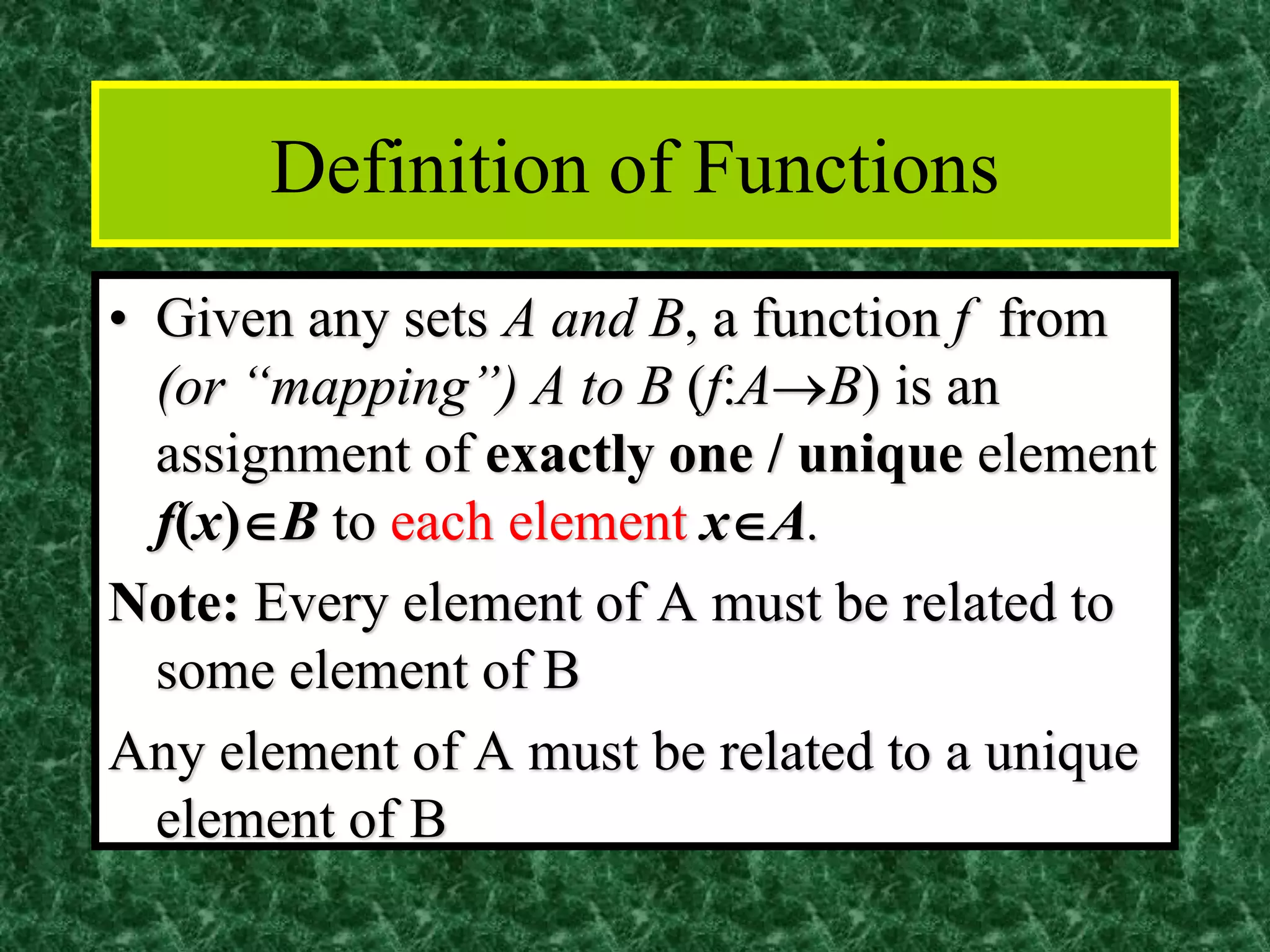
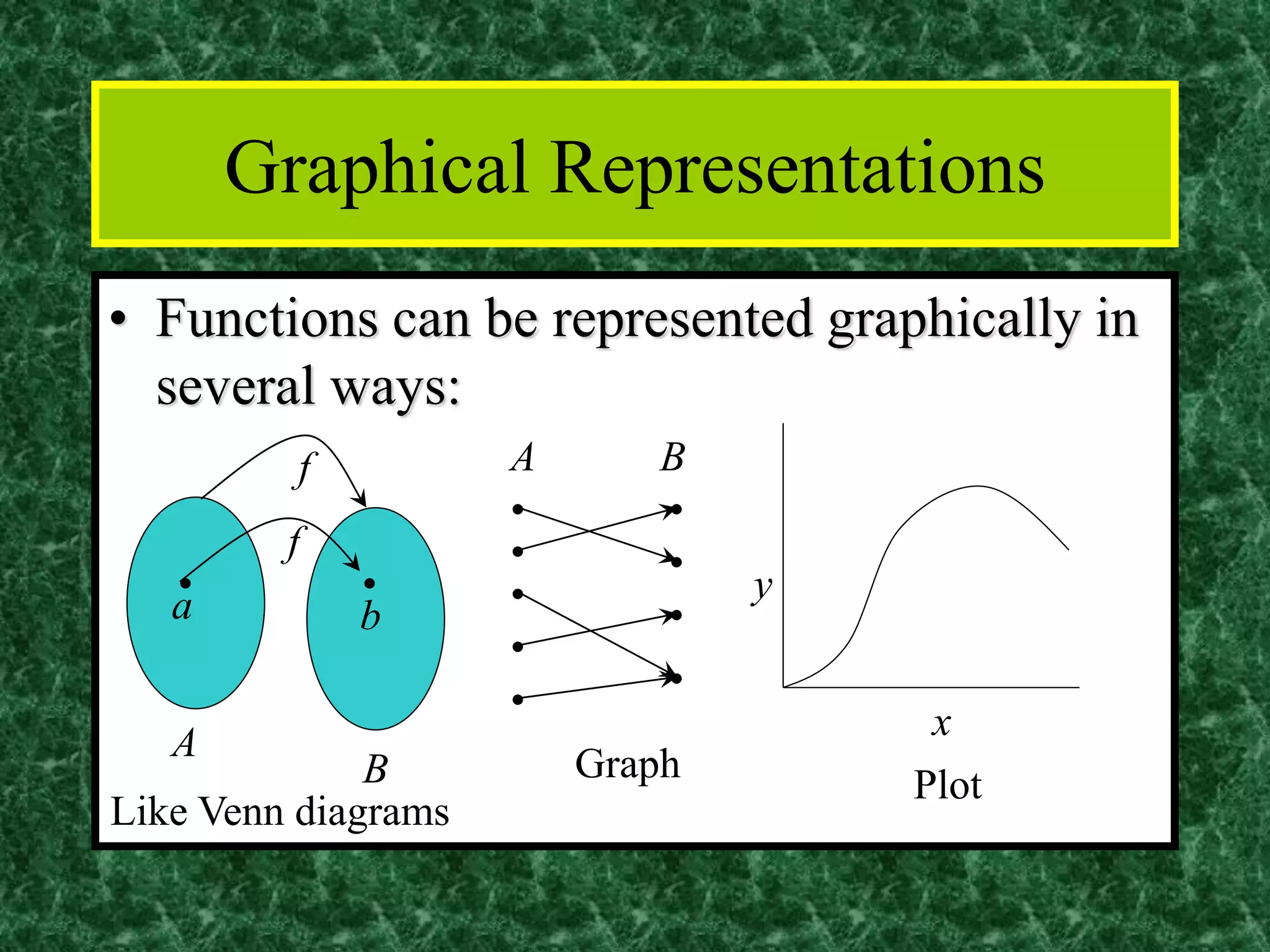
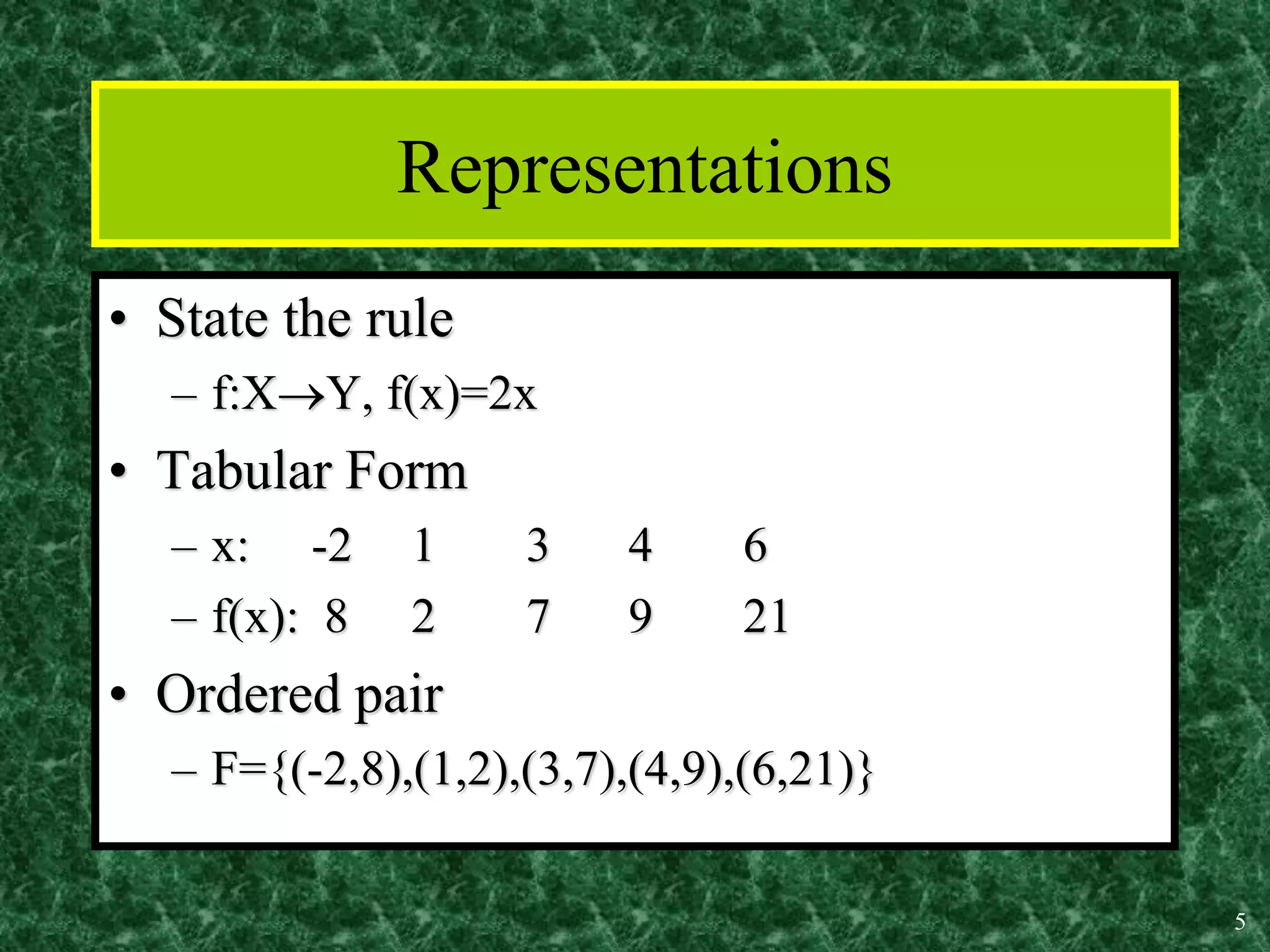
