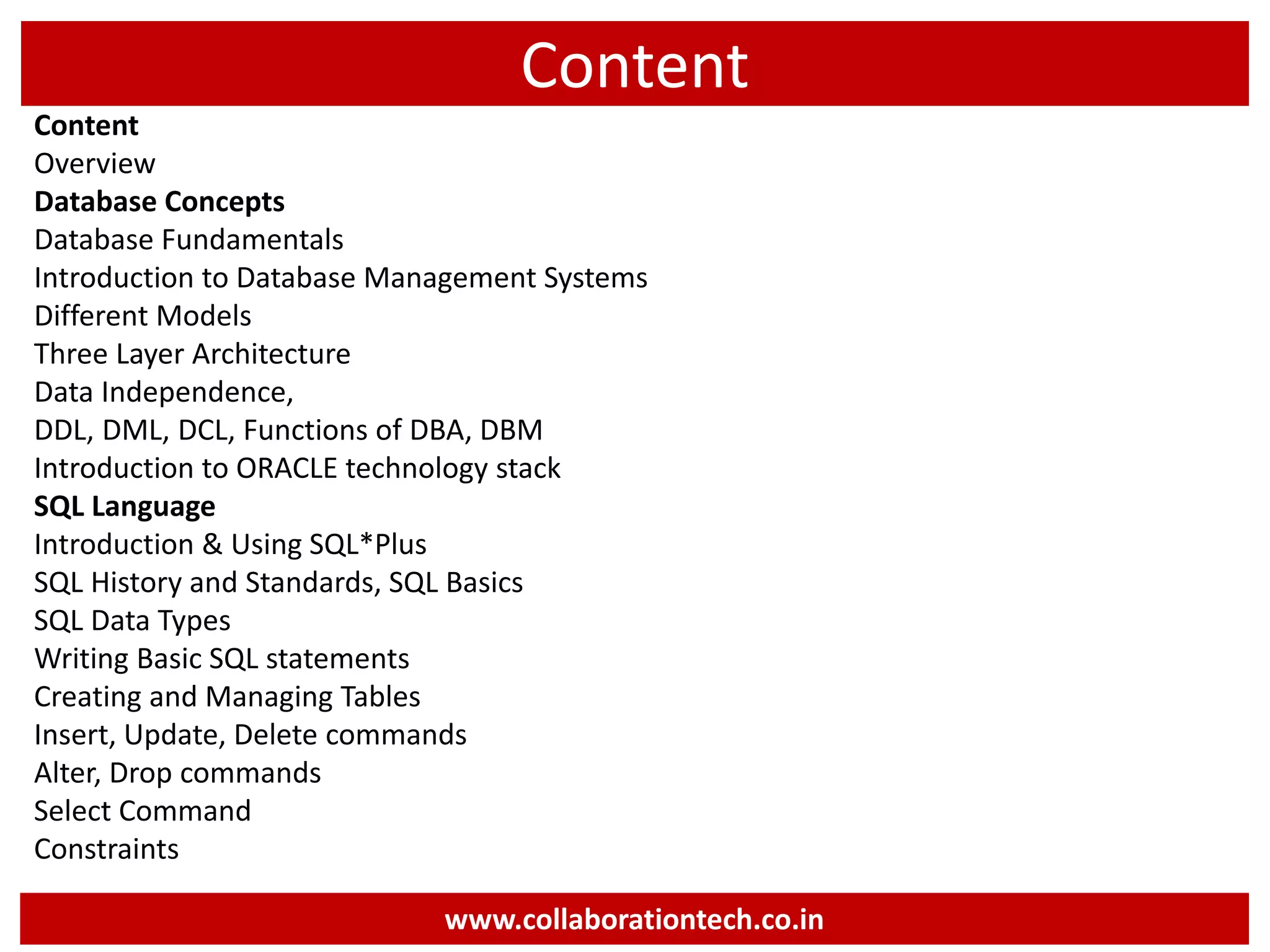
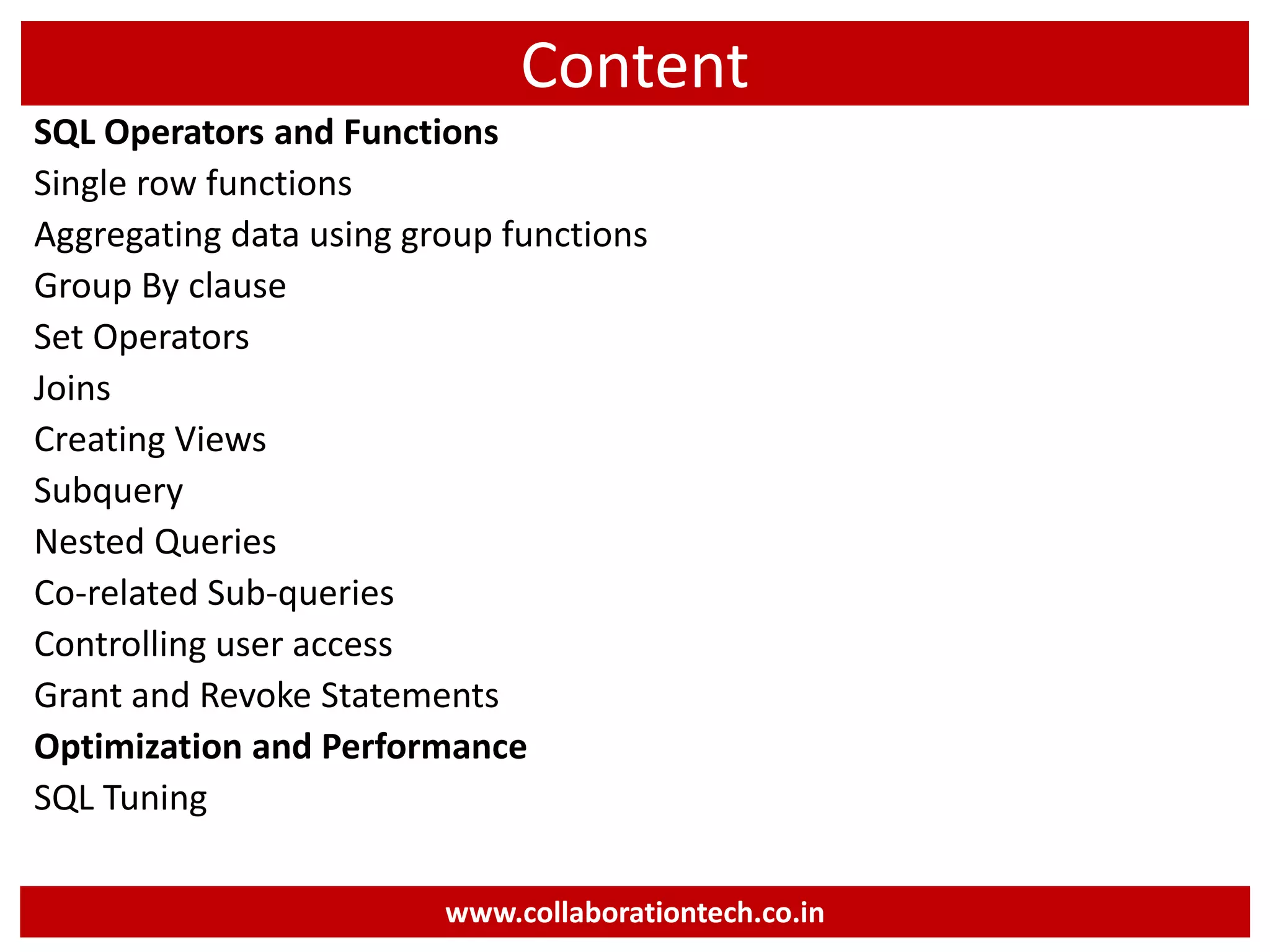
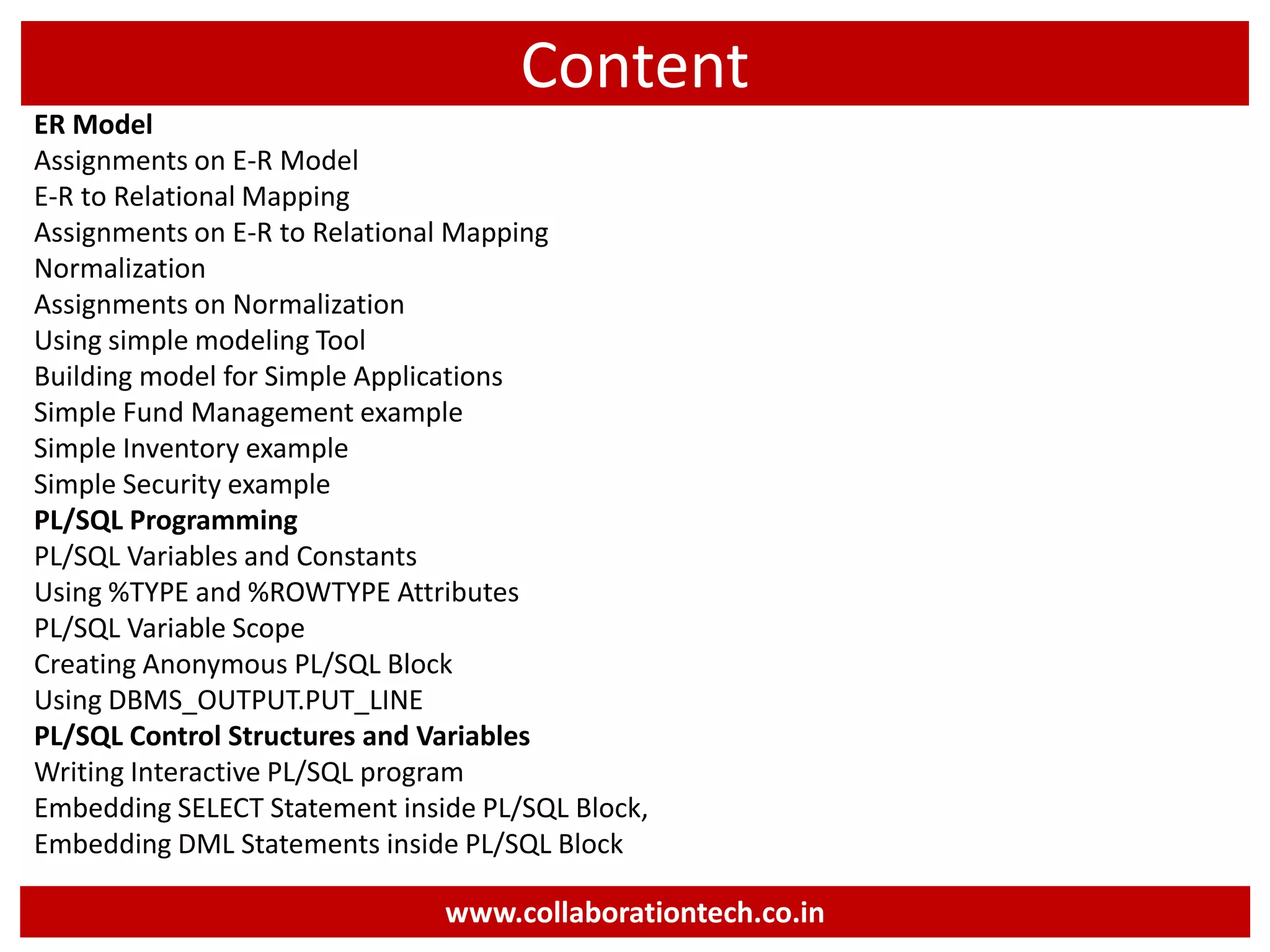
