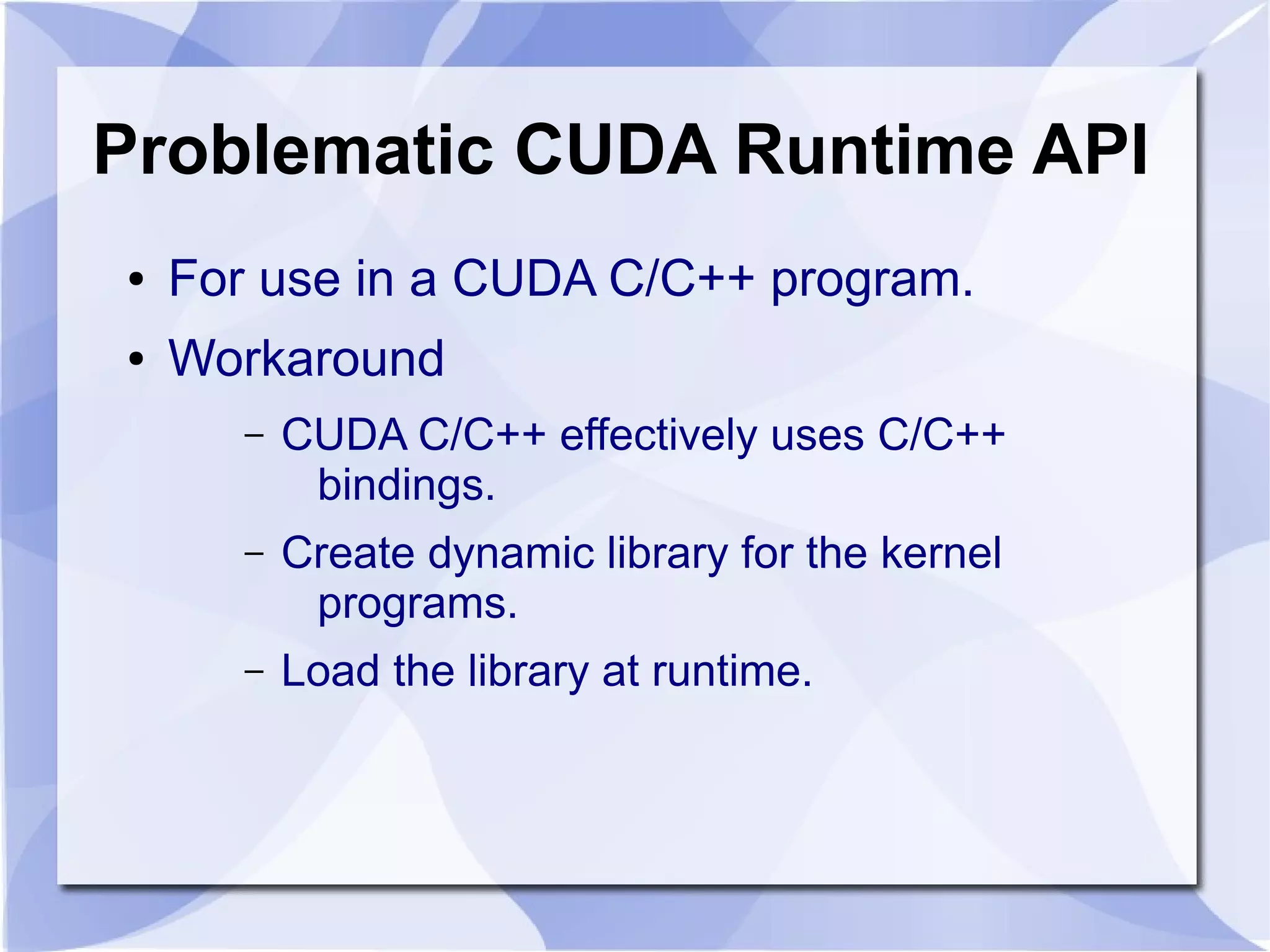
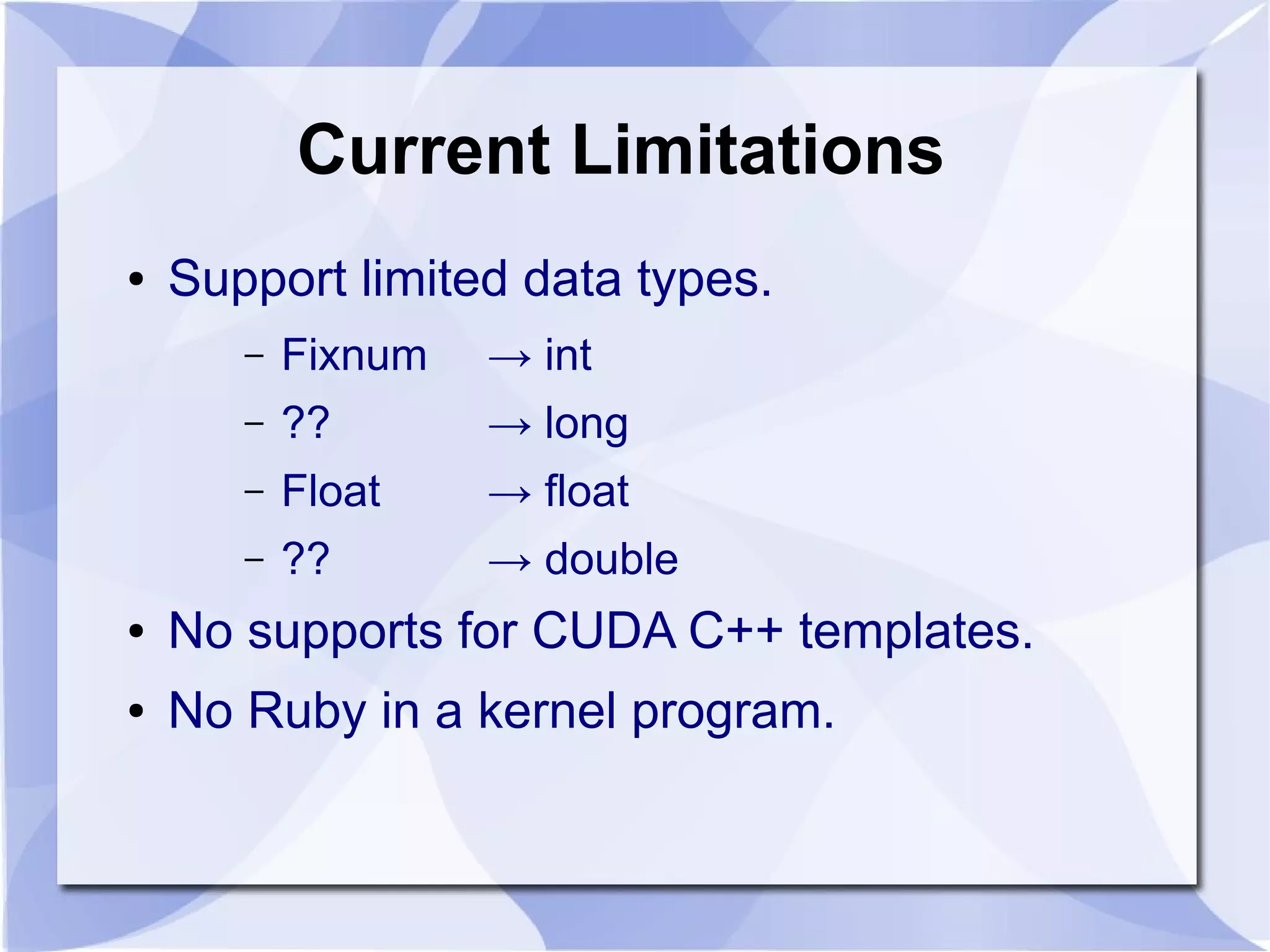
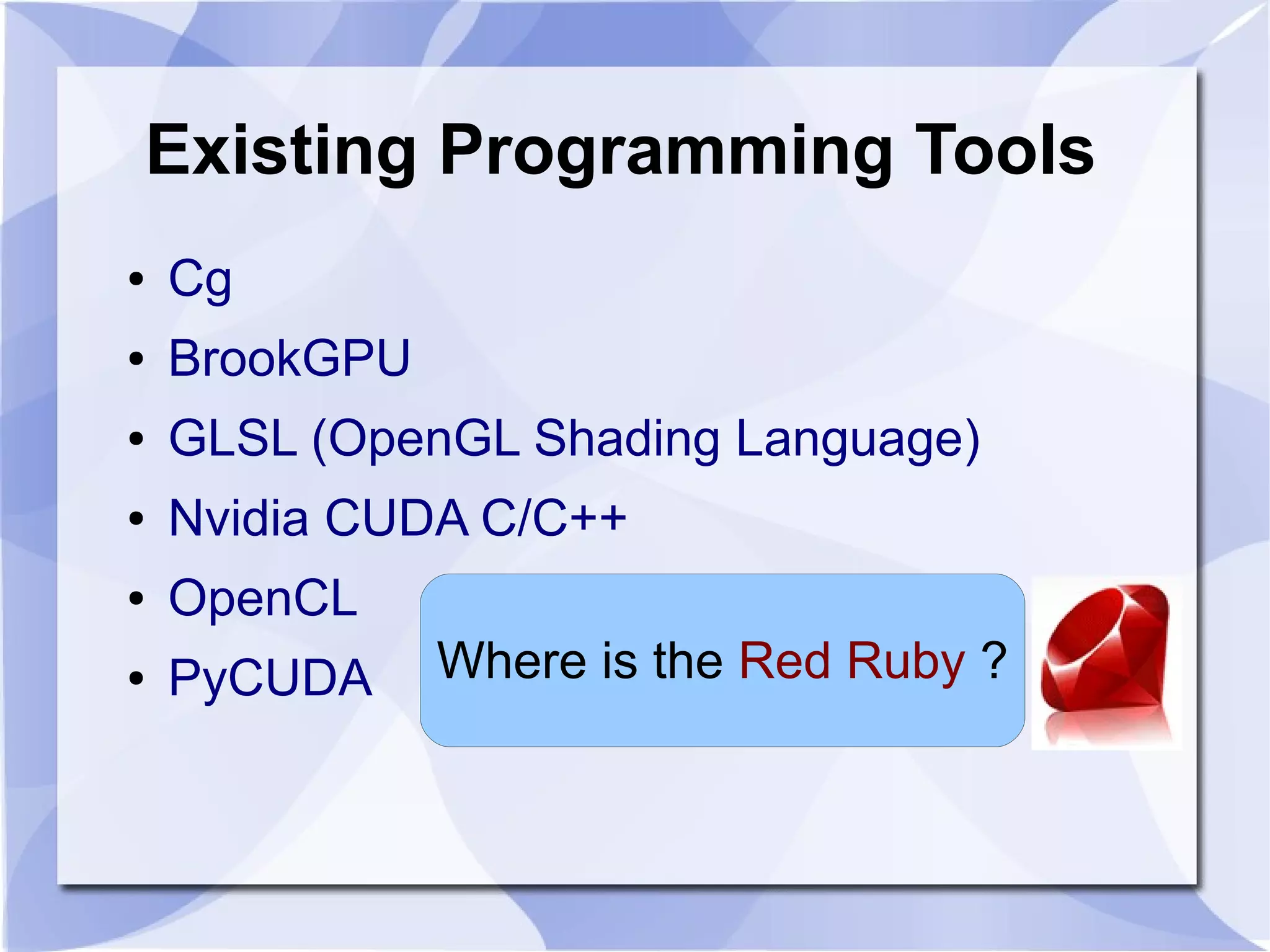
