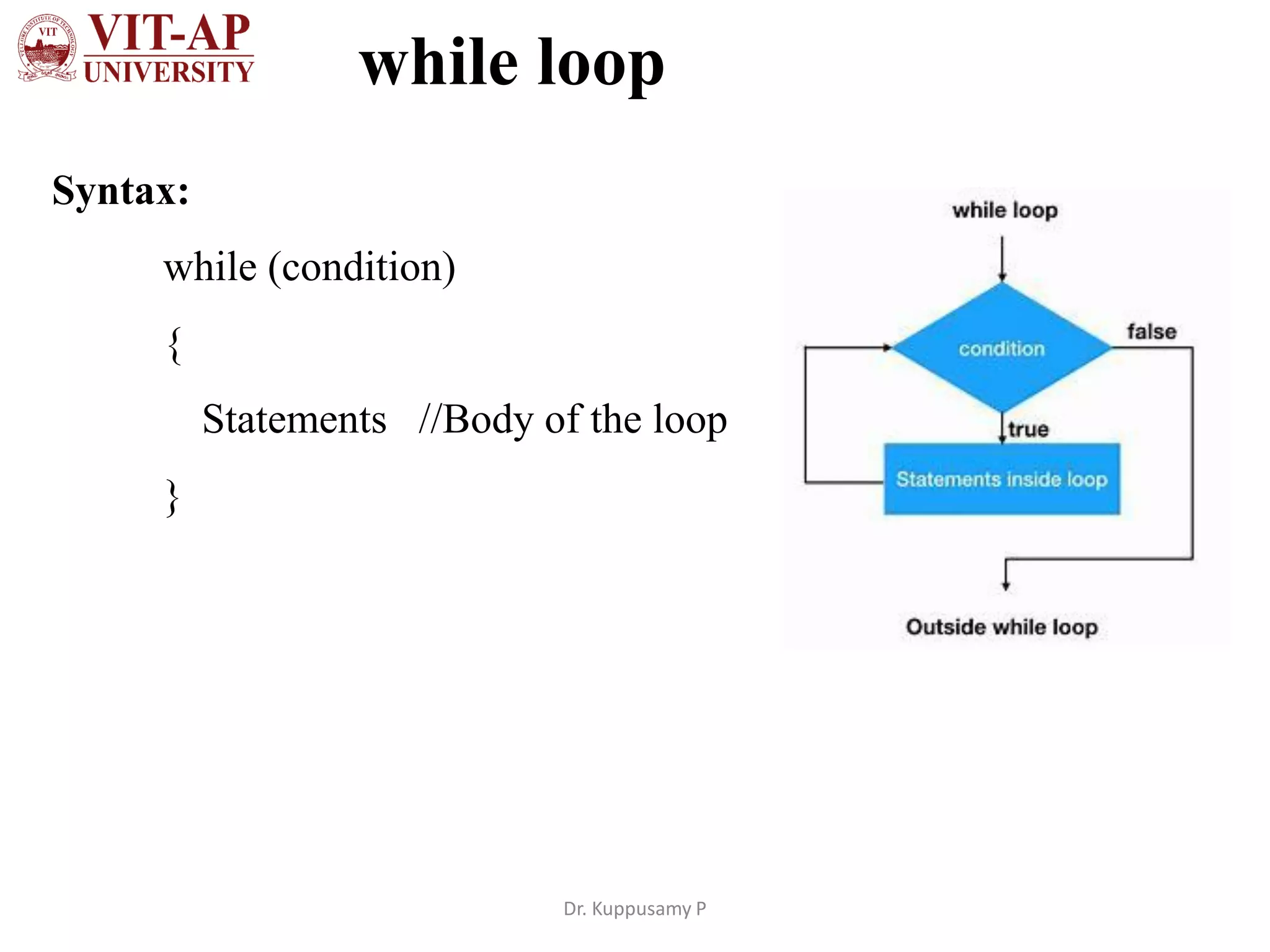
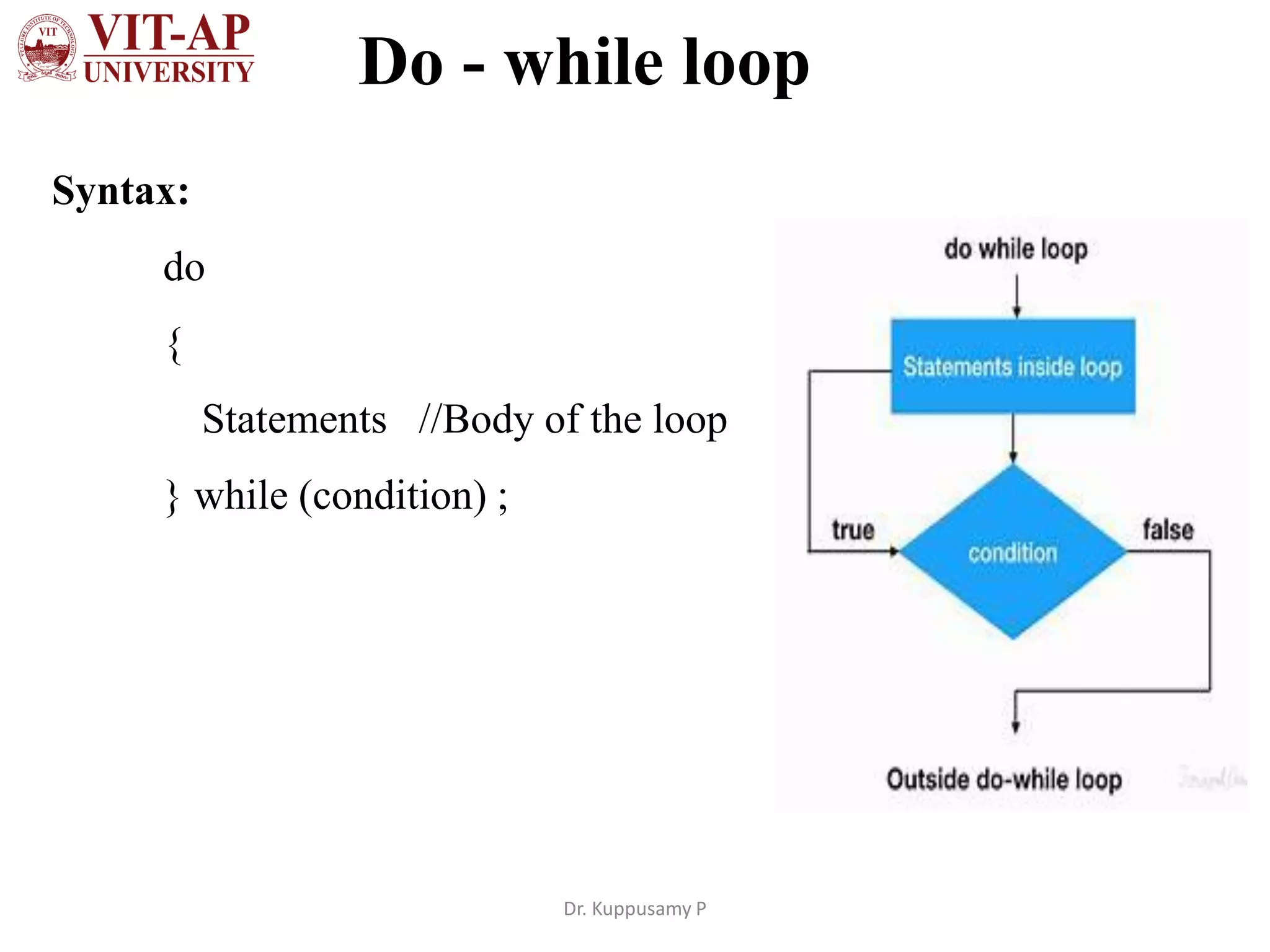
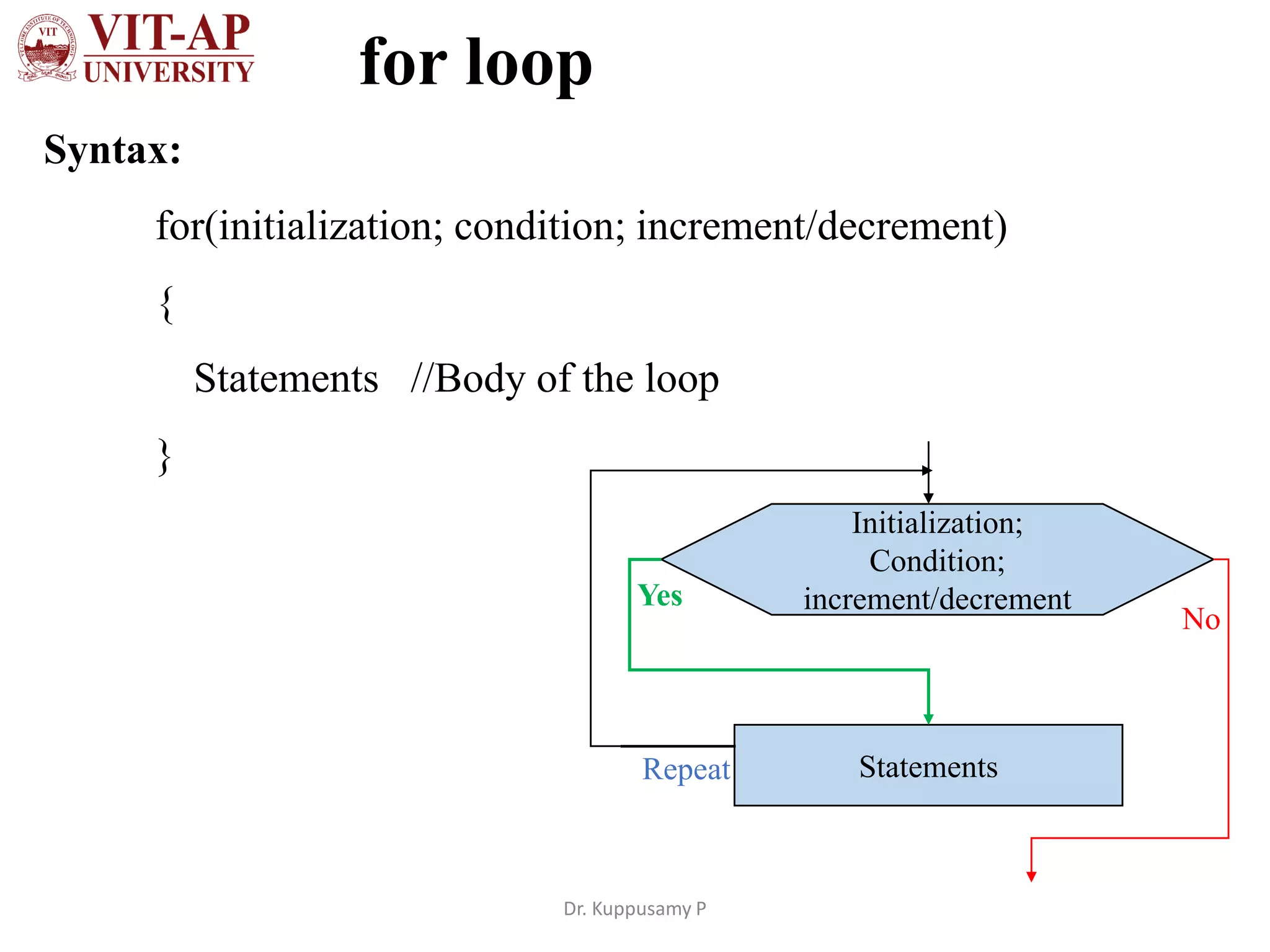
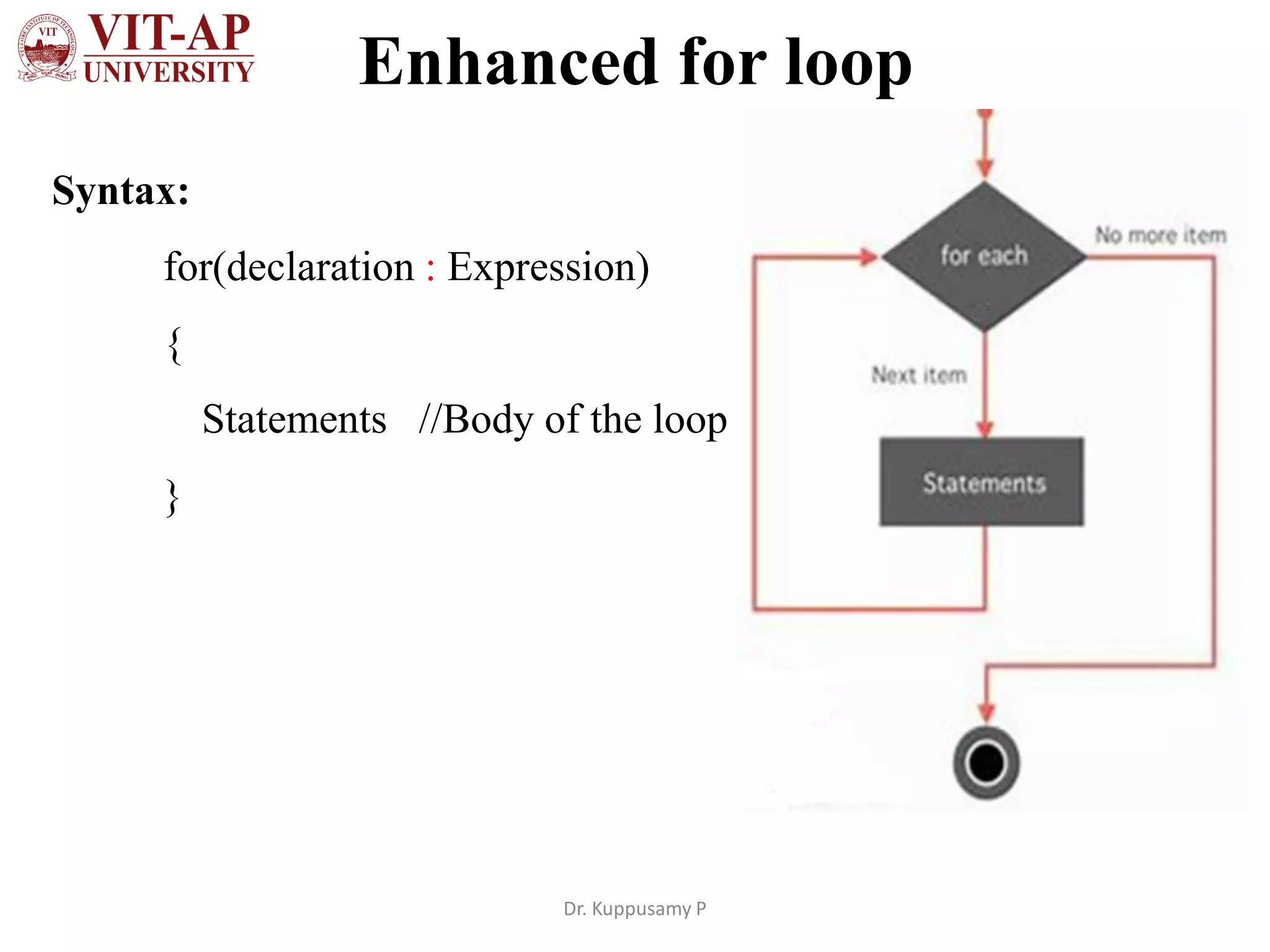
The document discusses different types of iterative statements in Java including while, do-while, for, enhanced for loops, and the continue statement. It provides the syntax and examples of each statement type. The while loop executes statements until a condition is false. The do-while loop executes statements once, then checks the condition. The for loop allows initialization, condition checking, and increment/decrement in the header. The enhanced for loop iterates over arrays or collections. The continue statement skips the current iteration in a loop.