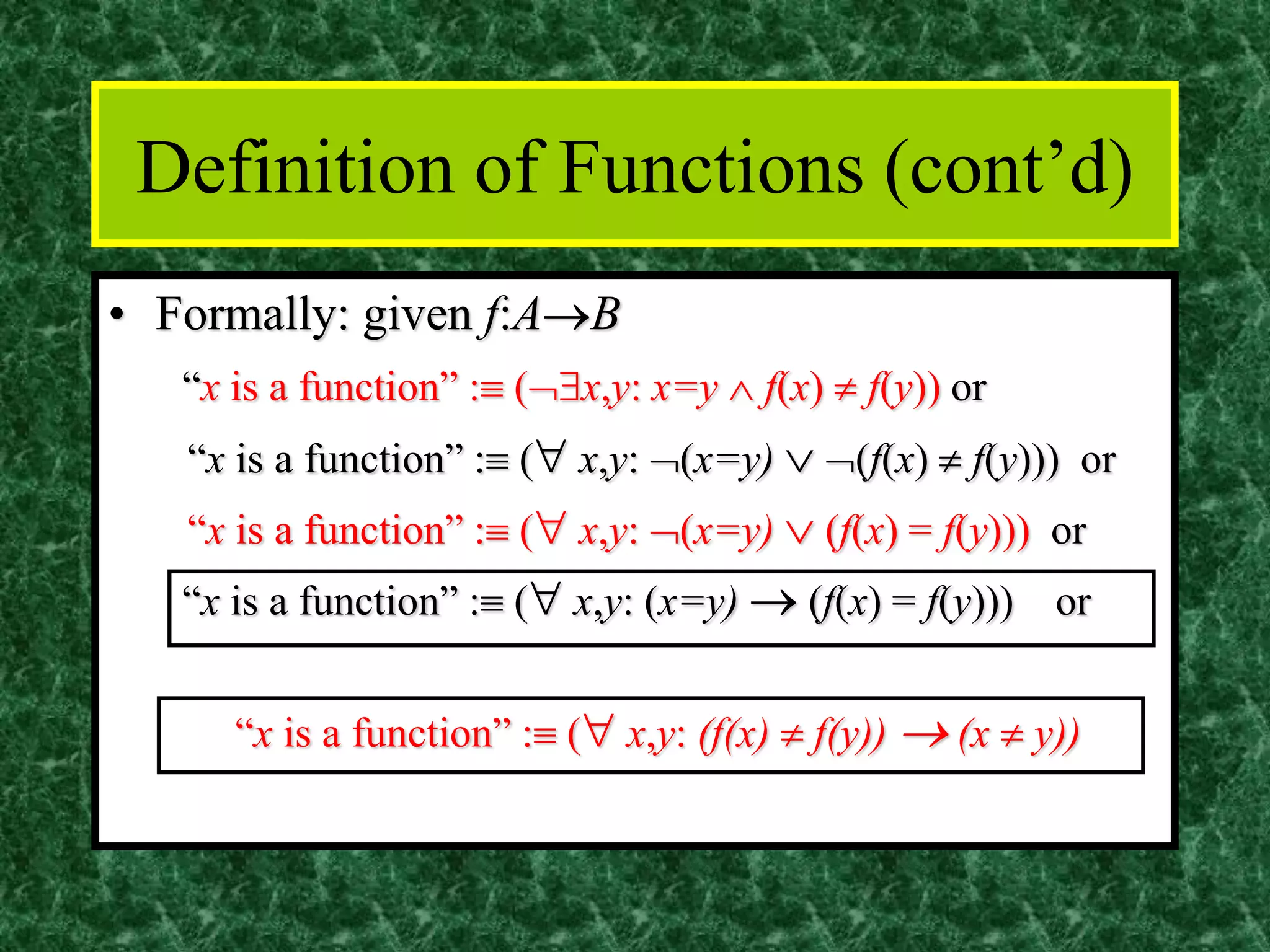
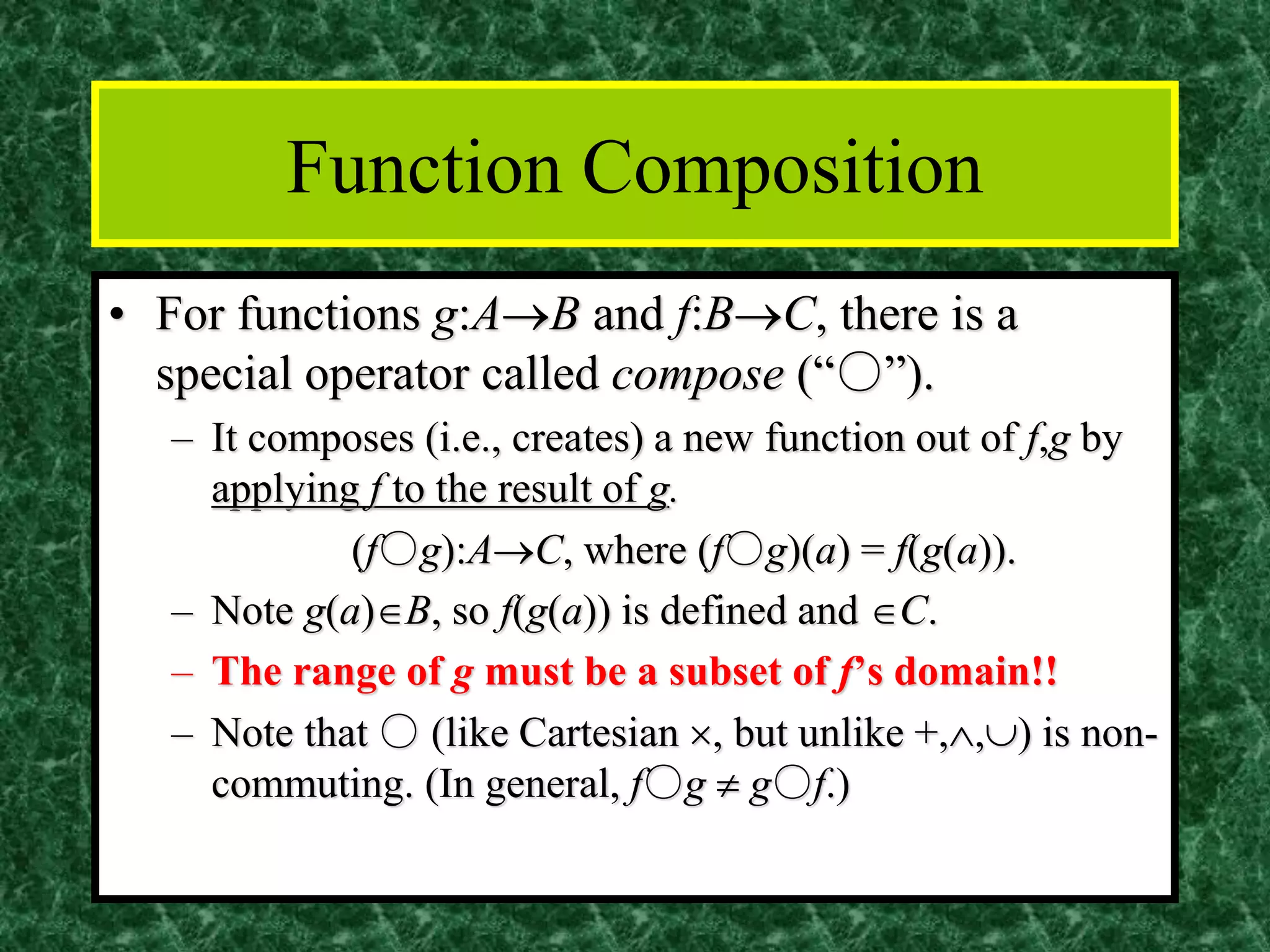
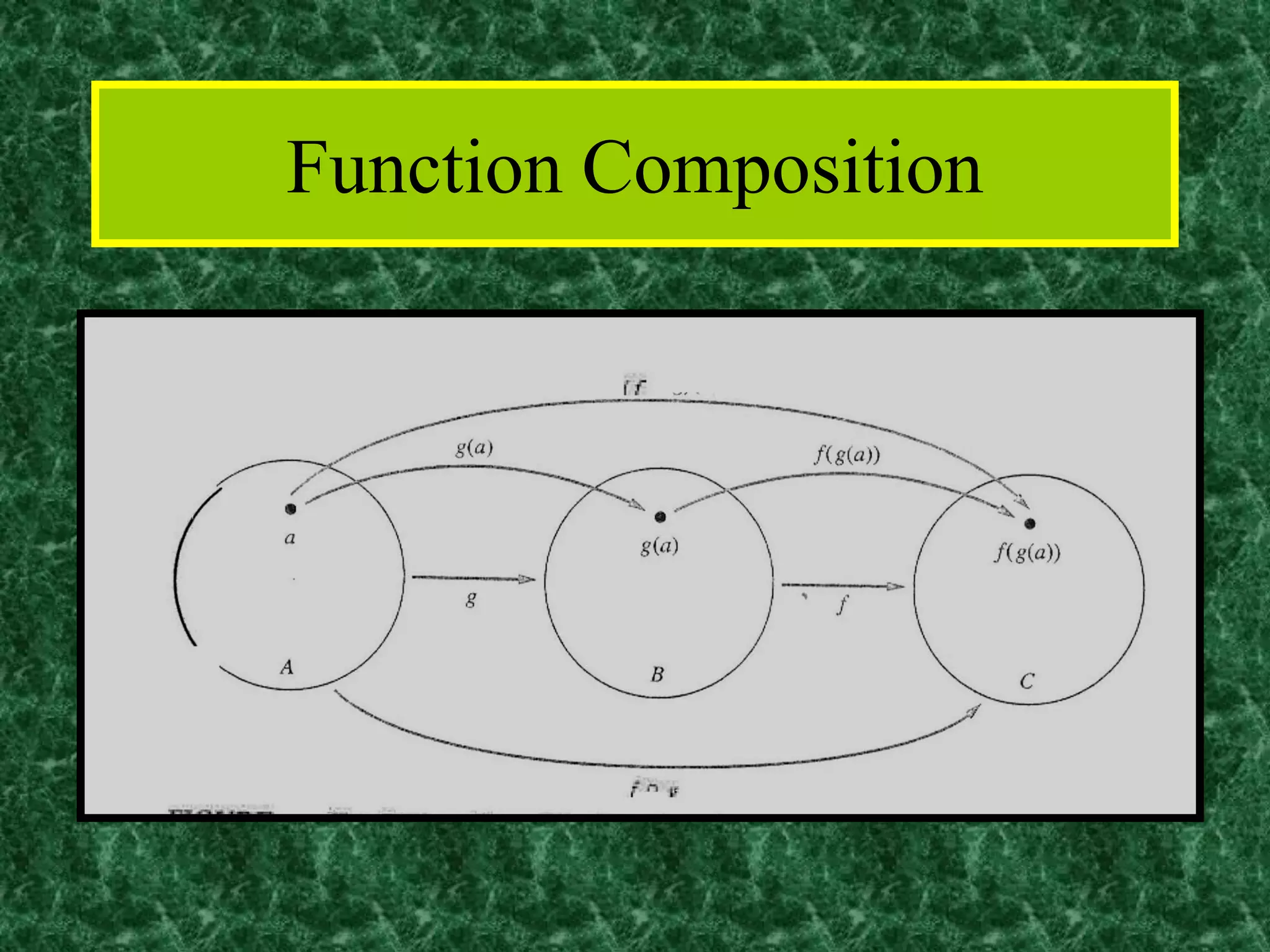
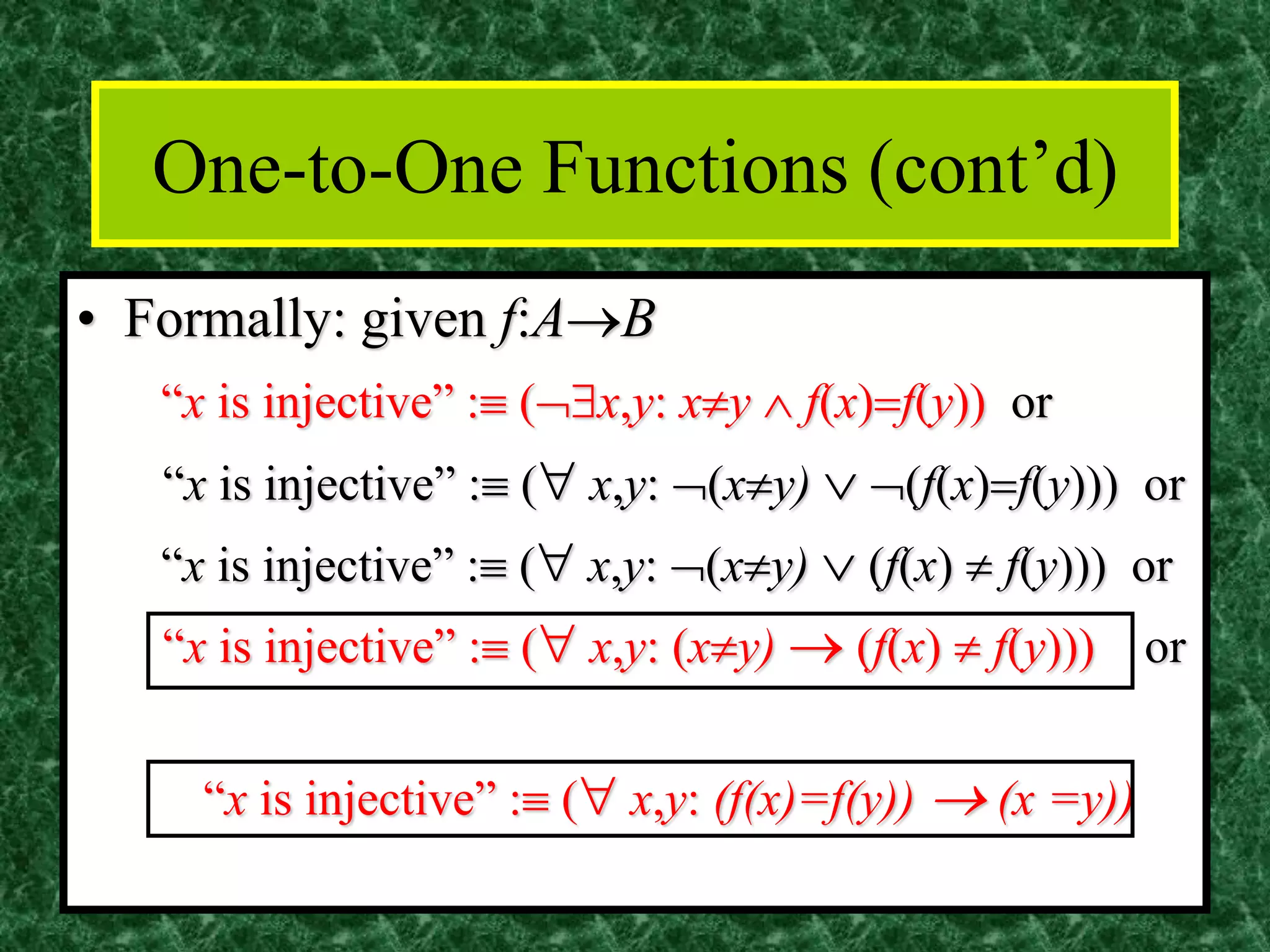
