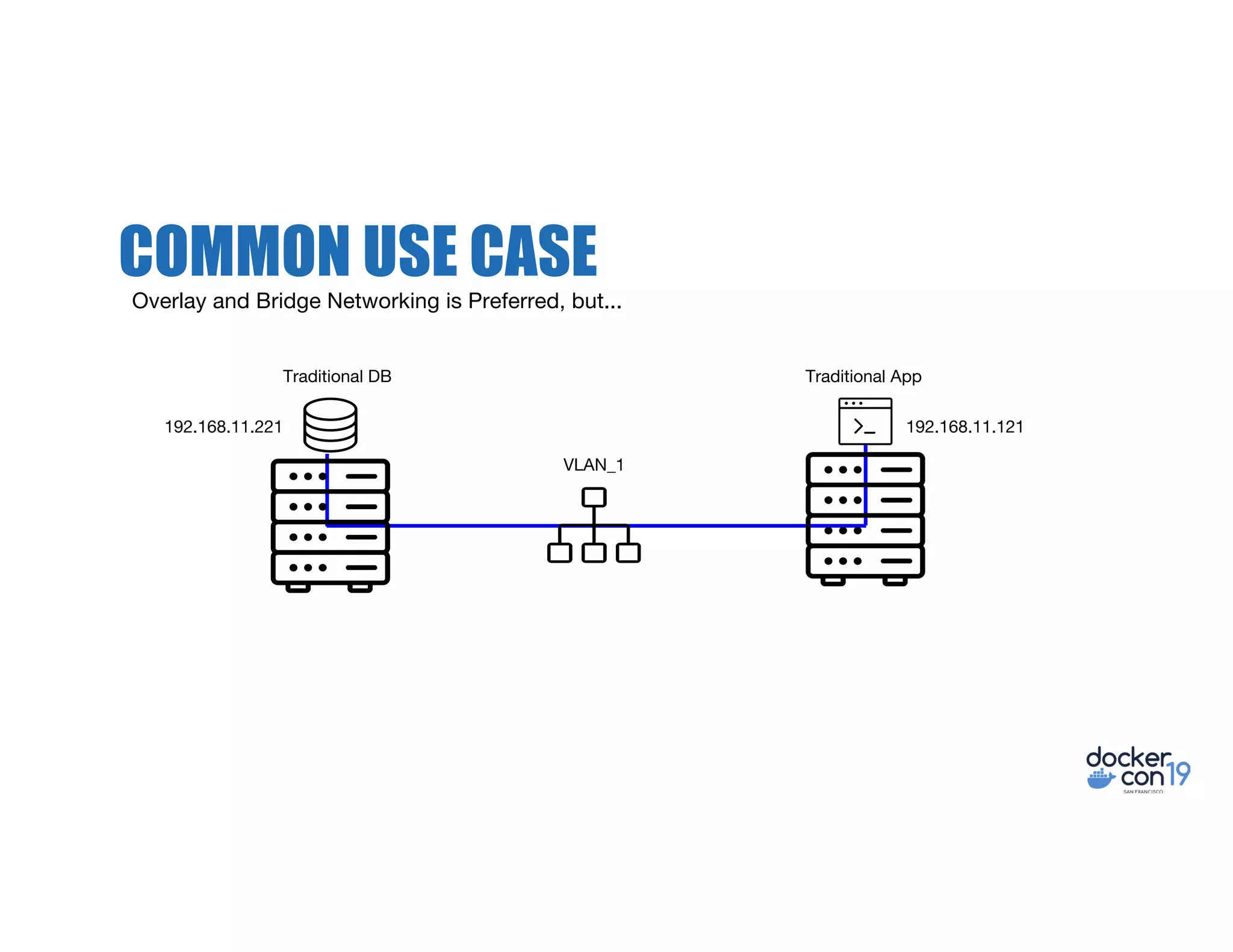
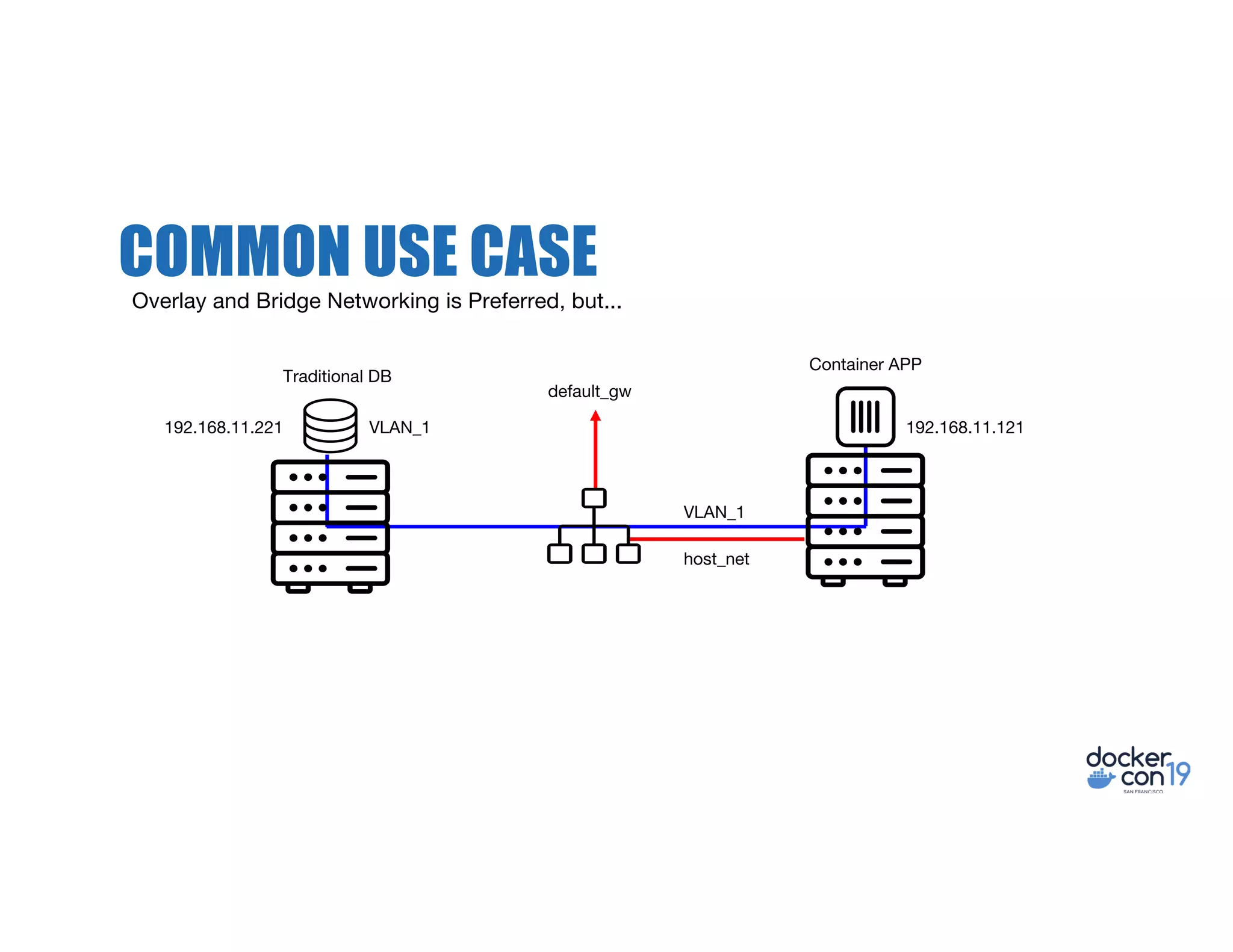
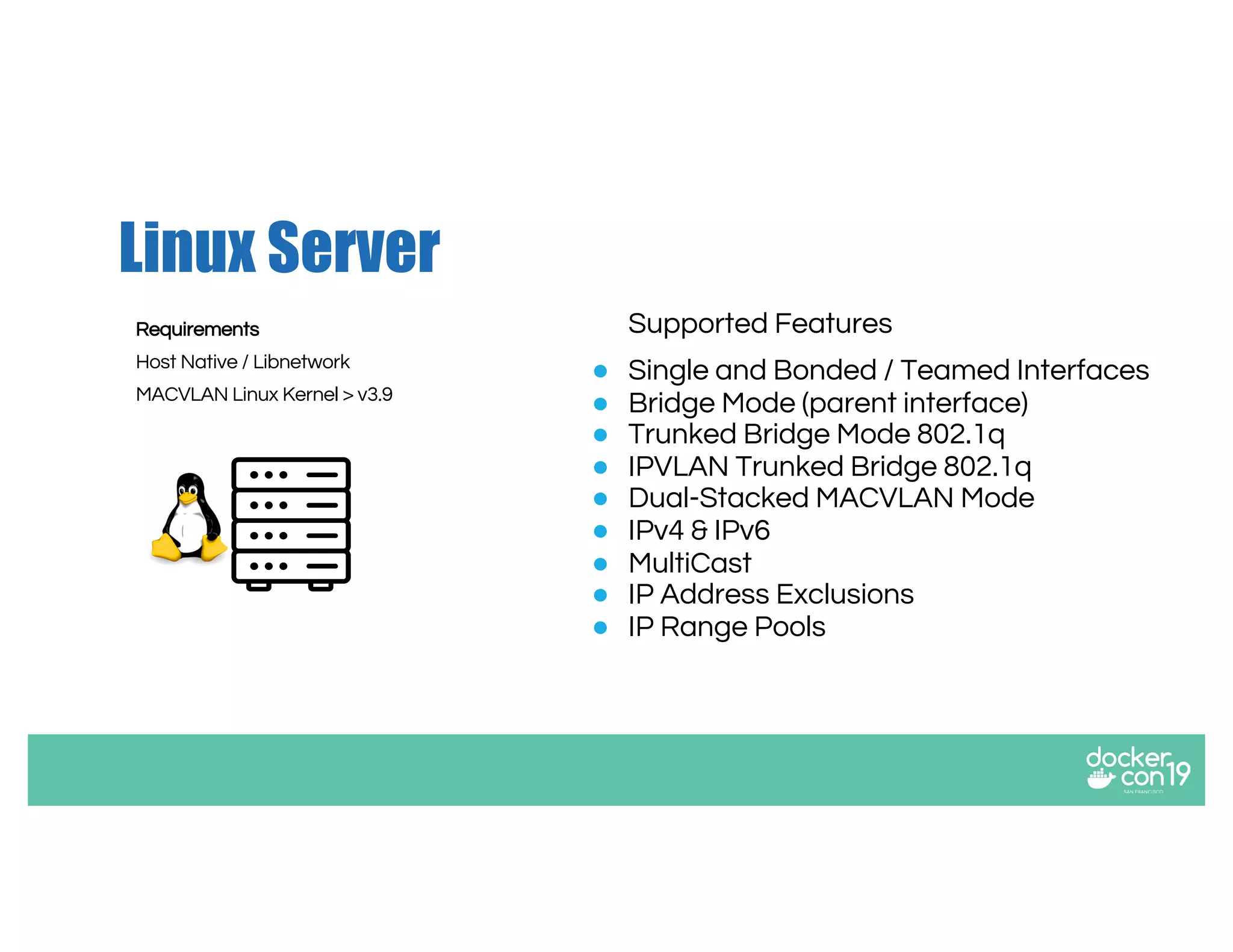
