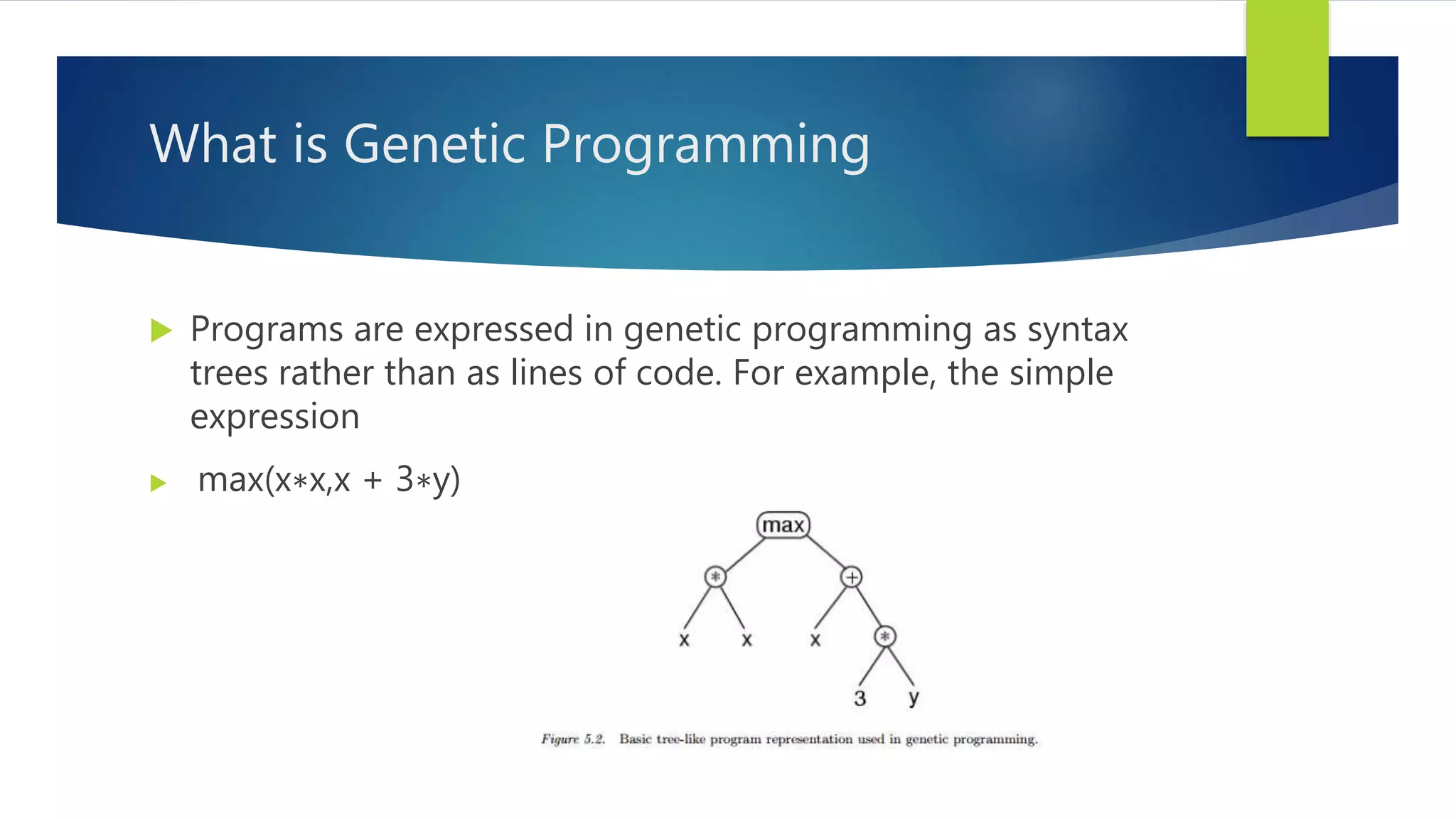
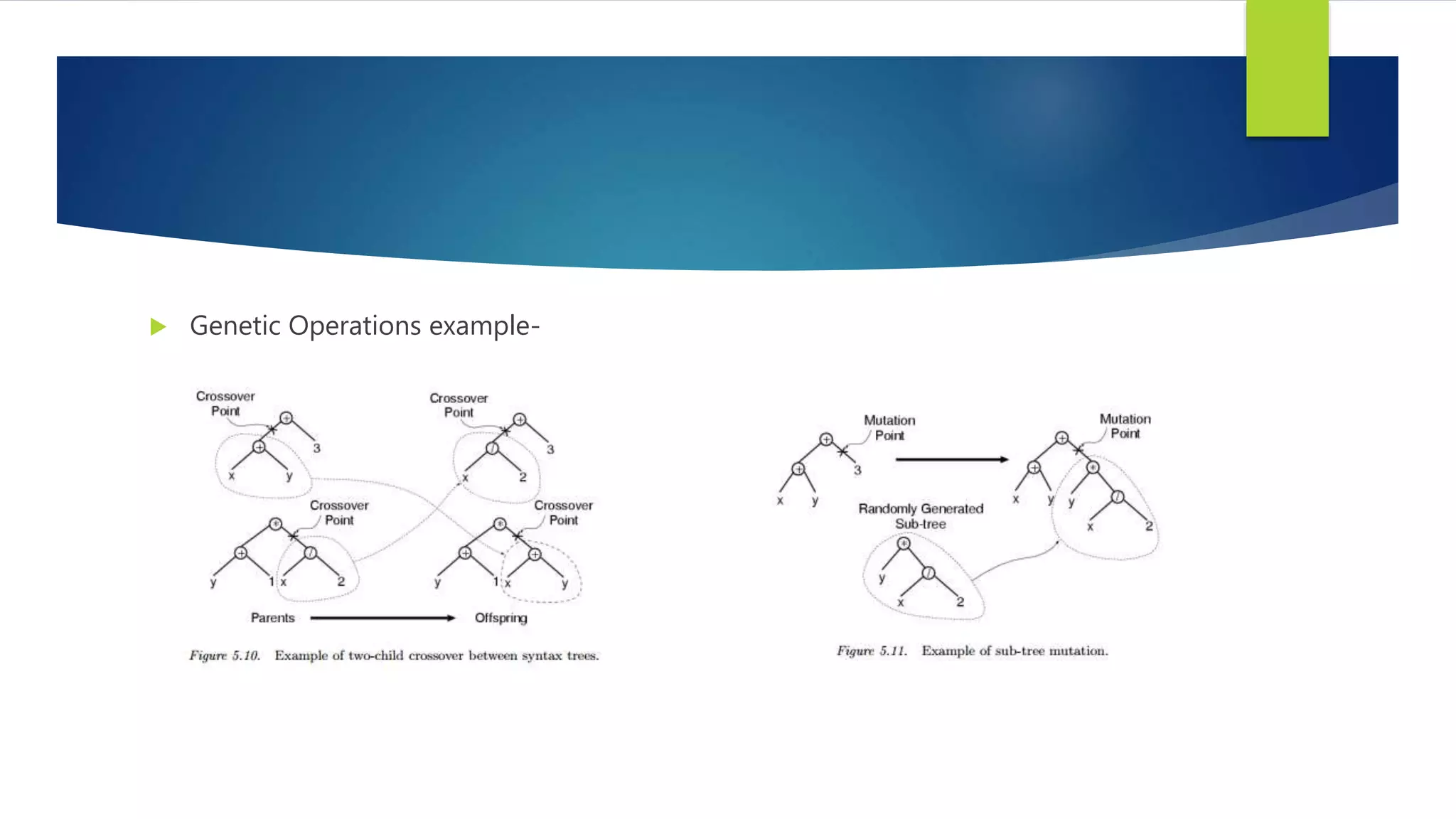
Genetic programming is a method for automatically solving problems by evolving computer programs through simulated natural selection processes, using genetic operations like crossover, mutation, and reproduction. It employs syntax trees to represent programs, offering a more adaptable solution for complex problems compared to genetic algorithms, which typically work with fixed-length strings. Applications of genetic programming span various fields, including neural network optimization, image analysis, and hardware evolution.









![Real world Applications
Neural Network Optimization [Zhang, Mühlenbein, 1993]
Image Analysis [Poli, 1996a]
Generation of a knowledge base for expert systems [Bojarczuk, Lopes, Freitas,
2000]
Fuzzy Logic Control [Akbarzadeh, Kumbla, Tunstel, Jamshidi, 2000]
Hardware Evolution (Field-Programmable Gate Array) [Thompson, 1997].
Symbolic Regression
Problem: Given a set of data points, find a mathematical model](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatisgeneticprogramming-151128130202-lva1-app6891/75/Introduction-to-genetic-programming-12-2048.jpg)