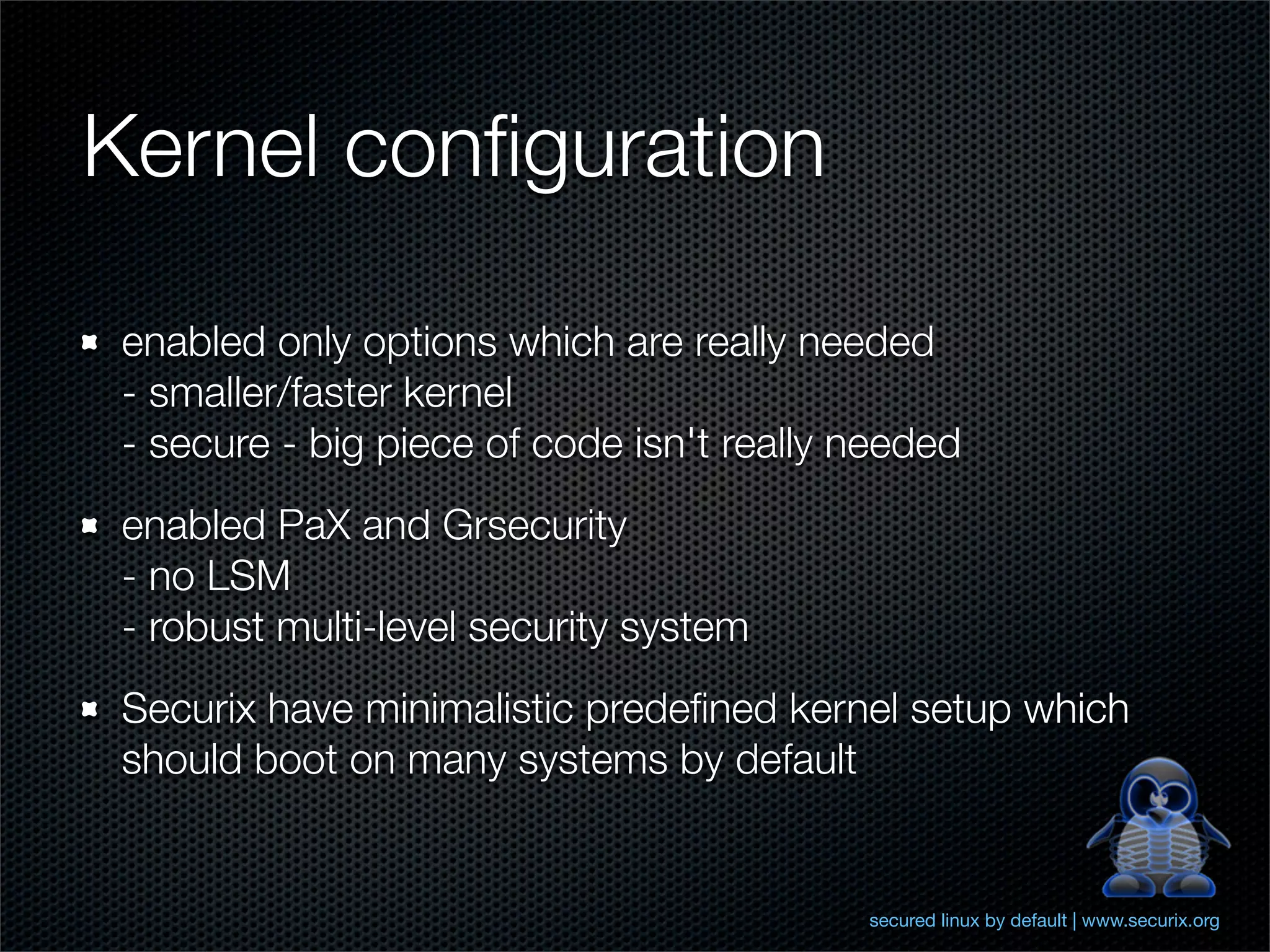
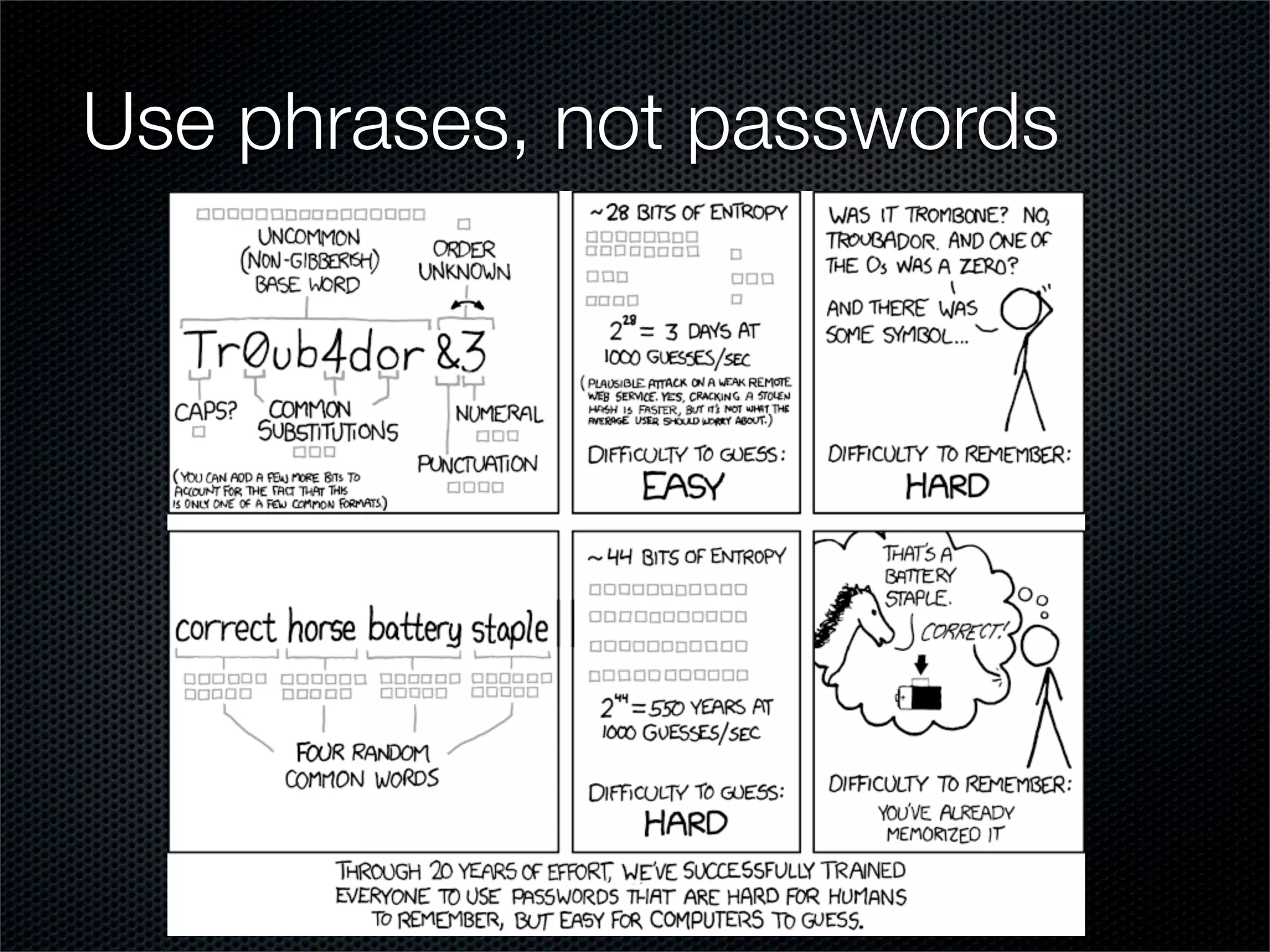
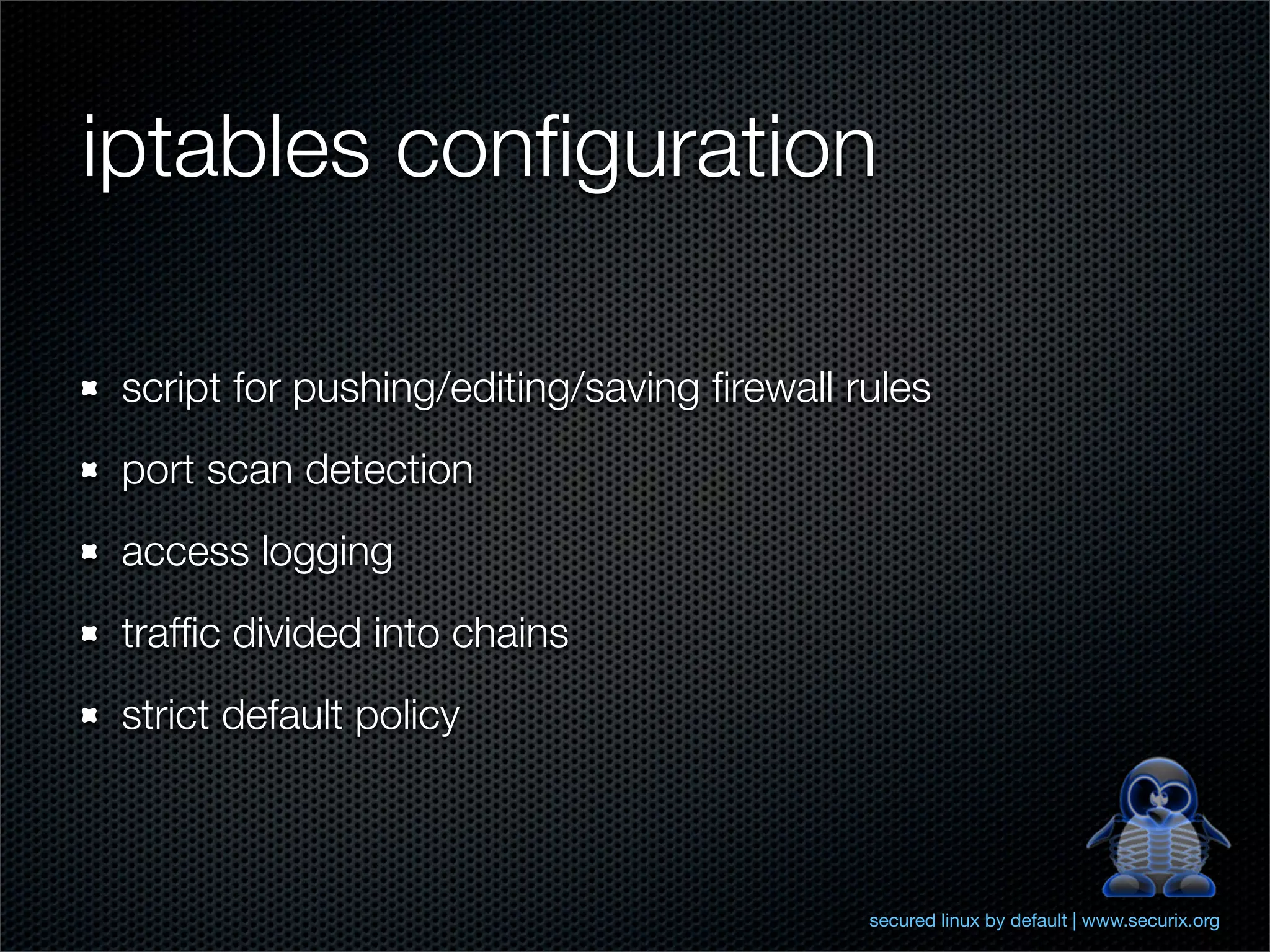
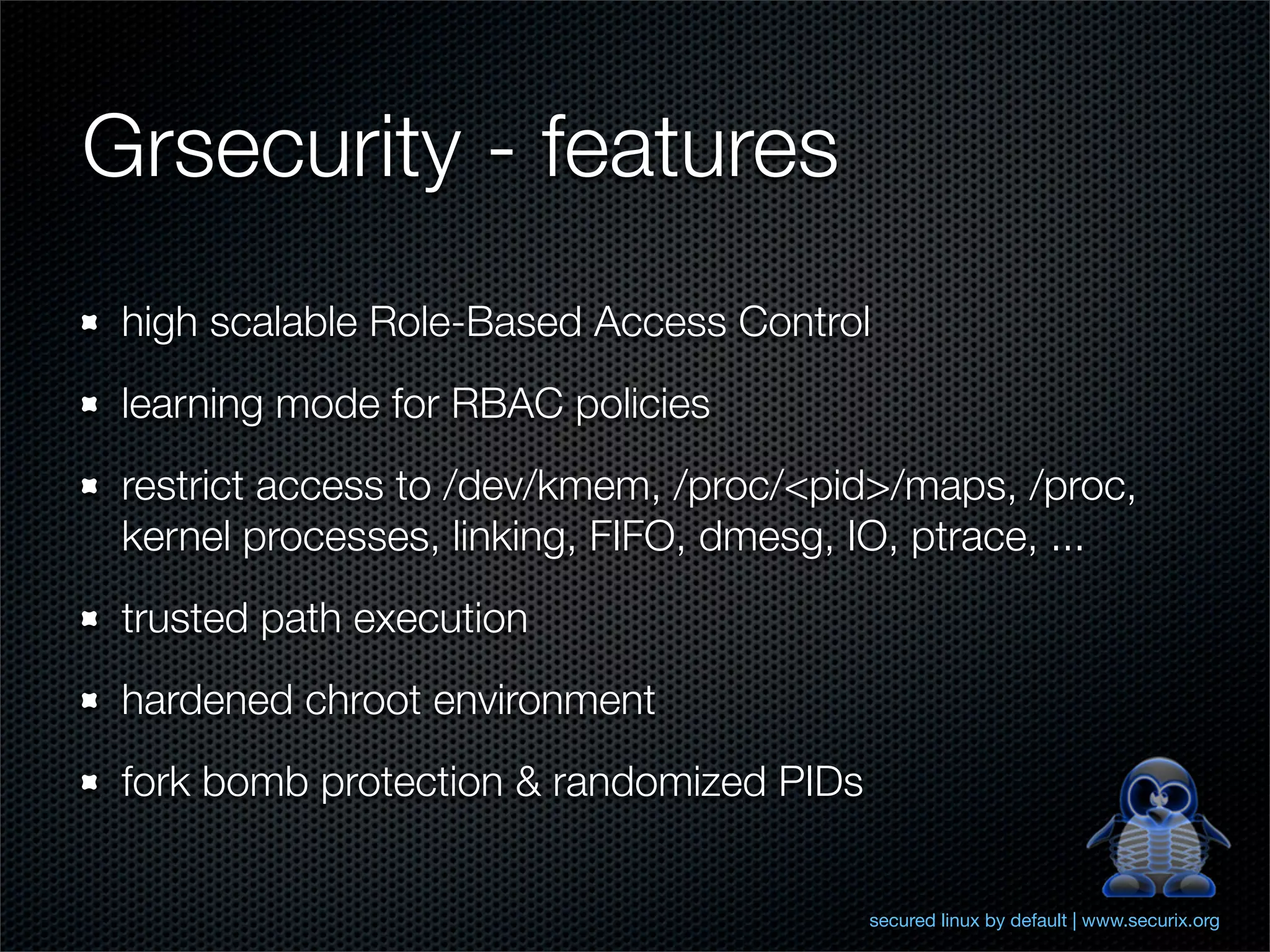
The document outlines comprehensive hardening techniques for the Securix GNU/Linux operating system, covering system and application tuning, physical security, encryption, and security configurations. Key recommendations include using LUKS for partition encryption, configuring GRUB with a password, limiting root access, and implementing advanced security features through Pax and Grsecurity. The Securix