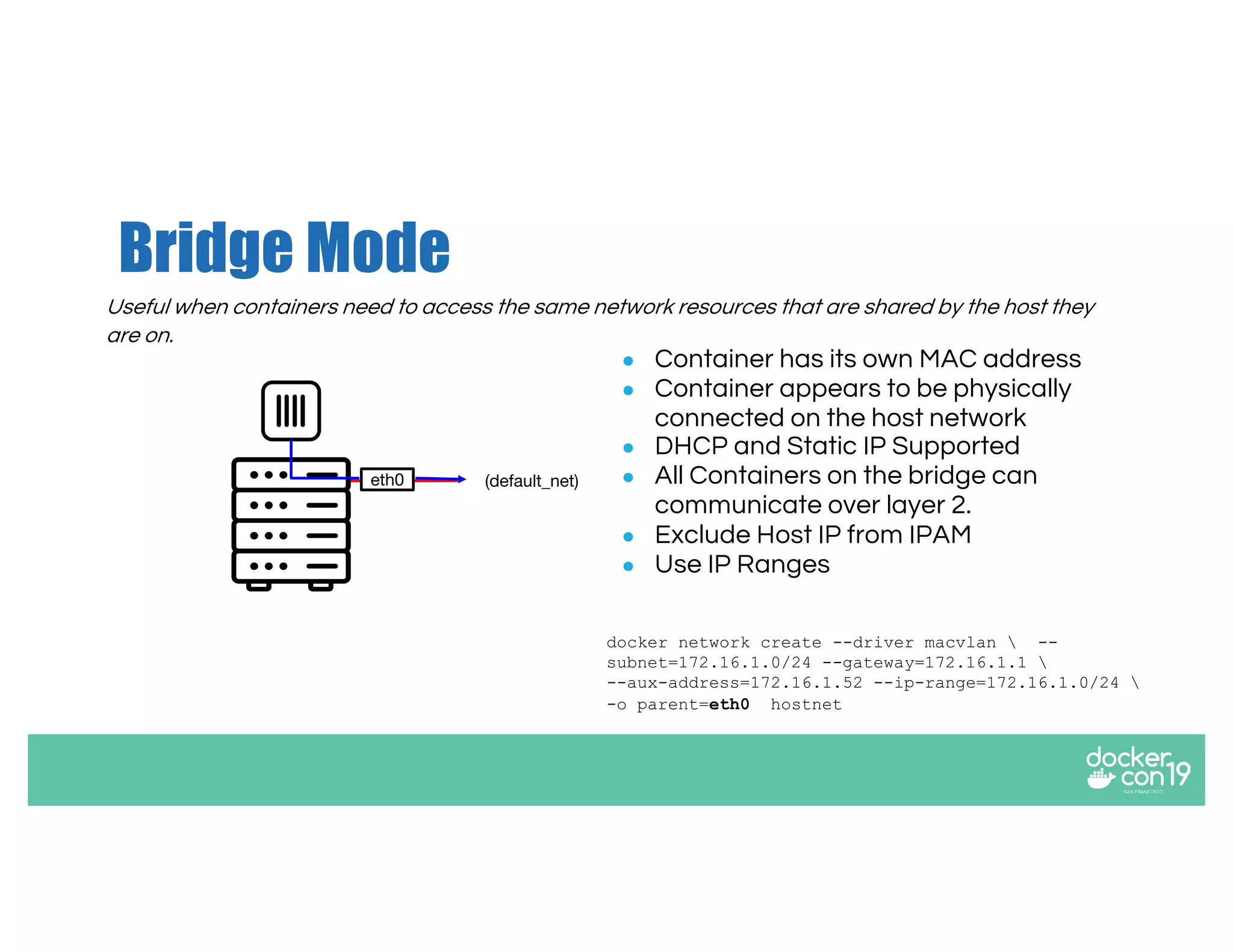
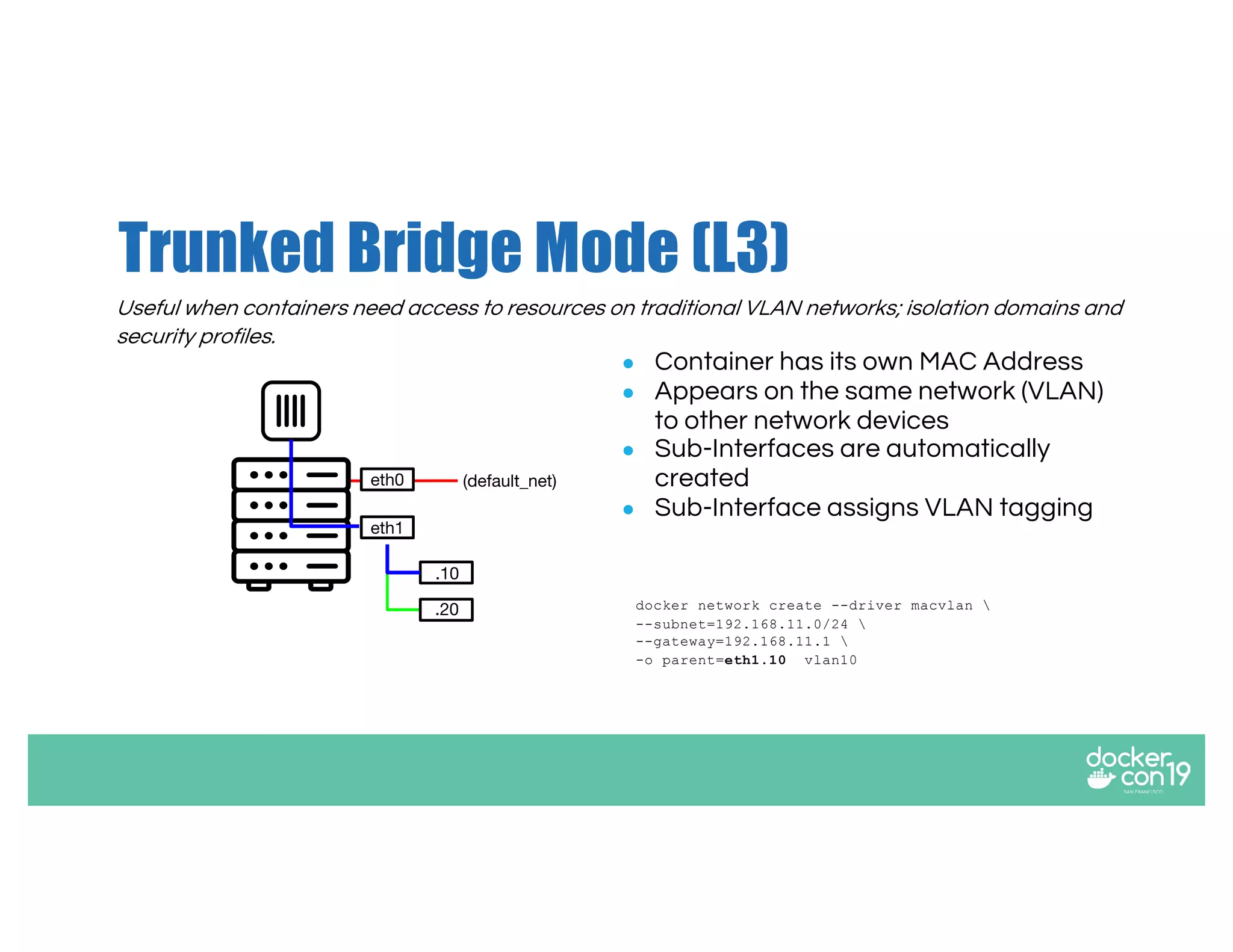
