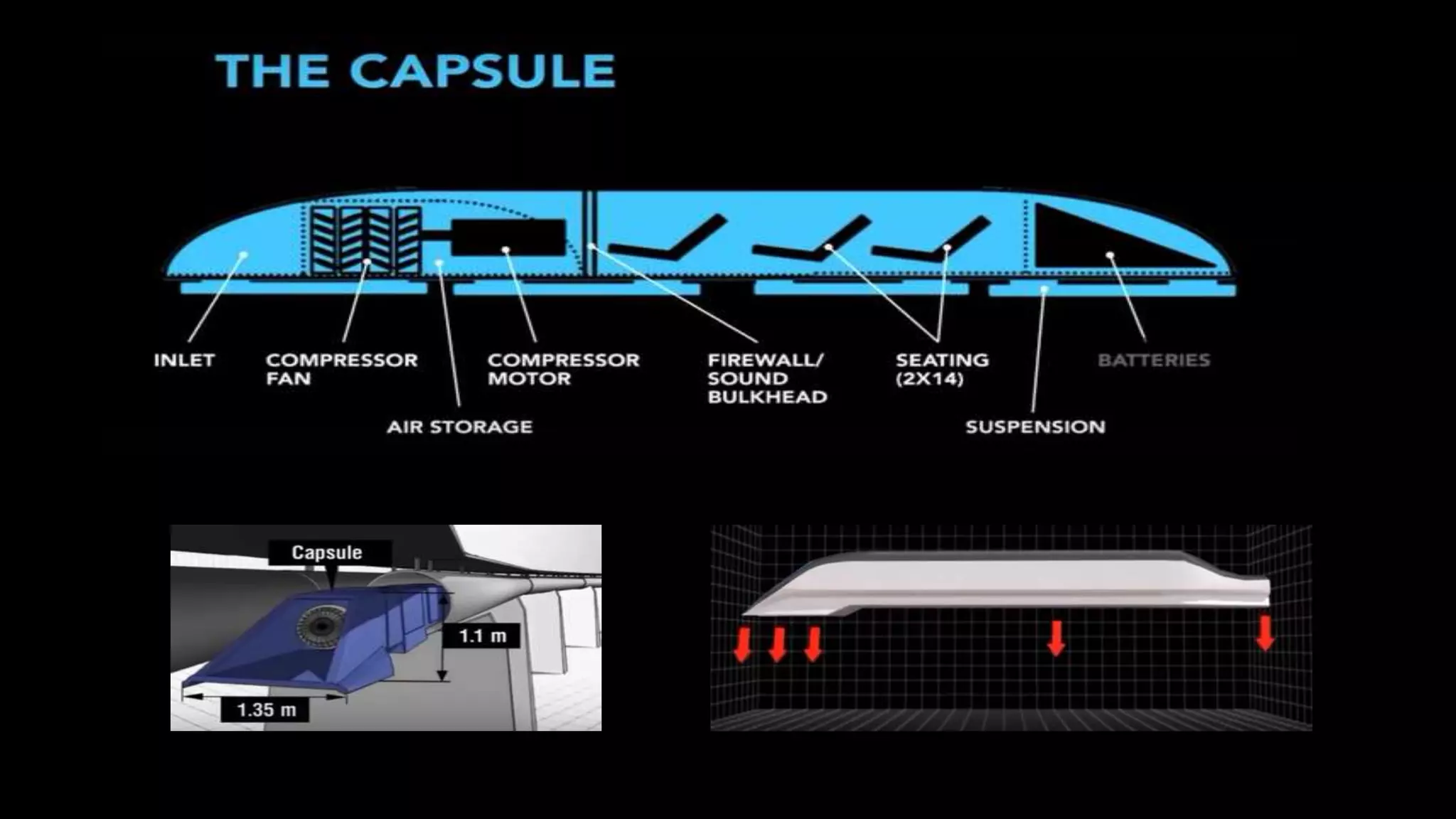
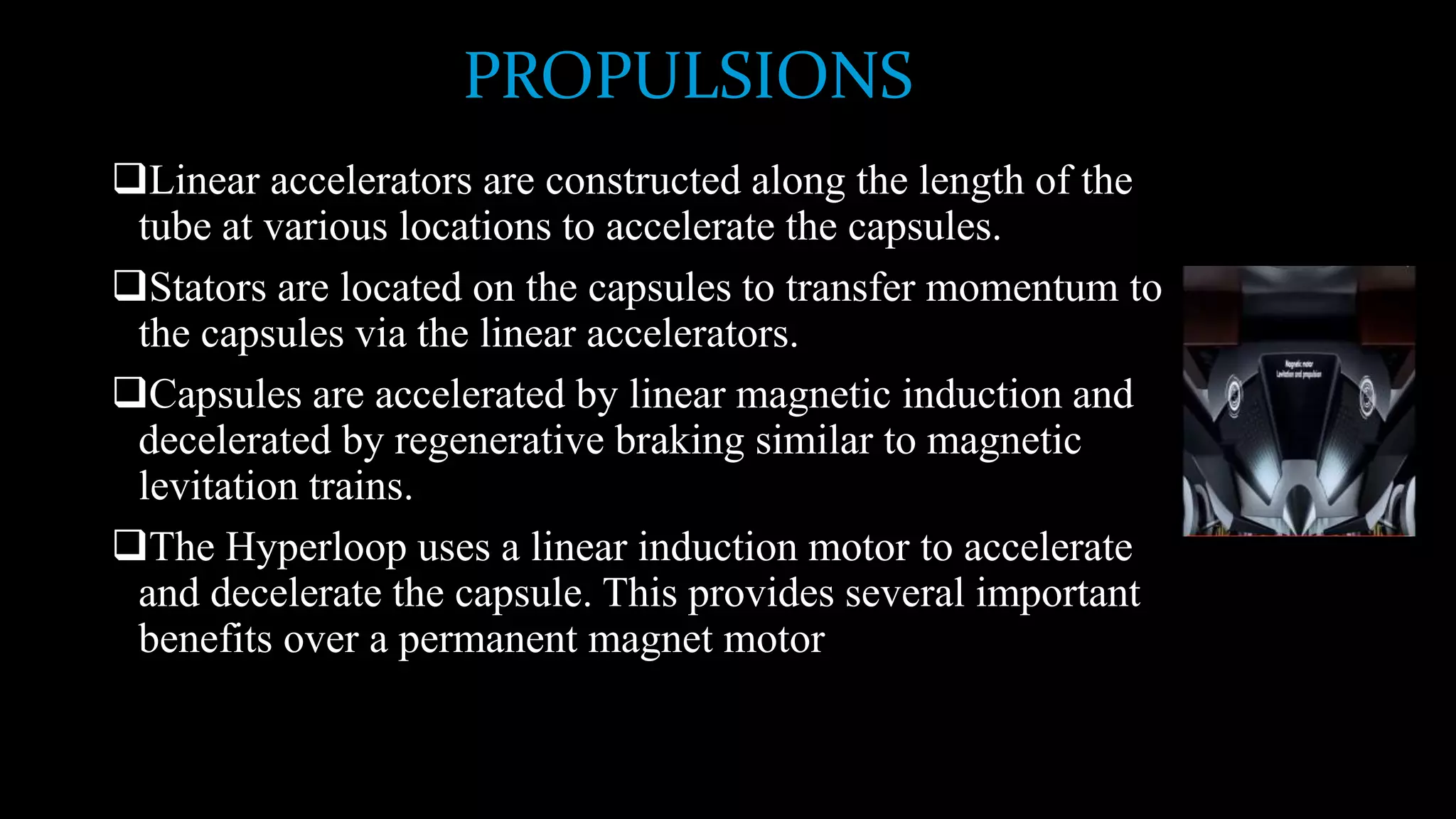
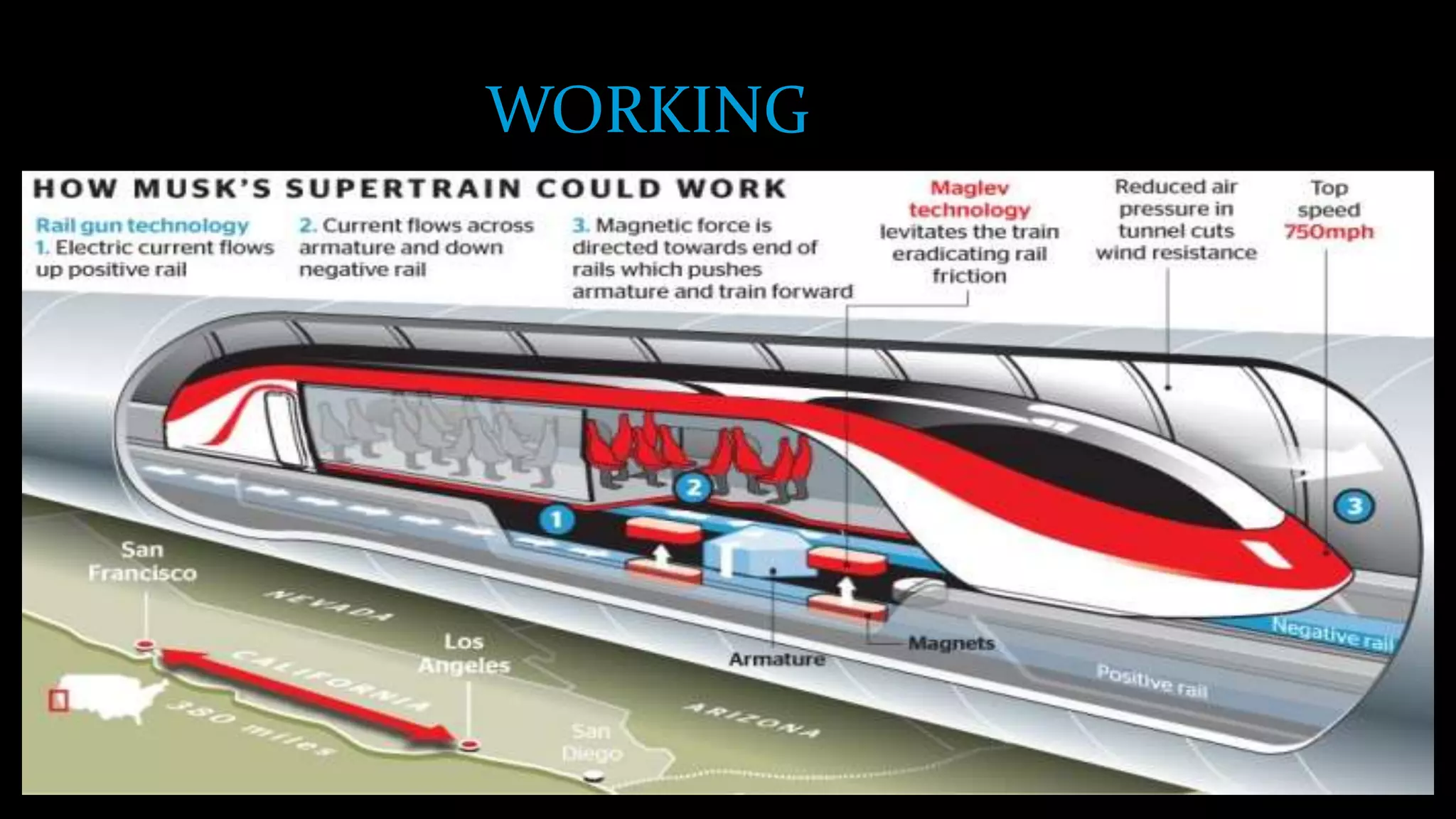
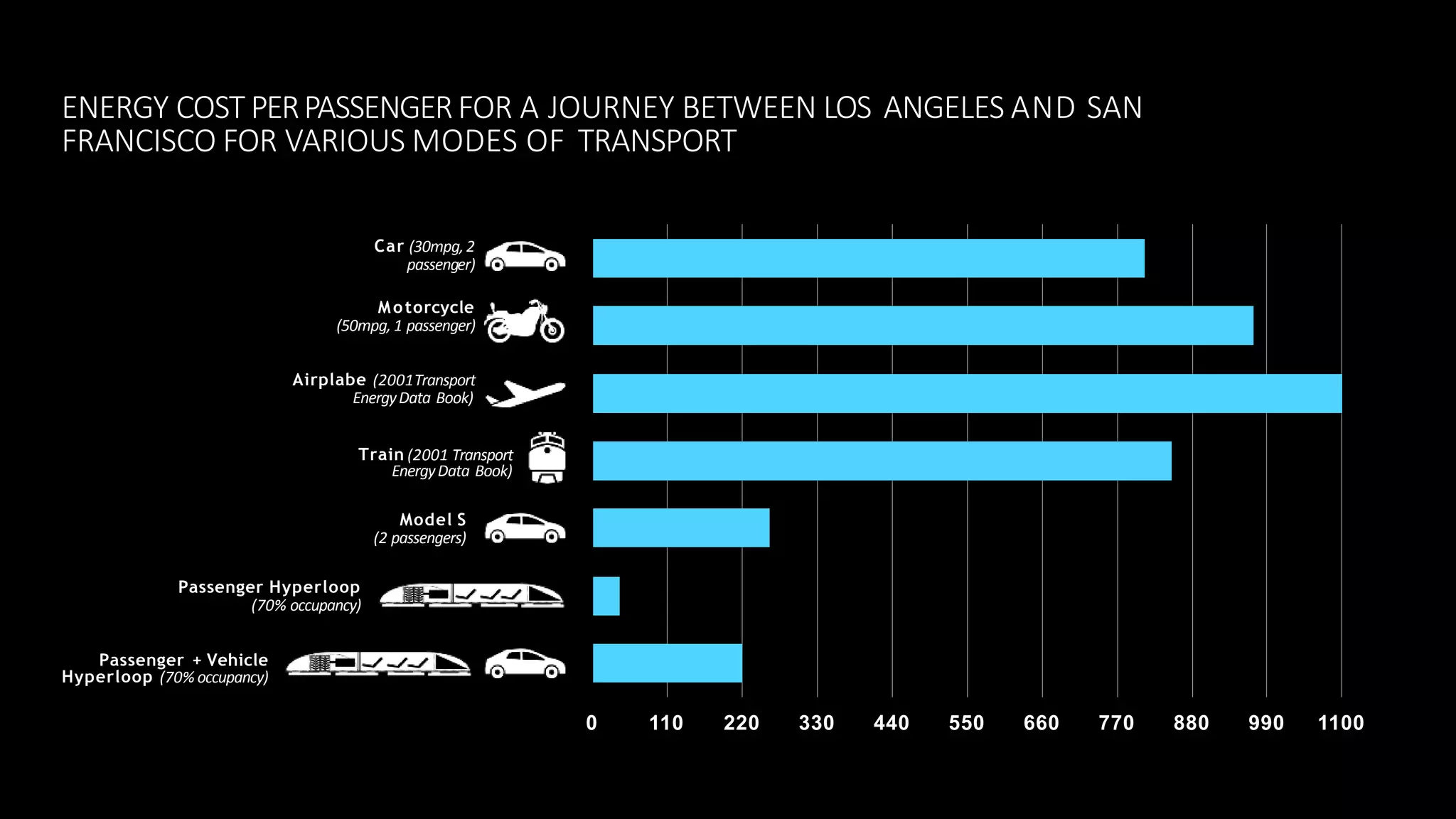
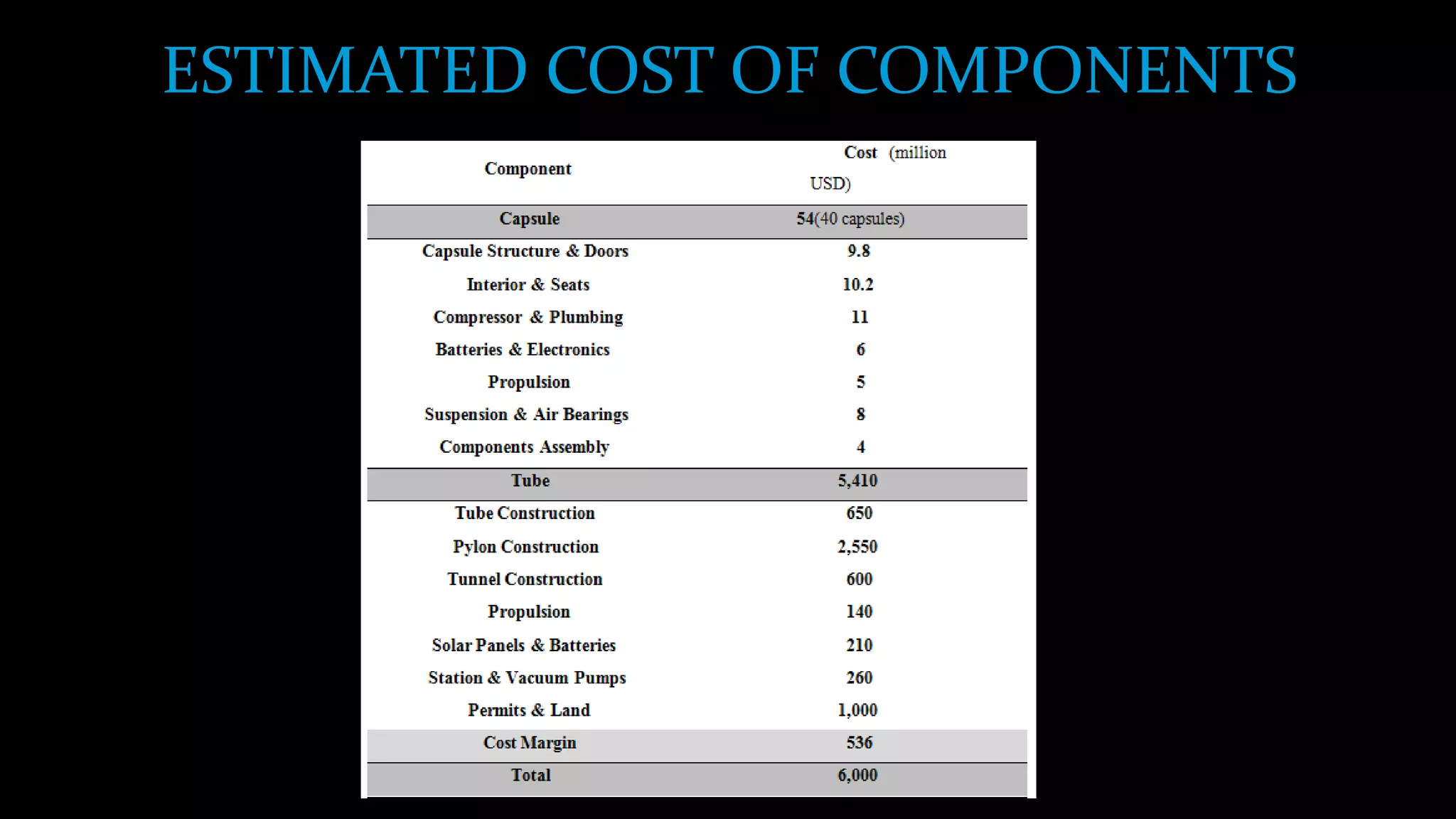
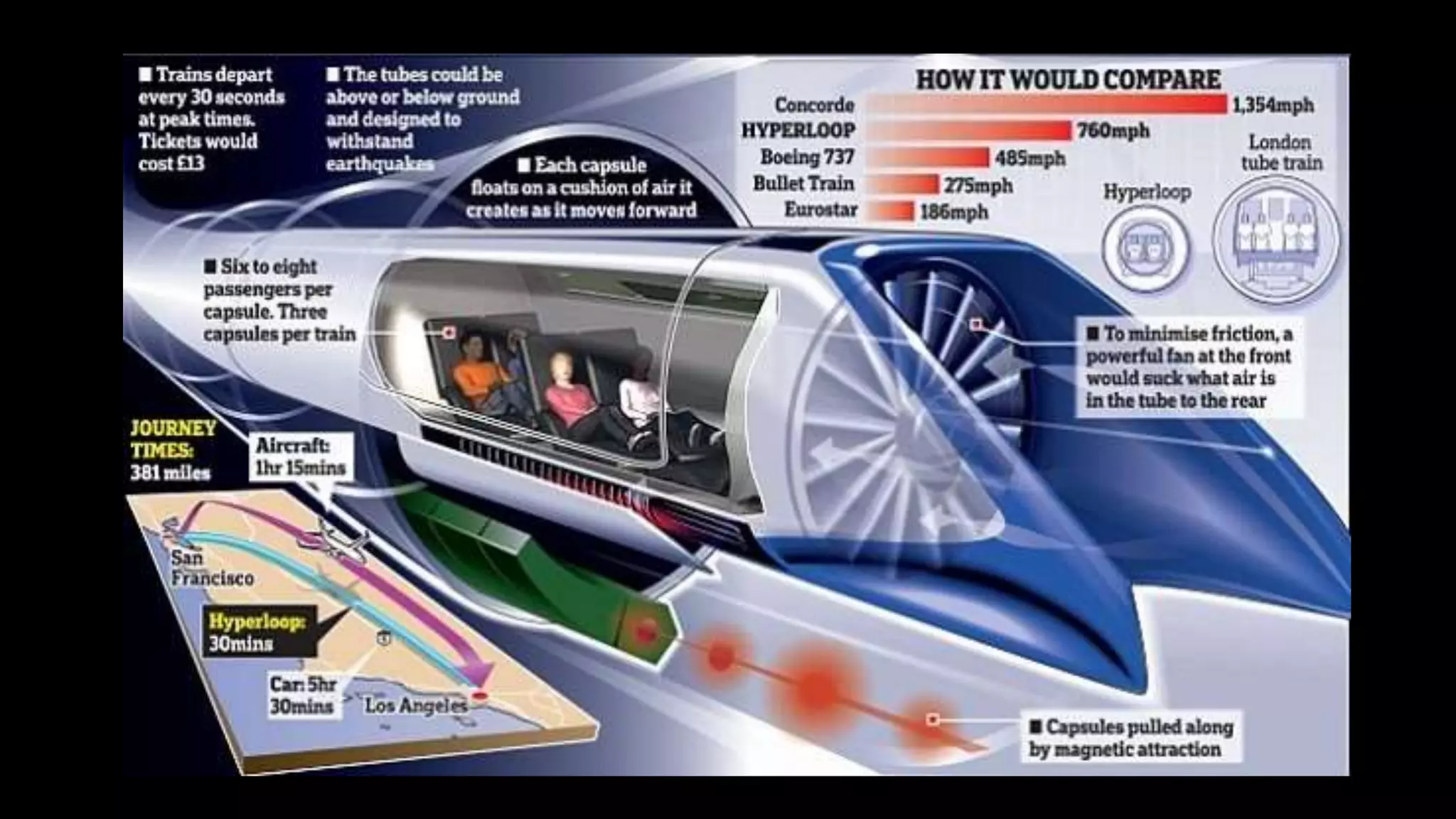
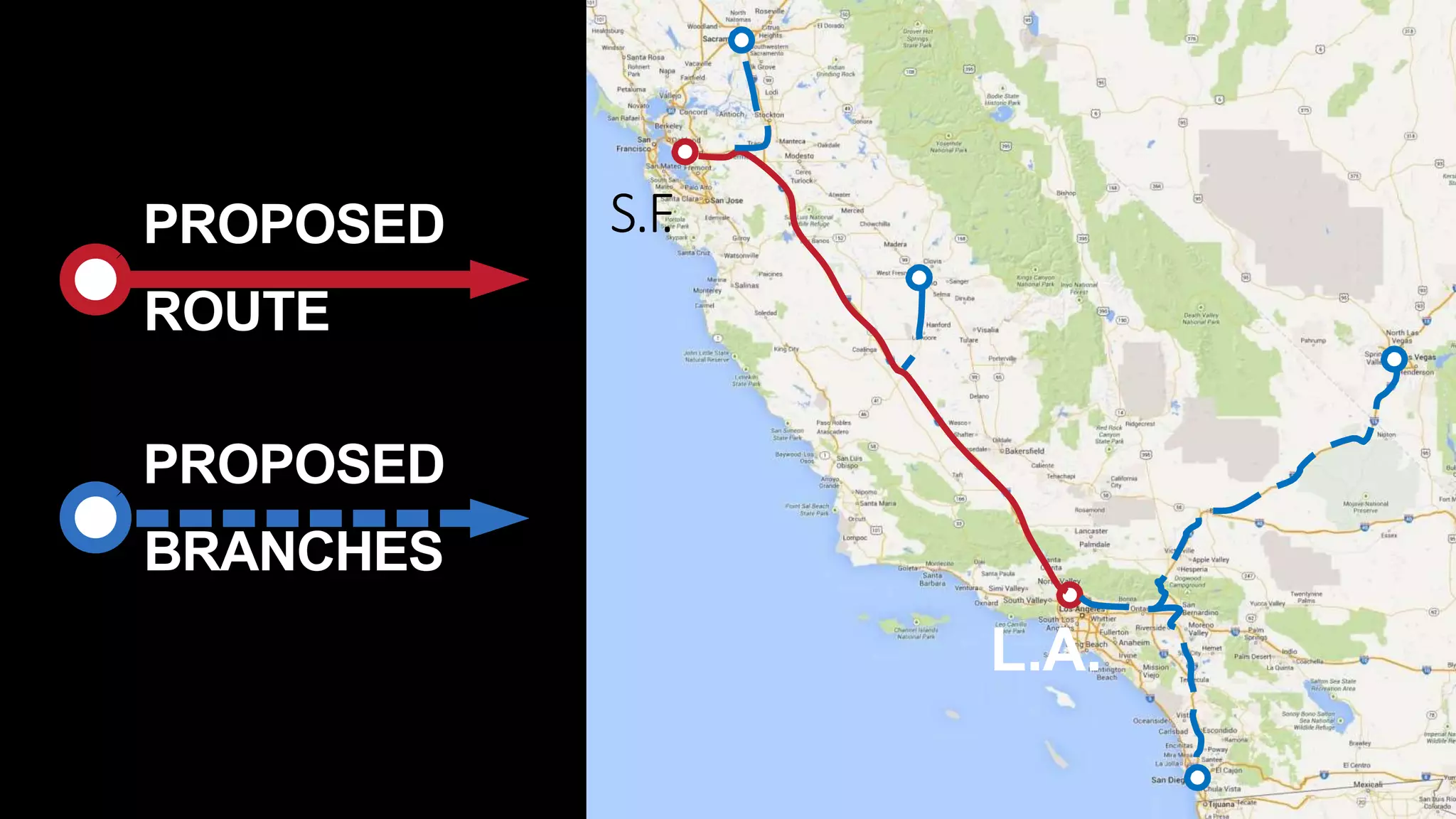
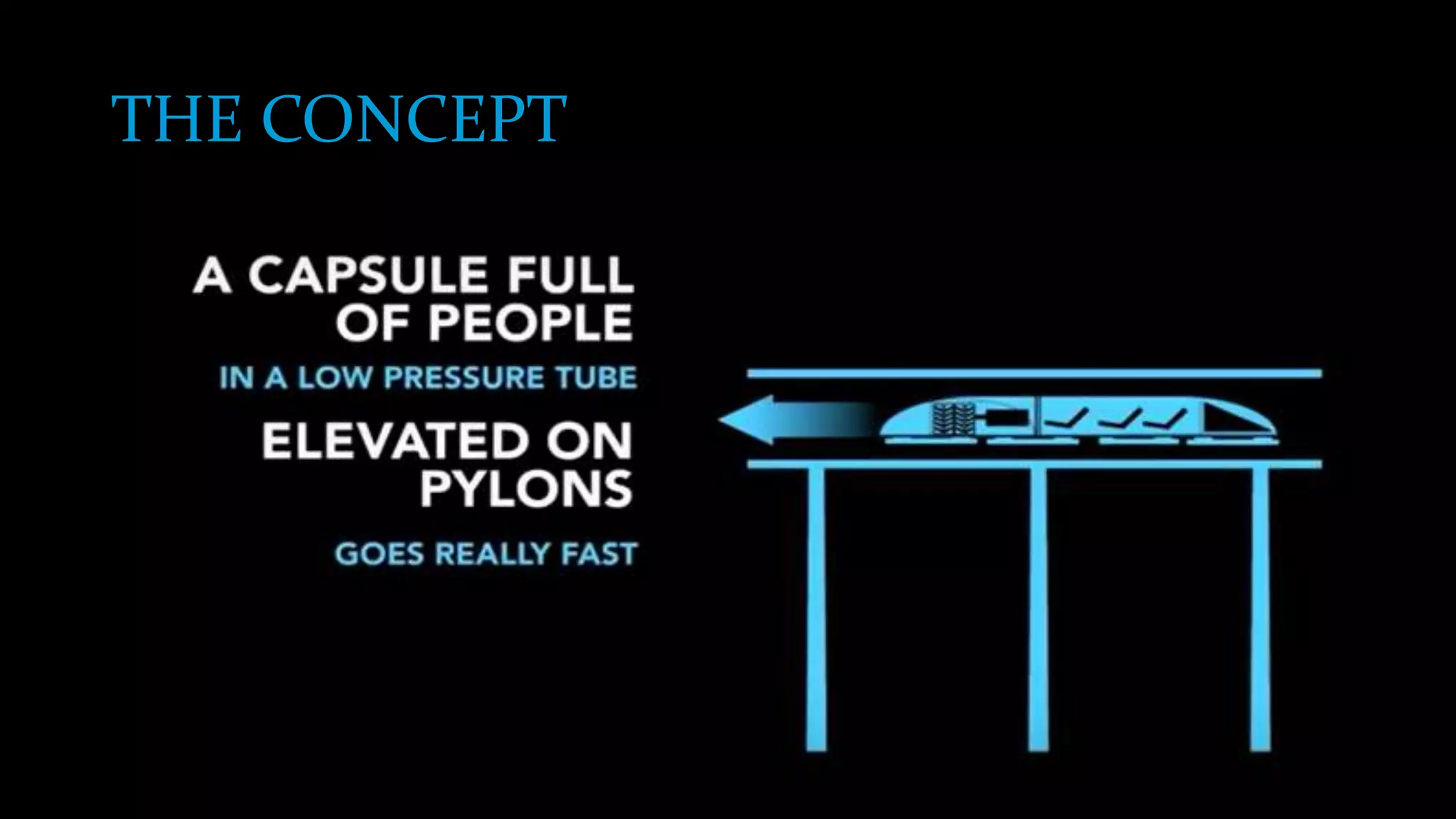
