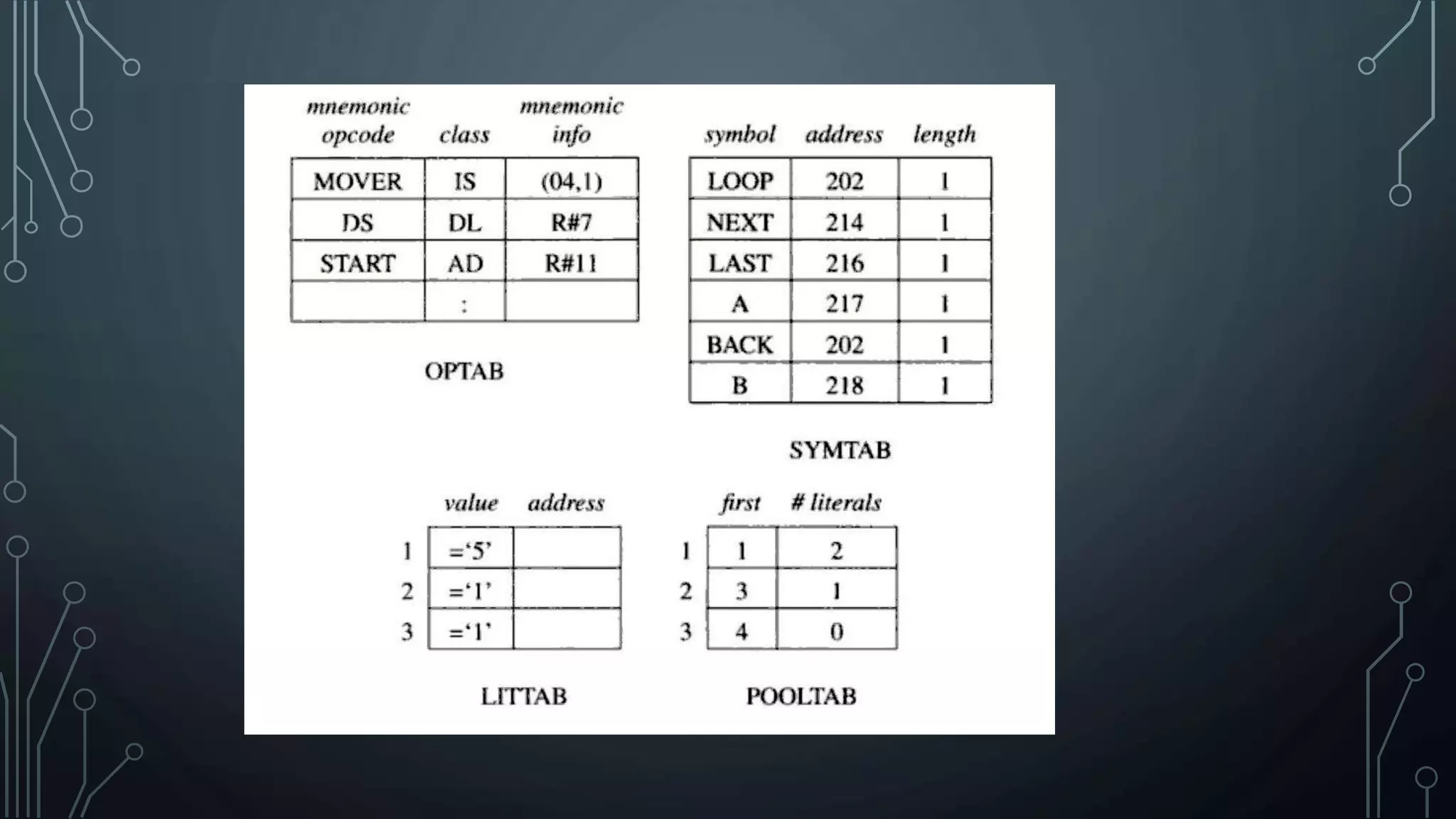
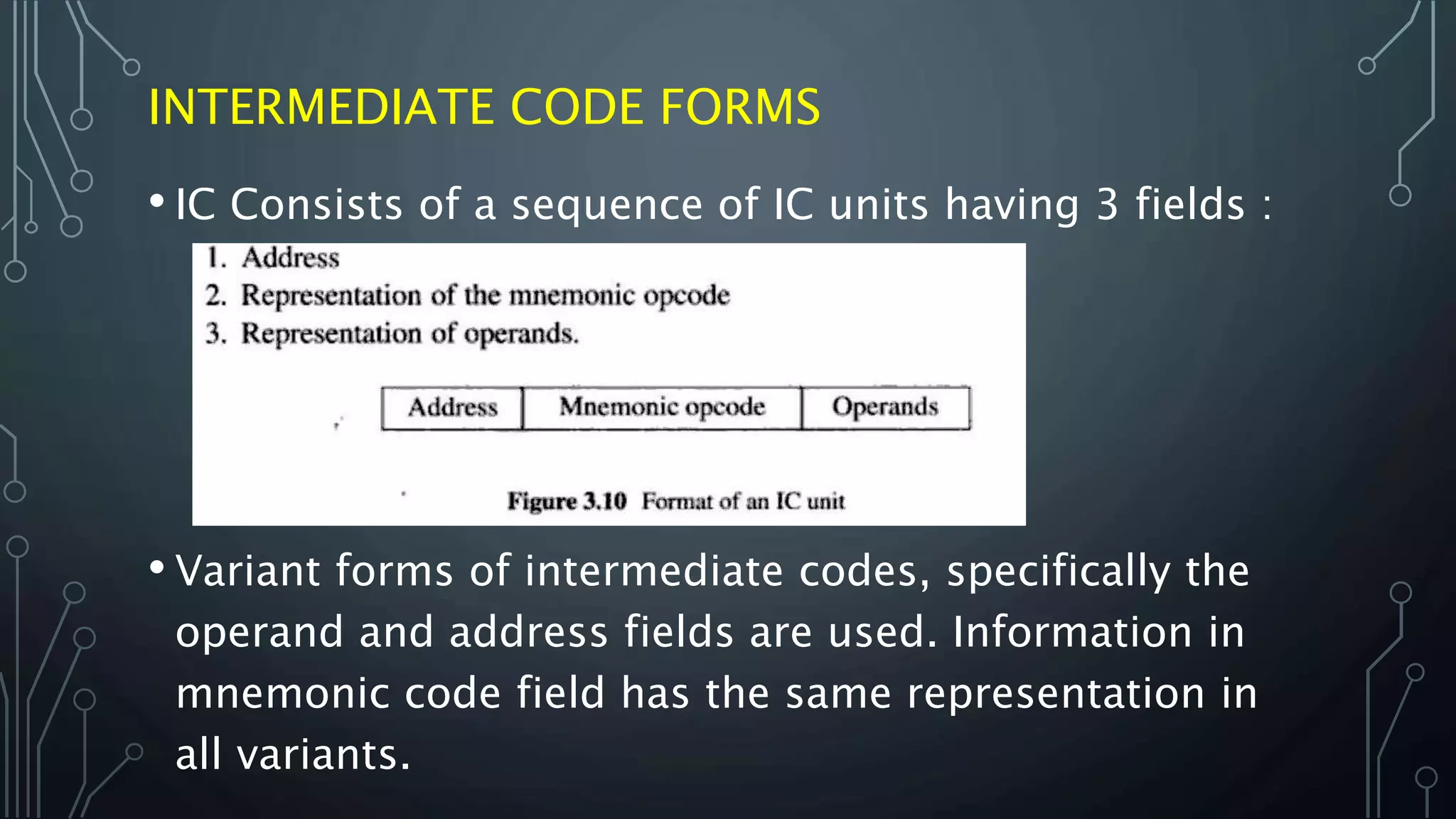
The document outlines the design of a two-pass assembler, detailing the tasks performed in each pass, such as building a symbol table and synthesizing the target program. It explains the data structures utilized during processing, like optab and symtab, and provides examples of intermediate code formats across variant forms. The variants differ in how operands are represented, with specific approaches for handling defined symbols and forward references.