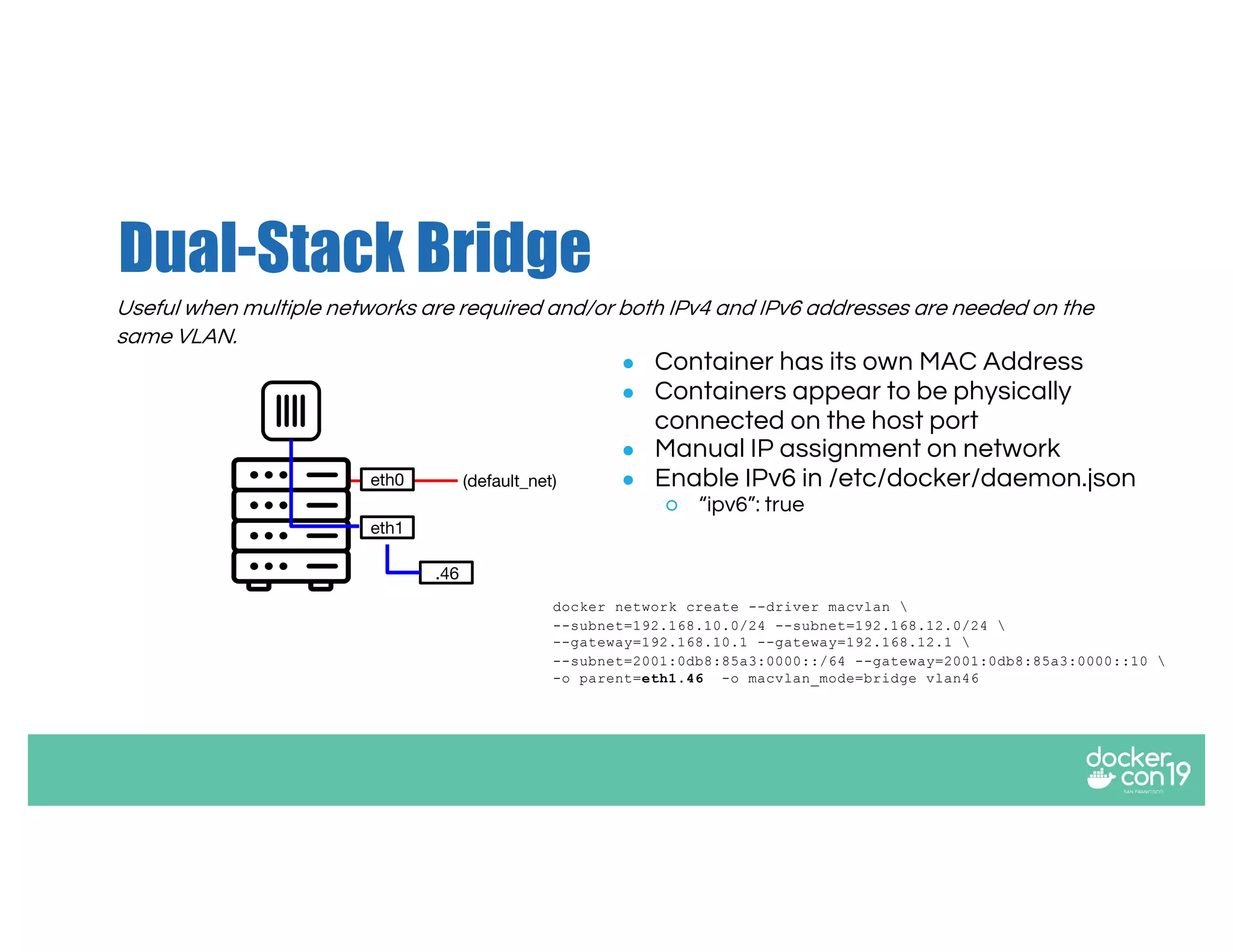
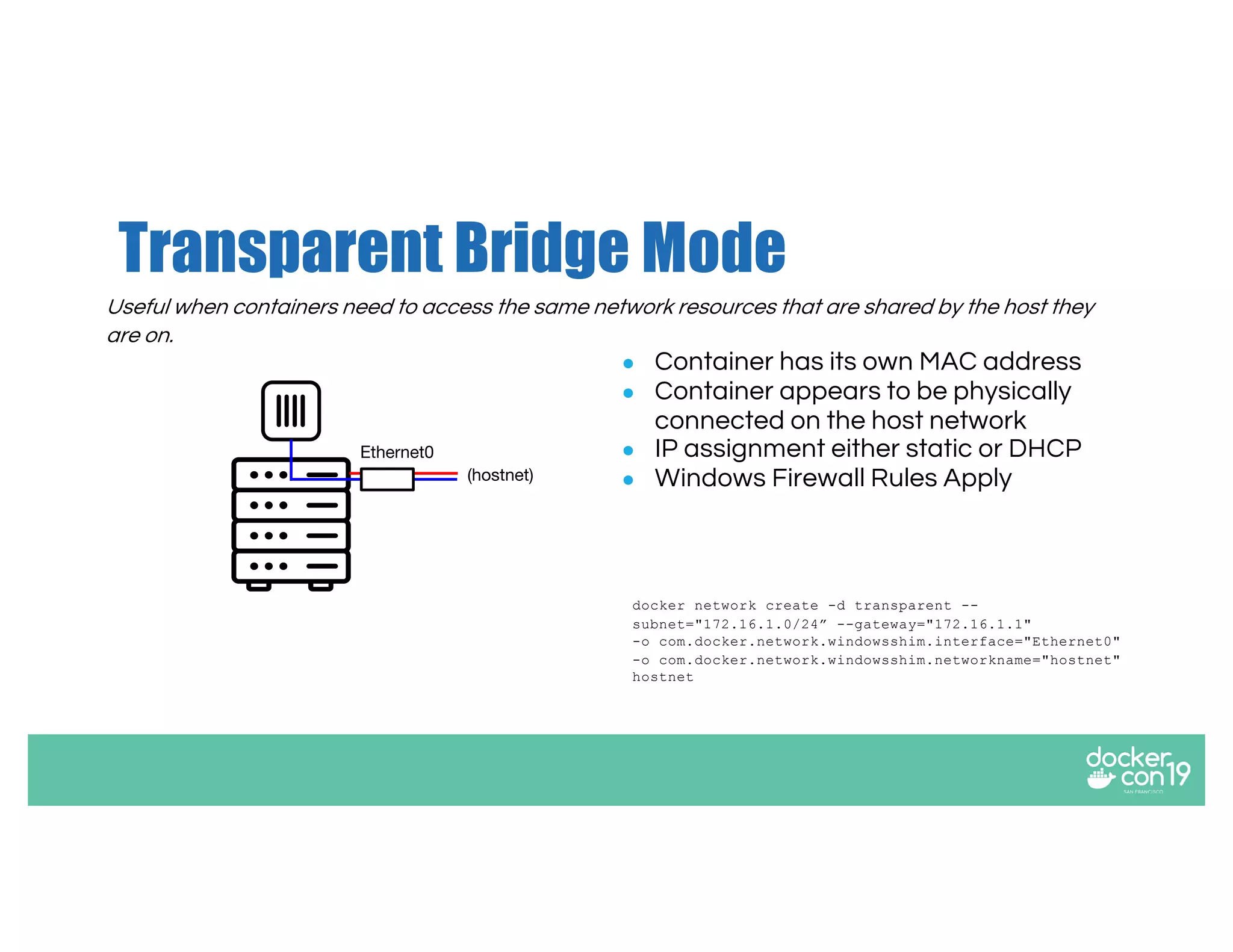
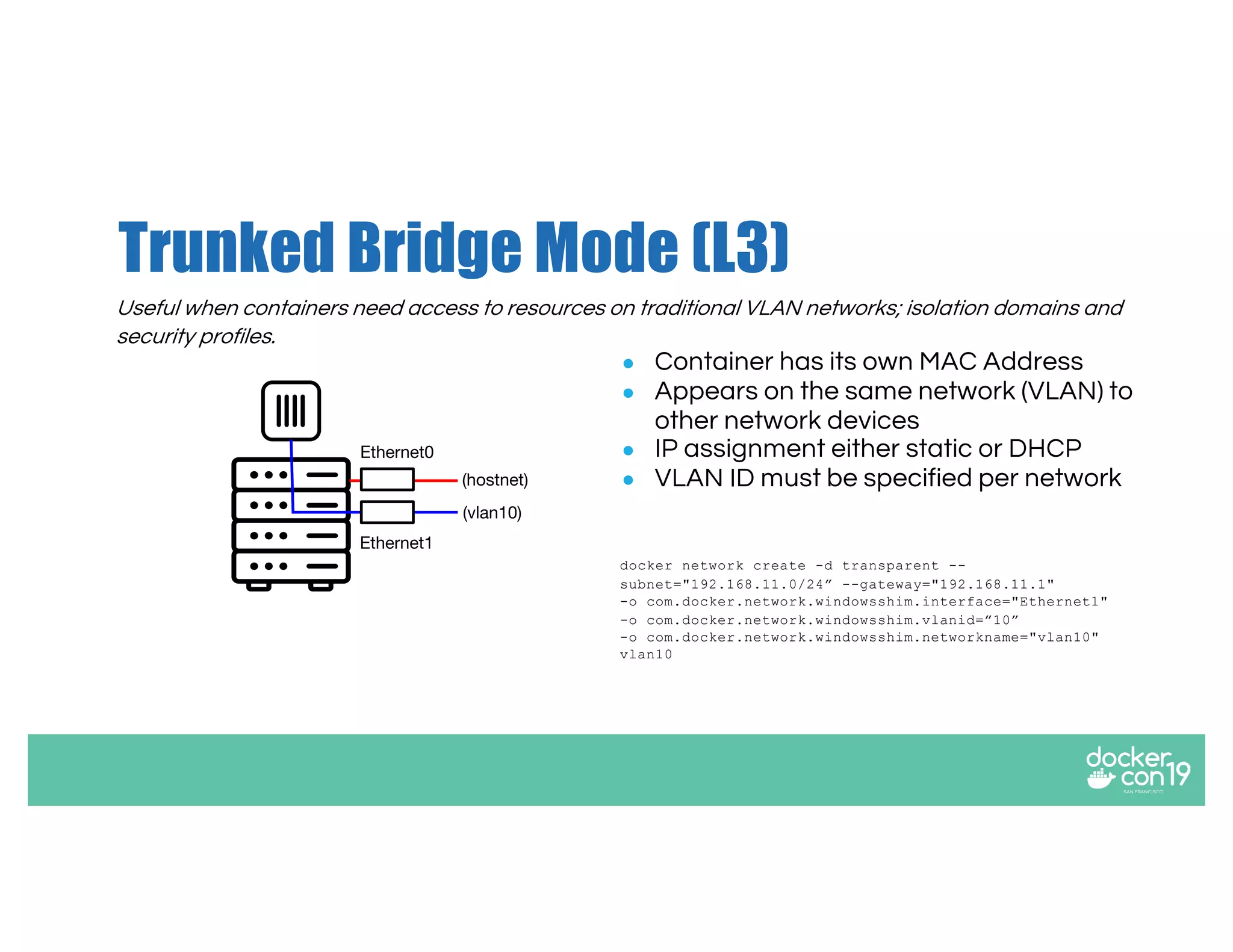
