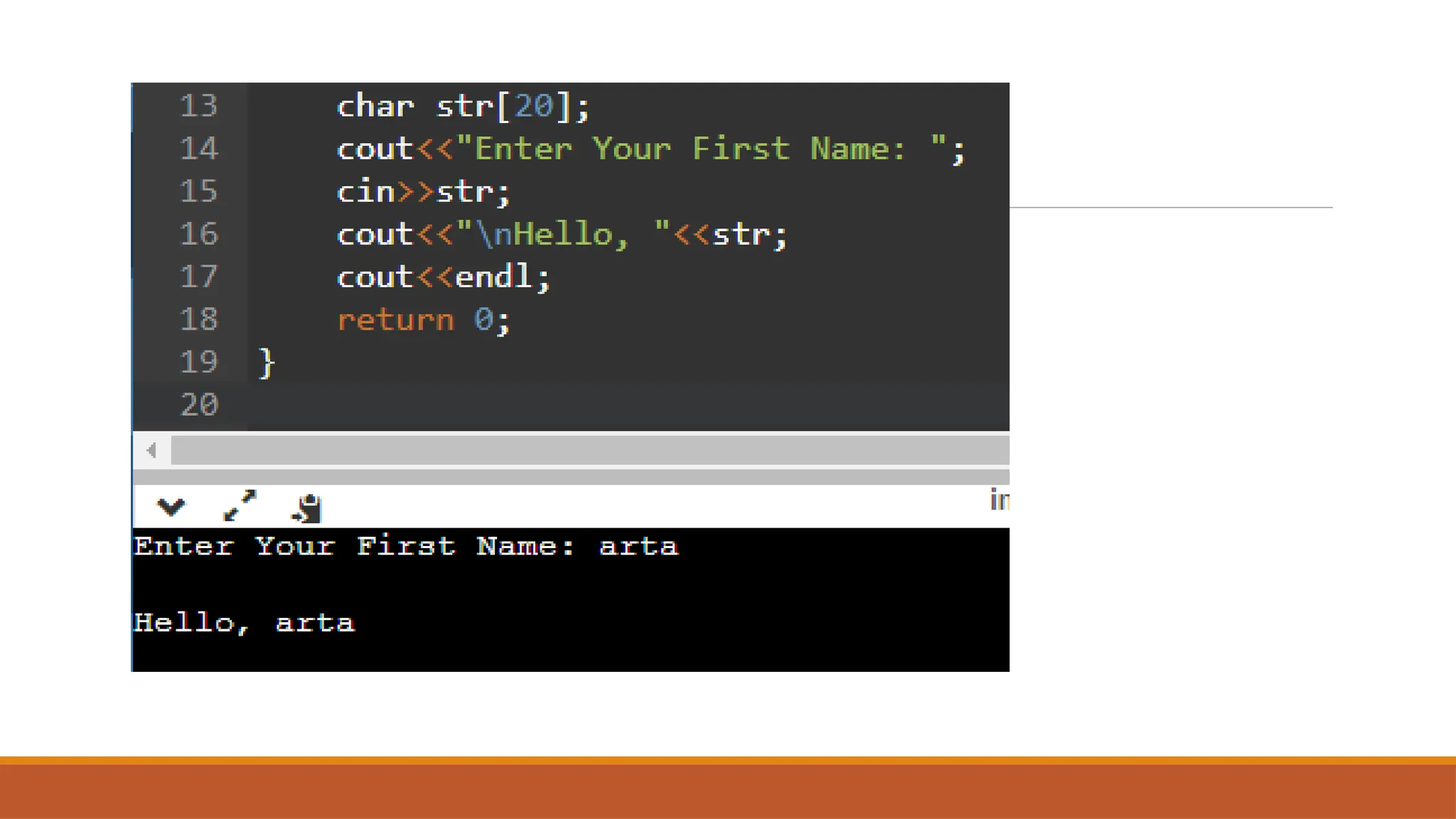
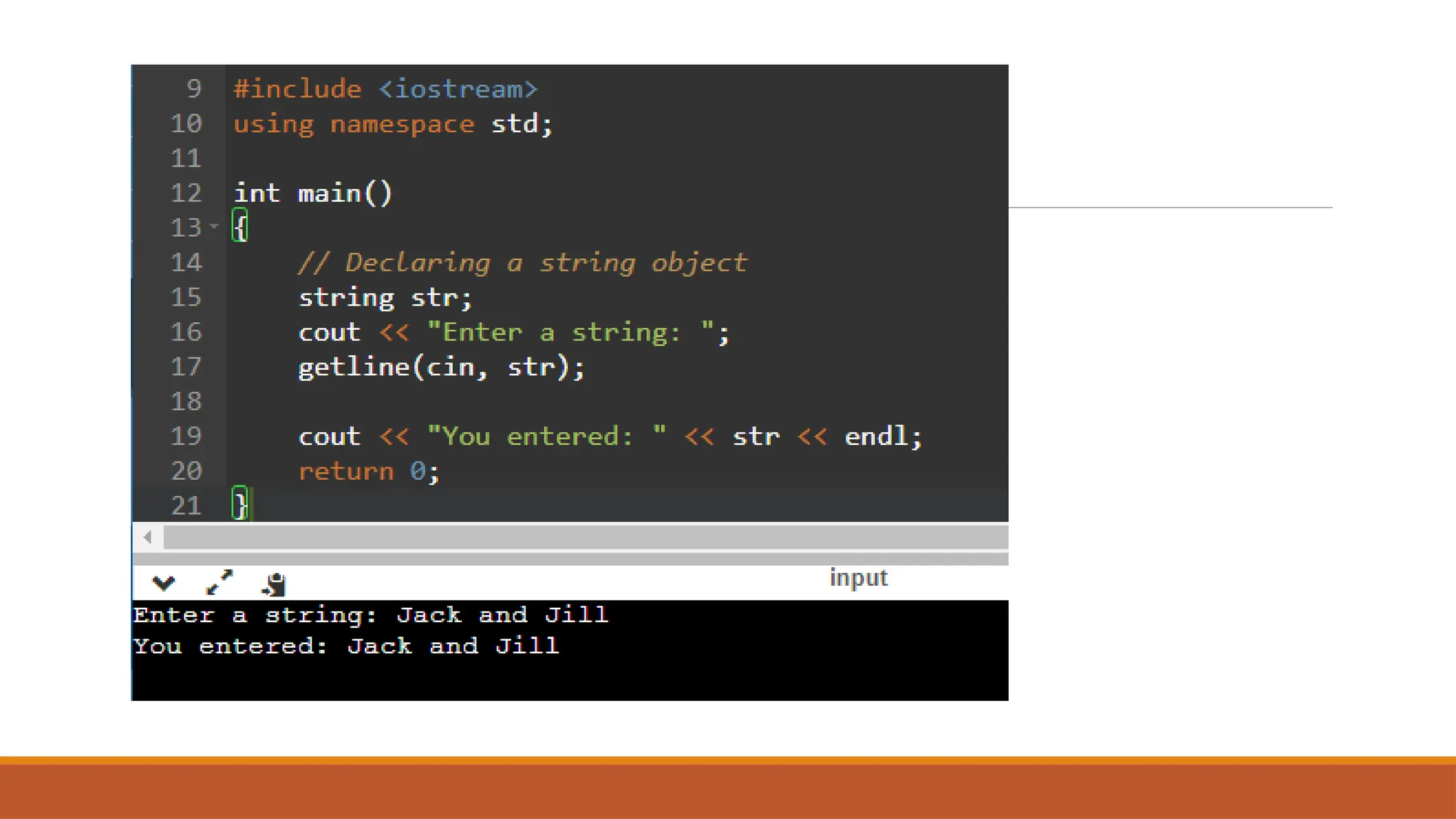