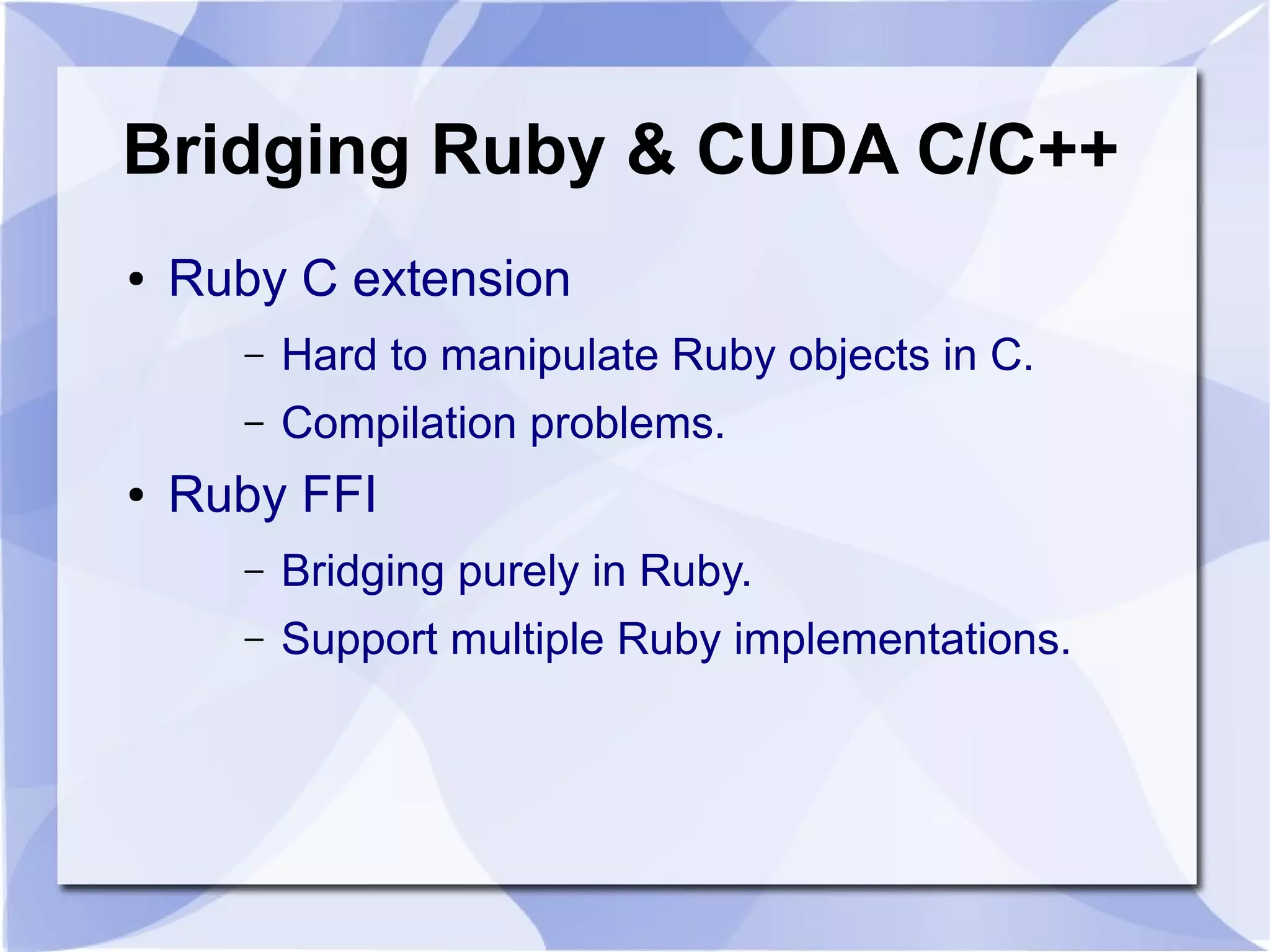
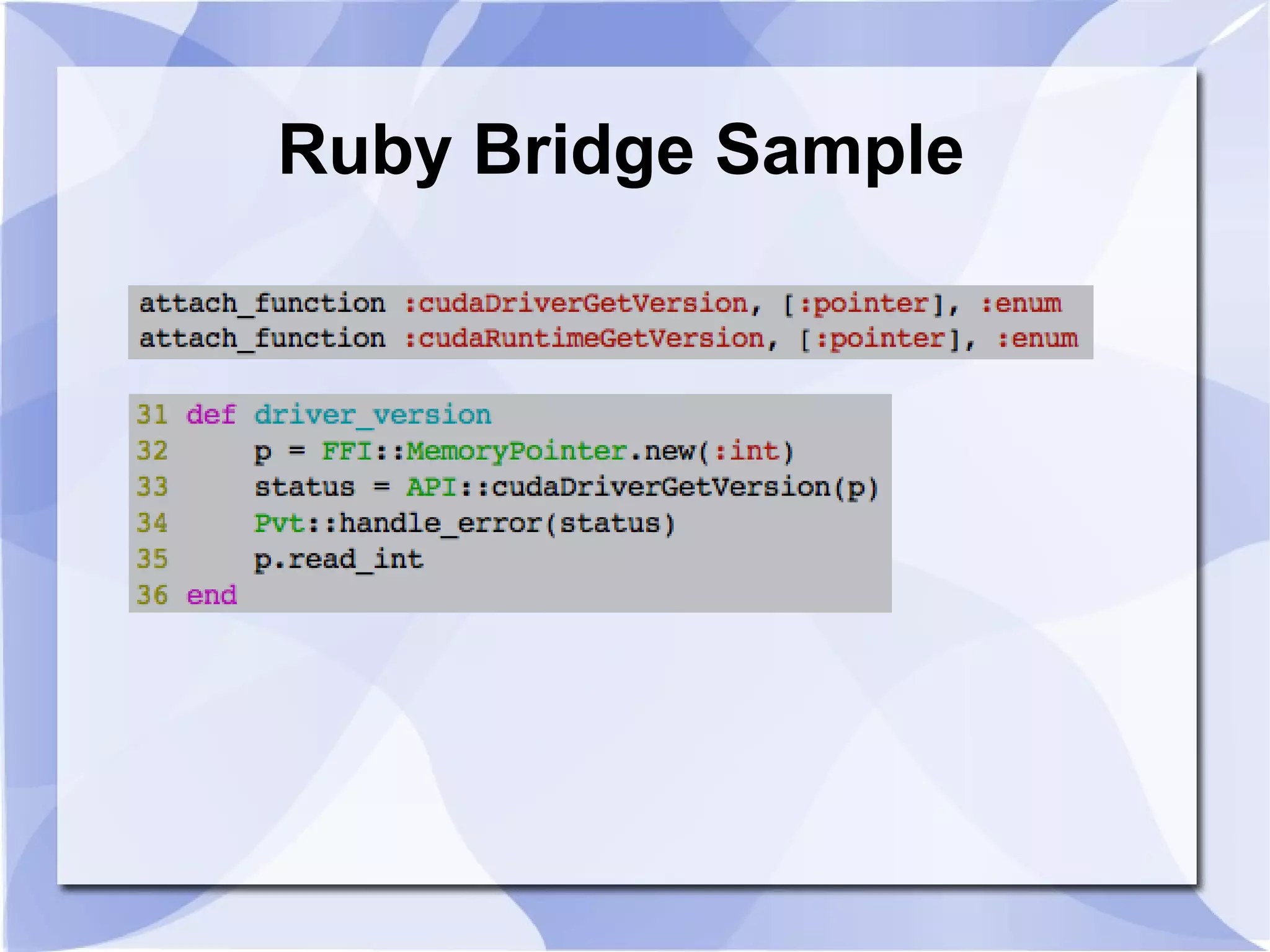
The document introduces SGC Ruby CUDA, a Ruby library that provides an object-oriented API for CUDA programming to bridge Ruby and CUDA C/C++. It allows performing operations like memory allocation and transfer as well as kernel launching from Ruby. The library aims to make CUDA programming accessible from Ruby while hiding complexity of the low-level CUDA driver and runtime APIs.