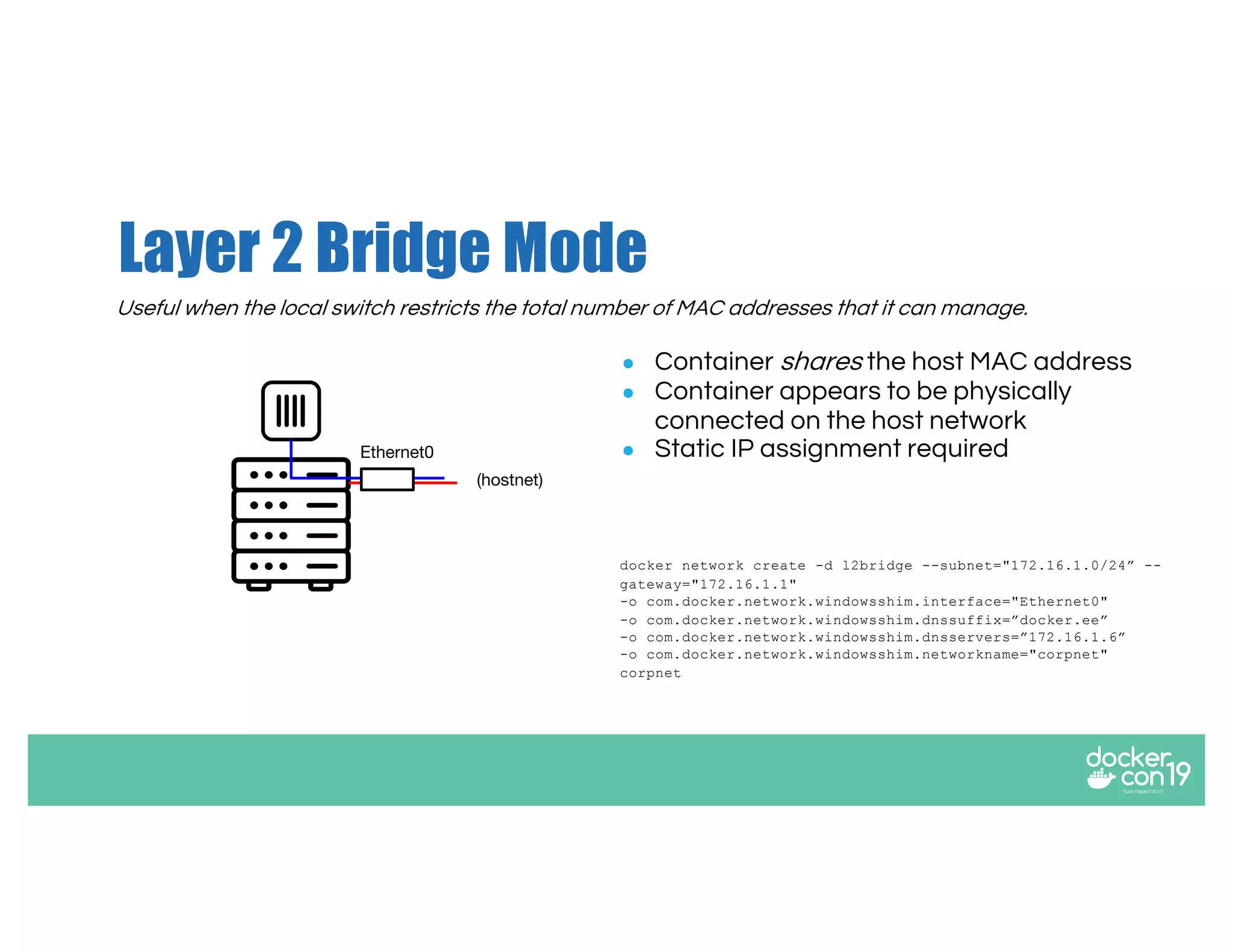
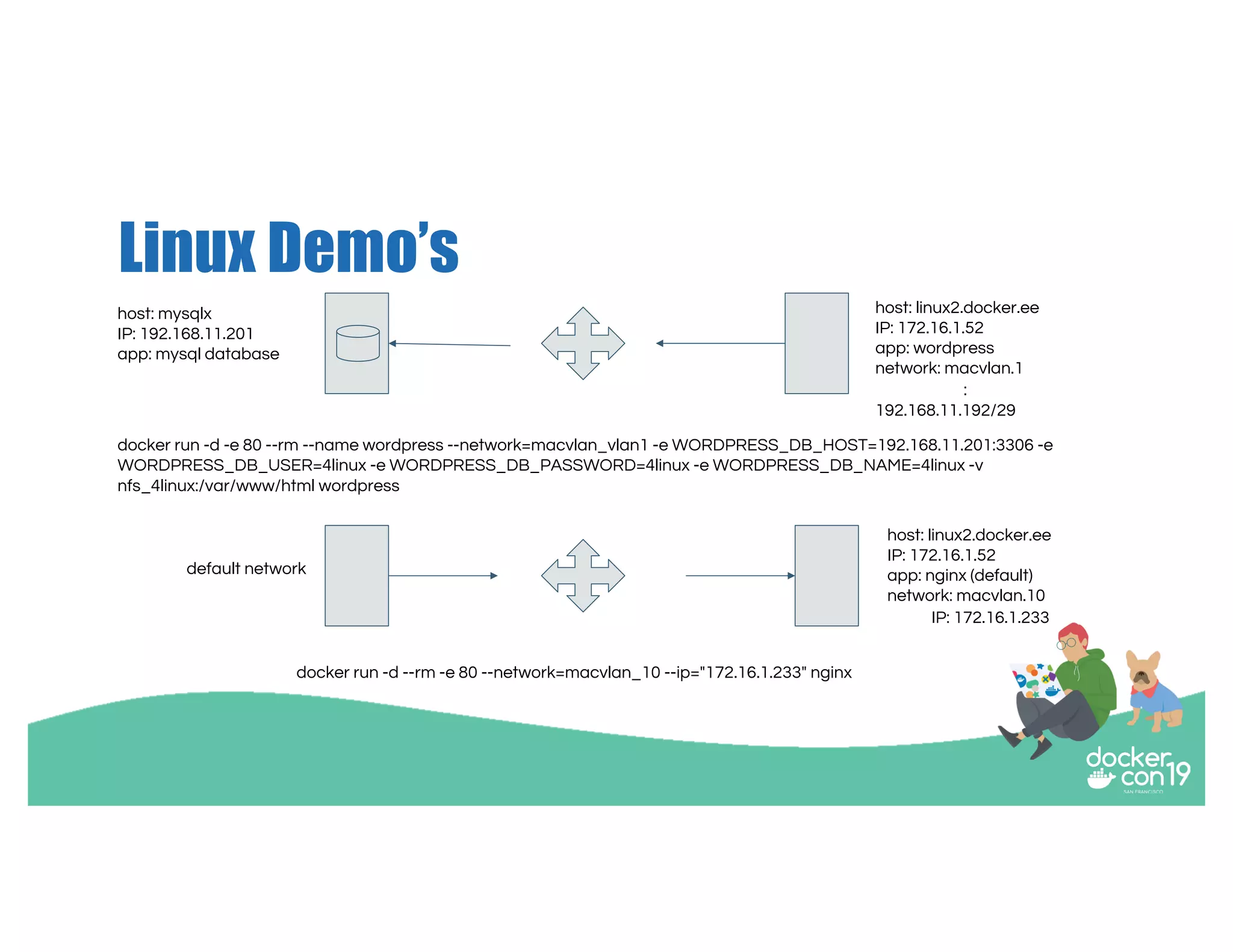
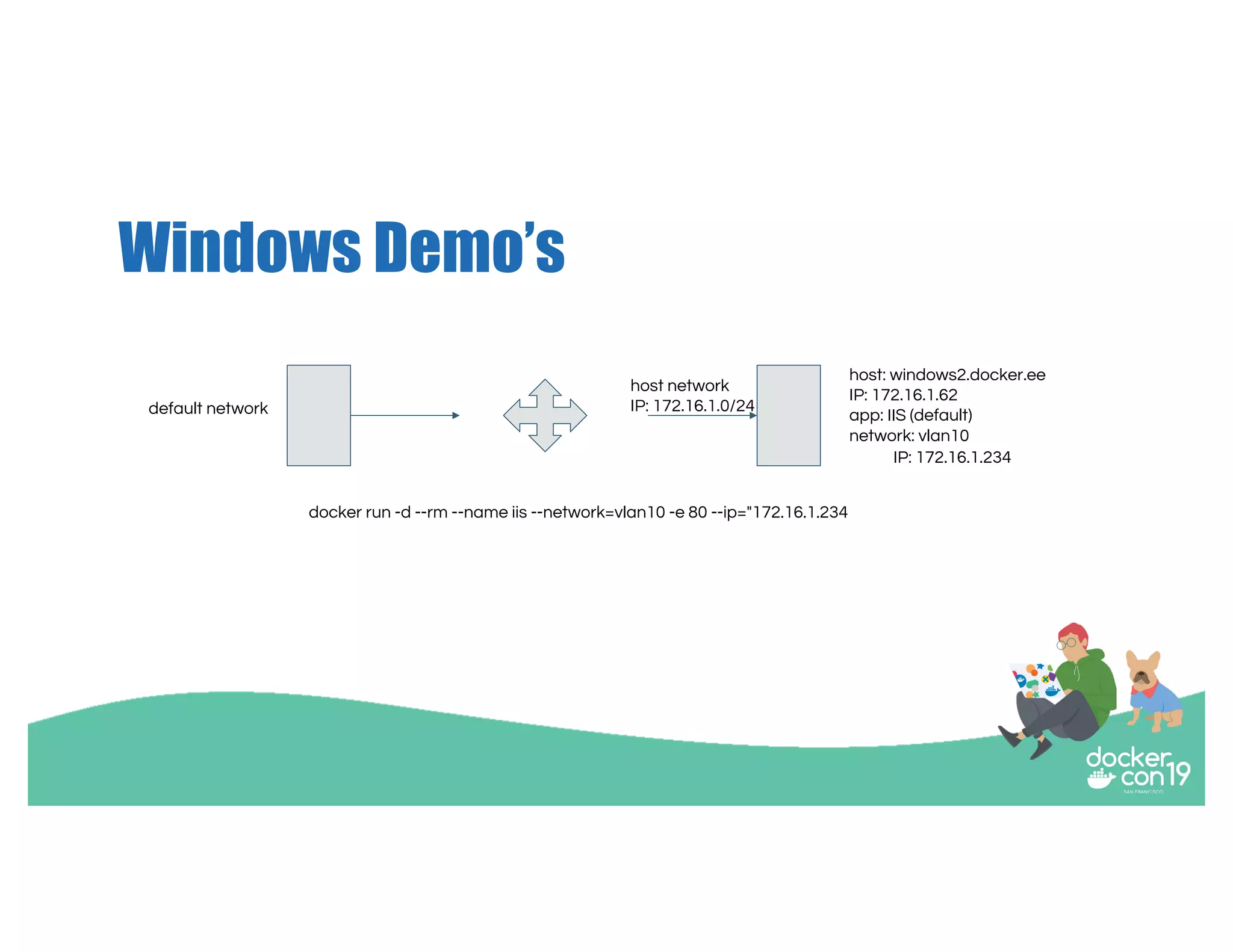
