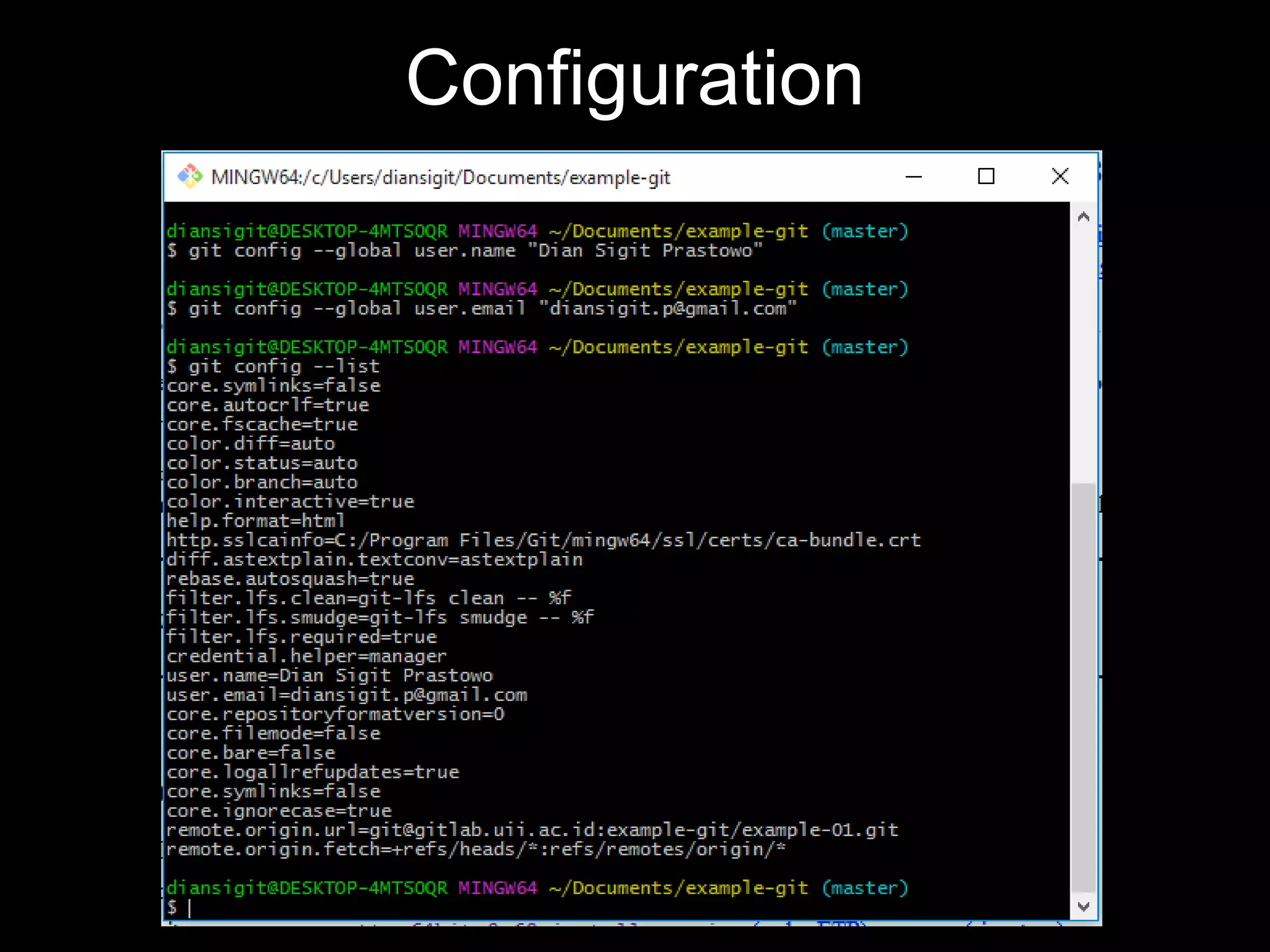
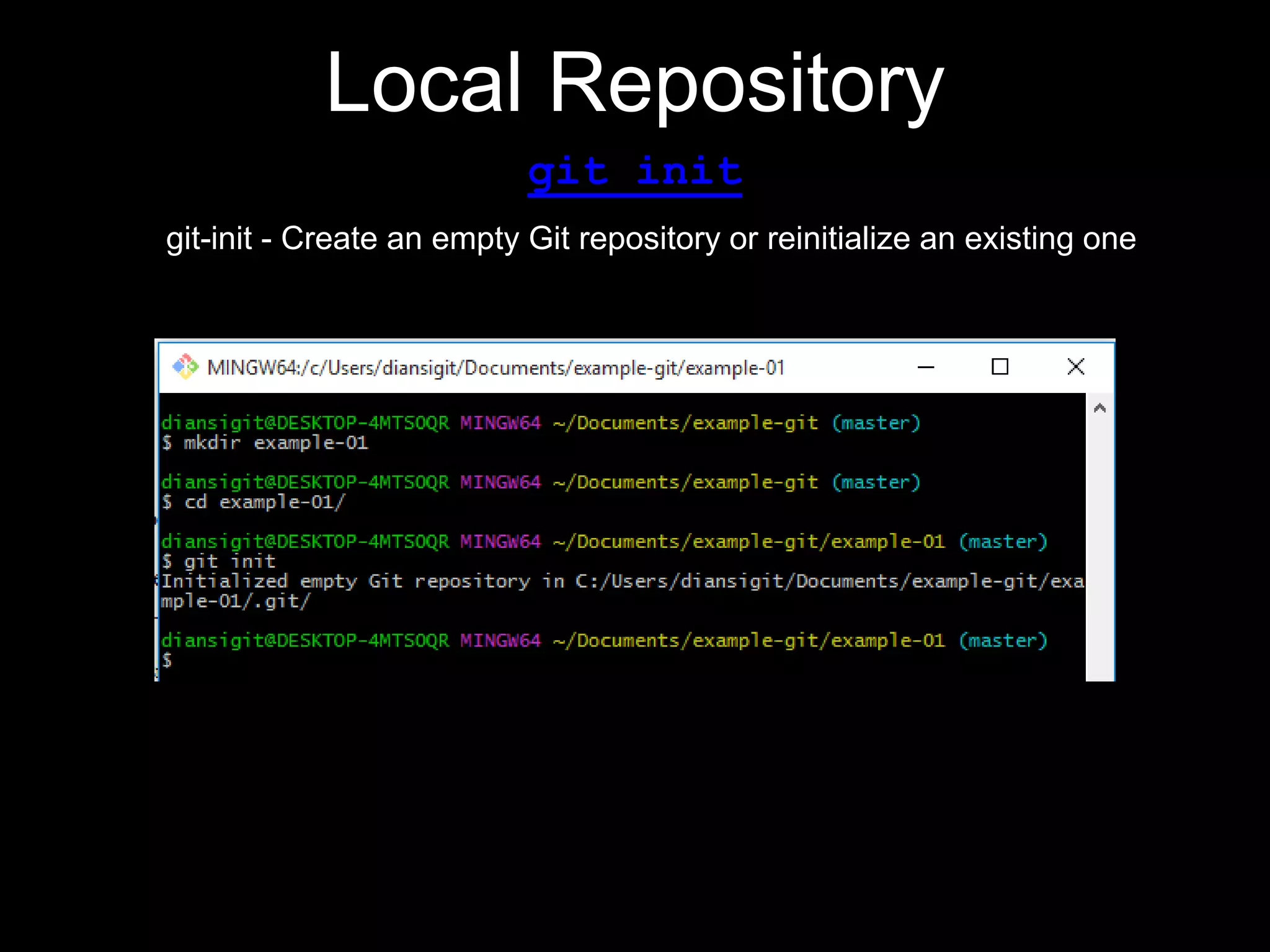
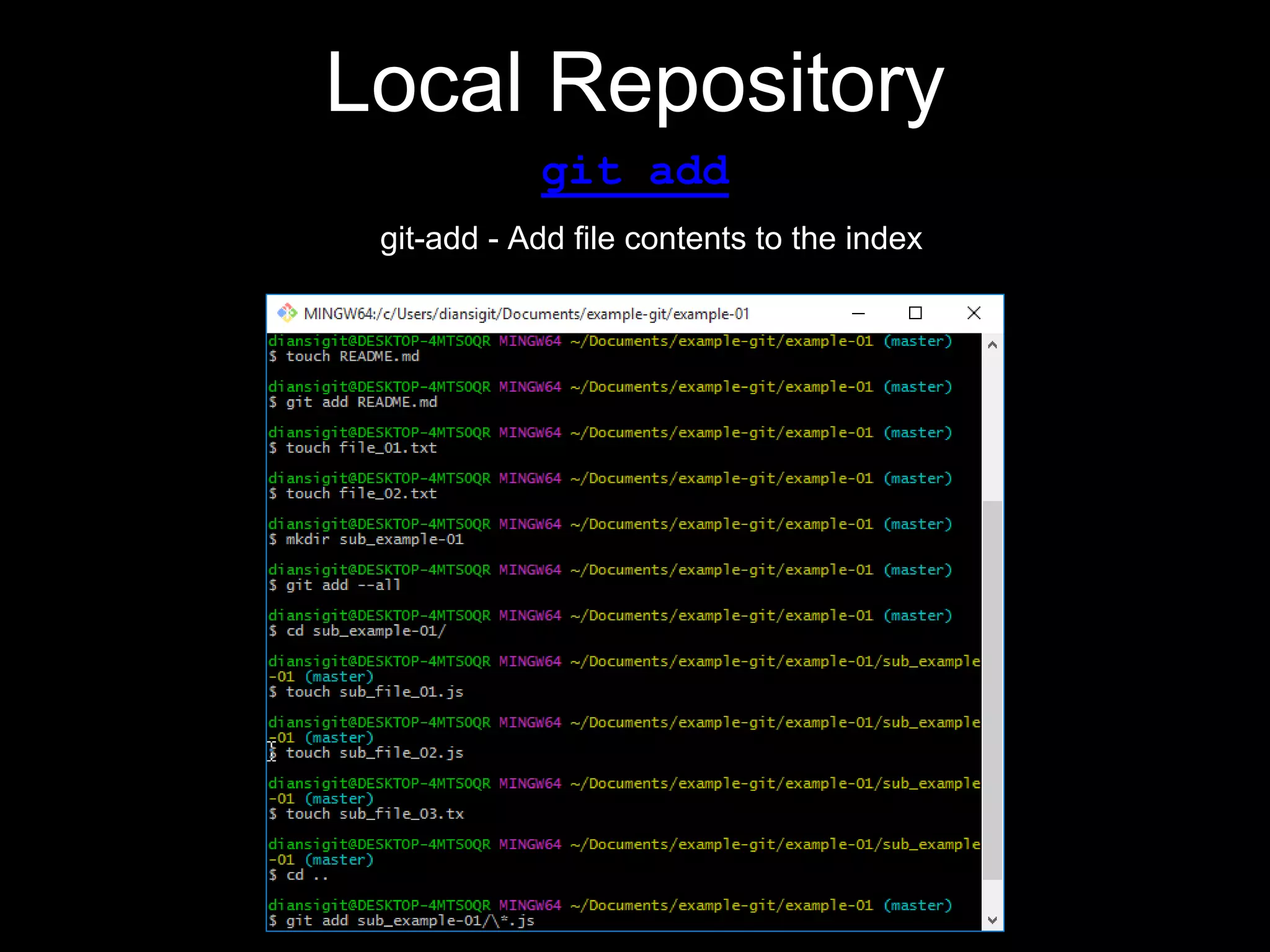
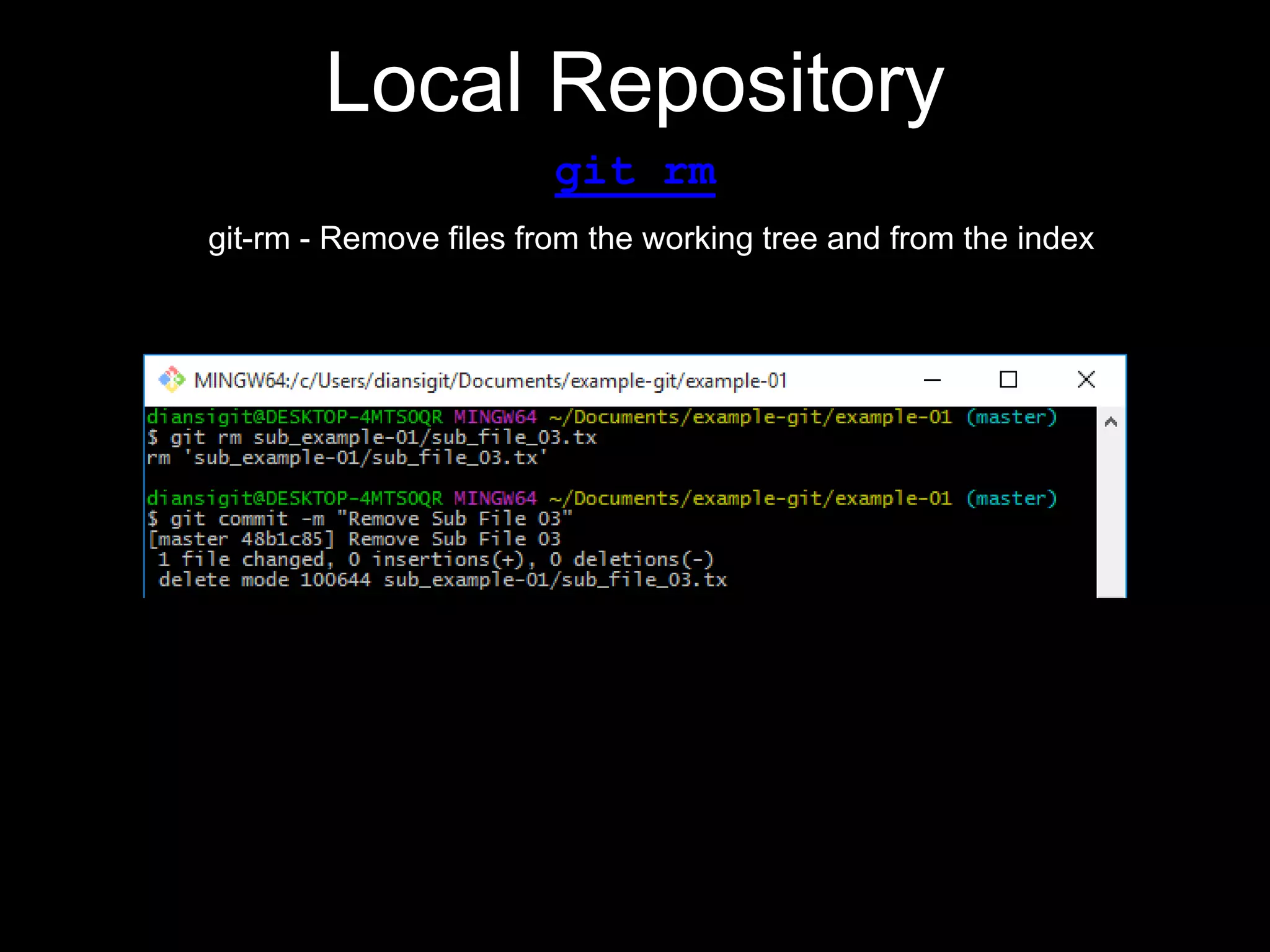