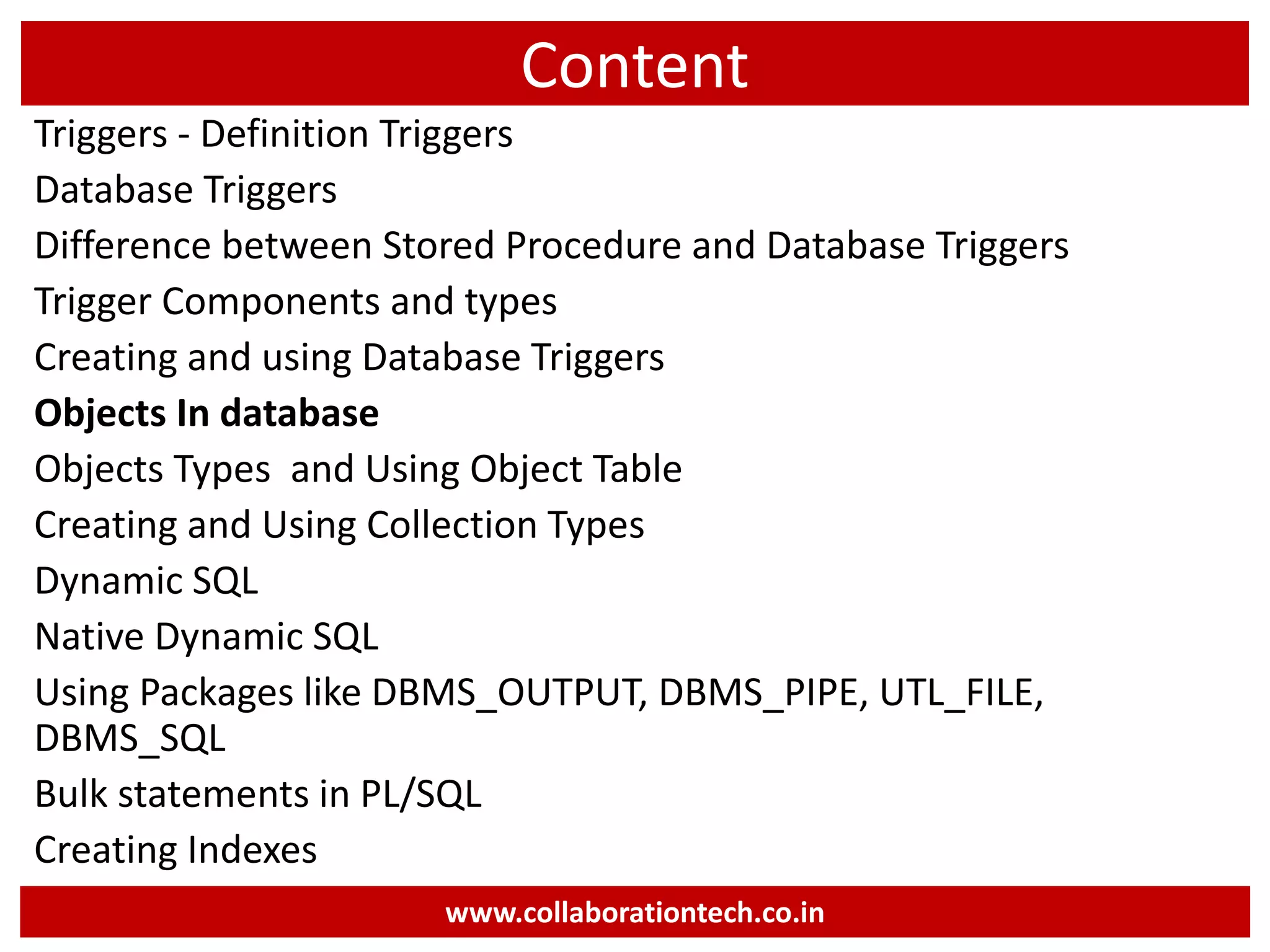
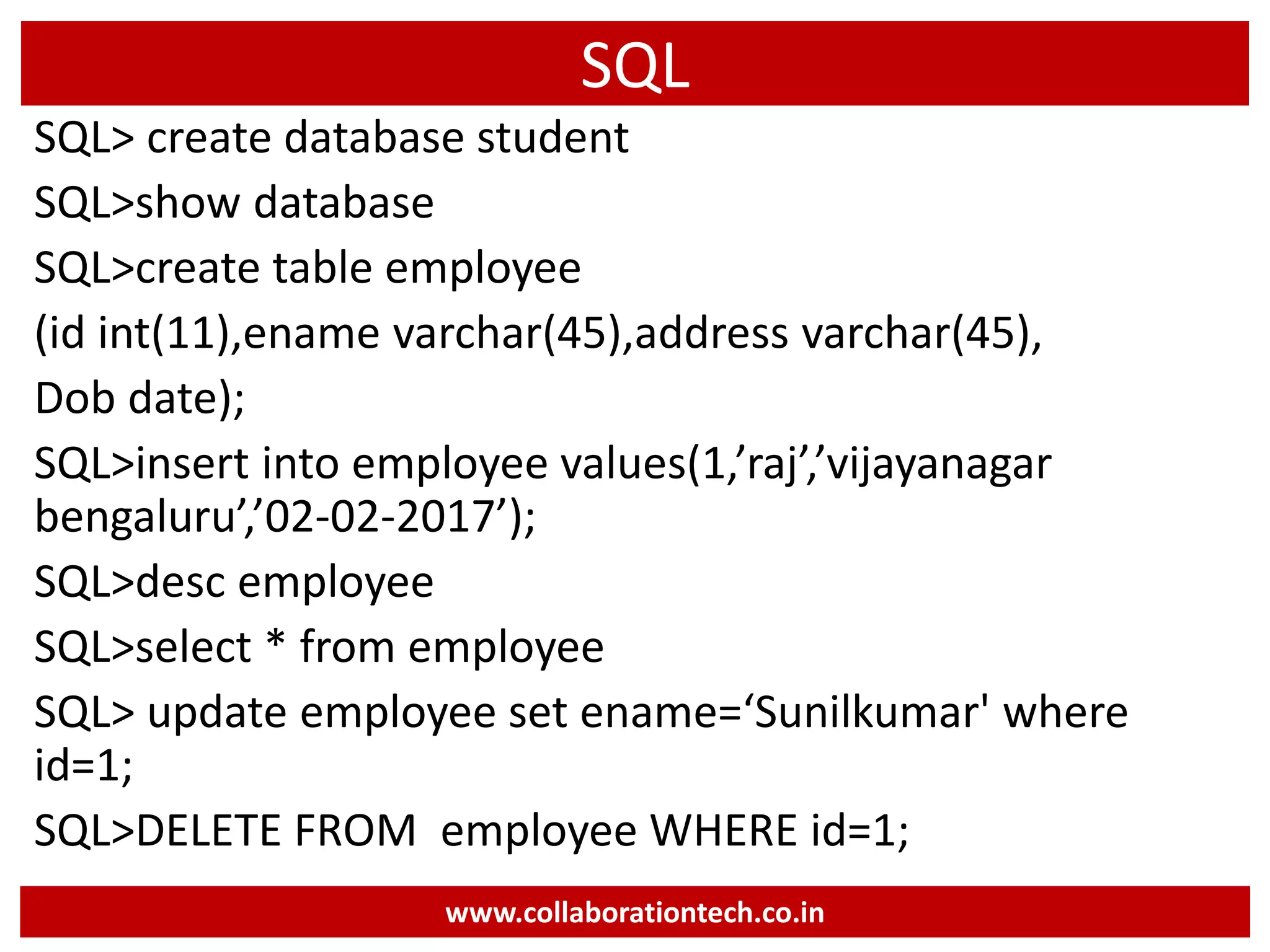