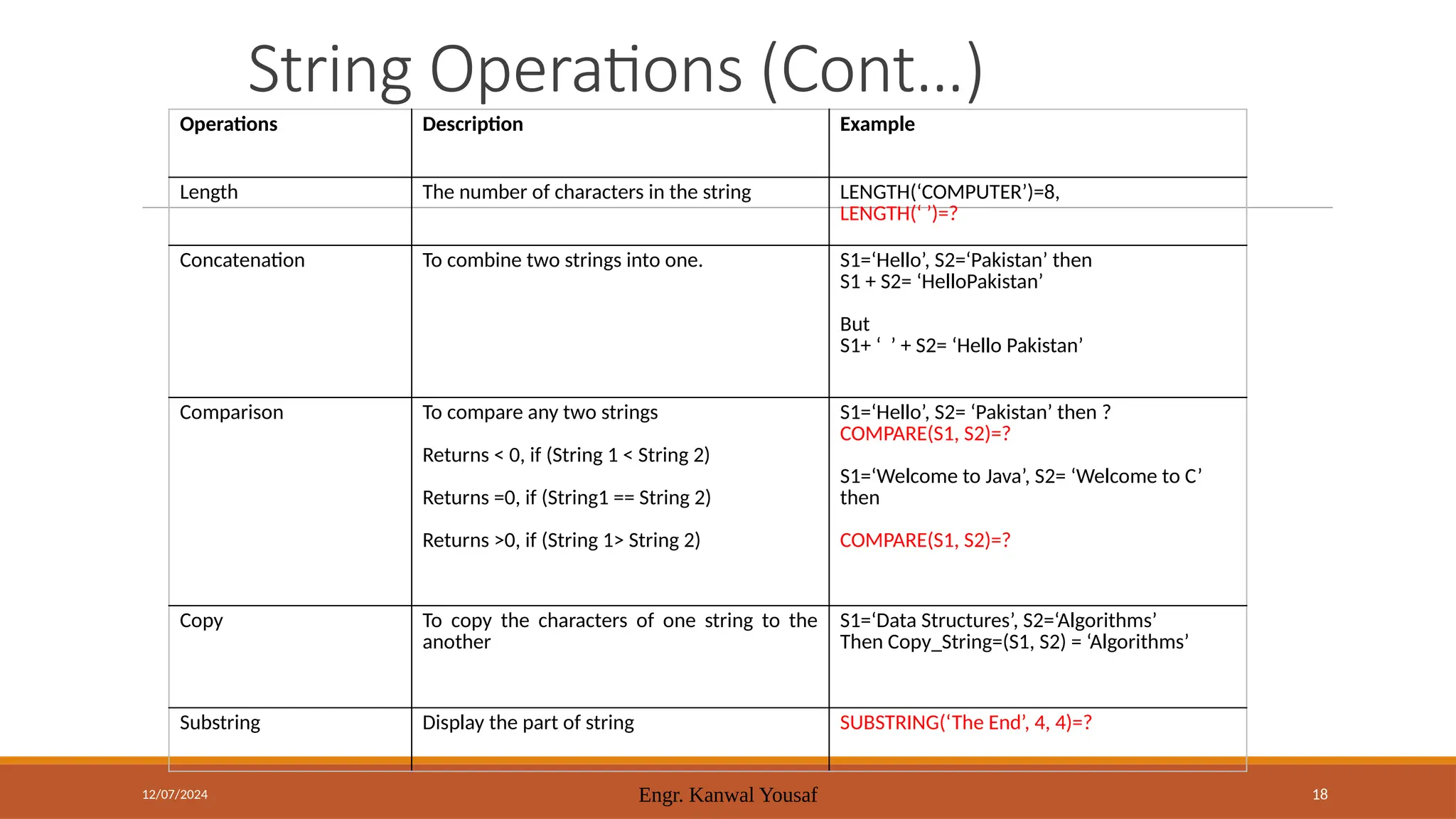
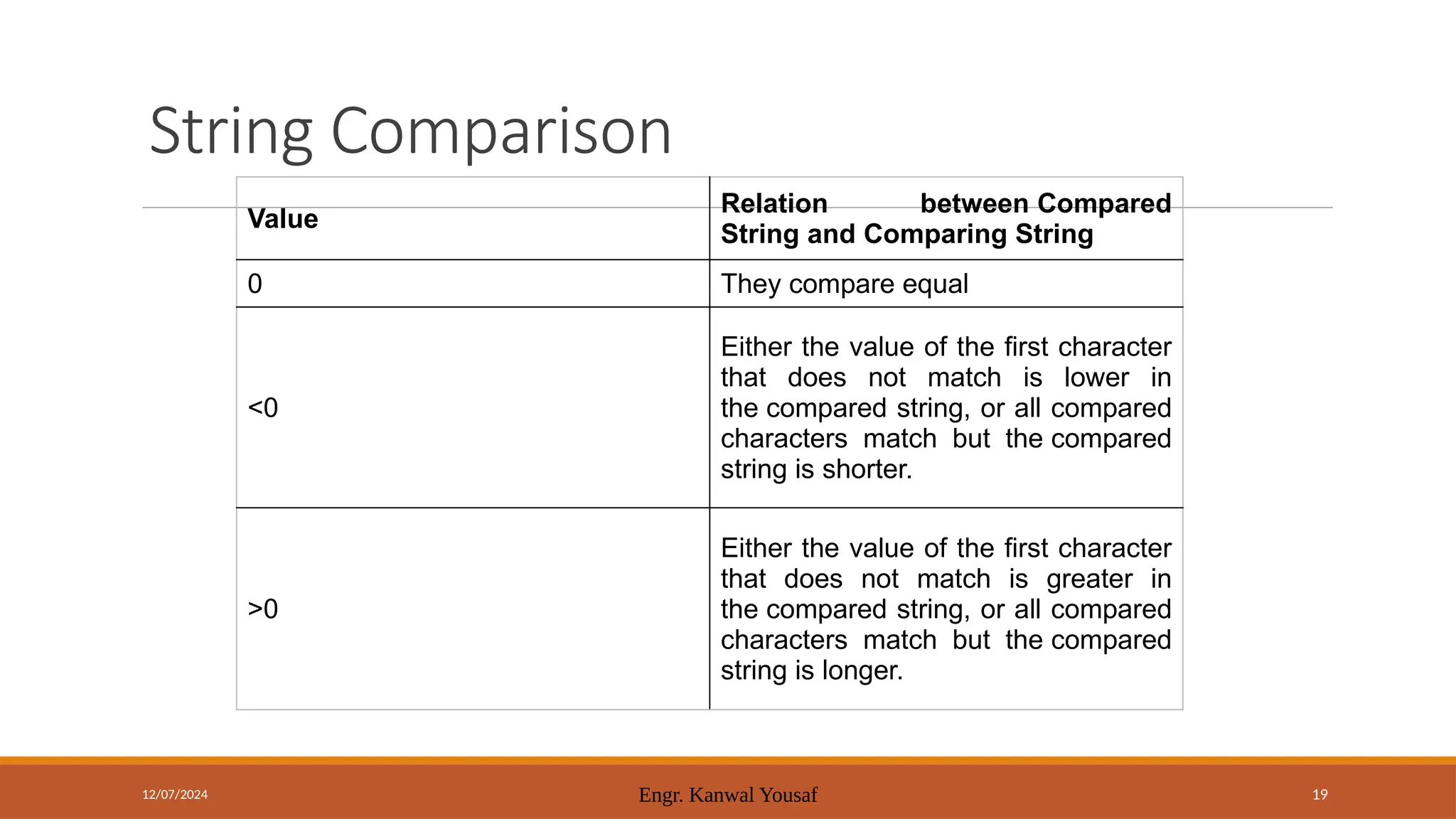
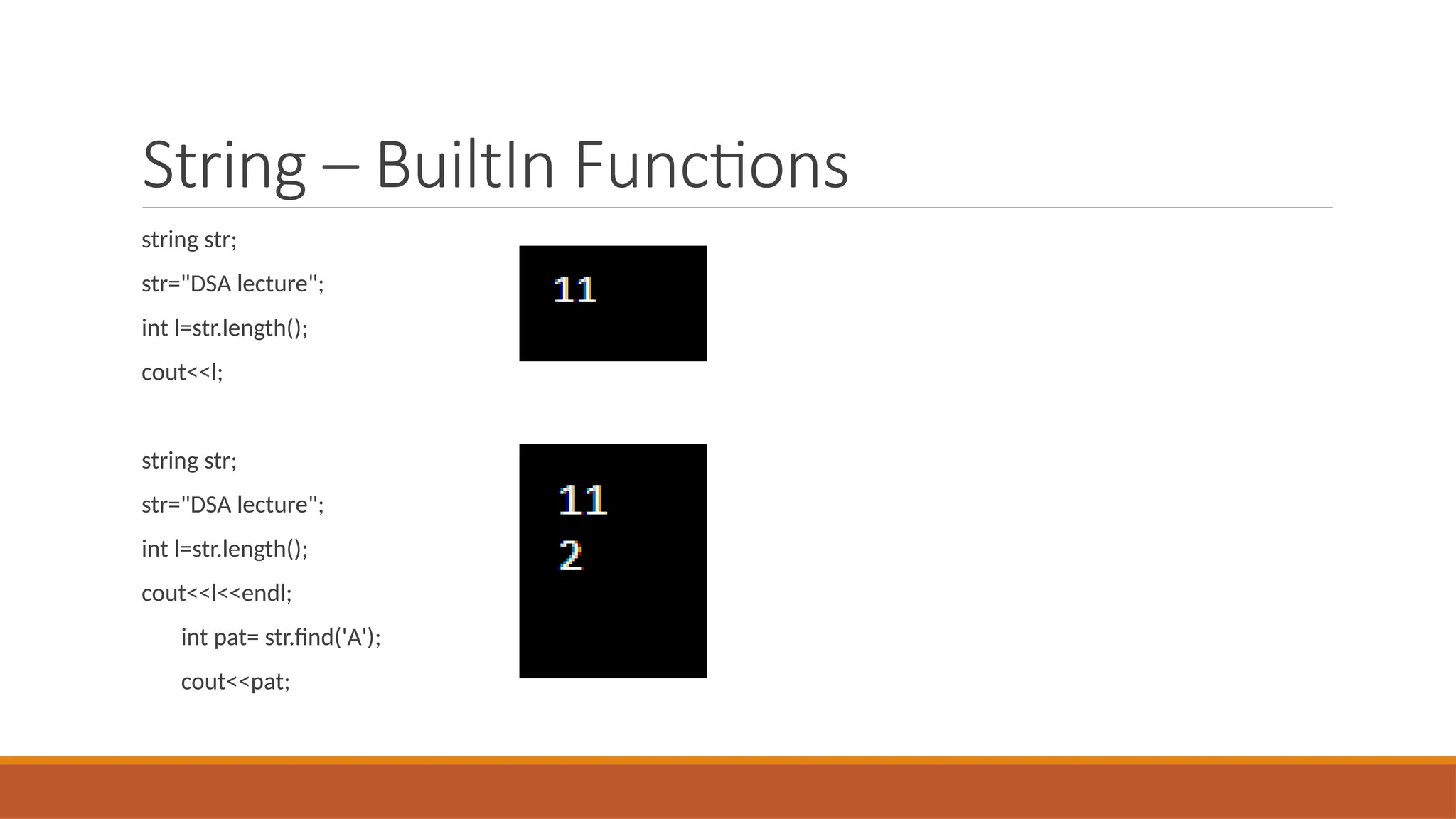
