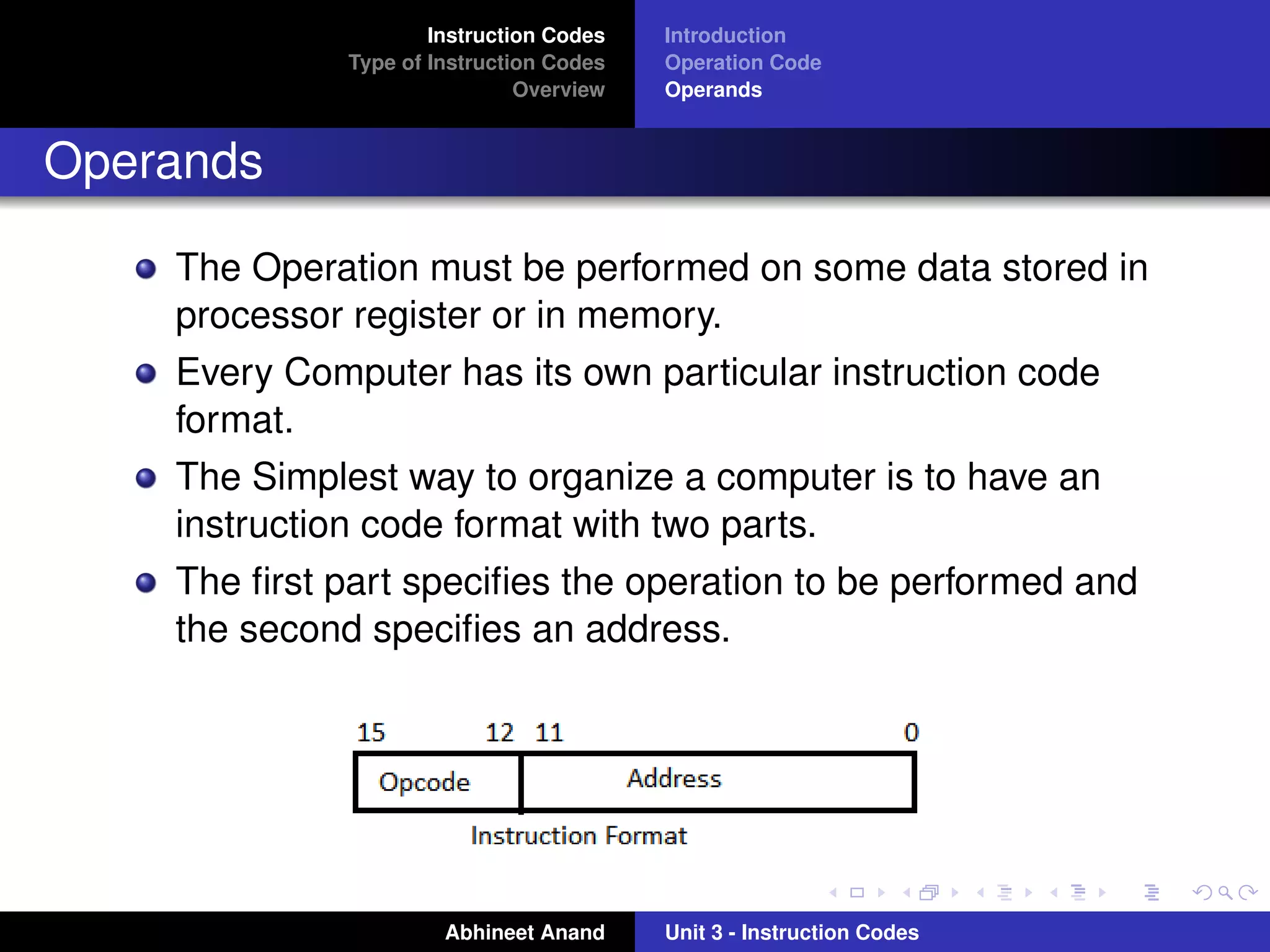
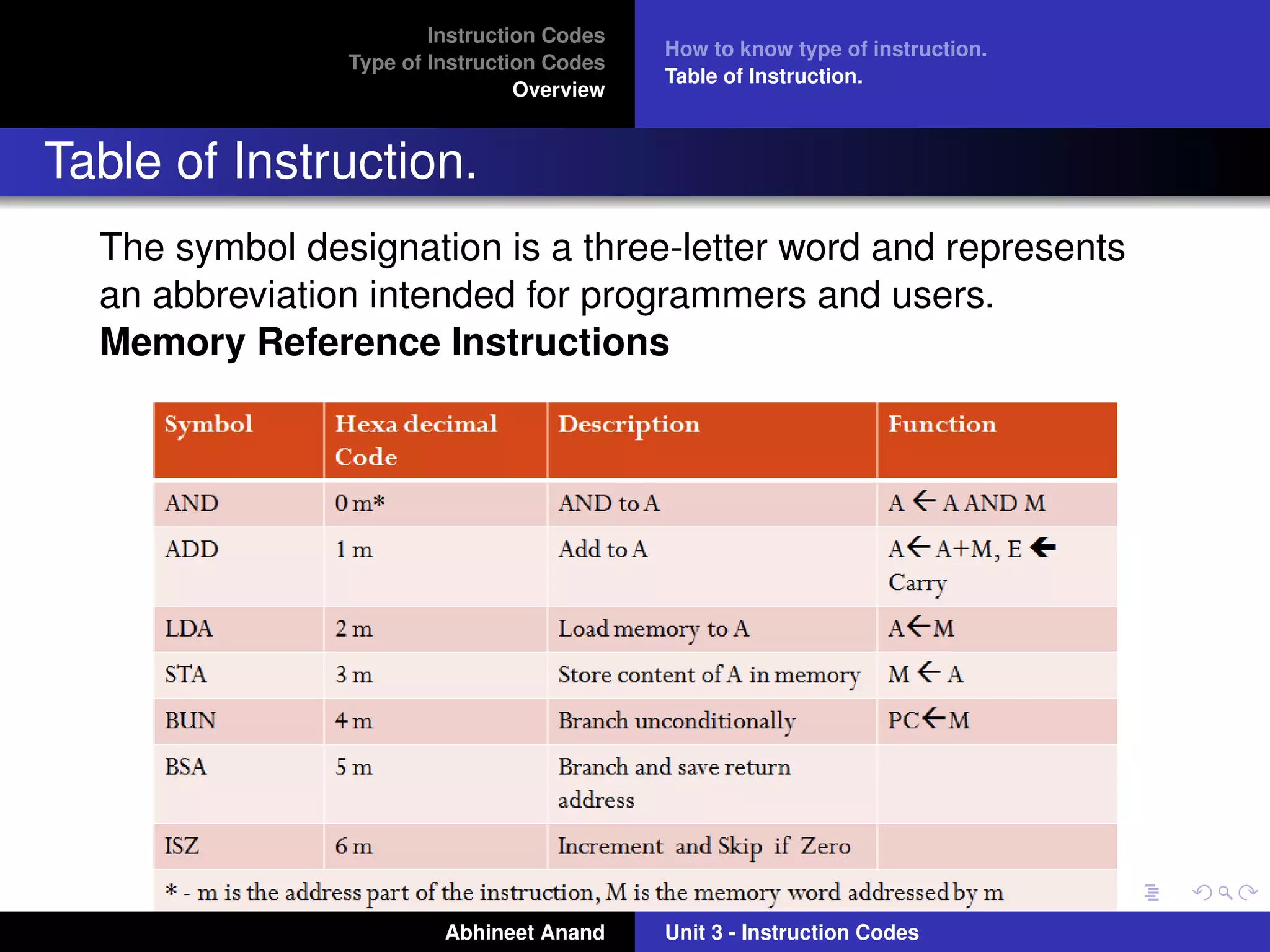
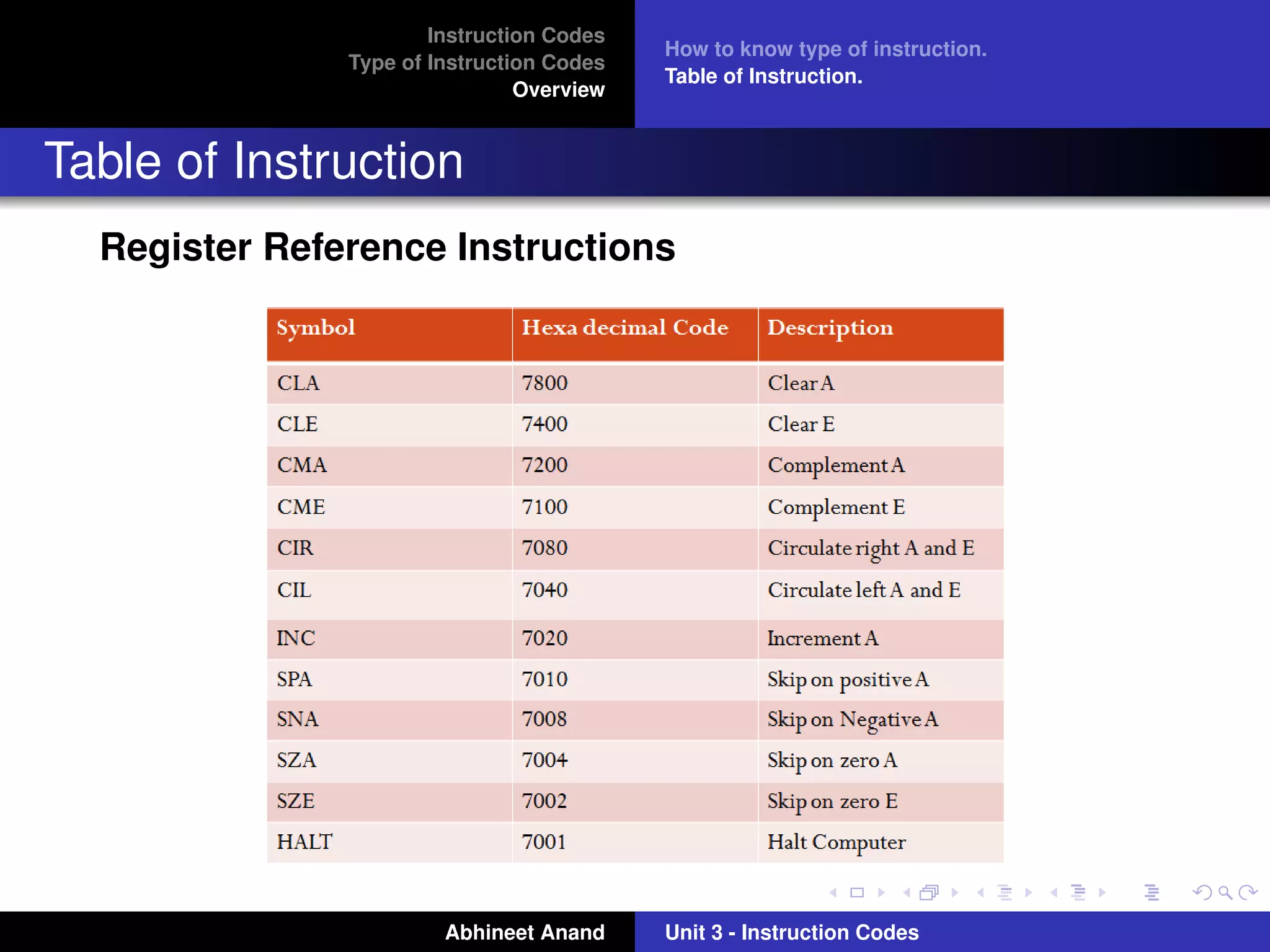
The document discusses different types of instruction codes used in computers. It explains that instruction codes contain operation codes and operands. The operation code specifies the operation to be performed, like addition, subtraction, etc. The operands specify the data on which the operation will be performed, which can be stored in memory or registers. The document outlines three main types of instruction codes - memory reference instructions, register reference instructions, and input-output instructions. It describes the format of each type of instruction and how they are interpreted by the computer.