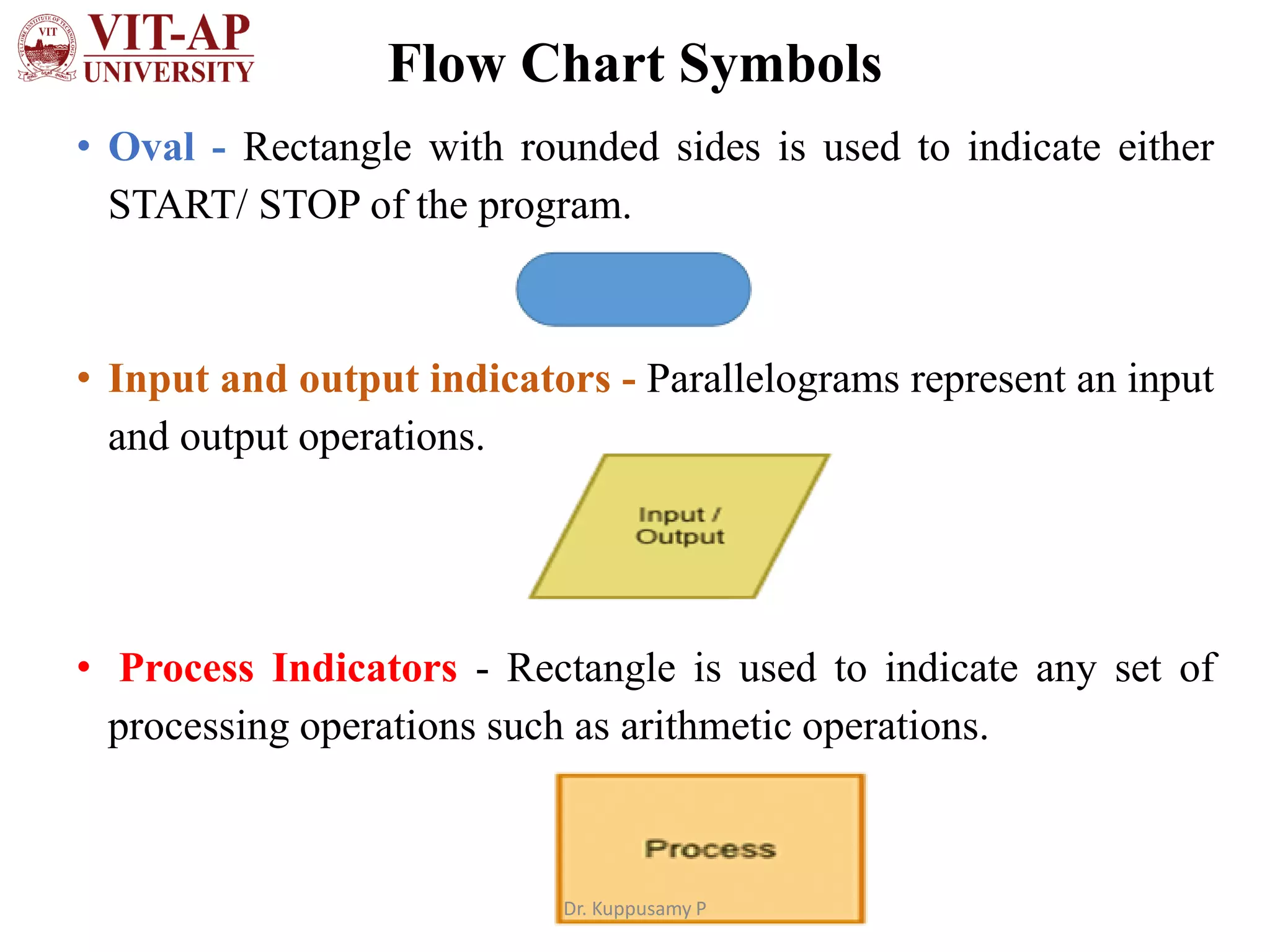
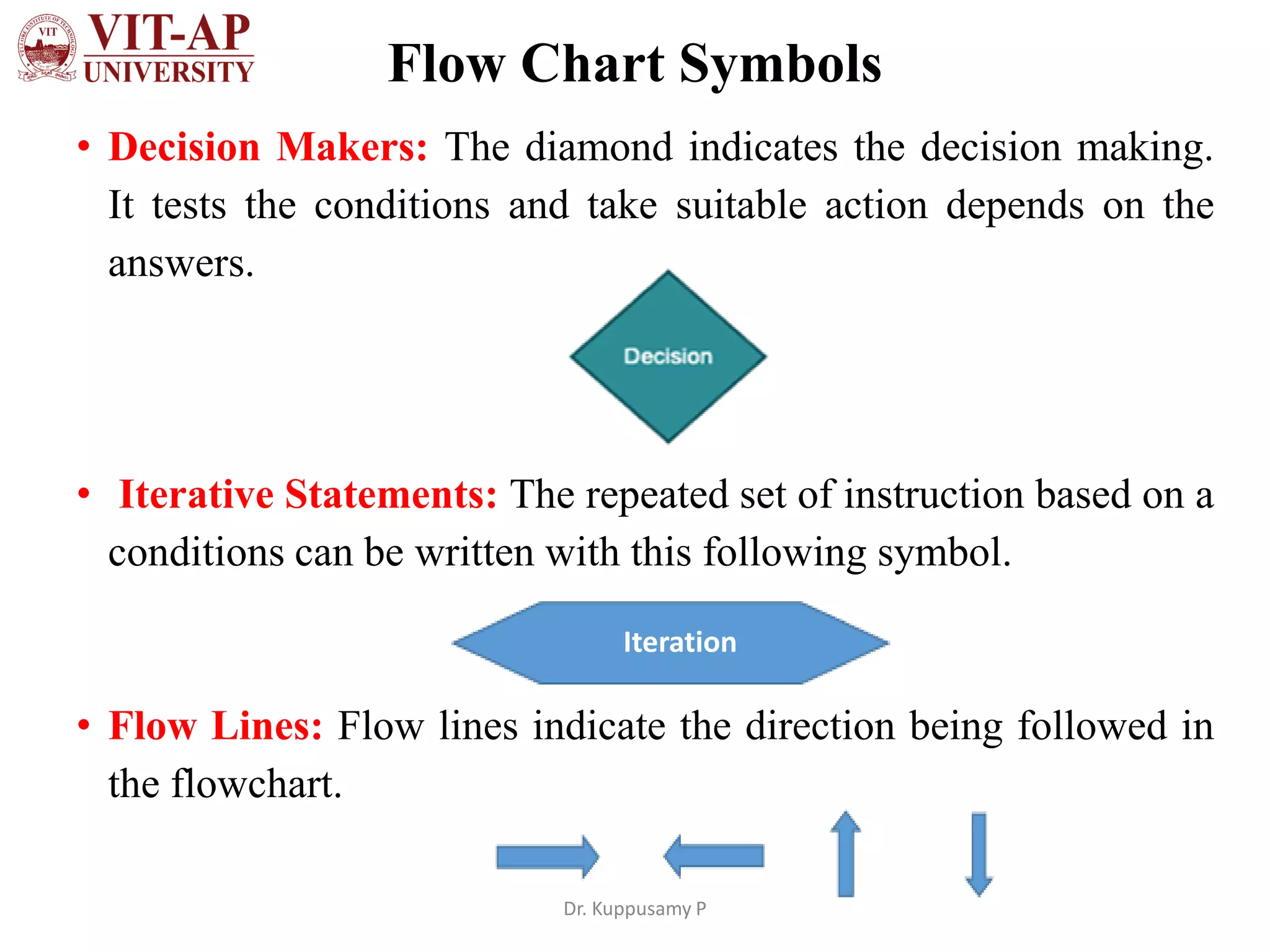
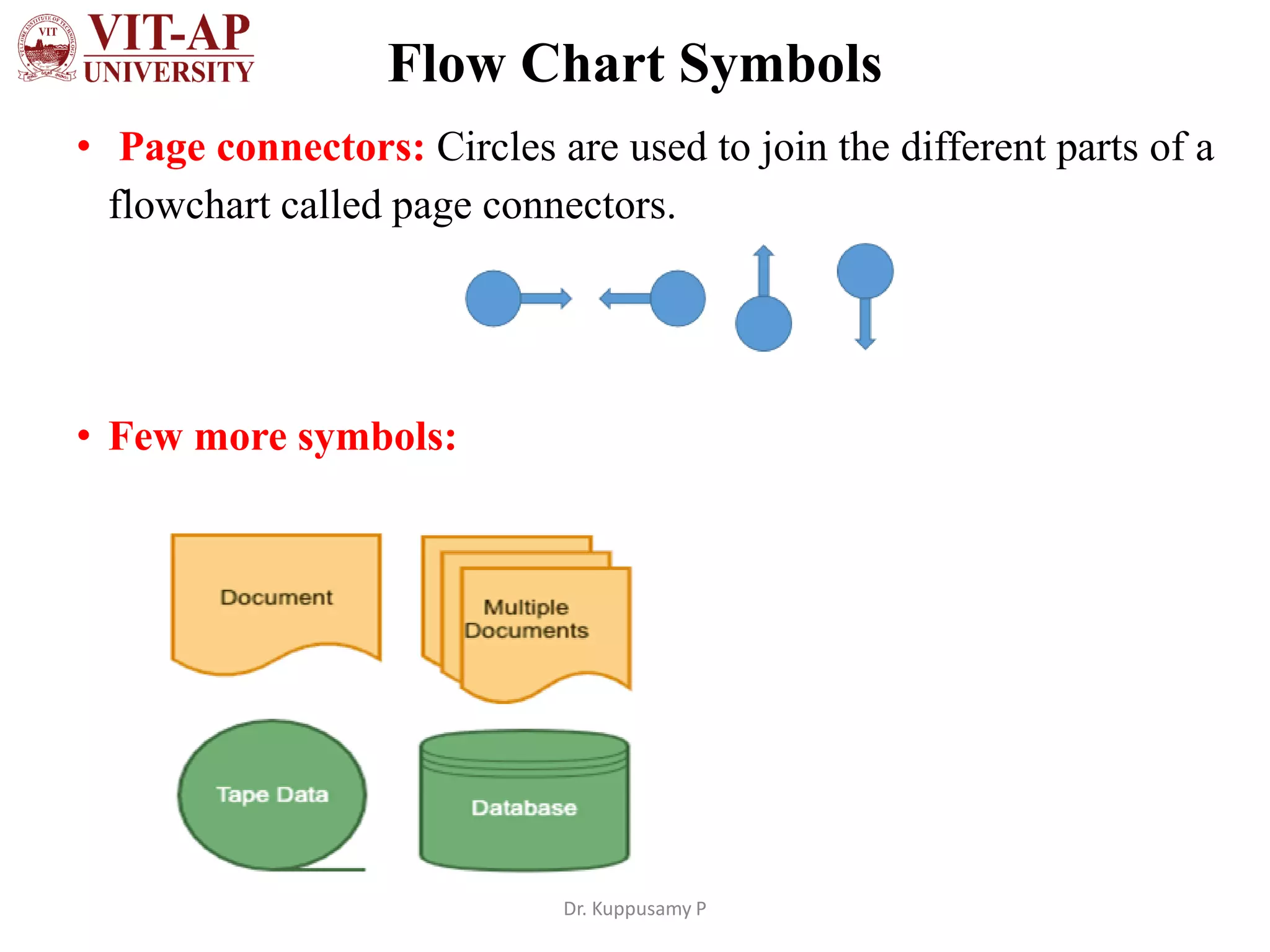
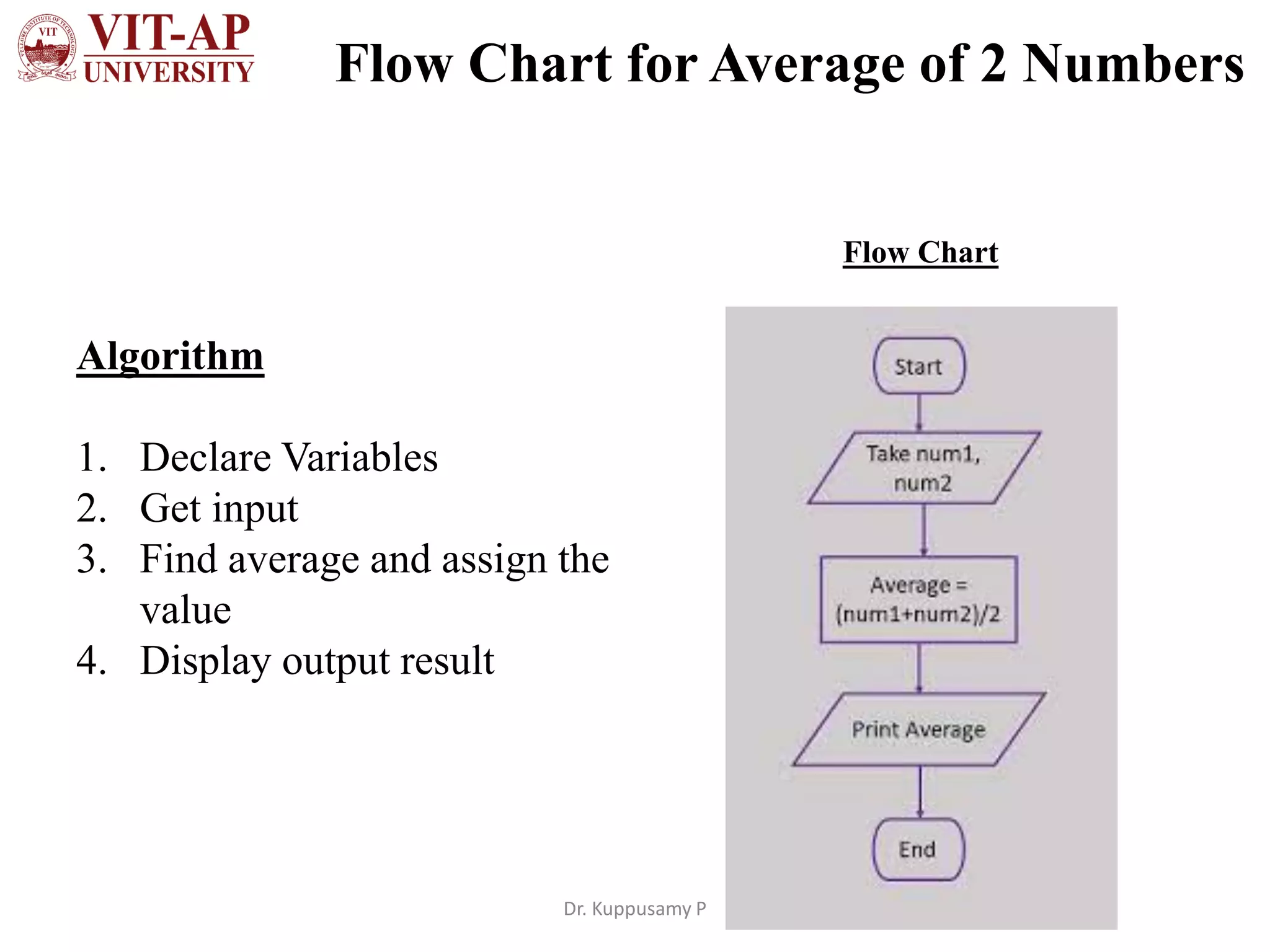
