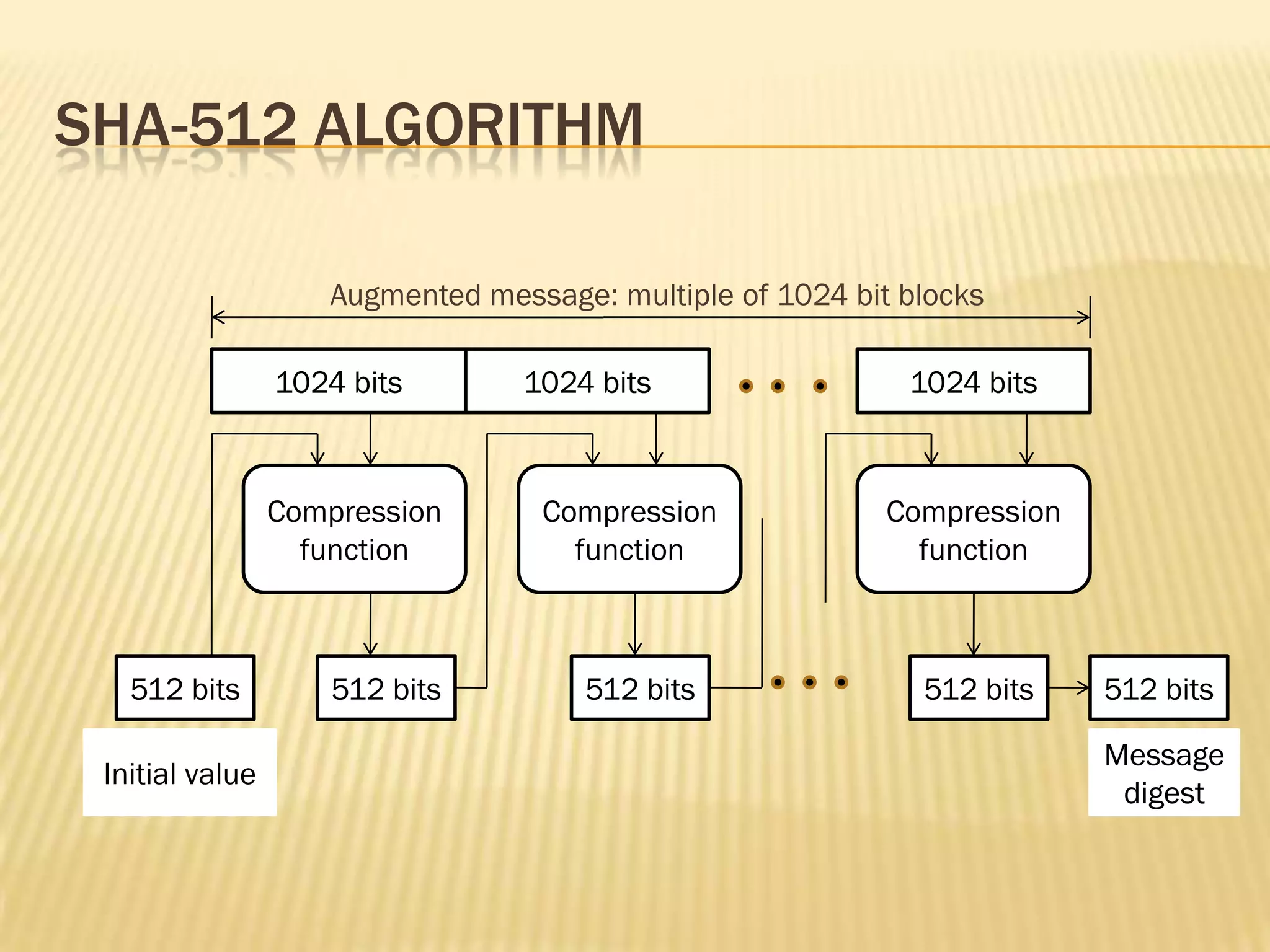
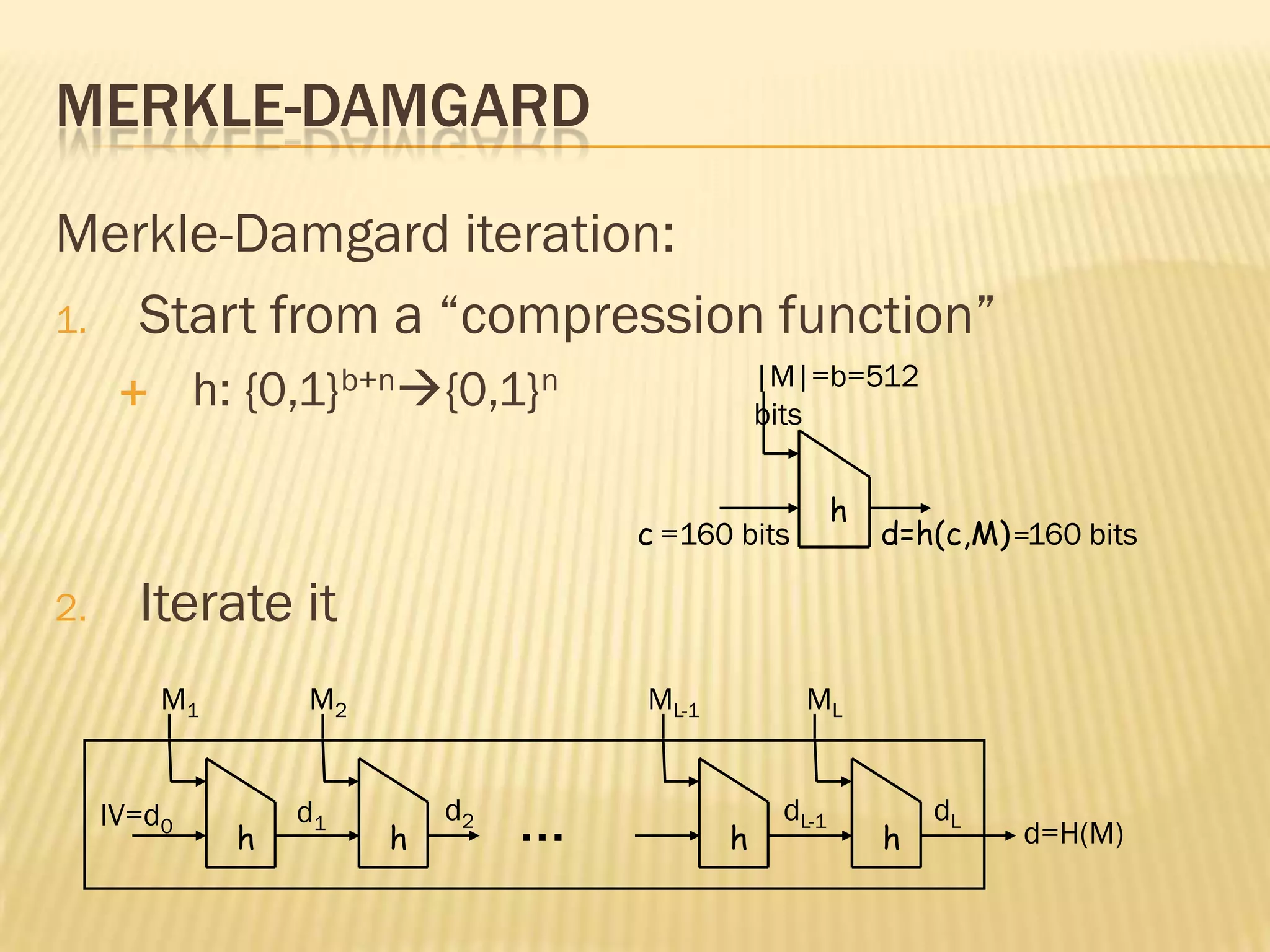
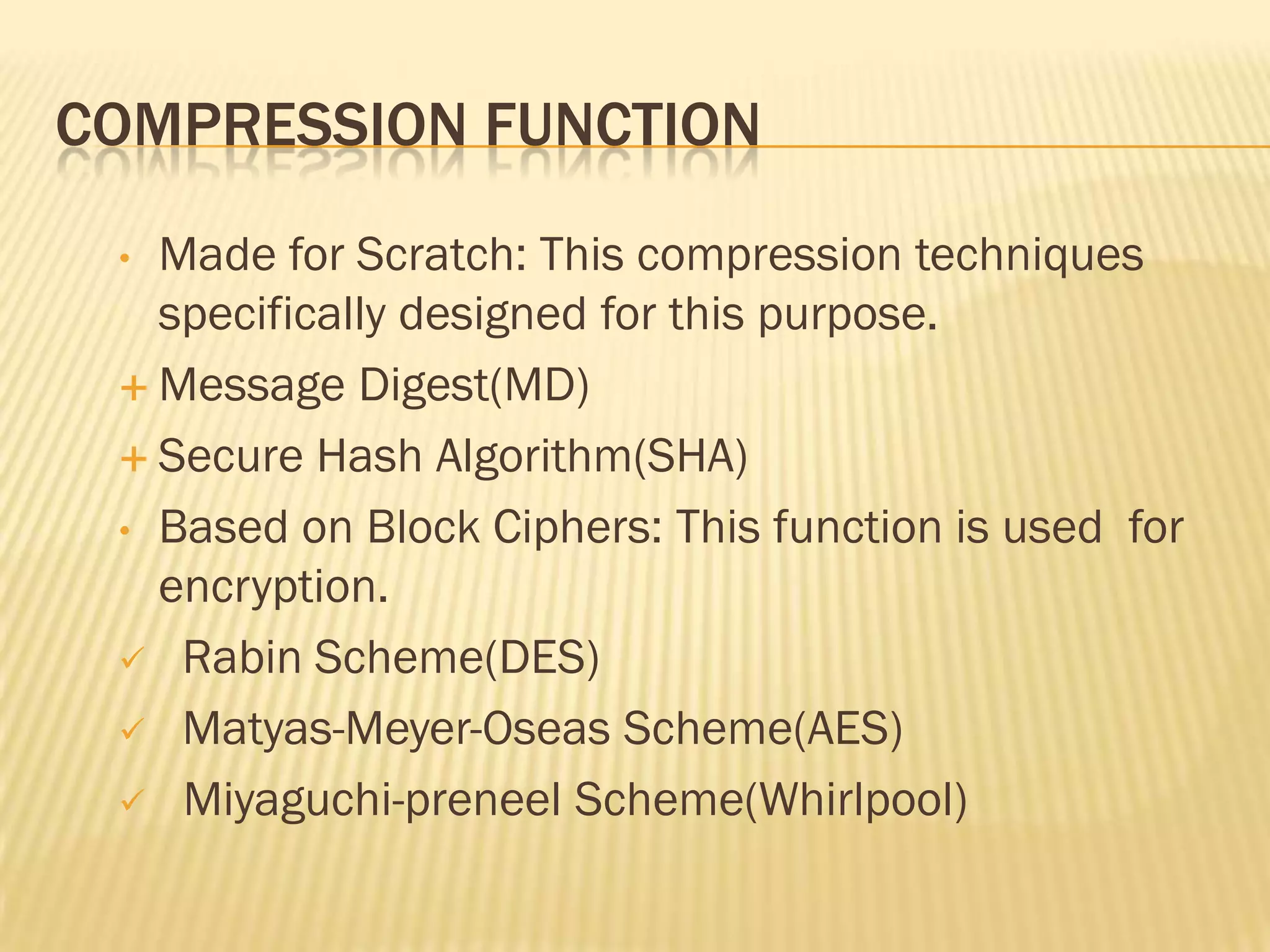
Hash functions are used to compress variable length messages into fixed length digests. They provide compression, efficiency, and hide message content. Properties include one-way, weak collision, and strong collision resistance. Merkle-Damgard iteration is used to build cryptographic hash functions from compression functions. Applications include digital signatures, message authentication codes, and key derivation. Common hash functions are MD4, MD5, and SHA which use Boolean functions and updating rules in their algorithms. Hash functions provide security by making it difficult to find collisions or inputs that result in specific outputs.










