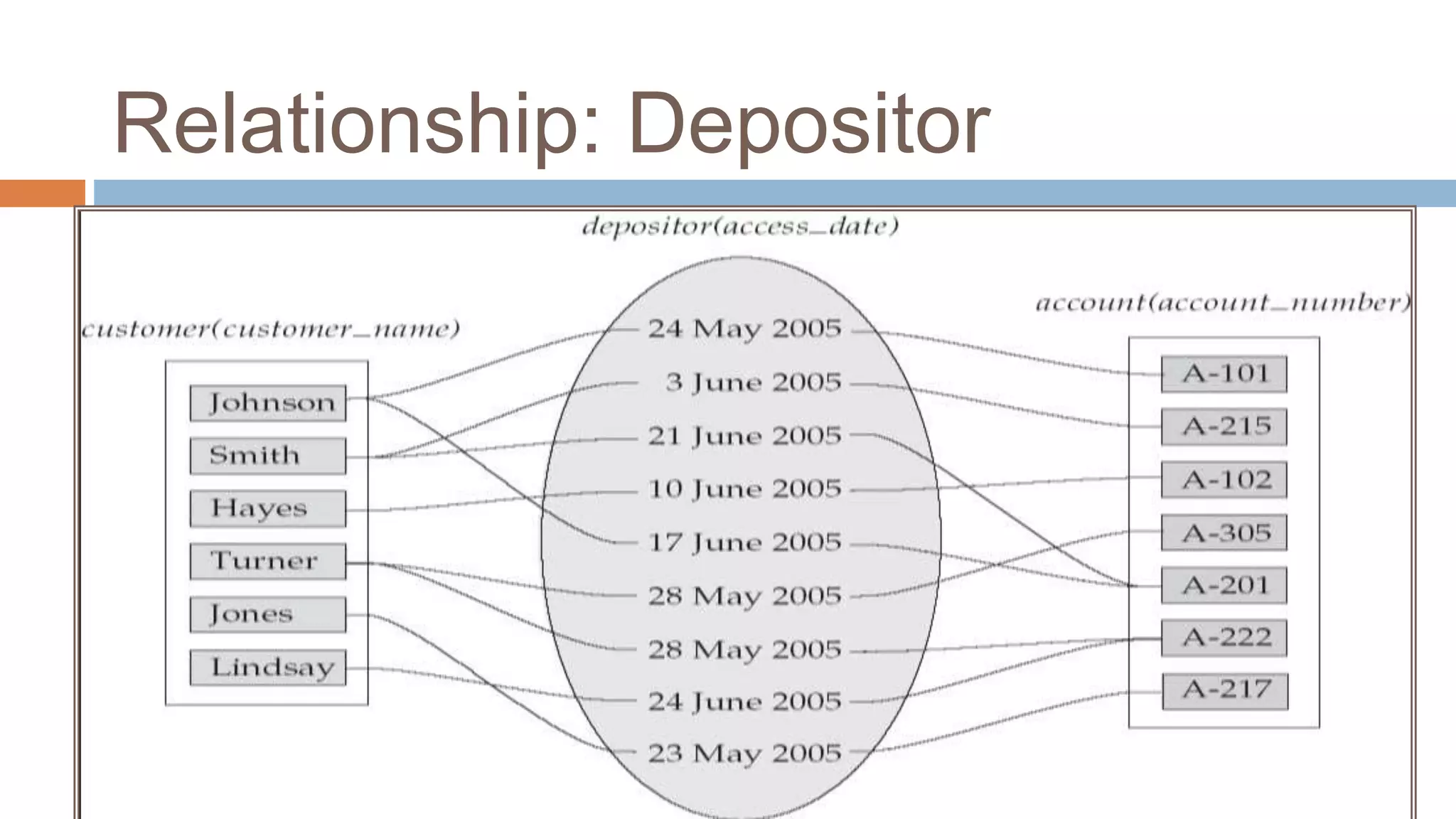
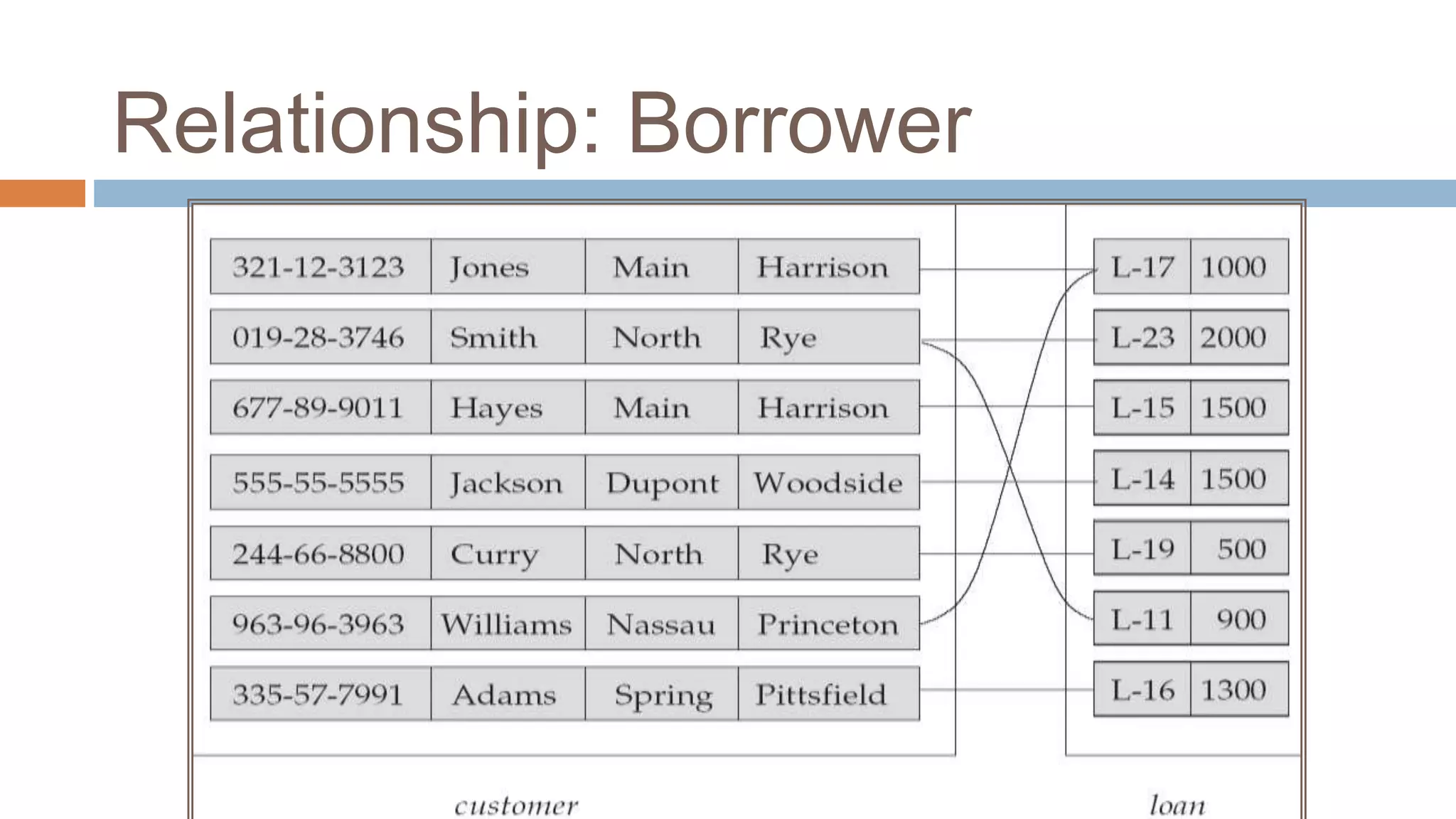
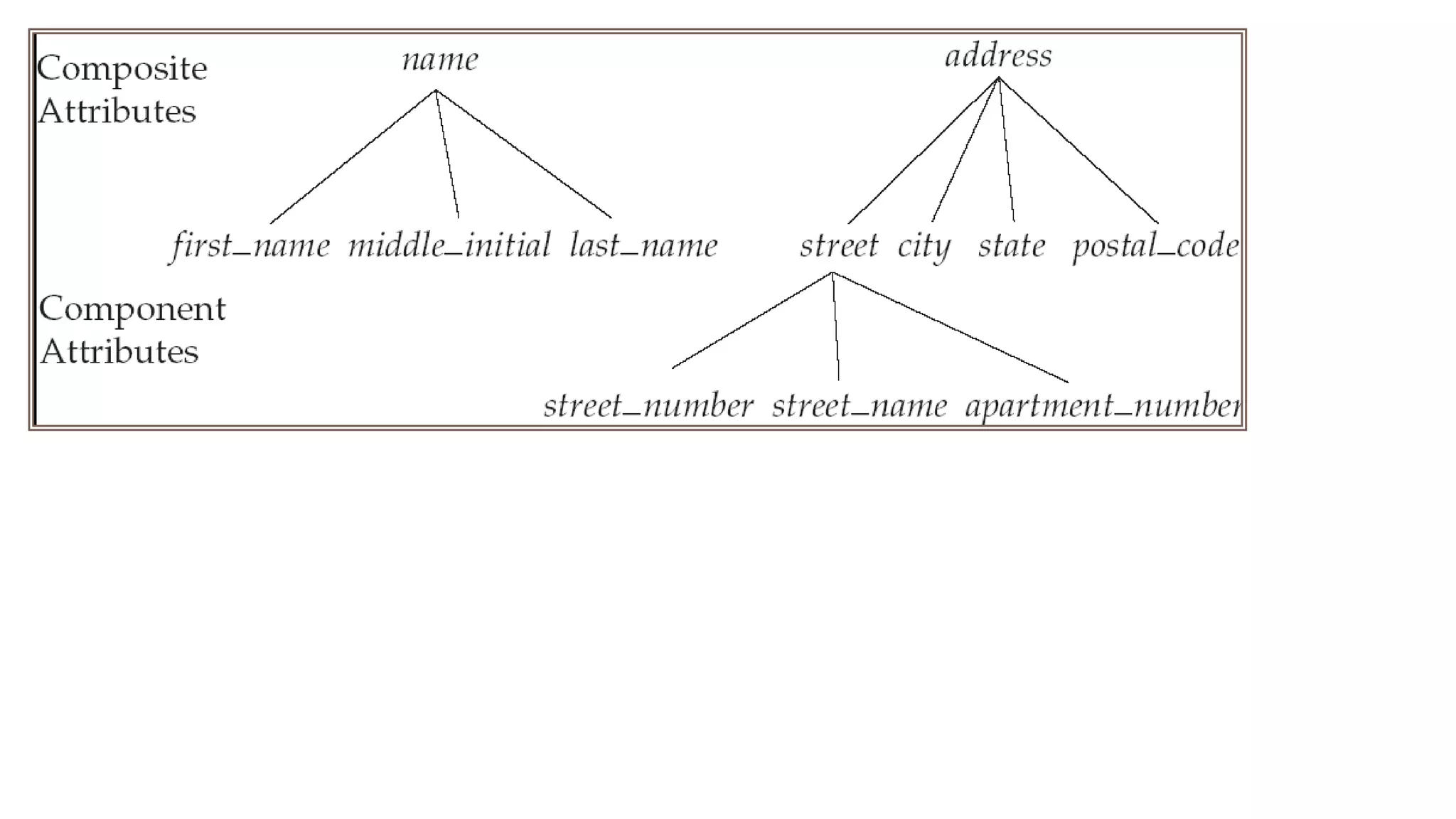
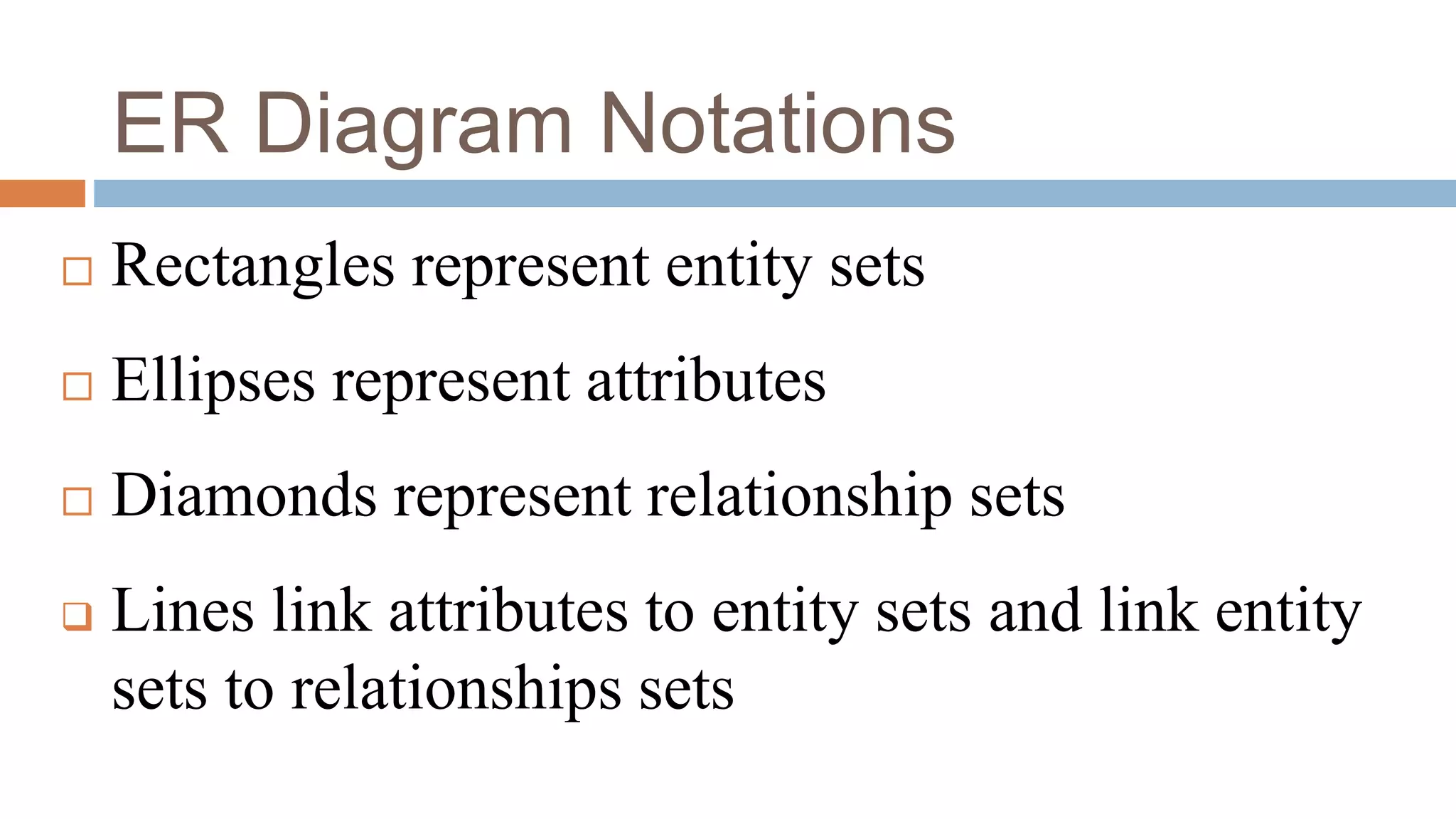
The document discusses topics related to database management systems including database users, architecture, data definition language, data manipulation language, entity relationship modeling, and SQL commands. It provides examples of using SQL commands like CREATE TABLE, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE, RENAME, COMMIT, ROLLBACK, GRANT and REVOKE. It also explains concepts of entity sets, relationship sets, attributes, and ER diagram notations and provides examples of ER diagrams.