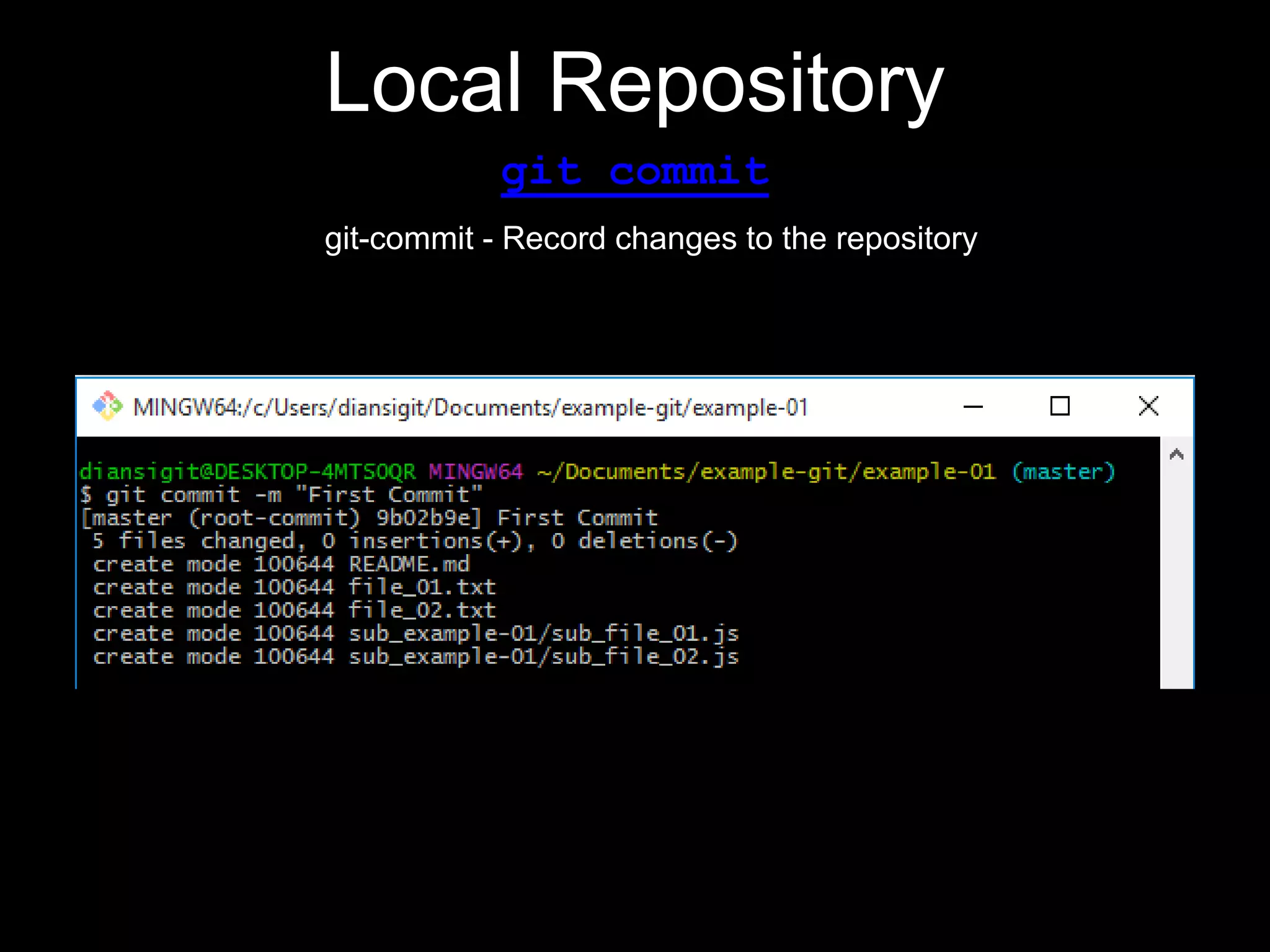
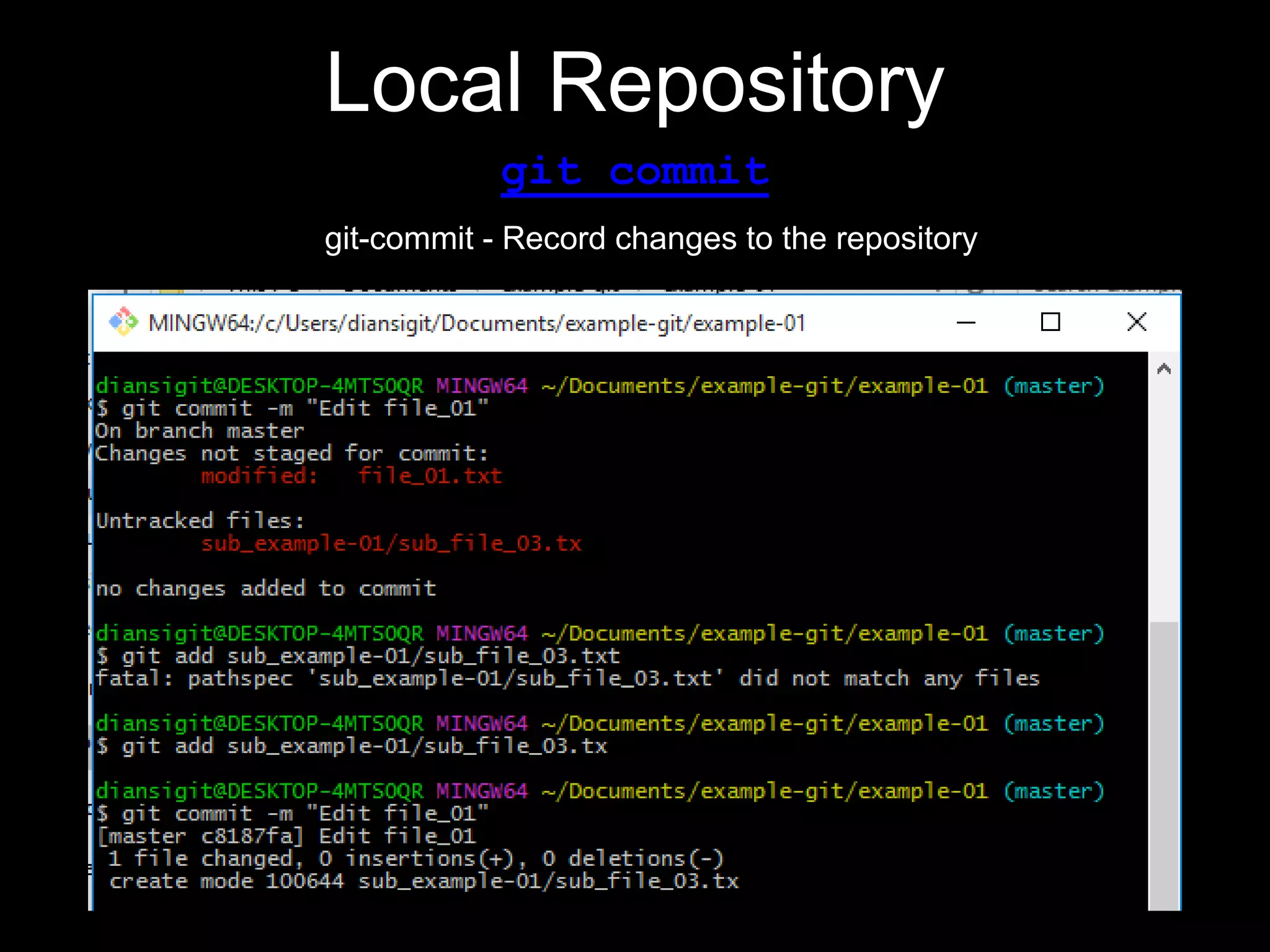
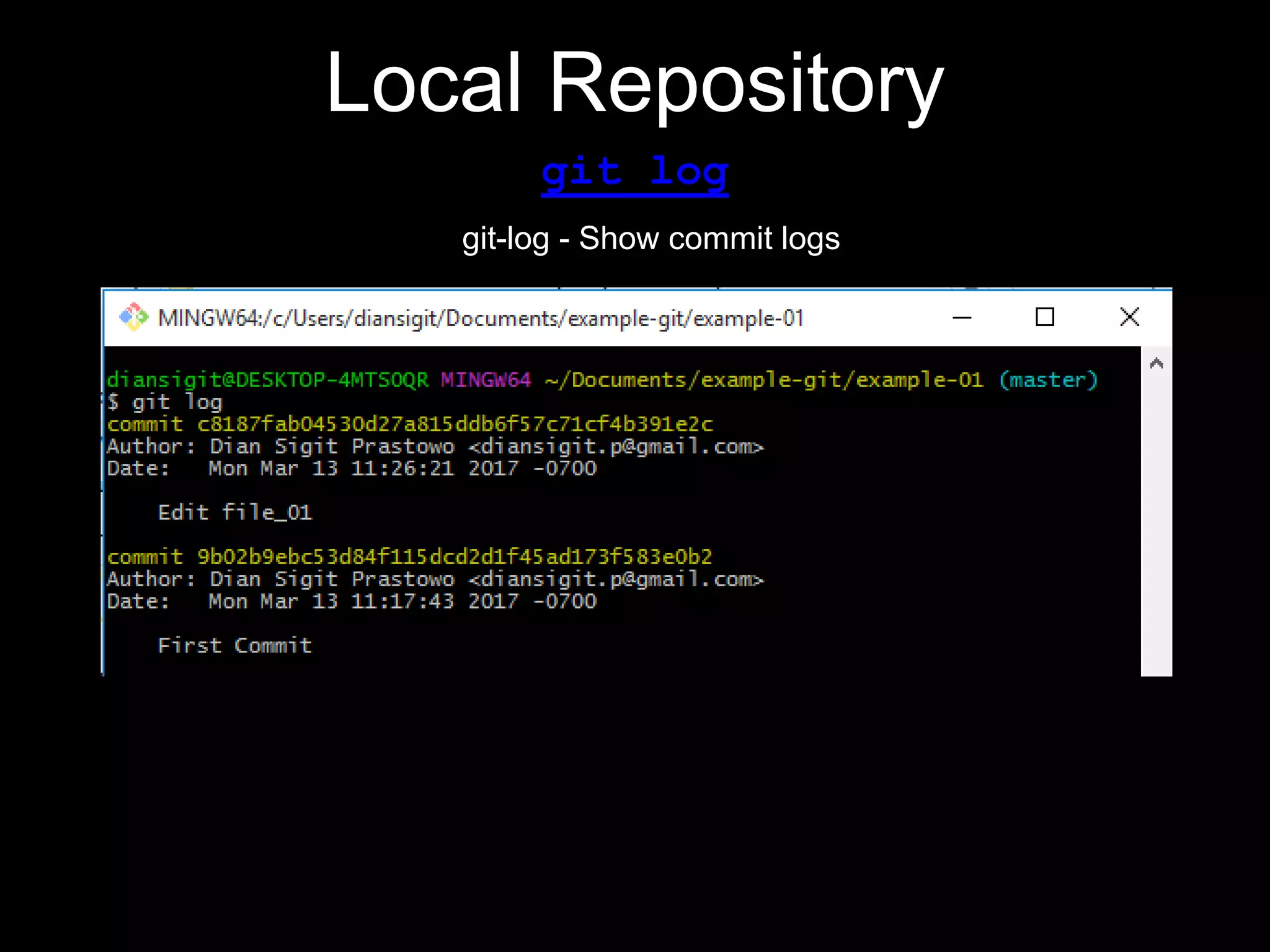
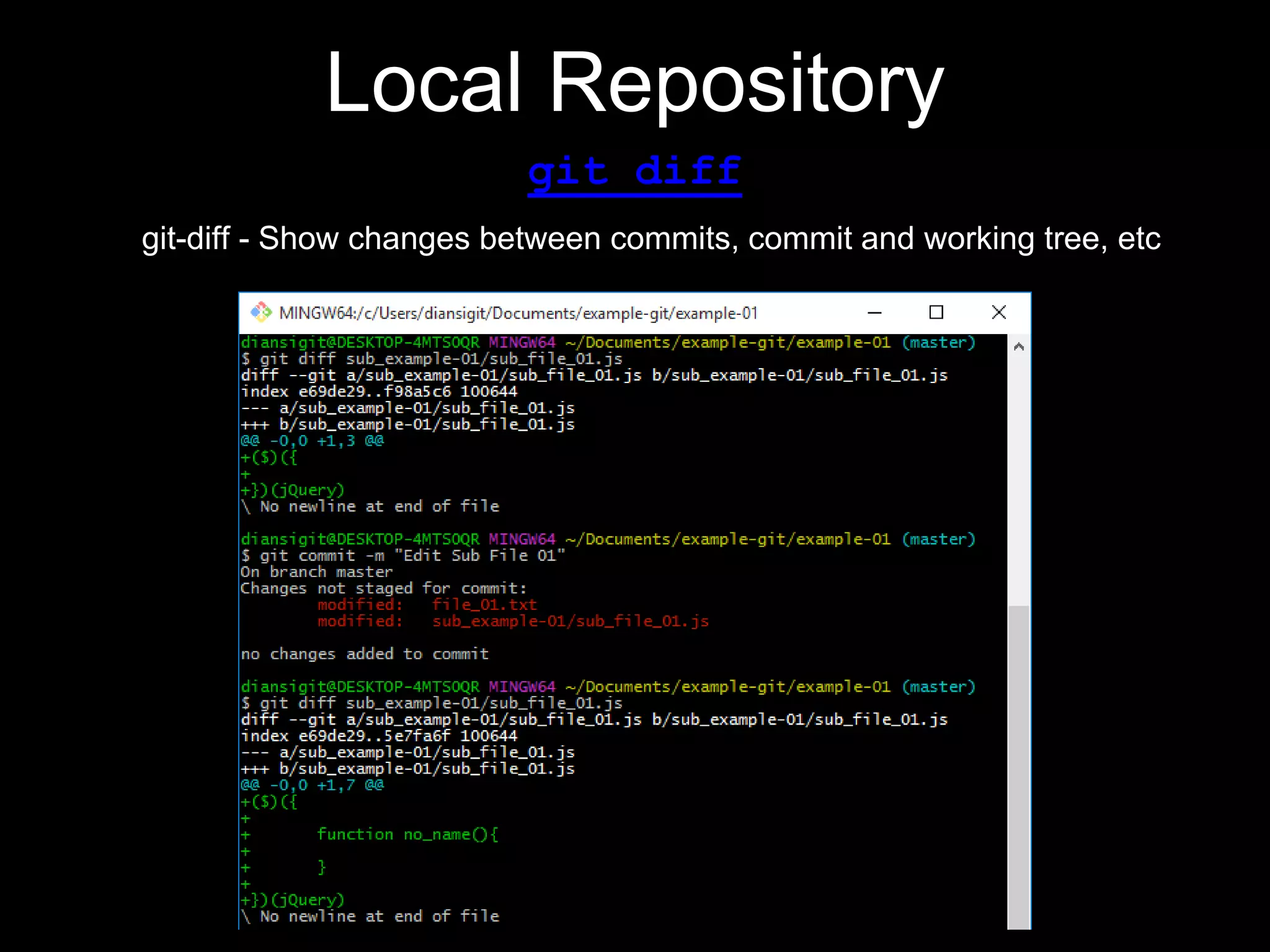
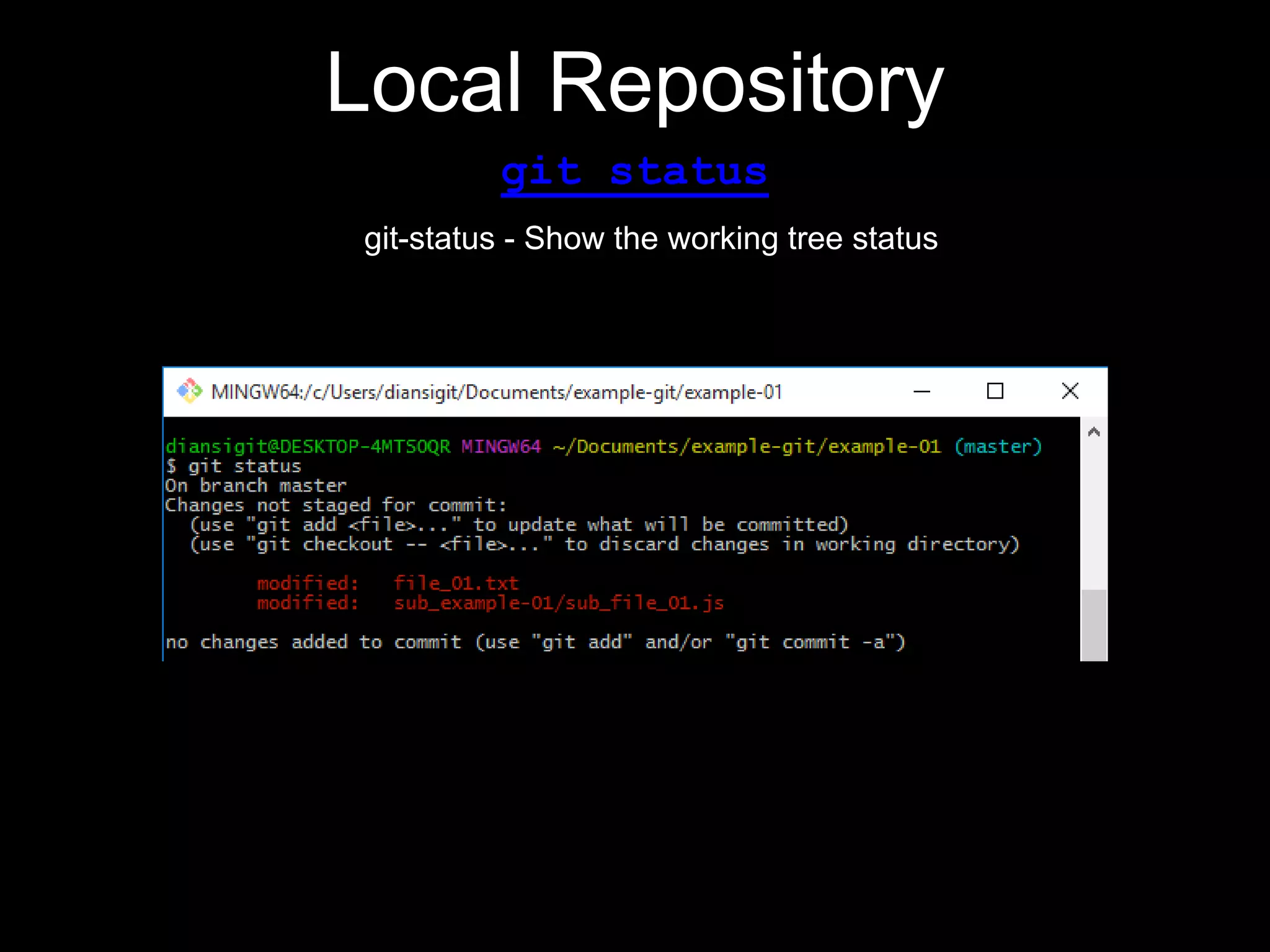
