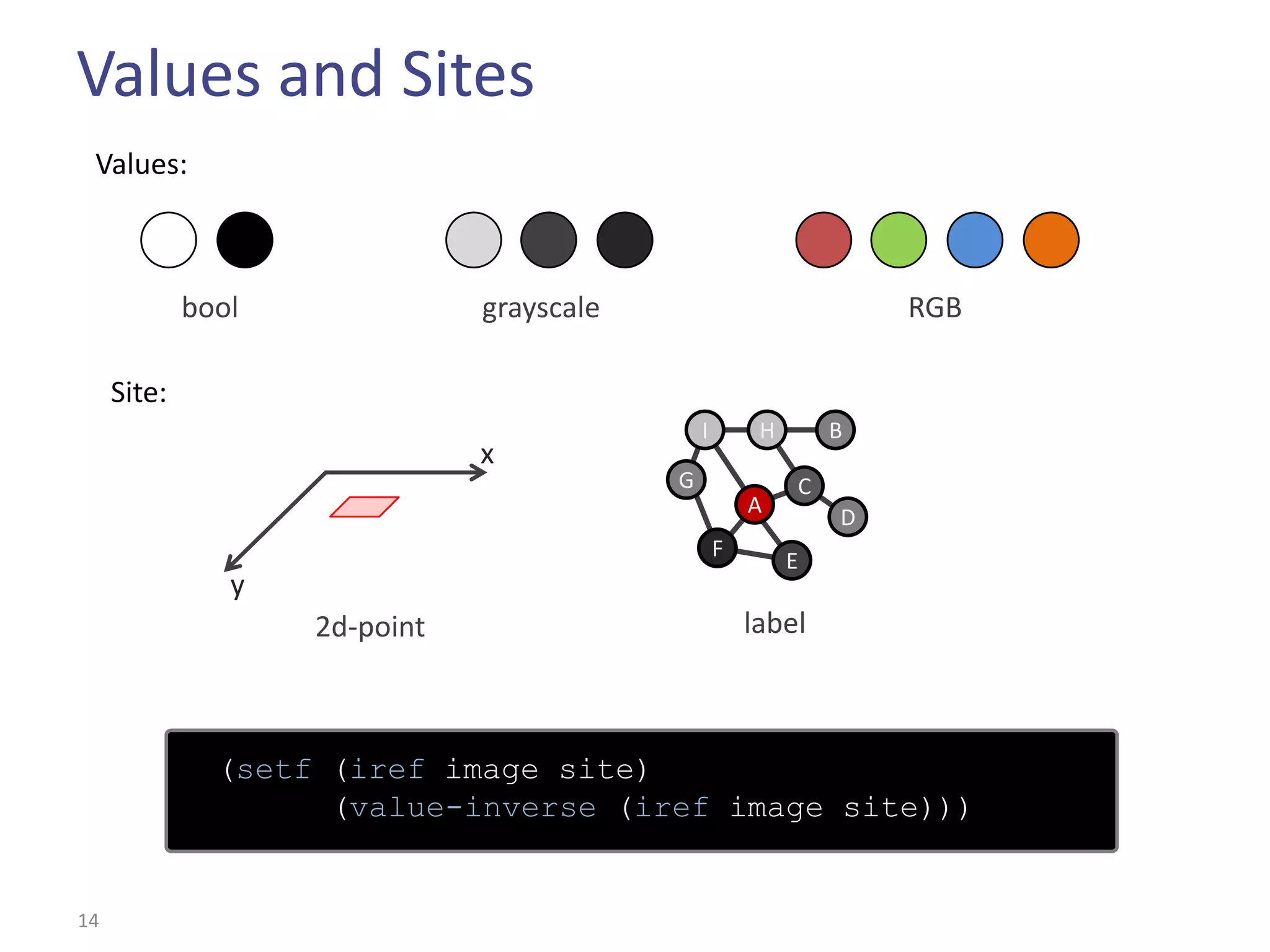
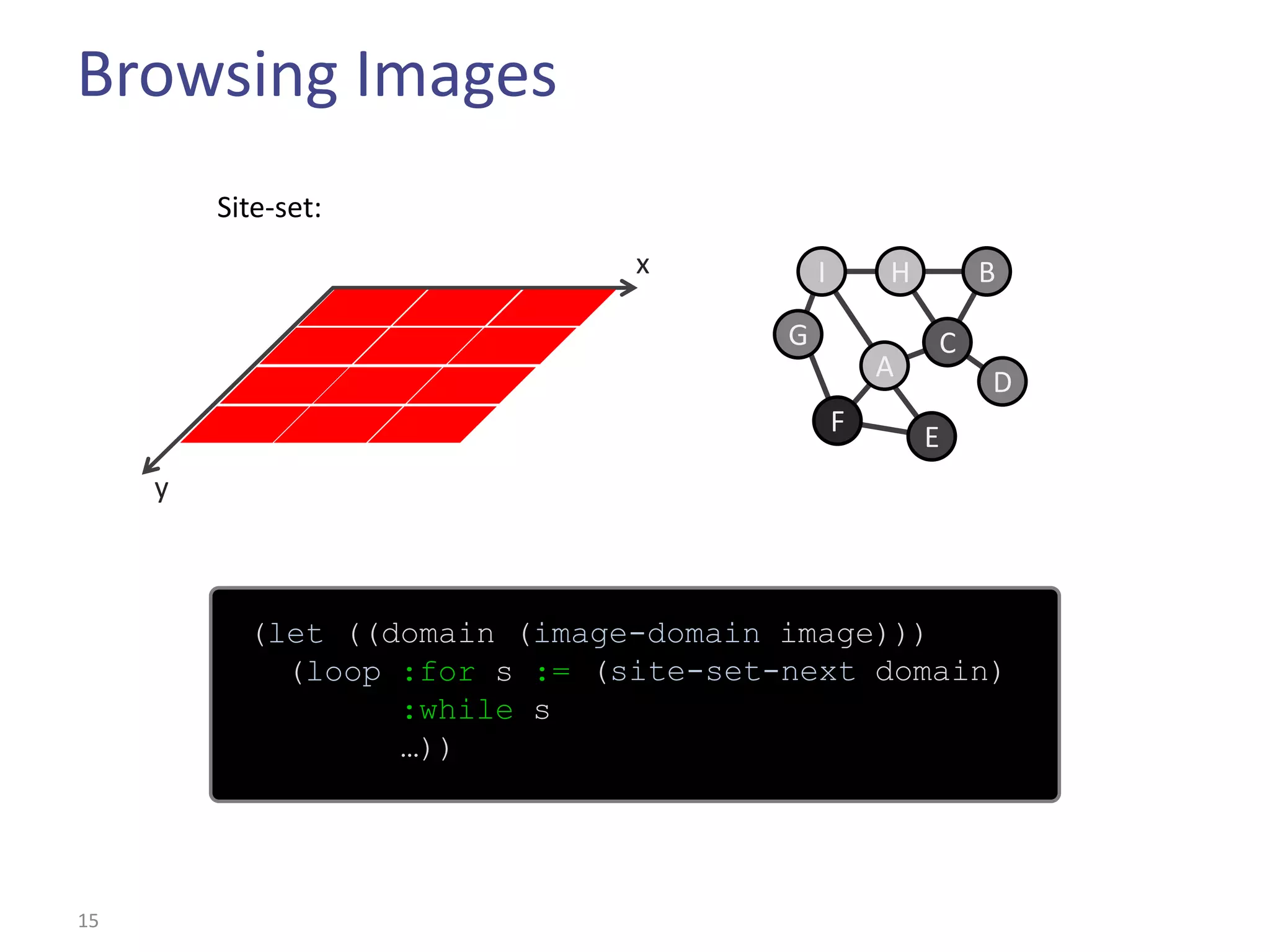
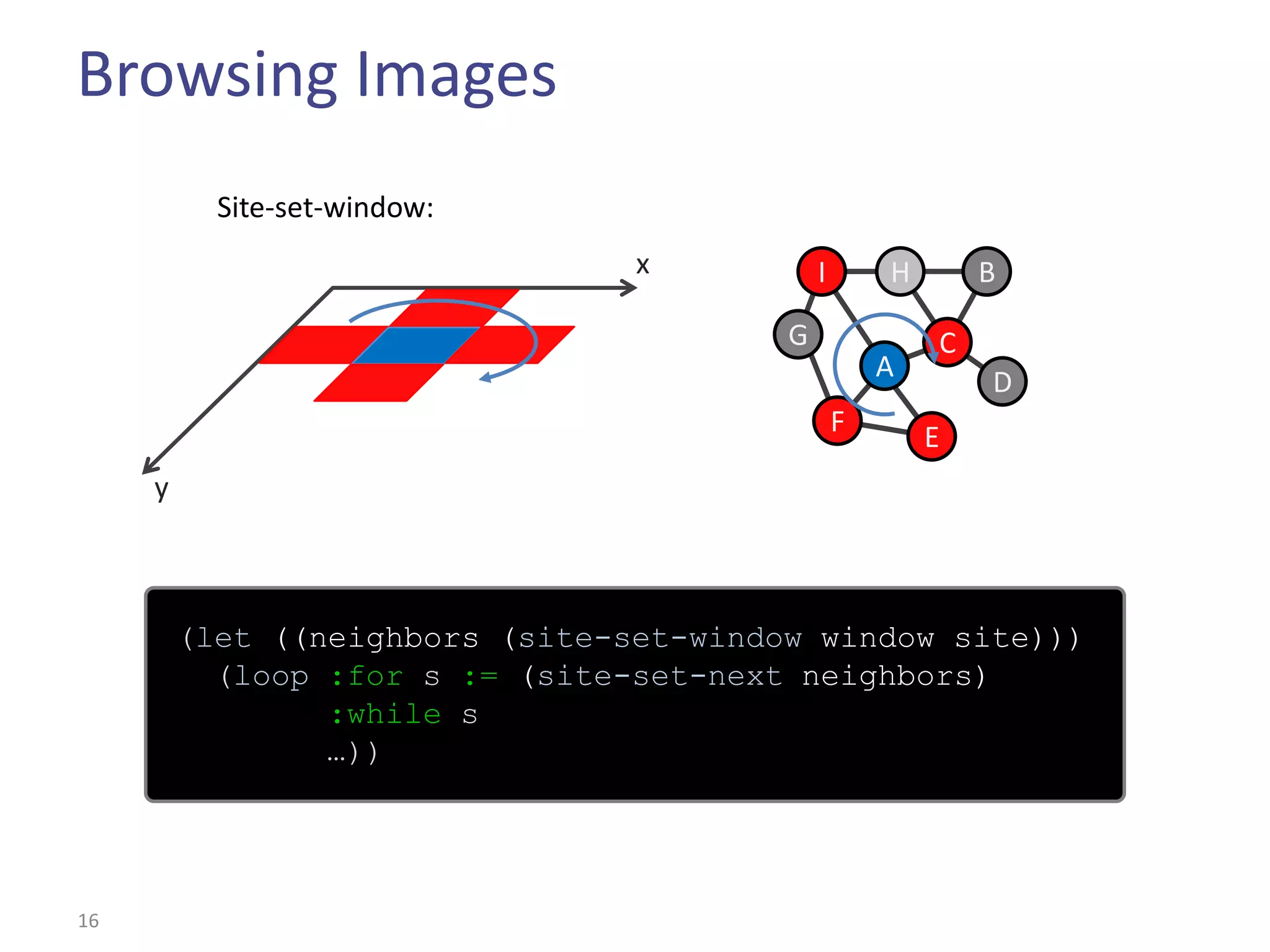
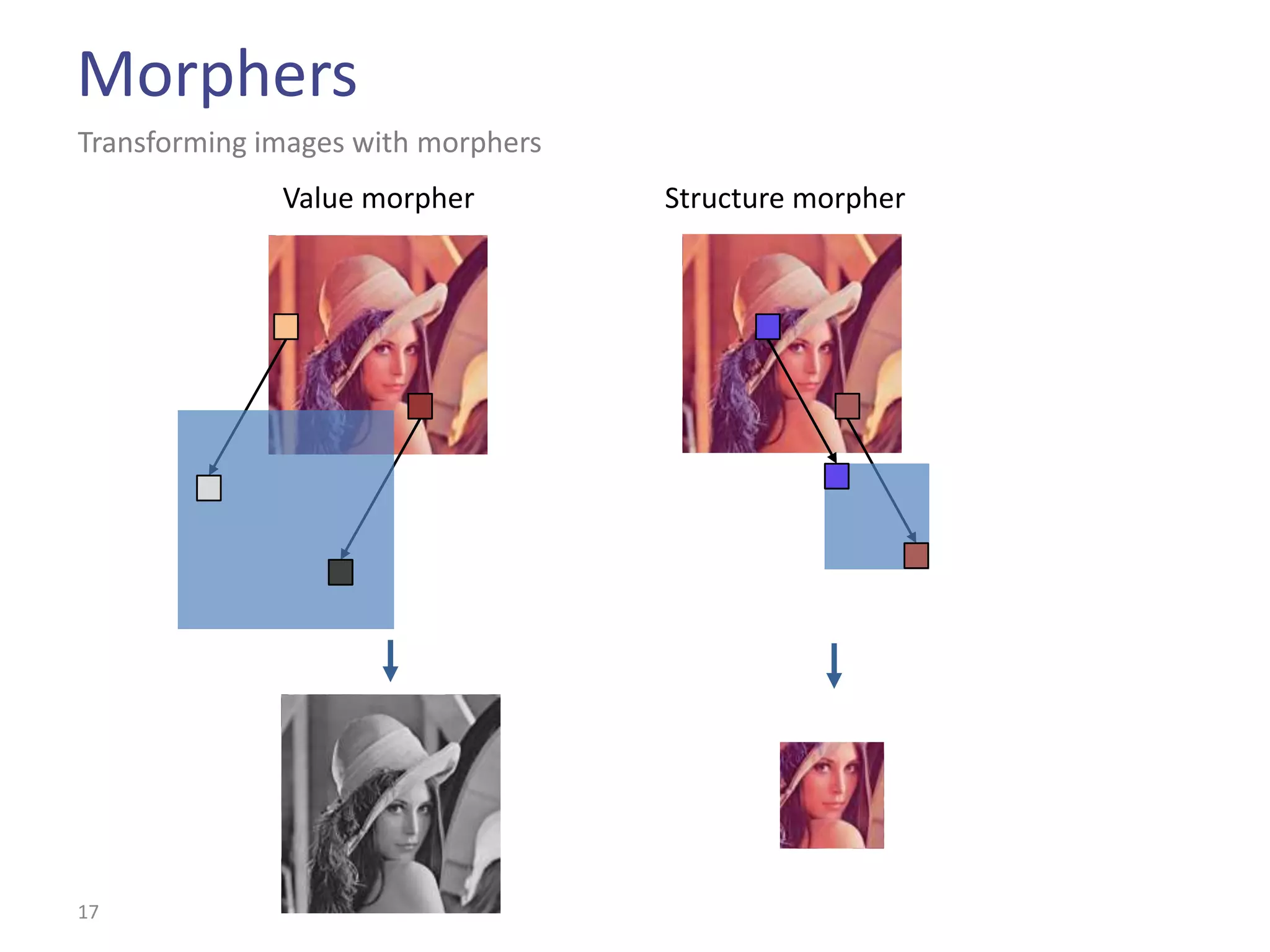