system follows best practices for security and performance, offering proactive measures to address vulnerabilities and ensuring system integrity.











![PaX - NOEXEC
The goal of NOEXEC is to prevent the injection and
execution of code into a task's address space and render
this exploit technique unusable under PaX.
- segmentation based non-executable page protection [IA-32 only]
(SEGMEXEC)
- paging based non-executable page protection (PAGEEXEC)
- mmap() and mprotect() restrictions (MPROTECT)
secured linux by default | www.securix.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardening-linux-securix-120306033044-phpapp02/75/Hardening-Linux-and-introducing-Securix-Linux-15-2048.jpg)
![Pax - ASLR
decrease success rate of attacks that require advanced
knowledge of memory addresses via Address Space Layout
Randomization (ASLR)
- Main executable code/data/bss segment base address
randomization (RANDEXEC) - ET_EXEC ELF
- mmap() and brk() managed memory [libraries, heap, thread
stacks, shared memory, etc] address randomization (RANDMMAP)
ET_DYN ELF
- User stack base address randomization (RANDUSTACK)
- Kernel stack base address randomization (RANDKSTACK)
secured linux by default | www.securix.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardening-linux-securix-120306033044-phpapp02/75/Hardening-Linux-and-introducing-Securix-Linux-16-2048.jpg)











![Thank you!
Martin Čmelík
[ cm3l1k1 ]
martin.cmelik [ at ] security-portal.cz
www.security-portal.cz
www.securix.org
secured linux by default | www.securix.org](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hardening-linux-securix-120306033044-phpapp02/75/Hardening-Linux-and-introducing-Securix-Linux-30-2048.jpg)