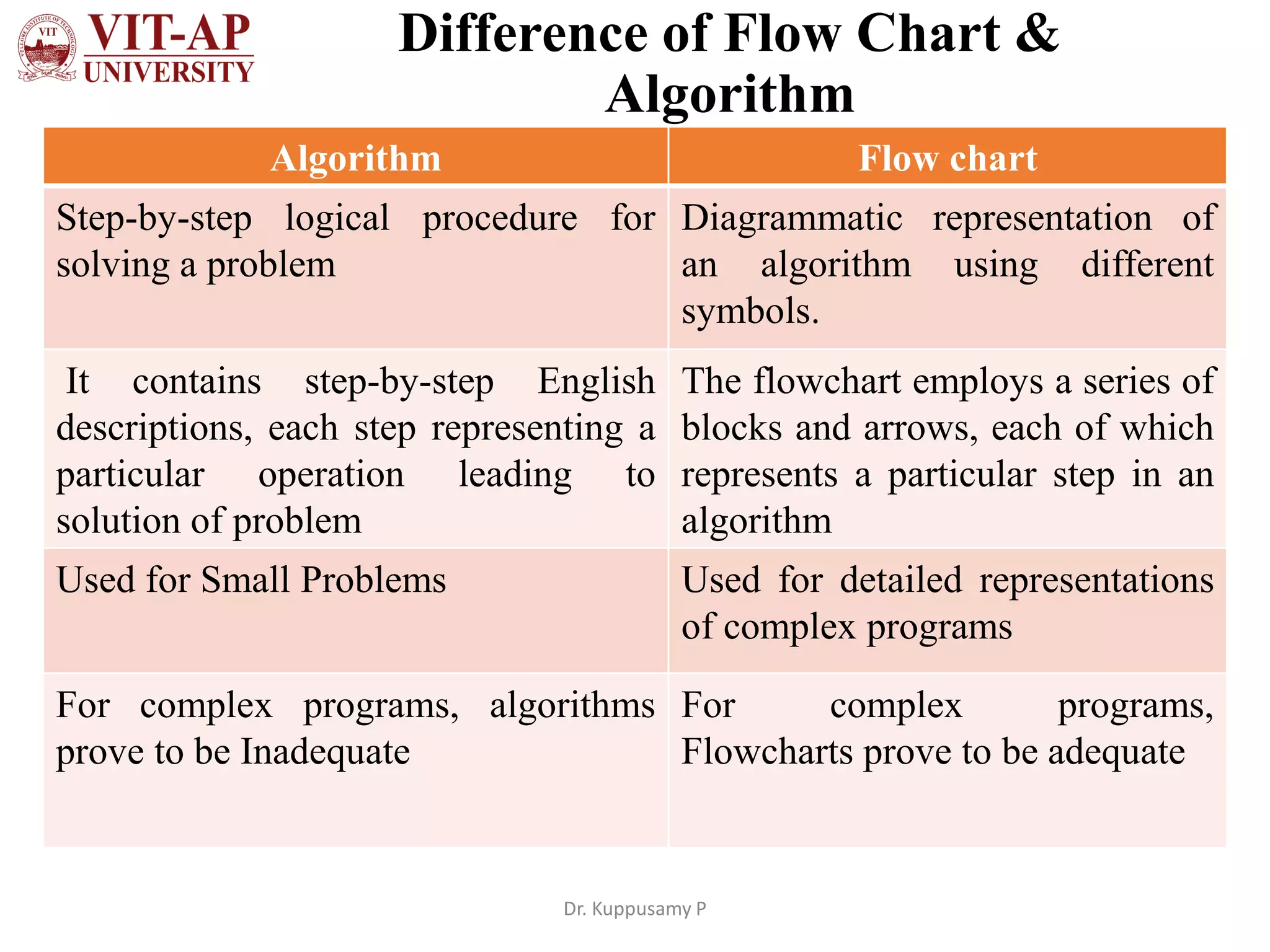
The document discusses flowchart design and symbols. It explains that a flowchart is a graphical representation of an algorithm that shows the sequence of steps in a process or workflow. The main advantages are that flowcharts make algorithms easier to understand visually through symbols, allow for better communication of the logic, and help split problems into smaller parts. Standard flowchart symbols are described, including shapes that represent start/stop, inputs/outputs, decisions, iterations, and connecting arrows. The key difference between an algorithm and flowchart is that an algorithm explains the steps in text while a flowchart shows the same steps graphically using standardized symbols.