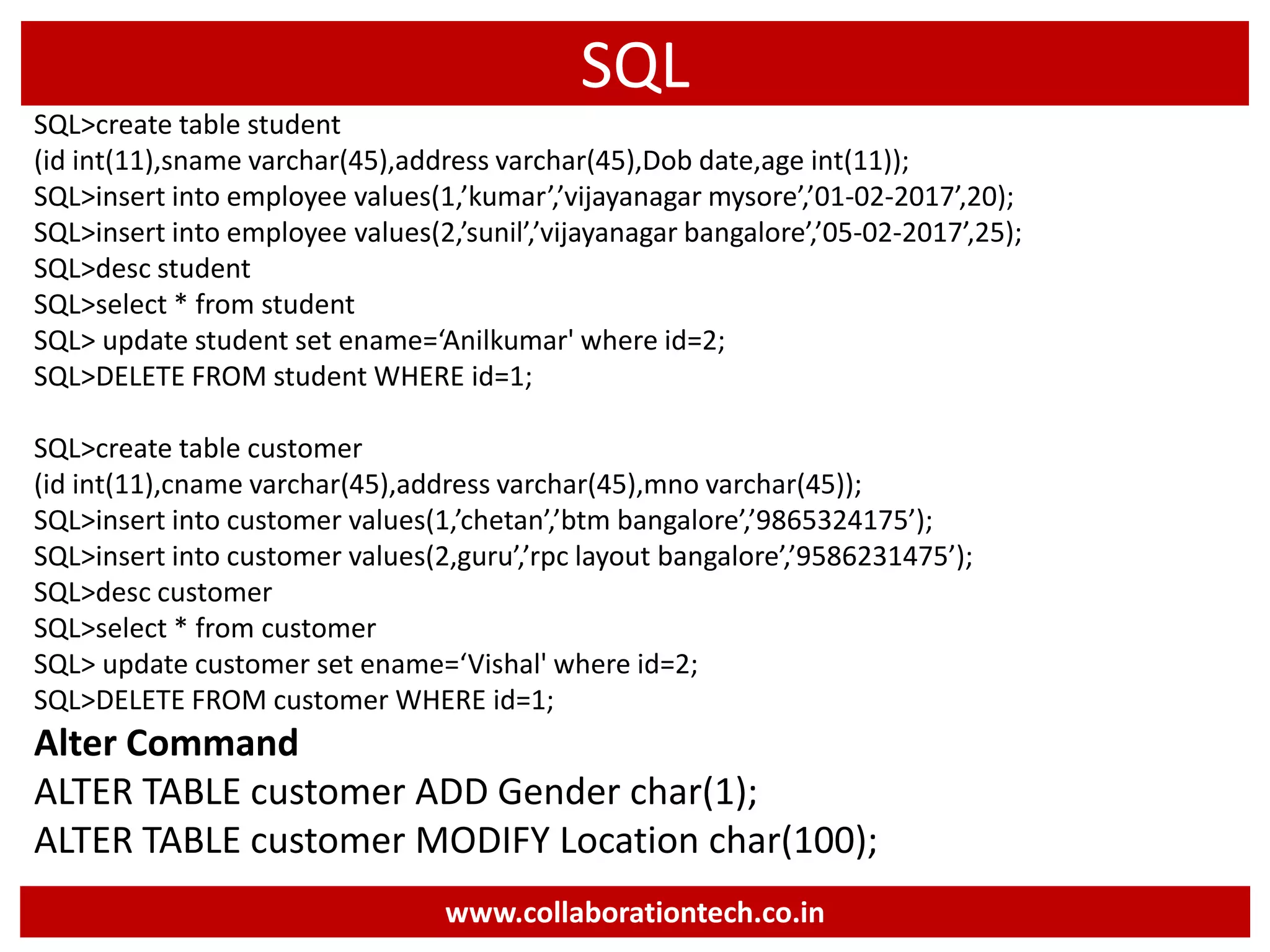
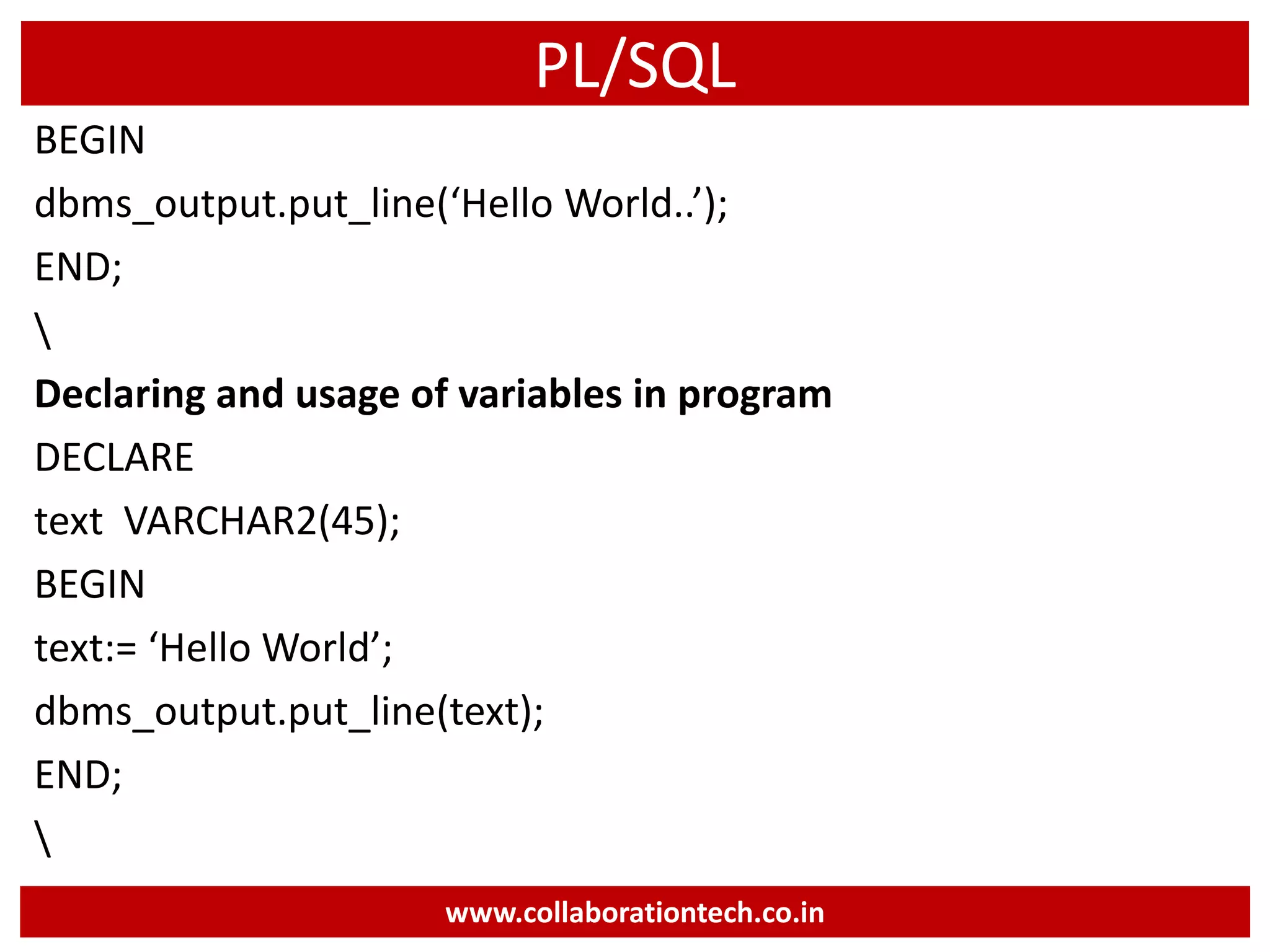
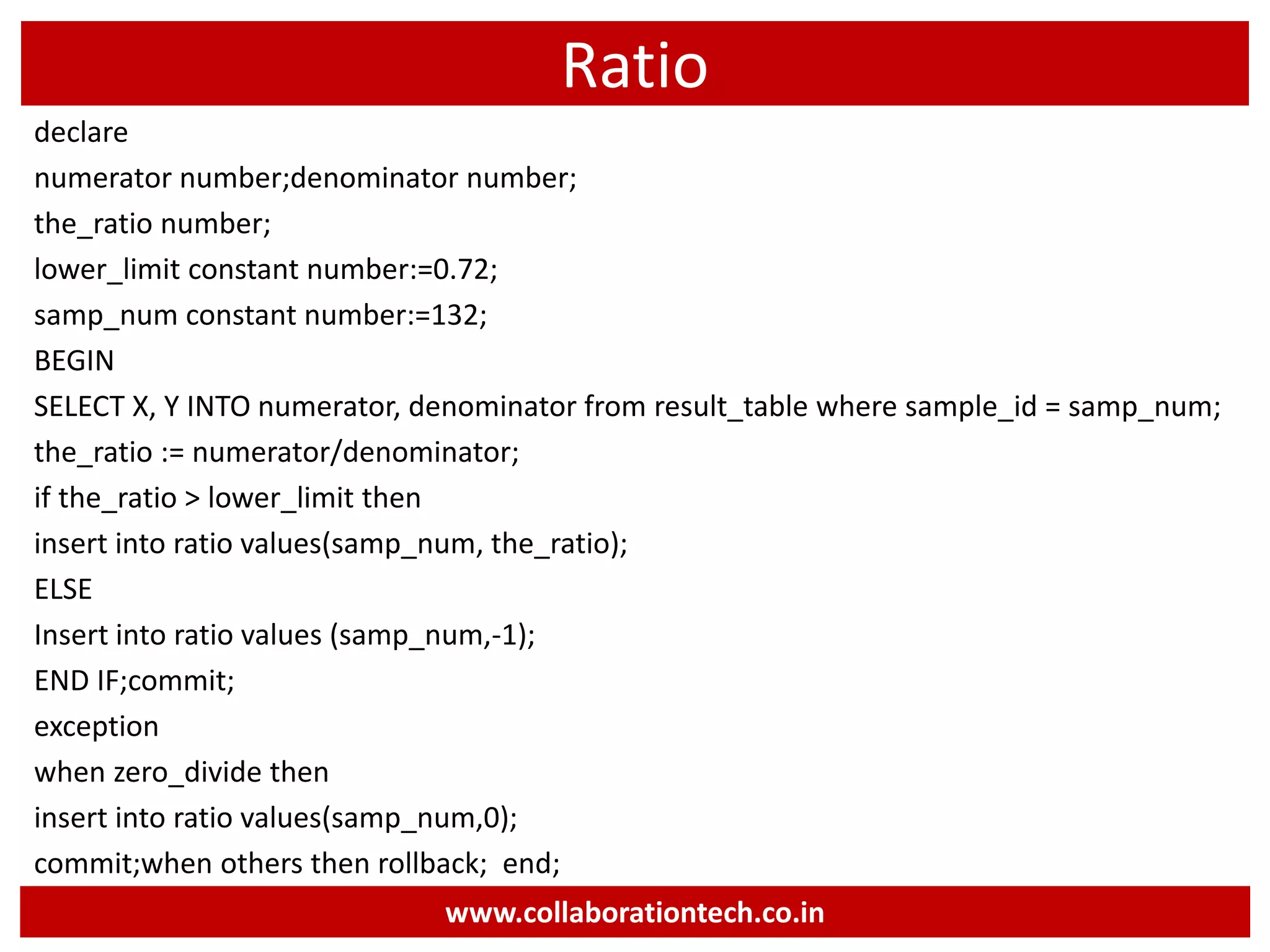
