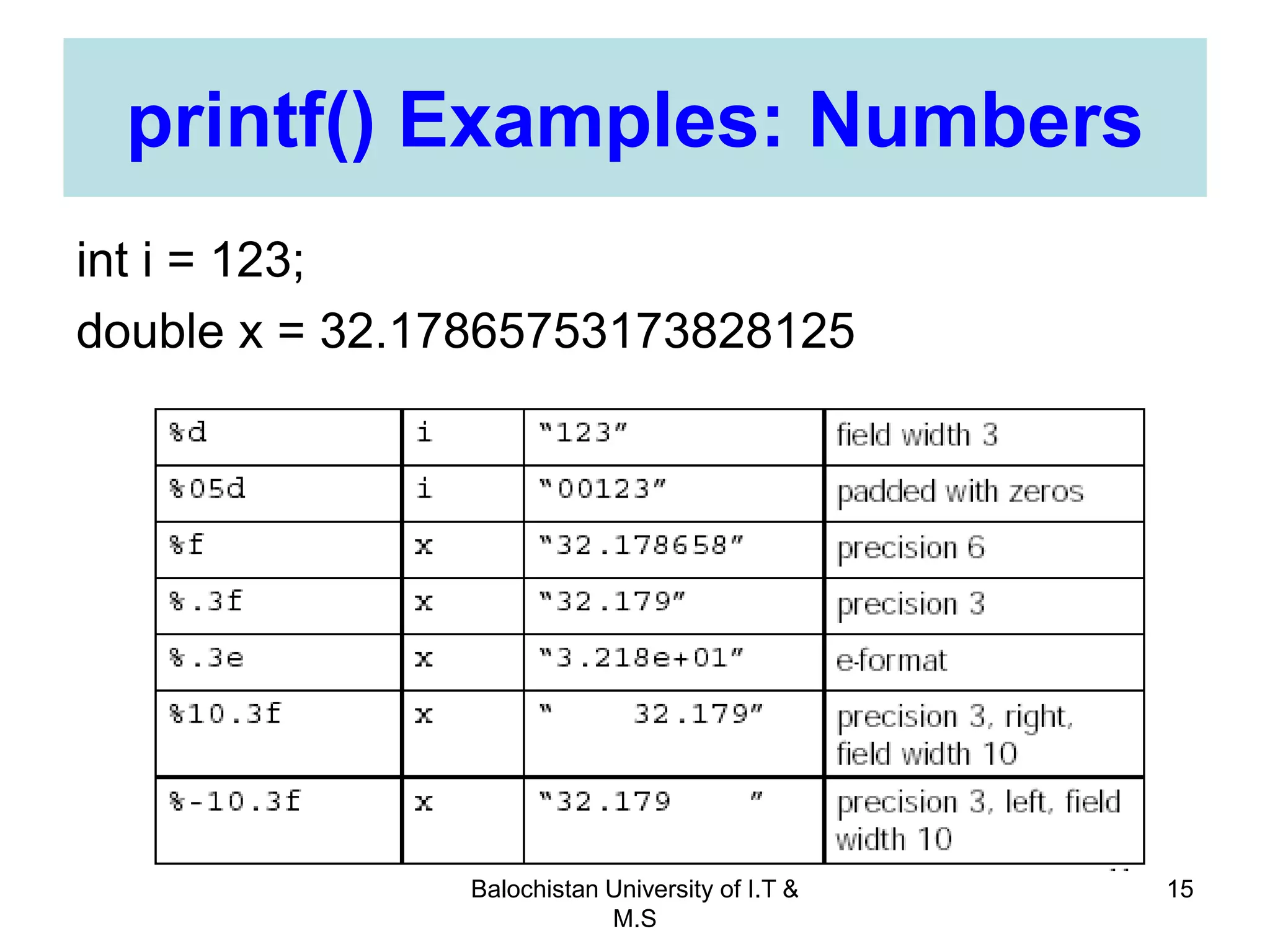
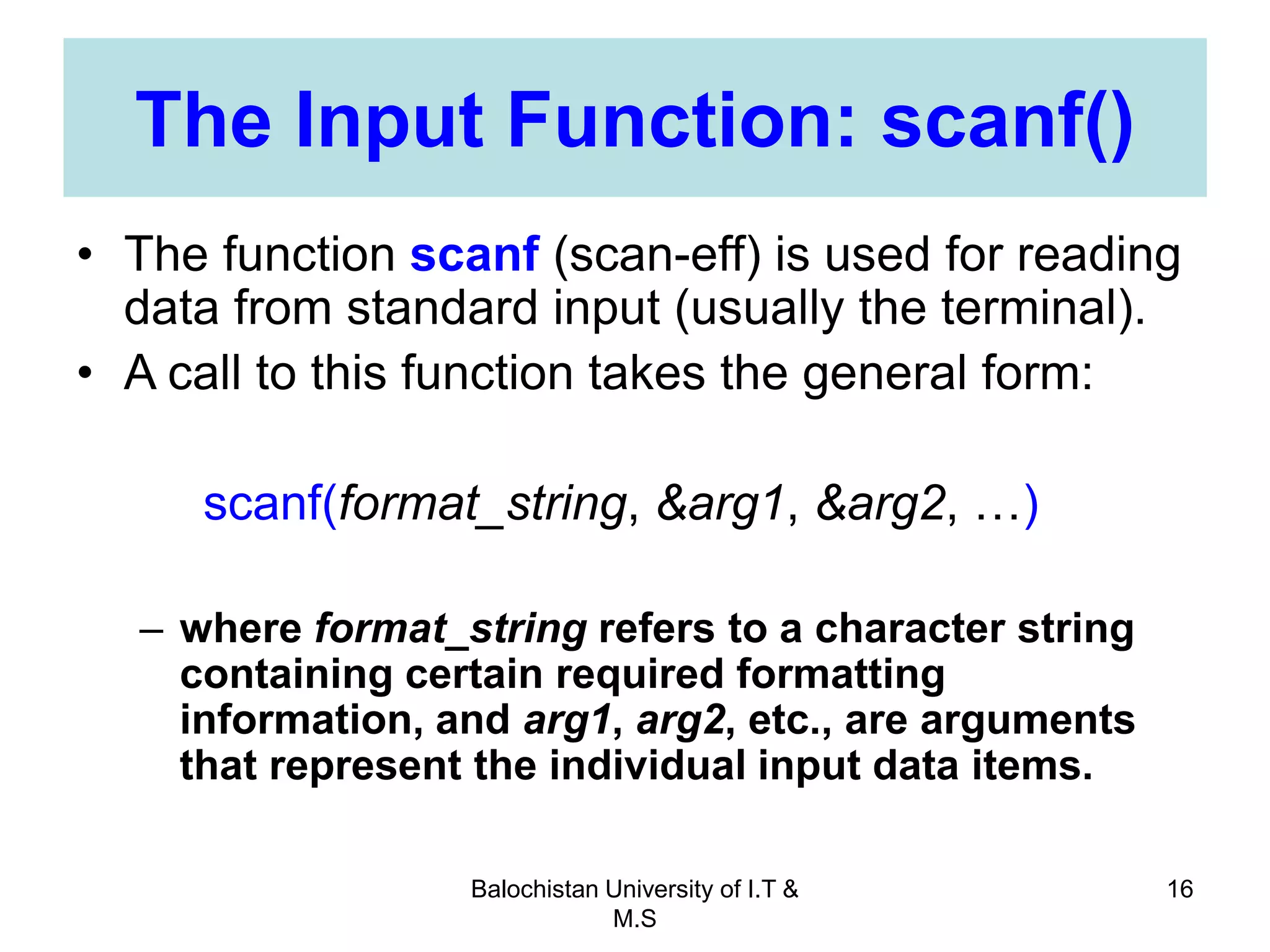
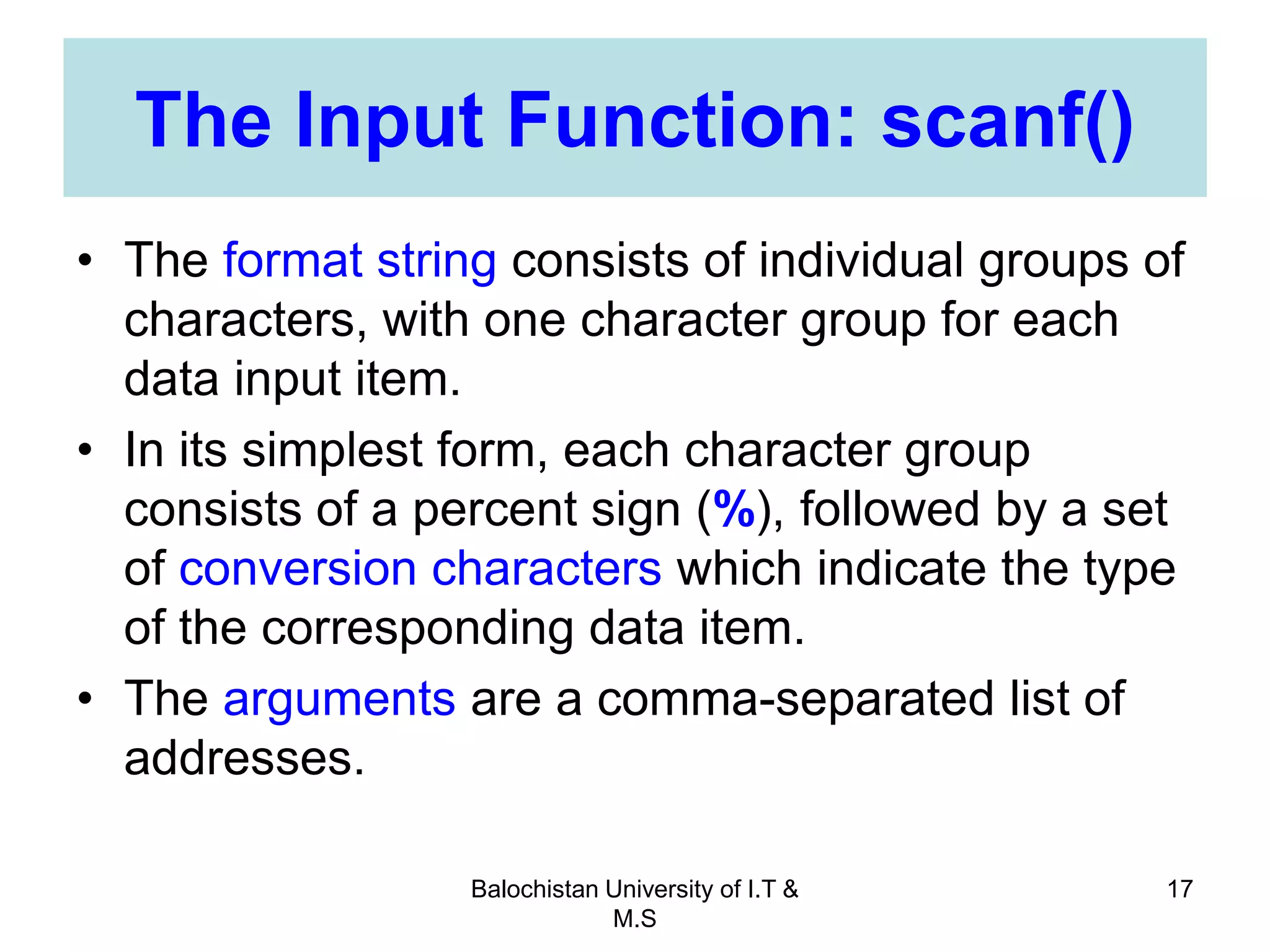
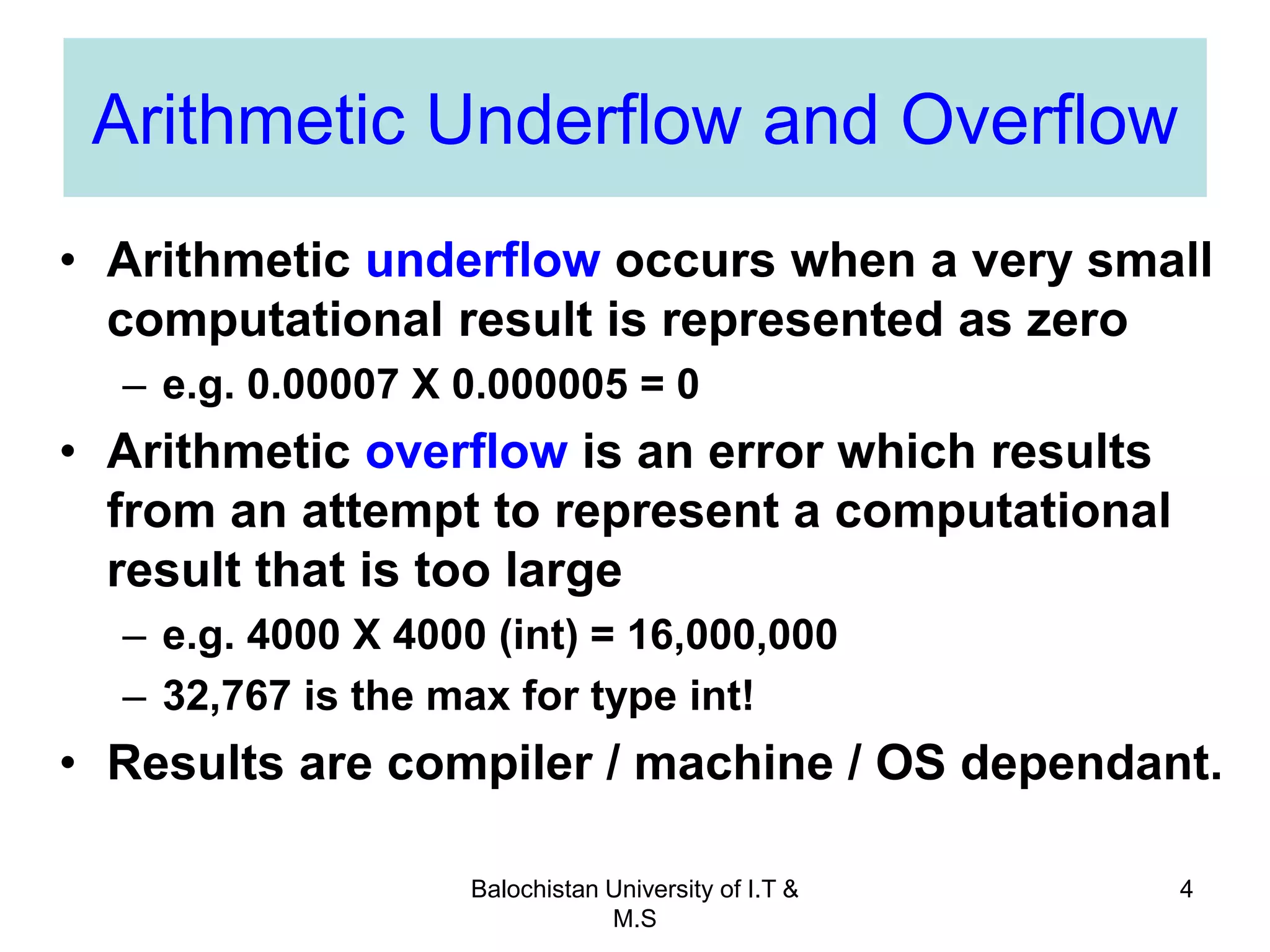