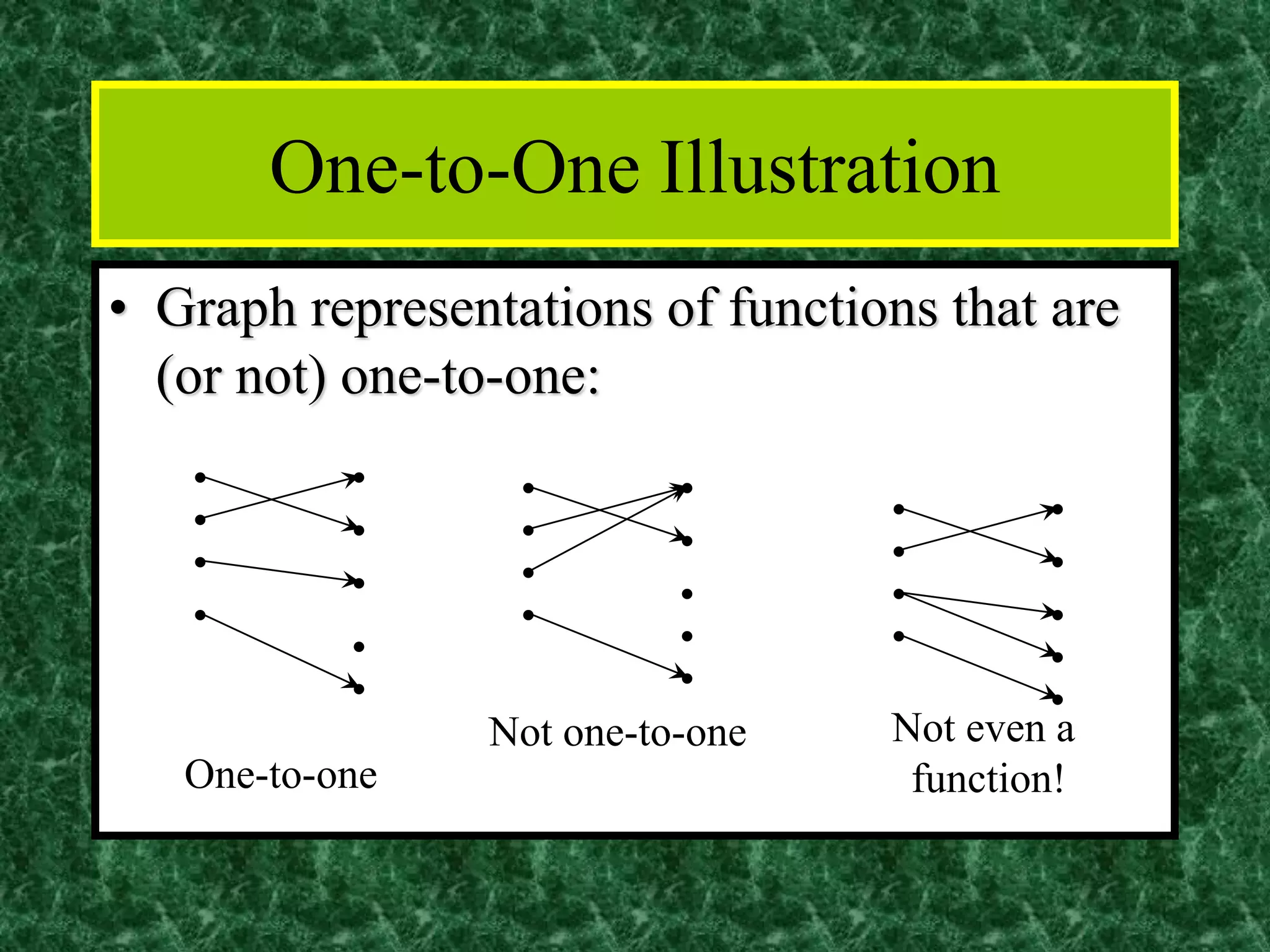
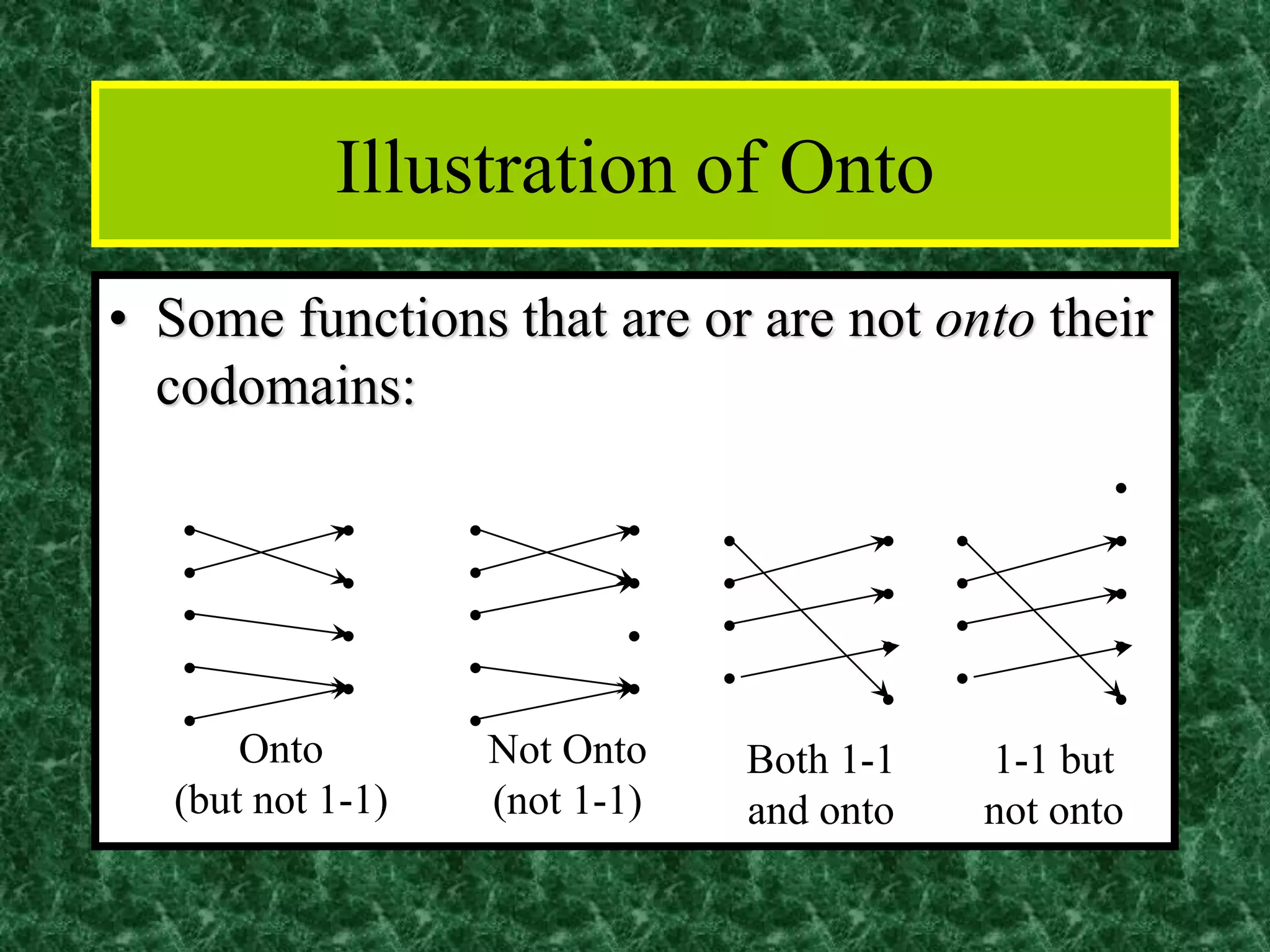
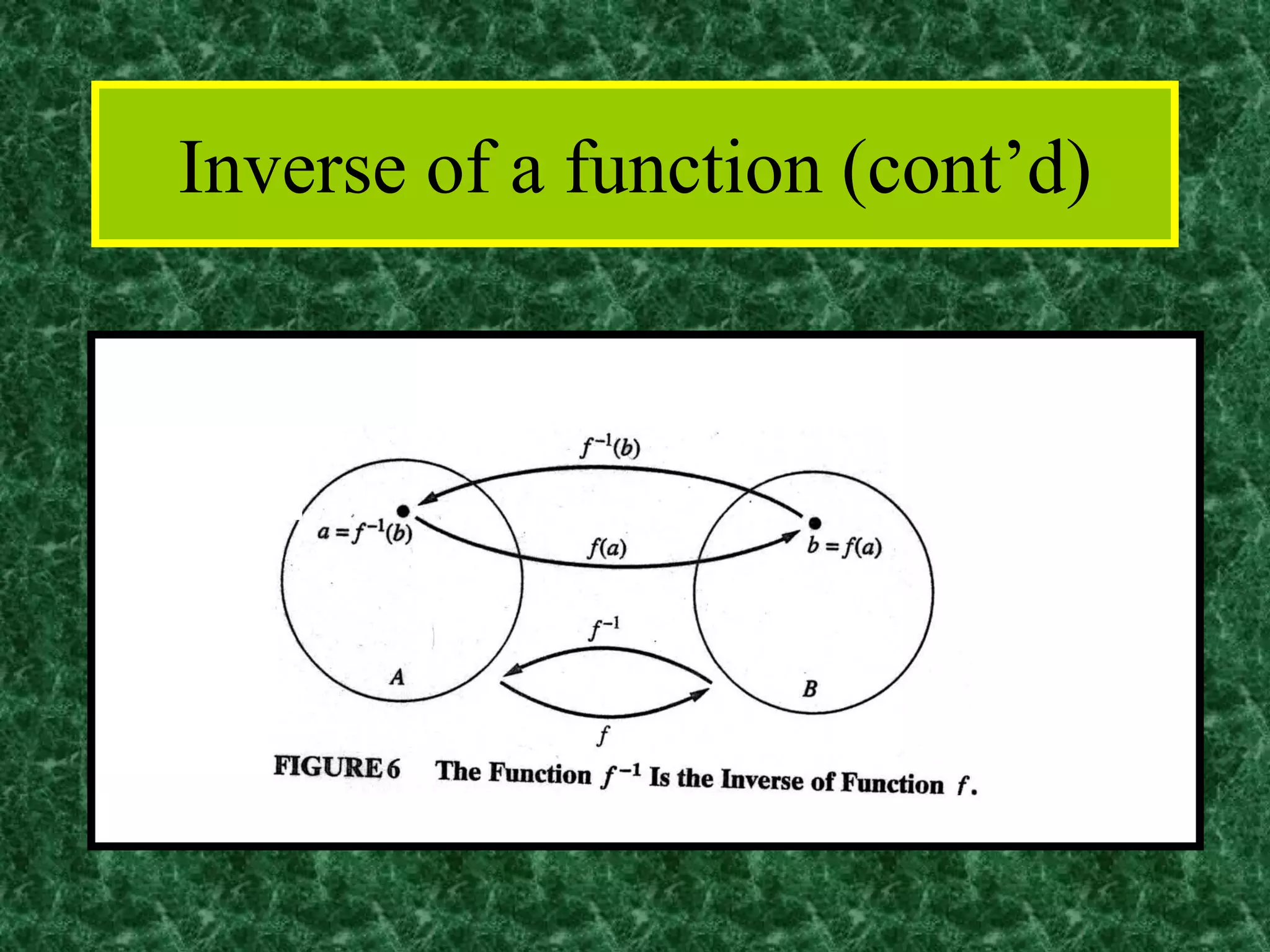