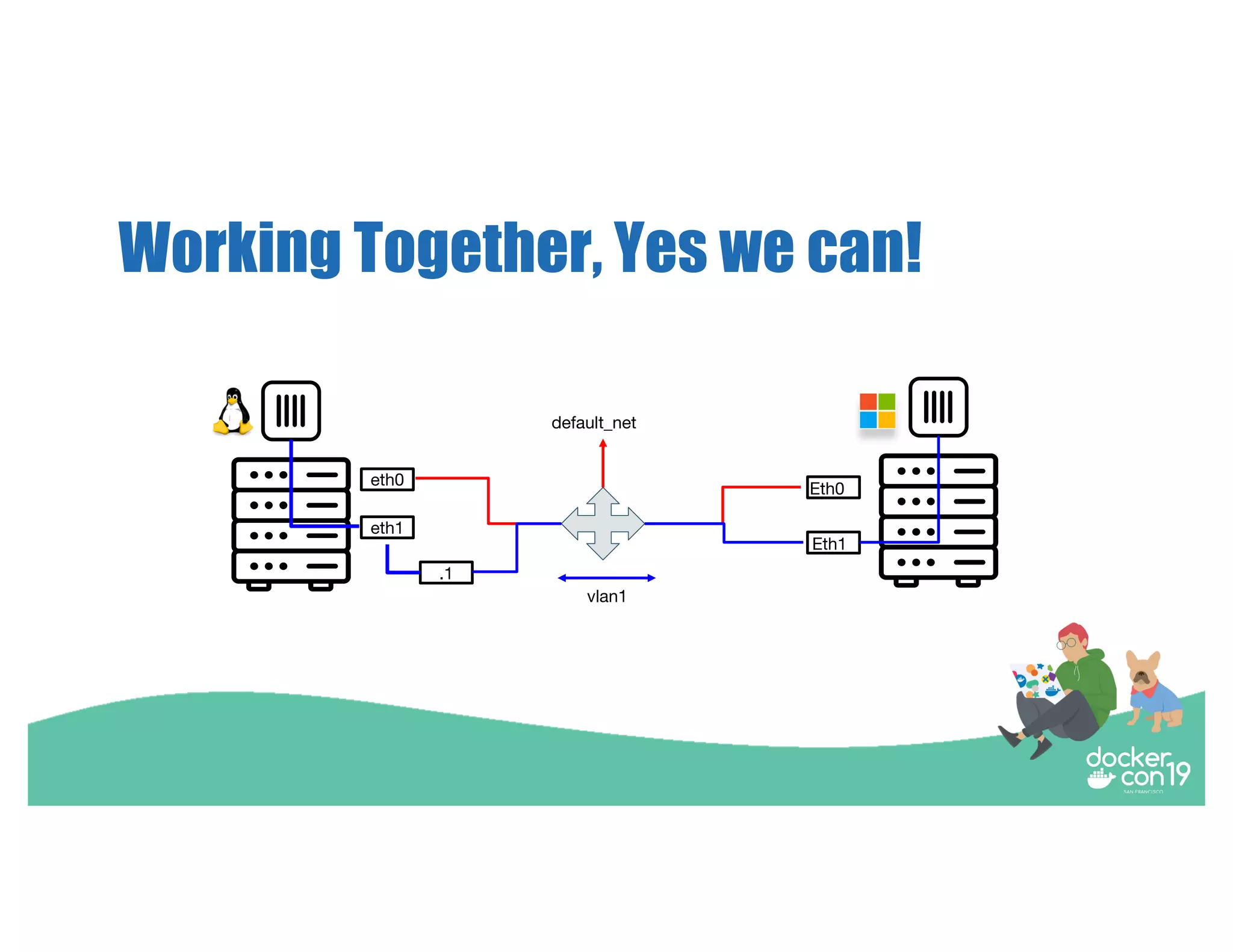
The document discusses networking options for Docker containers, including various macvlan and transparent networking modes. It outlines use cases, comparisons of support, and caveats such as the limitations of Docker services and network encryption. Additionally, it provides command examples for setting up different networking configurations on both Linux and Windows servers.