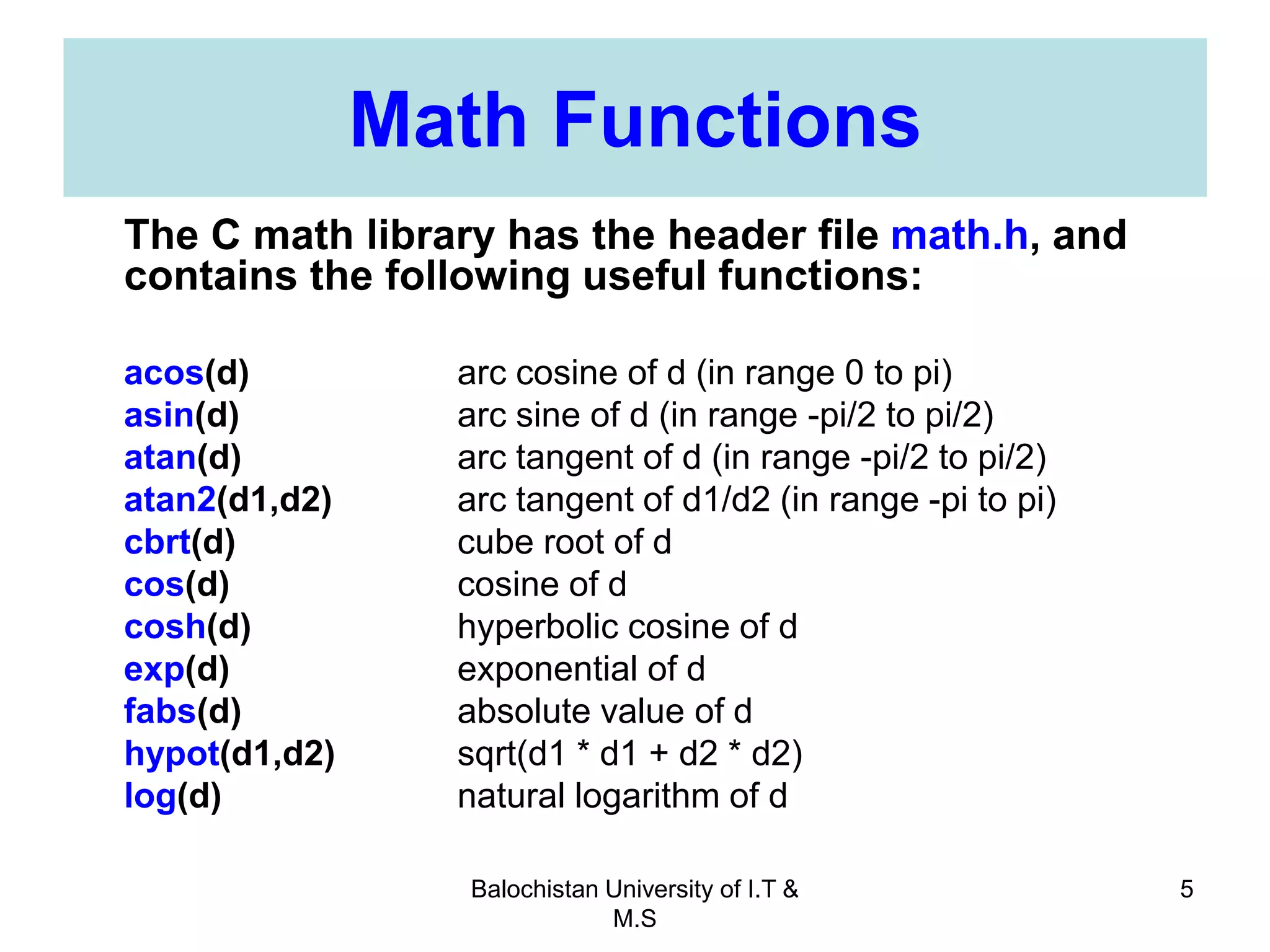
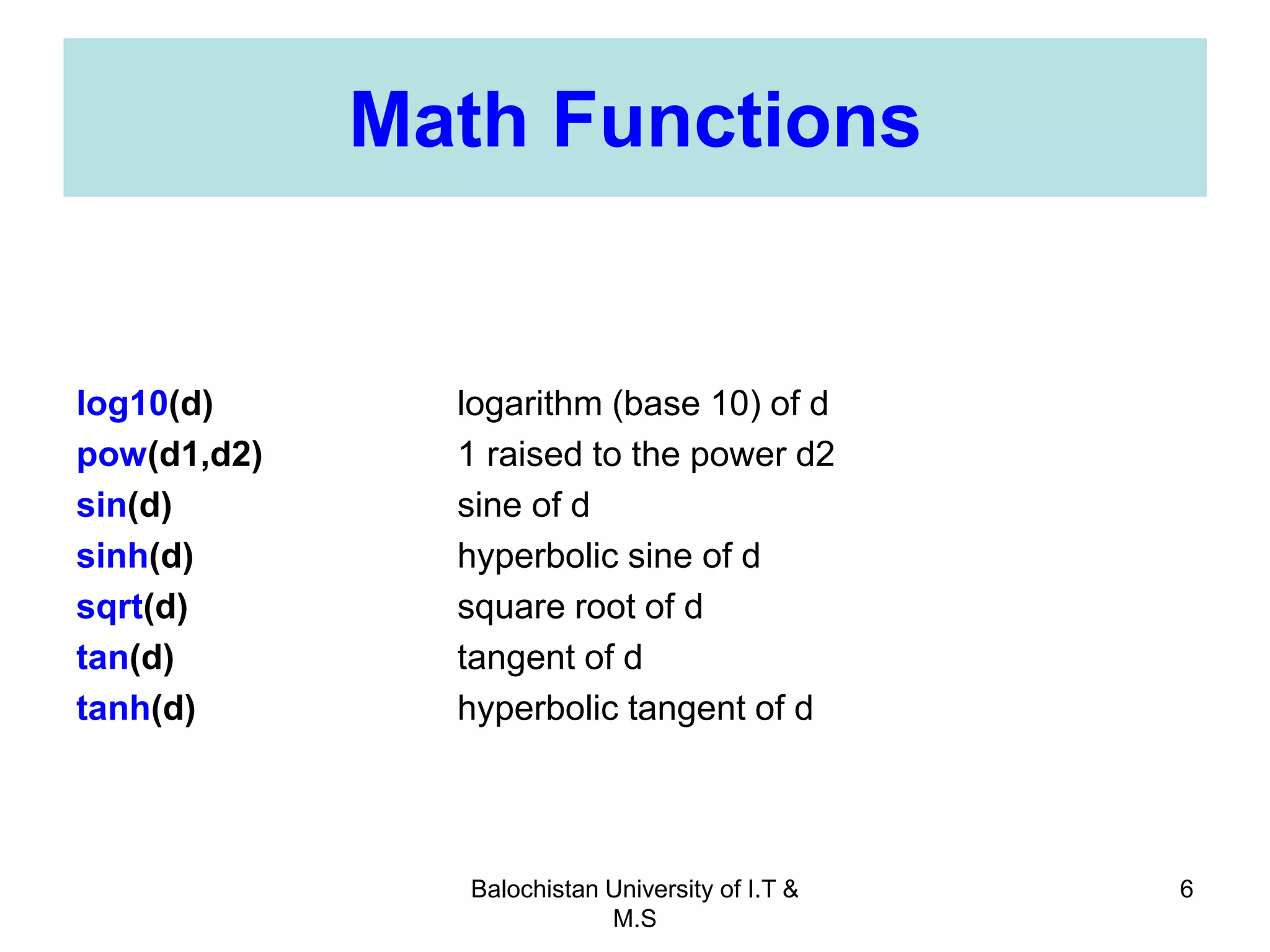
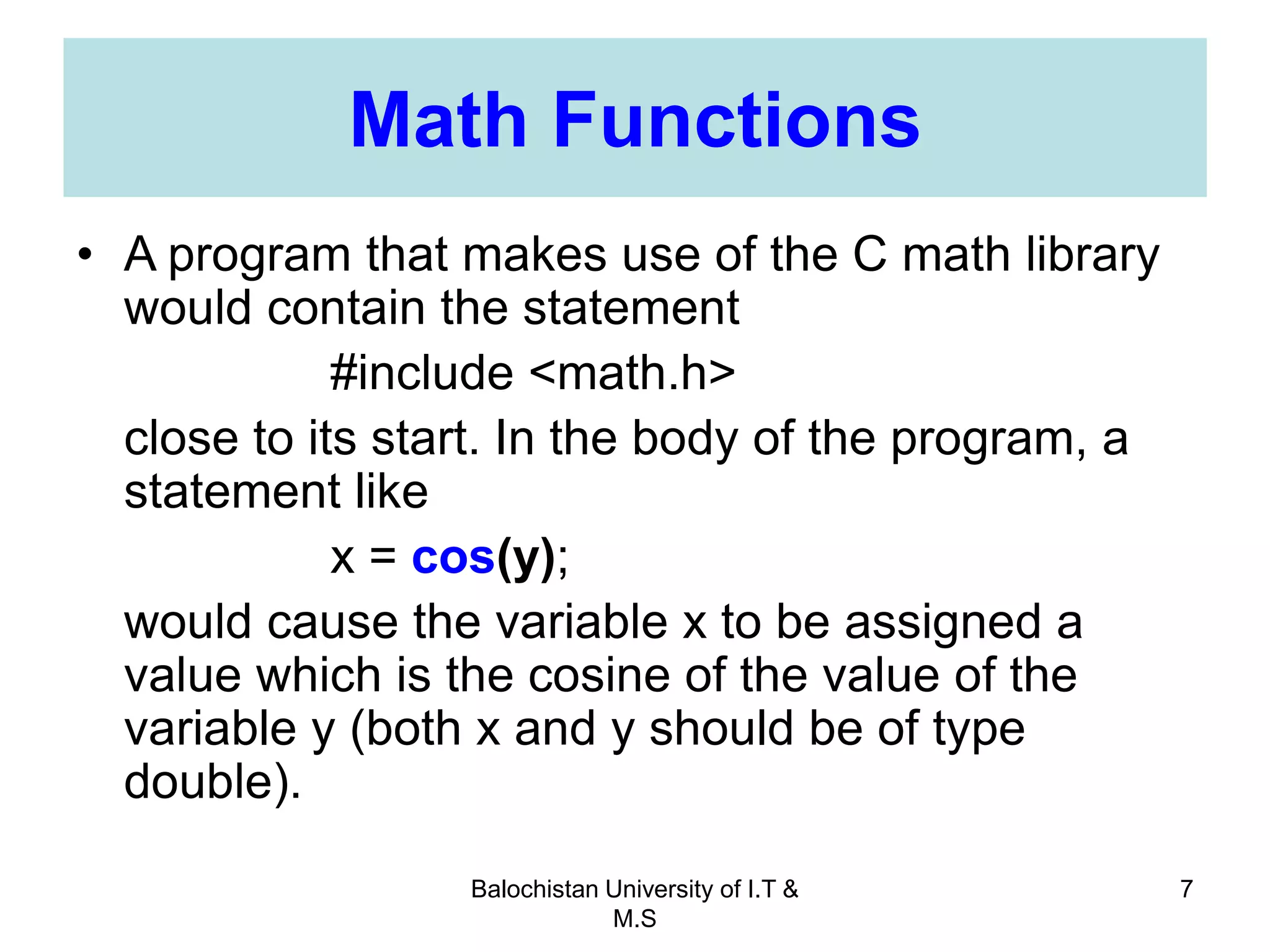