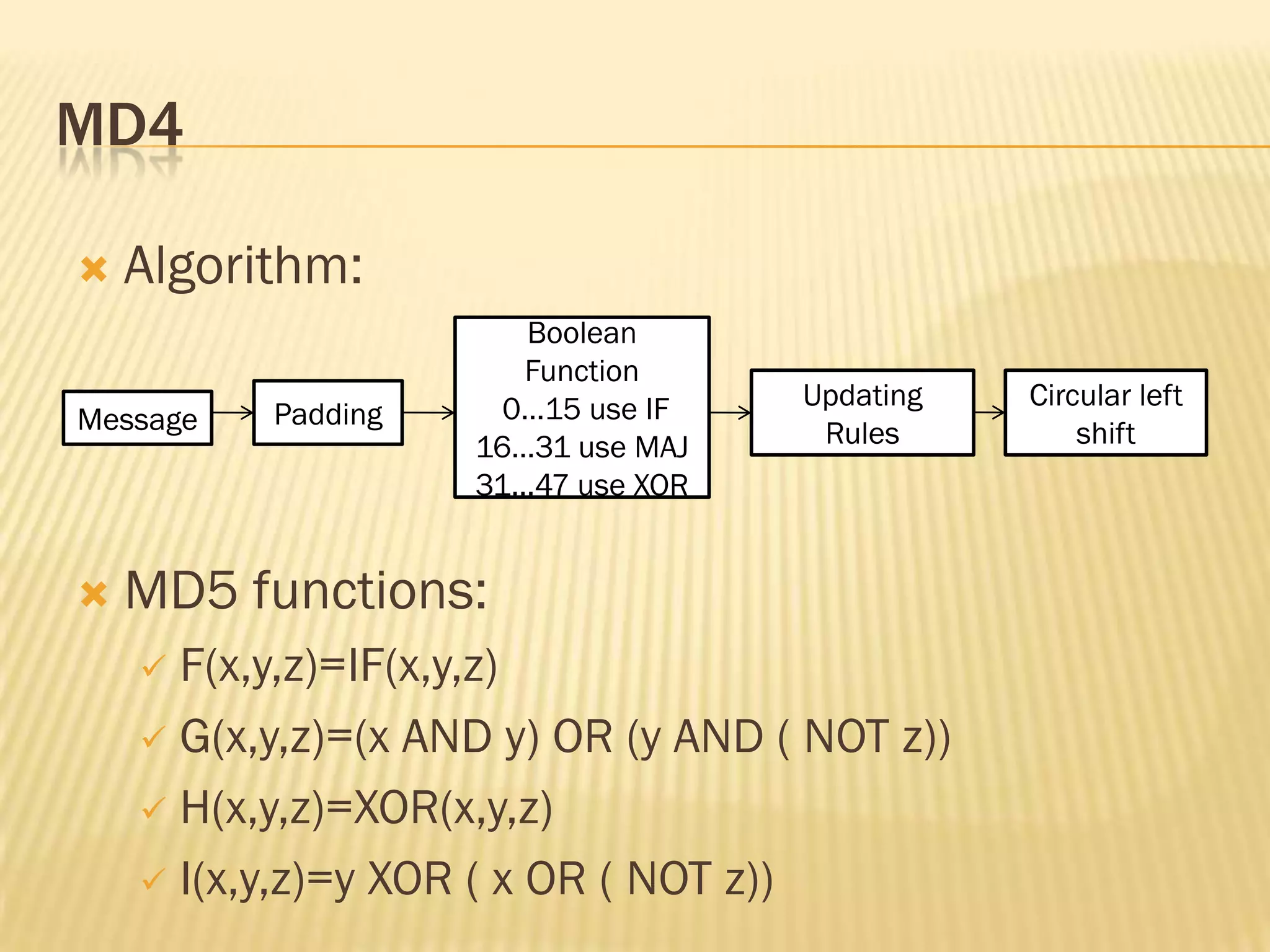
![MD4
Inputs: Message M of 512 bits
i.e. m0,m1,..,m15 each 32bits.
Register : A [a0,a1,a2,..,a47 ] can update using updating
rules.
Bitwise Boolean Function :
XOR(x,y,z)
MAJ(x,y,z)
IF(x,y,z)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myhash-130212122658-phpapp02/75/Hash-Techniques-in-Cryptography-13-2048.jpg)