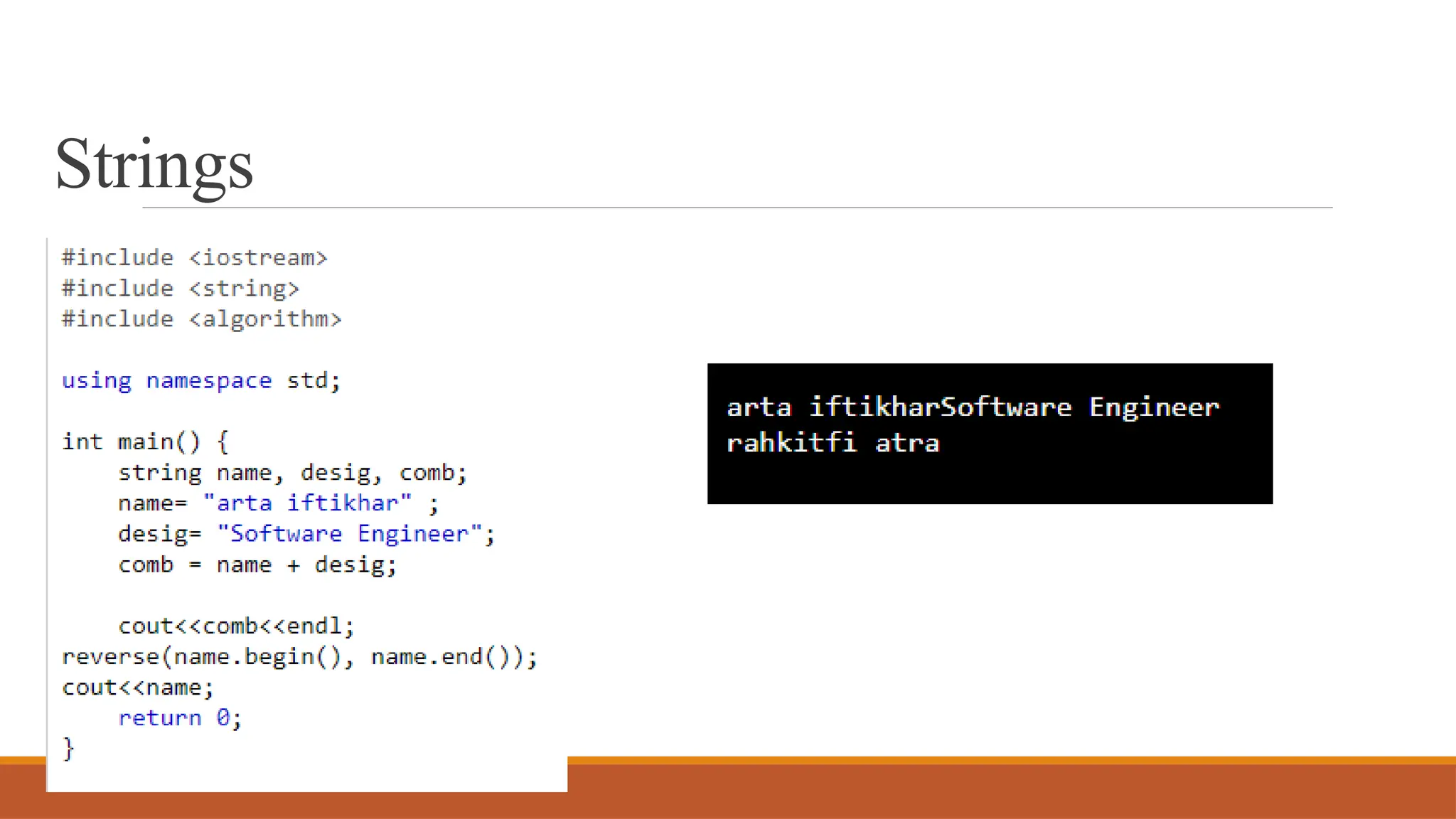
Today's agenda includes discussions on pointers and strings in C++, referencing Chapter 1 of DSA by Adam Drozdek. Key topics cover pointer arithmetic, reference variables, and string operations such as length, concatenation, and comparison. The session will also include a quiz and hands-on coding examples demonstrating these concepts.