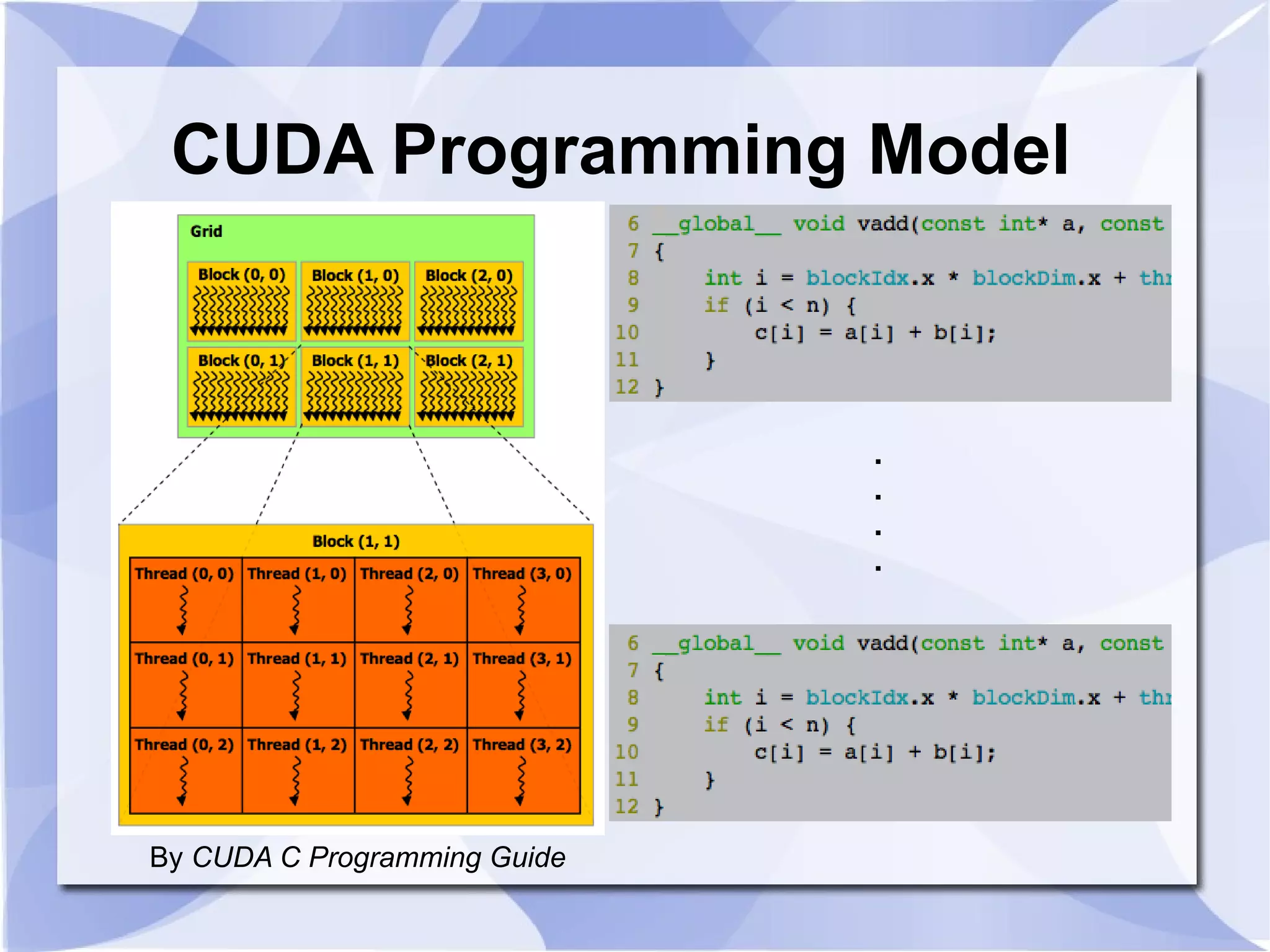

![Using SGC Ruby CUDA
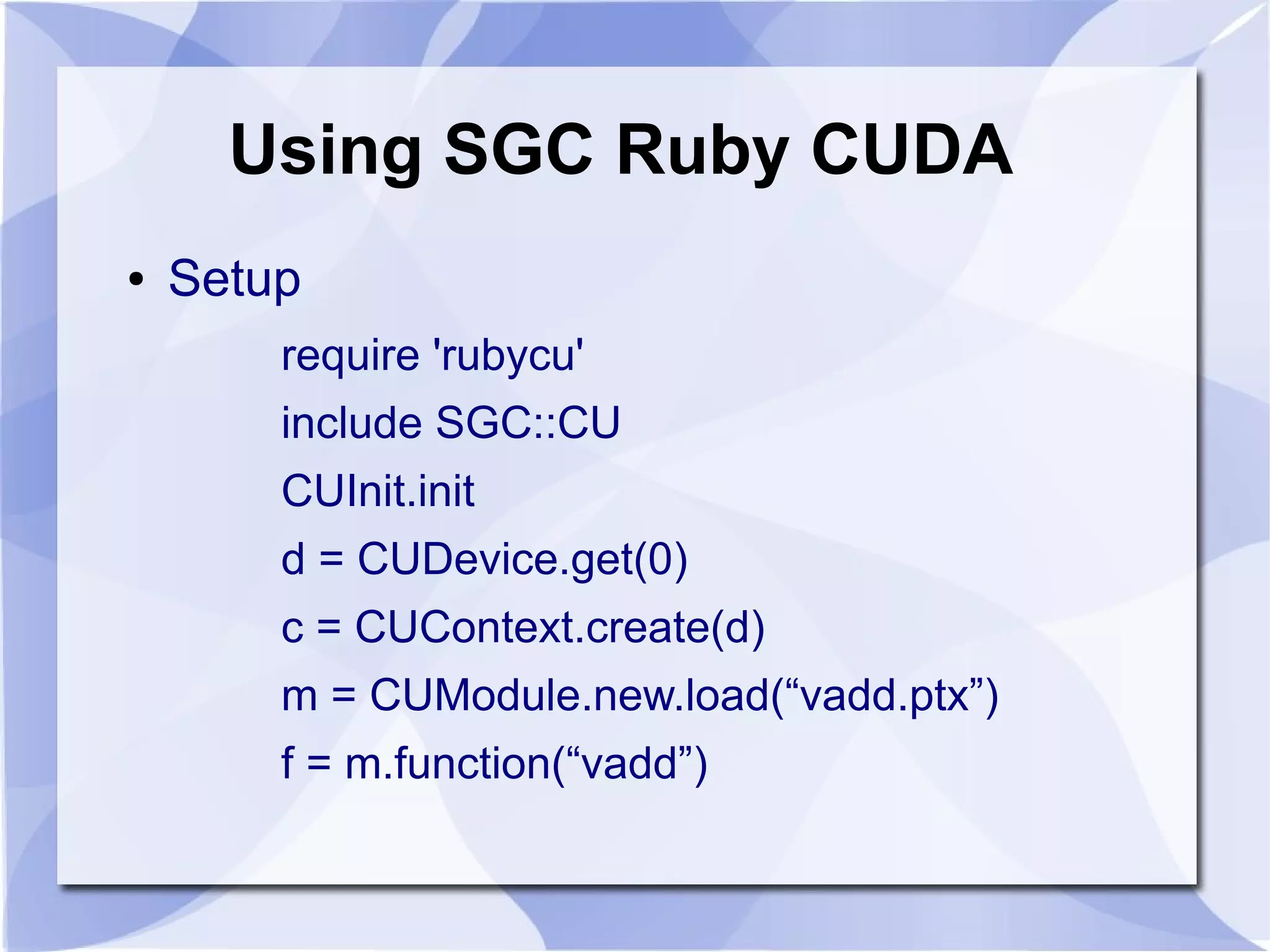
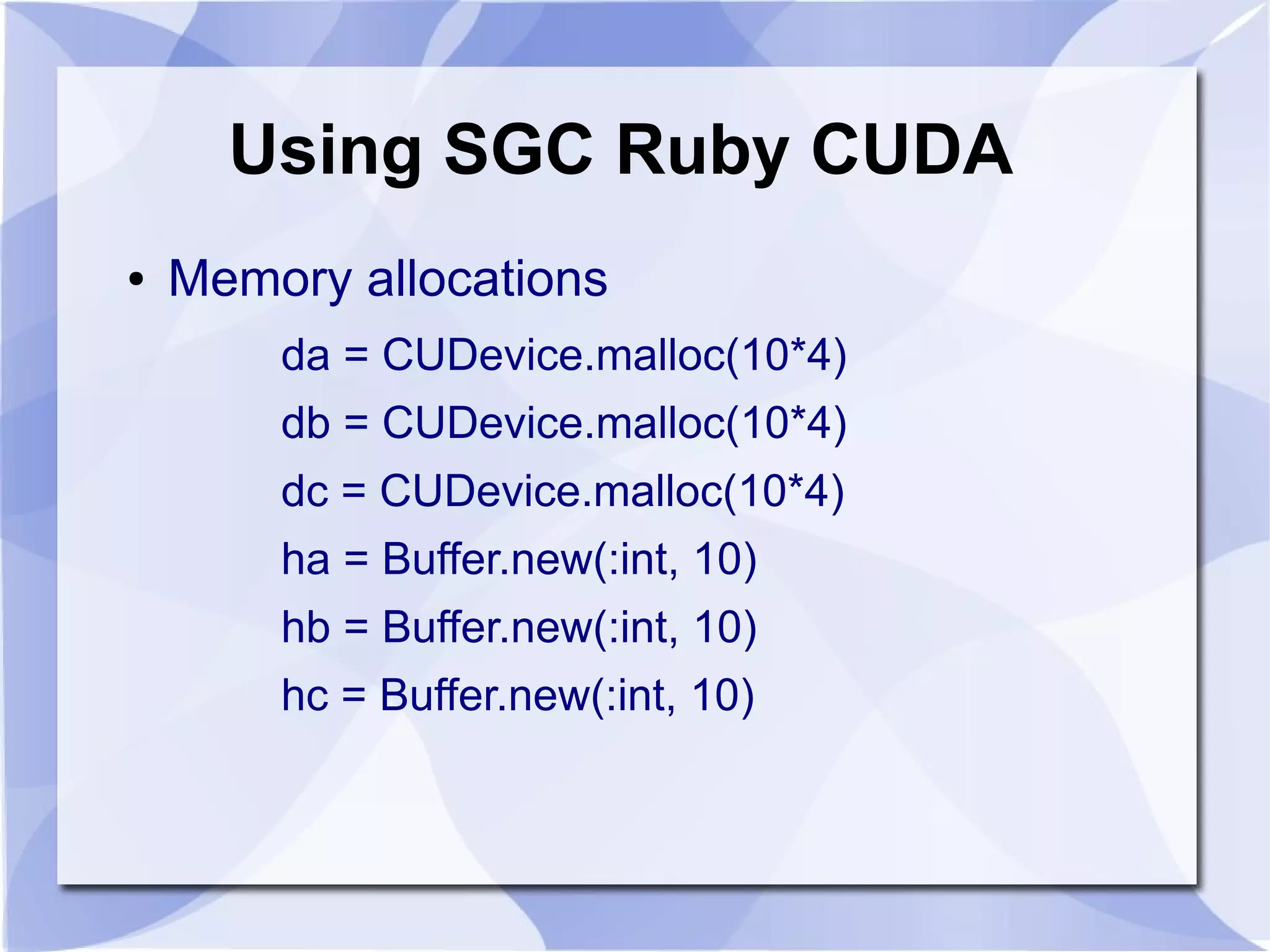
● Initialization
(0...10).each { |i|
ha[i] = i
hb[i] = 1
hc[i] = ha[i] + hb[i]
hd[i] = 0
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gpucomputingwithruby-110423205748-phpapp01/75/GPU-Computing-with-Ruby-13-2048.jpg)

![Using SGC Ruby CUDA
● Launch kernel on GPU
# Launch with 1x1x1 grid,
# 10x1x1 blocks,
params = [da, db, dc, 10]
f.launch_kernel(1, 1, 1, 10, 1, 1, 0, 0, params)
By CUDA C Programming Guide By CUDA C Programming Guide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gpucomputingwithruby-110423205748-phpapp01/75/GPU-Computing-with-Ruby-15-2048.jpg)
![Using SGC Ruby CUDA
● Transfer results back to system memory
CUMemory.memcpy_dtoh(hd, dc, 4*10)
● Verify results
(0...10).each { |i|
assert_equal(hc[i], hd[i])
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gpucomputingwithruby-110423205748-phpapp01/75/GPU-Computing-with-Ruby-16-2048.jpg)