The document provides an overview of the Hyperloop high-speed transportation concept proposed by Elon Musk as an alternative to high-speed rail. The Hyperloop would involve capsules traveling at over 700 mph through a low-pressure tube, supported by air bearings and accelerated by linear induction motors. Key components would include the capsule, tube made of steel and supported by pillars, and propulsion system. The Hyperloop aims to be faster, cheaper, and more energy efficient than other transportation options like cars, planes, and high-speed rail. Safety, costs, and technical challenges are still being evaluated for this novel transportation concept.







![DESIGN
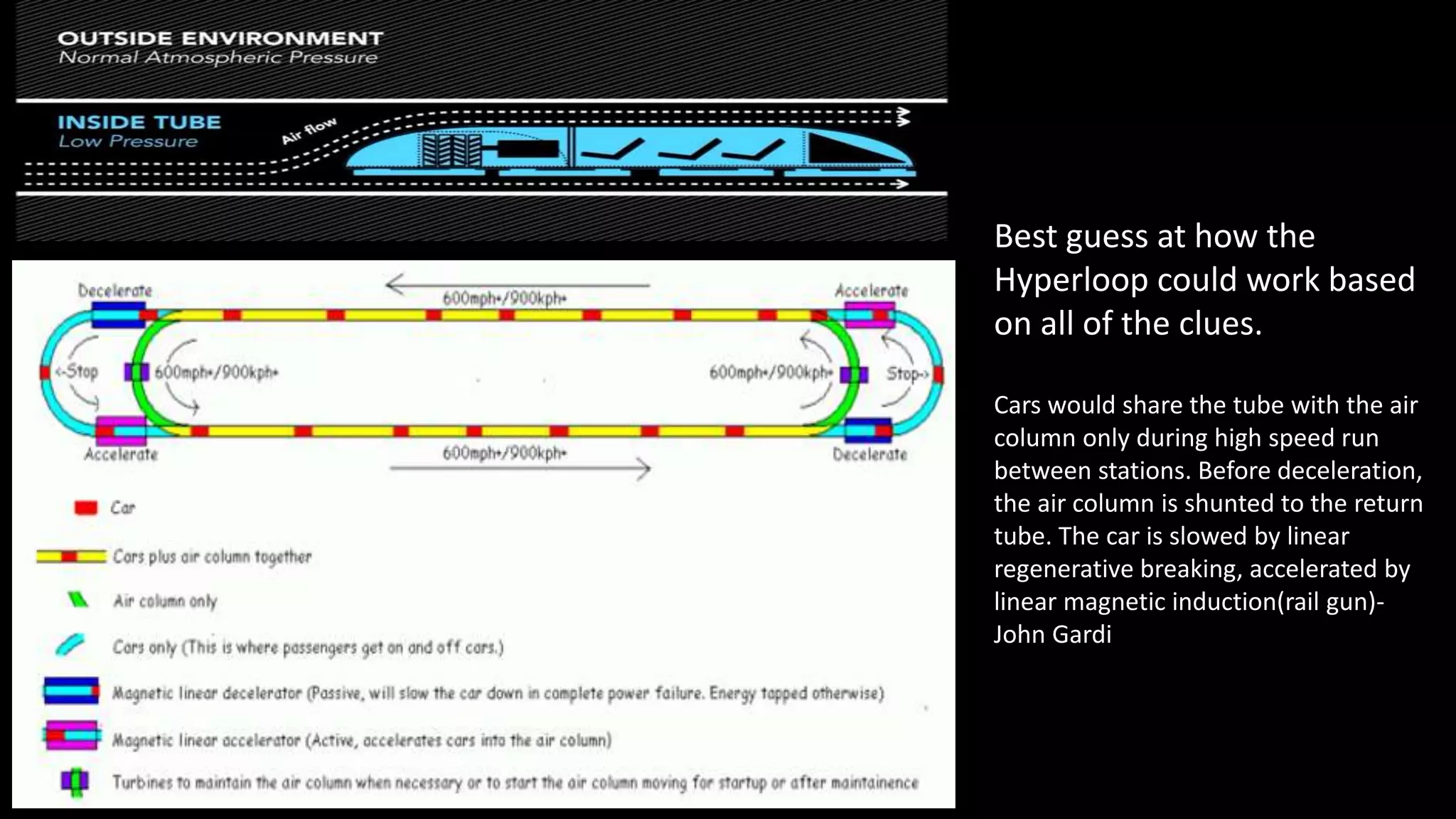
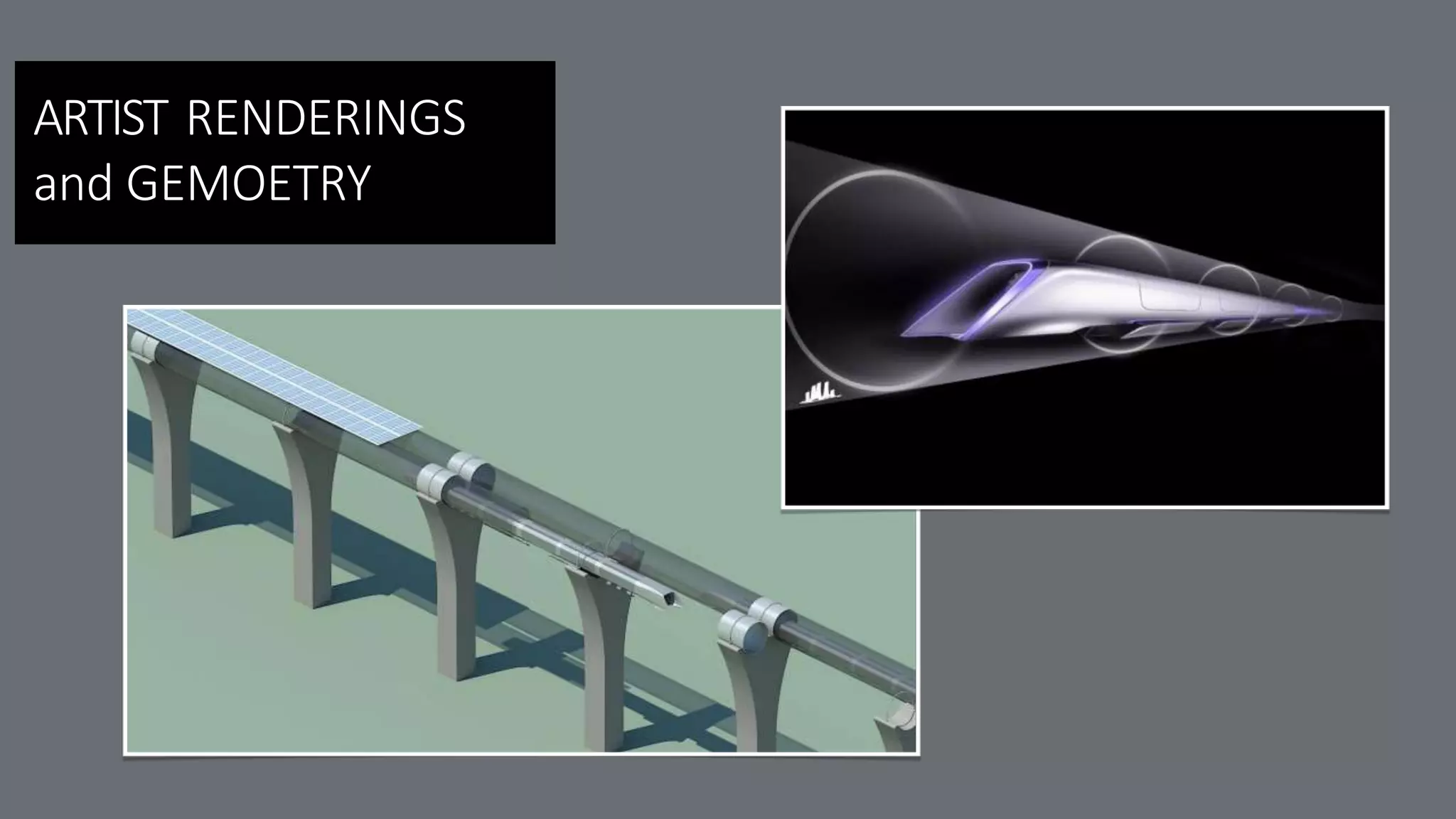
The Hyperloop concept is proposed to operate by sending specially designed "capsules" or "pods"