![while loop example
public class WhileExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i = 0;
while (i < 10)
{
System.out.println("i: “ +i);
i++;
}
}
}
Dr. Kuppusamy P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaiterativestatements-210722070040/75/Java-iterative-statements-5-2048.jpg)
![Do-while loop example
public class DoWhileExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i = 1;
do
{
System.out.println("i: “ +i);
i++;
} while (i < 10) ;
}
}
Dr. Kuppusamy P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaiterativestatements-210722070040/75/Java-iterative-statements-7-2048.jpg)
![for loop example
public class ForExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
for (int i=1; i<=5; i++ )
{
System.out.println("i: “ +i);
}
}
}
Dr. Kuppusamy P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaiterativestatements-210722070040/75/Java-iterative-statements-9-2048.jpg)
![Enhanced for loop example
public class EnhancedForExample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int [] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
for(int i : numbers ) // for(int i=0; i < numbers; length(); i++)
{
System.out.println("i: “ +i); // System.out.println( “i: “+numbers[i] );
}
}
}
Dr. Kuppusamy P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaiterativestatements-210722070040/75/Java-iterative-statements-11-2048.jpg)
![continue statement
• The continue statement skips the current iteration of a loop
• In while and do loops, continue causes the control to go directly to the test
condition and then continue the iteration process
• In case of for loop, the increment section of the loop is executed before the test
condition is evaluated.
public class ContinueExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int [] num = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
for(int i : num )
{
if( i == 3 )
continue;
}
System.out.println( "i: "+i );
}
Dr. Kuppusamy P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaiterativestatements-210722070040/75/Java-iterative-statements-12-2048.jpg)
