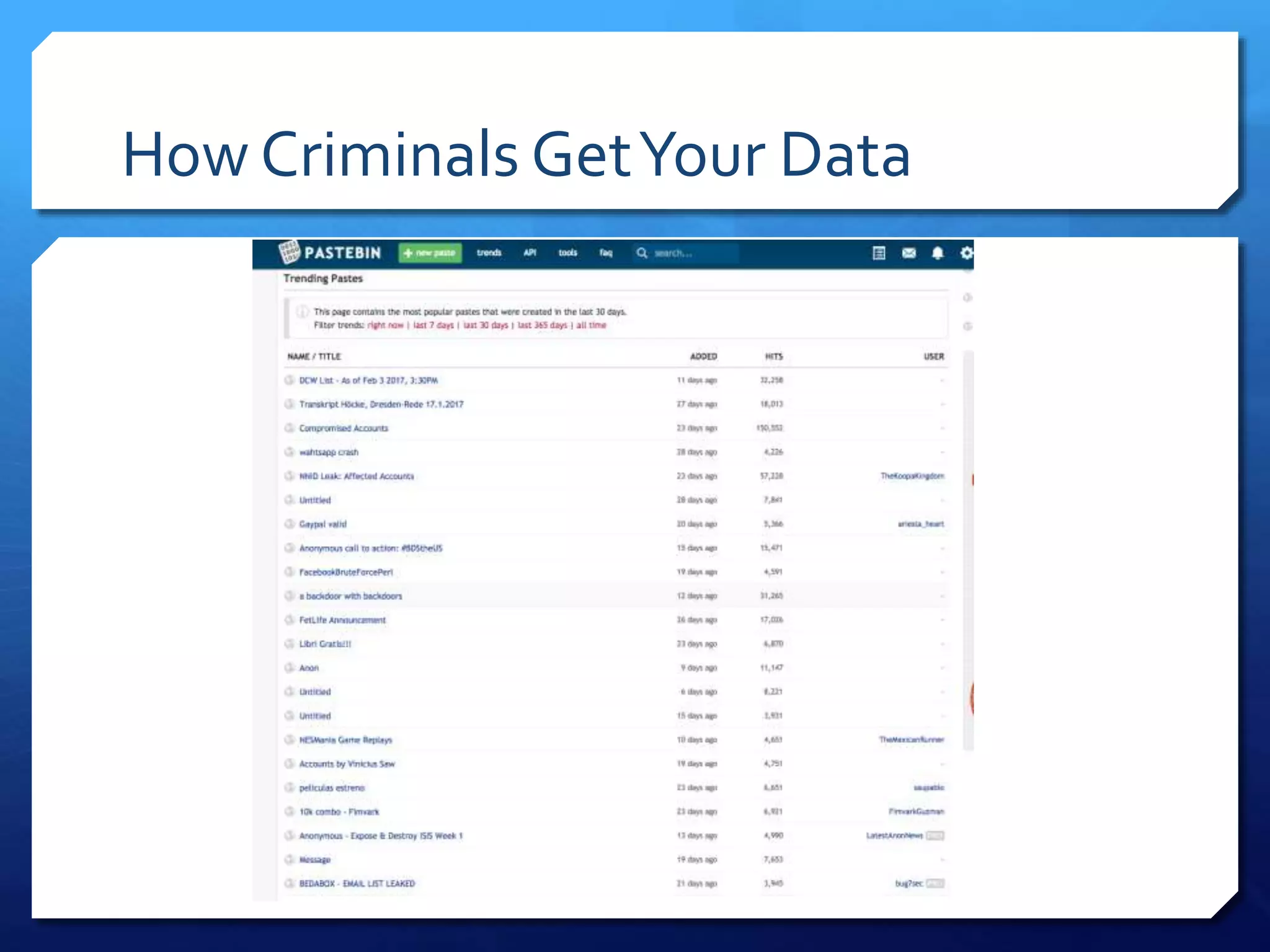
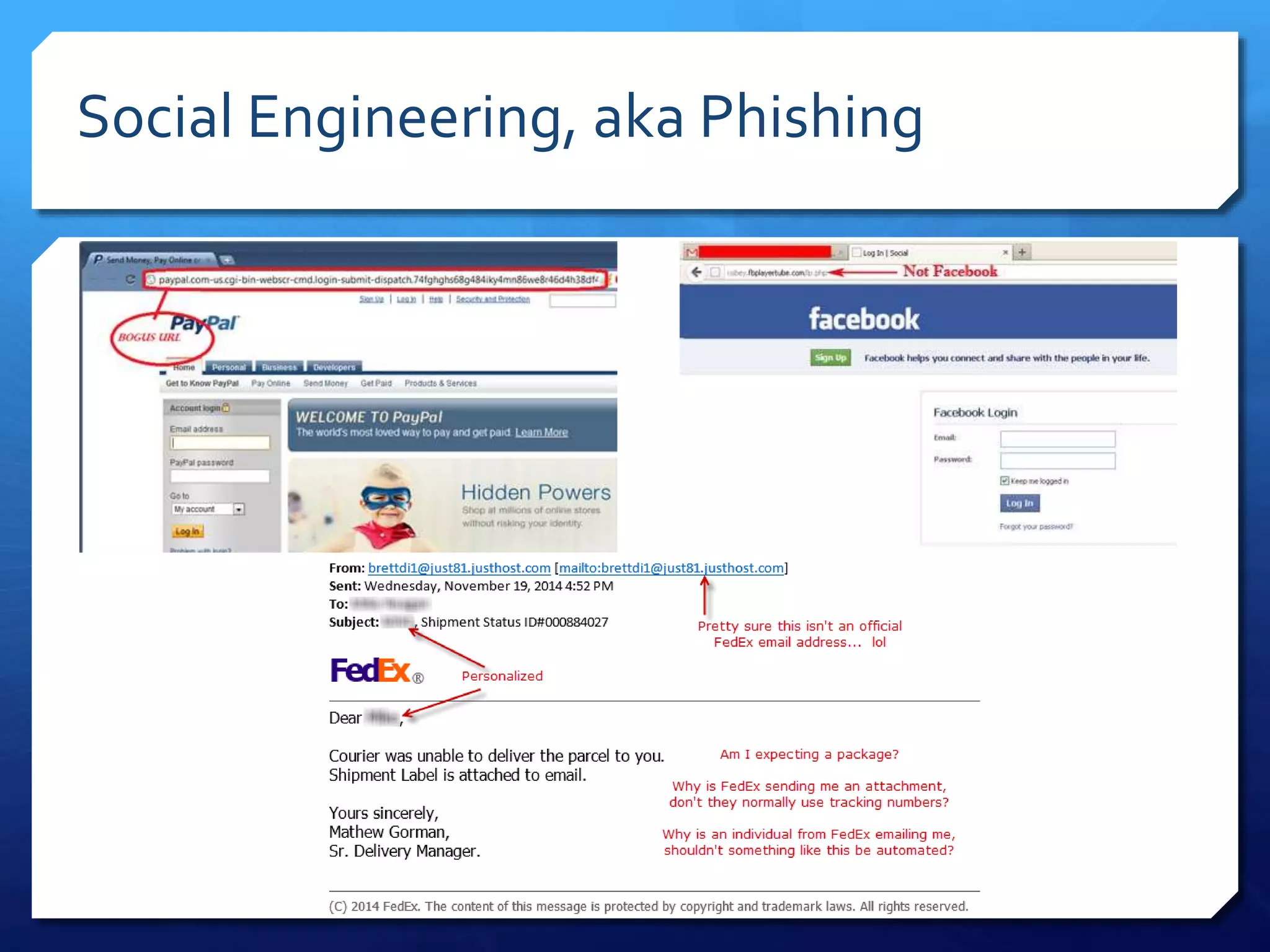
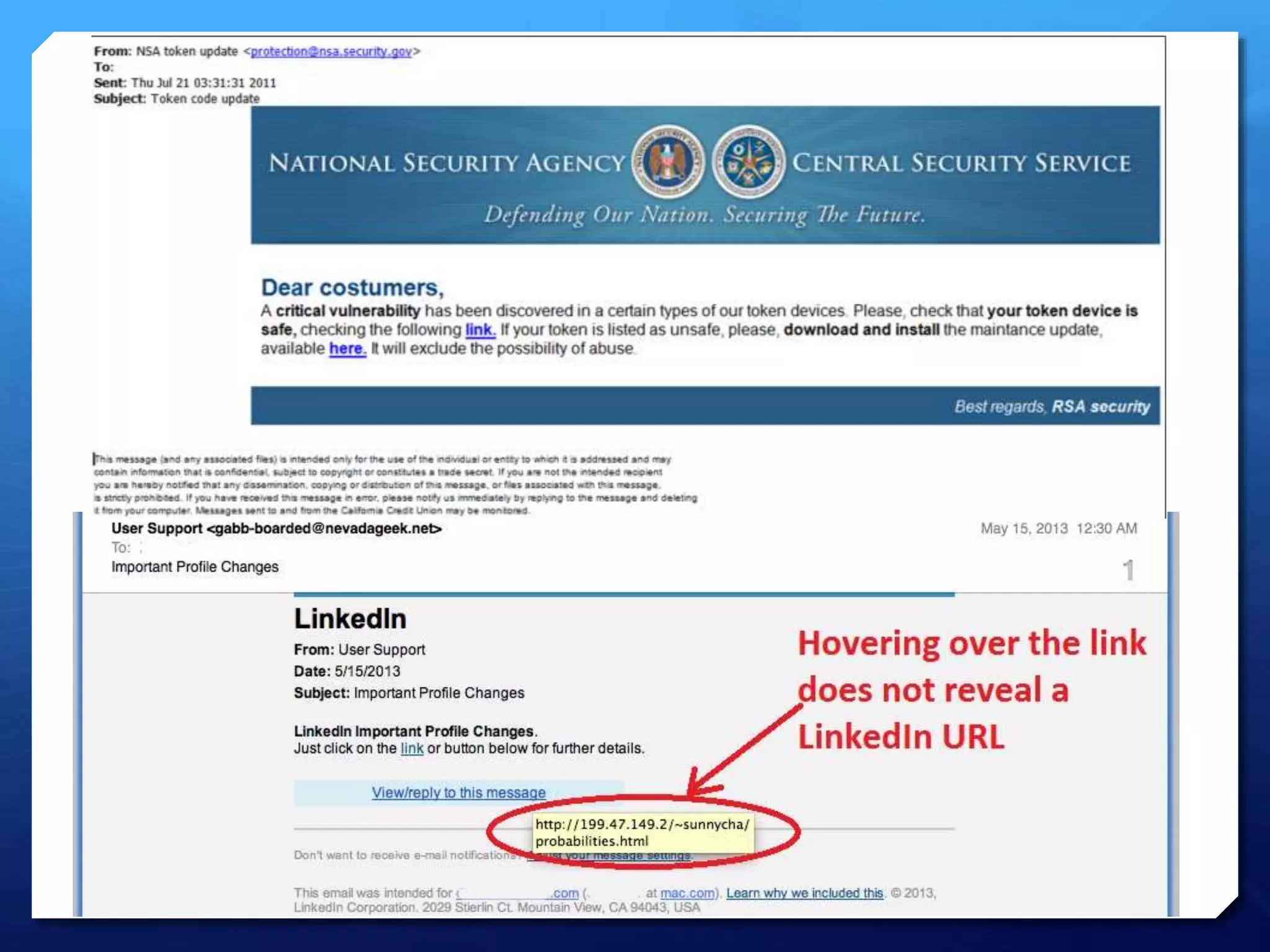
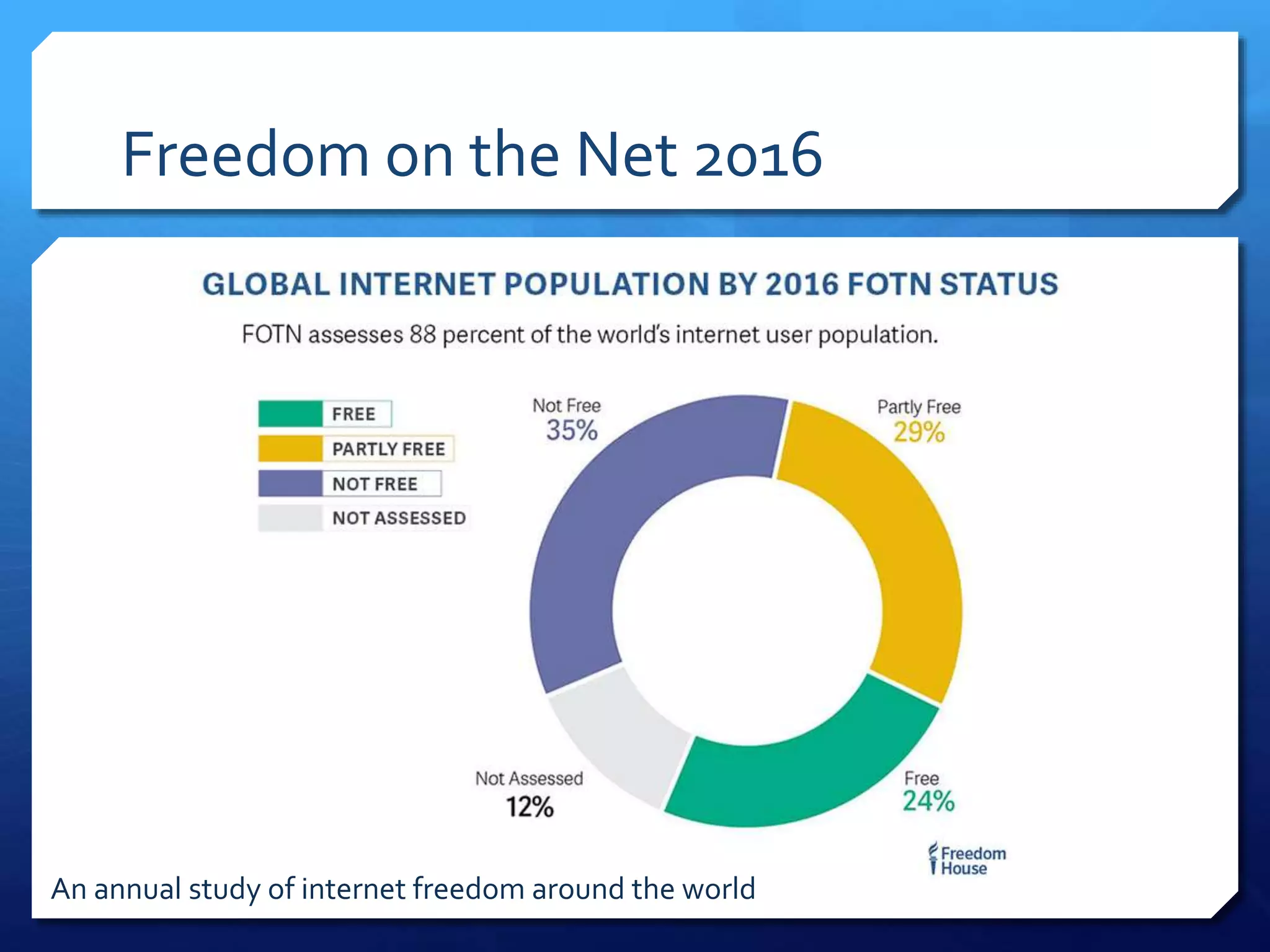
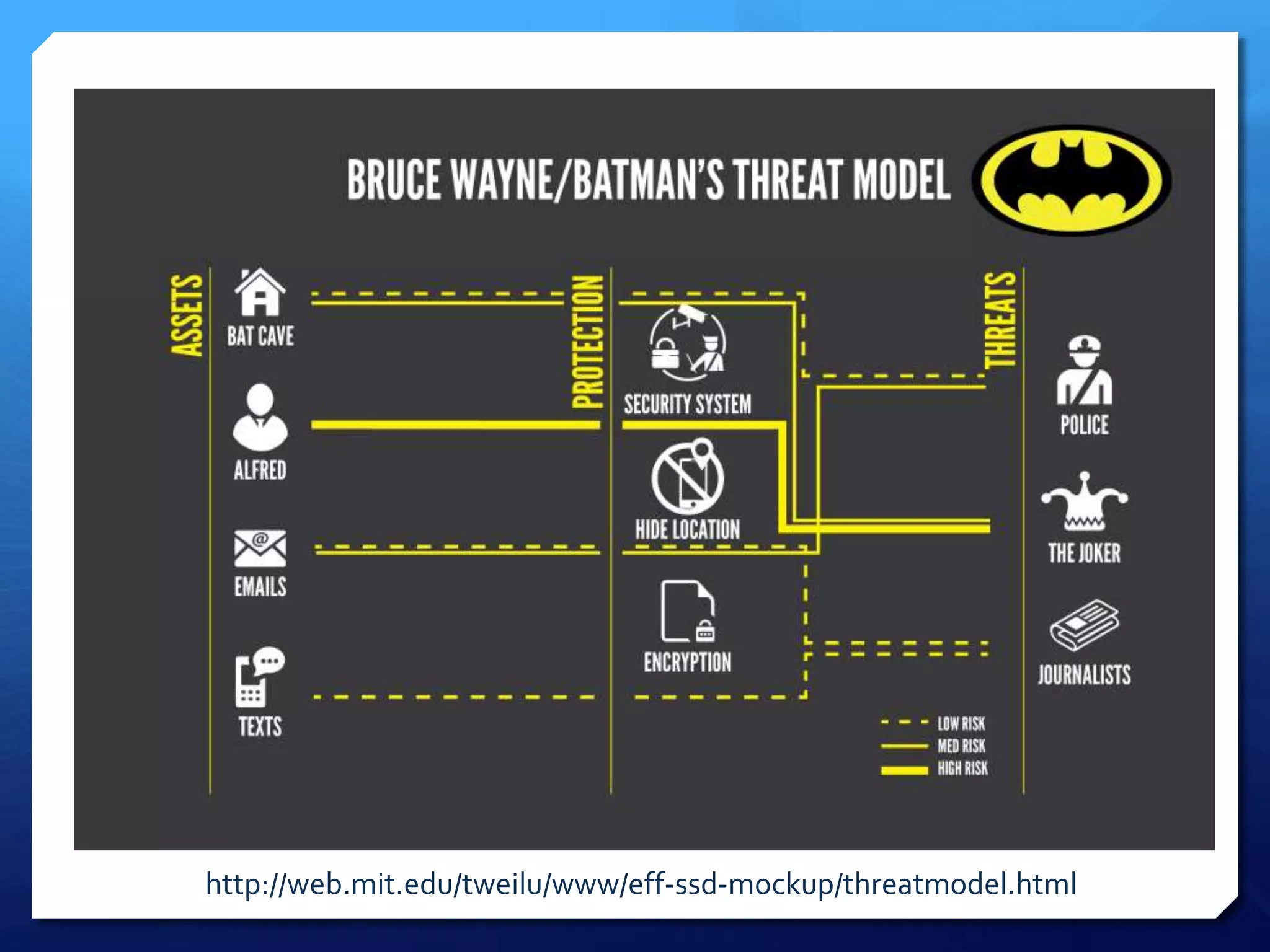
