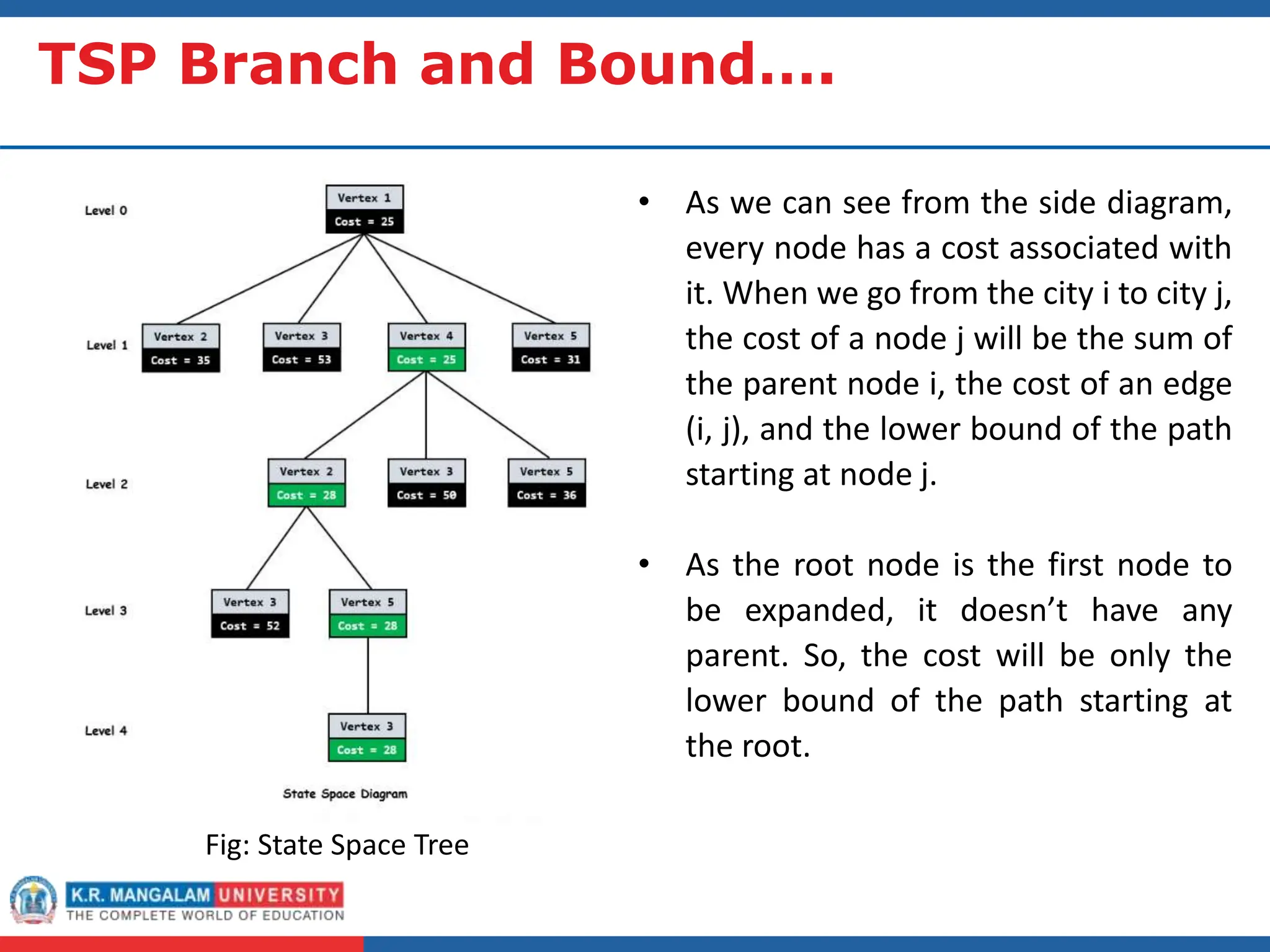
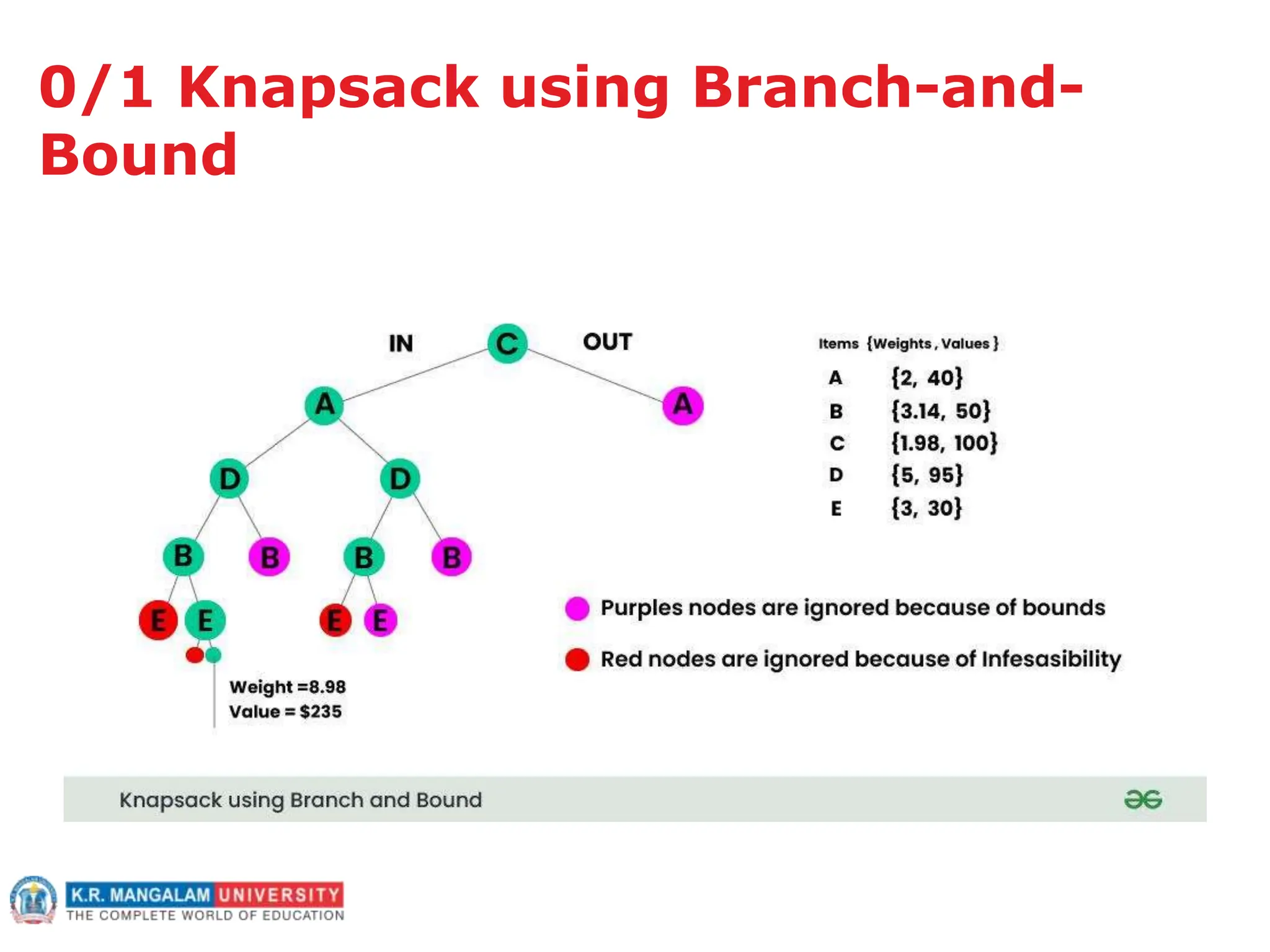
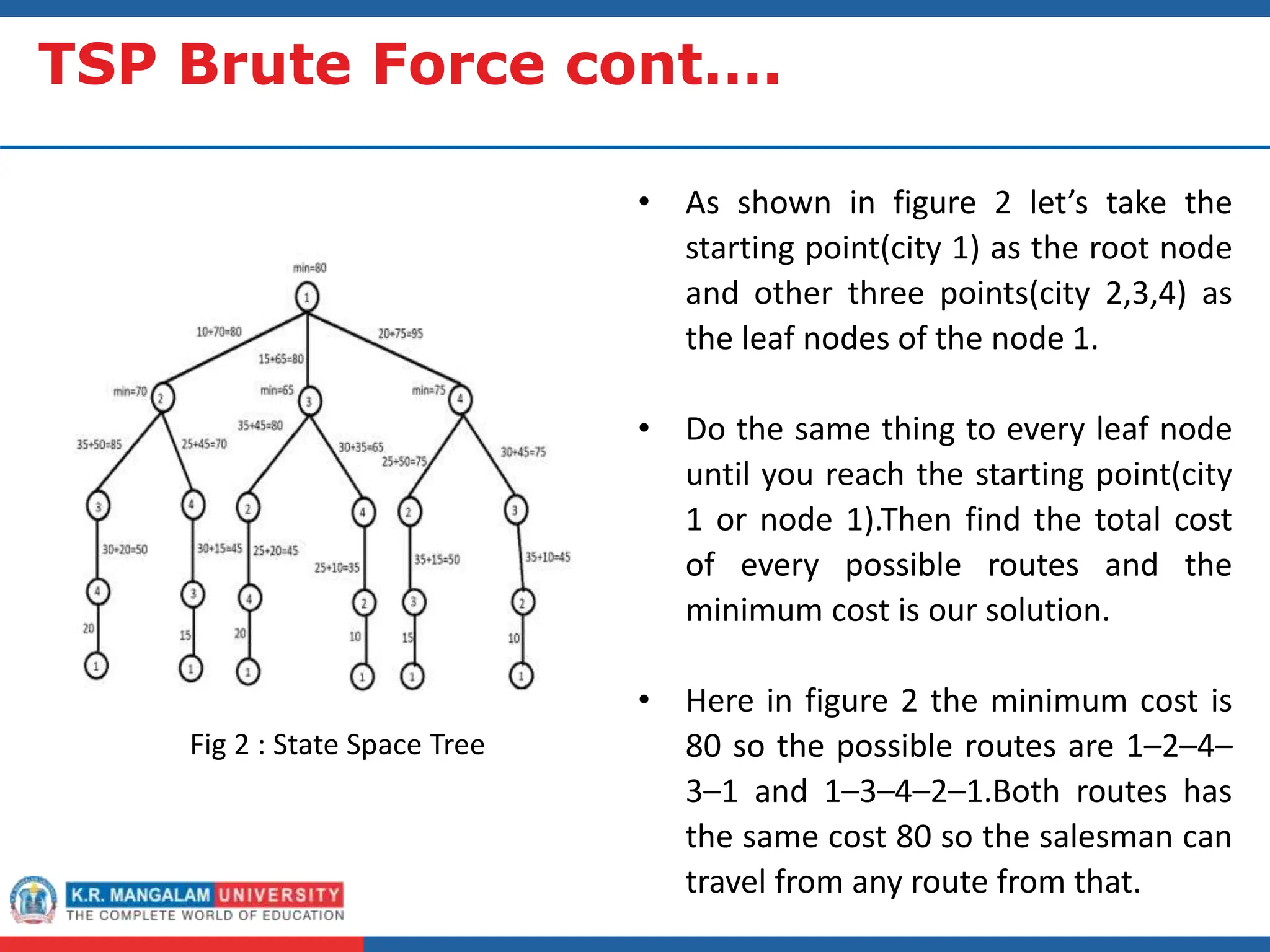
This document outlines an agenda for a course on analysis and design of algorithms. It discusses several fundamental algorithmic strategies including brute force, branch-and-bound, and heuristics. Brute force is defined as exhaustively checking all possible solutions. Branch-and-bound systematically prunes branches that cannot lead to optimal solutions. Heuristics provide approximate solutions through rules of thumb to guide problem solving. Examples are provided for solving the traveling salesman problem using brute force and branch-and-bound, and the 0/1 knapsack problem using these strategies. Characteristics and application domains of heuristics are also summarized.







![0/1 Knapsack using Brute Force
approach
Given N items where each item has some weight and profit associated with it
and also given a bag with capacity W, [i.e., the bag can hold at most W
weight in it]. The task is to put the items into the bag such that the sum of
profits associated with them is the maximum possible.
Note: The constraint here is we can either put an item completely into the
bag or cannot put it at all [It is not possible to put a part of an item into the
bag].
For the knapsack problem, the brute force approach involves generating all
possible combinations of items and checking which combination provides
the maximum value without exceeding the weight limit of the knapsack.
For n items, there will be 2^n solutions. Therefore, the time complexity will
be O(2^n) for this problem if we use a brute-force solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/etcs262a-ada-240402085546-b94c19cd/75/ETCS262A-Analysis-of-design-Algorithm-pptx-9-2048.jpg)