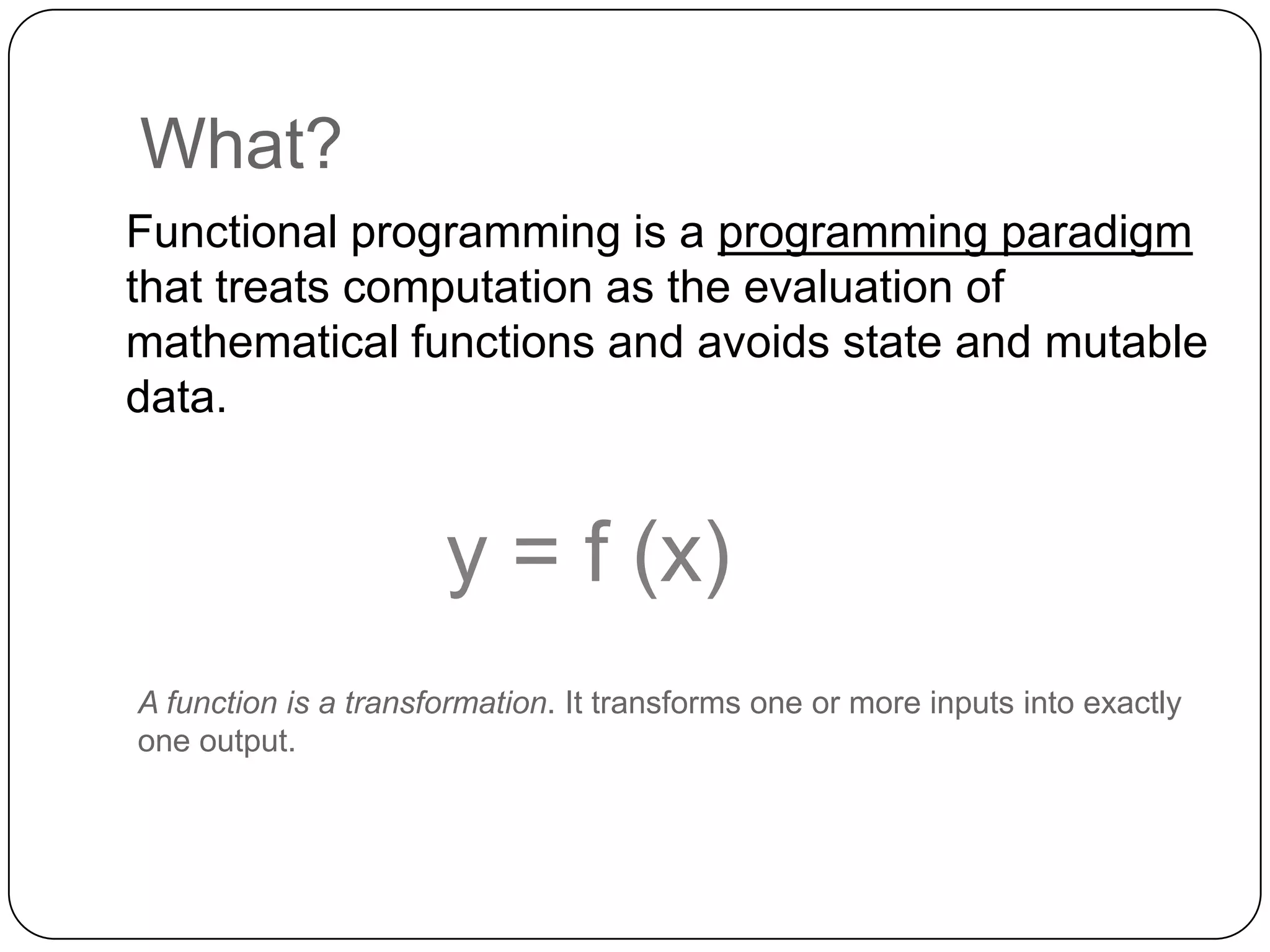
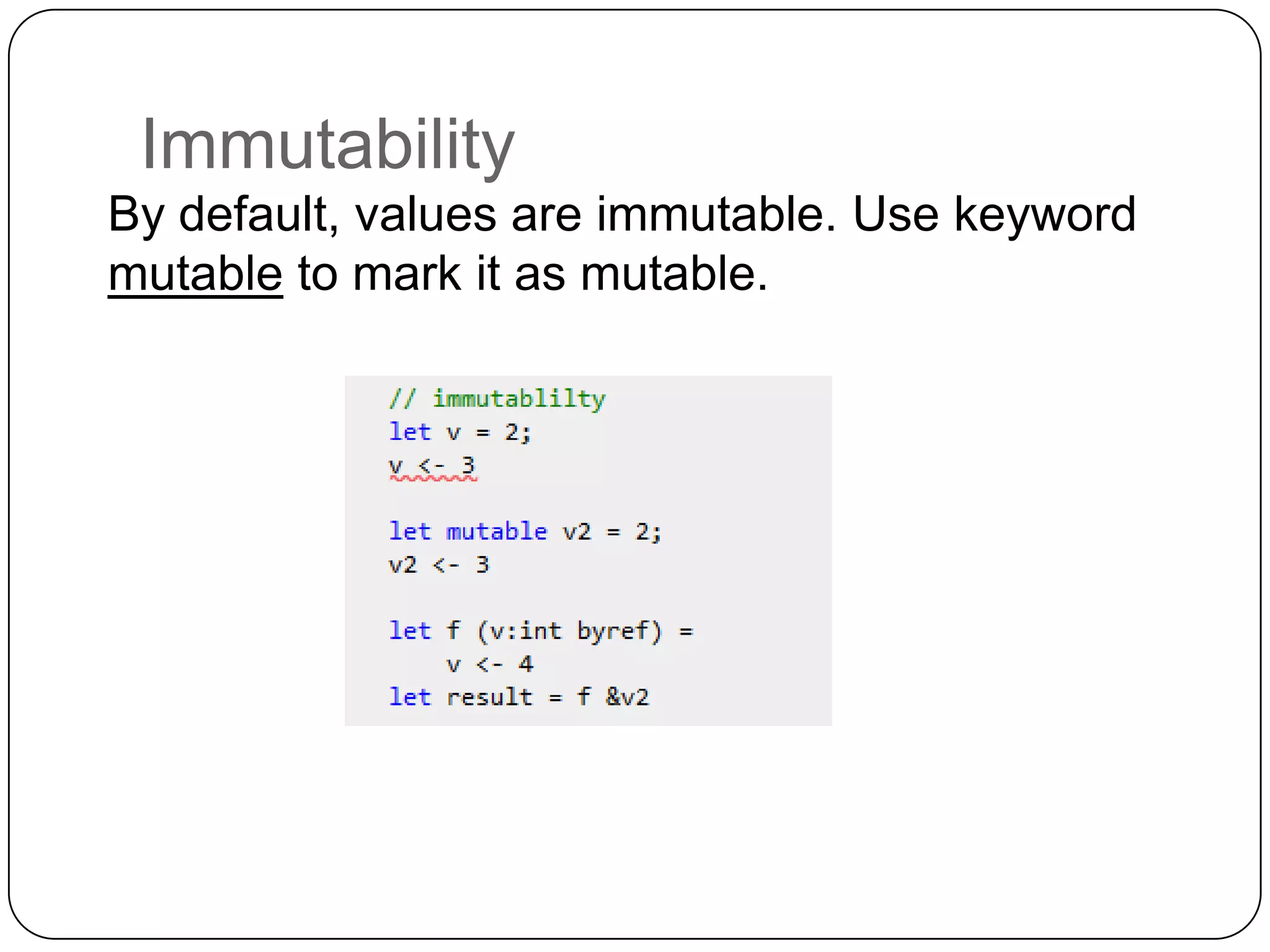
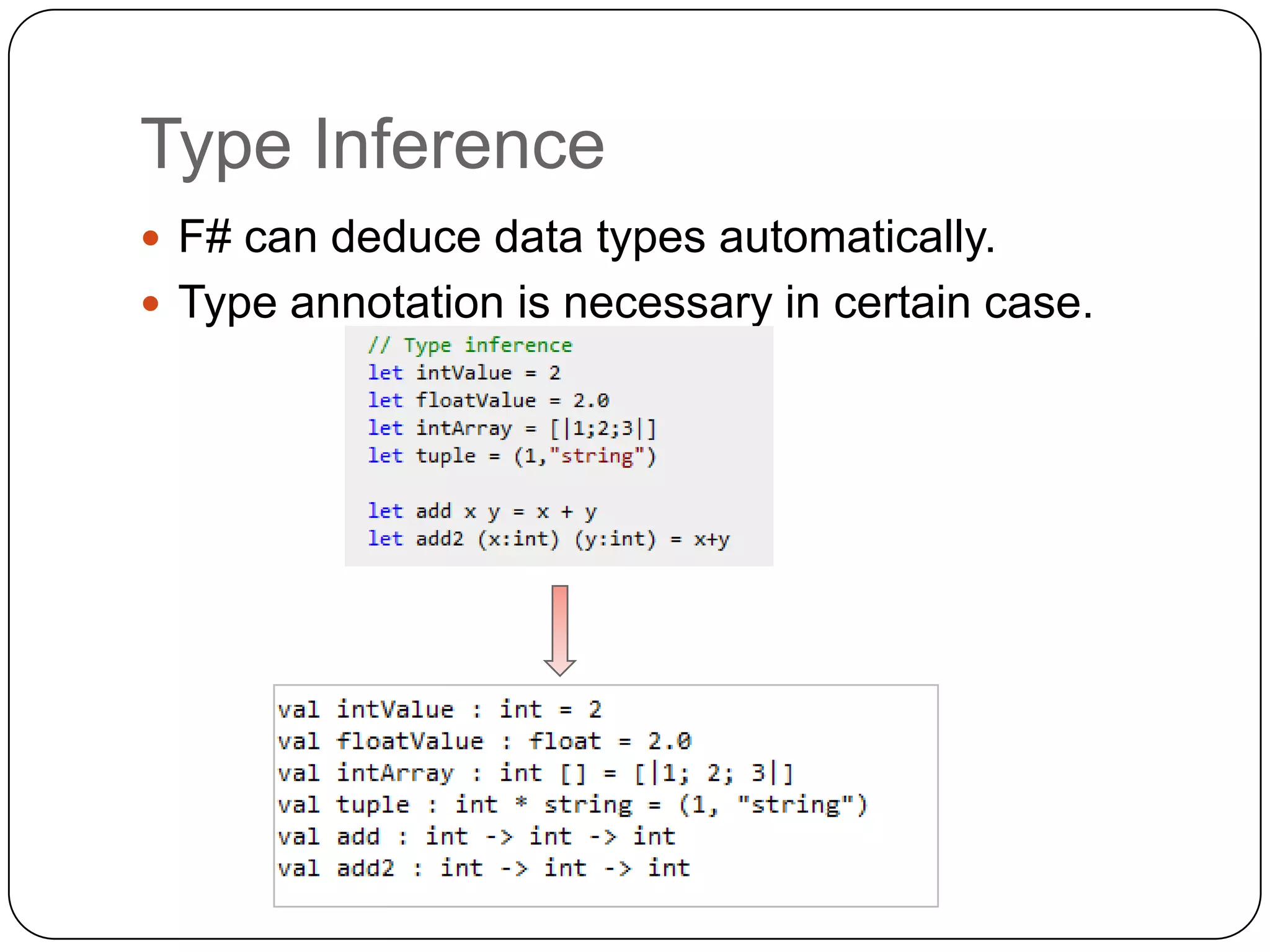