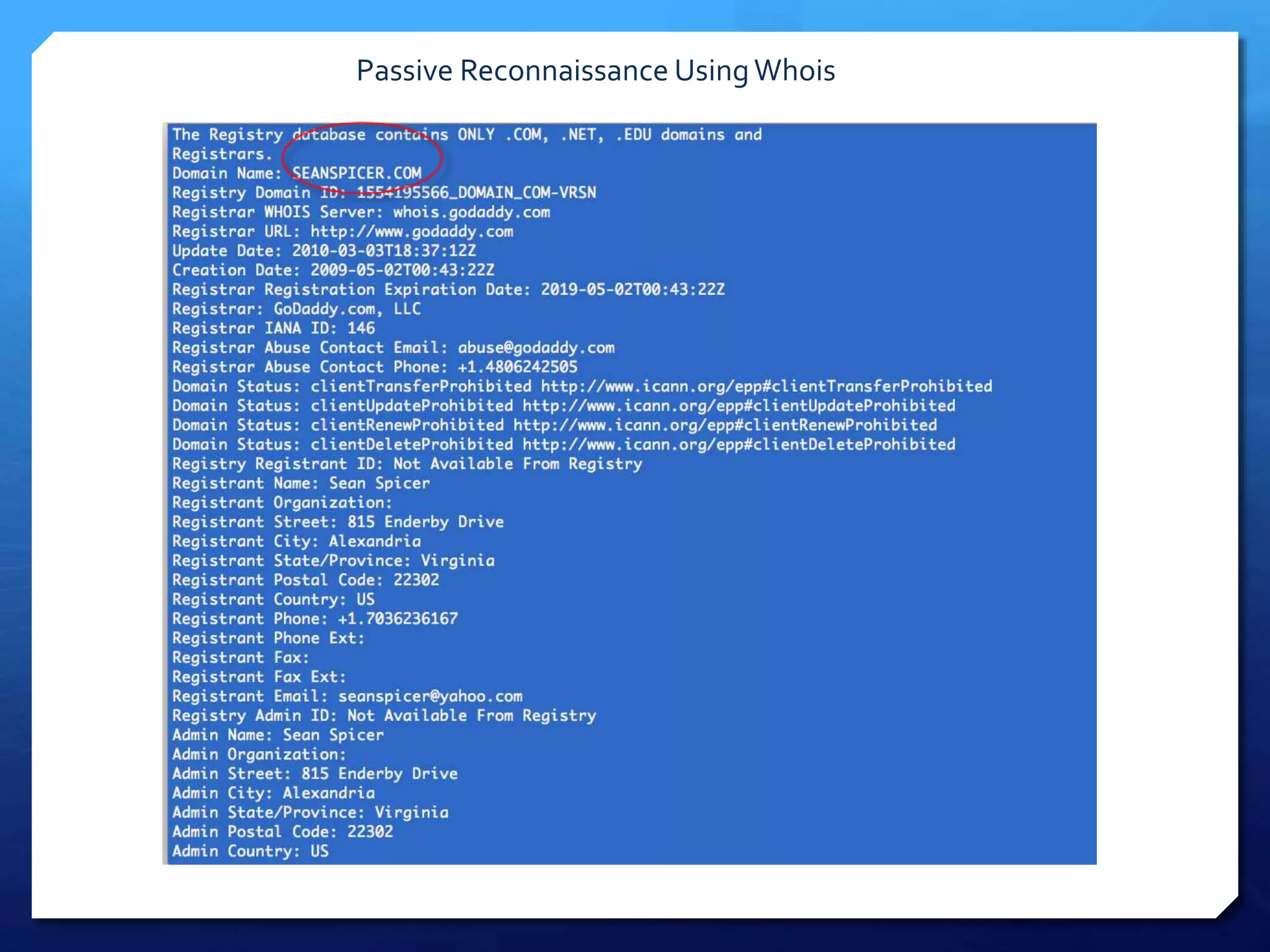
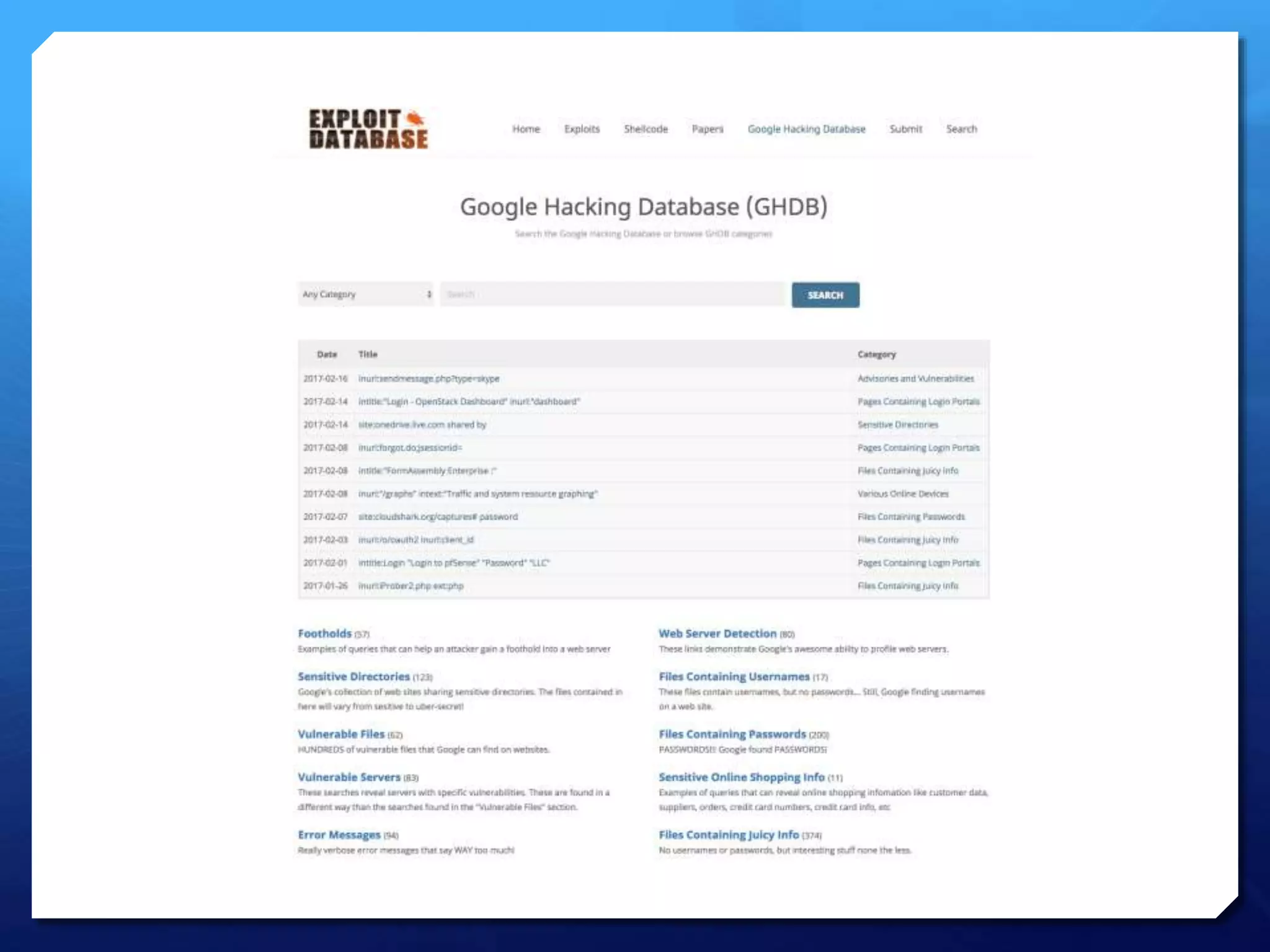
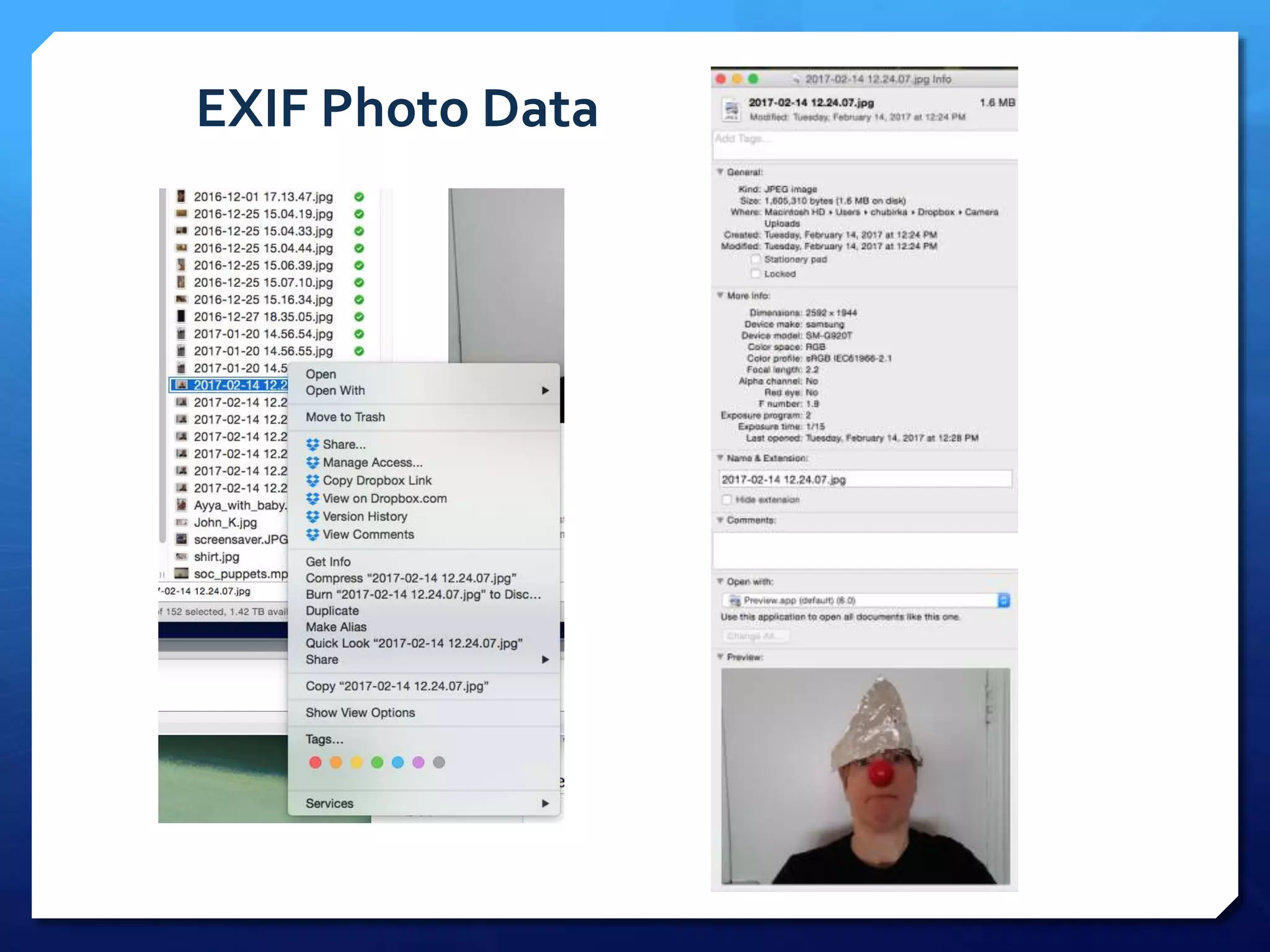
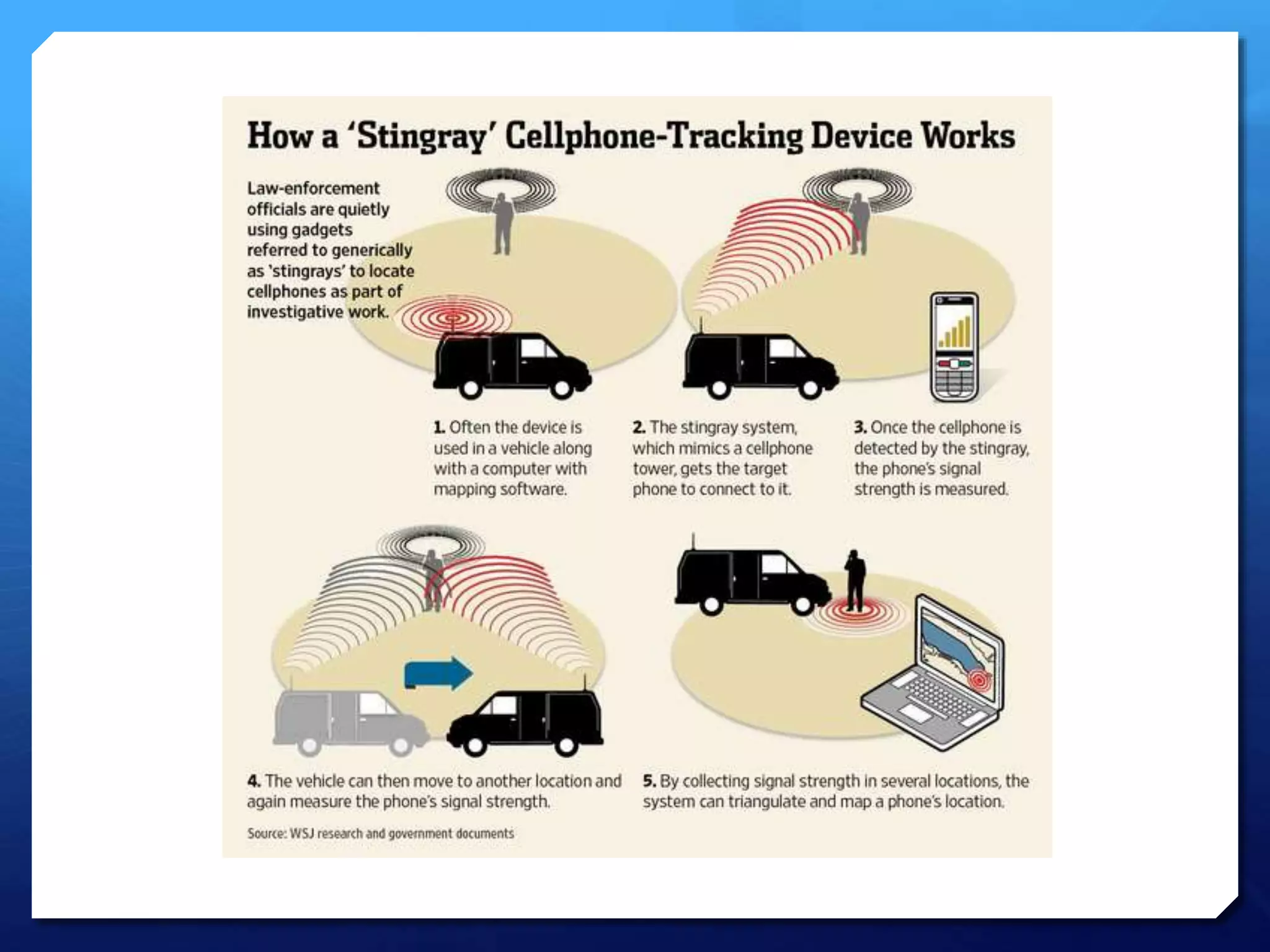
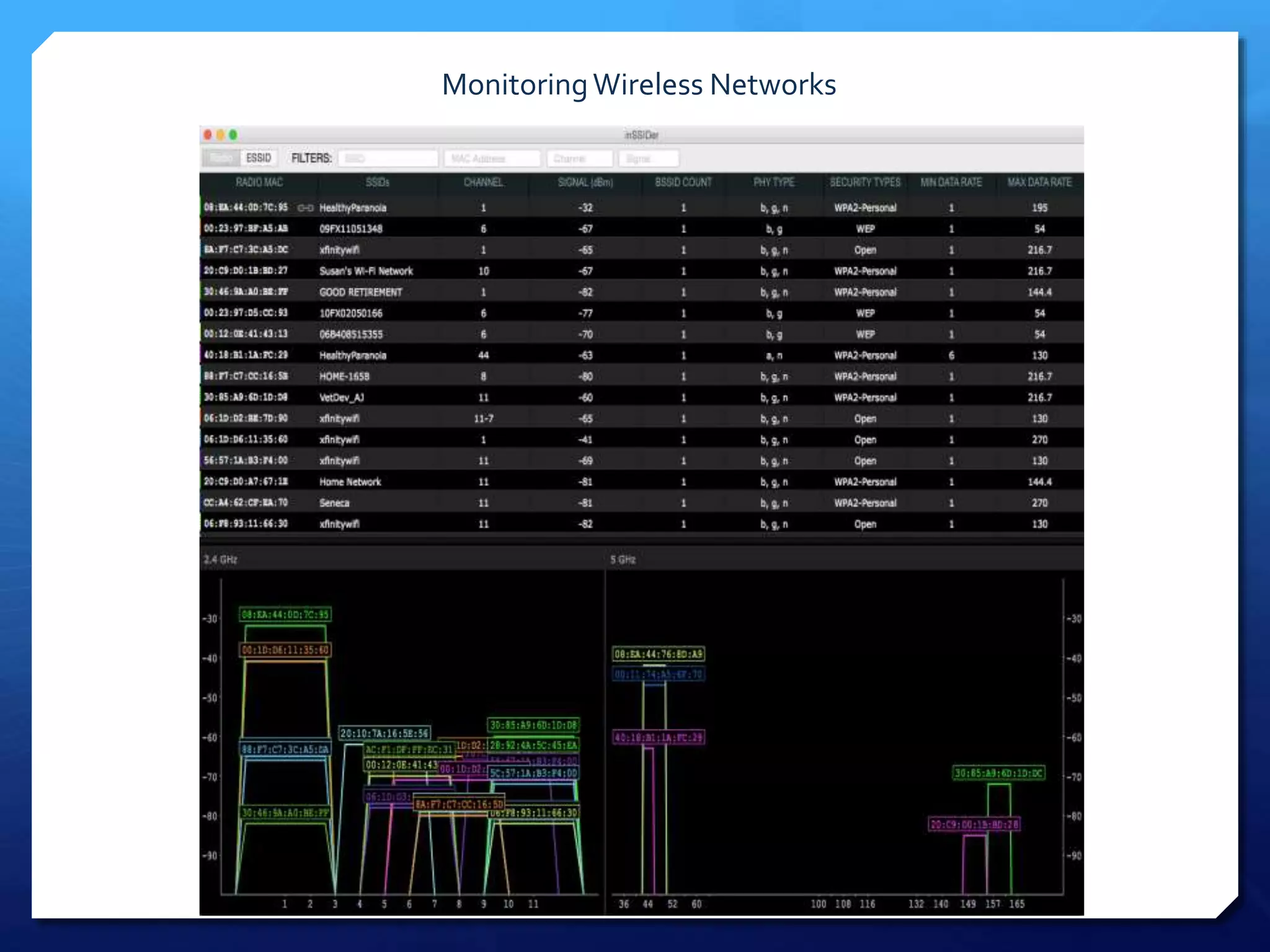