![Pointers & Arrays
int arr[2]={6,87};
int* p1= &arr[0];
cout<<*p1<<" " <<p1<<endl;
cout <<*arr<<" " <<arr;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsa-lecture03-pointersstringsoutputs-241207163841-50f7aa3e/75/DSA-Lecture03-Pointers-Strings-outputs-pptx-7-2048.jpg)
![int arr[2]={6,87};
int* p1= &arr[0];
cout <<p1 << " " <<*p1;
cout<<" n " << *p1++ <<" " <<*p1;
_______________________________________________________
int arr[2]={6,87};
int* p1= &arr[0];
cout <<p1 << " " <<*p1;
cout<<" n " << (*p1)++ <<" " <<*p1;
Pointers & Arrays contd..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsa-lecture03-pointersstringsoutputs-241207163841-50f7aa3e/75/DSA-Lecture03-Pointers-Strings-outputs-pptx-8-2048.jpg)
![Pointers & Arrays contd..
int arr[2]={6,87};
int* p1= &arr[0];
cout <<p1 << " " <<*p1;
cout<<" n " << *++p1 <<" " <<*p1;
_________________________________________________
int arr[2]={6,87};
int* p1= &arr[0];
cout <<p1 << " " <<*p1;
cout<<" n " << ++*p1 <<" " <<*p1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsa-lecture03-pointersstringsoutputs-241207163841-50f7aa3e/75/DSA-Lecture03-Pointers-Strings-outputs-pptx-9-2048.jpg)
![Pointers & Arrays contd..
void scan(int* p, int n)
{ for (int i =0; i<n; i++)
cout<<*(p+i)<<"n";}
int main() {
int arr[4]= {1, 2, 7, 8};
scan(arr, 4);
_______________________________________________
void scan(int* p, int n)
{ for (int i =0; i<n; i++)
cout<<*(p+i)<<"n";
*(p+2)=3;}
int main() { int arr[4]= {1, 2, 7, 8};
scan(arr, 4);
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{cout<< arr[j]<<" ";}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsa-lecture03-pointersstringsoutputs-241207163841-50f7aa3e/75/DSA-Lecture03-Pointers-Strings-outputs-pptx-10-2048.jpg)
![Pointers and Strings
char str[]= "computer";
char *ptr= str;
cout<<str<<endl;
cout<<*ptr<<endl;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsa-lecture03-pointersstringsoutputs-241207163841-50f7aa3e/75/DSA-Lecture03-Pointers-Strings-outputs-pptx-11-2048.jpg)
![Array of Pointers
char *ptr[] = { "car", "bus", "bike", "truck"};
cout<<*ptr;
char *ptr[] = { "car", "bus", "bike", "truck"};
cout<<*ptr<<endl;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{ cout<<*ptr[i]<<endl;}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsa-lecture03-pointersstringsoutputs-241207163841-50f7aa3e/75/DSA-Lecture03-Pointers-Strings-outputs-pptx-12-2048.jpg)




![Q1. What is the difference between function member
that are virtual and those that are not?
Q2. Write an algorithm or Pseudo code that Counts al
zeros, Odd numbers and even number in a linear array
Q3. Consider 2D.Linear arrays AAA[4][5].
(a) Find the total number of elements.
(b) Suppose Base(AAA) = 300 and w=4 words per
memory cell for AAA. Find the address of AAA[3][2] .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsa-lecture03-pointersstringsoutputs-241207163841-50f7aa3e/75/DSA-Lecture03-Pointers-Strings-outputs-pptx-24-2048.jpg)