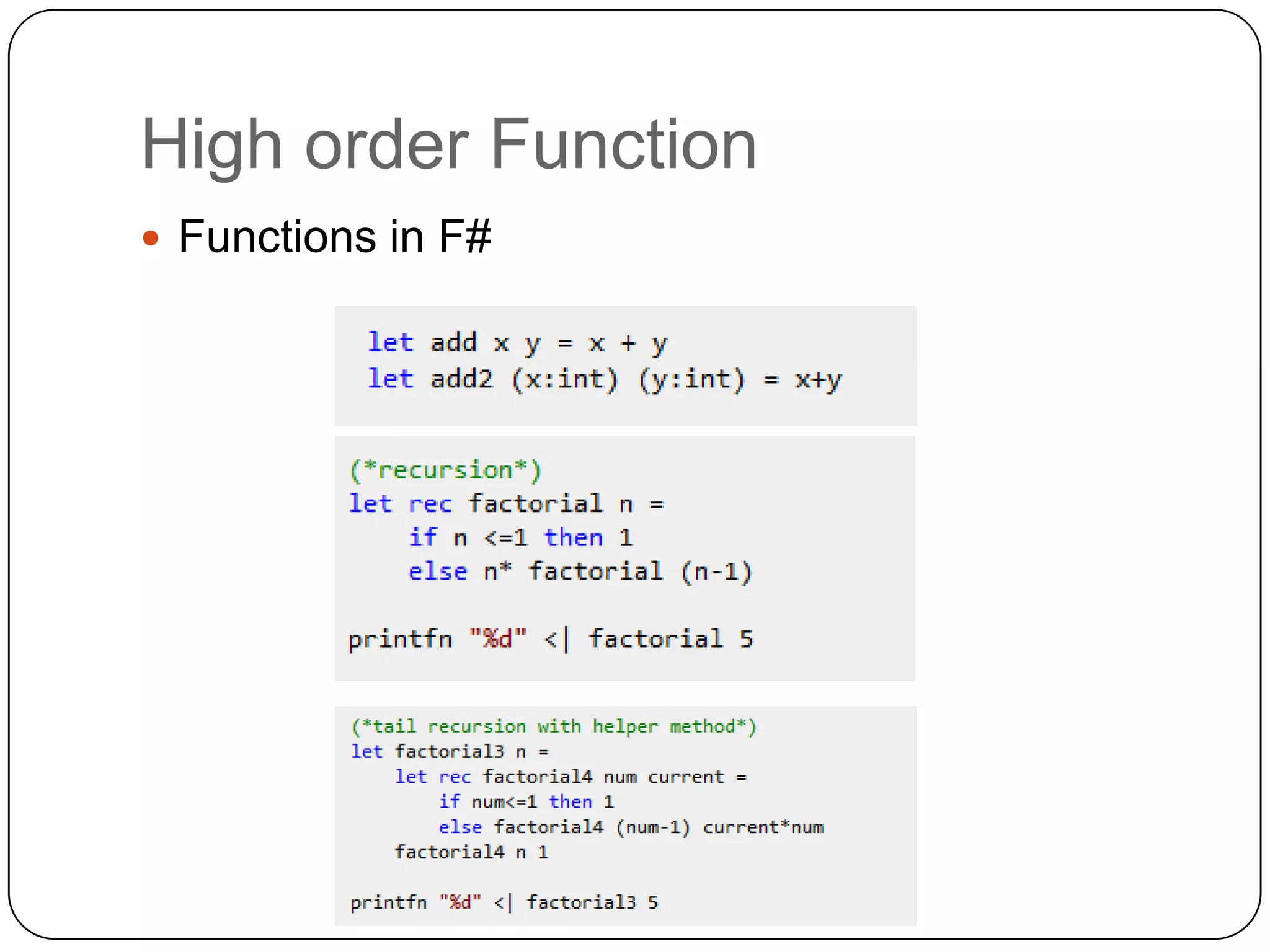
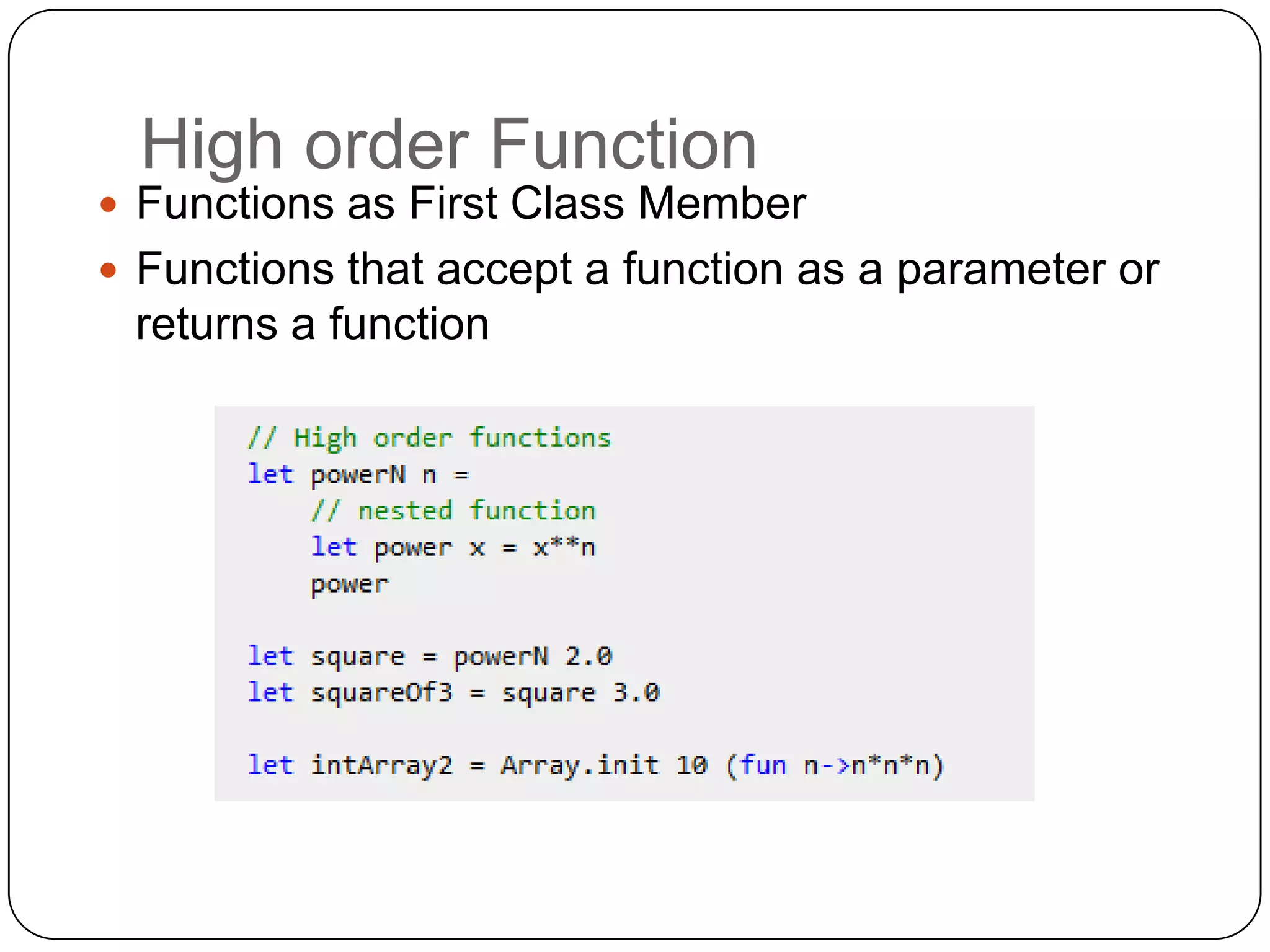
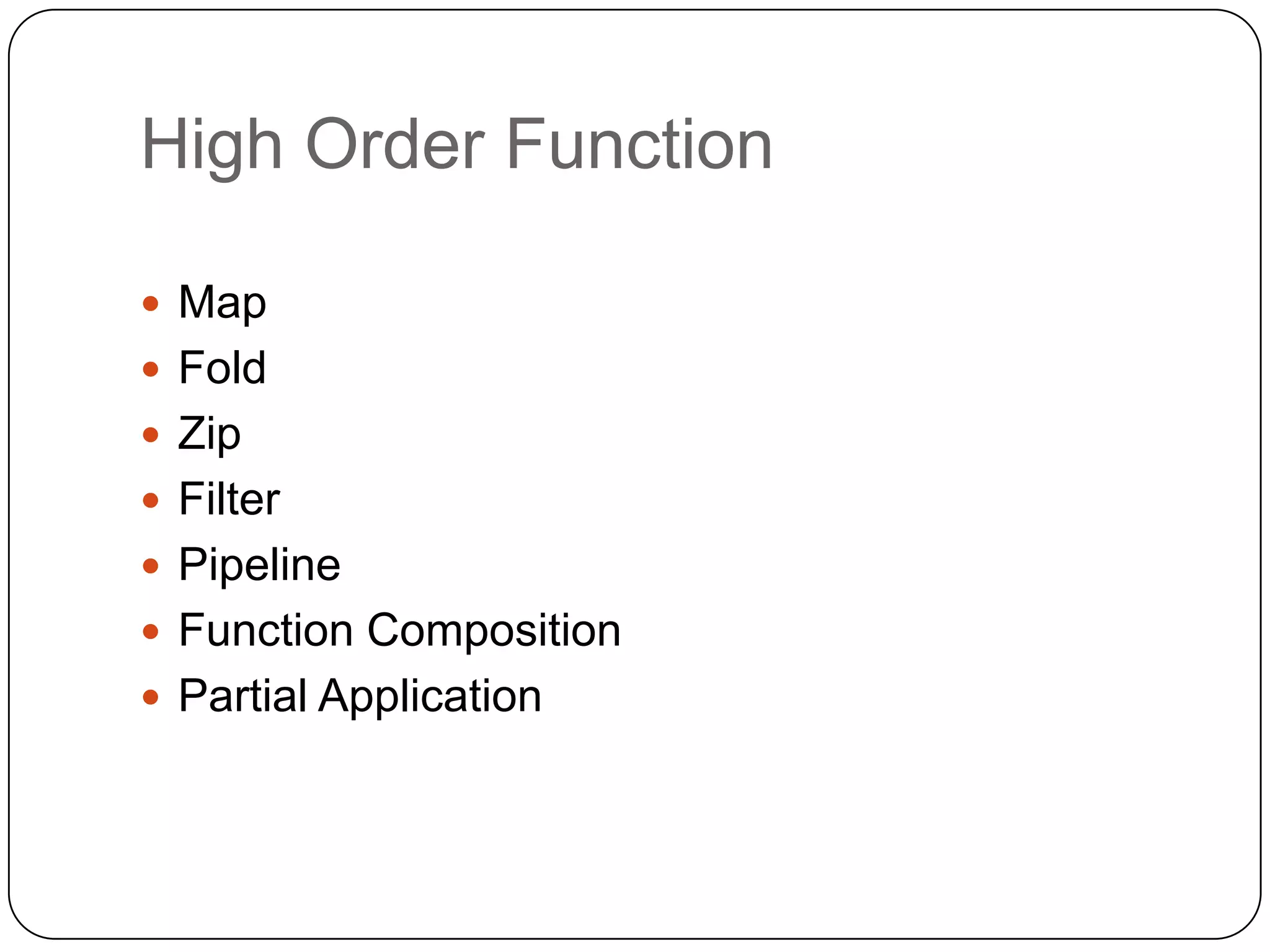