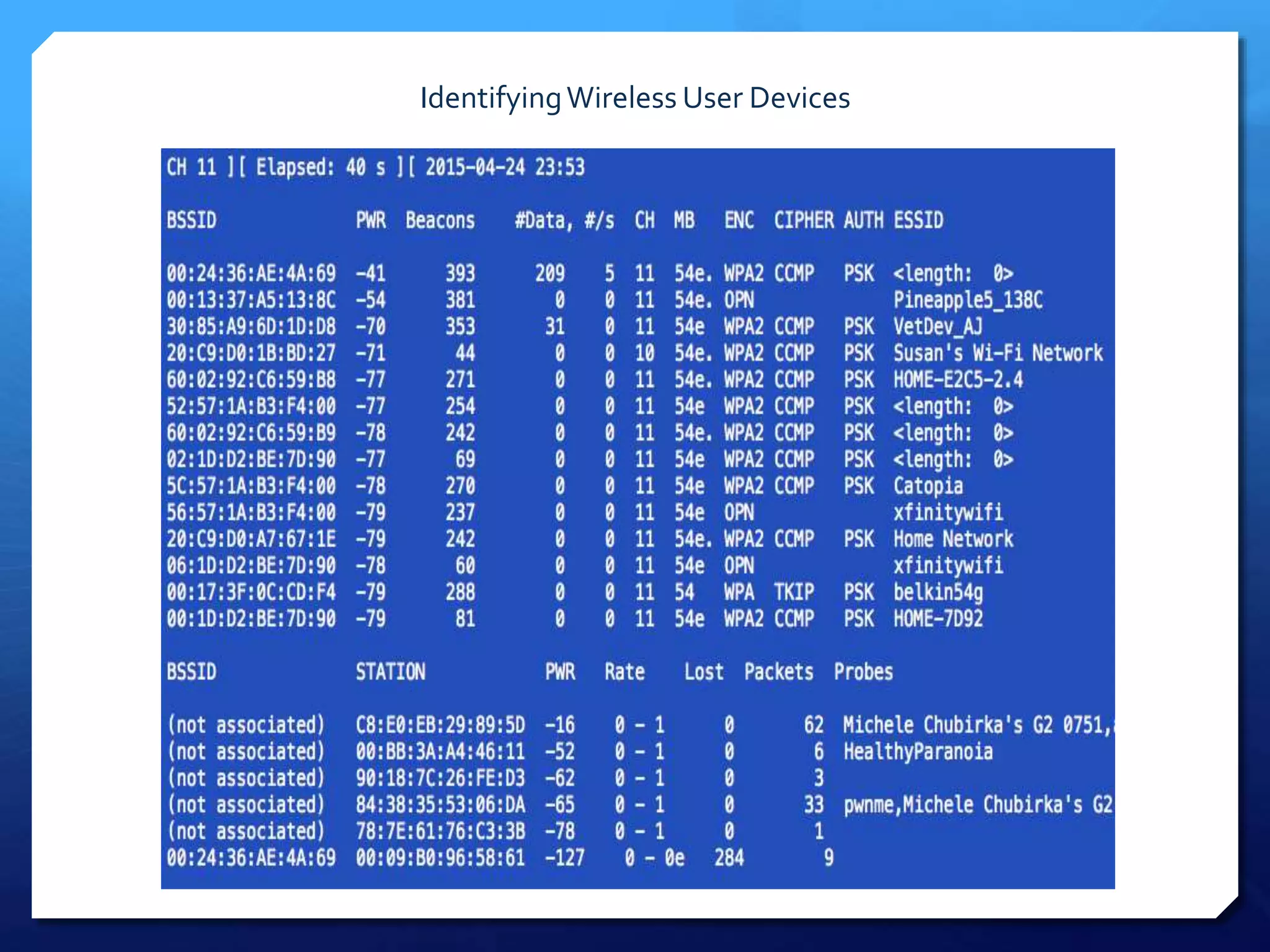
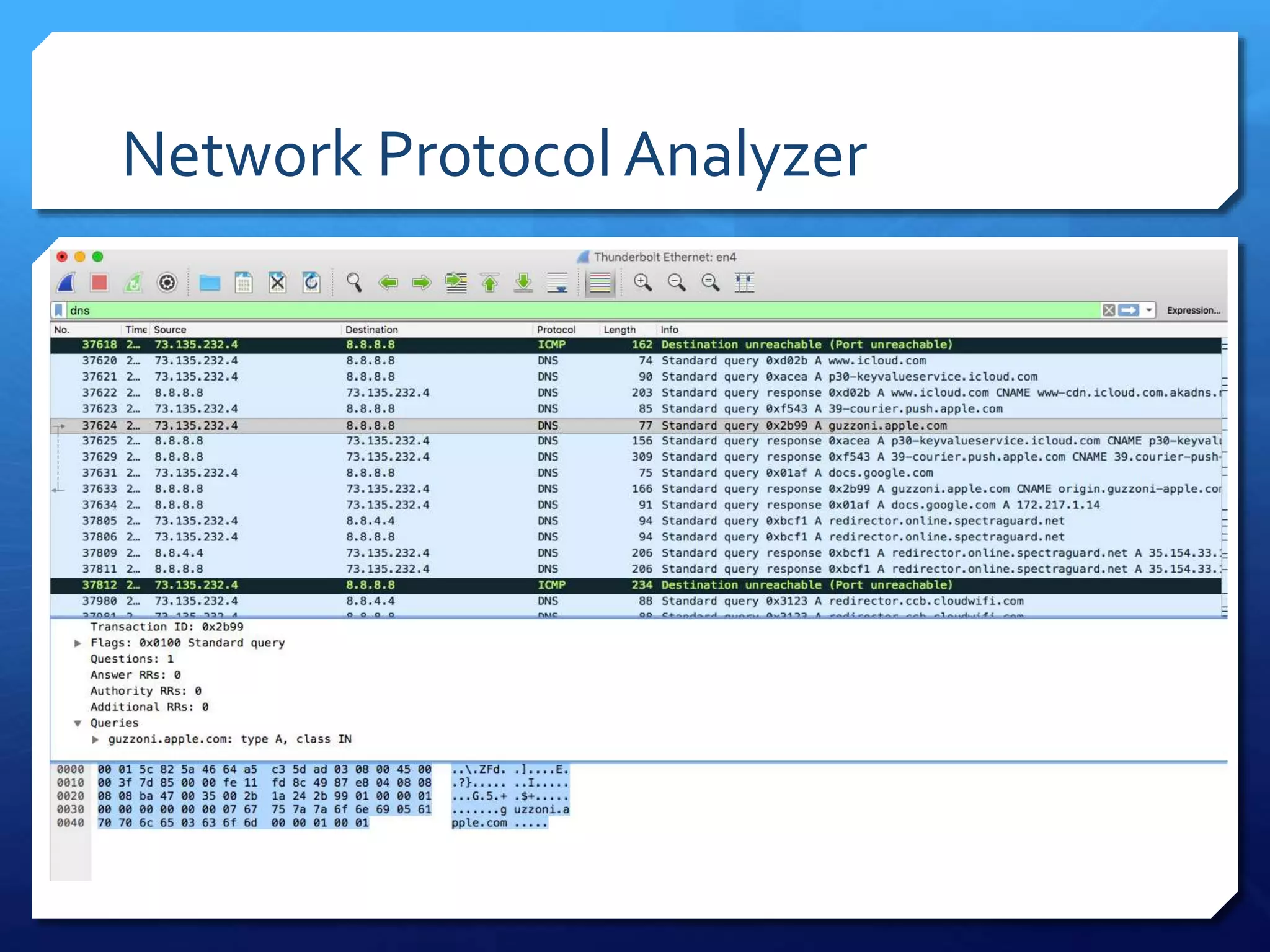
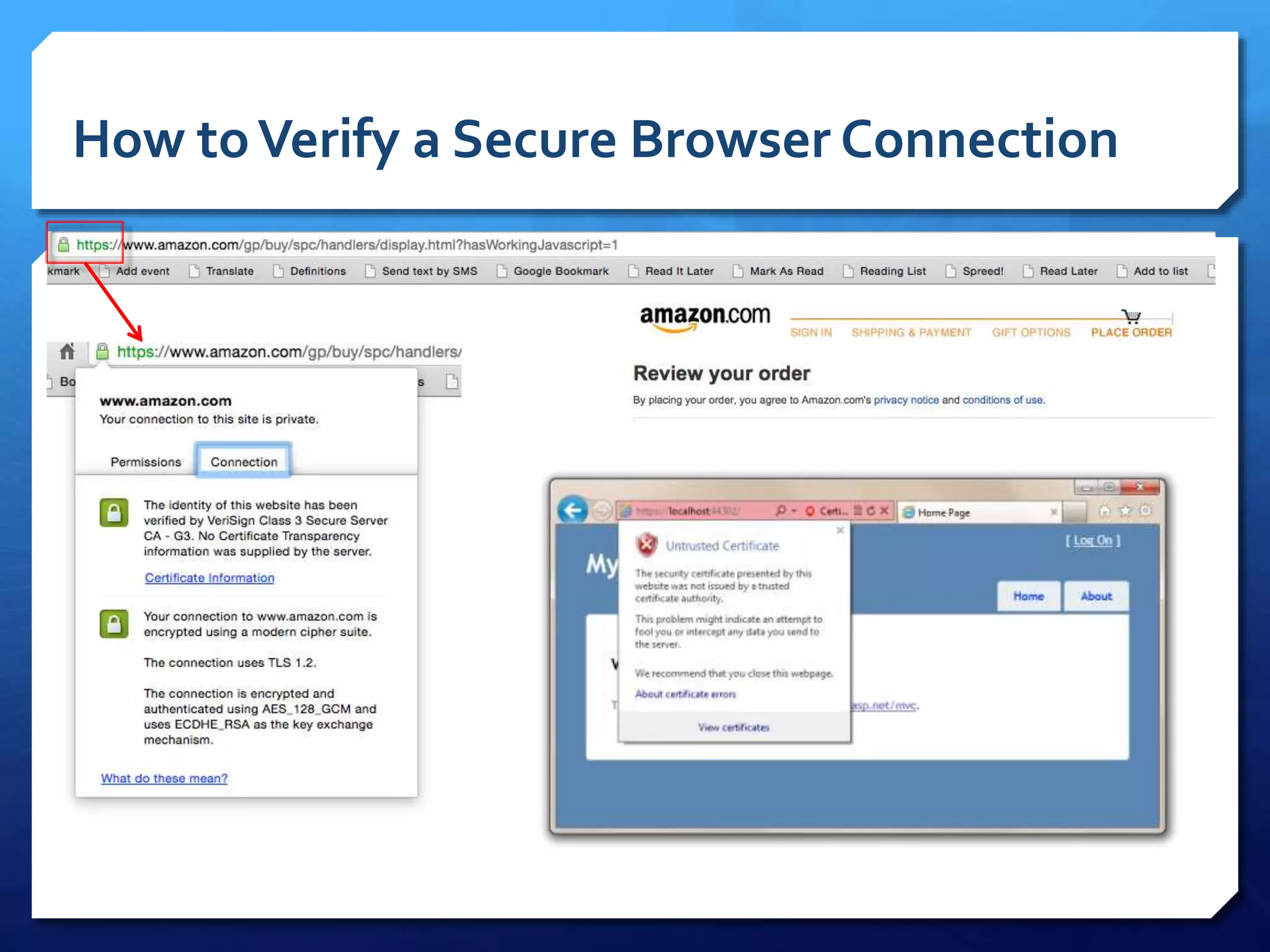
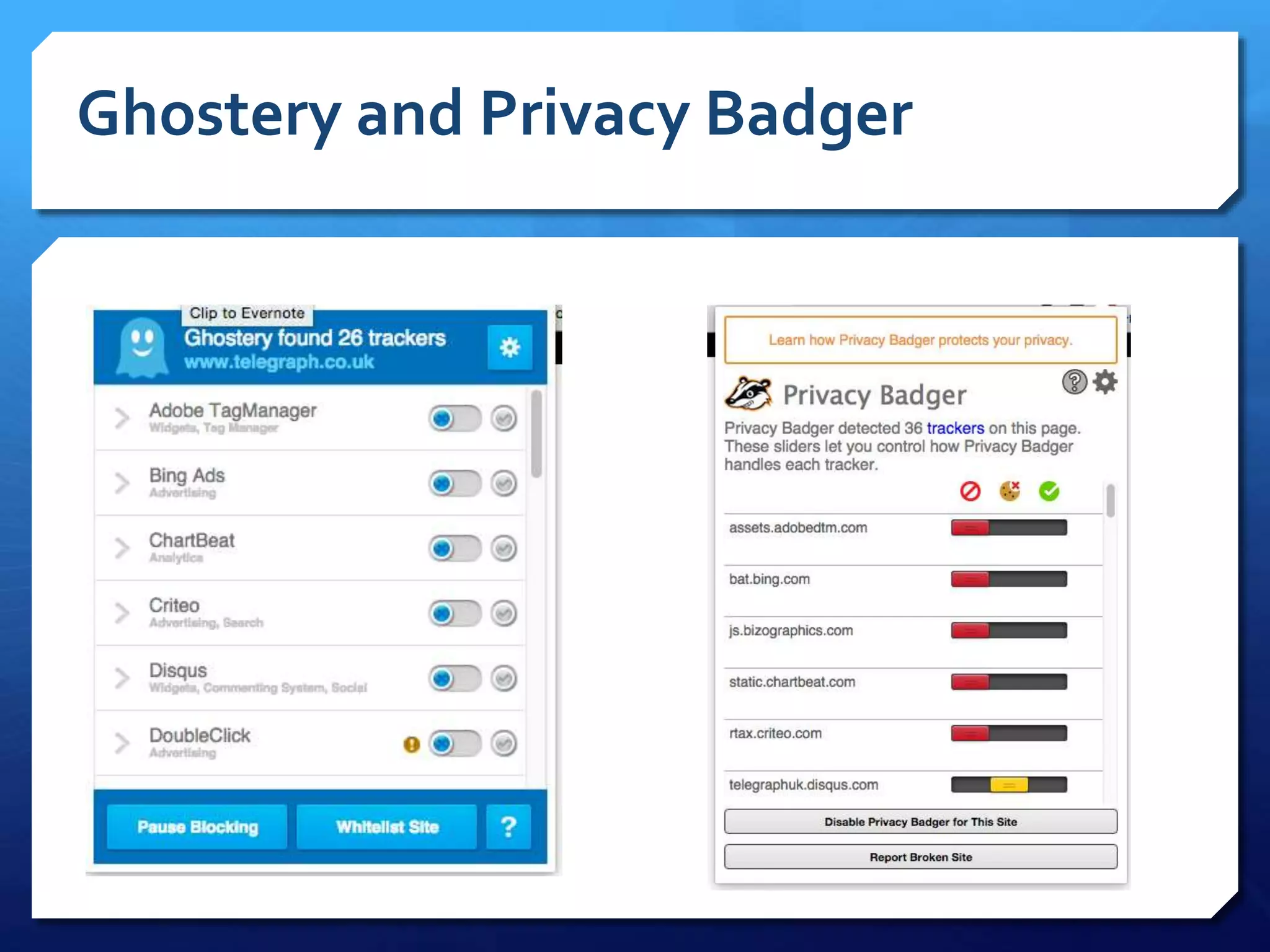
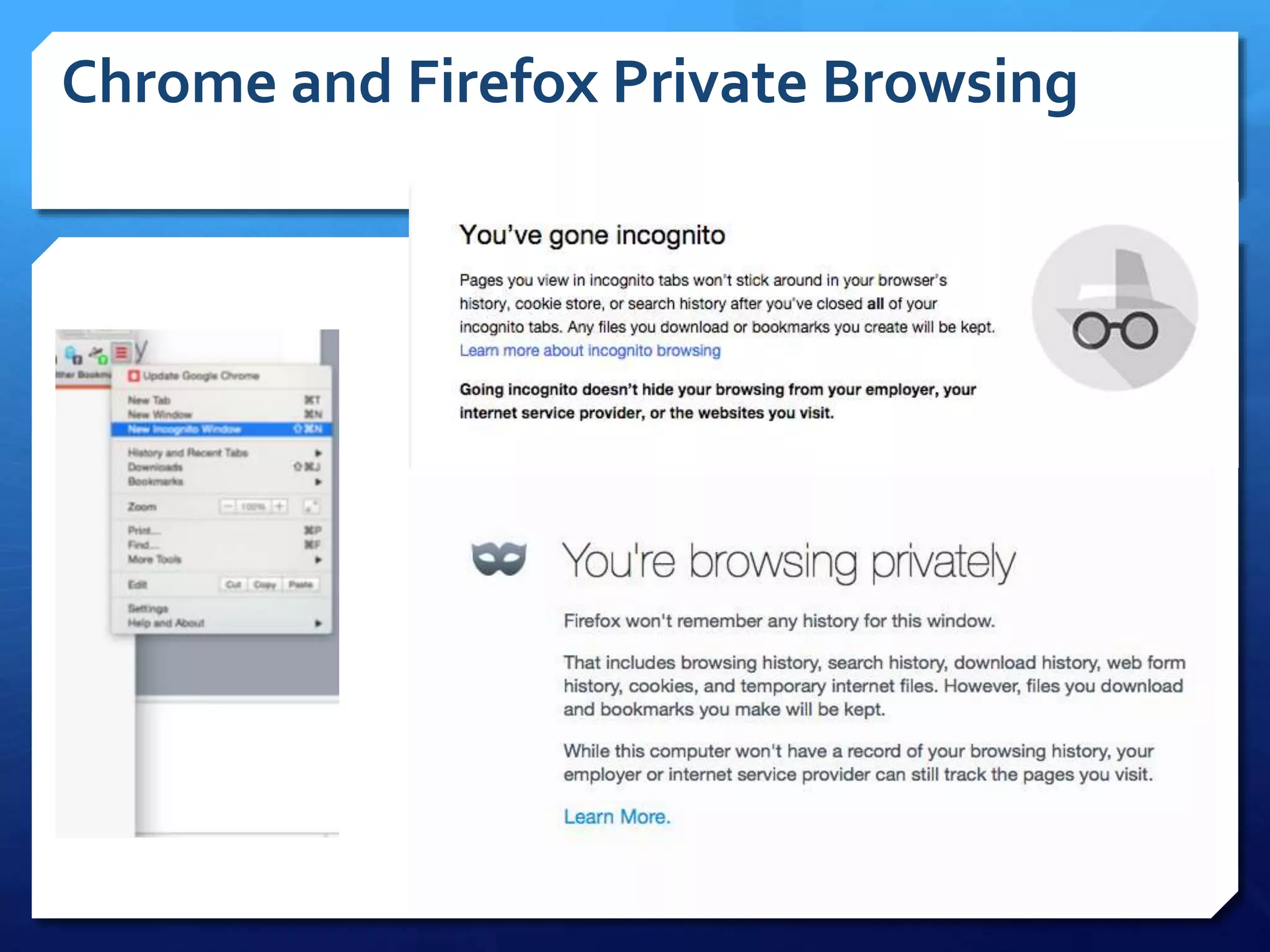