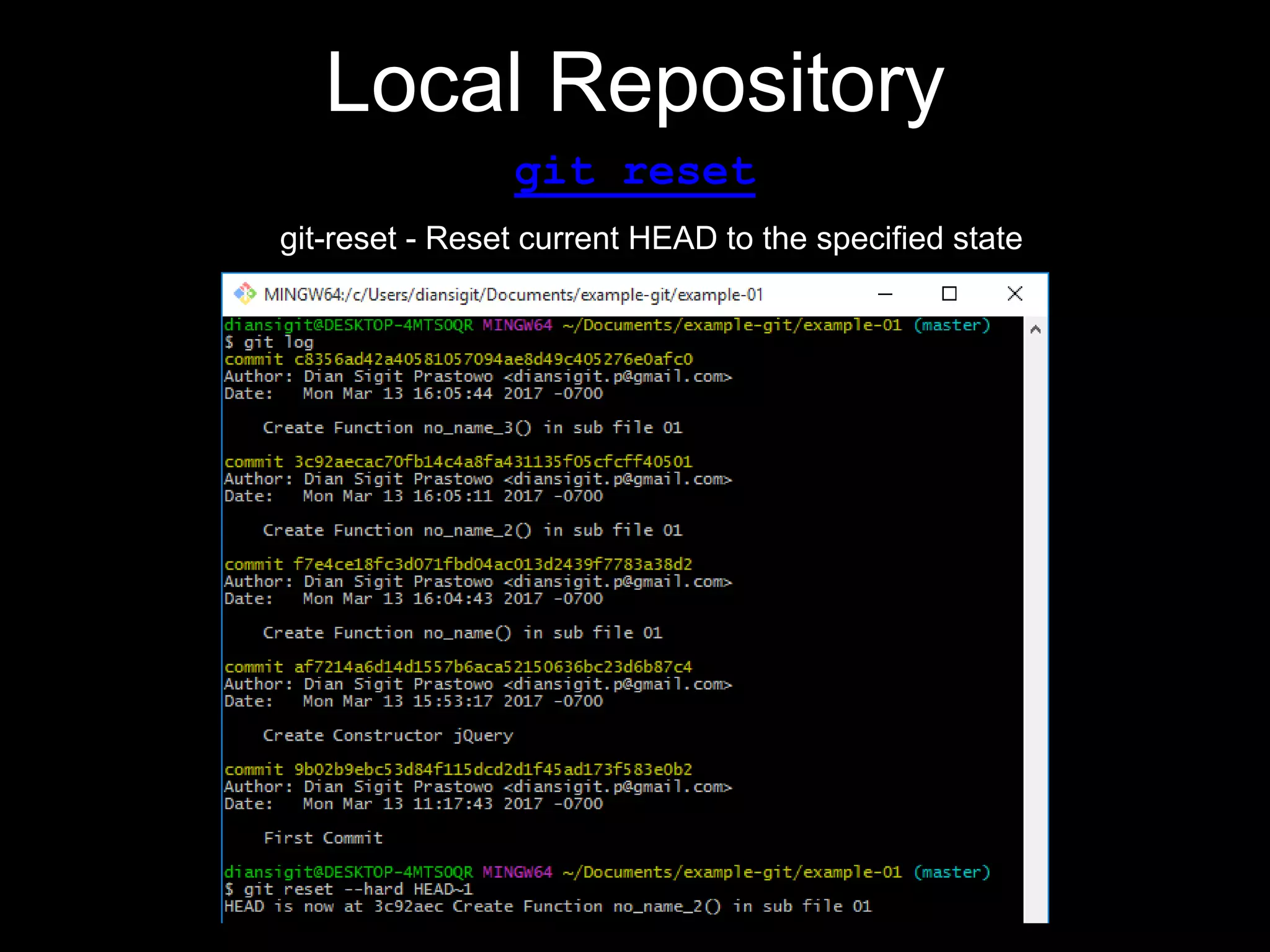
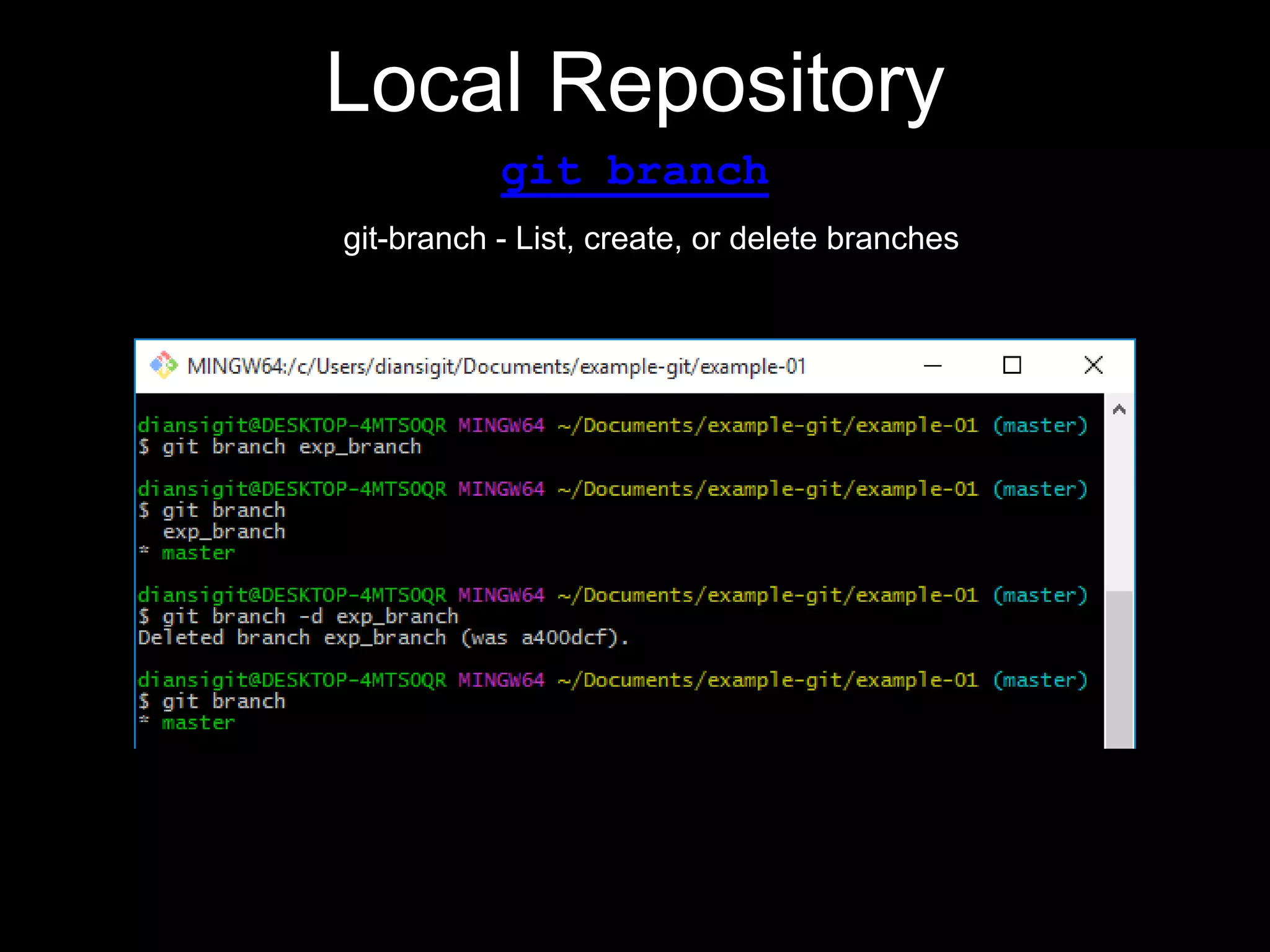
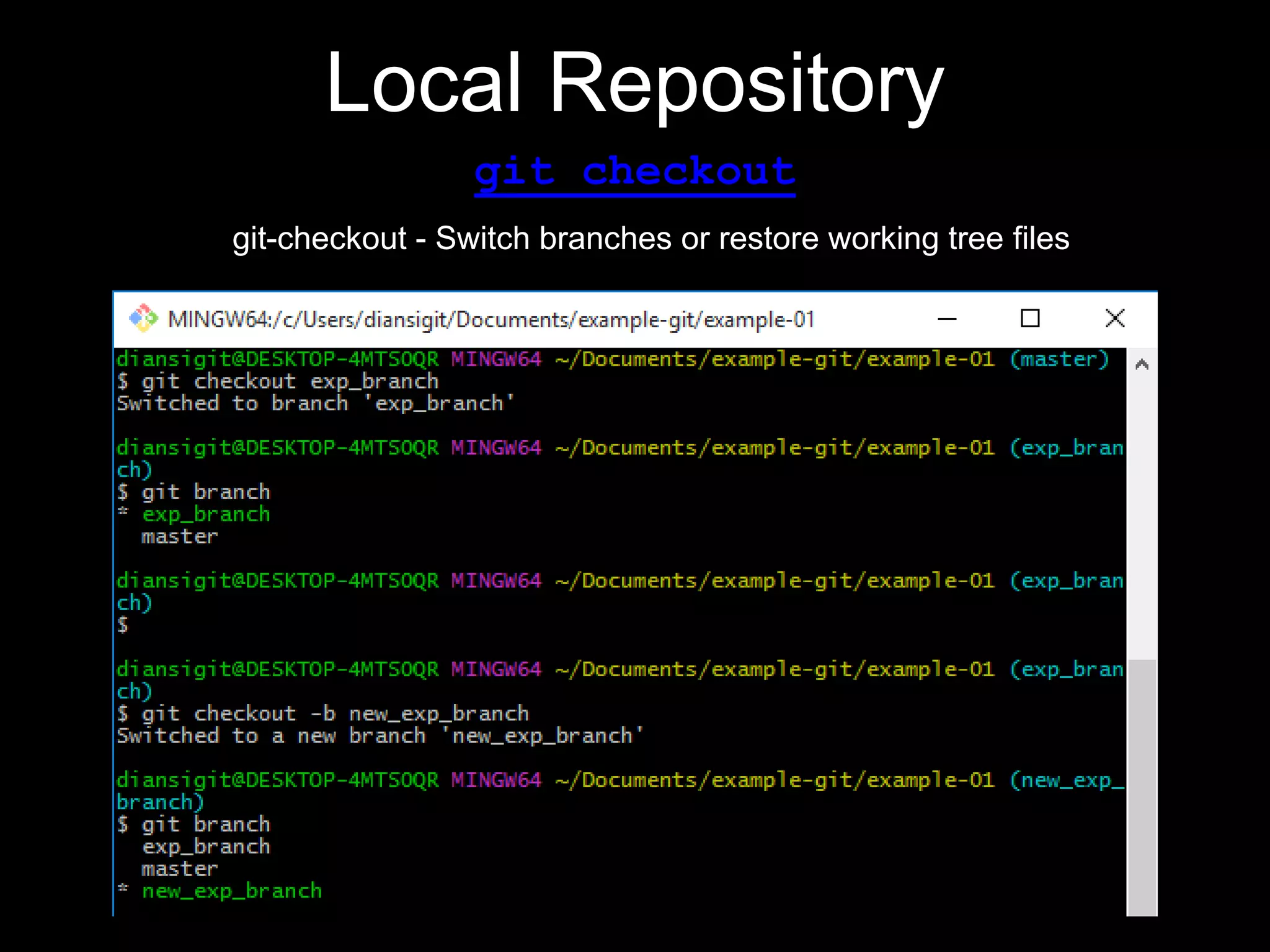
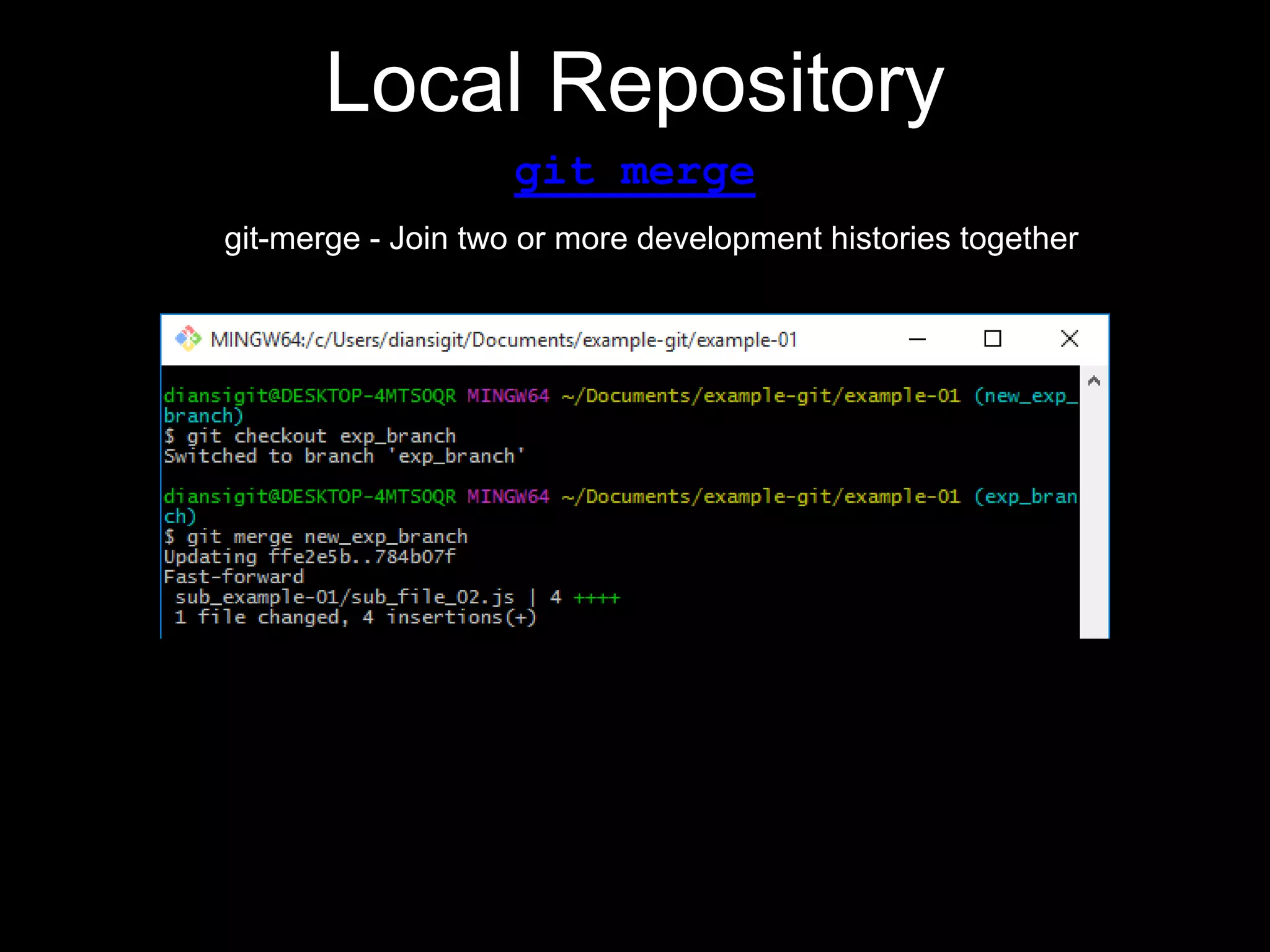
