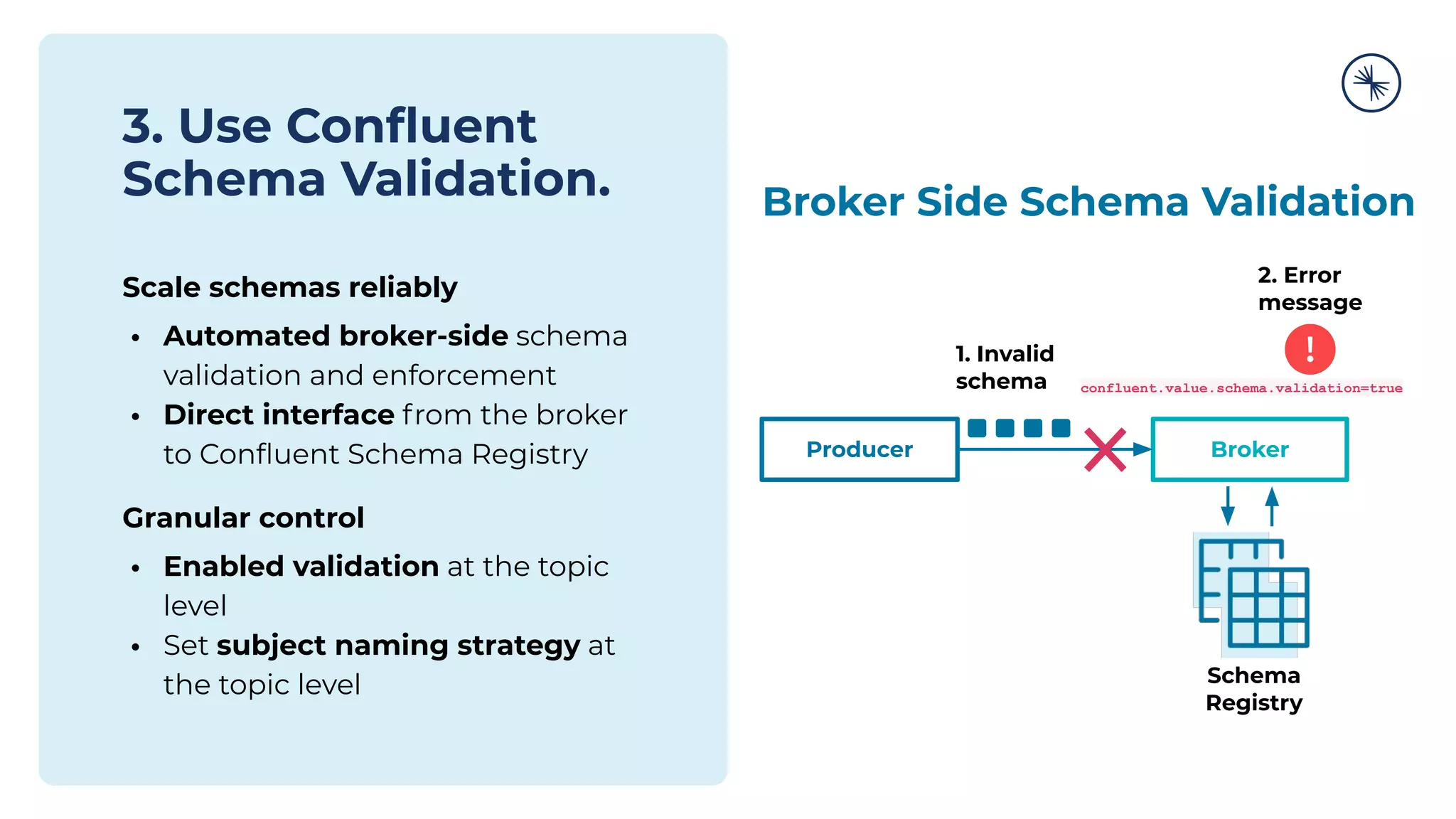
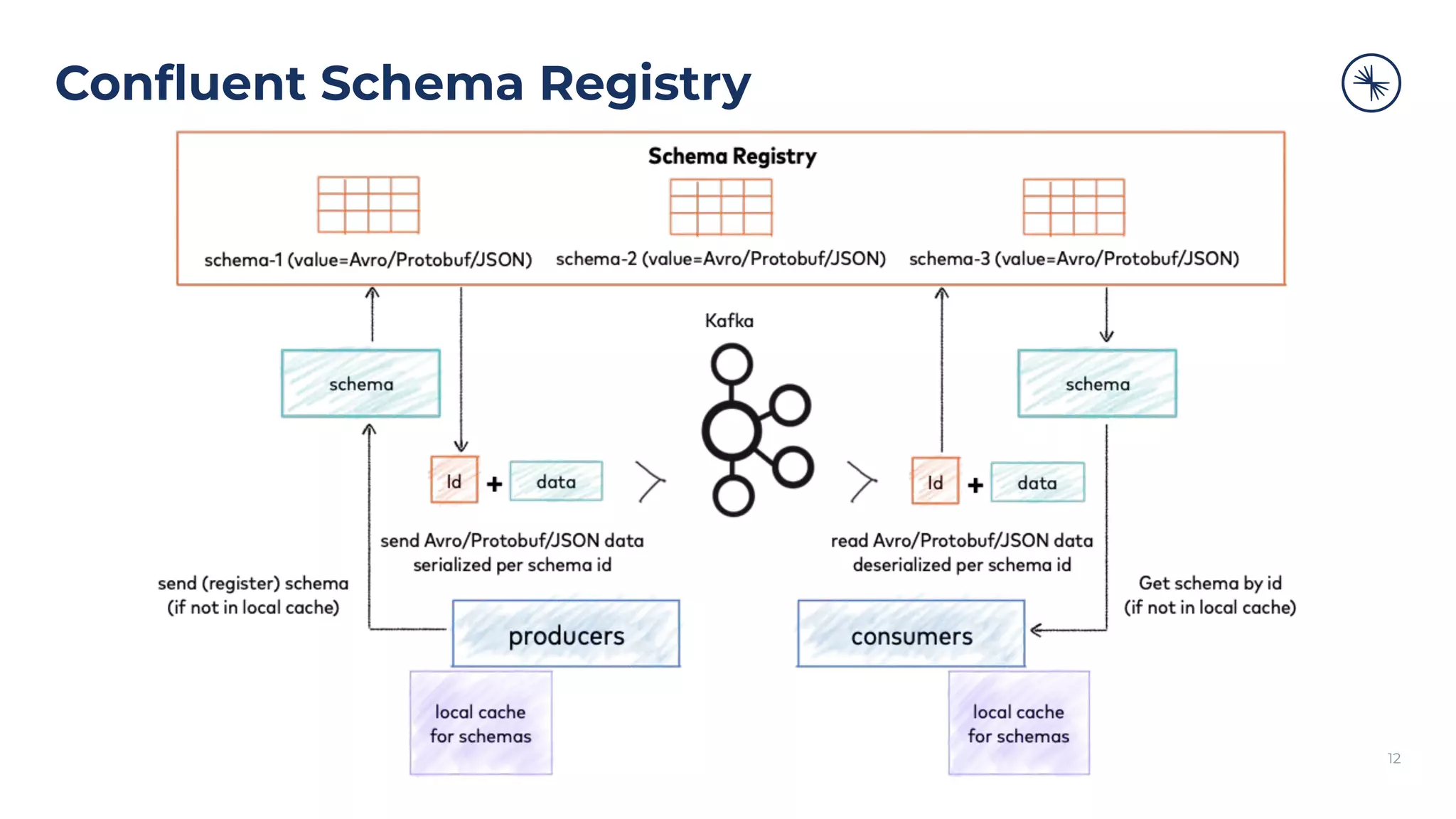
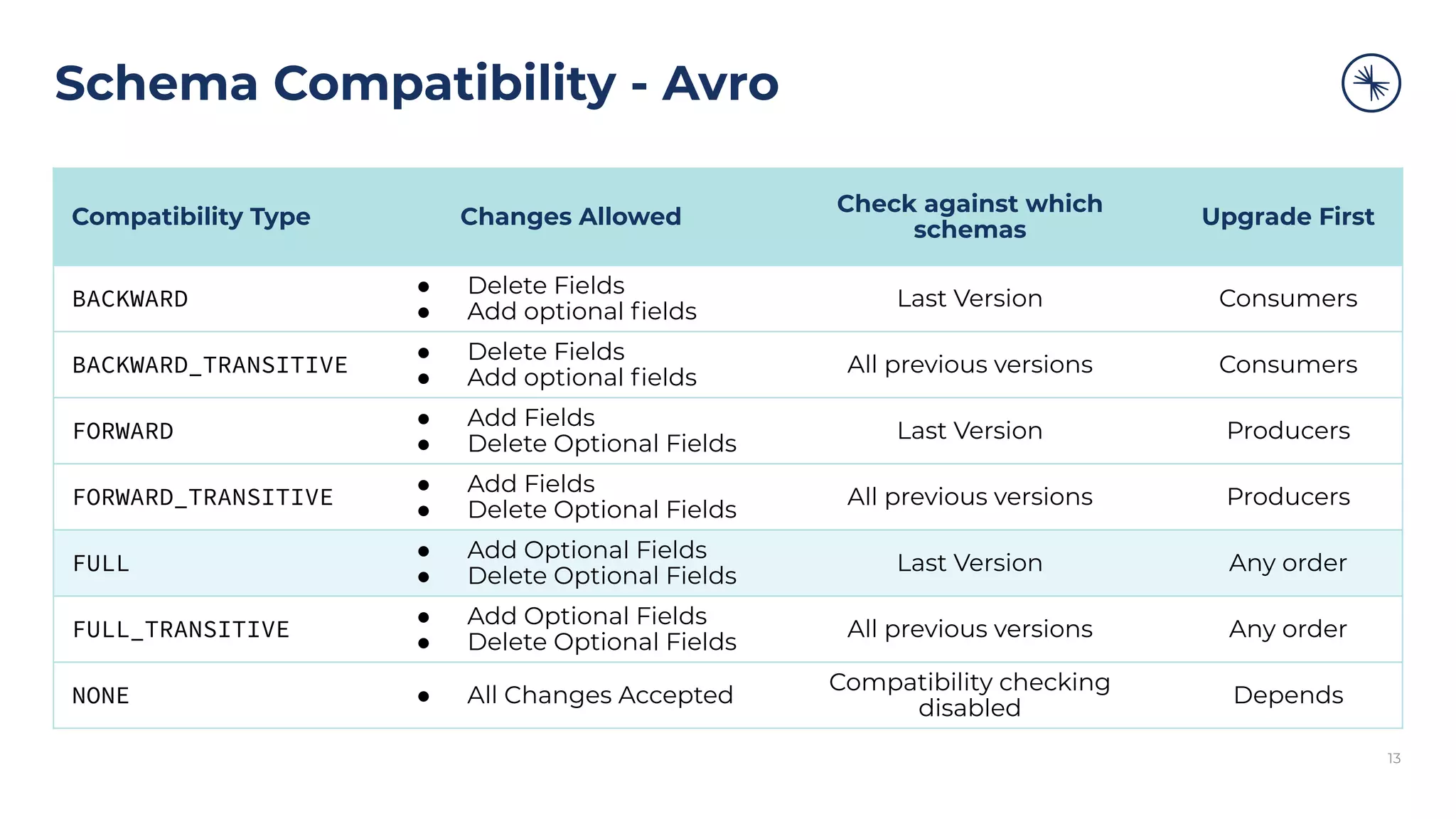
The document discusses the Confluent Schema Registry and its importance in managing schema evolution in Kafka by preventing issues caused by incompatible schema changes. It outlines best practices for schema management, including avoiding automatic schema registration in production, creating new topics for breaking compatibility, and utilizing broker-side schema validation. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of having a robust CI/CD process for handling schemas to ensure consistent data compatibility across consumers.




![What Happened?