through a continuous steel tube maintained at a partial vacuum. Each capsule floats on a 0.5-to-1.3-
millimetre (0.02 to 0.05 in) layer of air provided under pressure to air-caster "skis", similar to how
pucks are suspended in an air hockey table, thus avoiding the use of maglev while still allowing for
speeds that wheels cannot sustain. Linear induction motors located along the tube would accelerate
and decelerate the capsule to the appropriate speed for each section of the tube route. With rolling
resistance eliminated and air resistance greatly reduced, the capsules are theorized to be able
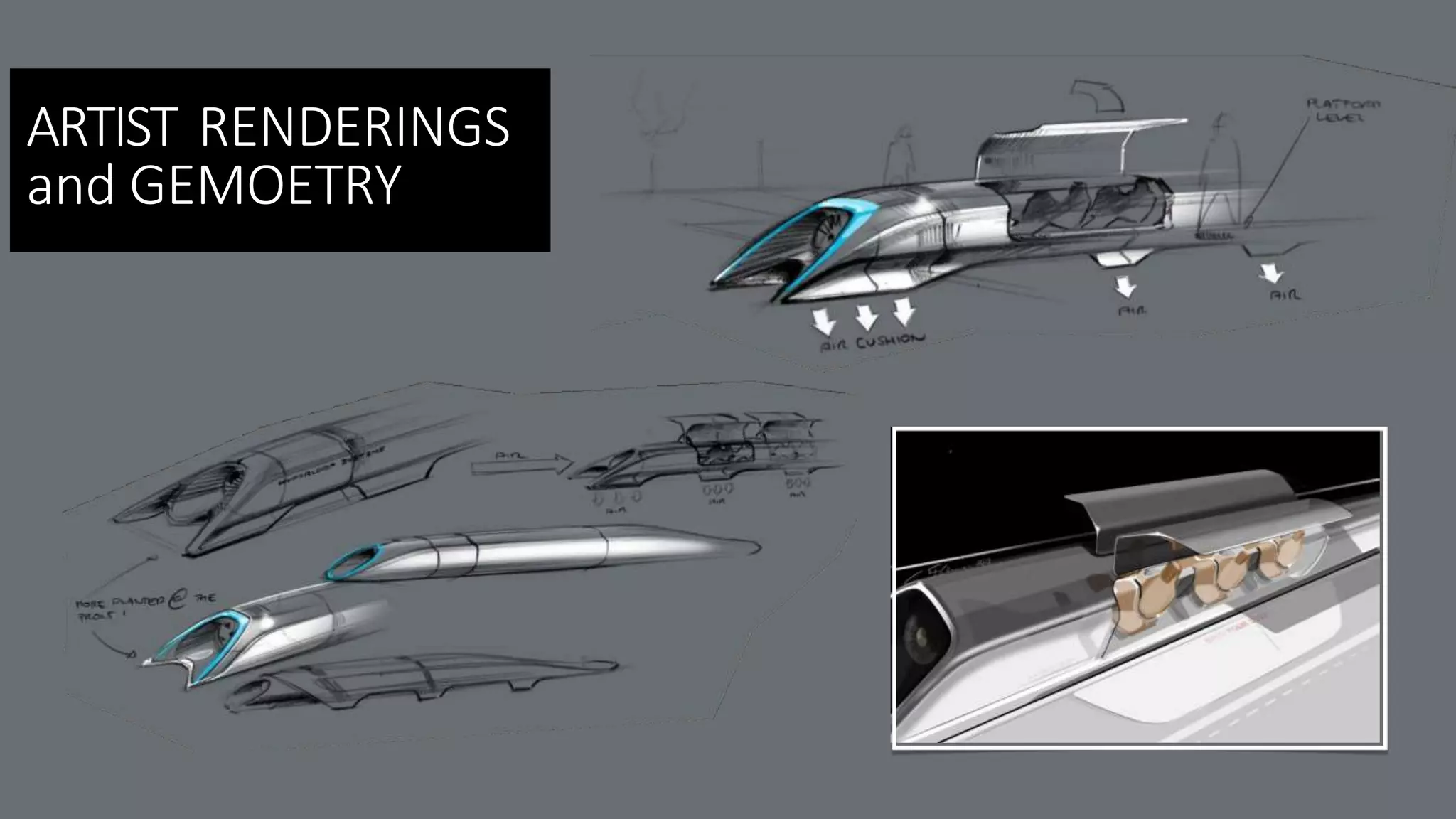
to glide for the bulk of the journey. In the Hyperloop concept, an electrically driven inlet fan and air
compressor would be placed at the nose of the capsule in order to "actively transfer high pressure
air from the front to the rear of the vessel," resolving the problem of high speed transport in a tube
that is not a hard vacuum, wherein pressure builds up in front of the vehicle, slowing it down.[2] A
fraction of the air is shunted to the skis for additional air pressure, augmenting that gain passively
from lift due to their shape.
In the alpha-level concept, passenger-only pods are to be 2.23 metres (7 ft 4 in) in diameter[2] and
projected to reach a top speed of 760 mph (1,220 km/h) so as to maintain aerodynamic
efficiency;[citation needed] the design proposes passengers experience a maximum inertial acceleration
of 0.5 g, about 2 or 3 times that of a commercial airliner on takeoff and landing. At those speeds
there would not be a sonic boom; with low-pressure warm air inside the tubes, Musk hypothesizes
the pods could travel at high speeds without exceeding Mach 1.[25]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/94f93983-001d-4483-b8f4-2ec74982fb1a-160410154758/75/Hyperloop-12-2048.jpg)