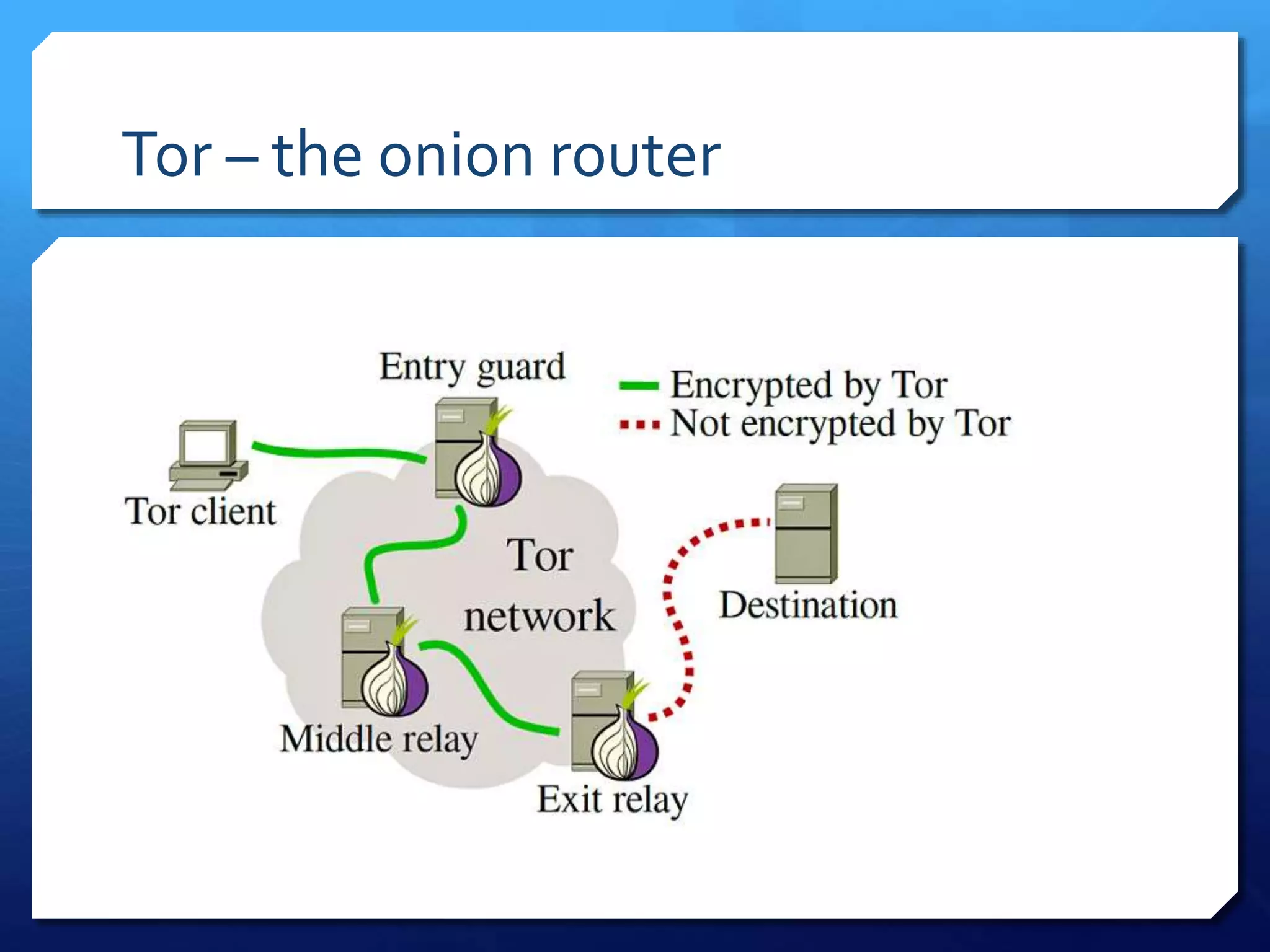
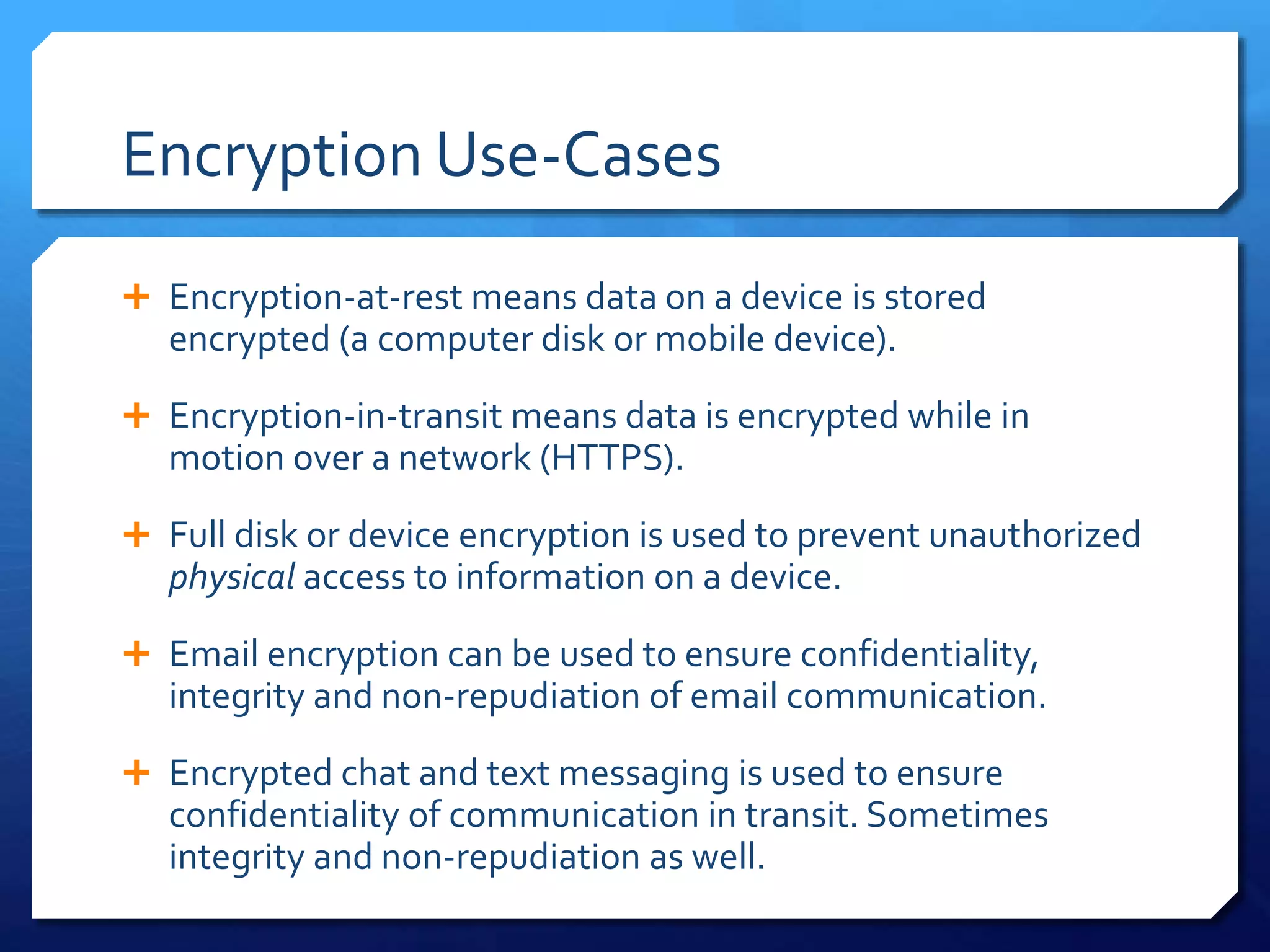
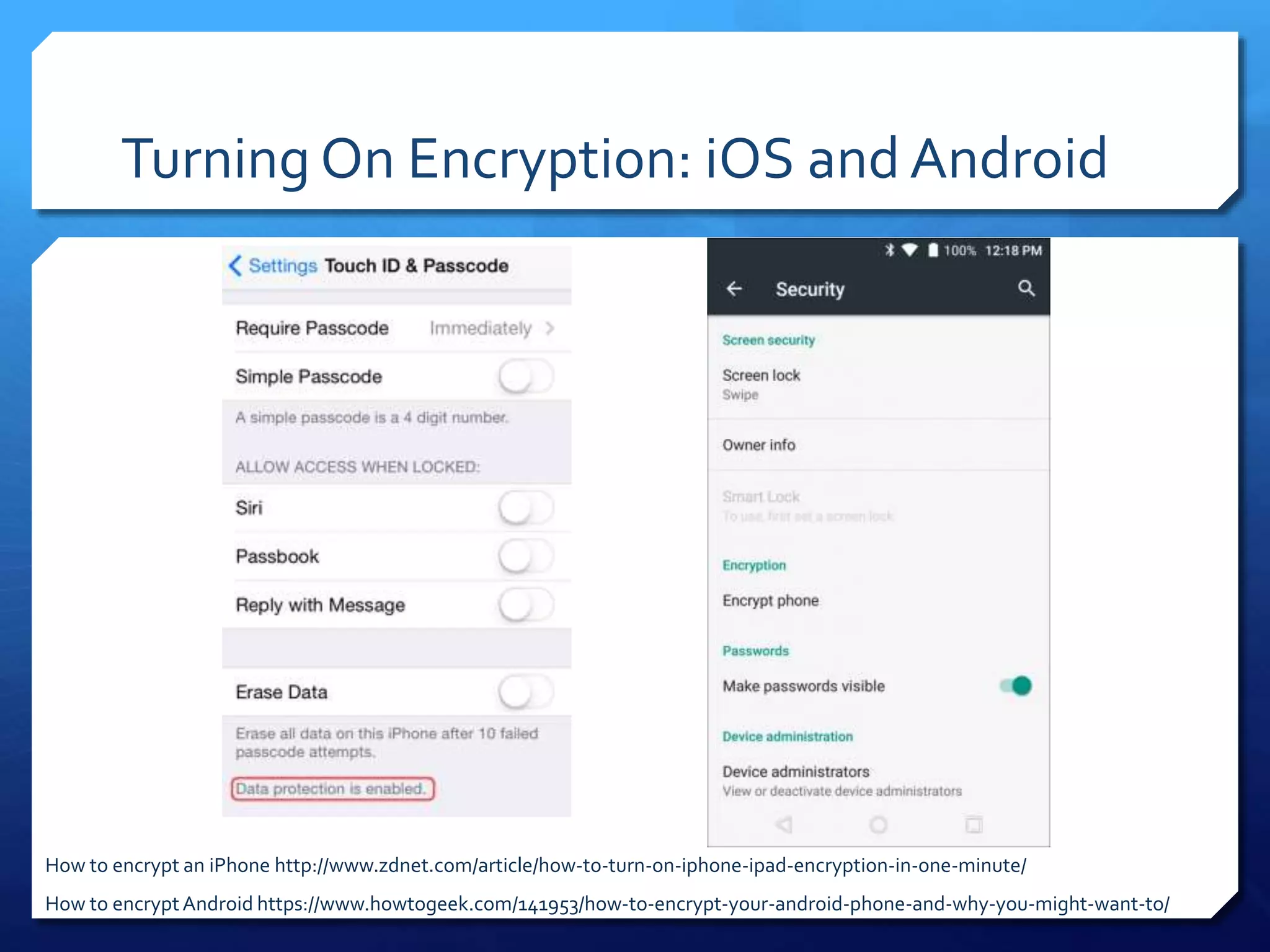
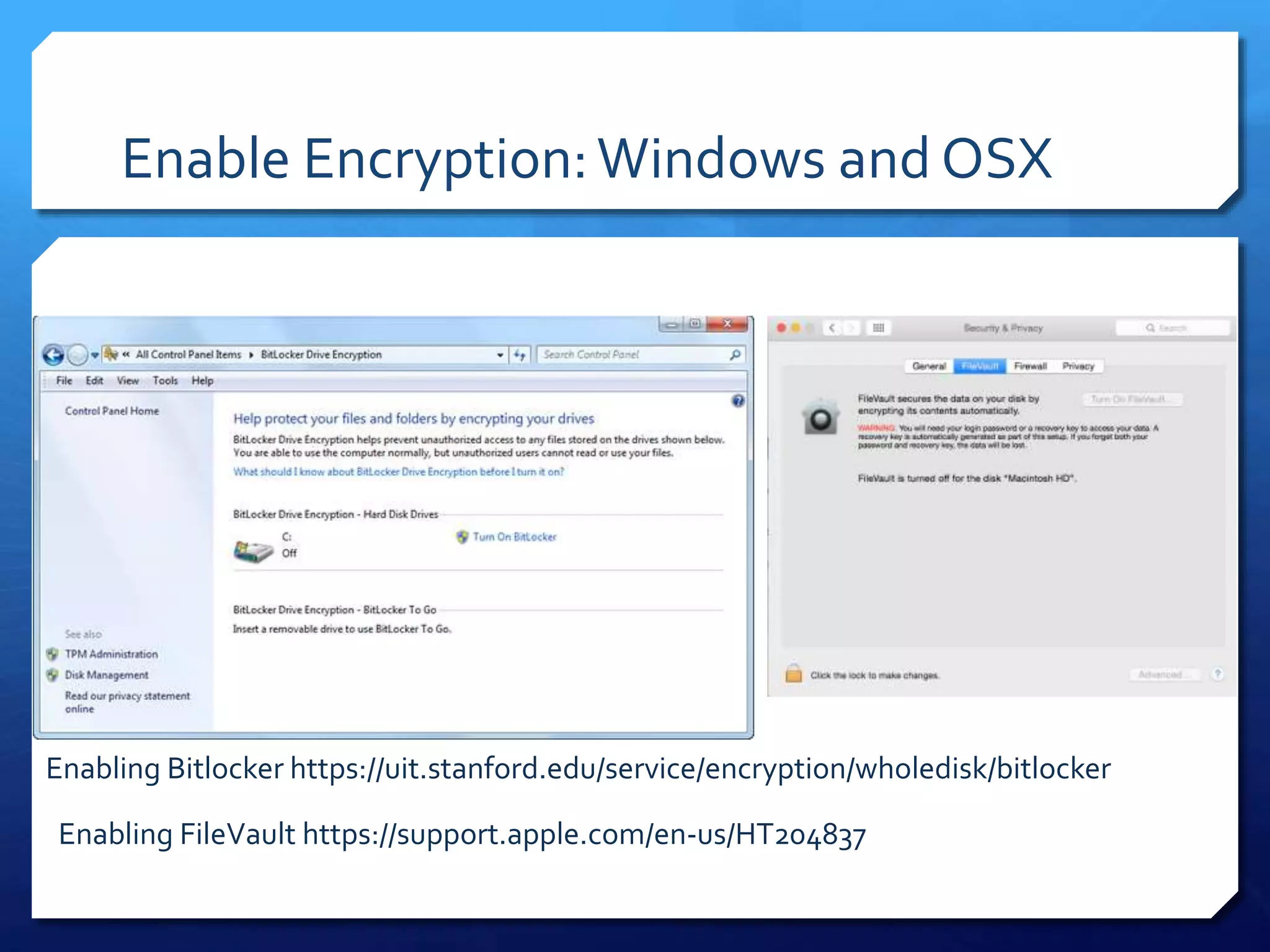
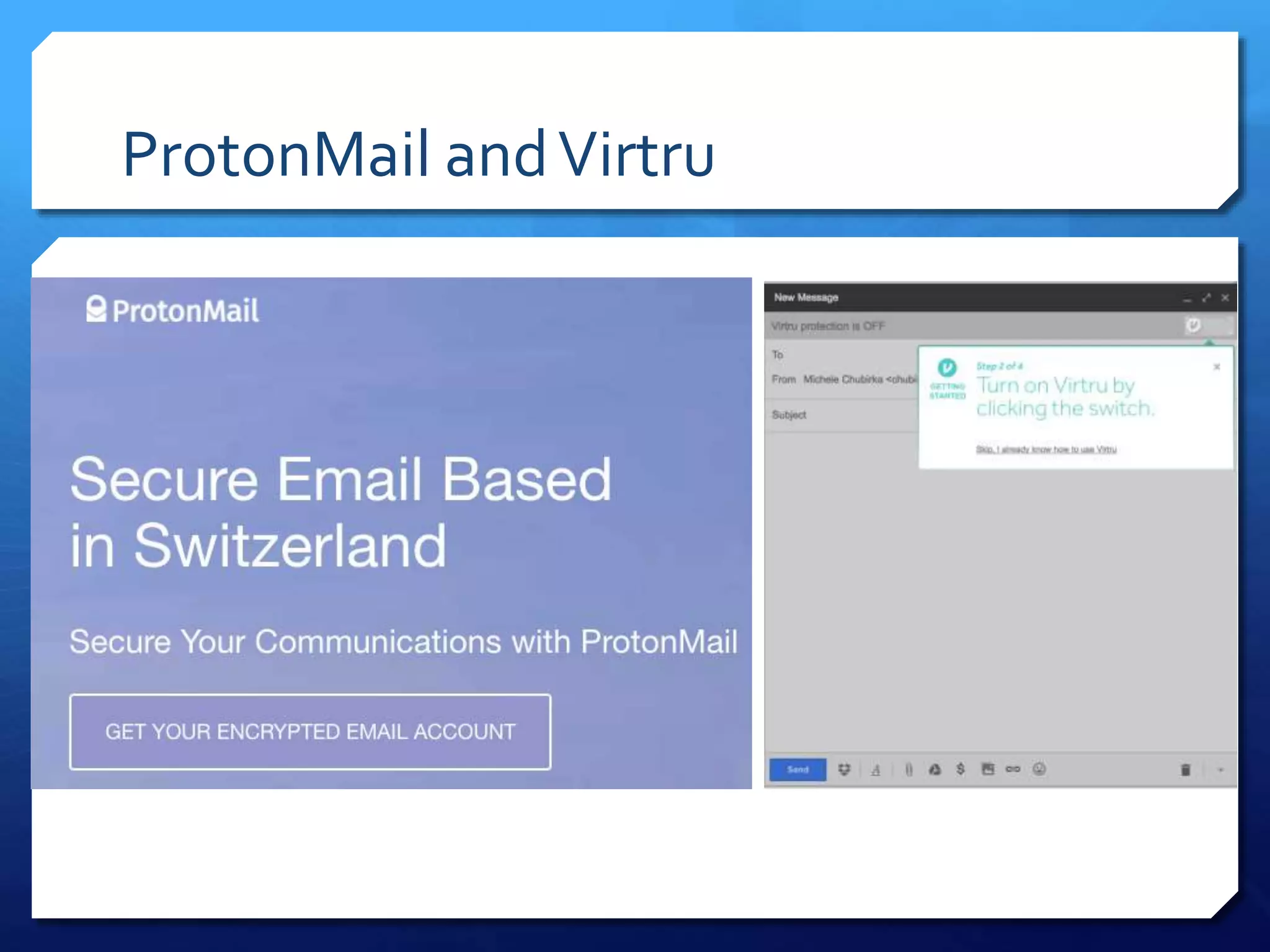