10
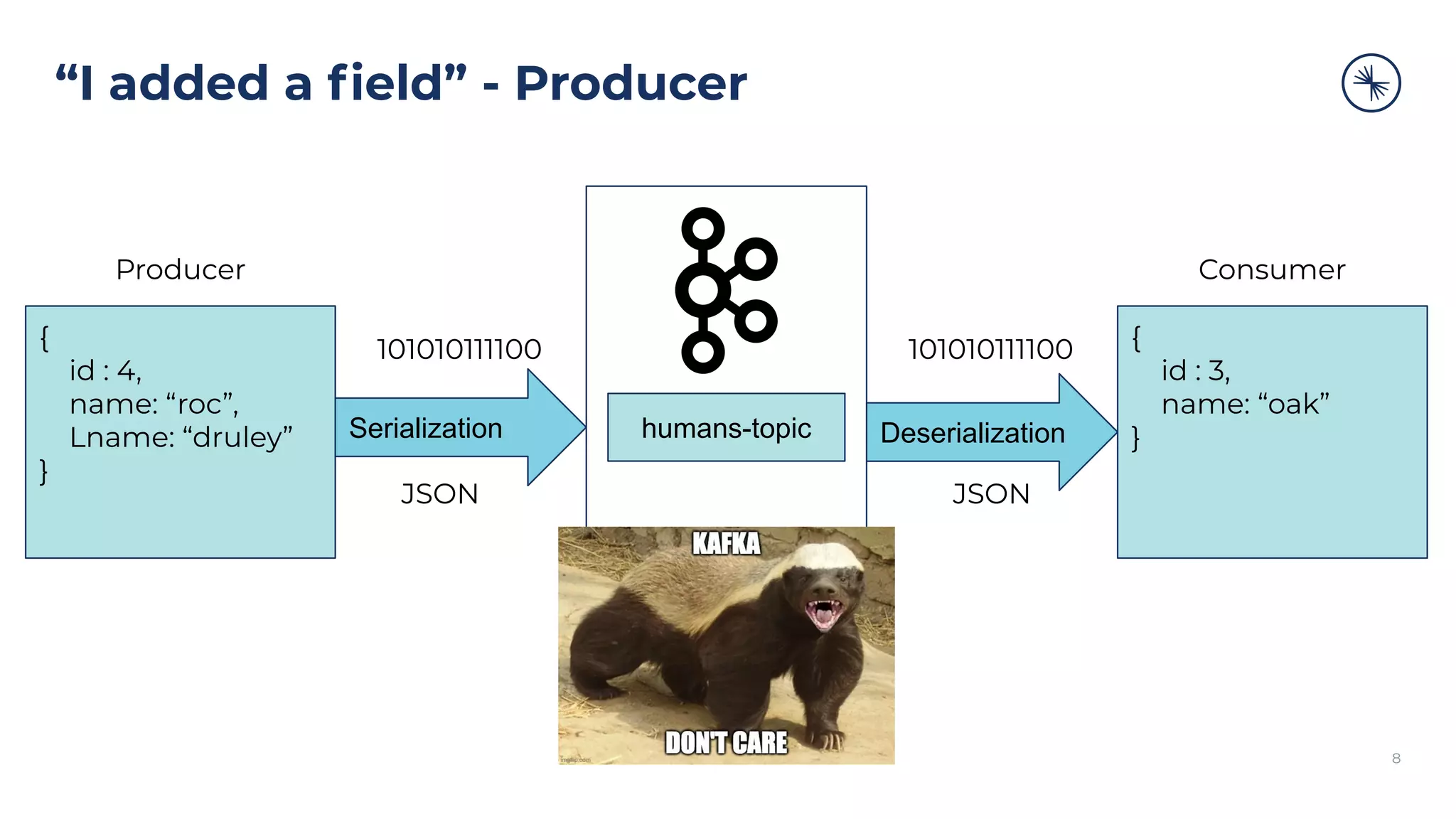
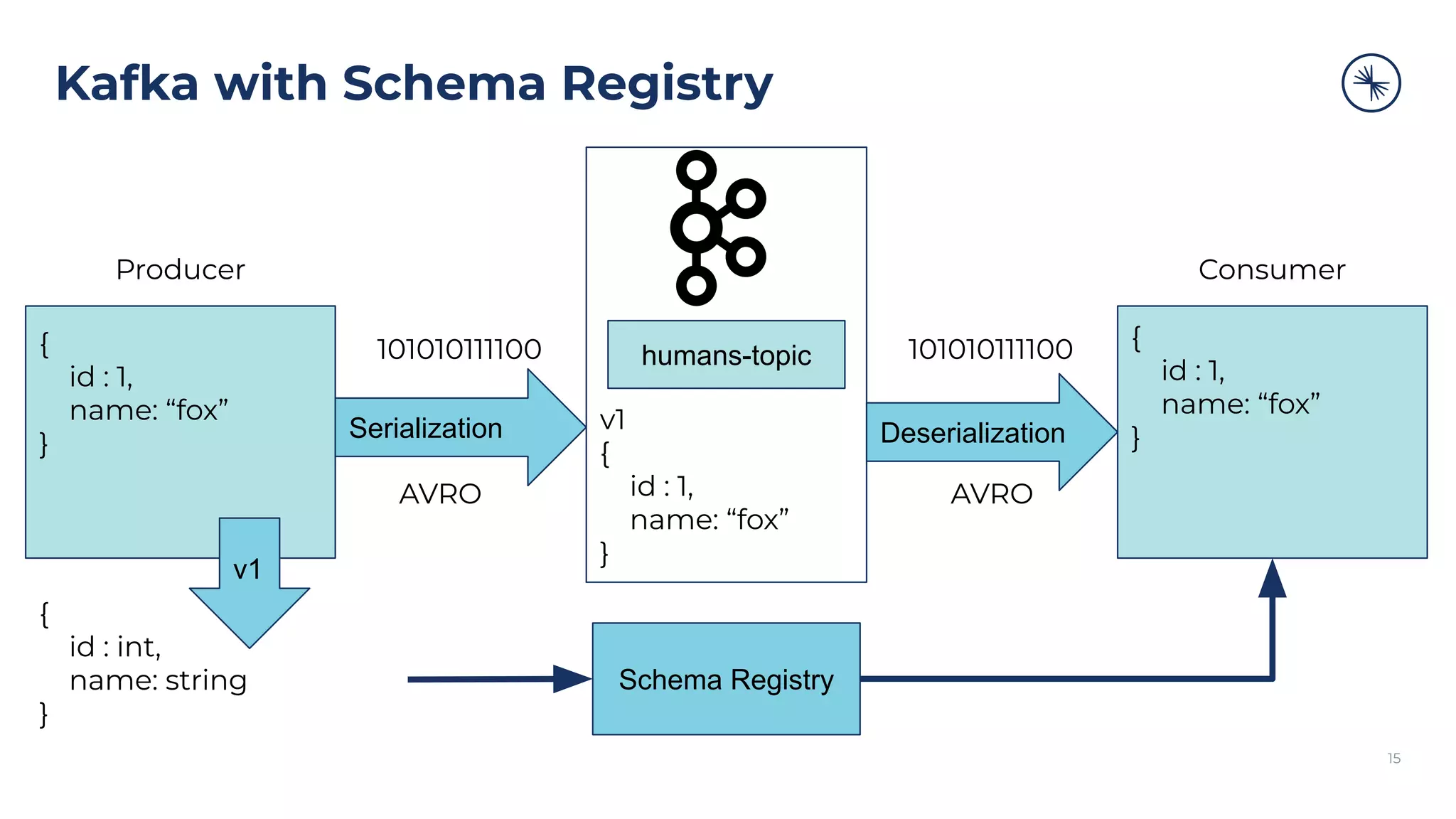
{
id : 1,
name: “patrick”
}
{
id : 2,
name: “roc”
}
{
id : 3,
name: “oak”
}
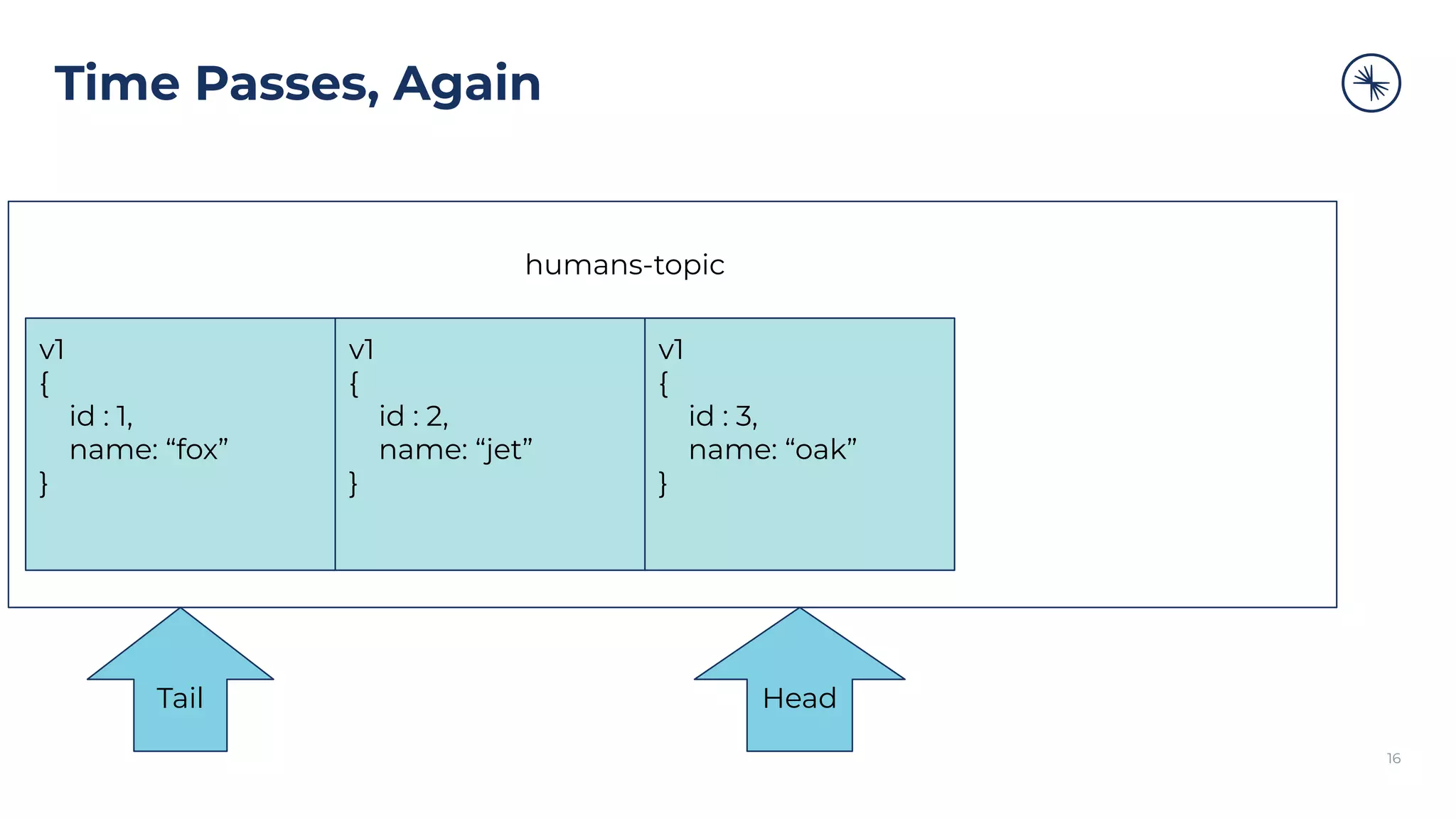
humans-topic
Tail Head
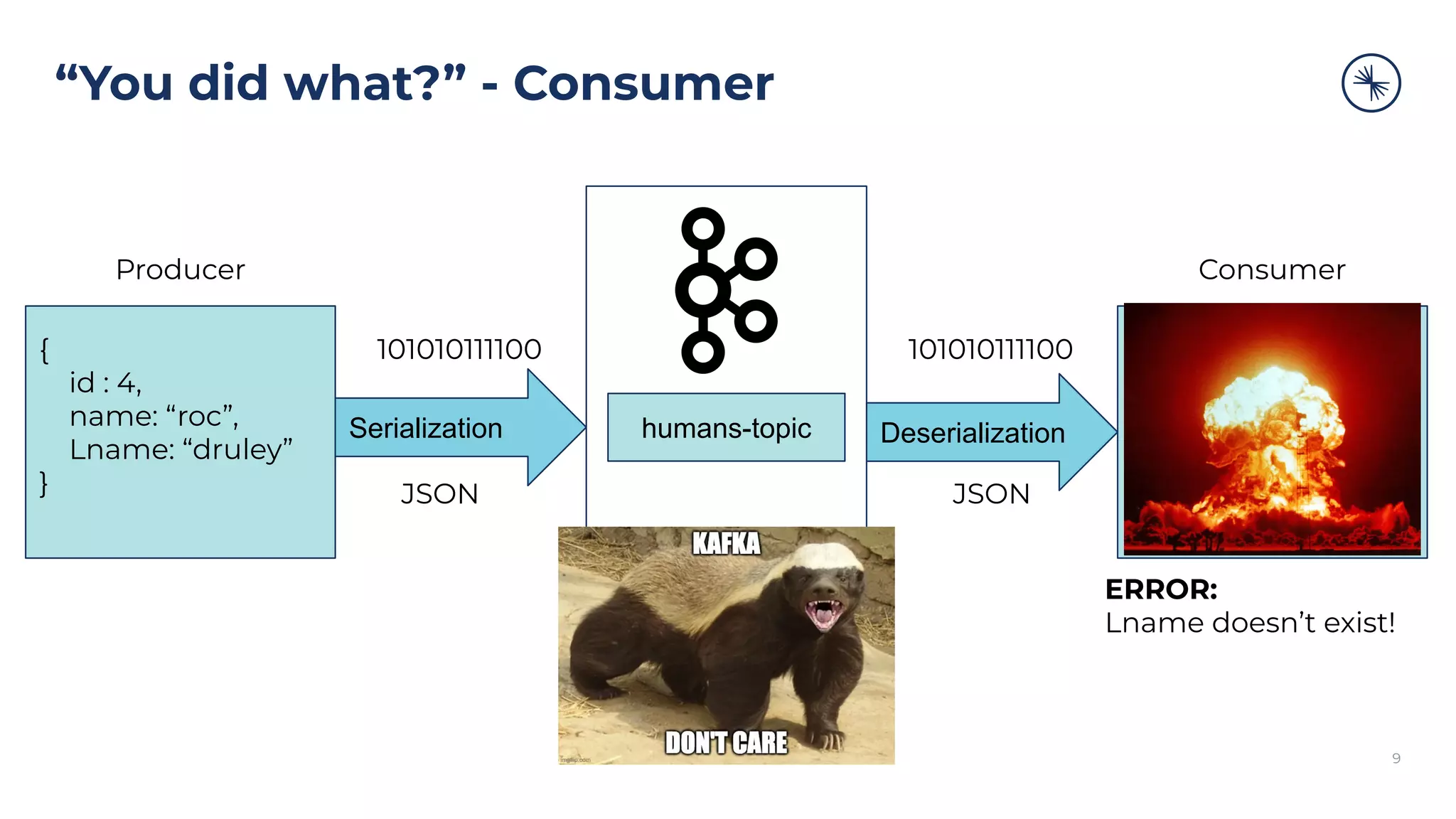
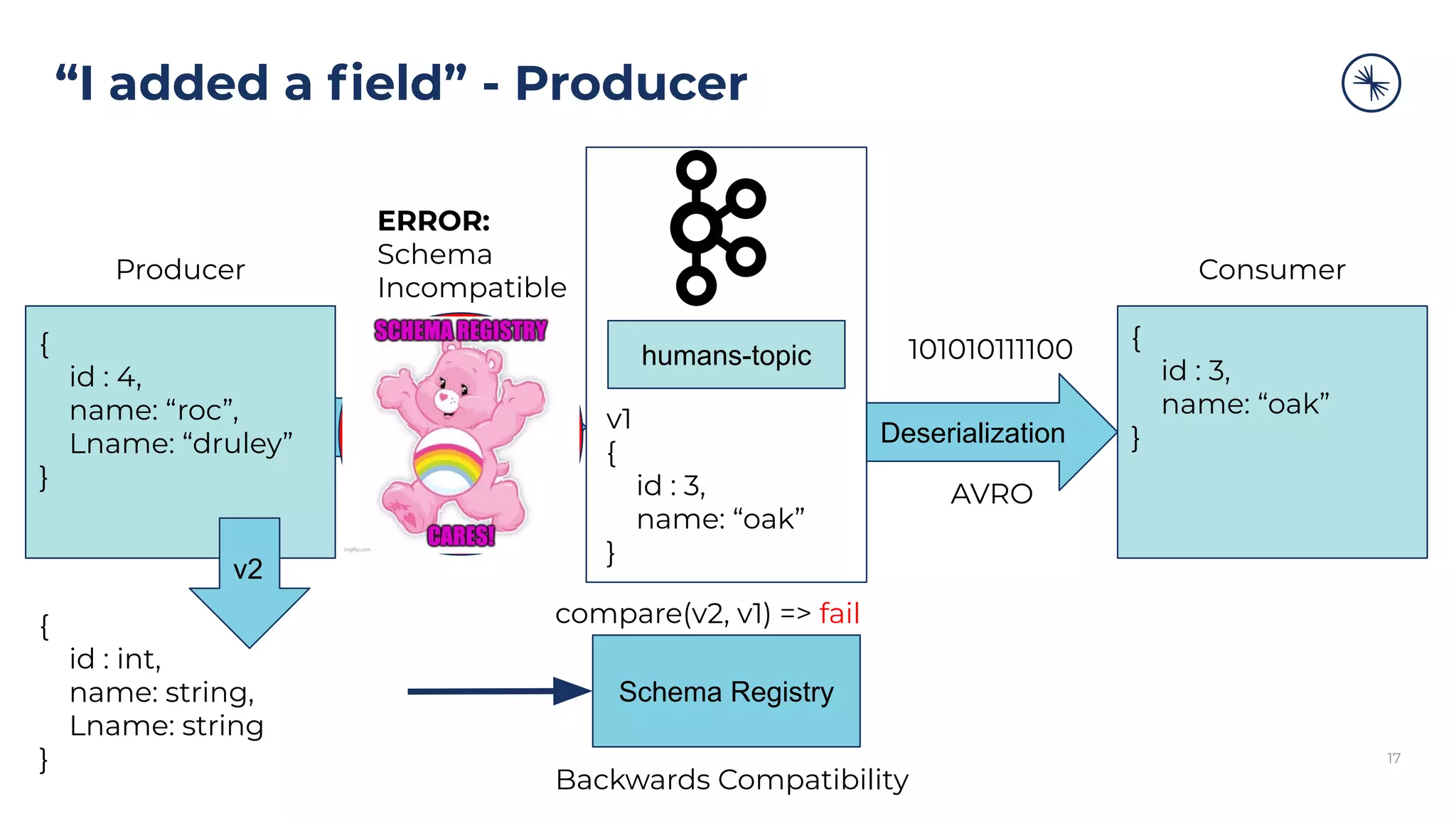
{
id : 4,
name: “roc”,
Lname: “druley”
}
Consumer code breaks:
#new field Lname
Lname = humans[“Lname”]