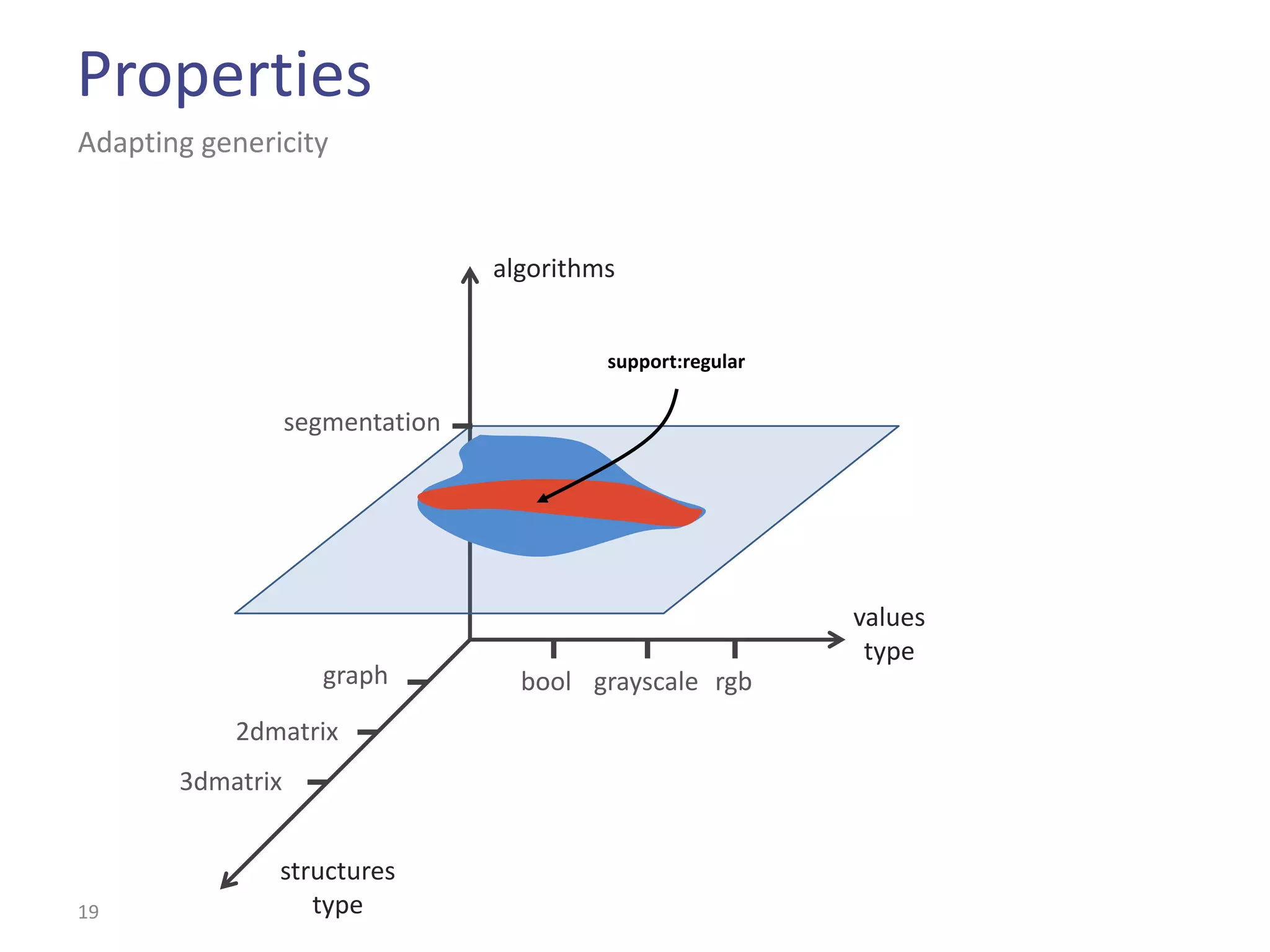
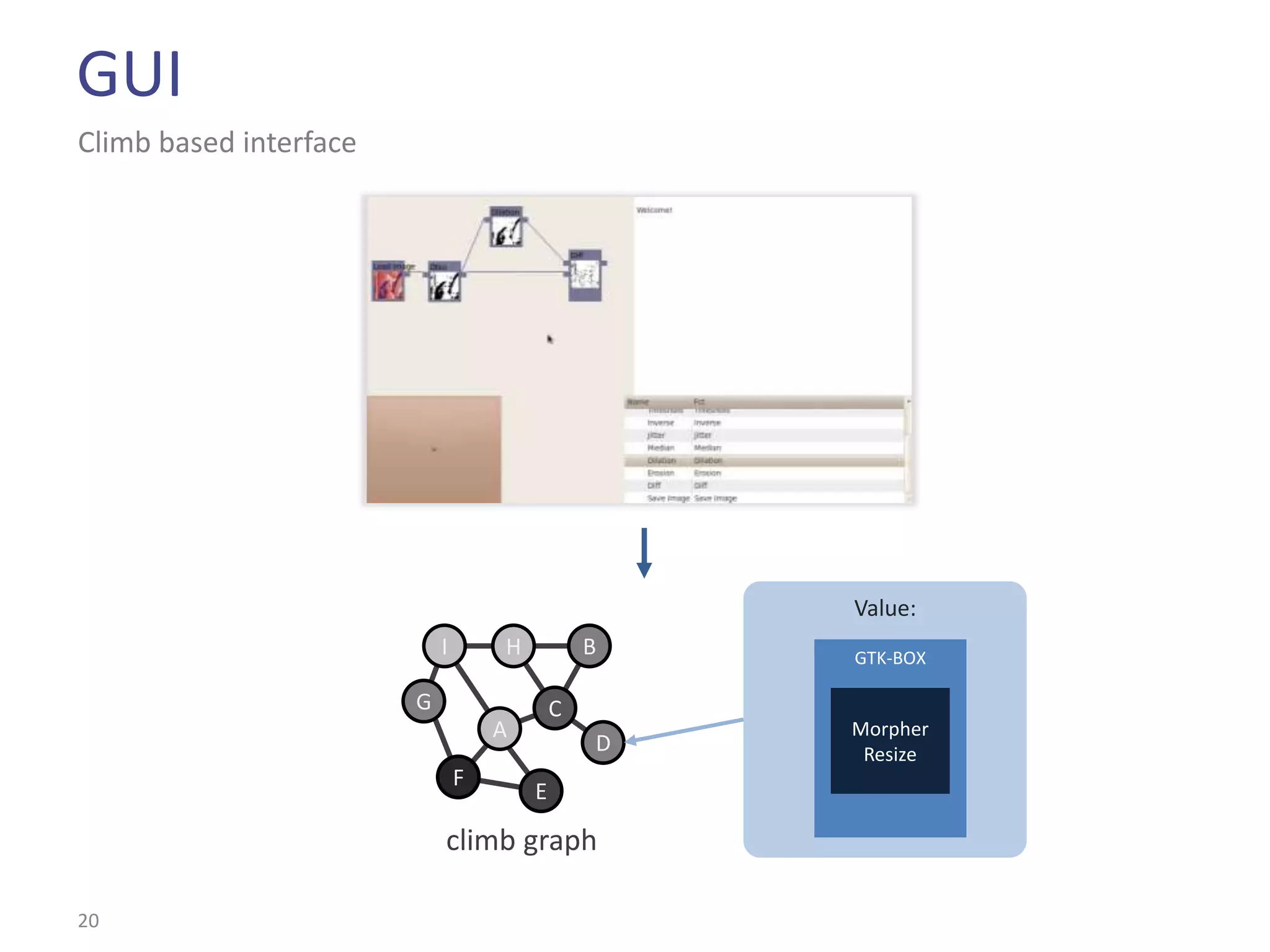
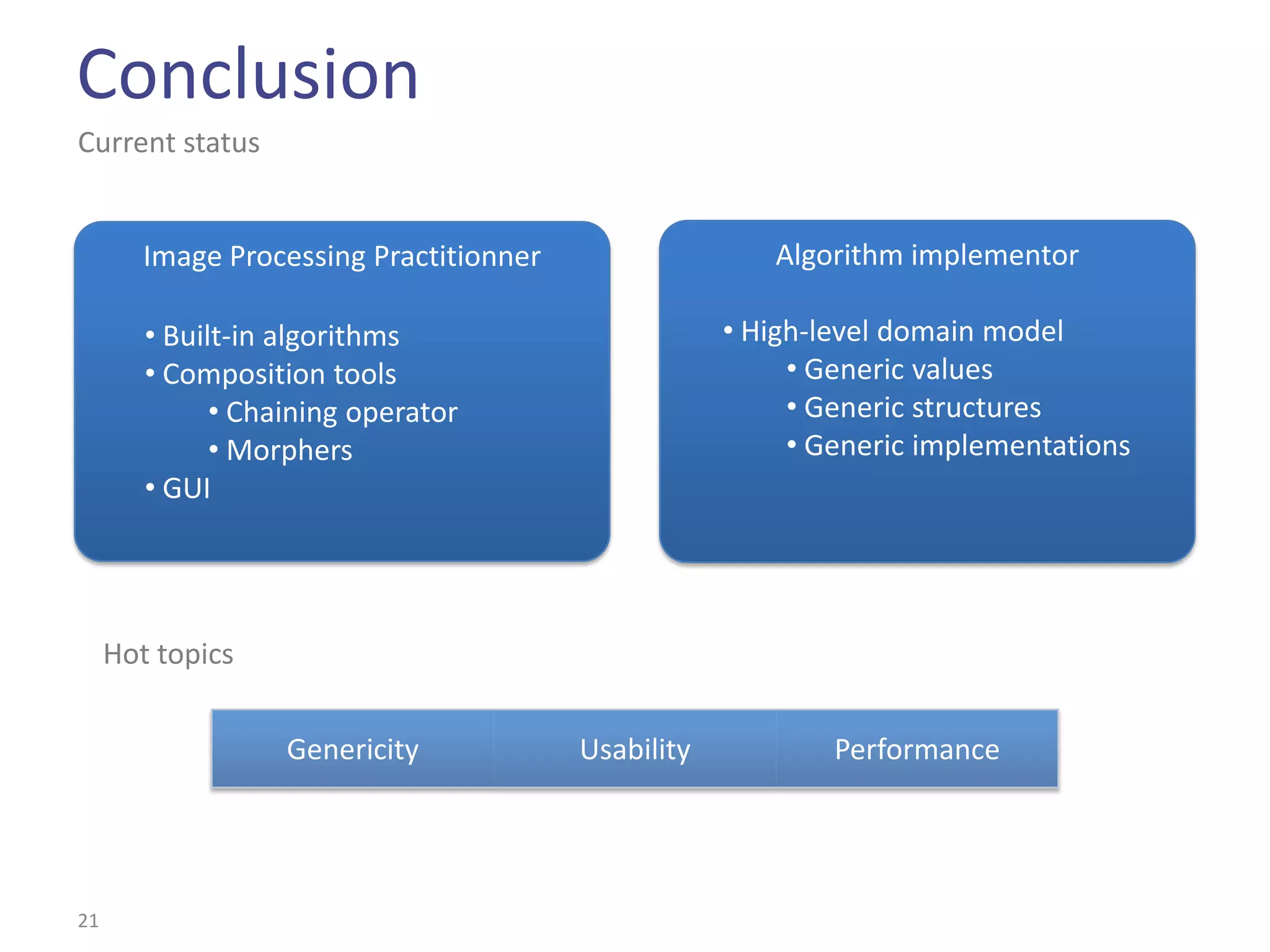
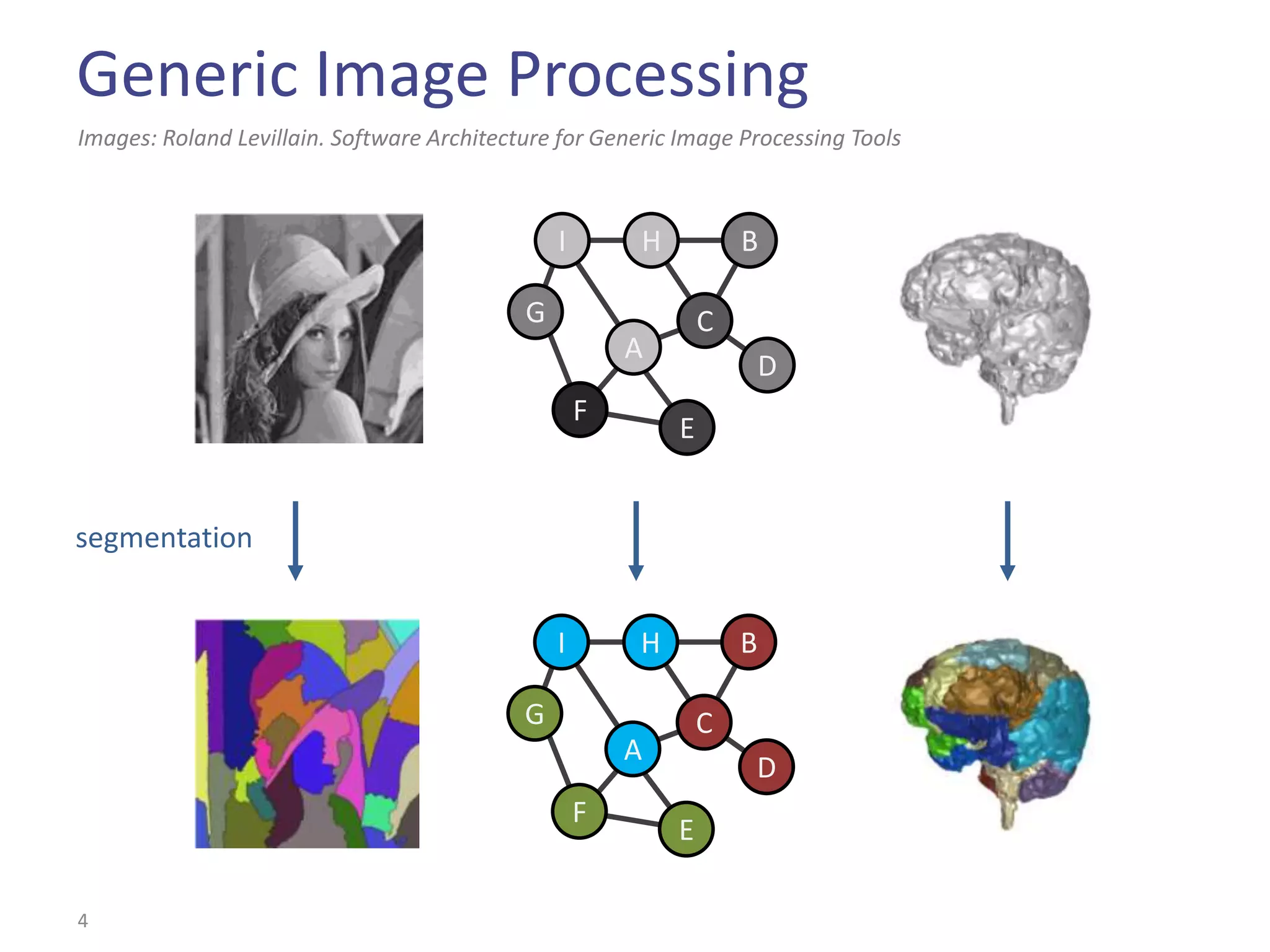
