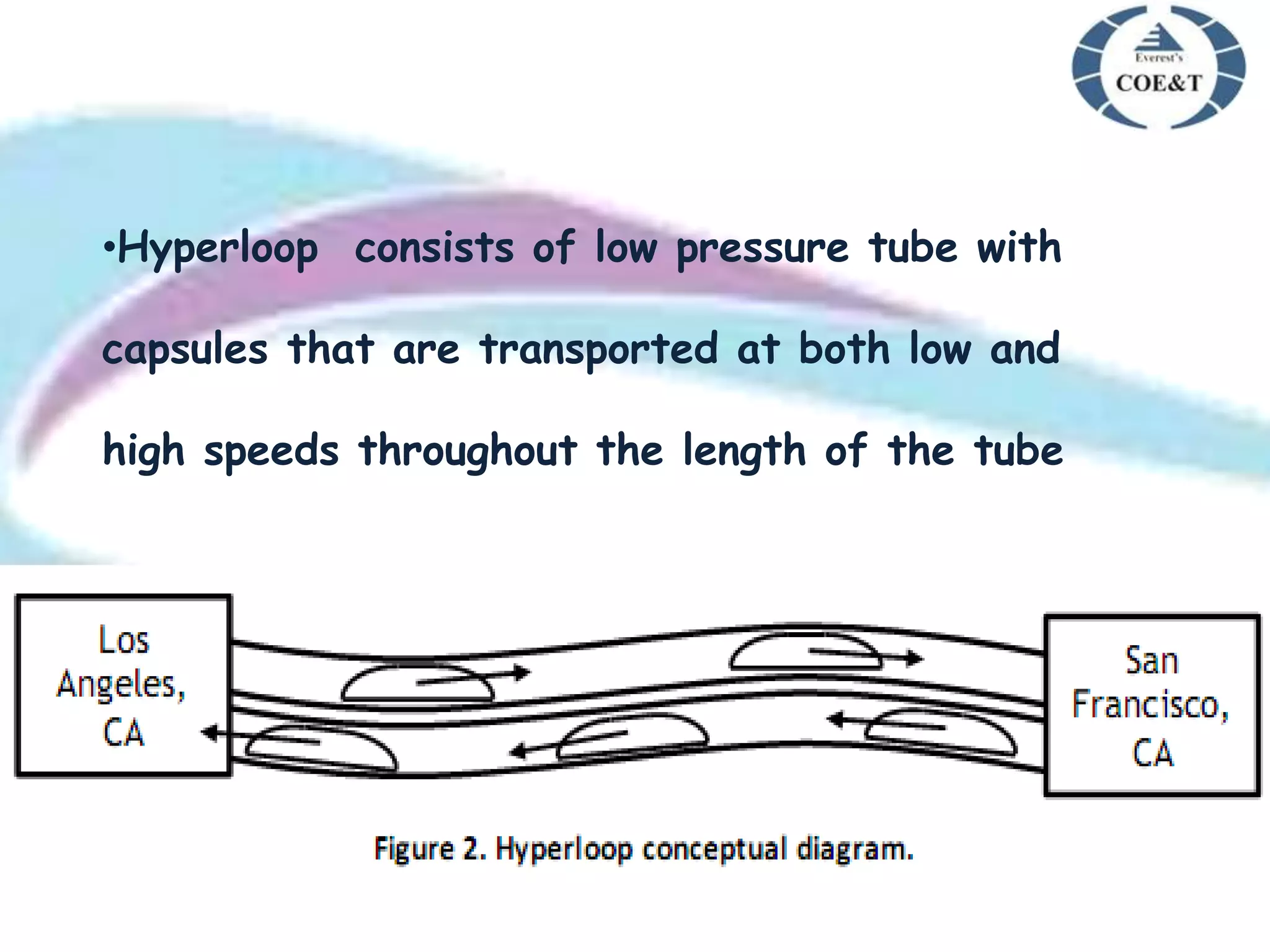
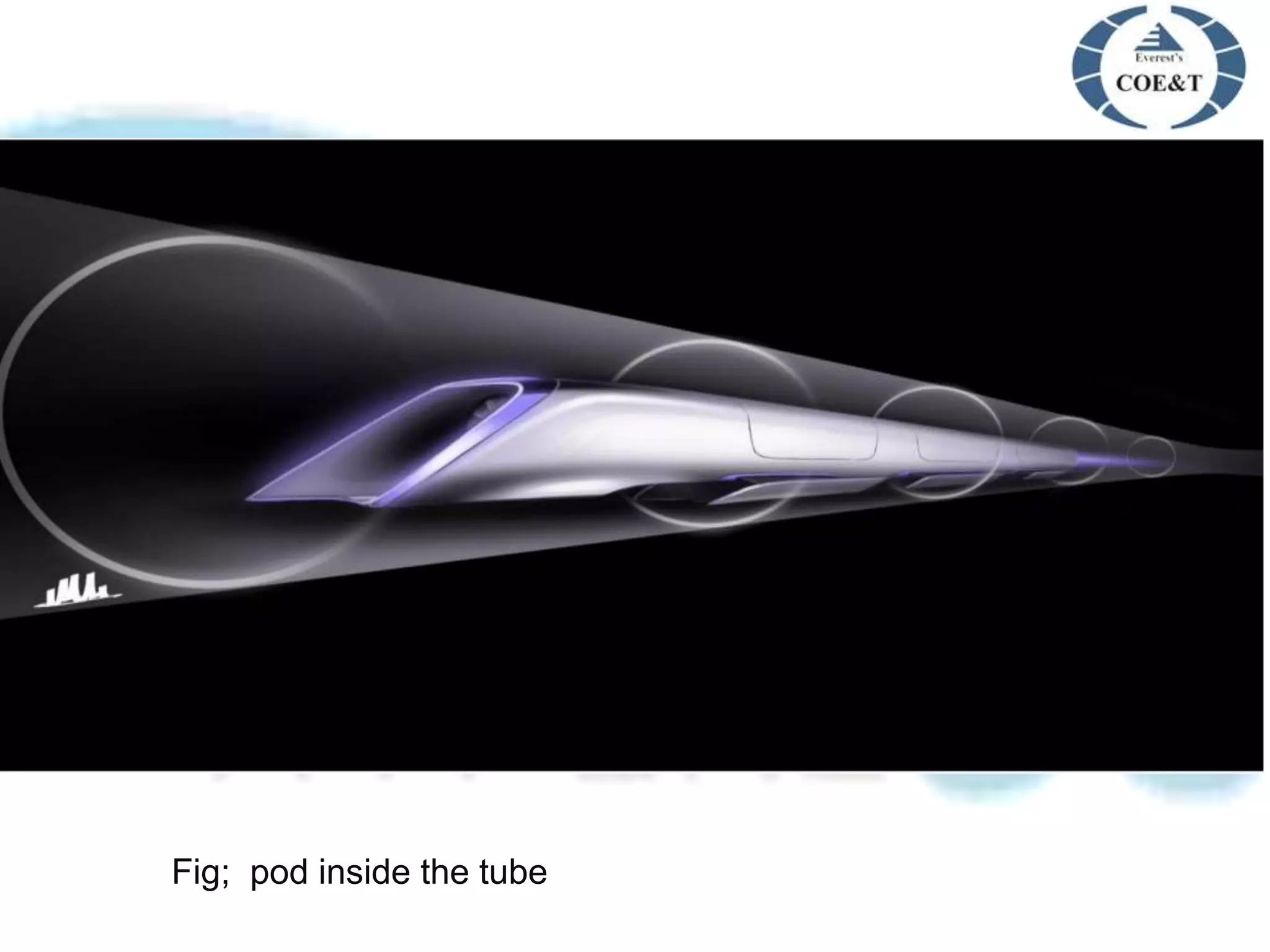
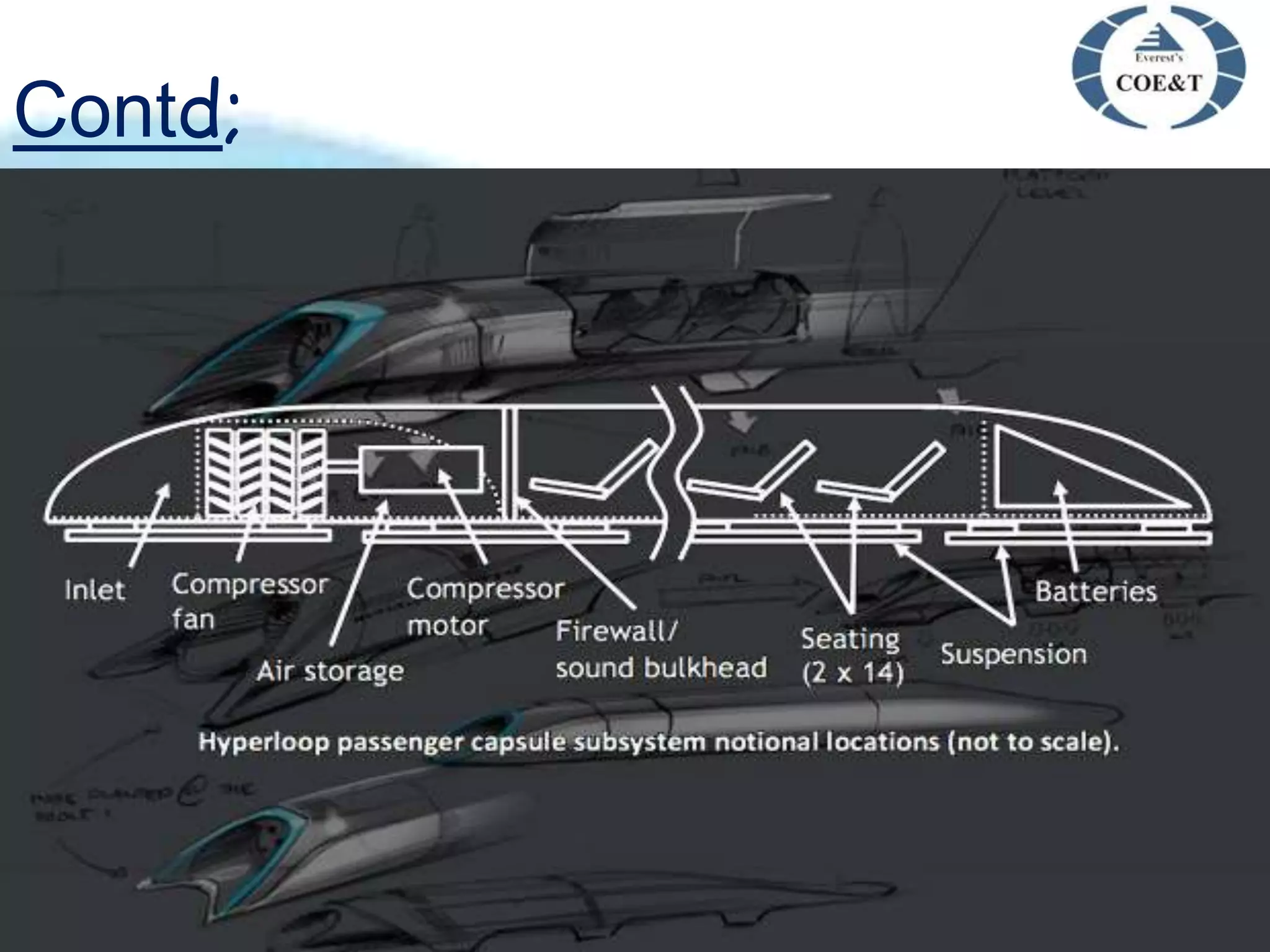
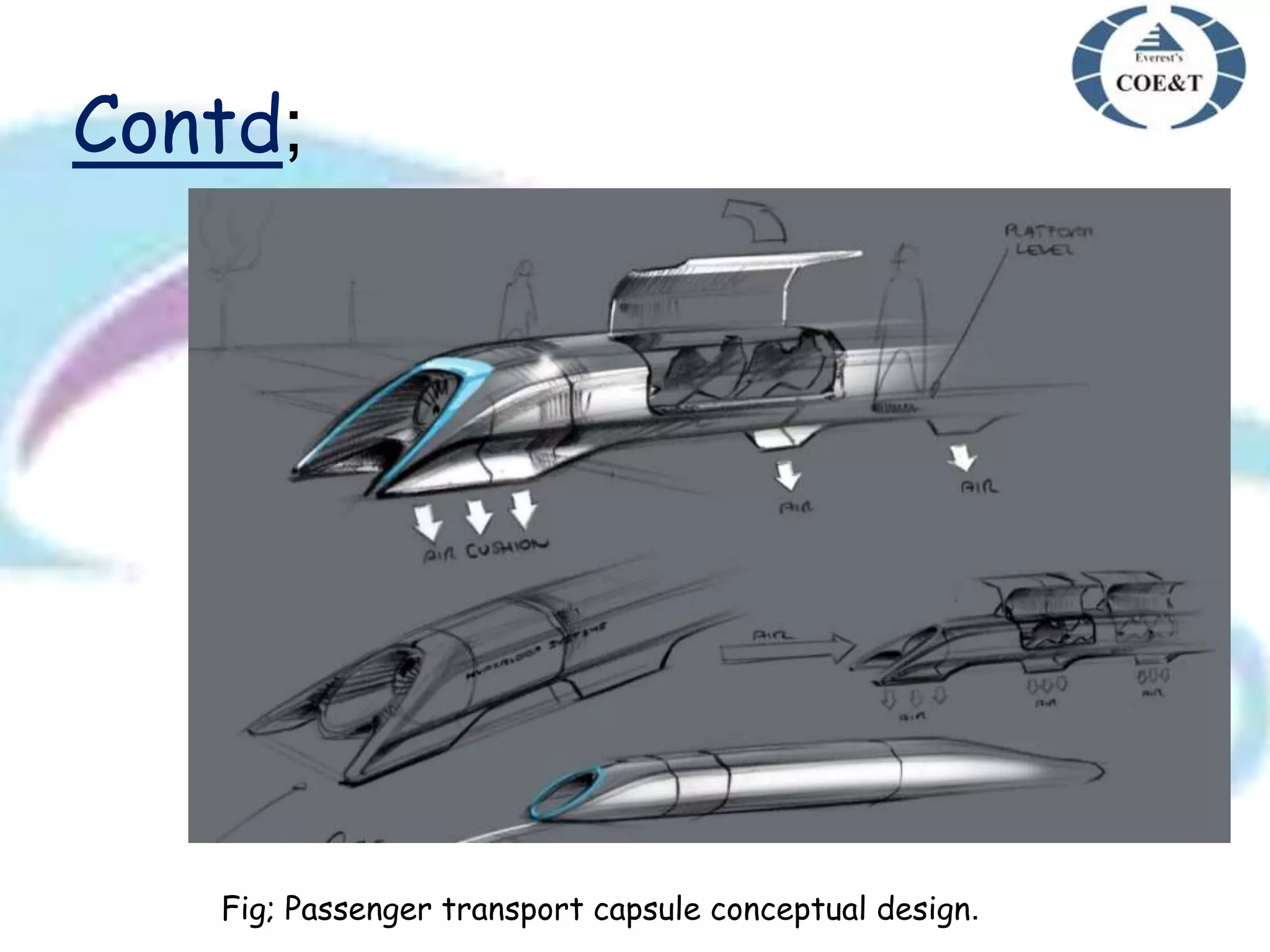
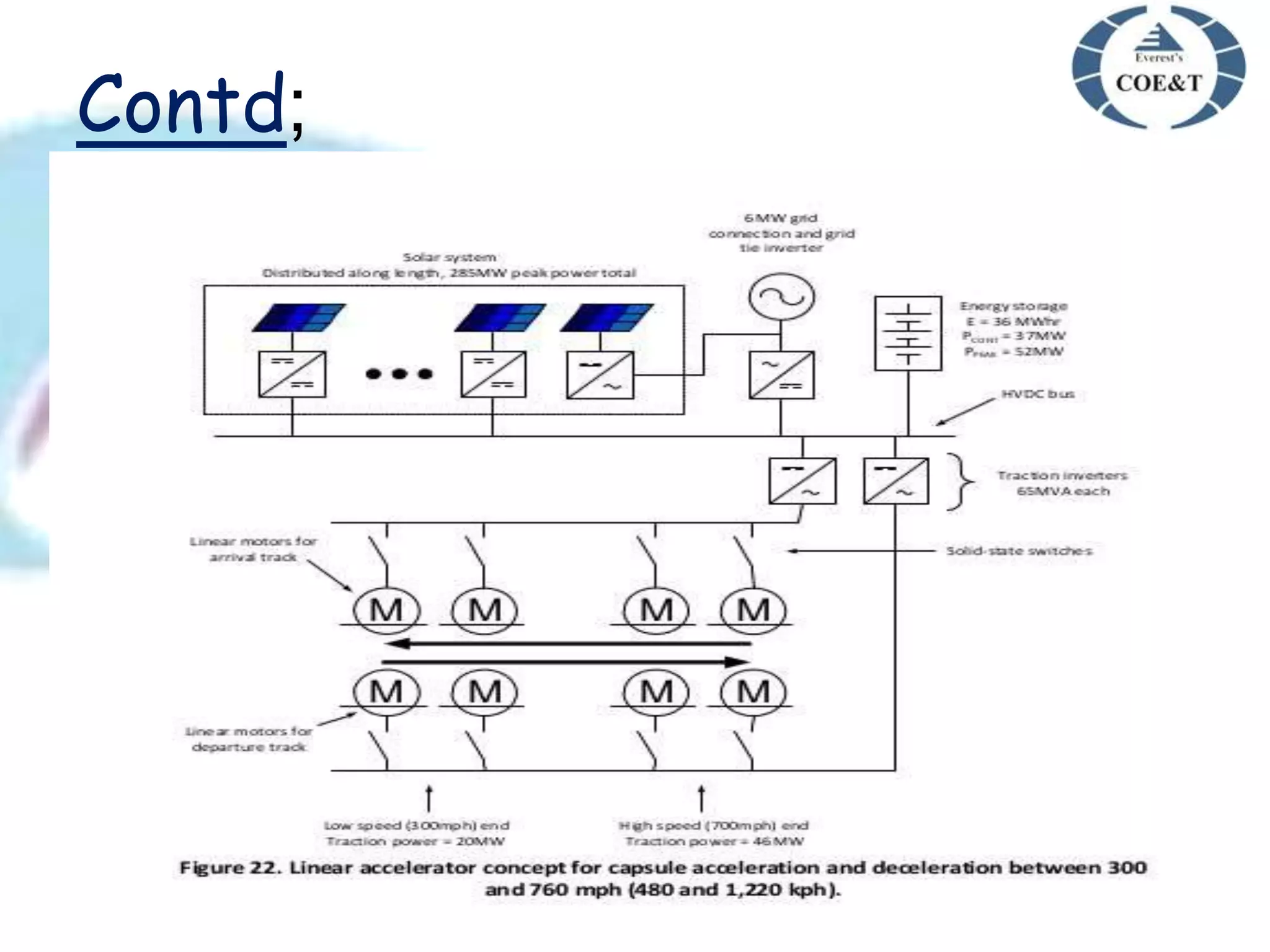
Hyperloop is a proposed new mode of transportation involving traveling inside floating pods that travel inside low pressure tubes at high speeds of over 1000 km/h. It was proposed by Elon Musk as an alternative to high speed rail or air travel. The system would use magnetic acceleration and air bearings to levitate and propel pods through tubes, allowing them to travel at airline speeds but without air resistance or friction. Key components include the passenger pods, low pressure steel tubes mounted on pylons, and linear accelerators to propel the pods through the tubes at high speeds. Major challenges include issues of air drag, friction, and ensuring safety, but benefits could include faster, cheaper, and more sustainable travel compared to existing options