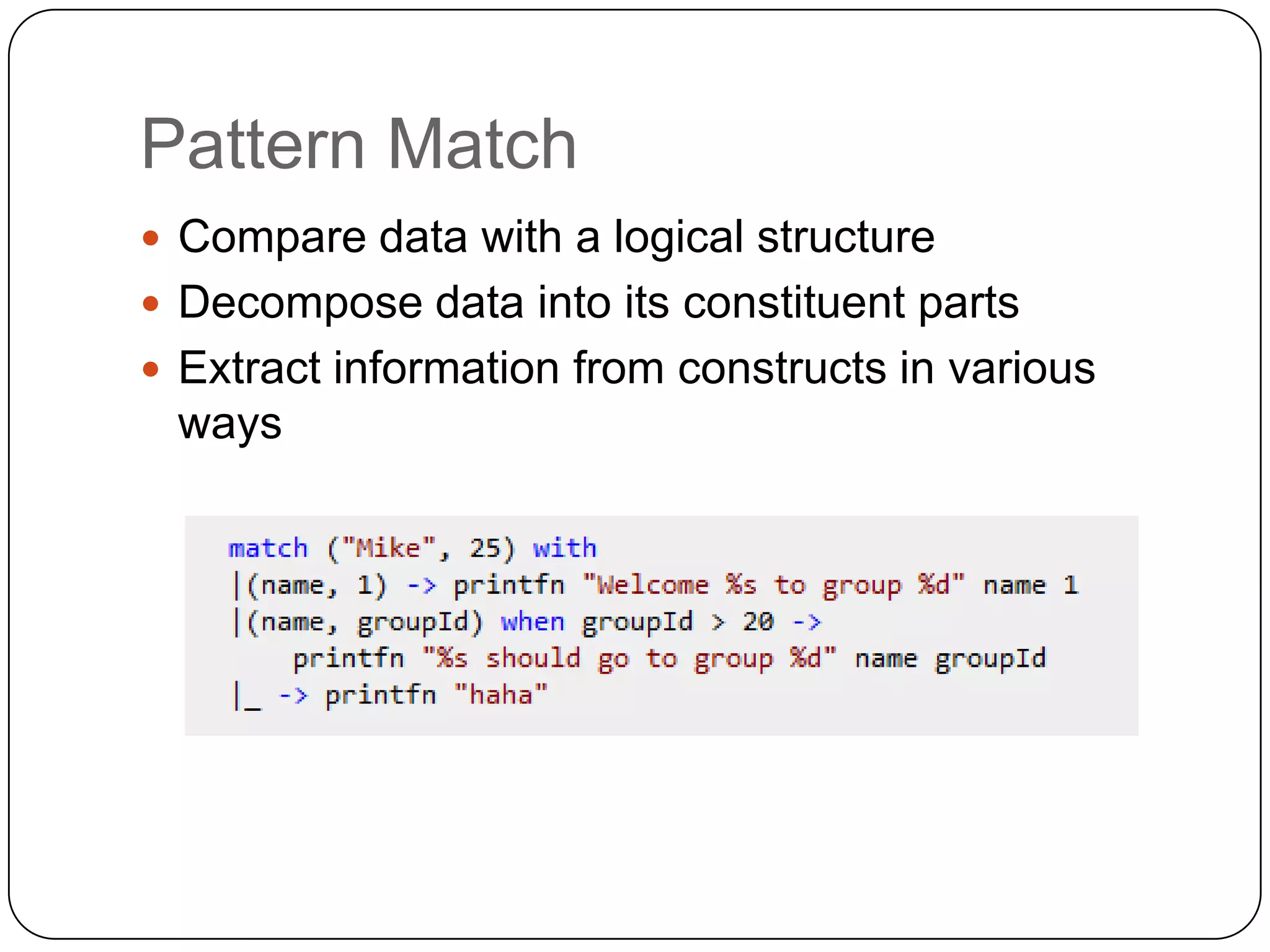
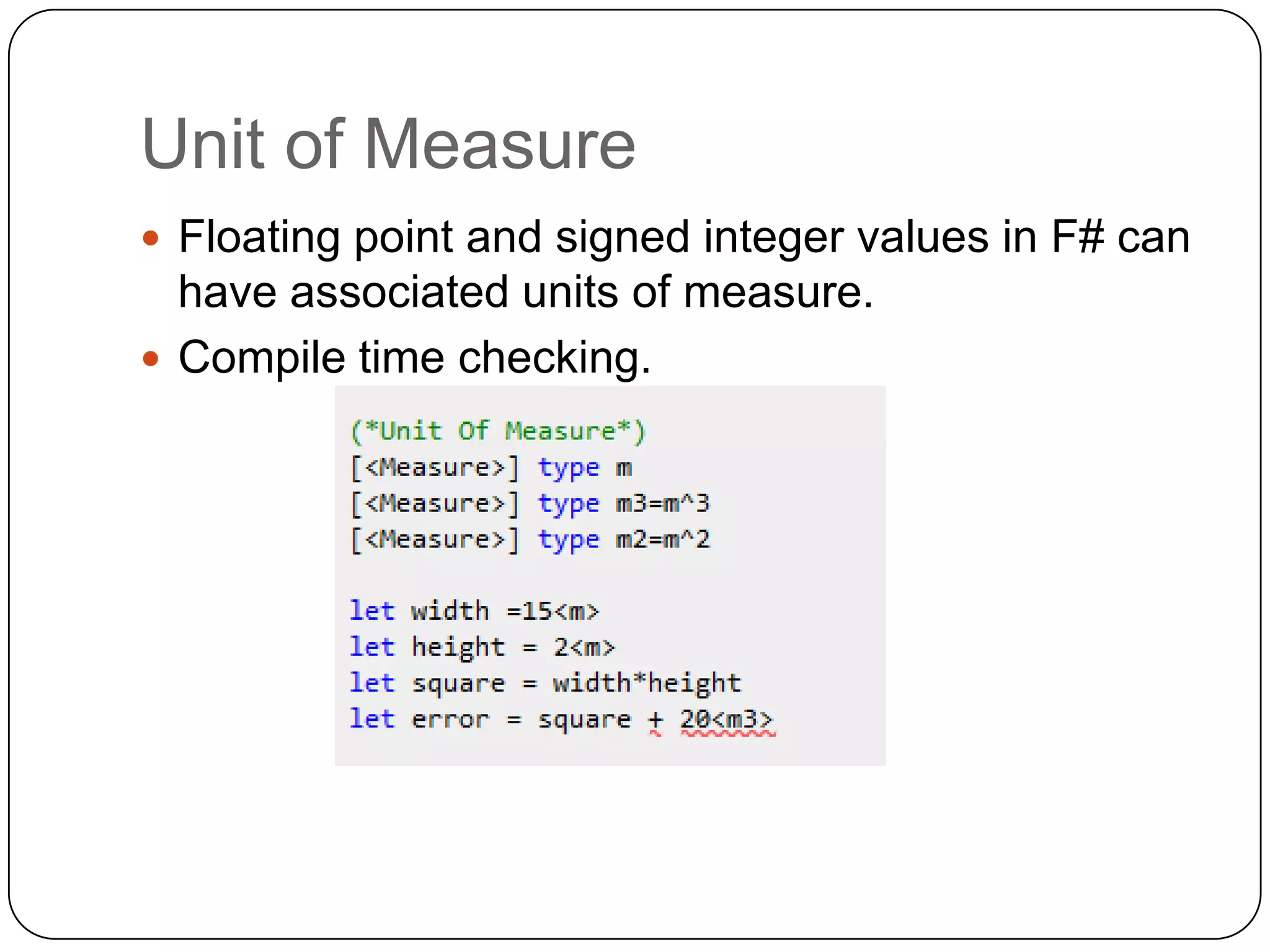
Functional programming is a paradigm that treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions, avoiding state and mutable data. It uses immutable values by default and features like type inference, recursion, higher-order functions, pattern matching and unit of measure checking. Functional programming enables more succinct and simpler programs with powerful ways to structure code using immutability, high-order functions and other techniques. It is used widely in industries like communications, finance and AI, and supported by languages like F#, Haskell, Scala and Clojure.