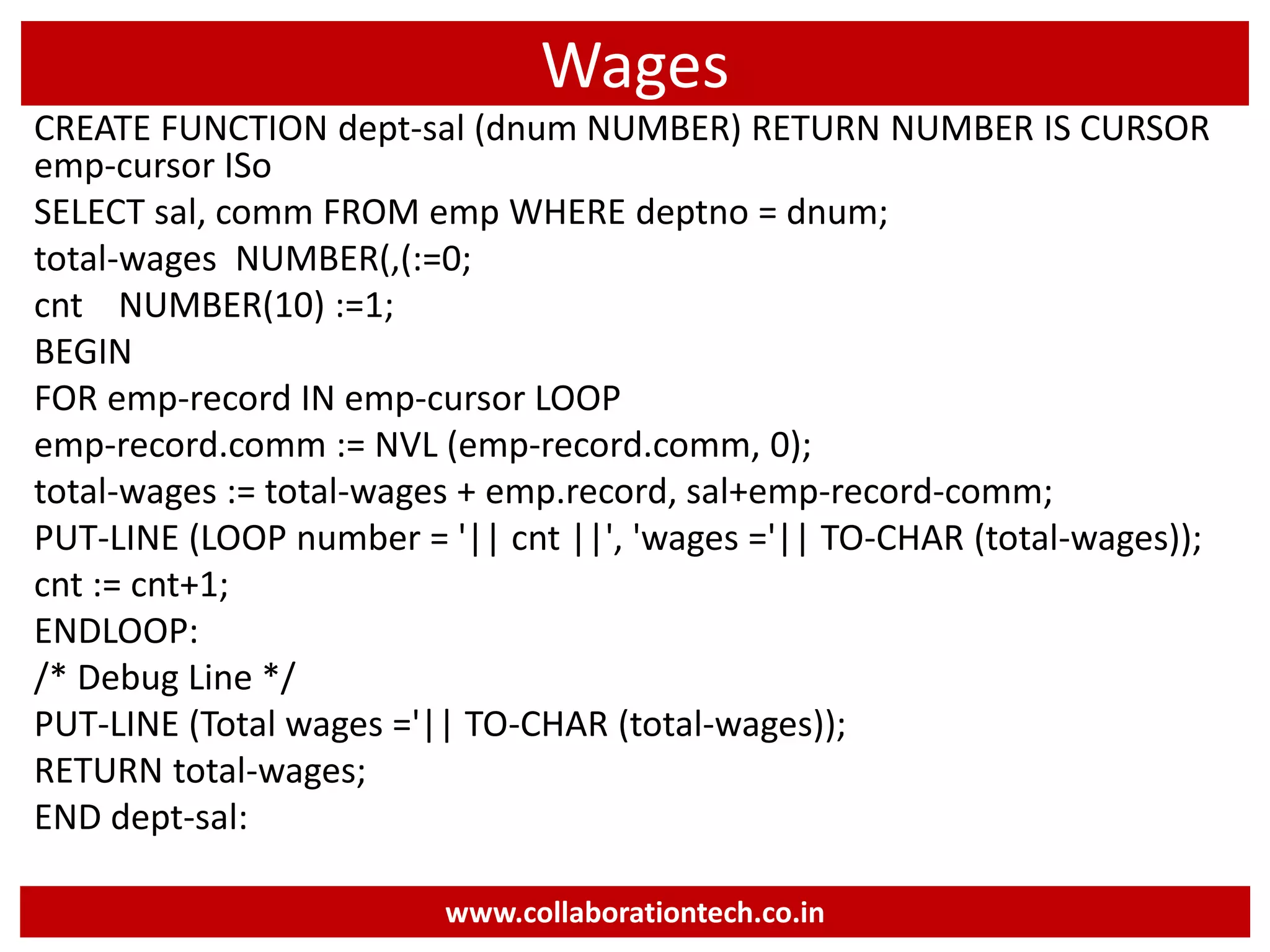
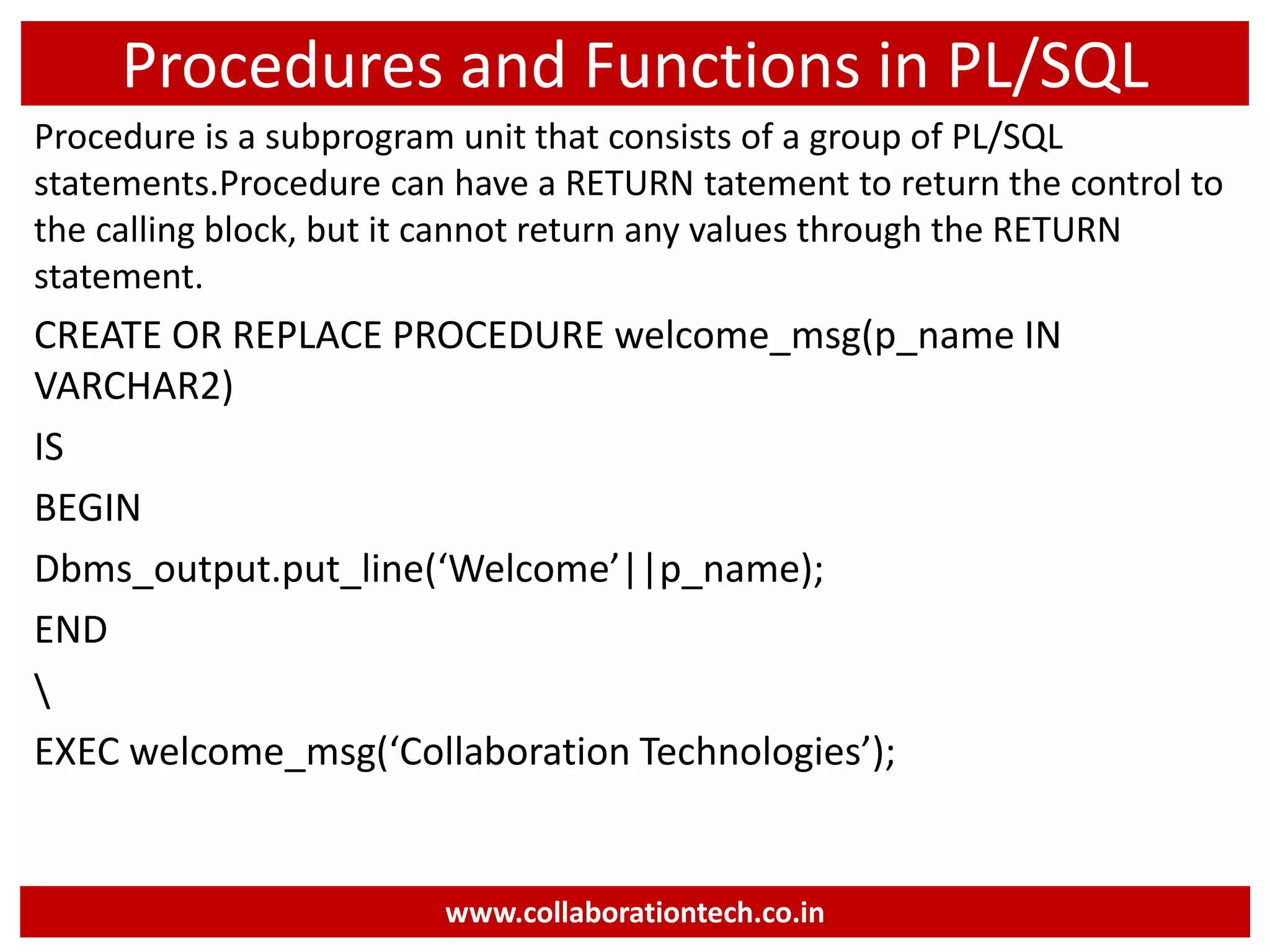
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to database concepts, focusing on database management systems, SQL, and PL/SQL programming. It covers fundamental topics such as data manipulation and definition languages, various SQL commands, PL/SQL control structures, and database triggers. Additionally, it includes examples demonstrating the creation and management of tables, procedures, and functions.