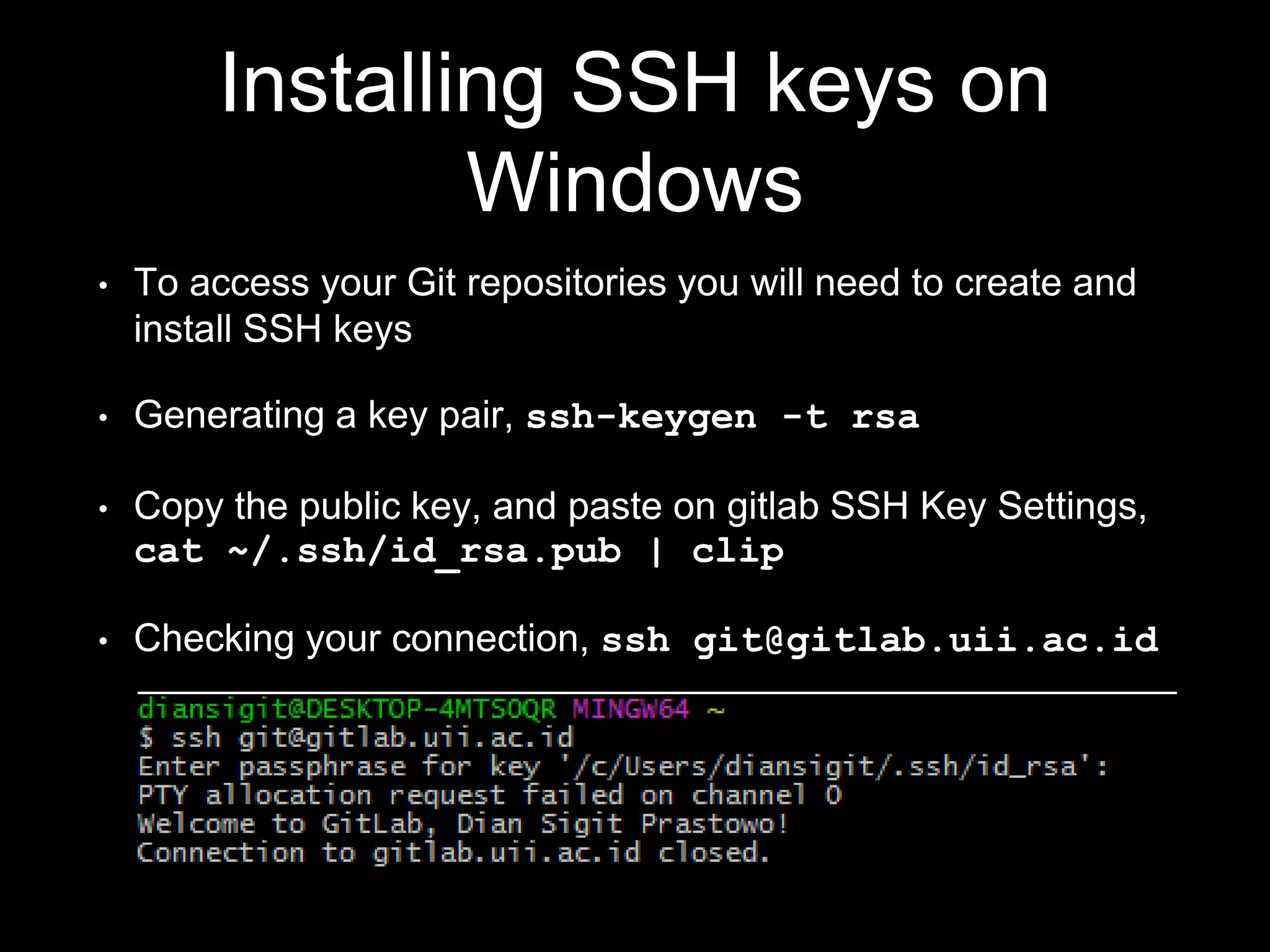
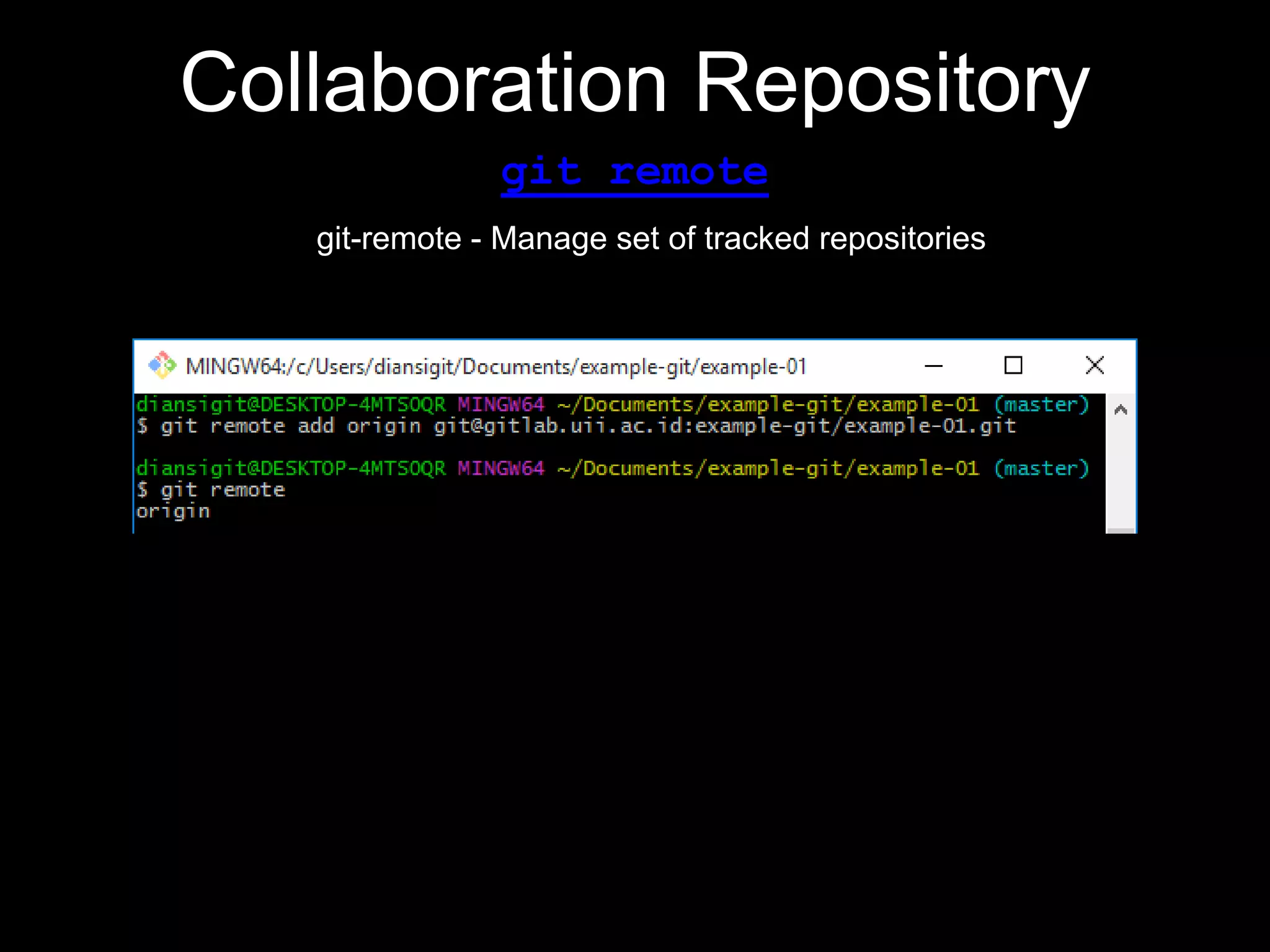
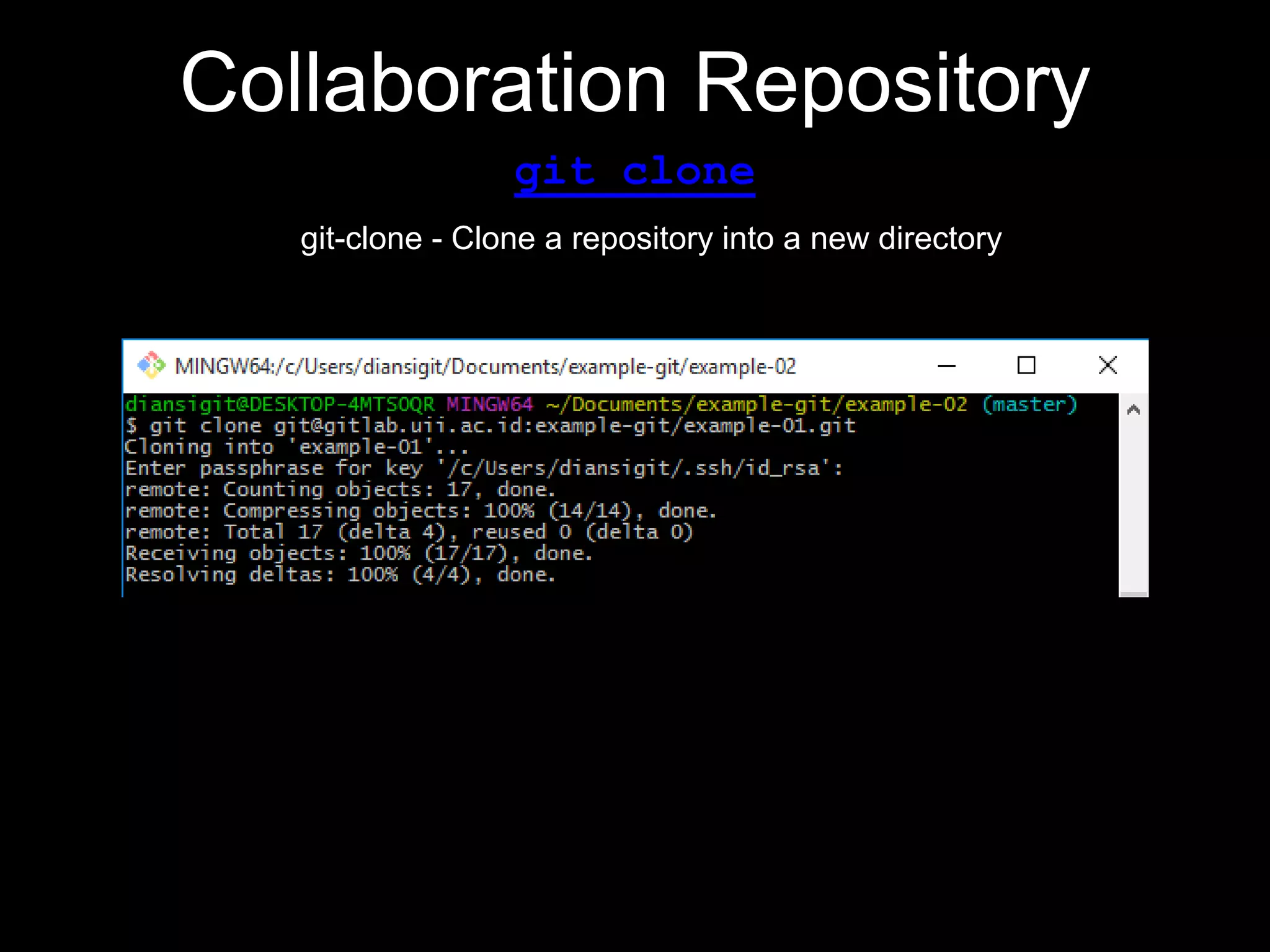
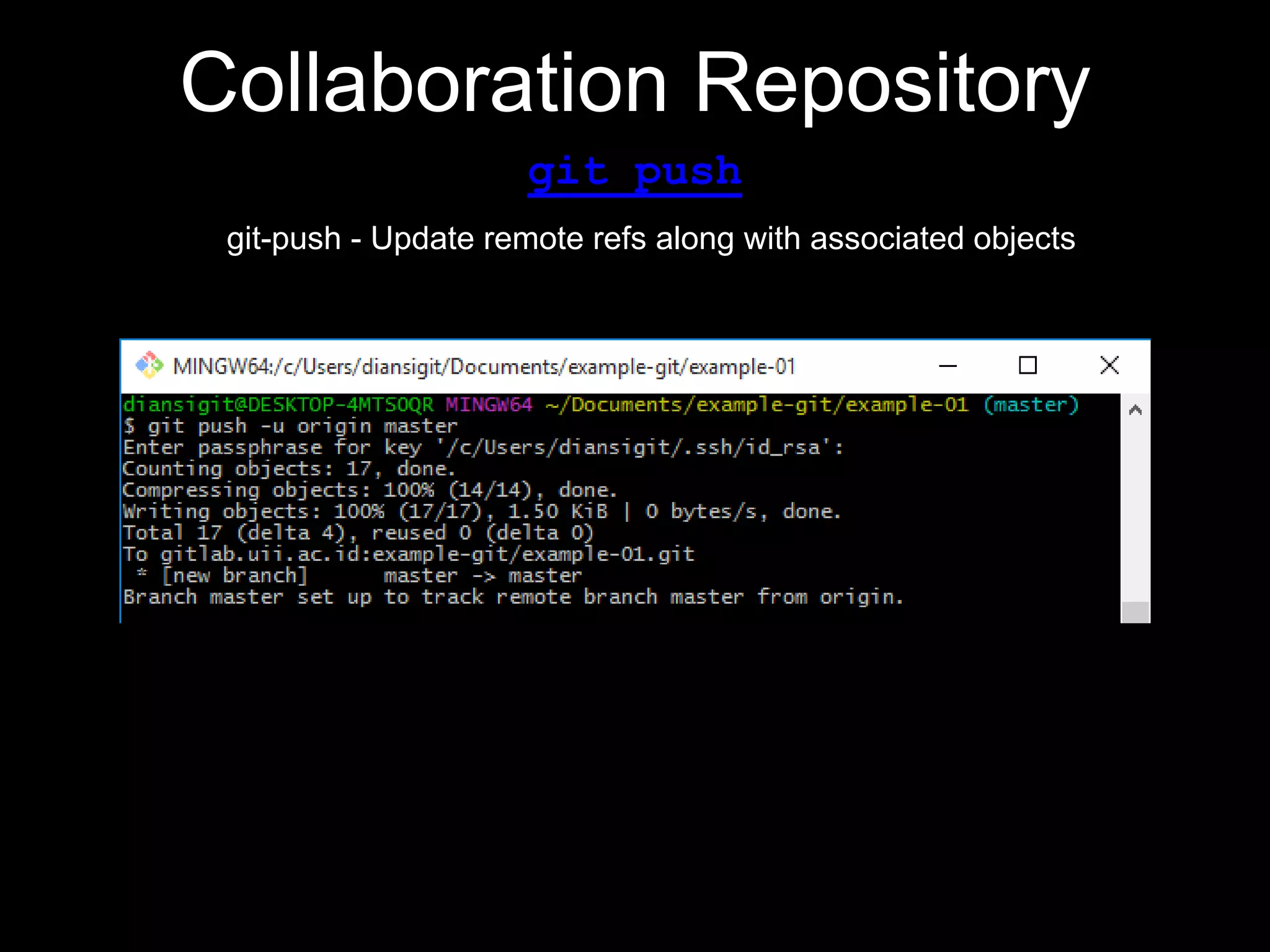
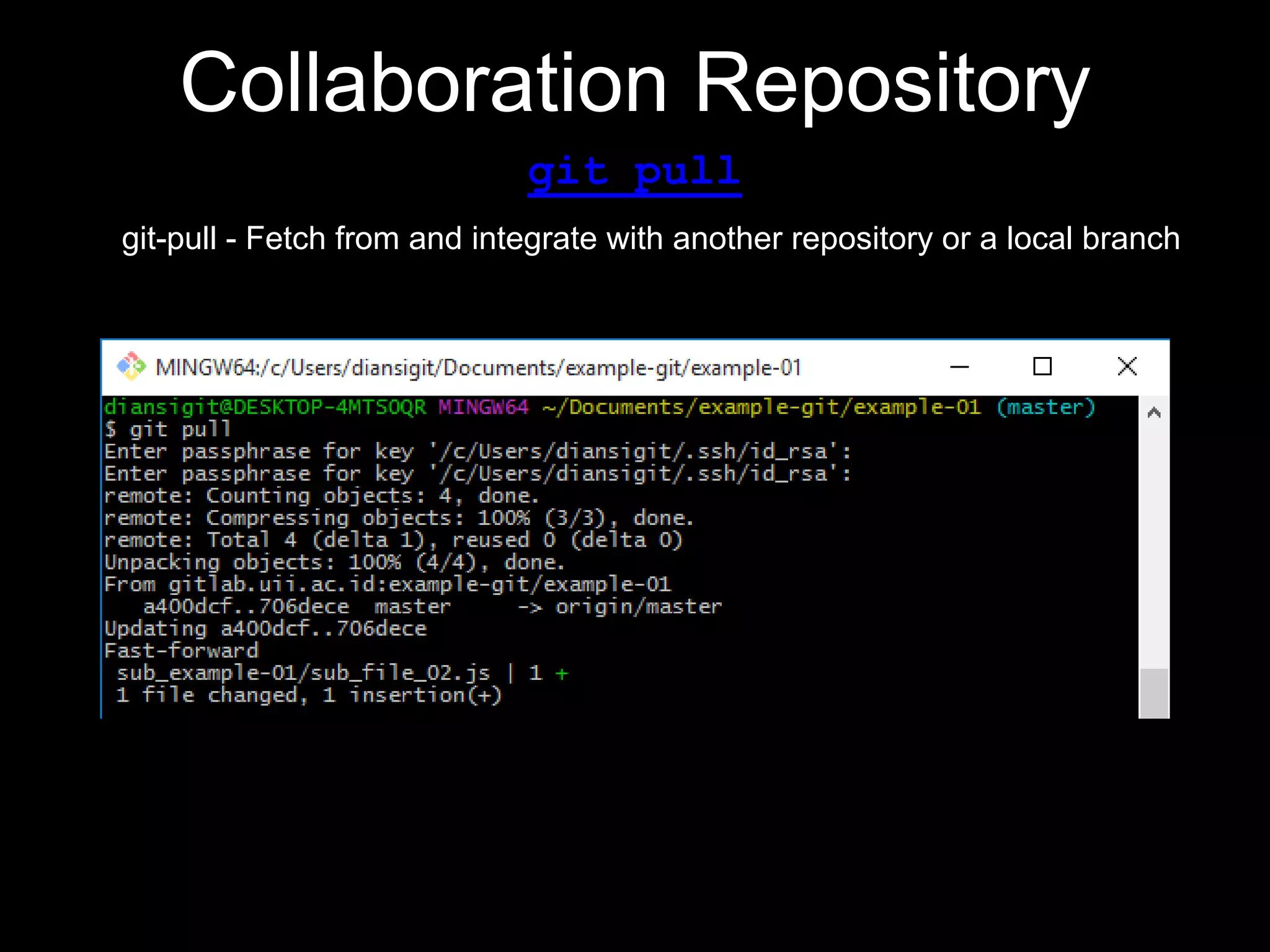
This document provides an introduction to the version control system Git. It defines key Git concepts like the working tree, repository, commit, and HEAD. It explains that Git is a distributed version control system where the full history of a project is available once cloned. The document outlines Git's history, with it being created by Linus Torvalds to replace the commercial BitKeeper tool. It then lists and briefly describes important Git commands for local and collaboration repositories, including config, add, commit, log, diff, status, branch, checkout, merge, remote, clone, push, and pull. Lastly, it covers installing Git and generating SSH keys on Windows for accessing Git repositories.