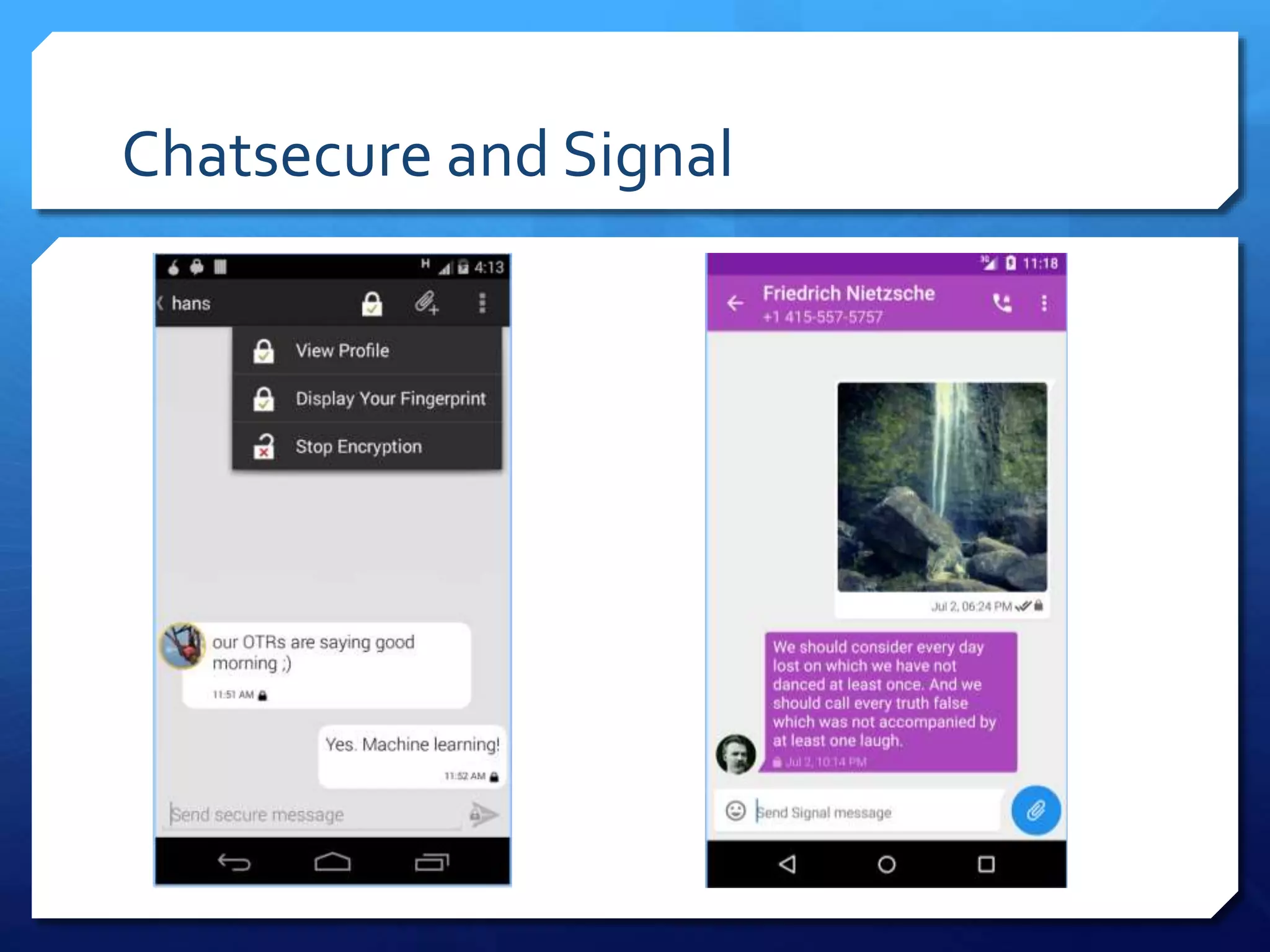
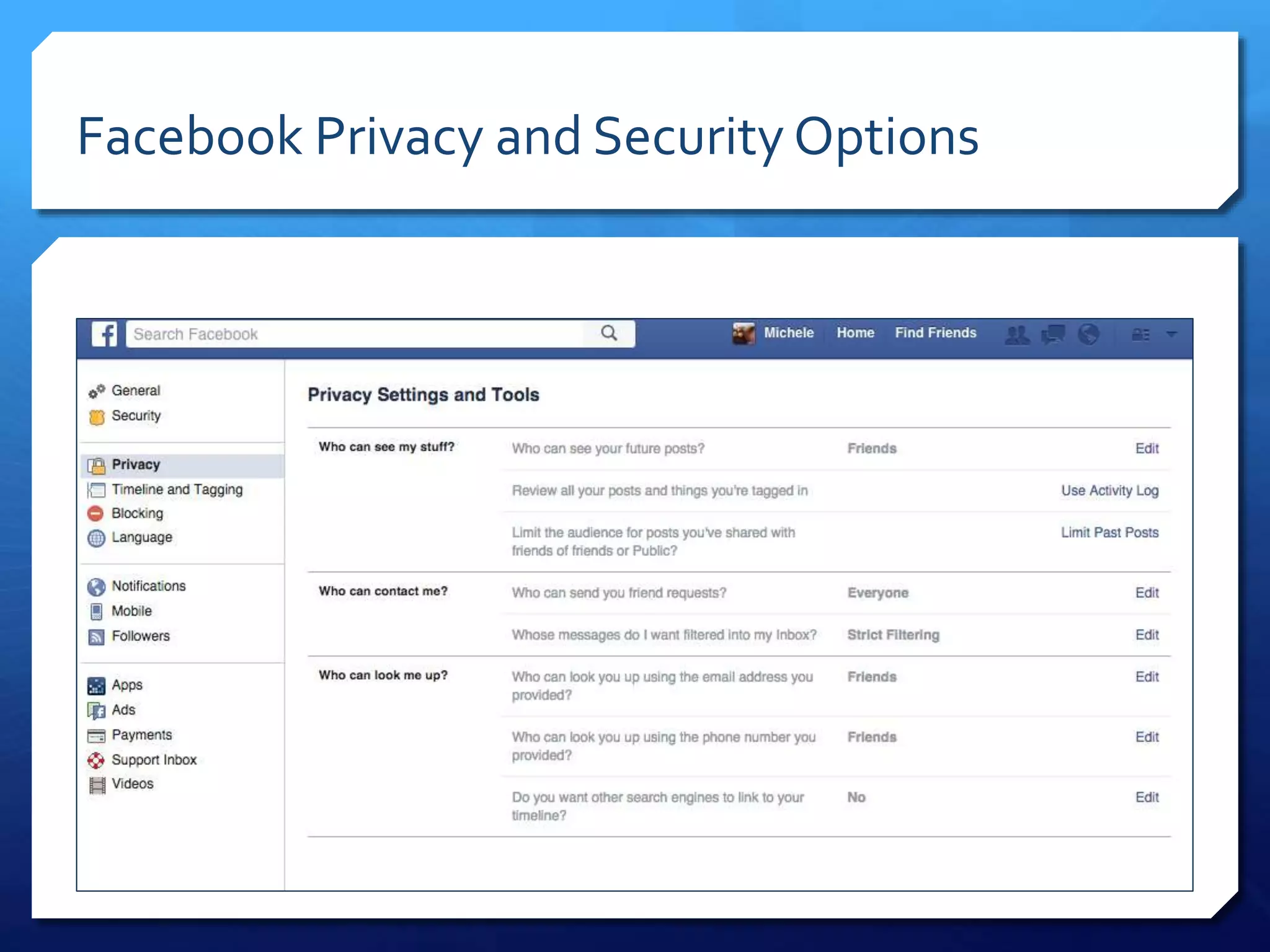
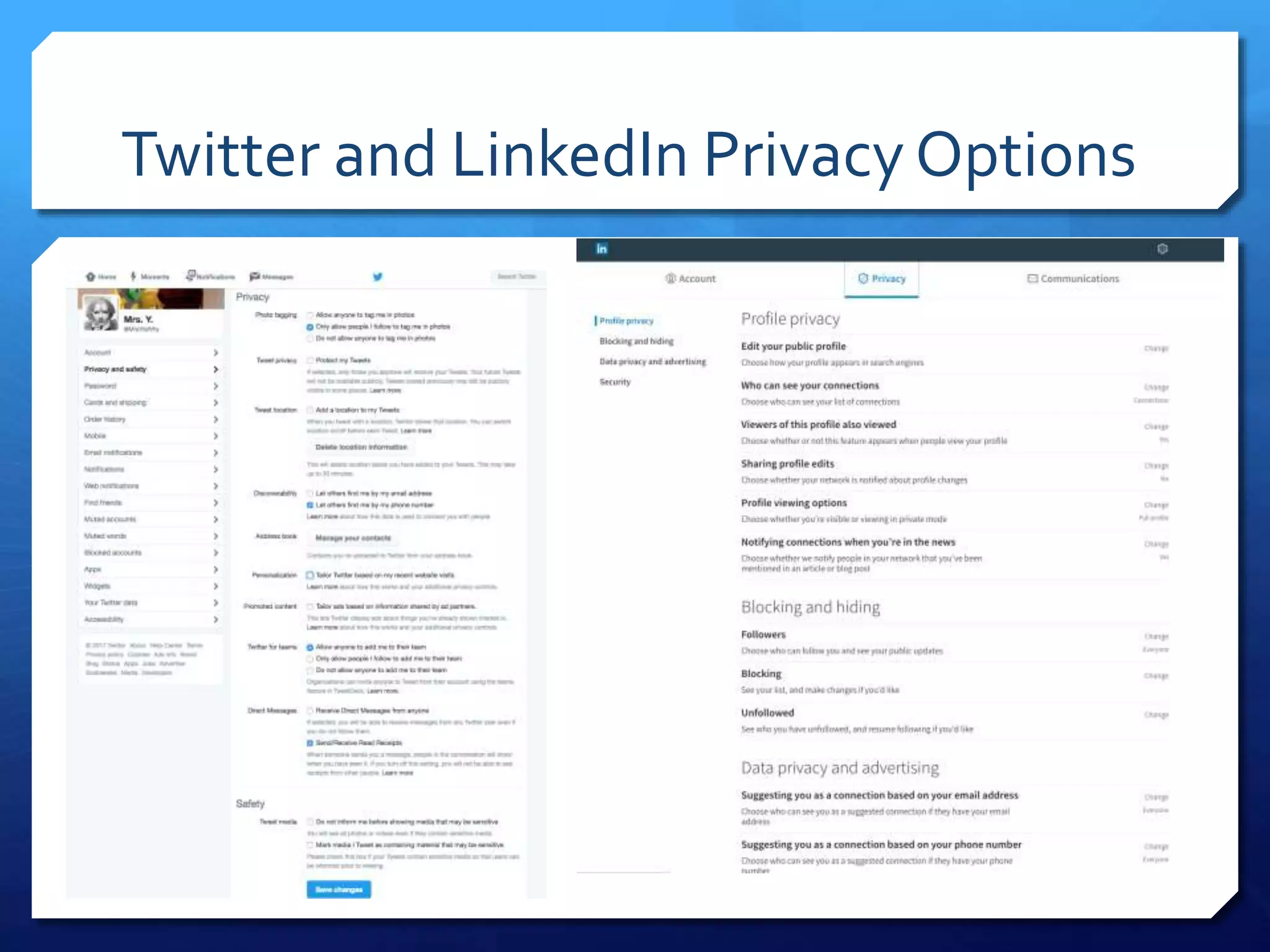
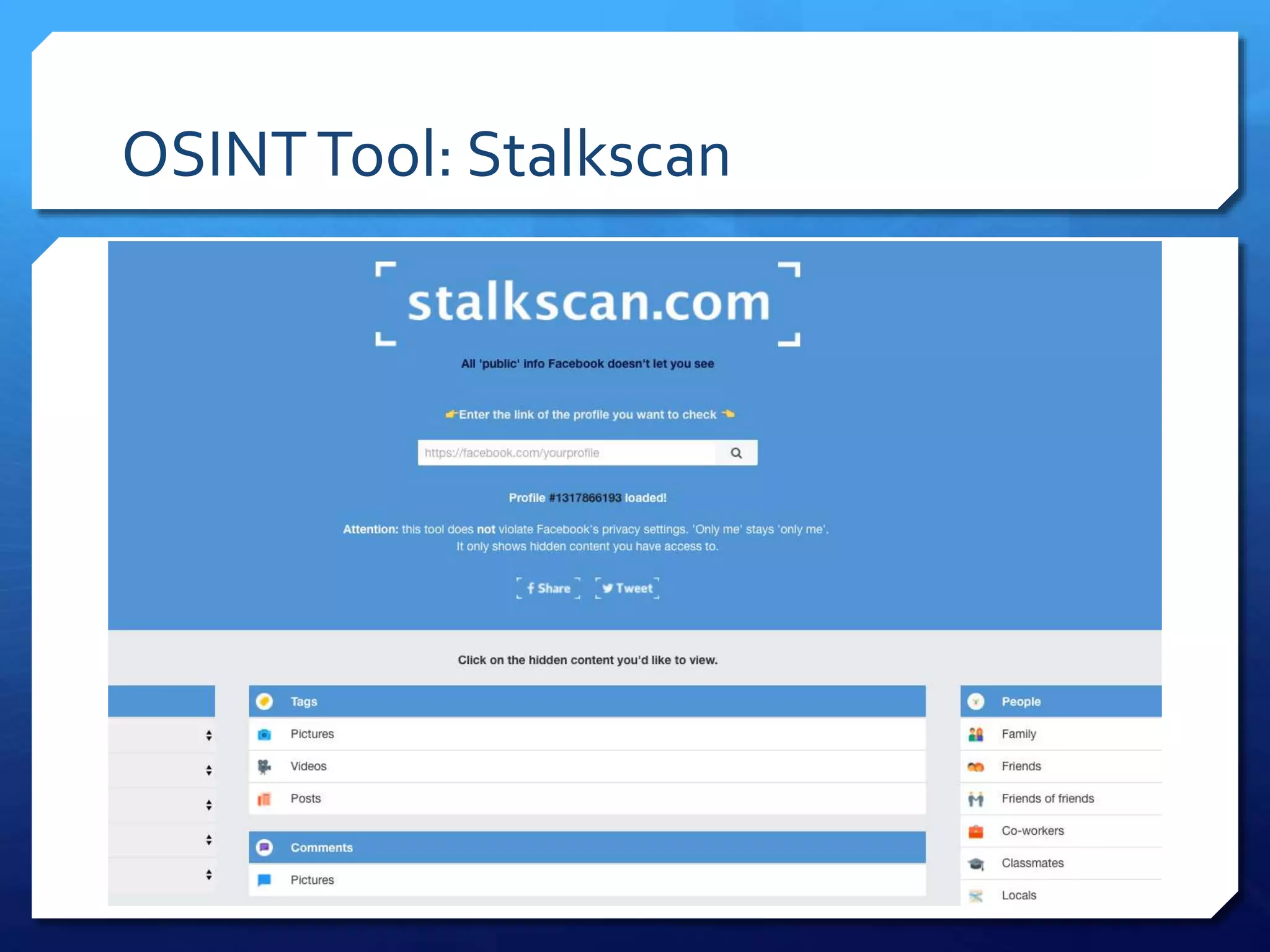
This document provides an overview of digital defense techniques for activists and others concerned about online privacy and security. It begins with introductions and an outline of topics to be covered, which include the current security landscape, risk management principles, and specific defense techniques. The document discusses common online threats such as surveillance, hacking, and social engineering. It provides tips for securing web browsers, encrypting data, using anonymity tools like Tor and VPNs, and choosing secure communication platforms and passwords. Overall, the document aims to educate readers on digital risks and best practices for online privacy and security.