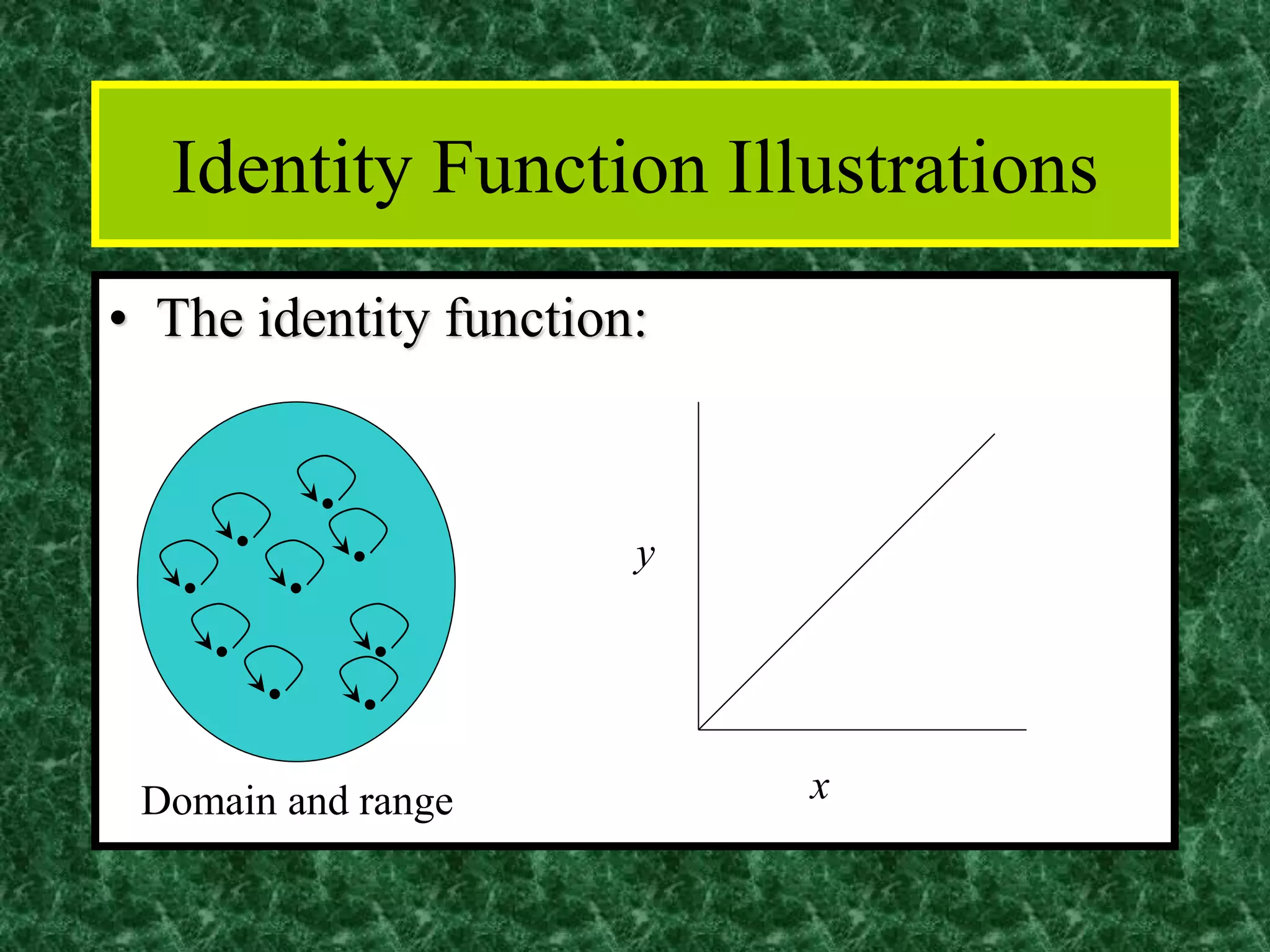
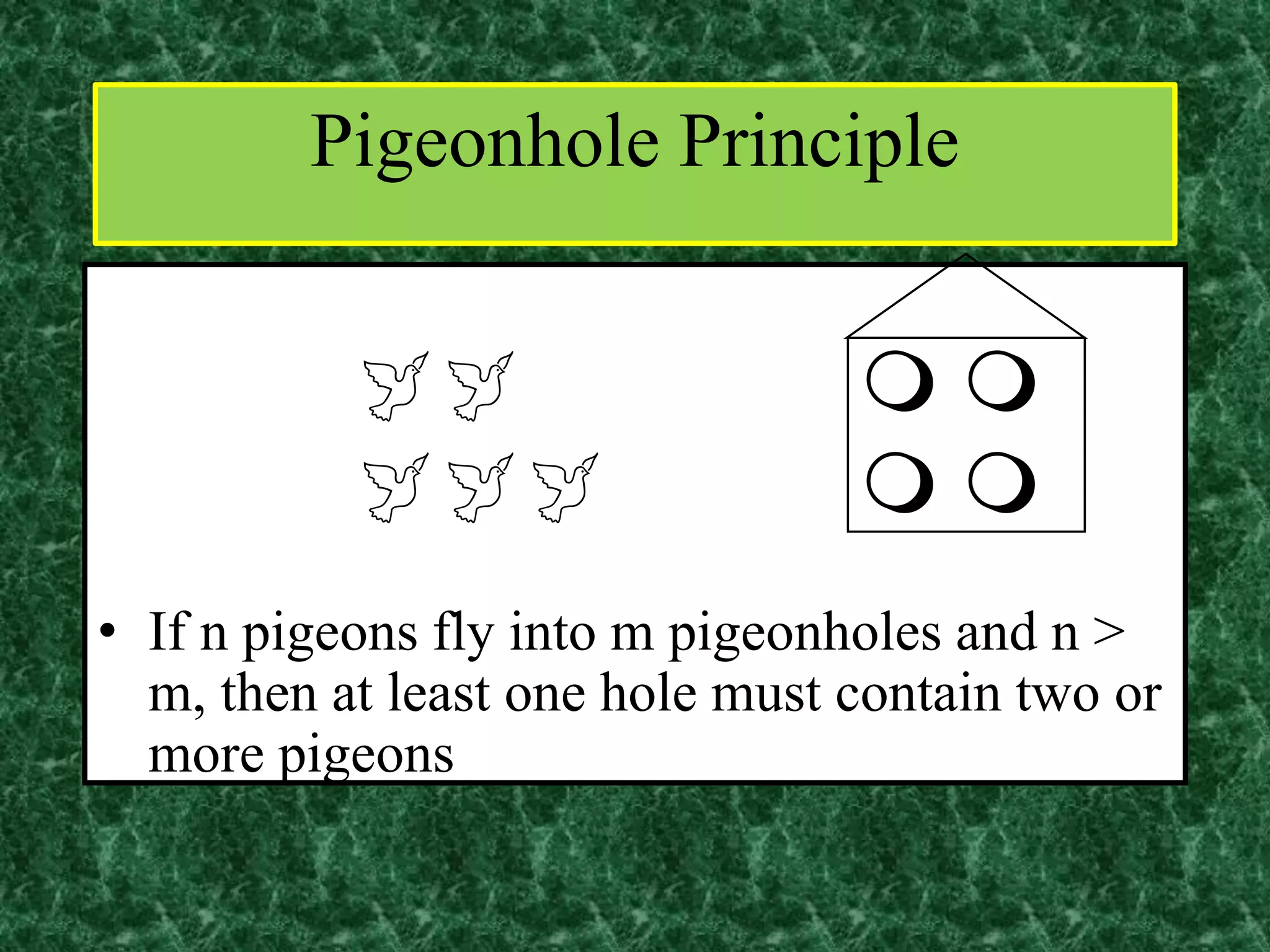
The document discusses functions and the pigeonhole principle. It defines what a function is, how functions can be represented graphically and with tables and ordered pairs. It covers one-to-one, onto, and bijective functions. It also discusses function composition, inverse functions, and the identity function. The pigeonhole principle states that if n objects are put into m containers where n > m, then at least one container must hold more than one object. Examples are given to illustrate how to apply the principle to problems involving months, socks, and selecting numbers.