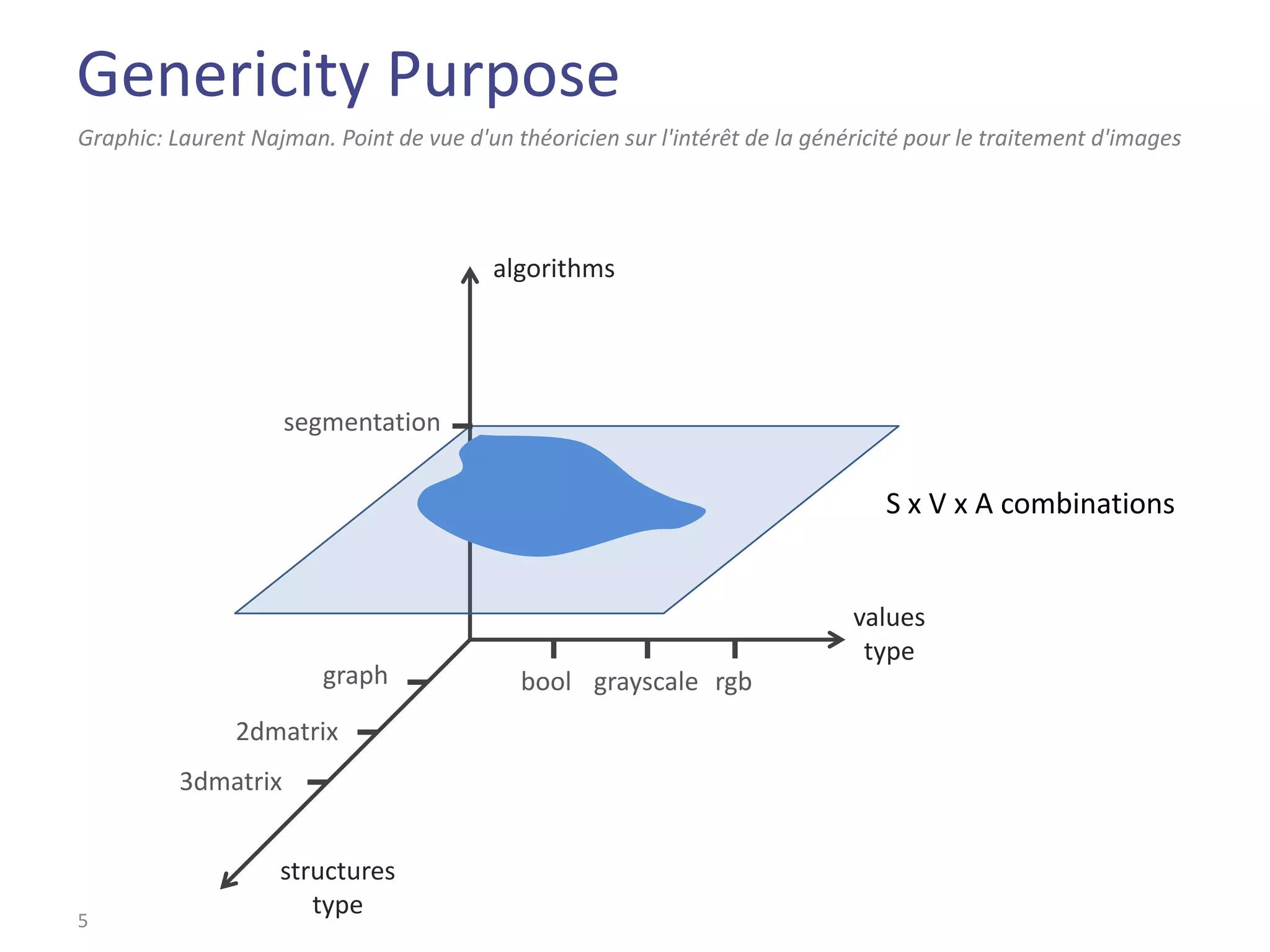
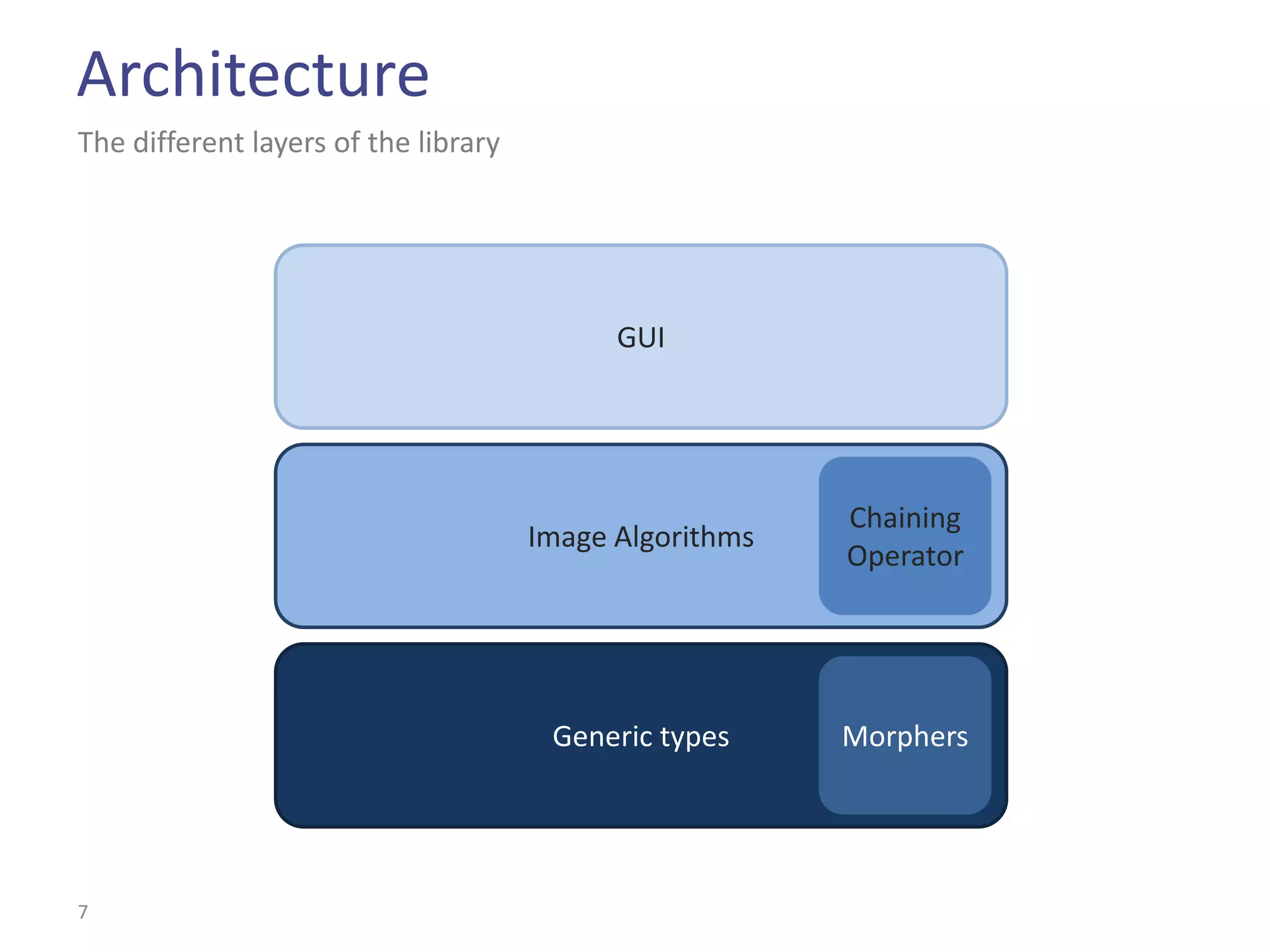
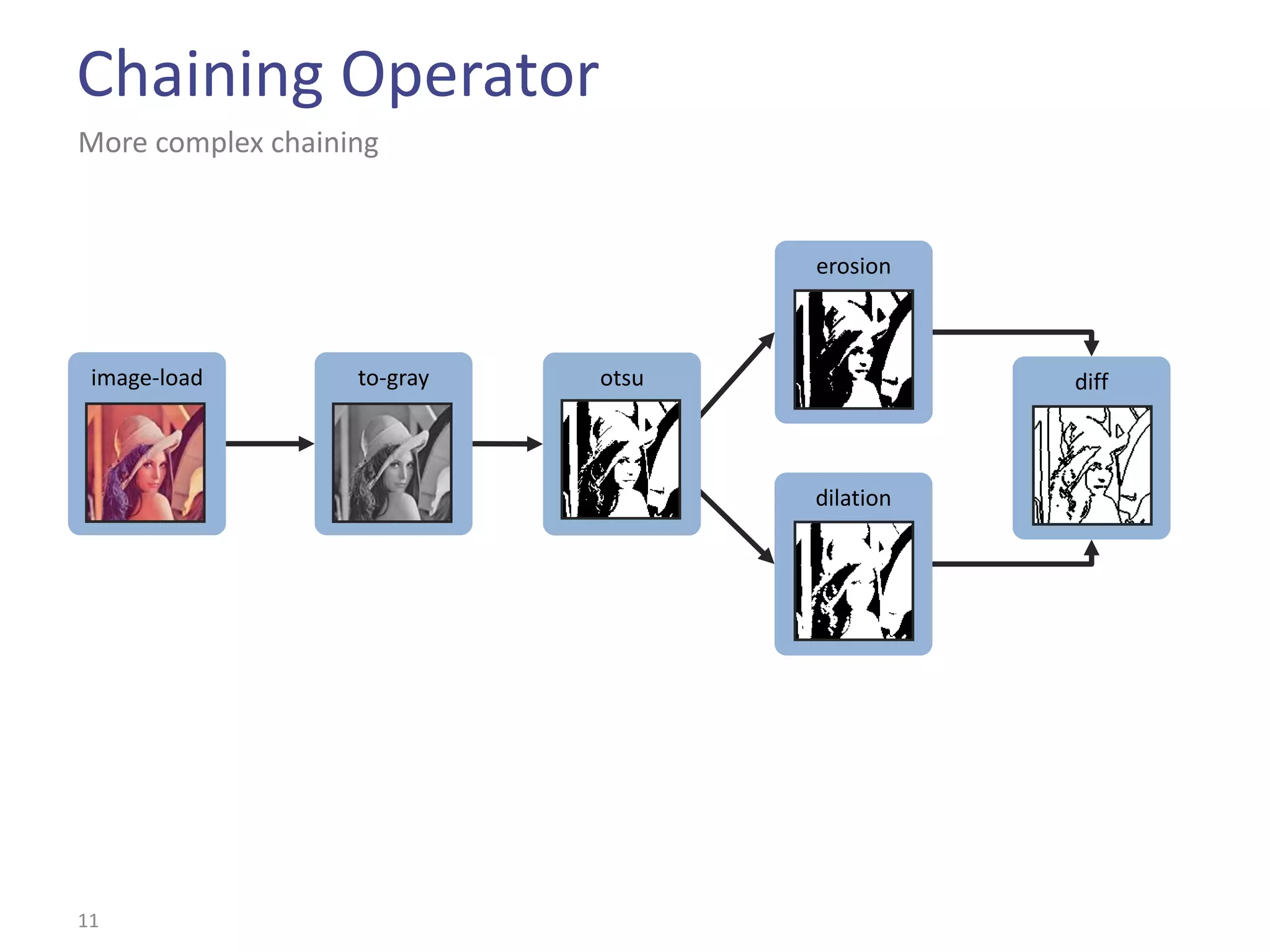
This document summarizes the Climb image processing library. Climb allows generic image processing through algorithms that can process different image types defined by their values (e.g. bool, grayscale, RGB) and sites (e.g. 2D points, graphs). The library provides common algorithms, chaining operators to combine them, and a GUI. It aims to balance genericity with usability and performance. The document outlines Climb's architecture, use, development aspects like the image definition, and potential future directions around genericity, usability, and performance.







![Image Definition
I H B
G C
A
D
F
E
Image access
• matrix[x, y] → pixelvalue
• graph.getNode(label) → nodevalue
• model[x, y, z] → voxelvalue
Generalization: image(site) = value
Lisp: (setf (iref image site) value)
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climb-v6-120502060810-phpapp02/75/Generic-Image-Processing-With-Climb-Slides-13-2048.jpg)