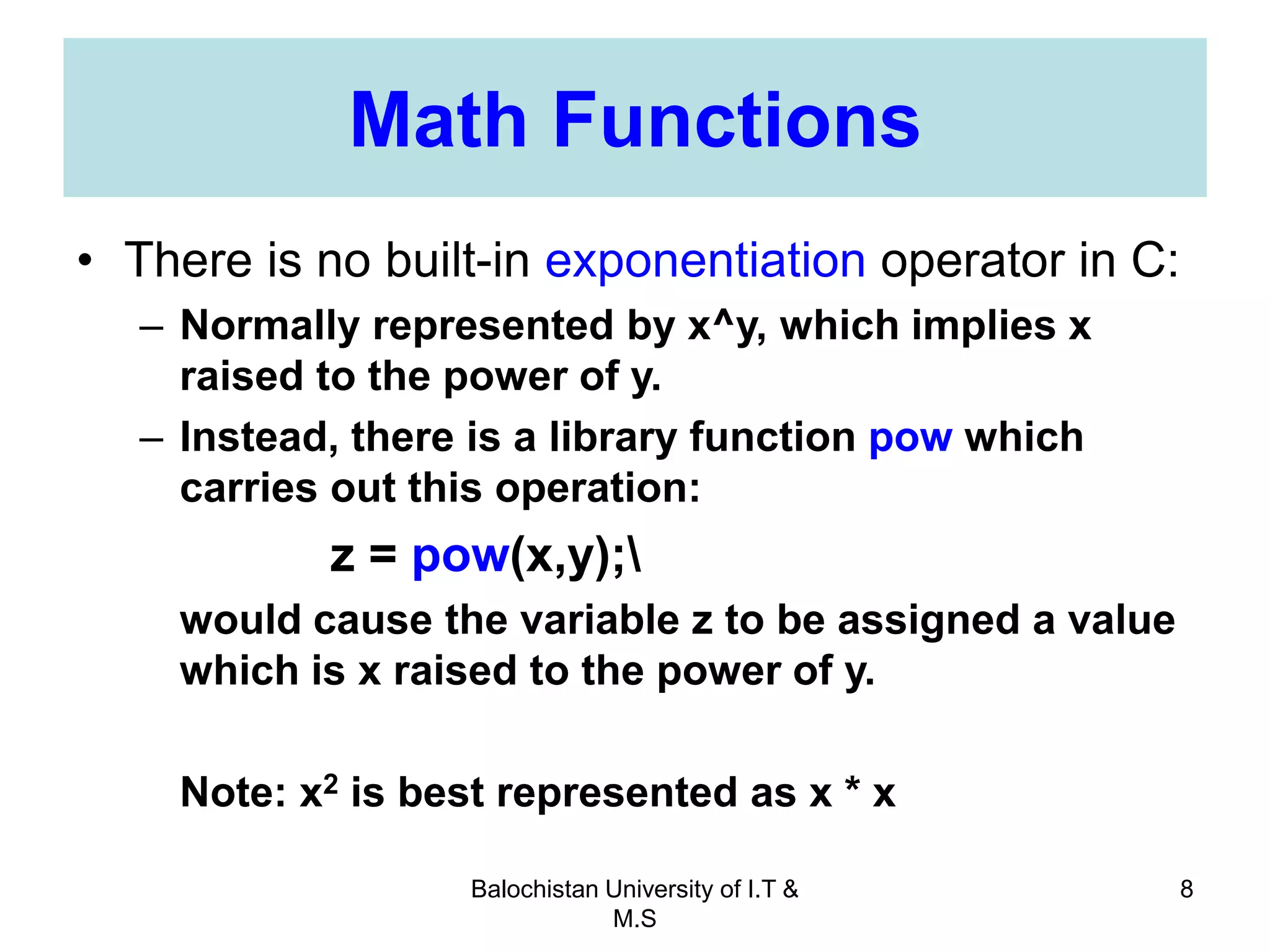
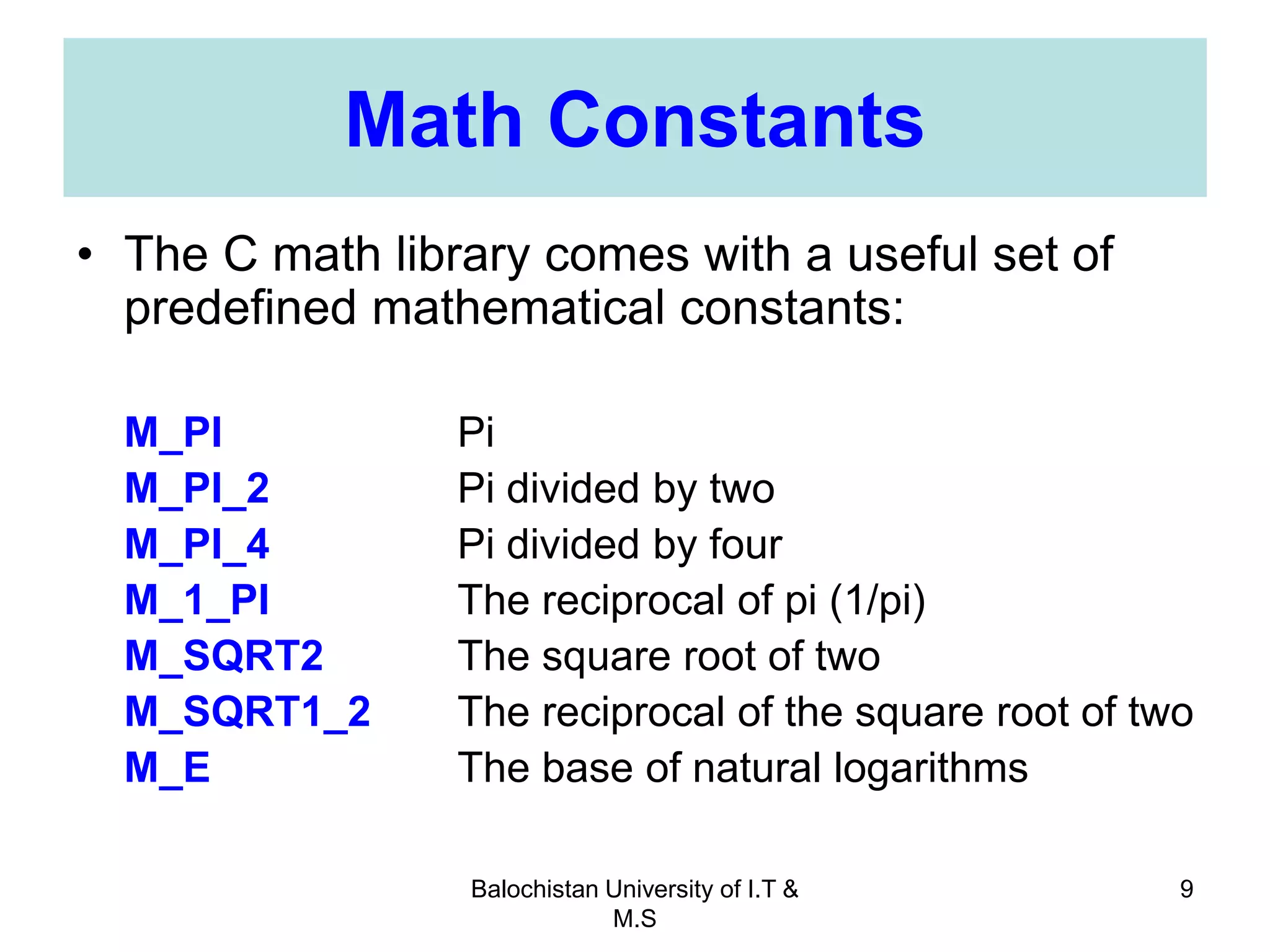
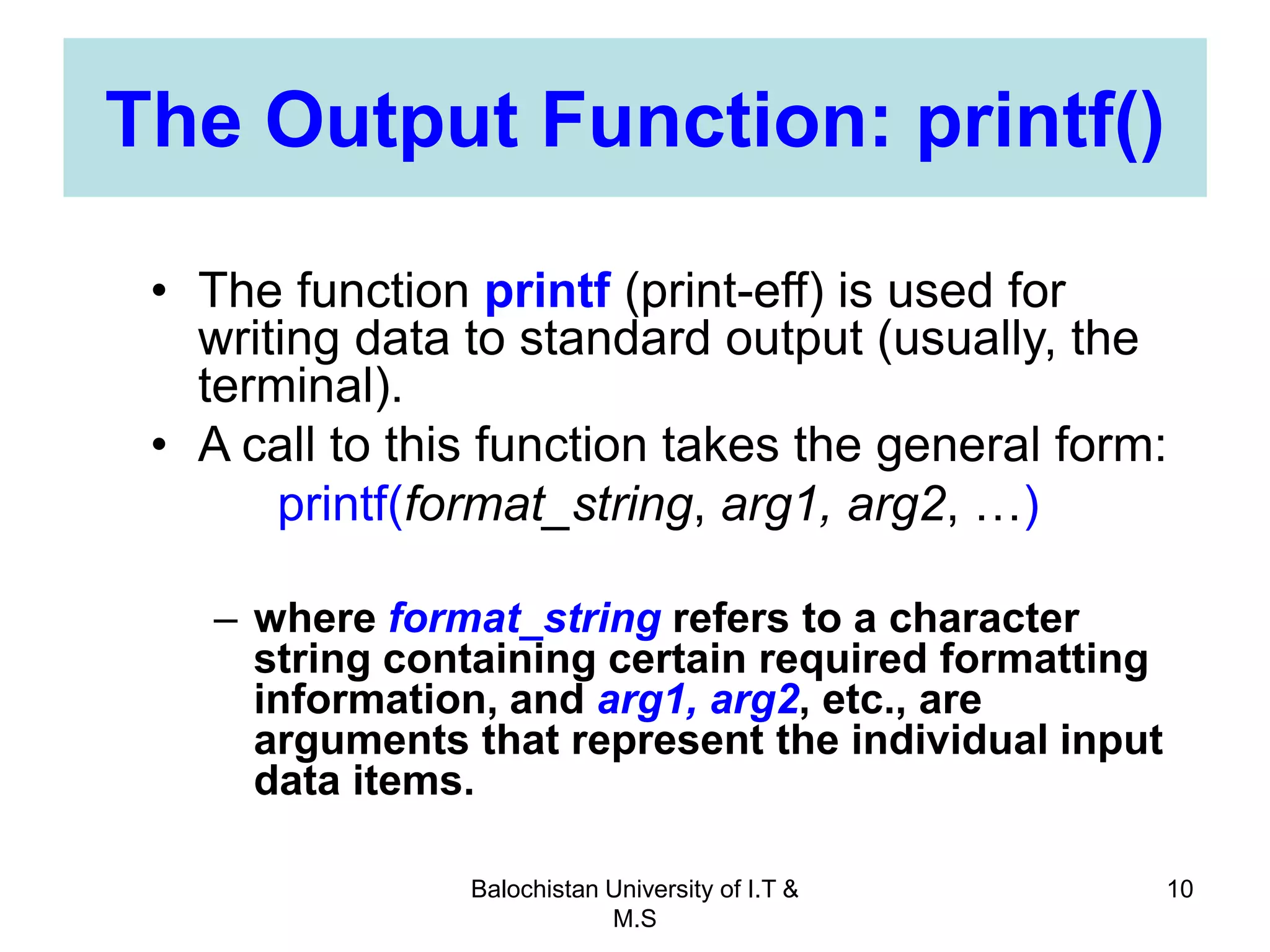
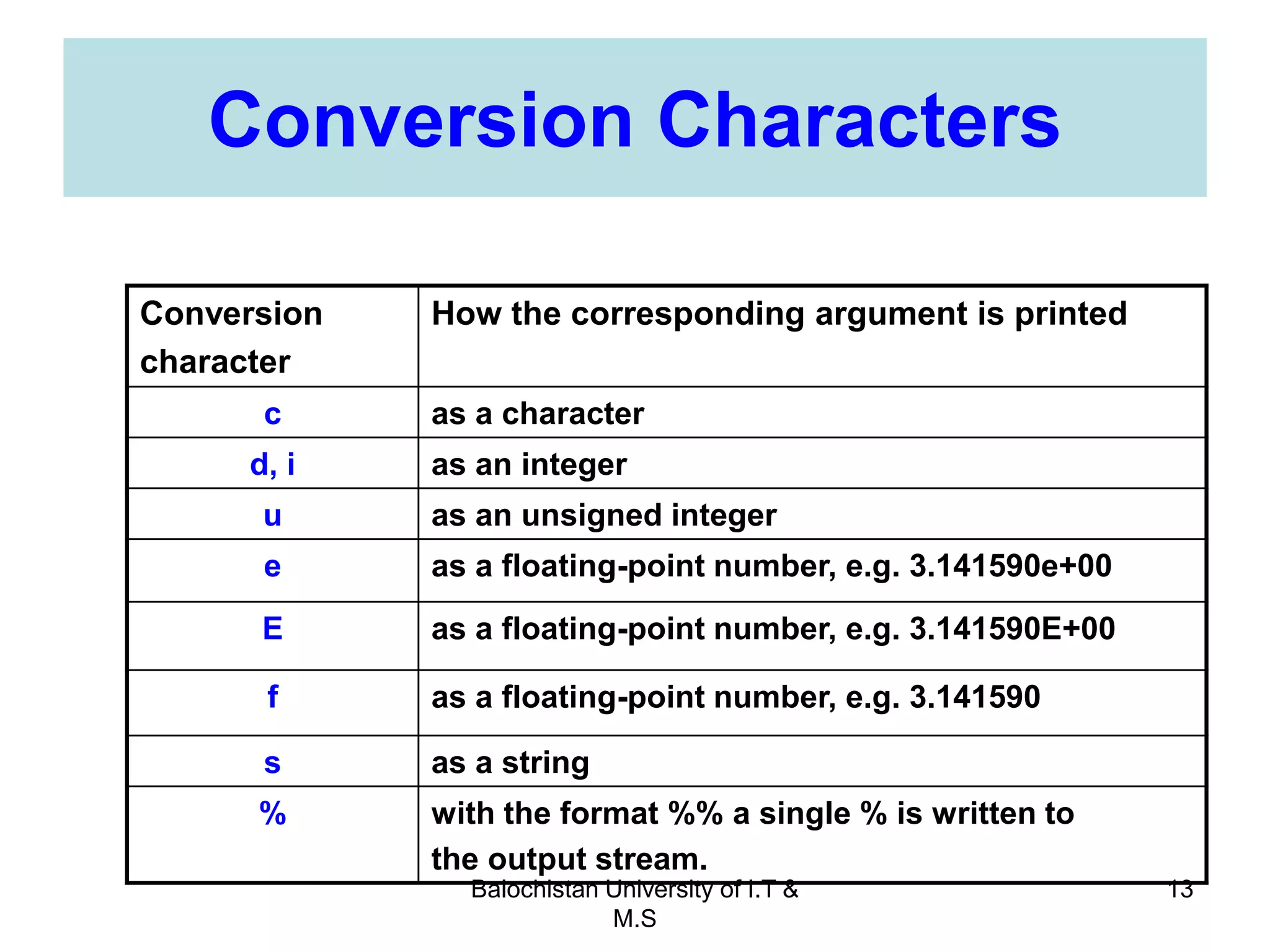
This document discusses numerical inaccuracies that can occur when representing real numbers in computers using floating point types. It then describes some ways to avoid errors, such as using double precision instead of float. The document also covers arithmetic overflow and underflow issues. Furthermore, it introduces common mathematical functions in C like trigonometric, logarithmic and exponential functions. It provides examples of using the printf() and scanf() functions to output and input data in C programs.



![Balochistan University of I.T &
M.S
14
printf() Examples: Characters
& Strings
char c=‘M’, s[]=“blue moon”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l-5mathfunctions-200128162004/75/Math-Functions-in-C-Scanf-Printf-14-2048.jpg)