KeyError: 'Lname'
Consumer
But there’s no “Lname”
in event 3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettingstartedwithconfluentschemaregistry-200909190617/75/Getting-Started-with-Confluent-Schema-Registry-10-2048.jpg)

![Subject Naming Strategies
14
TopicNameStrategy
Subject Name =
Topic Name + [key|value]
Example:
Topic Name = mytopic
Value Subject Name = mytopic-value
Default
RecordNameStrategy
Subject Name =
Record Name + [key|value]
Example:
{"type":"record",
"name":"myrecord",
"fields":
[{"name":"f1",
"type":"string"}]
}
Value Subject Name = myrecord-value
Time Ordered Events
TopicRecordNameStrategy
Subject Name =
Topic Name + Record Name + [key|value]
Example:
Topic Name = mytopic
Record Name = myrecord
Value Subject Name = mytopic-myrecord-value
Most Granular
https://docs.confluent.io/current/schema-registry/serdes-develop/index.html#subject-name-strategy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettingstartedwithconfluentschemaregistry-200909190617/75/Getting-Started-with-Confluent-Schema-Registry-14-2048.jpg)
![“I added an optional field” - Producer
18
{
id : 4,
name: “roc”,
Lname: “druley”
}
Serialization
humans-topic
Deserialization
{
id : 3,
name: “oak”,
Lname: “druley”
}
101010111100 101010111100
Producer Consumer
AVRO AVRO
{
id : int,
name: string,
Lname: string [druley]
}
Schema Registry
v1
{
id : 3,
name: “oak”
}v2
use “druley” as the default,
it’s optional
Backwards Compatibility
compare(v2, v1) => ok](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettingstartedwithconfluentschemaregistry-200909190617/75/Getting-Started-with-Confluent-Schema-Registry-18-2048.jpg)